Ecotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Ecotoxicity–Antibacterial Activity
2.2.2. Hemolytic Activity
3. Results
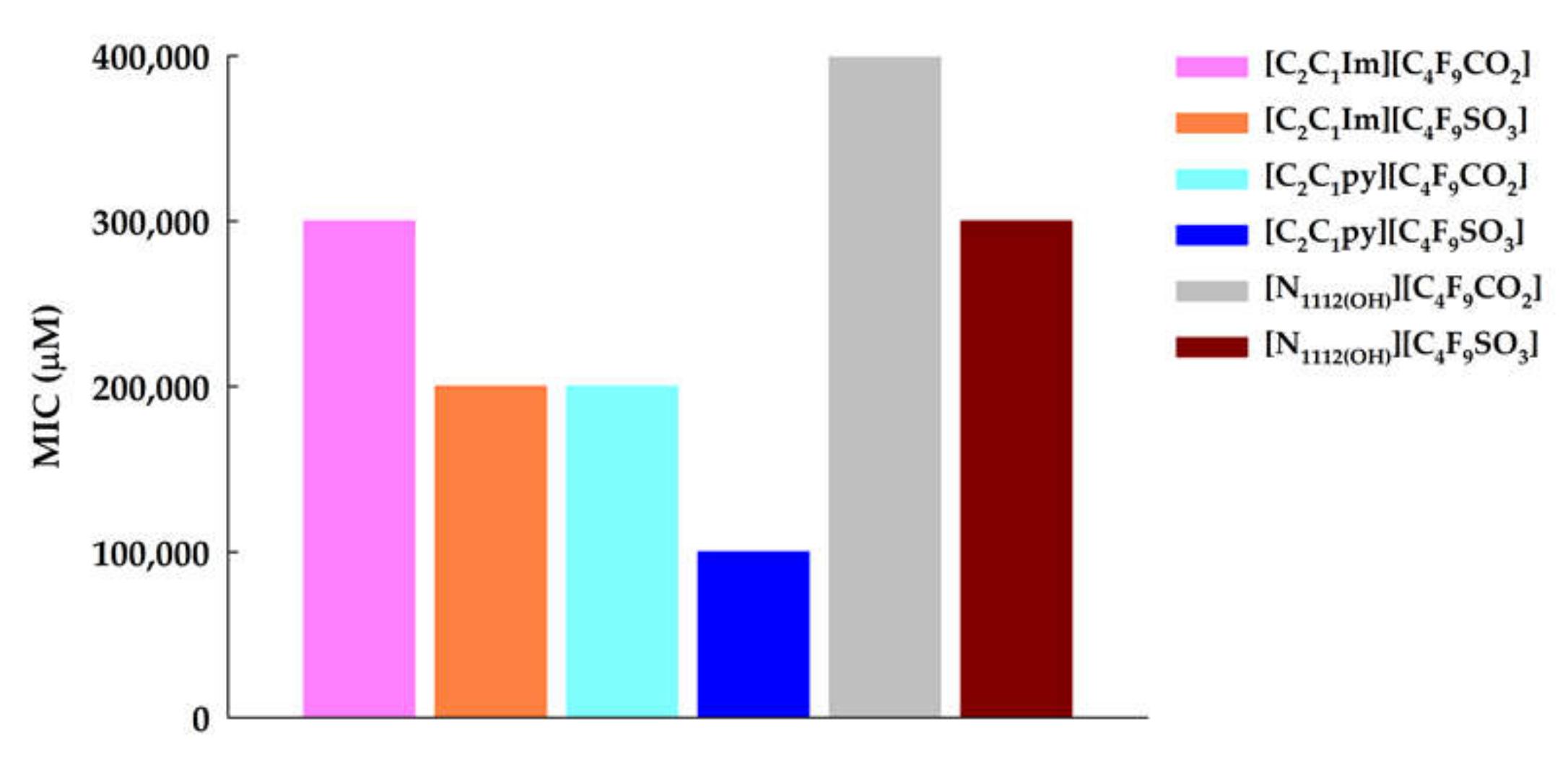
3.1. Ecotoxicity–Antibacterial Activity
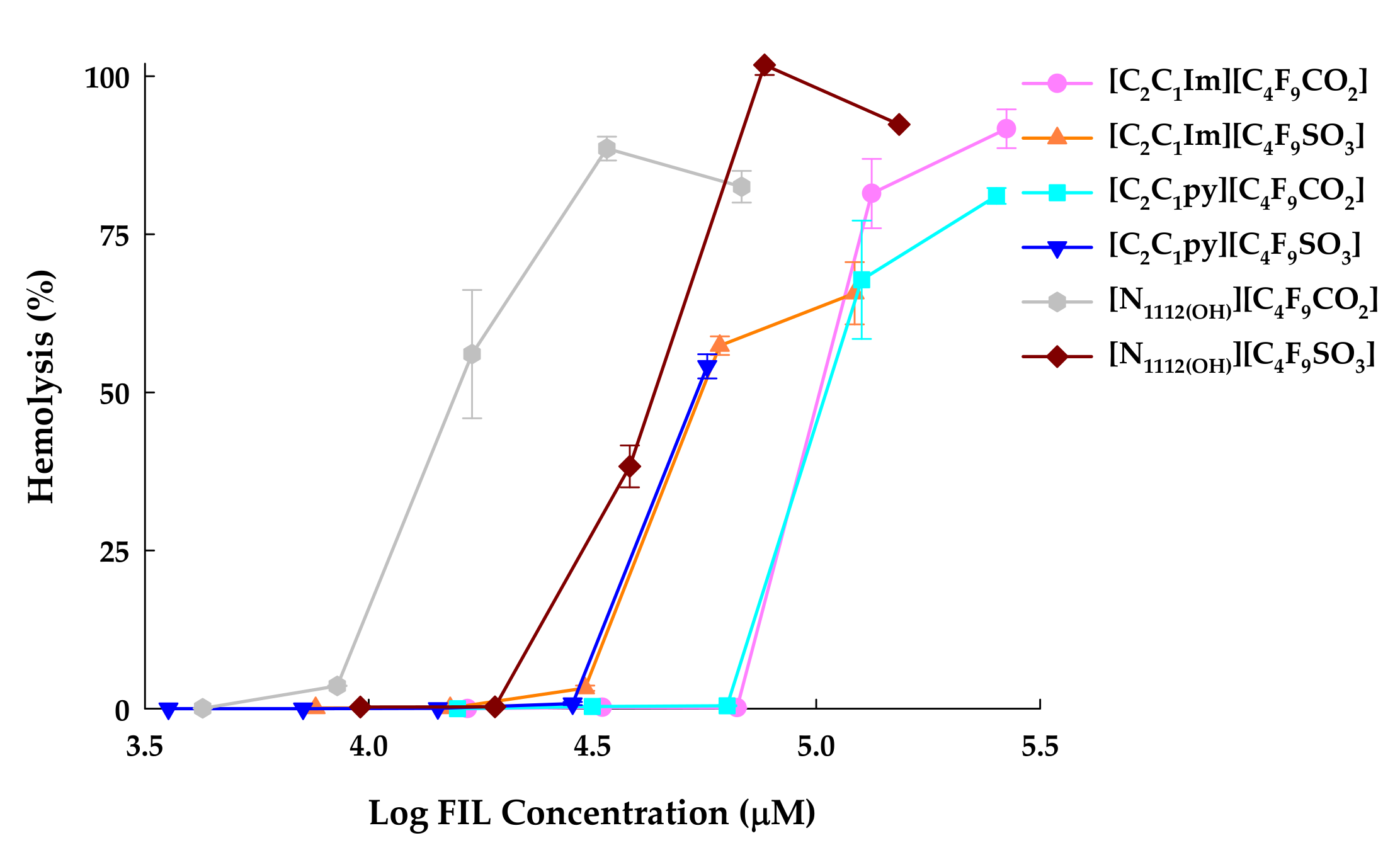
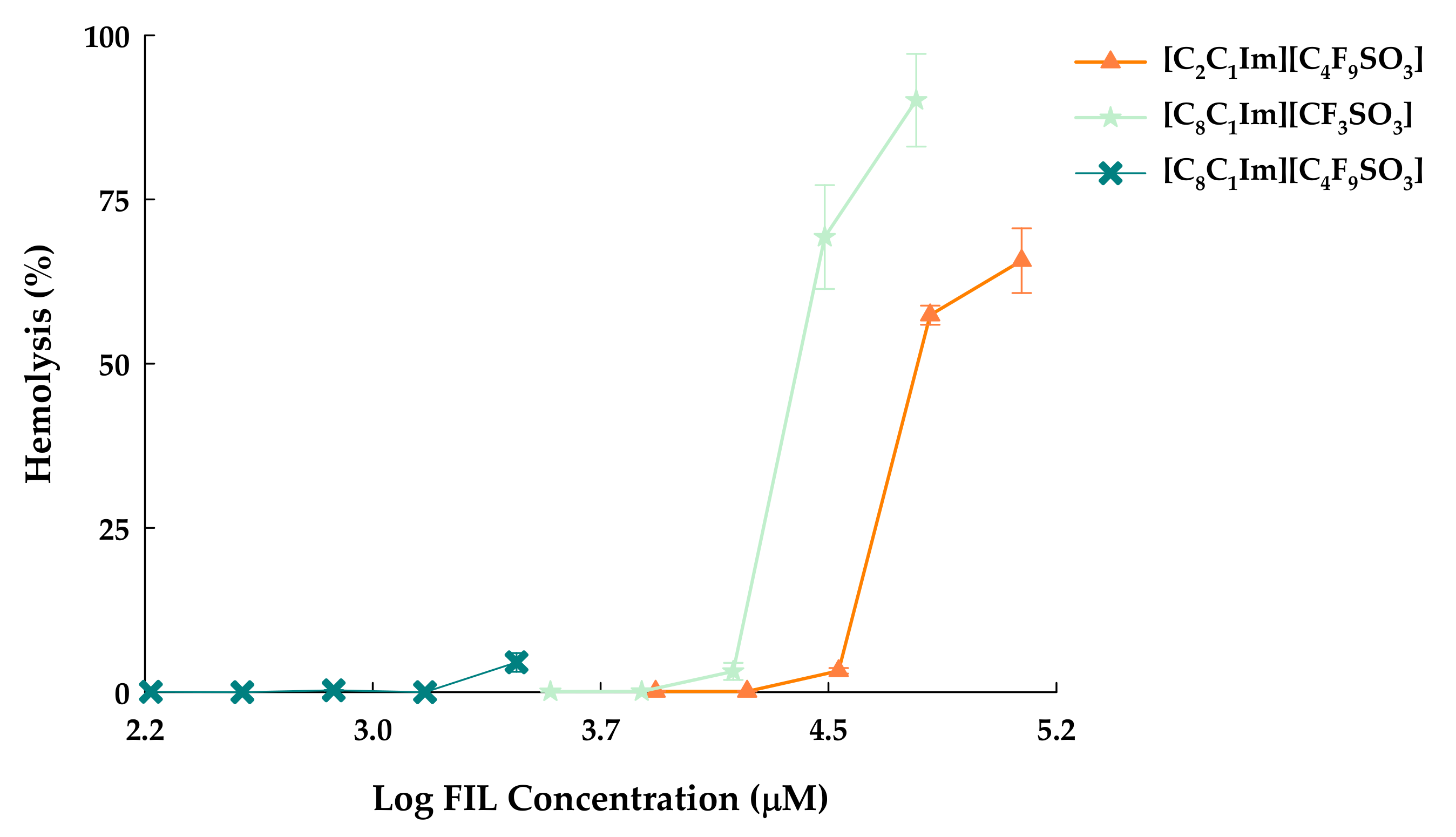
3.2. Hemolytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padvi, S.A.; Dalal, D.S. Task-specific Ionic Liquids as a Green Catalysts and Solvents for Organic Synthesis. Curr. Green Chem. 2020, 7, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, W.; Chen, C.; Hou, Z. Temperature-responsive ionic liquids: Fundamental behaviors and catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6881–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmero, L.; Mezzetta, A.; Pomelli, C.S.; Chiappe, C.; Guazzelli, L. Evaluation of the effect of the dicationic ionic liquid structure on the cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Thomas, M.L.; Zhang, S.; Ueno, K.; Yasuda, T.; Dokko, K. Application of ionic liquids to energy storage and conversion materials and devices. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7190–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Yu, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, F. Ionic liquid lubricants: When chemistry meets tribology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7753–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Shi, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Highly Efficient Nitric Oxide Capture by Azole-Based Ionic Liquids through Multiple-Site Absorption. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 14576–14580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; e Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: Past, present, and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Cai, P.; Zhao, X.; Kong, Y.; Pan, Y. Recent progress of task-specific ionic liquids in chiral resolution and extraction of biological samples and metal ions. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoronsk, E.; Fernandes, M.; Malaret, F.J.; Hallet, J.P. Use of phosphonium ionic liquids for highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhan, T.; Zhang, K. Ionic Liquid-Based Stimuli-Responsive Functional Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Zeng, X. Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents and Electrolytes for Robust Chemical Sensor Development. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z. Ionic liquids: Green and tailor-made.solvents in drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agatemor, C.; Ibsen, K.N.; Tanner, E.E.L.; Mitragotri, S. Ionic liquids for addressing unmet needs in healthcare. