Lifecycle Analysis of Green Roofs in the Mediterranean Climate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Effects of Green Roofs on Buildings
1.2. Roof Garden Types
1.3. Significance of the Research
2. Methodology
2.1. Building Model
2.2. Environmental Analysis
2.3. Thermal Properties
3. Results
3.1. Energy
3.2. Emissions
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboulnaga, M.; Fouad, H. Urban Green Coverage: Importance of Green Roofs and Urban Farming Policies in Enhancing Liveability in Buildings and Cities—Global and Regional Outlook. In The Importance of Greenery in Sustainable Buildings; Sayigh, A., Trombadore, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 155–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCracken, M.C. Global warming: A science overview. In Global Warming and Energy Policy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, M.; Mukhopadhyaya, P.; Valeo, C. Effects of Extensive Green Roofs on Energy Performance of School Buildings in Four North American Climates. Water 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. 2022 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Towards a Zero-Emission, Efficient and Resilient Buildings and Construction Sector; United Nations: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IEA (International Energy Agency). Global Energy Review: CO2 Emissions in 2021; IEA: Paris, France, 2022; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-co2-emissions-in-2021-2 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- IEA (International Energy Agency). Tracking Clean Energy Progress 2023; IEA: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/tracking-clean-energy-progress-2023 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Zhong, X.; Hu, M.; Deetman, S.; Steubing, B.; Lin, H.X.; Hernandez, G.A.; Harpprecht, C.; Zhang, C.; Tukker, A.; Behrens, P. Global greenhouse gas emissions from residential and commercial building materials and mitigation strategies to 2060. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, U. Global warming: Causes, effects and solutions. Durreesamin J. 2015, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Huovila, P.; Ala-Juusela, M.; Melchert, L.; Pouffary, S.; Cheng, C.