Polysaccharide Films/Membranes for Food and Industrial Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Development of Films/Membranes for Food Applications
2.1. Films for Food Packaging
2.1.1. Films from Polysaccharides Extracted from Biomass
2.1.2. Films from Polysaccharides Extracted from Cactus
2.1.3. Films from Polysaccharides Obtained from Agrifood Residues
2.1.4. Films from Microbial Polysaccharides
2.2. Porous Adsorptive Membranes for Wine Clarification
3. Development of Polysaccharide Membranes for Industrial Applications
3.1. Membranes for Solvent and Gas Dehydration Processes
3.2. Membranes for Wastewater Treatment
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas, F.; Alves, V.D.; Reis, M.A.; Crespo, J.G.; Coelhoso, I.M. Microbial polysaccharide-based membranes: Current and future applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermagambetova, A.; Tazhibayeva, S.; Takhistov, P.; Tyussyupova, B.; Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Musabekov, K. Microbial Polysaccharides as Functional Components of Packaging and Drug Delivery Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.R.V.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Polysaccharide-Based Membranes in Food Packaging Applications. Membranes 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Montes, E. Polysaccharide-Based Biodegradable Films: An Alternative in Food Packaging. Polysaccharides 2022, 3, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenboom, J.G.; Langer, R.; Traverso, G. Bioplastics for a circular economy. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, S.; Bettencourt, A.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Novel Features of Cellulose-Based Films as Sustainable Alternatives for Food Packaging. Polymers 2022, 14, 4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; McClements, D.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, F.; Miao, M.; Tian, Y.; Jin, Z. Starch-based biodegradable packaging materials: A review of their preparation, characterization and diverse applications in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wu, W.; Liu, P.; Hou, H.; Li, X.; Cui, B. Preparation, and evaluation of hydrophobic biodegradable films made from corn/octenyl succinate starch incorporated with different concentrations of soybean oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junlapong, K.; Boonsuk, P.; Chaibundit, C.; Chantarak, S. Highly water-resistant cassava starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herniou-Julien, C.; Mendieta, J.R.; Gutiérrez, T.J. Characterization of biodegradable/non-compostable films made from cellulose acetate/corn starch blends processed under reactive extrusion conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Han, S.; Du, Y.; Fei, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, X. Engineered environment-friendly multifunctional food packaging with superior nonleachability, polymer miscibility and antimicrobial activity. Food Chem. 2025, 466, 142192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontominas, M.G. Use of Alginates as Food Packaging Materials. Foods 2020, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senturk Parreidt, T.; Müller, K.; Schmid, M. Alginate-Based Edible Films and Coatings for Food Packaging Applications. Foods 2018, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, W.; Nowotarski, M.; Ledniowska, K.; Shyntum, D.Y.; Krukiewicz, K.; Turczyn, R.; Sabura, E.; Furgoł, S.; Kudła, S.; Dudek, G. Modulation of physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity of sodium alginate films through the use of chestnut extract and plasticizers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez, M.; Guerra-Rodríguez, E.; Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Chitosan for food packaging: Recent advances in active and intelligent films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124 Pt B, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Rhim, J.-W. Chitosan-based biodegradable functional films for food packaging applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.M.P.; Coimbra, J.S.R.; Souza, V.G.L.; Sousa, R.C.S. Structure and Applications of Pectin in Food, Biomedical, and Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinas, C.; Ramos, M.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Recent Trends in the Use of Pectin from Agro-Waste Residues as a Natural-Based Biopolymer for Food Packaging Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, V.D.; Costa, N.; Coelhoso, I.M. Barrier properties of biodegradable composite films based on kappa-carrageenan/pectin blends and mica flakes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broek, L.A.M.; Knoop, R.J.I.; Kappen, F.H.J.; Boeriu, C.G. Chitosan films and blends for packaging material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fuente Arias, C.I.; Kubo, M.T.K.; Tadini, C.C.; Augusto, P.E.D. Bio-based multilayer films: A review of the principal methods of production and challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2260–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichembach, L.H.; Guerrero, P.; Petkowicz, C.L.; de la Caba, K. Valorization of pectins from coffee wastes for the development of pectin-chitosan films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravartula, S.S.N.; Soccio, M.; Lotti, N.; Balestra, F.; Dalla Rosa, M.; Siracusa, V. Characterization of Composite Edible Films Based on Pectin/Alginate/Whey Protein Concentrate. Materials 2019, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Ren, H.; Du, M.; Tang, J. Improving the comprehensive properties of gelatin films by transglutaminase and chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Guo, S.; Wang, K.; Pang, X.; Asres, B.S.; Ding, Z. Aminated graphene oxide reinforced gelatin-chitosan composite films toward biopackaging: Preparation and properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 284, 138104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.; Galus, S.; Debeaufort, F. Surface, mechanical and barrier properties of bio-based composite films based on chitosan and whey protein. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2014, 1, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, L.B.; Pinto, D.; Silva, L.F.O.; de Farias, B.S.; Moraes, C.C.; Da Rosa, G.S.; Dotto, G.L. Antimicrobial Bilayer Film Based on Chitosan/Electrospun Zein Fiber Loaded with Jaboticaba Peel Extract for Food Packaging Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Sadiku, E.R.; Mochane, M.J.; Ray, S.S.; John, M.J.; Mtibe, A. Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofibril papers and their bionanocomposites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, J.; Paula, C.D.d.; Souza, V.G.L.; Fernando, A.L.; Coelhoso, I. Understanding the Barrier and Mechanical Behavior of Different Nanofillers in Chitosan Films for Food Packaging. Polymers 2021, 13, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, M.; Xin, Z.; Wang, H.; Komarneni, S.; Zhang, K.; Ni, Z.; Hu, G. Intelligent double-layer films based on gellan gum/mica nanosheets/anthocyanin/konjac glucomannan/carrageenan for food real-time freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.; Pires, J.; Rodrigues, P.; Lopes, A.; Fernandes, F.M.B.; Duarte, M.P.; Coelhoso, I.; Fernando, A.L. Bionanocomposites of chitosan/montmorillonite incorporated with Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil: Development and physical characterization. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 16, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyszewska, A.; Barbosa, C.H.; Pires, F.; Pires, J.R.A.; Rodrigues, C.; Galus, S.; Souza, V.G.L.; Alves, M.M.; Santos, C.F.; Coelhoso, I.; et al. Packaging of Fresh Poultry Meat with Innovative and Sustainable ZnO/Pectin Bionanocomposite Films—A Contribution to the Bio and Circular Economy. Coatings 2023, 13, 1208. [Google Scholar]
- Bandeira, M.; Giovanela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.; Crespo, J.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of the synthesis methodology and mechanism of formation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.M.; Andrade, S.M.; Grenho, L.; Fernandes, M.H.; Santos, C.; Montemor, M.F. Influence of apple phytochemicals in ZnO nanoparticles formation, photoluminescence, and biocompatibility for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Bravo, R.K.; Guzmán-Maldonado, S.H.; Araiza-Herrera, H.A.; Zegbe, J.A. Storage alters physicochemical characteristics, bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of cactus pear fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 150, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaoui, M.; D’Antuono, I.; D’Imperio, M.; Linsalata, V.; Boukhchina, S.; Logrieco, A.F.; Cardinali, A. Characterization of micronutrients, bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of prickly pear cladodes as functional ingredient. Molecules 2020, 25, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefsih, K.; Delattre, C.; Pierre, G.; Michaud, P.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Dahmoune, F.; Madani, K. Extraction, characterization and gelling behavior enhancement of pectins from the cladodes of Opuntia ficus indica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Paula, C.D.d.; Lahbouki, S.; Meddich, A.; Outzourhit, A.; Rashad, M.; Pari, L.; Coelhoso, I.; Fernando, A.L.; Souza, V.G.L. Opuntia spp.: An Overview of the Bioactive Profile and Food Applications of This Versatile Crop Adapted to Arid Lands. Foods 2023, 12, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Souza, V.G.L.; Coelhoso, I.; Fernando, A.L. Bio-Based Sensors for Smart Food Packaging—Current Applications and Future Trends. Sensors 2021, 21, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouahioune, L.A.; Wrona, M.; Pezo, D.; Nerín, C.; Djenane, D. Sustainable and green strategies for active biopackaging: Application for seafood products—A critical review. Food Biosci. 