Abstract
Proteins are bioactive compounds with high potential to be applied in the biopharmaceutical industry, food science and as biocatalysts. However, protein stability is very difficult to maintain outside of the native environment, which hinders their applications. Fluorinated ionic liquids (FILs) are a promising family of surface-active ionic liquids (SAILs) that have an amphiphilic behavior and the ability to self-aggregate in aqueous solutions by the formation of colloidal systems. In this work, the protein lysozyme was selected to infer on the influence of FILs in its stability and activity. Then, the cytotoxicity of FILs was determined to evaluate their biocompatibility, concluding that the selected compounds have neglected cytotoxicity. Therefore, UV–visible spectroscopy was used to infer the FIL-lysozyme interactions, concluding that the predominant interaction is the encapsulation of the lysozyme by FILs. The encapsulation efficiency was also tested, which highly depends on the concentration and anion of FIL. Finally, the bioactivity and thermal stability of lysozyme were evaluated, and the encapsulated lysozyme keeps its activity and thermal stability, concluding that FILs can be a potential stabilizer to be used in protein-based delivery systems.
1. Introduction
Proteins are complex bioactive entities playing a wide variety of roles in all living systems, and having high relevance in different fields such as the biopharmaceutical industry, therapeutic components, food science and biocatalysts [1,2,3,4]. Proteins’ functionality is entirely dependent on the maintenance of their three-dimensional structure in solution, which is the result of weak interactions, such as hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic and ionic interactions. Outside of the proteins’ native environment, it is very difficult to maintain their stability and consequently their bioactivity due to the disruption of their intramolecular interactions, leading to irreversible unfolding, aggregation, and consequently inactivation [3,4]. It is known that the activity, specificity, and stability of the proteins are entirely dependent on the characteristics of their local environment such as the polarity, viscosity, hydrophobicity, hydrogen-bonding ability, and the presence of impurities. Then, the low stability at room temperature for long periods of time, the high sensitivity to temperature and pH value variation, and the presence of organic compounds to ease the solubilization of substrates that are poorly soluble in water can cause irreversible denaturation of proteins. Moreover, protein-based pharmaceuticals have their function hindered due to lack of stability in the steps of formulation, production, and storage of the drug as well as due to the external factors regarding the route of administration of the pharmaceutical [1,2,3,4]. The preservation of both the structure and bioactivity of the protein depends on the fragile equilibrium of the interactions between the amino acid residues present in the surface of the protein and the compounds in their environment [5], demanding a large amount of knowledge of these interactions and the formulation of mechanisms capable of protecting the integrity and activity of the proteins. Some examples of strategies for the maintenance of protein stability are: immobilization by a physical barrier like microencapsulation within micelles or colloidal structures and nanoencapsulation; stabilization by physical adsorption through weak attractive forces to a specific support; by chemical bonding processes, immobilizing the protein in activated supports; and by adding stabilizer agents to the media involving the protein such as sugars, salts, synthetic polymers, or cryoprotectant agents [1].
Lysozyme (Lys) is a small globular protein with 129 amino acid residues, a molecular weight of approximately 14.7 kDa, and a positively charged surface, found in different living organisms and biological fluids. Lys is an enzyme with multifaceted properties which enable its unique antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antihistaminic activities [6,7]. This enzyme was selected for this study as a model protein due to its vast applicability in biochemical, pharmaceutical, and food industry fields; easy availability due to the high homology of human Lys with hen egg white Lys; and irreversible aggregation which hinders its usage and increases the interest in it as a target of studies in the areas of protein stability, activity, interactions with other compounds, protein-based deliveries, crystallization, and separation processes [6,7].