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gilmore, B.F. The antimicrobial potential of ionic liquids: A source of chemical diversity for infection and biofilm control. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z. Ionic Liquids as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, G.; Lin, W.; Bai, H.; Li, H.; Tang, G.; Wang, C. Design and tuning of ionic liquid–based HNO donor through intramolecular hydrogen bond for efficient inhibition of tumor growth. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids-Solvents of the future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earle, M.J.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Gilea, M.A.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Magee, J.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Widegren, J.A. The distillation and volatility of ionic liquids. Nature 2006, 439, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzetta, A.; Perillo, V.; Guazzelli, L.; Chiape, C. Thermal behavior analysis as a valuable tool for comparing ionic liquids of different classes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 3335–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.J.; Bui-Le, L.; Hallett, J.P.; Licence, P. Thermally Stable Imidazolium Dicationic Ionic Liquids with Pyridine Functional Groups. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8762–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids: Eco(cyto)activity as complicated, but unavoidable parameter for task-specific optimization. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Fundamental importance of ionic interactions in the liquid phase: A review of recent studies of ionic liquids in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.M.; Kulpa, J.C.F. Toxicity and Antimicrobial Activity of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojtášková, J.; Koutník, I.; Vráblová, M.; Sezimová, H.; Maxa, M.; Obalová, L.; Pánek, P. Antibacterial, Antifungal and Ecotoxic Effects of Ammonium and Imidazolium Ionic Liquids Synthesized in Microwaves. Molecules 2020, 25, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornellas, A.; Perez, L.; Comelles, F.; Ribosa, I.; Manresa, A.; Garcia, M.T. Self-Aggregation and Antimicrobial Activity of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Based Ionic Liquids in Aqueous Solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 355, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, W.; Becherini, S.; D’Andrea, F.; Lupetti, A.; Chiappe, C.; Guazzelli, L. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial activity of different types of ionicliquids. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demberelnyamba, D.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Yoo, I. Synthesis and antimicrobial properties of imidazolium and pyrrolidinonium salts. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, Q.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Mao, H.; Wang, B.; Yan, F. Structure–Antibacterial Activity Relationships of Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Monomers, Poly(ionic liquids) and Poly(ionic liquid) Membranes: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trush, M.M.; Semenyuta, I.V.; Vdovenko, S.I.; Rogalsky, S.P.; Lobko, E.O.; Metelytsia, L.O. Synthesis, spectroscopic and molecular docking studies of imidazolium and pyridinium based ionic liquids with HSA as potential antimicrobial agents. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 137, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Stolte, S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereiro, A.B.; Markiewicz, M. Acute aquatic toxicity and biodegradability of fluorinated ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, B.F.; Andrews, G.P.; Borberly, G.; Earle, M.J.; Gilea, M.A.; Gorman, S.P.; Lowry, A.F.; McLaughlina, M.; Seddon, K.R. Enhanced antimicrobial activities of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids based on silver or copper containing anions. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, L.; Chau, P.K.W.; Earle, M.J.; Gilea, M.A.; Gilmore, B.F.; Gorman, S.P.; McCann, M.T.; Seddon, K.R. Antibiofilm activities of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.R.; Li, M.; El-Zahab, B.; Janes, M.E.; Hayes, D.; Warner, I.M. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of β-lactam antibiotic-based imidazolium- and pyridinium-type ionic liquids. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.S.; Deive, F.J.; Sanromán, M.Á.; Rodríguez, A. Microbial Adaptation to Ionic Liquids Increases the “Talent” to Treat Contaminants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet, M.; Datta, S.; Dibble, D.C.; Tamrakar, P.R.; Benke, P.I.; Li, C.; Singh, S.; Sale, K.L.; Adams, P.D.; Keasling, J.D.; et al. Impact of ionic liquid pretreated plant biomass on Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth and biofuel production. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.G.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Alviano, D.S.