-C.; Ürge-Vorsatz, D.; Koeppel, S.; Svenningsen, N.; Graham, P. Buildings and Climate Change: Summary for Decision-Makers; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, F.; Hewage, K. Probabilistic social cost-benefit analysis for green roofs: A lifecycle approach. Build. Environ. 2012, 58, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, F.; Farshidpour, R.; Pouramini, M.; Mousavi, M.; Esfahani, A.N. Sustainability rating of lightweight expanded clay aggregates using energy inputs and carbon dioxide emissions in life-cycle analysis. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Life Cycle Civil Engineering, Ghent, Belgium, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, B.R.; Chaudhry, H.N.; Ghani, S.A. A review of sustainable cooling technologies in buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3112–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.G.; Huynh, N.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Tartarini, F.; Lipczynska, A.; Li, J.; Sultan, Z.; Goh, E.; Karunagaran, G.; Natarajan, A.; et al. Energy savings and thermal comfort in a zero energy office building with fans in Singapore. Build. Environ. 2023, 243, 110674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, P. Climate Change: Implications for Buildings. Key Findings from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fifth Assessment Report; World Business Council for Sustainable Development, University of Cambridge’s Judge Business School, Institute for Sustainability Leadership: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani, F.M.; Nelson, D. From Sustainability to Resilience: A Practical Guide to ENVISION. In Objective Resilience: Objective Processes; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2022; pp. 81–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Tehrani, F. Is resilience… sustainable? APWA Rep. 2018, 85, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Štilić, A.; Puška, A. Integrating Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods with Sustainable