In recent decades, a huge effort has been made to unveil the biological properties of ionic liquids (ILs) to use them as solubility enhancers of poorly soluble macromolecules, additives in the formulation of biopharmaceuticals, biomedical analytics, drug carriers, enhancers of conventional drugs, antimicrobial agents, antibiofilm agents, and others [2,3,4,8,9]. The tunable nature of ILs confers versatility to use them in different fields of research, by combining different cations and anions, enabling the synthesis of a compound with desirable properties for a specific application. The reputation of ILs as “green solvents” is derived from their lower vapor pressure combined with low flammability, thermodynamic stability, and tunable physicochemical and biological properties. These properties make them more biocompatible and efficient solvents for protein stability and activity research [2]. A specific family has grown in this direction, the surface-active ionic liquids (SAILs), which are characterized by their enhanced solubilization mechanisms due to their amphiphilic nature granted by the long cationic and/or anionic hydrogenated chains. The superior surface activity of SAILs compared with conventional surfactants allows self-assembly in aqueous solutions into more efficient colloidal systems, such as micelles or vesicles, with greater control of their shape, size, stability, and specific utility [7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. These advantages highlight the substitution of surfactants by SAILs in the protein stability field, successfully demonstrated by some works in the specific case of lysozyme. Bisht et al. [10] reported the influence on structural stability and activity of lysozyme by different ammonium-based ILs, included one that is highly hydrophobic, methyl-trioctylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. This work concluded that the increment of the hydrophobicity decreases the stability and activity of the protein, as well as the increment of IL concentration, for all studied ILs. The same conclusions were found in another work with imidazolium-based ILs [11]. Mandal et al. [12] studied the interactions between 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium octylsulfate and lysozyme, discovering a destabilizing effect of the IL which highly depends on the variation of the solution pH and of the increment of IL concentration added to the solution. Kumari et al. [13] highlighted the binding of 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium chloride at the active site of lysozyme mainly by hydrophobic interactions, inducing conformational change by reducing the intramolecular hydrogen bond of the enzyme and enhancing the protein activity. In another work, Kumari et al. [14] selected 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride as an additive to prevent protein aggregation. This IL maintains the conformational and thermal stability of lysozyme at lower concentrations, increasing the activity of the protein with the increment of IL concentration up to a certain concentration. Rather et al. [15] studied the structural–functional integrity of lysozyme in the presence of two SAILs, 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, in the concentration range of critical aggregation concentrations (CACs) and the SAIL saturation concentration of the protein backbone. They found out that this IL is an efficient additive agent for the enhancement of lysozyme stability, increasing its activity and preserving the thermal and conformational stability, while the other studied IL has the opposite behavior. Singh et al. [7,16] recently showed in two different works the complexation of lysozyme by binding to bio-based SAILs, allowing the connection of lysozyme molecules to each other and providing enhanced structural stability and antimicrobial activity to the enzyme, depending on the concentration of SAILs and of their distinct interactions with the protein.
One new family of SAILs has gained much attention, the so-called fluorinated ionic liquids (FILs) [17]. They have enhanced solubilization power due to the formation of three nanosegregated domains, one polar and two non-polar, and are able to dissolve polar, hydrogenated, and fluorinated solutes [18,19]. FILs are characterized by low surface tension, high surfactant power, elevated surface activity with a highly amphiphilic character, and consequently a high aggregation behavior [20,21,22,23]. The possibility to design FILs that are completely miscible in water [21,22,23], with negligible cytotoxicity and ecotoxicity [24,25], and maintaining all the characteristics mentioned above, makes them even more biocompatible. FILs in a water-rich phase show smaller CACs than the conventional hydrogenated and fluorinated surfactants, which proves their rich aggregation behavior [21,22,23]. At least three different CACs were found for different FILs, which indicates the formation of different colloidal structures [21], having improved mechanisms of solubilization and opening the possibility of using FILs as protein stabilizers and as drug delivery systems. Our research group has successfully shown the encapsulation and release of lysozyme by FILs [26,27] as well as the enhanced stability, encapsulation, and interactions of FILs with bovine serum albumin protein [28]. The nature of FILs is very versatile and it is impossible to apply a universal rule to understand how proteins react to their presence, and unveiling the mechanisms of stability, activity, and interaction of the protein with a specific IL requires a separate study. More studies are needed in this regard, to better understand the mechanisms of FILs as stabilizers and/or carriers of proteins, by assessing their interactions, and the power of stabilization and encapsulation, to enable their application in the biological field.