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids toward Microorganisms Interesting to the Food Industry. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37157–37163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Malhotra, S.V.; Francis, A.J. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids to Clostridium sp. and Effects on Uranium Biosorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Martinho, S.; Alves, F.; Nunes, S.; Matias, A.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Fluorinated ionic liquids: Properties and applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Shimizu, K.; Marrucho, I.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. On the Formation of a Third, Nanostructured Domain in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 10826–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Libelo, E.L.; Field, J.A. Guest comment: Perfluoroalkyl acid focus issue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7951–7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.; Resnati, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Weber, E.; Hulliger, J. Organic fluorine compounds: A great opportunity for enhanced materials properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3496–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Teixeira, F.S.; Marrucho, I.M.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aggregation behavior and total miscibility of fluorinated ionic liquids in water. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, F.S.; Vieira, N.S.M.; Cortes, O.A.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Marrucho, I.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereiro, A.B. Phase equilibria and surfactant behavior of fluorinated ionic liquids with water. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 82, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Bastos, J.C.; Hermida-Merino, C.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Aggregation and phase equilibria of fluorinated ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Bastos, J.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Matias, A.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Human cytotoxicity and octanol/water partition coefficients of fluorinated ionic liquids. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.; Vieira, N.S.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B.; Archer, M. Fluorinated ionic liquids for protein drug delivery systems: Investigating their impact on the structure and function of lysozyme. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Castro, P.J.; Marques, D.F.