Comparative Study on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Alkali-Treated and Untreated Sida acuta Fiber-Reinforced Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Treatment
2.3. Composite Preparation
2.4. Density Test
2.5. Compression Test
2.6. Hardness Test
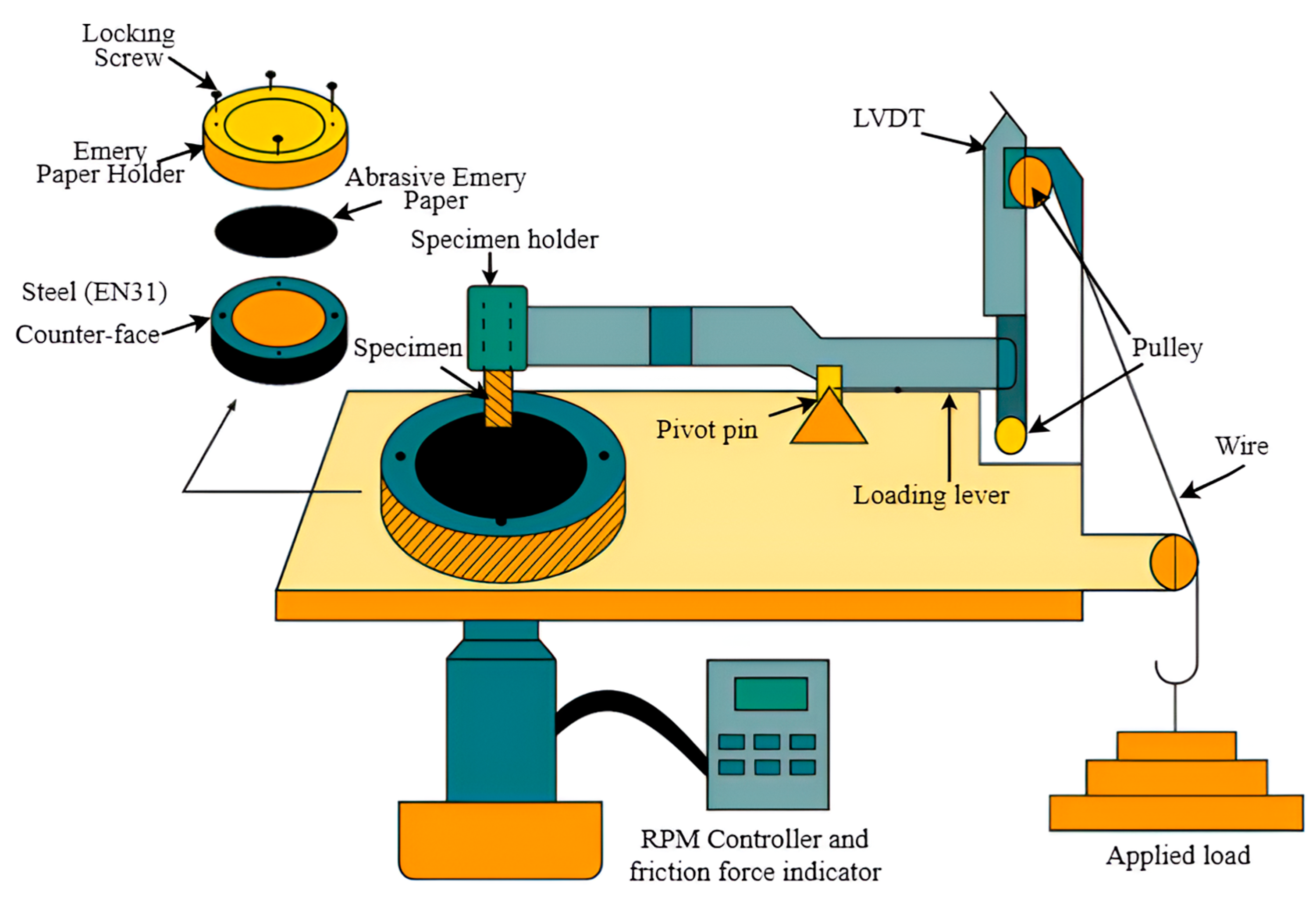
2.7. Wear Test
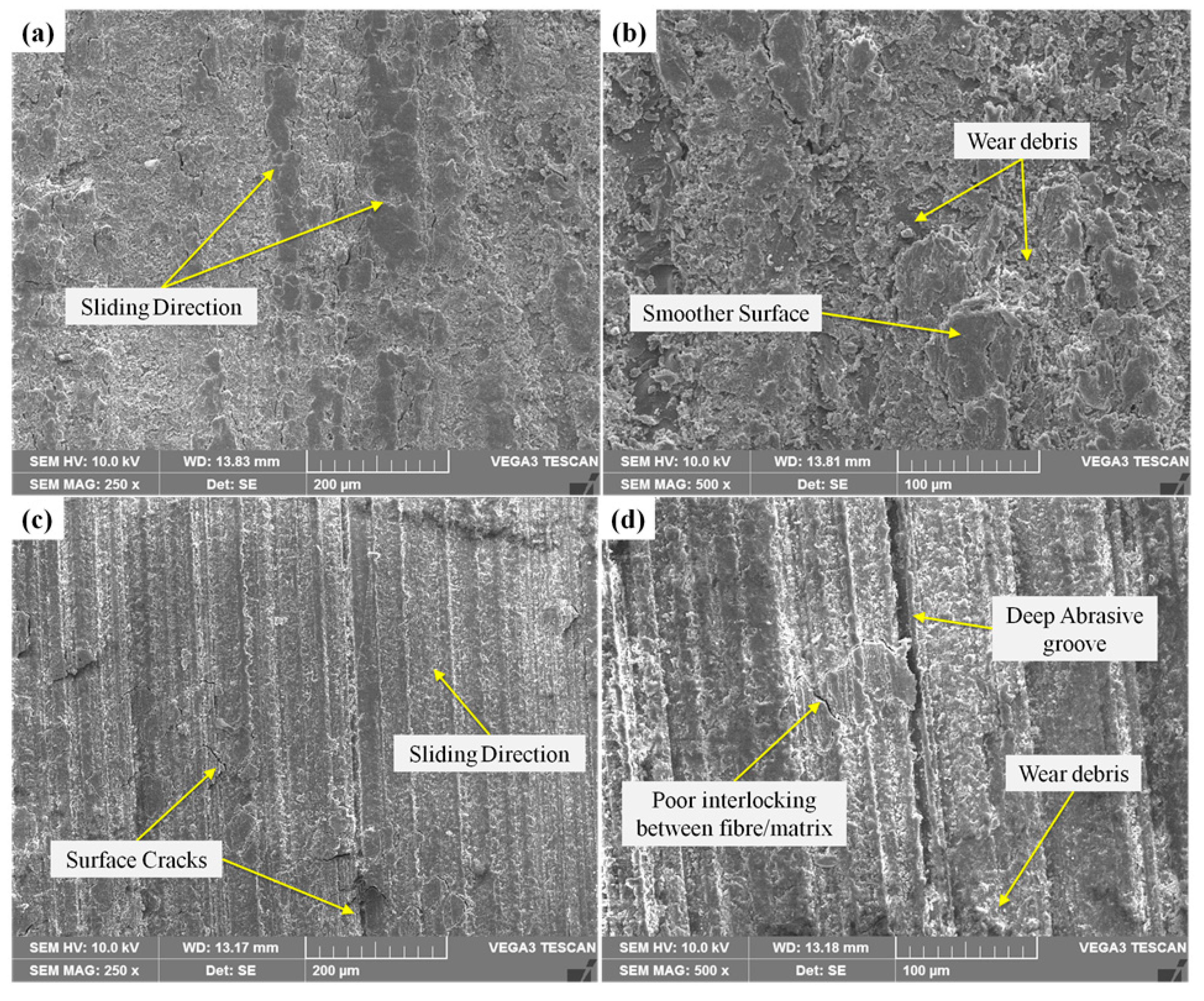
2.8. Worn Surface Morphology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Density
3.2. Rockwell Hardness
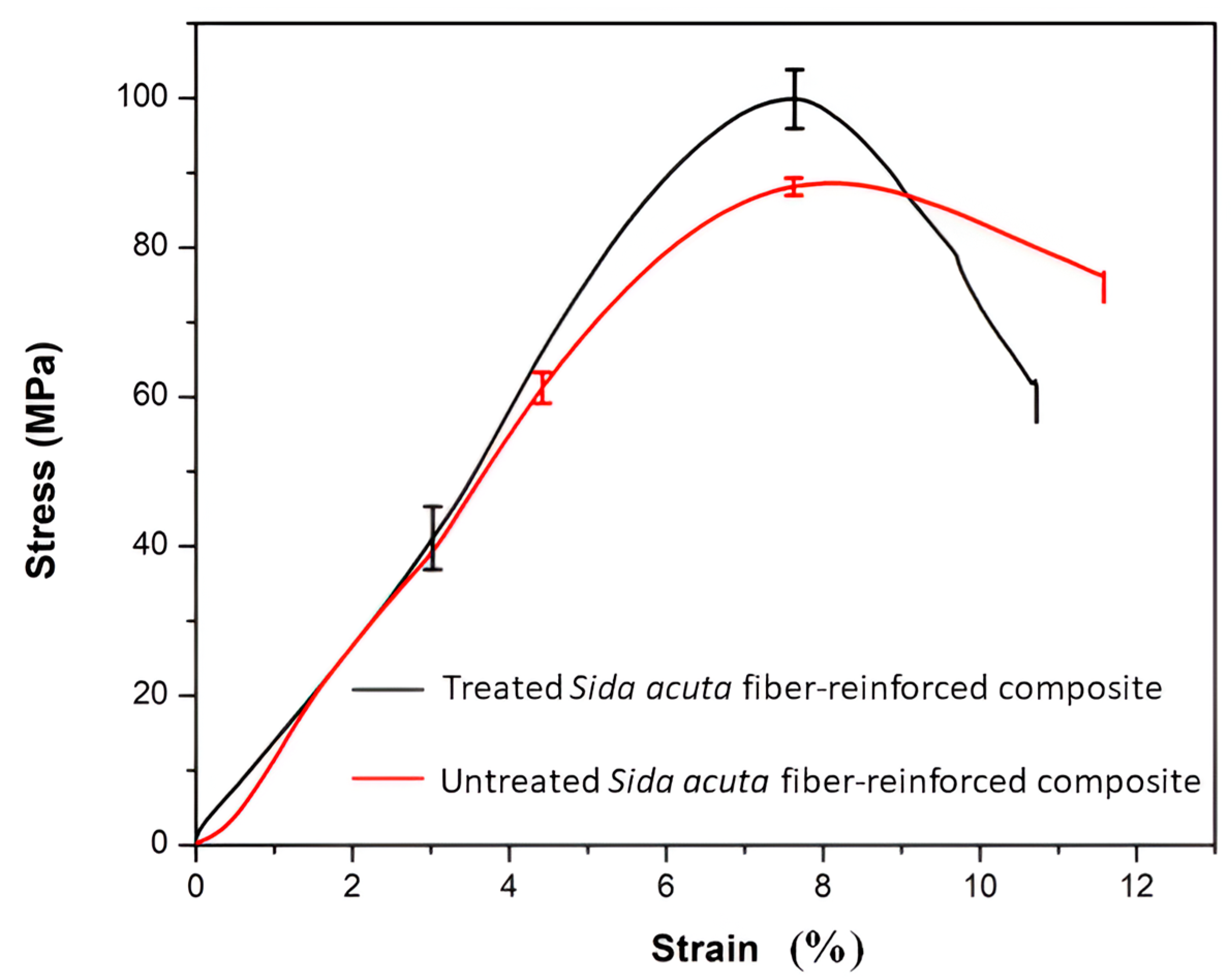