In this work, efforts have been made to find how the structural features of FILs (such as cation, anion, and functionalization of cation) influence the mechanisms of the solubilization and stabilization of lysozyme, which should be granted by the encapsulation of the protein. The cytotoxicity of the studied FILs was firstly determined to ensure biocompatibility. UV–visible spectrophotometry was used as a method of screening of the different interactions between FILs and lysozyme. The FILs that significantly altered the lysozyme spectroscopy profile were chosen to determine the encapsulation efficiency by a BCA™ Protein Assay Kit and to study the effect on the bioactivity of the enzyme. Finally, the thermal stability of lysozyme was evaluated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to verify the influence of the mechanism of encapsulation and stabilization of lysozyme by the most efficient FILs. This study proved the greater ability of FILs to enhance the stability and activity of the lysozyme, protecting it from the external factors of its local environment by efficient encapsulation of the protein. Then, it is possible to design compounds with enhanced surface activity, compared to SAILs, but with lower hydrophobic content. This combination bypasses the problems of the highly hydrophobic SAILs where the increment of concentration can have a destabilizing and denaturant effect. In our work, the lysozyme is highly active in concentrations higher than 30% (wt/wt) of FIL. On one hand, FILs allow a new mechanism of stabilization and protection of the protein by its encapsulation and, on the other hand, extend the range of concentrations where lysozyme is active and stable in the presence of ILs. This work opens doors to the application of FILs in the biopharmaceutical field, as a stabilizer of proteins in all the processes of formulation, production, and storage of new therapeutic products as well as in the administration route of the enzyme as a delivery system.
2. Materials and Experimental Methodology
2.1. Materials
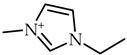
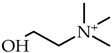
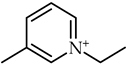
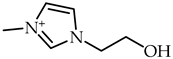
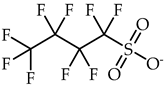
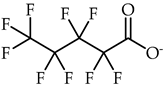
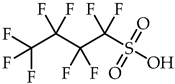
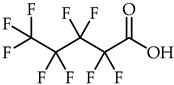
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perfluoropentanoate, ([C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], 98% mass fraction purity); 1-ethyl-3-methylpyridinium perfluoropentanoate, ([C2C1py][C4F9CO2], 98% mass fraction purity); (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium perfluoropentanoate ([N1112(OH)][C4F9CO2], 98% mass fraction purity); 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methylimidazolium perfluoropentanoate, ([C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2], 98% mass fraction purity); and 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methylimidazolium perfluorobutanesulfonate, ([C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3], 98% mass fraction purity) were synthesized by the ion exchange resin method as previously developed by Fukumoto et al. [29], and implemented in our lab [24,30,31,32]. 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perfluorobutanesulfonate ([C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], ≥97% mass fraction purity) and (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium perfluorobutanesulfonate ([N1112(OH)][C4F9SO3], >97% mass fraction purity) were supplied by IoLiTec GmbH (Heilbronn, Germany). The synthesized and commercial FILs were characterized by 1H and 19F NMR spectroscopy (NMR spectrometer, Bruker 400 MHz) and the synthesized FILs were checked by elemental analysis for purity determination. All FILs were dried under vigorous stirring and vacuum (4 Pa) for at least 48 h at 323.15 K prior to usage to guarantee the absence of volatile substances of the synthesis process and a water content lower than 100 ppm, determined by the Karl Fisher coulometric titration method (Metrohm 831 KF Coulometer). The perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (C4F9SO3H, ≥98% mass fraction purity, TCI, Tokyo, Japan) and perfluoropentanoic acid (C4F9CO2H, ≥97% mass fraction purity, Fluorochem, Hadfield, UK) were used for comparison purposes in the cytotoxicity assays. The nomenclatures and structures of FILs and fluorinated acids can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Structures and nomenclatures of fluorinated ionic liquid (FIL) cations and anions and the fluorinated acids used in the assays.
For the cytotoxicity assays, two types of human cell lines were used: human colon carcinoma cells (Caco-2, Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen, DSMZ, Germany) and human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2, European Collection of Cell Culture, ECACC; UK). The cell culture media and supplements were supplied by Gibco (Invitrogen Corporation, UK): RPMI 1640 medium, MEM medium; fetal bovine serum (FBS), L-Glutamine, penicillin–streptomycin solution, MEM nonessential amino acids (MEM-NEAA), sodium pyruvate and trypsin-EDTA solution. The cell viability was determined by a CellTiter 96® AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay from Promega (Madison, WI, USA).