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Tailor-made fluorinated ionic liquids for protein delivery. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Martins, I.C.; Pereiro, A.B.; Archer, M. Insights into the interaction of bovine serum albumin with surface-active ionic liquids in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 332, 114537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalucat, J.; Bennasar, A.; Bosch, R.; García-Valdés, E.; Palleroni, N.J. Biology of Pseudomonas stutzeri. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 510–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, C.C.C.; Andrade da Silva, G.O.; Bitencourt, J.A.P.; Chequer, L.P.T.; Pennafirme, S.; Jurelevicius, D.A.; Seldin, L.; Crapez, M.A.C. Potential application of Pseudomonas stutzeri W228 for removal of copper and lead from marine environments. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240486. [Google Scholar]
- Moscoso, F.; Deive, F.J.; Longo, M.A.; Sanromán, M.A. Technoeconomic assessment of phenanthrene degradation by Pseudomonas stutzeri CECT 930 in a batch bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscoso, F.; Deive, F.J.; Villar, P.; Pena, R.; Herrero, L.; Longo, M.A.; Sanromán, M.A. Assessment of a process to degrade metal working fluids using Pseudomonas stutzeri CECT 930 and indigenous microbial consortia. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthipan, P.; Narenkumar, J.; Elumalai, P.; Preethi, P.S.; Nanthini, A.U.R.; Agrawal, A.; Rajasekar, A. Neem extract as a green inhibitor for microbiologically influenced corrosion of carbon steel API 5LX in a hypersaline environments. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalej, H.; Boisset, C.; Hmidet, N.; Colin-Morel, P.; Buon, L.; Nasri, M. Depolymerization of Pseudomonas stutzeri exopolysaccharide upon fermentation as a promising production process of antibacterial compounds. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Reis, P.M.; Shimizu, K.; Cortes, A.O.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Pereiro, A.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N. A thermophysical and structural characterization of ionic liquids with alkyl and perfluoroalkyl side chains. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65337–65350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Luís, A.; Reis, P.M.; Carvalho, P.J.