3.3. Compression Strength
3.4. Weight Loss of the Composite
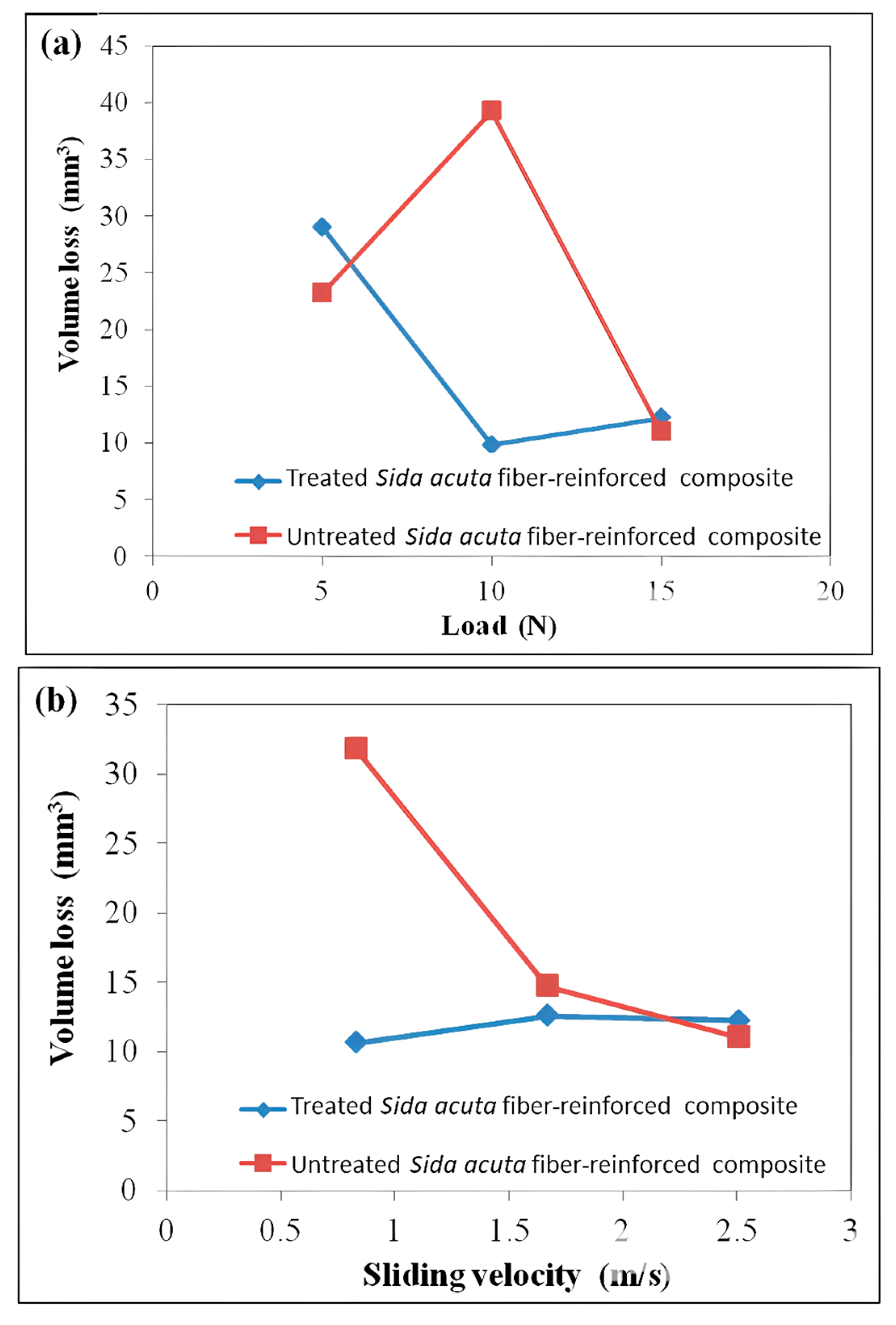
3.5. Volume Loss of the Composite
3.6. Wear Rate of the Composite
3.7. Surface Morphology of the Composite
4. Conclusions
- The density of both untreated and alkali-treated Sida acuta composites was found to be approximately the same, with an average value of 0.827 g/cc. This occurs because the alkali treatment primarily removes the surface impurities (non-cellulosic components like lignin, hemicellulose, and pectin) without altering fiber volume.