2024, 63, 105647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadije, S.; Shekarchizadeh, H. An intelligent cellulose pad loaded with copper nanoparticles for real-time freshness monitoring of beef. LWT-Food Sci. Tech. 2024, 212, 1096–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Gou, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, S. Smart carrageenan/carboxymethyl cellulose films combined with zein/gellan gum microcapsules encapsulated by composite anthocyanins for chilled beef freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirpan, A.; Deliana, Y.; Ainani, A.F.; Irwan; Bahmid, N.A. Exploring the Potential of Pectin as a Source of Biopolymers for Active and Intelligent Packaging: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Xie, L.; Dang, X. Engineering a Natural Multifunctional Biomass-Based Composite Nanosystem for Active Smart Packaging and Colorimetric Labels. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
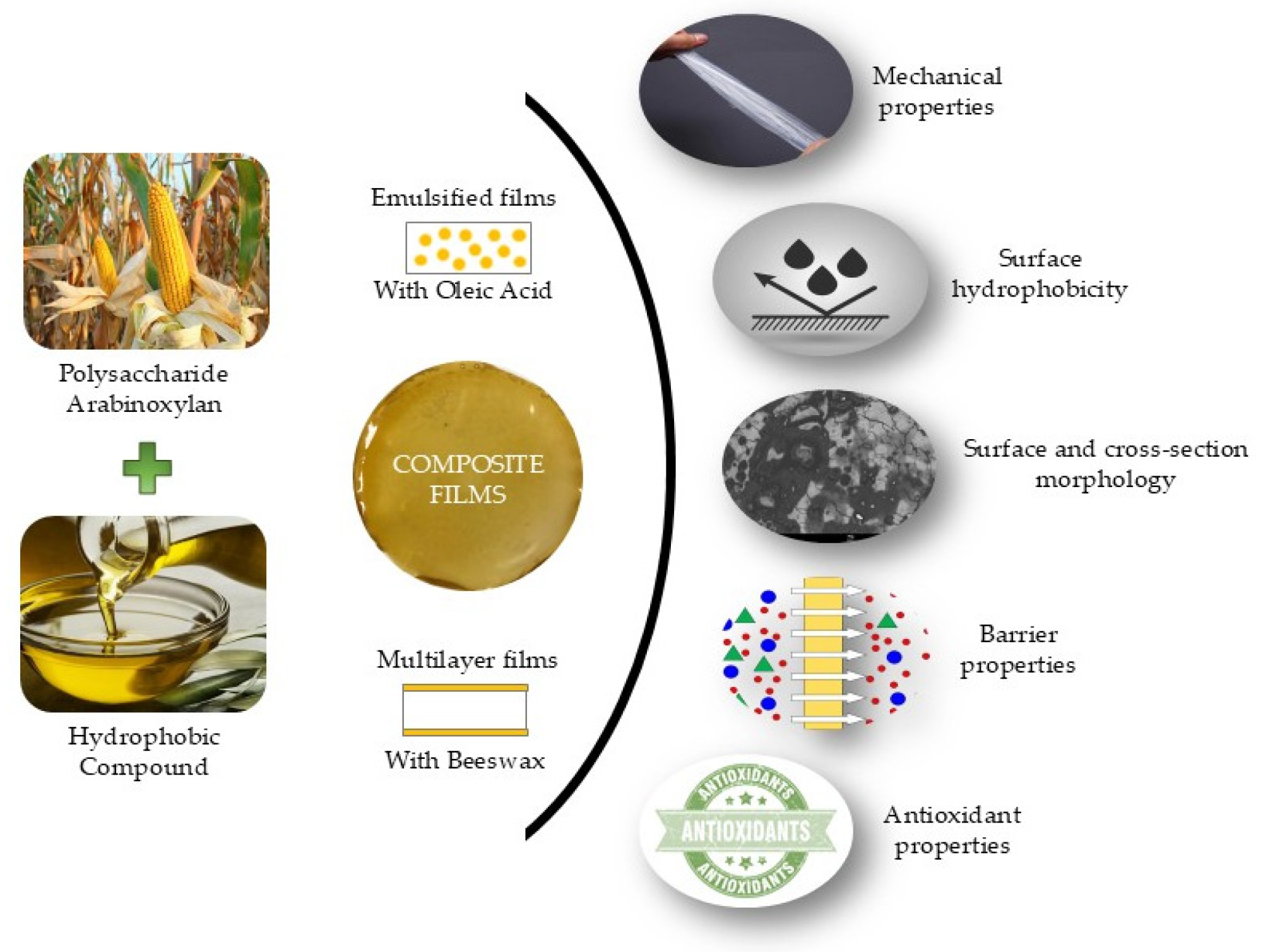
- Weng, V.; Brazinha, C.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Alves, V.D. Decolorization of a Corn Fiber Arabinoxylan Extract and Formulation of Biodegradable Films for Food Packaging. Membranes 2021, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvada, J.; Alke, B.; Brazinha, C.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Development and Characterisation of Arabinoxylan-Based Composite Films. Coatings 2022, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Ruiz, H.A.; Fougnies, C.; Richel, A.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Aguedo, M. Use of wheat bran arabinoxylans in chitosan-based films: Effect on physicochemical properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, J.J.; Castillo, P.M.; del Río, J.C.; León-Camacho, M.; Domínguez, E.; Heredia, A.; Guzmán-Puyol, S.; Athanassiou, A.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A. Valorization of Tomato Processing By-Products: Fatty Acid Extraction and Production of Bio-Based Materials. Materials 2018, 11, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manricha, A.; Moreira, F.K.V.; Otoni, C.G.; Lorevicea, M.V.; Martins, M.A.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Hydrophobic Edible Films Made up of Tomato Cutin and Pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, A.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Alves, V.D.; Brazinha, C. Recovery and Purification of Cutin from Tomato By-Products for Application in Hydrophobic Films. Membranes 2023, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, K.; Guo, H.; Li, R.; Li, G. Advancements in Gellan Gum-Based Films and Coatings for Active and Intelligent Packaging. Polymers 2024, 16, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Arauz, Á.O.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.I.; del Rocío López-Cuellar, M.; Martínez-Juárez, V.M.; Chavarría-Hernández, N. Films based on pectin, gellan, EDTA, and bacteriocin-like compounds produced by Streptococcus infantarius for the bacterial control in fish packaging. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Zou, X.; Huang, X.; Zhai, X.; Shi, J.; Shen, T.; Gong, Y.; et al. Novel gellan gum-based probiotic film with enhanced biological activity and probiotic viability: Application for fresh-cut apples and potatoes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chang, X.; Xu, H.; Fu, X.; Ding, S.; Wang, R. Gellan gum-based functional films integrated with bacterial cellulose and nano-TiO2/CuO improve the shelf life of fresh-cut pepper. Food Package Shelf Life 2023, 38, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Bacterial cellulose as a biodegradable food packaging material: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, F.; Alves, V.D.; Torres, C.A.V.; Cruz, M.; Sousa, I.; João, M.; Ramos, A.M.; Reis, M.A.M. Fucose-Containing Exopolysaccharide Produced by the Newly Isolated Enterobacter strain A47 DSM 23139. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.R.V.; Torres, C.A.V.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Development and characterization of bilayer films of FucoPol and chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Yu, D.; Regenstein, J.M.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, J.; Chen, W.; Xia, W. Modulating physicochemical, antimicrobial and release properties of chitosan/zein bilayer films with curcumin/nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chang, X.; Ding, Z.; Xu, H.; Kong, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, R.; Shan, Y.; Ding, S. Fabrication and Characterization of Eco-Friendly Polyelectrolyte Bilayer Films Based on Chitosan and Different Types of Edible Citrus Pectin. Foods 2022, 11, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sluyter, S.C.; McRae, J.M.; Falconer, R.J.; Smith, P.A.; Bacic, A.; Waters, E.J.; Marangon, M. Wine protein haze: Mechanisms of formation and advances in prevention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4020–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwukamike, K.N.; Grelier, S.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H.; Meier, M.A.R. Critical Review on Sustainable Homogeneous Cellulose Modification: Why Renewability Is Not Enough. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 1826–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, R.B.; Coelhoso, I.; Velizarov, S. Compound, Method of Production and Uses Thereof. Patent WO2019197884A1, 17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
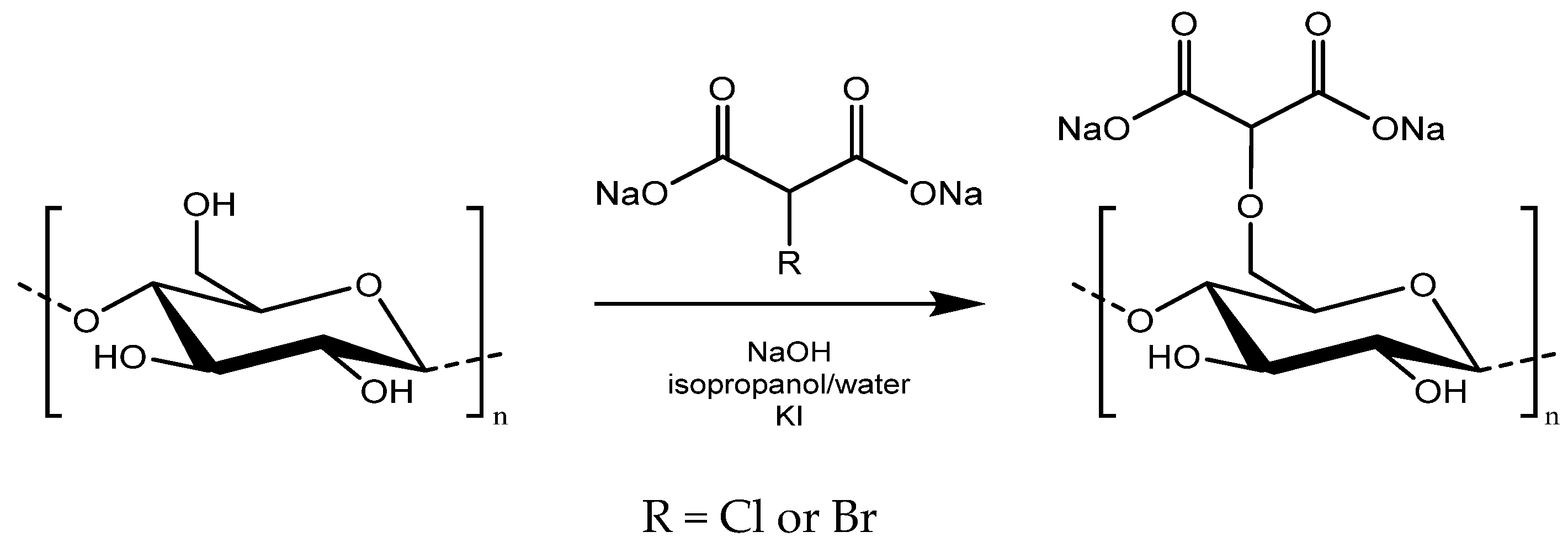
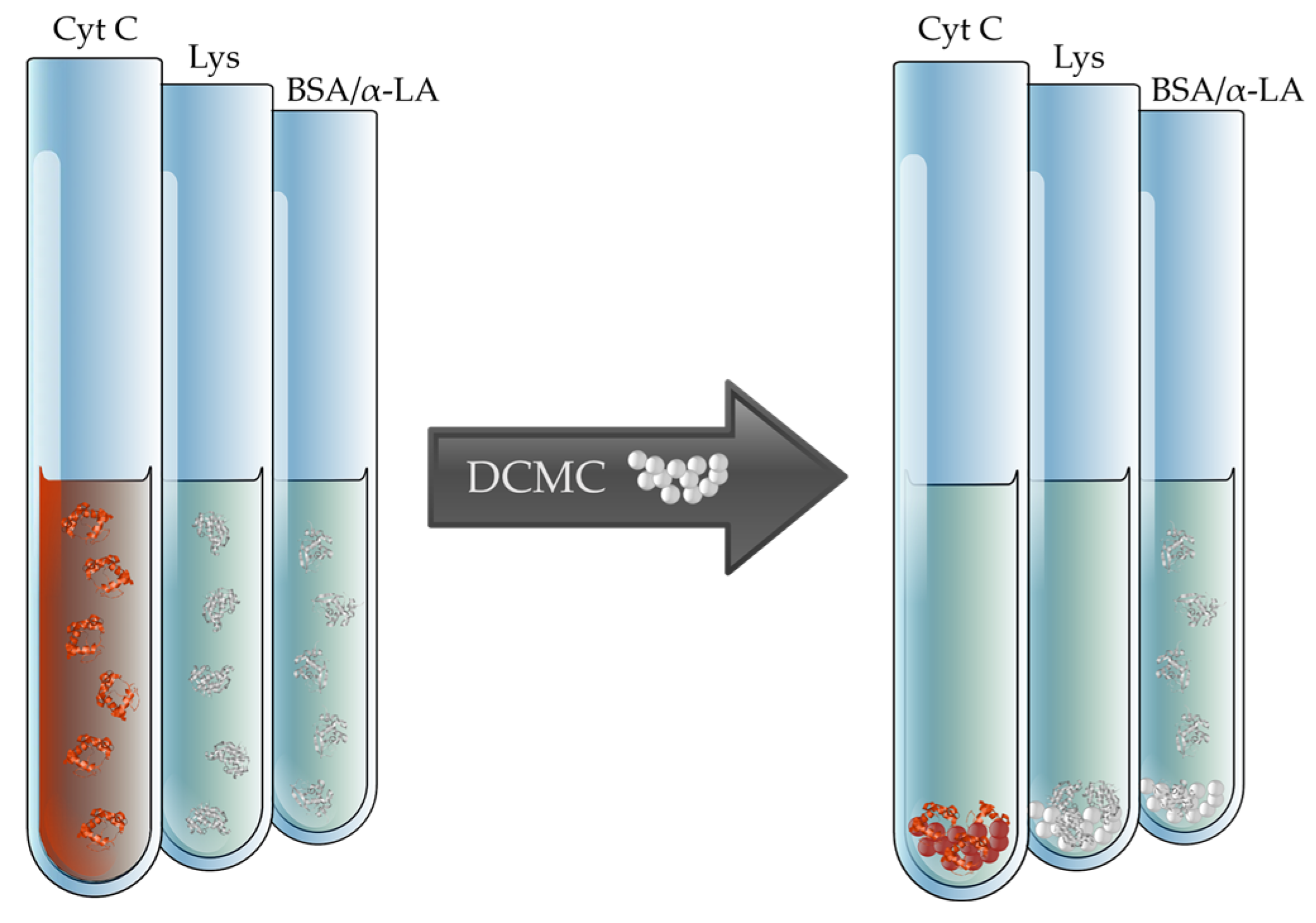
- Gago, D.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, L.M. The Effect of Dicarboxymethyl Cellulose on the Prevention of Protein Haze Formation on White Wine. Beverages 2021, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, D.; Corvo, M.C.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Coelhoso, I. Protein Adsorption Performance of a Novel Functionalized Cellulose-Based Polymer. Polymers 2022, 14, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Gassara, S.; Cambedouzou, J.; Bechelany, M.; Miele, P. Development of novel h-BNNS/PVA porous membranes via Pickering emulsions. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4319–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Ondo, D.A.; Gassara, S.; Bechelany, M.; Balme, S.; Miele, P.; Kalkura, N.; Pochat-Bohatier, C. Porous Gelatin Membrane Obtained from Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Graphene Oxide. Langmuir 2018, 34, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.G.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Cambedouzou, J.; Bechelany, M.; Miele, P. Pickering emulsions stabilized with two-dimensional (2D) materials: A comparative study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 563, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Ursino, C.; Avruscio, E.; Desiderio, G.; Perrone, A.; Santoro, S.; Galiano, F.; Figoli, A. Innovative Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Preparation Using DMSO as a Low Toxicity Solvent. Membranes 2020, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Talukder, M.E.; Mishu, M.R.; Buonerba, A.; Del Gaudio, P.; Stylios, G.K.; Hasan, S.W.