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Freire, M.G.; Pereiro, A.B. Fluorination effects on the thermodynamic, thermophysical and surface properties of ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 97, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.M.; Calado, S.; Pereira, J.; Ferronha, H.; Correia, I.; Castro, H.; Tomás, A.M.; Cruz, M.E.M. Targeted delivery of paromomycin in murine infectious diseases through association to nano lipid systems. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, M.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Nanoformulations of a potent copper-based aquaporin inhibitor with cytotoxic effect against cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messali, M.; Aouad, M.R.; El-Sayed, W.S.; Ali, A.A.; Hadda, T.B.; Hammouti, B. New Eco-Friendly 1-Alkyl-3-(4-phenoxybutyl) Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids Derivatives: A Green Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial Activity and POM Analyses. Molecules 2014, 19, 11741–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Ferguson, J.L.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Ferreira, R.; Leitão, M.C.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereira, C.S. Novel biocompatible cholinium-based ionic liquids—Toxicity and biodegradability. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Nasrullahc, A.; Ullah, Z.; Bhat, A.H.; Ghanem, O.B.; Muhammad, N.; Rashid, M.U.; Man, Z. Thermophysical properties and ecotoxicity of new nitrile functionalized protic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silhavy, T.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S. The Bacterial Cell Envelope. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, R.A.; Bouchelle, L.D.; Ferrell, B.D.; Buck, R.C. Comparative Acute Freshwater Hazard Assessment and Preliminary PNEC Development for Eight Fluorinated Acids. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, N.; Malferarri, D.; Kolusheva, S.; Galletti, P.; Tagliavini, E.; Jelinek, R. Membrane interactions of ionic liquids: Possible determinants for biological activity and toxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 2967–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A.; Papaıconomou, N.; Lee, J.; Salminen, J.; Clark, D.S.; Prausnitz, J.M. In vitro cytotoxicities of ionic liquids: Effect of cation rings, functional groups, and anions. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 24, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.R.; Silva, C. Ionic liquids: A pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, J.; Molter, K.; Stock, F.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Poczobutt, J.; Hoffmann, J.; Ondruschka, B.; Filser, J.; Jastorff, B. Biological effects of imidazolium ionic liquids with varying chain lengths in acute vibrio fischeri and WST-1 cell viability assays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 58, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