- An increase of 12.57% in Rockwell hardness was observed in the alkali-treated fiber epoxy composite (32 ± 1 wt.% fiber loading) compared to the untreated composite, primarily due to enhanced interfacial bonding between the fiber and matrix.
- The average compressive strength of the treated Sida acuta composite was 99.89 ± 3.92 MPa, which is 13.5% higher than that of the untreated composite (88.01 ± 1.14 MPa), indicating improved mechanical performance due to alkali treatment.
- The wear rate of the 5% NaOH-treated Sida acuta epoxy composite was lower compared to that of the untreated composite, likely due to the increased hardness of the treated fiber-reinforced laminate.
- The alkali-treated SAF composite significantly improves the wear resistance at 1.0 kg load, resulting in a more than 70% increase in performance compared to the untreated SAF composite. However, at higher sliding speeds (600 rpm at 0.5 kg load) or loads (1.5 kg), the alkali treatment did not show any improvement, possibly due to increased thermal degradation or fiber–matrix debonding.
- Finally, alkali-treated Sida acuta fiber-reinforced composites demonstrated enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance over untreated counterparts, suggesting their suitability for lightweight structural and tribological applications in household and industrial settings.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thapliyal, D.; Verma, S.; Sen, P.; Kumar, R.; Thakur, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Arya, R.K. Natural fibers composites: Origin, importance, consumption pattern, and challenges. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M. Natural fibres as construction materials. Mater. Technol. (NOCMAT) 2009, 6, 9. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.; Sreekala, M.S.; Thomas, S. A review on interface modification and characterization of natural fibre reinforced plastic composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1471–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Kuriakose, B.; Thomas, S. Stress relaxation in short sisal-fibre-reinforced natural rubber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 53, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridonos, E.; Dahy, H. Application of natural fibre pultruded profiles in diverse lightweight structures and architectural scenarios. Archit. Struct. Constr. 2025, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyavihalli Girijappa, Y.G.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Natural fibers as sustainable and renewable resource for development of eco-friendly composites: A comprehensive review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaleh, I.; Abbassi, F.; Habibi, M.; Ahmad, F.; Guedri, M.; Nasri, M.; Garnier, C. A comprehensive review of natural fibers and their composites: An eco-friendly alternative to conventional materials. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungani, R.; Aditiawati, P.; Aprilia, S.; Yuniarti, K.; Karliati, T.; Suwandhi, I.; Sumardi, I. Biomaterial from oil palm waste: Properties, characterization and applications. In Palm Oil; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Volume 31, pp. 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, M.; Bali, A. Green manufacturing of natural fiber composite. In Sustainable Machining and Green Manufacturing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 79–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.S.S.; Allamraju, K.V. A review of natural fiber composites [Jute, Sisal, Kenaf]. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Sustainable bio-composites from renewable resources: Opportunities and challenges in the green materials world. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevan Rao, H.; Gara, D.K.; Reddy, S.; Shreya, V.R.; Kumar, T.; Sequeria, E.; Jha, A. Influence of chemical treatment on the microstructural properties of Sida acuta natural fiber. In International Conference on Mechanical Engineering: Researches and Evolutionary Challenges; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra Mohan, H.K.; Gnanendra Reddy, G.V.; Chowde Gowda, M. Physical and mechanical behaviour of Sida acuta fibre reinforced epoxy composite at different fibre loading. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, M.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.K. Chemistry and pharmacology of genus Sida (Malvaceae): A review. J. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. 2002, 24, 430–440. [Google Scholar]
- Greenway, P.J. Vegetable fibres and flosses in East Africa. East Afr. Agric. J. 1950, 15, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholkute, S.D.; Munshi, S.R.; Naik, S.D.; Jathar, V.S. Antifertility activity of indigenous plants Sida carpinifolia Linn. and Podocarpus brevifolius Stapf in female rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1978, 16, 696–698. [Google Scholar]