Lyophilized lysozyme from chicken egg white and Micrococcus lysodeikticus lyophilized cells were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4, purity ≥ 99.0%, Fluka, Charlotte, NC, USA) was used as a lysozyme buffer. For encapsulation efficiency assays, the BCA™ Protein Assay Kit was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Milli-Q water was used for buffer preparation.
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
The cytotoxicity of FILs ([C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], [C2C1py][C4F9CO2], [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2], [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3], and [N1112(OH)][C4F9CO2]) and fluorinated acids was tested in two different cell lines: human colon carcinoma cells, Caco-2, and human hepatocellular carcinoma cells, HepG2. The complete details of cell culture maintenance and cytotoxicity assays can be found in previous work [25]. Briefly, the cell lines were cultured and grown with routine maintenance under conditions specific to each type of cell. The stock solutions of FILs were prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) due to the low solubility in culture medium, and then diluted in 0.5% FBS culture medium (up to a maximum of 1% v/v DMSO) for a range of FIL concentrations between 500 and 10,000 μM. The FIL solutions were incubated within each cell line for 24 h, as well as the negative (culture medium with DMSO 1% v/v) and the positive control (in 100% v/v of DMSO). After the incubation, the medium was removed, and CellTiter 96® Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay reagent was added. After 4 h of incubation, the absorbance was measured at 490 nm by a Thermo Scientific Multiskan GO microplate reader (Waltham, MA, USA). Therefore, the cell viability was quantified by the ratio between the measured absorbance of cells that have contact with the FIL and the values of control cells (incubated only in culture medium). The samples were incubated in three distinct wells and the curves of viability were determined from the average of three independent assays within an experimental error of ±10%.
2.3. Preparation of Solutions for Protein Assays
The potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) was prepared at 66 mM using Milli-Q water (pH = 6.2) and was used as a solvent for all the samples in the studies with lysozyme. For most assays, the lysozyme was studied at a fixed concentration of 0.2 mg/mL, whereas for nano-DSC assays, a concentration of 1 mg/mL of lysozyme was used due to the method sensitivity. The FIL concentrations were chosen according to the specific critical aggregation concentrations (CACs) previously determined for each compound [21,22,23]. The detailed concentrations used for each FIL can be found in Table 2. In all the assays, the blanks of buffer, lysozyme in buffer, and FILs in buffer were included. All the solutions were prepared, stirred, and left to equilibrate for 30 min following the measurement at 298.15 K, considering this measurement as time zero (0 h). Afterwards, these solutions were incubated at 4 °C for 48 and 96 h, and measured after each incubation time (first equilibrating for approximately 30 min at room temperature). The incubation temperature was chosen based on previously obtained results, where ideal activity of lysozyme was found [26,27].

Table 2.
Concentrations of FIL aqueous solutions (mass fraction, wtFIL) used in this work.
2.4. UV–Visible Spectrophotometry
A double beam UV–vis spectrophotometer, model UV-6300PC, from VWR® (Radnor, PA, USA), was employed for absorbance measurements of the solutions found in Table 2. A matched pair of quartz cuvettes with a 1 cm path length was used and 400 μL of each sample were placed in the dried cuvettes and measured in a wavelength range of 190 to 400 nm. For the solutions of lysozyme in buffer and FILs in buffer, the buffer was used as a blank. For the solutions of lysozyme + FILs + buffer, the FILs in buffer solutions were used as blanks in order to follow the profile of the protein. Each sample was recorded at least three times and the absorbance at 280 nm was analyzed as well as the overall alterations of the lysozyme profile in the presence of FILs at the different selected concentrations.