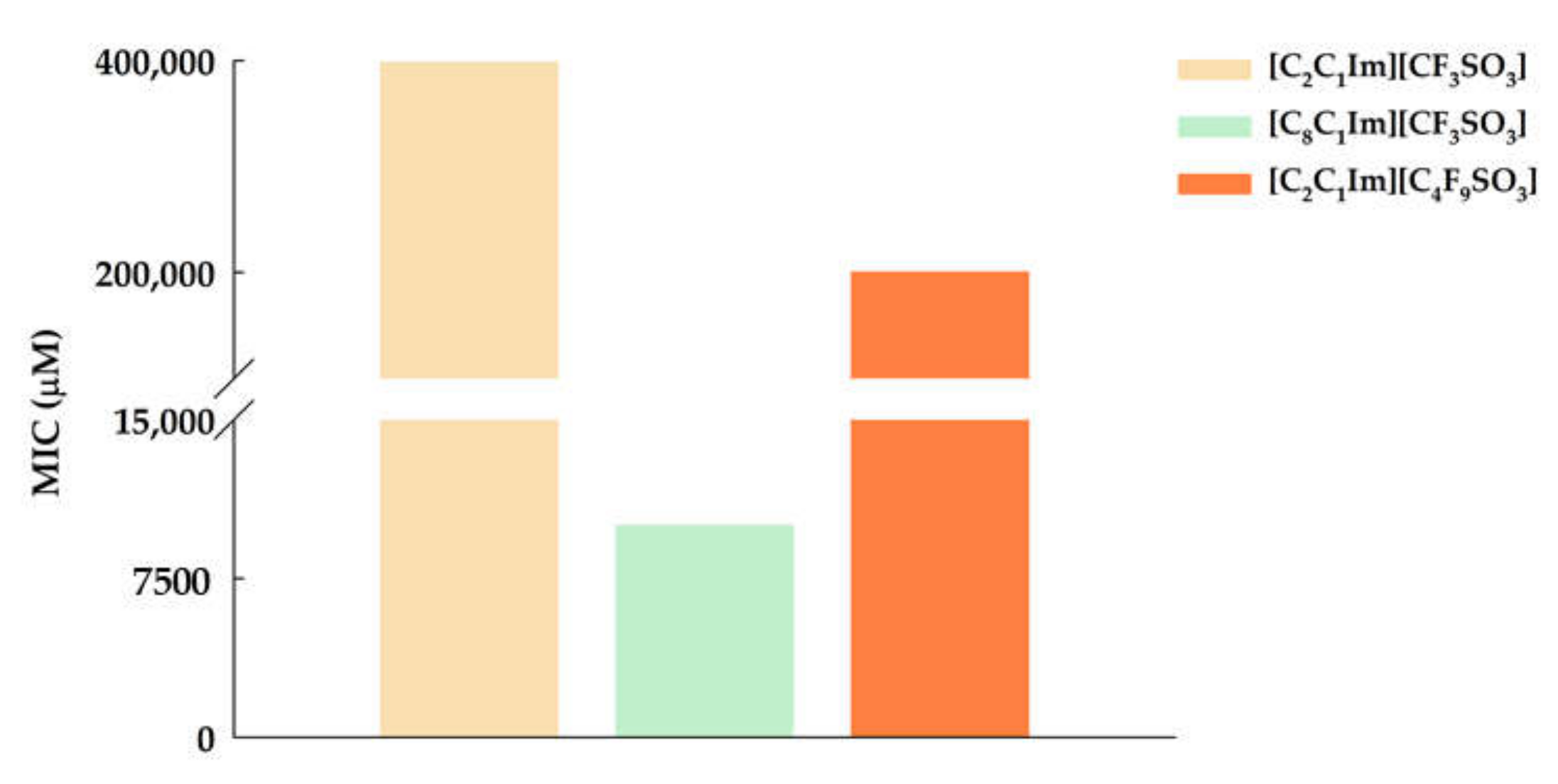
| FIL Designation | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|
| 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perfluoromethanesulfonate [C2C1Im][CF3SO3] | 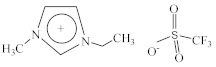 |
| 1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium perfluoromethanesulfonate [C8C1Im][CF3SO3] | 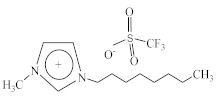 |
| 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perfluorobutanesulfonate [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] | 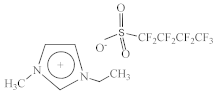 |
| 1-Methyl-3-octylimidazolium perfluorobutanesulfonate [C8C1Im][C4F9SO3] | 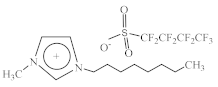 |
| 1-Ethyl-3-methylpyridinium perfluorobutanesulfonate or 1-ethyl-3-picolinium perfluorobutanesulfonate [C2C1py][C4F9SO3] |  |
| Choline perfluorobutanesulfonate [N1112(OH)][C4F9SO3] | 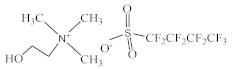 |
| 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perfluoropentanoate [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2] | 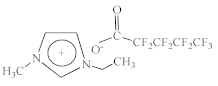 |
| 1-Ethyl-3-methylpyridinium perfluoropentanoate [C2C1py][C4F9CO2] | 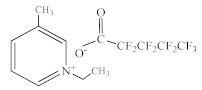 |
| Choline perfluoropentanoate [N1112(OH)][C4F9CO2] | 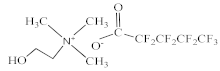 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, N.S.M.; Oliveira, A.L.S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Gaspar, M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Ecotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 2, 115-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010008
Vieira NSM, Oliveira ALS, Araújo JMM, Gaspar MM, Pereiro AB. Ecotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids. Sustainable Chemistry. 2021; 2(1):115-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Nicole S. M., Ana L. S. Oliveira, João M. M. Araújo, Maria Manuela Gaspar, and Ana B. Pereiro. 2021. "Ecotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids" Sustainable Chemistry 2, no. 1: 115-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010008
APA StyleVieira, N. S. M., Oliveira, A. L. S., Araújo, J. M. M., Gaspar, M. M., & Pereiro, A. B. (2021). Ecotoxicity and Hemolytic Activity of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids. Sustainable Chemistry, 2(1), 115-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010008