- Karou, D.; Dicko, M.H.; Sanon, S.; Simpore, J.; Traore, A.S. Antimalarial activity of Sida acuta Burm. f. (Malvaceae) and Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. (Fabaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra Mohan, H.K.; Gnanendra Reddy, G.V.; Chowde Gowda, M. Mechanical properties of untreated Sida acuta stem fibre fabric–reinforced epoxy composites at different fibre fabric orientation. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Mohan, H.K.; Devaraj, S.; Ranganatha, R.; Narayana Swamy, K.S. Mechanical and moisture absorption behaviour of alkali treated Sida acuta composite. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Mohan, H.K.; Devaraj, S. Free-vibration and moisture absorption behaviour of Sida acuta fibre polymer composites. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2021, 10, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijwe, J.; Indumathi, J.; Ghosh, A.K. On the abrasive wear behaviour of fabric-reinforced polyetherimide composites. Wear 2022, 7, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath Kumaran, P.; Seetharamu, S.; Murali, A.; Kumar, R.K. Dry sliding wear behavior of glass-epoxy composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1999, 18, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh Joh, J.; Bijwe, J. Statistical analysis of abrasive wear data of aramid fabric-reinforced polyethersulfone composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, B.; Chandramohan, G.; Seetharamu, S.; Vynatheya, S. Friction and wear characteristics of carbon-epoxy and glass-epoxy woven roving fiber composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2006, 25, 771–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Gnanamoorthy, R. Friction and wear behavior of vinylester resin matrix composites filled with fly ash particles. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Arnell, R.D.; Ren, L.G. Dry sliding wear behavior of bamboo. Wear 1998, 221, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.A.R.; Dwivedi, U.K.; Chand, N. Friction and sliding wear of UHMWPE modified cotton fiber reinforced polyester composites. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 21, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, U.K.; Ghosh, A.; Chand, N. Role of PVA modification in improving the sliding wear behaviour of bamboo. Bioresources 2009, 4, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.W.; Yousif, B.F. Tribological behaviour of KFRE composite. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2010, 24, 5589–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tayeb, N.S.M.; Yousif, B.F.; Yap, T.C. An investigation on worn surfaces of chopped glass fibre reinforced polyester through SEM observations. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tayeb, N.S.M.; Yousif, B.F.; Yap, T.C. Tribological studies of polyester reinforced with CSM 450-R-glass fiber sliding against smooth stainless steel counter face. Wear 2006, 261, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tayeb, N.S.M.; Yousif, B.F.; Yap, T.C. Study on the potential of sugarcane fibers/polyester composite for tribological applications. Wear 2008, 265, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.A.R.; Dwivedi, U.K.; Chand, N. Graphite modified cotton fibre reinforced polyester composites under sliding wear conditions. Wear 2007, 262, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, U.; Yousif, B.F.; Rilling, D.; Brevern, P.V. Effect of betelnut fibres treatment and contact conditions on adhesive wear and frictional performance of polyester composites. Wear 2010, 268, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, N.S.; Yousif, B.F. Wear and frictional performance of betelnut fibre-reinforced polyester composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. Eng. Tribol. 2009, 223, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.W.; Yousif, B.F. Potential of kenaf fibres as reinforcement for tribological applications. Wear 2009, 267, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Xu, C.G.; Qing, L.F. Friction properties of sisal fibre reinforced resin brake composites. Wear 2007, 262, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Fawzia, S.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Polymer matrix composite with natural and synthetic fibres. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 6, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Imran, R.; Arif, Z.U.; Akram, N.; Arshad, H.; Al Rashid, A.; García Márquez, F.P. Developments in chemical treatments, manufacturing techniques and potential applications of natural-fibers-based biodegradable composites. Coatings 2021, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, S.H.; Lawrence, T.D.; Amar, K.M.; Manjusri, M. Effect of surface treatments on the properties of laminated biocomposites from poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and kenaf fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Q.Y.; Dong, X.H. Influence of surface treatment of carbon fibers on interfacial adhesion strength and mechanical properties of PLA-based composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G99-17; Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Ap-paratus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E18 22; Standard Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Siripong, P.; Doungporn, P.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, S.W. Improvement of sugar recovery from Sida acuta (Thailand weed) by NaOH pretreatment and application to bioethanol production. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.A.; Zulkifli, R.; Azhari, C.H. Tensile properties and microstructure of single-cellulosic bamboo fiber strips after alkali treatment. Fibers 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, N.; Dwivedi, U.K. Effect of coupling agent on abrasive wear behaviour of chopped jute fibre-reinforced polypropylene composites. Wear 2006, 261, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Zhang, Z.; Klein, P. Wear of polymer composites. In Wear–Materials, Mechanisms and Practice; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 269–290. [Google Scholar]




| Load on Specimen (kg’s) | Speed (rpm) | Weight Loss (gm’s) | Volume Loss (mm3) | Wear Rate (mm3/N·m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 200 | 0.02 | 20.02 | 0.026 |
| 400 | 0.02 | 21.59 | 0.014 | |
| 600 | 0.01 | 29.05 | 0.013 | |
| 1.0 | 200 | 0.01 | 3.14 | 0.002 |
| 400 | 0.01 | 8.24 | 0.003 | |
| 600 | 0.01 | 9.81 | 0.002 | |
| 1.5 | 200 | 0.02 | 10.60 | 0.004 |
| 400 | 0.02 | 12.56 | 0.003 | |
| 600 | 0.01 | 12.21 | 0.002 |
| Load on Specimen (kg’s) | Speed (rpm) | Weight Loss (gm’s) | Volume Loss (mm3) | Wear Rate (mm3/N·m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 200 | 0.1 | 52.22 | 0.069 |
| 400 | 0.06 | 49.48 | 0.032 | |
| 600 | 0.03 | 23.17 | 0.010 | |
| 1.0 | 200 | 0.05 | 13.74 | 0.009 |
| 400 | 0.03 | 33.77 | 0.011 | |
| 600 | 0.02 | 39.26 | 0.008 | |
| 1.5 | 200 | 0.015 | 31.80 | 0.014 |
| 400 | 0.017 | 14.71 | 0.003 | |
| 600 | 0.02 | 10.99 | 0.002 |
| Load on Specimen (kg’s) | Speed (rpm) | Wear Rate of Untreated SAF Composite (mm3/N·m) | Wear Rate of Alkali-Treated SAF Composite (mm3/N·m) | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 200 | 0.069 | 0.026 | 62.3 |
| 400 | 0.032 | 0.014 | 56.3 | |
| 600 | 0.010 | 0.013 | −30.0 | |
| 1.0 | 200 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 77.8 |
| 400 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 72.7 | |
| 600 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 75.0 | |
| 1.5 | 200 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 71.4 |
| 400 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.0 | |
| 600 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnappa, C.M.H.H.; Sonnappa, D.; Saddashiva Reddy, N.S.K.; Rangaswamy, N.; Chate, G.R.; Gowdru Chandrashekarappa, M.P. Comparative Study on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Alkali-Treated and Untreated Sida acuta Fiber-Reinforced Composite. Eng 2025, 6, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6070143
Krishnappa CMHH, Sonnappa D, Saddashiva Reddy NSK, Rangaswamy N, Chate GR, Gowdru Chandrashekarappa MP. Comparative Study on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Alkali-Treated and Untreated Sida acuta Fiber-Reinforced Composite. Eng. 2025; 6(7):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6070143
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnappa, Chandra Mohan Heggade Halli, Devaraj Sonnappa, Narayana Swamy Kalavara Saddashiva Reddy, Nikhil Rangaswamy, Ganesh Ravi Chate, and Manjunath Patel Gowdru Chandrashekarappa. 2025. "Comparative Study on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Alkali-Treated and Untreated Sida acuta Fiber-Reinforced Composite" Eng 6, no. 7: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6070143
APA StyleKrishnappa, C. M. H. H., Sonnappa, D., Saddashiva Reddy, N. S. K., Rangaswamy, N., Chate, G. R., & Gowdru Chandrashekarappa, M. P. (2025). Comparative Study on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Alkali-Treated and Untreated Sida acuta Fiber-Reinforced Composite. Eng, 6(7), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6070143