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Figoli, A.; et al. One-Step Fabrication of Novel Polyethersulfone-Based Composite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Food Industry Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.D.; Oliveira, T.; Livingston, A.G.; Li, K. Membranes for the dehydration of solvents by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W. Pervaporation membrane materials: Recent trends and perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanti, P.; Srigowri, K.; Madhuri, K.; Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S. Dehydration of ethanol through blend membranes of chitosan and sodium alginate by pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.; Razzaq, H.; Razzaque, S.; Bibi, A.; Yaqub, A. Recent advances in sodium alginate-based membranes for dehydration of aqueous ethanol through pervaporation. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2435–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.; Saxena, C.; Singh, L.; Ramana, K.V.; Chauhan, R.S. Pervaporation of binary water-ethanol mixtures through bacterial cellulose membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 27, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, T.; Patrichi, C.A.M.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Aljanabi, A.A.A. Pervaporation of Aqueous Ethanol Solutions through Rigid Composite Polyvinyl-Alcohol/Bacterial Cellulose Membranes. Processes 2021, 9, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, I.T.; Huertas, R.M.; Torres, C.A.V.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Development and characterisation of hybrid polysaccharide membranes for dehydration processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 191, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, I.T.; Fraga, S.C.; Huertas, R.M.; Brazinha, C.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Evaluation of hybrid polysaccharide membranes for gas dehydration using on-line mass spectrometry. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 545, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, F.; Msahel, A.; Russo, F.; Rovella, N.; Policicchio, A.; Hamouda, S.B.; Hafiane, A.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Figoli, A. Enhancing the Separation Performance of Chitosan Membranes Through the Blending with Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Pervaporation of Polar/Non-Polar Organic Mixtures. Membranes 2024, 14, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorowska, M.A.; Bożejewicz, D. The Application of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants from Aqueous Solutions—A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzahar, M.M.H.; Bassyouni, M. Removal of direct dyes from wastewater using chitosan and polyacrylamide blends. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorraji, S.; Mirmohseni, M.S.; Tasselli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Carraro, M.; Gross, S.; Figoli, A. Preparation, characterization and application of iron (III)-loaded chitosan hollow fiber membranes as a new bio-based As (V) sorbent. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocenza, D.S.; de Moraes, M.A.; Beppu, M.M.; Fraceto, L.F. Use of Biopolymeric Membranes for Adsorption of Paraquat Herbicide from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 3093–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini de Moraes, M.; Cocenza, D.; Vasconcellos, F.; Fraceto, L.; Beppu, M. Chitosan and alginate biopolymer membranes for remediation of contaminated water with herbicides. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, S.; Lynch, I.; Shah, S.W.H.; Bashir, N. Remediation of Water Using a Nanofabricated Cellulose Membrane Embedded with Silver Nanoparticles. Membranes 2022, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhouchat, N.; Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Viseras, C. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution with activated organo-bentonite/sodium alginate encapsulated beads. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. A green composite hydrogel based on cellulose and clay as efficient absorbent of colored organic effluent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Cross-linked beads of activated oil palm ash zeolite/chitosan composite as a bio-adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue and acid blue 29 dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, D.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Velizarov, S.; Coelhoso, I. A Novel Cellulose-Based Polymer for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue. Membranes 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skwarczynska-Wojsa, A.; Puszkarewicz, A. Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solutions in an Adsorption Process. Materials 2024, 17, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-García, A.; García-Sanz-Calcedo, J.; Carrasco-Amador, J.P.; Segura-Cruz, R. Adsorption of Paracetamol in Hospital Wastewater Through Activated Carbon Filters. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Durães, L.; Simões, N.E.C.; Pereira, A.M.P.T.; Silva, L.J.G.; Feio, M.J. Pharmaceuticals in urban streams: A review of their detection and effects in the ecosystem. Water Res. 2025, 268 Pt B, 122657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.; Gago, D.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Coelhoso, I. Removal of micropollutants by dicarboxymethyl cellulose. In Proceedings of the Euromembrane 2024, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–12 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Film | PO2 × 1016 (mol/m·s·Pa) | PCO2 × 1016 (mol/m·s·Pa) | Pw × 1011 (mol/m·s·Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FucoPol | 1.9 | 6.5 | 0.8 |
| Chitosan | 2.4 | 15.0 | 4.1 |
| Bilayer | 0.5 | 5.8 | 1.7 |
| Membrane | [Water]feed (wt. %) | Selectivity (w–et) |
|---|---|---|
| FucoPol | 10.2 | 100 |
| Hybrid FucoPol | 10.0 | 570 |
| PERVAP® 4101 | 9.9 | 554 |
| Experiment Days | Pw × 1012 (mol/m·s·Pa) | Pet × 1013 (mol/m·s·Pa) | Selectivity (w–et) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.7 | 0.14 | 570 |
| 2 | 9.7 | 0.53 | 182 |
| 3 | 14.7 | 6.2 | 24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelhoso, I. Polysaccharide Films/Membranes for Food and Industrial Applications. Polysaccharides 2025, 6, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020048
Coelhoso I. Polysaccharide Films/Membranes for Food and Industrial Applications. Polysaccharides. 2025; 6(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelhoso, Isabel. 2025. "Polysaccharide Films/Membranes for Food and Industrial Applications" Polysaccharides 6, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020048
APA StyleCoelhoso, I. (2025). Polysaccharide Films/Membranes for Food and Industrial Applications. Polysaccharides, 6(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6020048