Engineering: A Comprehensive Review of Current Practices. Eng 2023, 4, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastan Diznab, M.A.; Tehrani, F.M. Mapping Standards and Rating Measures of Structural Green Roofs for Socio-Environmental Life Cycle Assessments Using Envision. In Leveraging Sustainable Infrastructure for Resilient Communities; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2022; pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhashimi, L.; Aljawi, L.; Gashgari, R.; Almoudi, A. The effect of rooftop garden on reducing the internal temperature of the rooms in buildings. In Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM’18), Madrid, Spain,, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, F. Rooftop gardening. A solution for energy saving and landscape enhancement in Mediterranean urban areas. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 223, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Du, X.; Zhao, H.; Hu, M.; Xu, X. Assessment of green roofs’ potential to improve the urban thermal environment: The case of Beijing. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, S.C.M. Study of Thermal and Energy Performance of Green Roof Systems; Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Hong Kong: Hong Kong, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coma, J.; Pérez, G.; Solé, C.; Castell, A.; Cabeza, L.F. Thermal assessment of extensive green roofs as passive tool for energy savings in buildings. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, E.; D’Orazio, M. Assessment of the effectiveness of cool and green roofs for the mitigation of the Heat Island effect and for the improvement of thermal comfort in Nearly Zero Energy Building. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2015, 58, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauda, I.; Alibaba, H.Z. Green roof benefits, opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Civ. Struct. Eng. Res. 2020, 7, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Drozd, W. Problems and benefits of using green roofs in Poland. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 214, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, F.M.; Zamani-Alaei, M. Sustainable Engineering for Resilient Food Security. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Agribusiness Management Conference, Fresno, CA, USA, 28 October–19 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Koroxenidis, E.; Theodosiou, T. Comparative environmental and economic evaluation of green roofs under Mediterranean climate conditions -Extensive green roofs a potentially preferable solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosareo, L.; Ries, R. Comparative environmental life cycle assessment of green roofs. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N.; Utaberta, N.; Yunos, M.Y.M.; Ismail, N.A.; Ismail, S.; Ariffin, N.F.M.; Jafari, N.; Valikhani, M. Benefits of roof garden in order to usage of urban agriculture at roof garden in high-rise building in Malaysia. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2015, 9, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, W.H.; Kent, M.G.; Schiavon, S.; Levitt, B.; Betti, G. A Window View Quality Assessment Framework. LEUKOS 2022, 18, 268–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermal Comfort Assessment of Green Roofs on an Office Building in Humid Continental Climate, China; Welsh University of Architecture, Cardiff University: Cardiff, UK, 2021.
- Raji, B.; Tenpierik, M.J.; Van Den Dobbelsteen, A. The impact of greening systems on building energy performance: A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permpituck, S.; Namprakai, P. The energy consumption performance of roof lawn gardens in Thailand. Renew. Energy 2012, 40, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, S.; Rashedi, M.R.; Ehsani, R.; Tehrani, F.M. A lifecycle analysis approach to the impact of green roofs on the structural and thermal performance of buildings. In Life-Cycle of Structures and Infrastructure Systems, Proceedings of the Eight International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering (IALCCE 2023), 2–6 July 2023, Politecnico Di Milano, Italy; Biondini, F., Frangopol, D.M., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 501–508. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, D.B.; Lawrie, L.K.; Winkelmann, F.C.; Buhl, W.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Pedersen, C.O.; Strand, R.K.; Liesen, R.J.; Fisher, D.E.; Witte, M.J. EnergyPlus: Creating a new-generation building energy simulation program. Energy Build. 2001, 33, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M. Green Roofs Energy Performance Simulation; Universidade de Lisboa: Lisbon, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sailor, D.J. A green roof model for building energy simulation programs. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1-2016; Goel, S.; Rosenberg, M.I.; Eley, C. Performance Rating Method Reference Manual. Pacific Northwest National Lab.(PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2017; 368p. [CrossRef]
- Statista. Average Size Residential Properties Sold/Purchased in Italy 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1014916/average-size-of-residential-properties-sold-purchased-by-macro-area-italy/ (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- National Centers for Environmental Information. Past Weather, Climate Monitoring. 2023. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/past-weather (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- ANSI/ASHRAE Standards 62.1–2022; American National Standards Institute; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers. Ventilation and Acceptable Indoor Air Quality. ANSI/ASHRAE: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Tehrani, F.M. The Comprehensive Guide to LECA; LECA: Tehran, Iran, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gerami, M.A.; Tehrani, F.M.; Esfahani, A.N. The Complete Guide to Lightweight Expanded Clay Aggregate in Agriculture and Landscaping; LECA: Tehran, Iran, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boudaghpour, S.; Hashemi, S. A study on light expanded clay aggregate (LECA) in a geotechnical view and its application on greenhouse and greenroof cultivation. Int. J. Geol. 2008, 4, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Effrosyni, G.; Charilaos, P.; Ifigeneia, T.; Agis, M.P. Life Cycle Analysis and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of green roofs in the Mediterranean climatic conditions. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuronuma, T.; Watanabe, H.; Ishihara, T.; Kou, D.; Toushima, K.; Ando, M.; Shindo, S. CO2 Payoff of Extensive Green Roofs with Different Vegetation Species. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
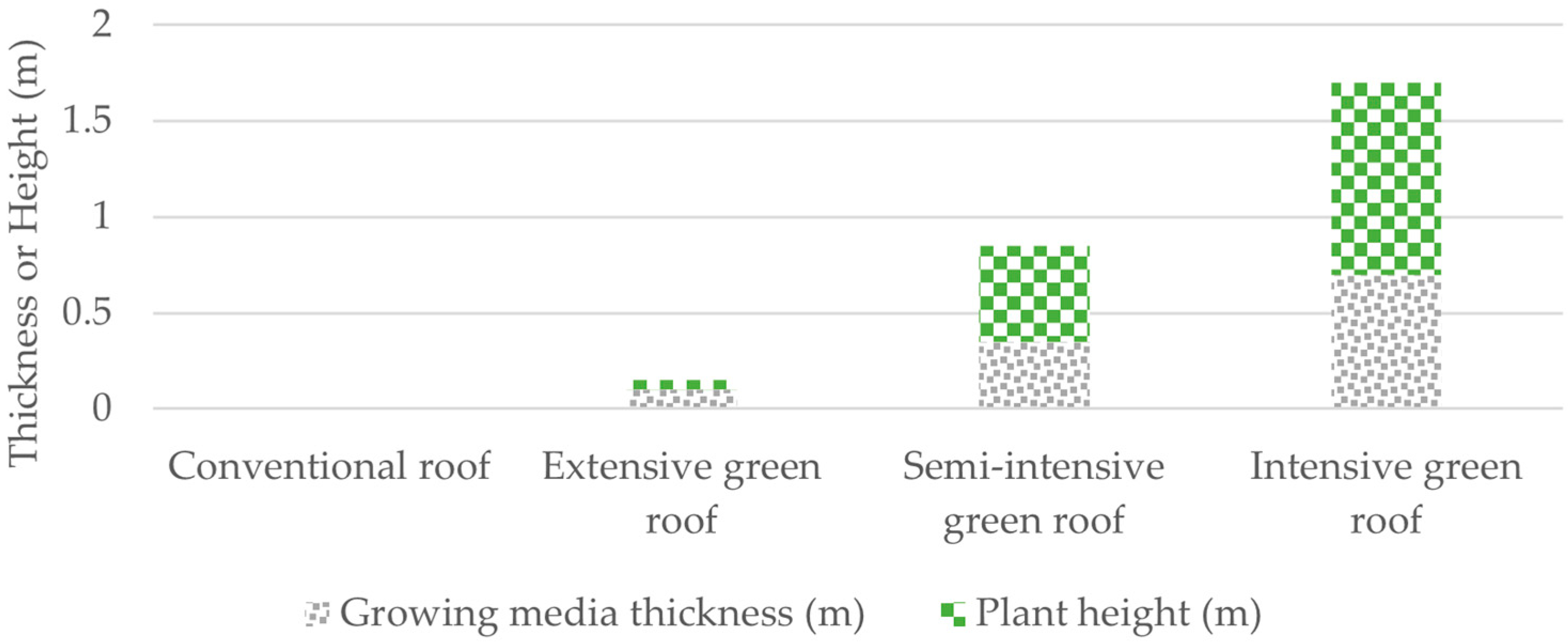



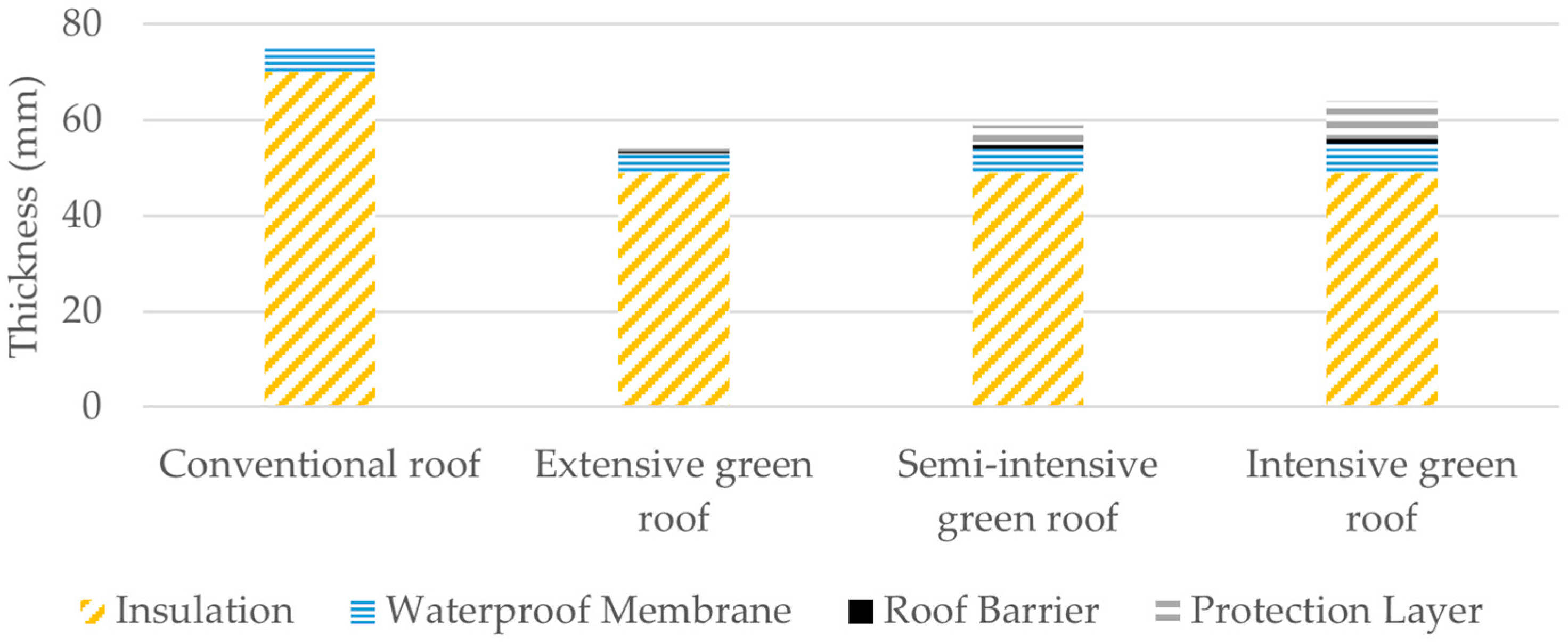
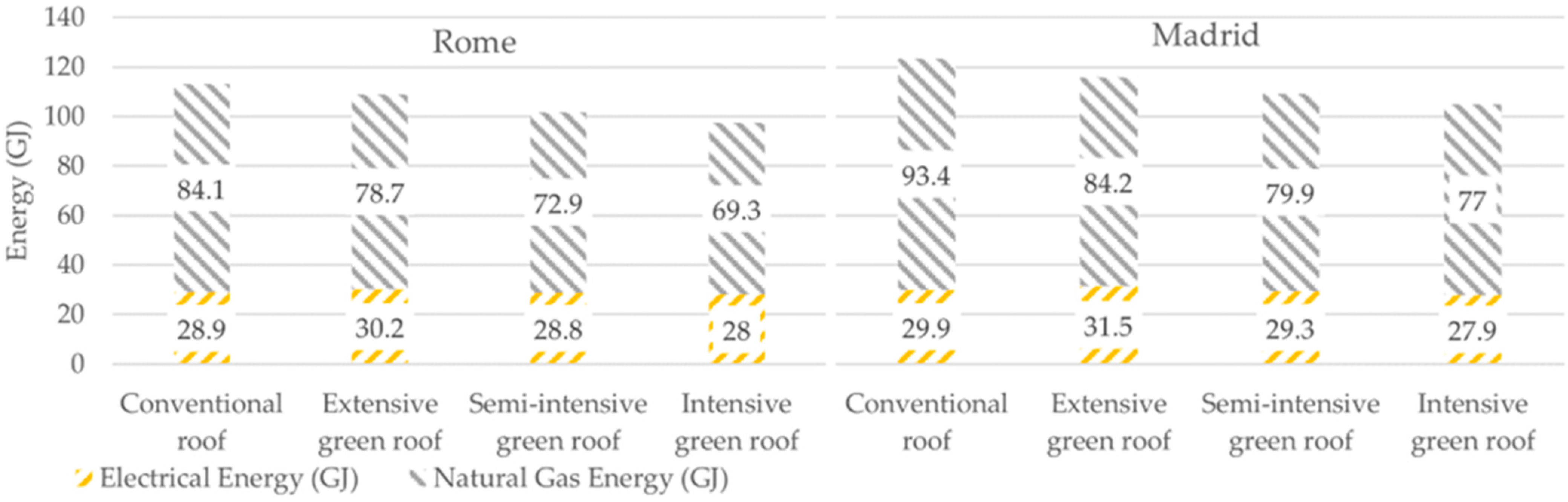
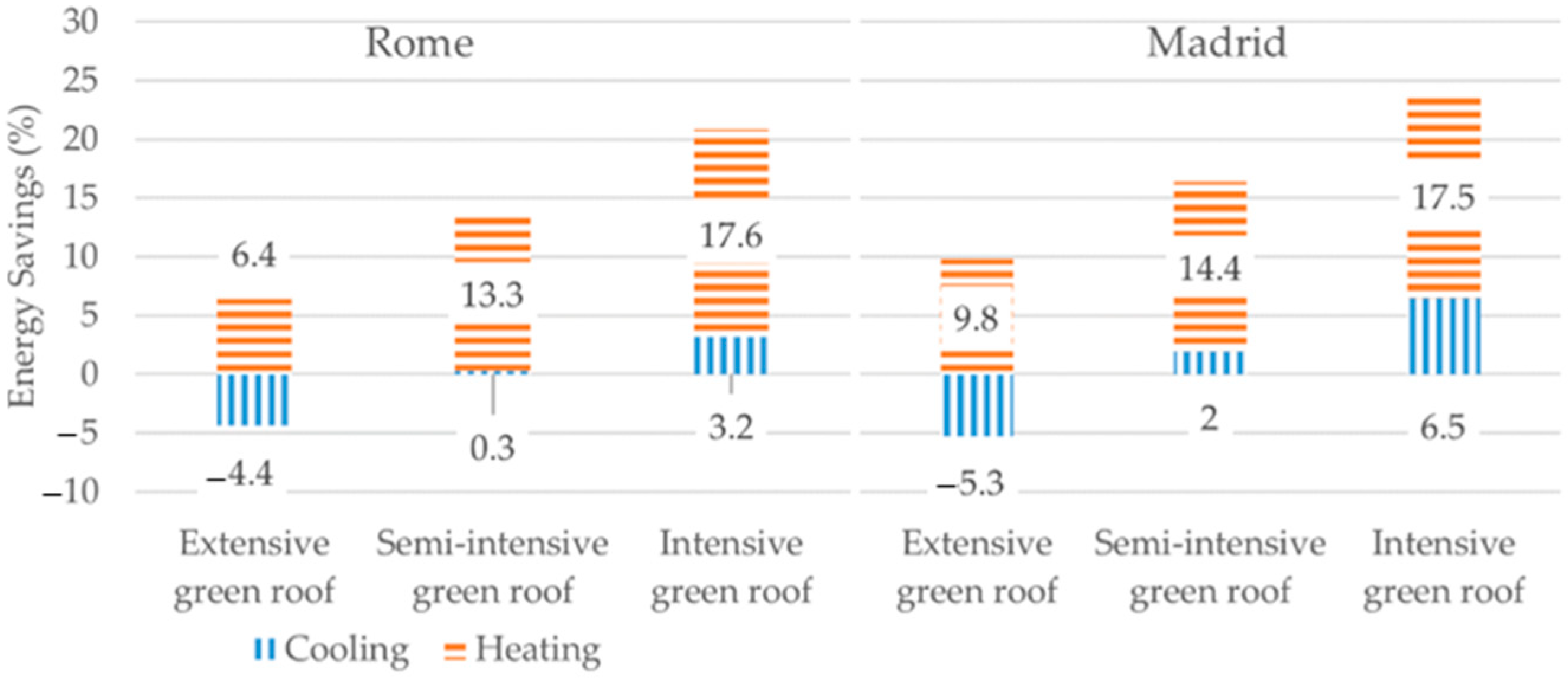

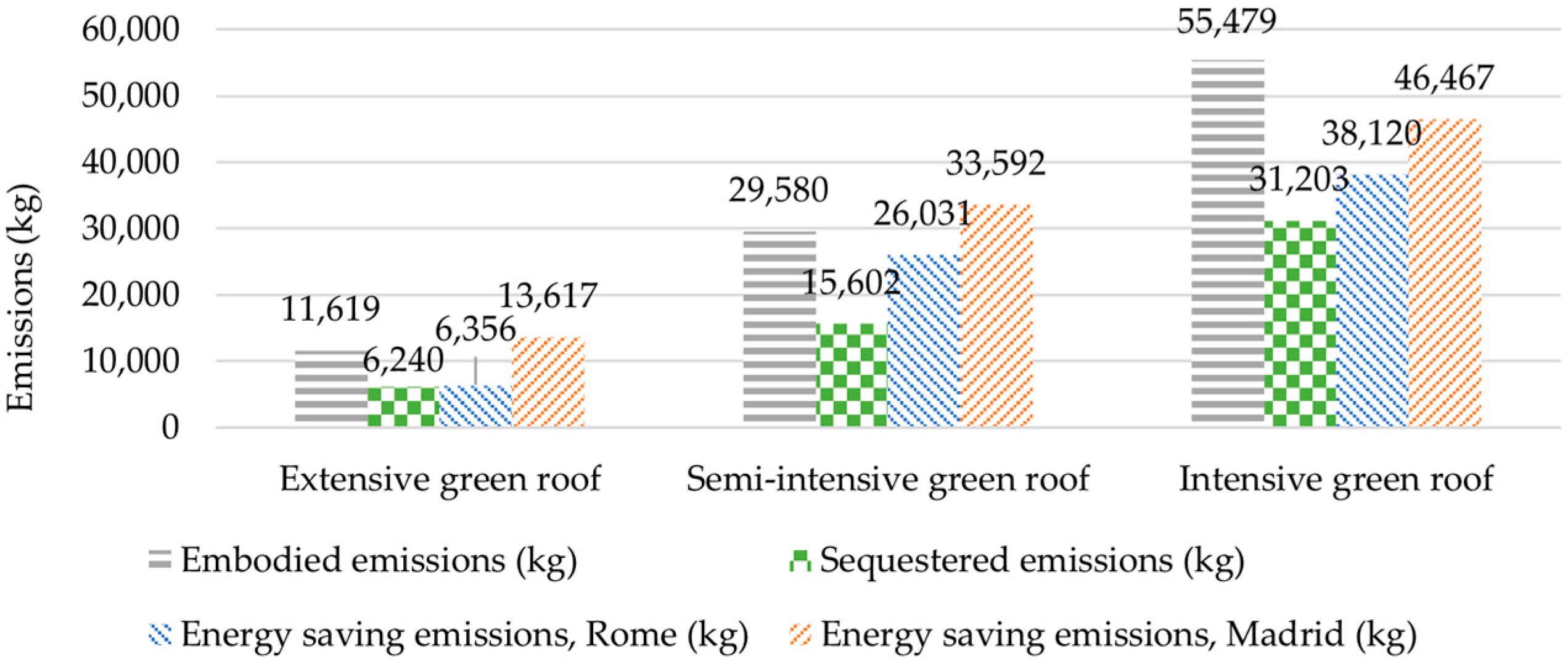

| Material | Description | Energy (kWh/kg) | Emissions (kg CO2/kg) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Polystyrene foam | 24.58 | 6.12 | 33.7 |
| Waterproof membrane | Bituminous membranes | 0.56 | 0.64 | 1100 |
| Root barrier | Polyethylene | 23.57 | 3.27 | 920 |
| Protection layer | Polypropylene | 20.93 | 3.64 | 905 |
| Substrate | 63% crushed brick, 7% compost, and 30% lightweight aggregate | 1.01 | 0.294 | 858.7 |
| Green Roof Type | Annual Emissions Reduction (kg CO2/m2/yr) |
|---|---|
| Extensive | 0.55 |
| Semi-intensive | 1.39 |
| Intensive | 2.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashedi, M.R.; Ehsani, R.; Kalantari, S.; Tehrani, F.M. Lifecycle Analysis of Green Roofs in the Mediterranean Climate. Eng 2023, 4, 2571-2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4040147
Rashedi MR, Ehsani R, Kalantari S, Tehrani FM. Lifecycle Analysis of Green Roofs in the Mediterranean Climate. Eng. 2023; 4(4):2571-2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4040147
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashedi, Mohammad Raoof, Rojina Ehsani, Sara Kalantari, and Fariborz M. Tehrani. 2023. "Lifecycle Analysis of Green Roofs in the Mediterranean Climate" Eng 4, no. 4: 2571-2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4040147
APA StyleRashedi, M. R., Ehsani, R., Kalantari, S., & Tehrani, F. M. (2023). Lifecycle Analysis of Green Roofs in the Mediterranean Climate. Eng, 4(4), 2571-2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4040147