2.5. Encapsulation Efficiency
The encapsulation efficiency of lysozyme was determined for [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3], and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2] by preparation of the solutions in the concentrations indicated in Table 2 and as explained in Section 2.3. After each incubation, the solutions were centrifuged at 4 °C for 30 min at 10,000 rpm. For the concentrations where encapsulation of lysozyme occurred, a white pellet was formed. The pellet corresponded to the encapsulated lysozyme and was separated from the supernatant (free lysozyme in solution) and subsequently resuspended in the same volume of buffer [27]. The protein concentration was determined for both the resuspended pellet and supernatant solutions and for the solutions where no pellet was formed, by adding 100 µL to U-bottom 96-well plates using the colorimetric BCA Protein Assay Kit. A set of samples with known concentrations of lysozyme in a range of 0.004 and 0.24 mg/mL was also prepared and added to the plate as standards. The polynomial fitting of the standard curve was used to determine the final concentration of lysozyme in each solution and the encapsulation efficiency estimated by the ratio of the amount of lysozyme encapsulated to the total amount of lysozyme in solution. The measurements were taken in triplicate in at least two independent experiments with errors within ±10%. More details of this assay can be found in previous work [27].
2.6. Lysozyme Activity
The influence of FILs on the bioactivity of lysozyme was evaluated and the detailed protocol can be found in previous work [26]. Briefly, the bioactivity was determined by the lytic activity of lysozyme against the cell wall of Micrococcus lysodeikticus, changing the turbidity of the bacterial suspension. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured at 298.15 K in U-bottom 96-well plates in a Multiskan GO microplate reader, also from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). The solutions with [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3], and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2] were prepared as described in Section 2.3 at the concentrations indicated in Table 2. A solution of M. lysodeikticus (substrate) at 0.3 mg/mL was prepared in the protein buffer and left to equilibrate for at least 30 min. The samples were tested before and after the assay of encapsulation efficiency by adding 10 μL of each tested solution to the wells and, immediately before measurement of absorbance, 100 μL of substrate were added to the wells. The measurements of absorbance were monitored at 30 s intervals for 5 min and taken in triplicate. At least two independent experiments were executed, and the errors were within ±10%. The lysozyme activity was determined through the linear turbidity decline of the plotted absorbances.
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
[C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] samples were prepared as explained in Section 2.3 and measured only at time zero (0 h). The samples were centrifuged at 4 °C for 30 min at 10,000 rpm, to separate the lysozyme in solution (detected in the supernatant) from the protein interacting with the FIL (detected in the pellet). The pellet was afterwards resuspended with buffer in the same initial volume of solution. The DSC assays were executed by a Nano DSC (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). The baseline was obtained by filling the cells with the respective reference solution and recorded before the assays. The samples (supernatant and pellet when detected) and references were degassed for 7 min at 20 °C and subsequently measured at a scan rate of 1 °C/min in a temperature range of 20 to 90 °C under a pressure of 3 atm. The software NanoAnalyze (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) was used to obtain the melting temperature (Tm) of lysozyme.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cytotoxicity of FILs
The application of FILs in the biopharmaceutical and biomedicine fields is highly dependent on their toxicity and biological properties [2,33]. Information on the correlation between structure and toxicity is imperative to design “greener” FILs. The study of cytotoxicity provides information of the biocompatibility of these compounds with the human body, which has specially importance in the administration route of biopharmaceuticals. Few works have focused attention on the cytotoxicity of FILs [17,25,34] and more complementary data are needed. The cytotoxicity of FILs was determined in HepG2 and Caco-2 cell lines, which are in vitro models of liver (HepG2) and intestinal (Caco-2) tissues. These cell lines are widely used in toxicity studies to obtain information on the oral and rectal administration routes of pharmaceuticals [17,25,35,36,37]. The in vitro cytotoxicity of [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], [C2C1py][C4F9CO2], [N1112(OH)][C4F9CO2], [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2], and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] FILs was determined in this work. These FILs were selected to infer the influence of the anion [C4F9CO2]‾ and the functionalization of the cation with a hydroxyl group in the cytotoxicity assay. The cytotoxicity of two fluorinated acids (C4F9SO3H and C4F9CO2H), which are the starting reagents used in the synthesis of the FILs, was also determined for comparison purposes. The cytotoxicity of these acids was already studied in other work, where no significant cytotoxicity was found for a human placental choriocarcinoma cell line [38]. These acids are used as a more biocompatible option to substitute the toxic polyfluoroalkyl acids with longer perfluorinated chains [39]. The cytotoxicity of FILs and fluorinated acids was evaluated in a concentration range of 500 to 10,000 μM for 24 h of exposure time. The cellular viability determined using the CellTiter 96® Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation assay can be found in Figure 1, where Figure 1a illustrates the results of the Caco-2 cell line and Figure 1b of the HepG2 cell line.

Figure 1.
Cellular viability of FILs and fluorinated acids in (a) Caco-2 and (b) HepG2 cell lines. The lines are a guide for the eye.
The results indicate that none of the compounds shows acute toxicity to both cell lines in the concentration range studied. These results are in concordance with those previously obtained for the homologous FILs composed of [C4F9SO3]‾ anion conjugated with short cationic hydrogenated chains [17,25]. Both [C4F9CO2]‾ anion and the OH‾ group in the cation do not have a negative influence on the cytotoxicity in the studied range of concentrations. Only the fluorinated acid composed of the SO3‾ functional group (orange inverse triangles in Figure 1) shows a slight decrease in the cellular viability at a concentration close to 10,000 μM. This behavior is not found for the FIL based on [C4F9SO3]‾ anion (red triangles in Figure 1). The reduced toxicity of all these compounds can be sustained by the complete miscibility in water and high surfactant power [17,25]. It is well established that the hydrophobic nature of cations and anions is highly related to a higher toxicity of ILs [2,33]. The cations composing the FILs studied here have a lower hydrophobic nature due to the short alkyl chains, which can explain the lower cytotoxicity. Furthermore, the results regarding the fluorinated acids show a low cytotoxicity, proving that the anion does not contribute to cytotoxicity in the studied FILs. Therefore, we can design FILs with more hydrophilic cations and fluorinated anions, maintaining their highly surfactant power and adding negligible cytotoxicity. This makes them promising candidates to substitute the conventional surfactants, characterized by their high hydrophobic nature and subsequently higher toxicity.
3.2. Absorption Measurements
The absorption measurements by UV–visible spectrophotometry are very useful to obtain insights into the interactions between ILs and proteins [10,11,12,13,14]. The aromatic amino acids, such as tryptophan, that compose the structure of the proteins are very sensitive to the visible range, and are used as spectral probes of protein conformational changes. Lysozyme has six tryptophan residues with a key role in preserving its stability and activity, located in the active site and in the hydrophobic core of the protein [13,14]. Therefore, an absorbance band between 260 and 300 nm with a strong peak around 280 nm characterizes the spectral profile of this enzyme, and any alteration in the spectra can give information on the modifications occurring in the local environment of the characteristic lysozyme tryptophan residues. Usually, these changes are based on the shift to lower or higher wavelength values of the absorbance maximum that can indicate the unfolding of a protein. Several works show an increase or decrease in absorbance intensity in the presence of different families of ILs [10,11,12,13,14].
In this work, six different FILs ([C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], [N1112(OH)][C4F9SO3], [N1112(OH)][C4F9CO2], [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3], and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2]) were selected to study their influence on the conformation of lysozyme. The assays were executed at 298.15 K and for three different durations of incubation (0, 24, and 48 h) to infer the influence of time on the FIL–lysozyme interactions. Different CACs can be determined for FILs in aqueous solutions and these CACs indicate the formation of various self-assembled structures [21,22,23]. These distinct transitions can be translated into changes in the shape of the self-assembled structures, from monomers to spherical micelles (1st CAC), from spherical to globular micelles (2nd CAC), and from globular to cylindrical or lamellar micelles (3rd CAC) [21,22,23]. In the case of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], a 4th CAC was identified by isothermal titration calorimetry. However, the shape of the self-assembled structures in this transition was impossible to characterize by visual or theoretical methods [21]. The formation of these stable aggregates is the main mechanism that controls the total miscibility of these FILs in water [21,22,23]. Therefore, concentrations between the different aggregation transitions of each FIL were selected, to understand how the different self-assembled structures can interact with the lysozyme. The FILs can encapsulate the lysozyme, as previously demonstrated [26,27], by the entrapment of the enzyme inside the self-assembled structures. In this work, the search for the most favorable FIL concentrations, to encapsulate the lysozyme, and the study of the different interactions, are carried out. To ease the analysis and discussion, we categorized the studied concentrations as: (i) below the 1st CAC, where no aggregation is found; (ii) between the 1st and 2nd CACs, the first transition; (iii) between the 2nd and 3rd CAC, the second transition; (iv) between the 3rd and 4th CACs, the third transition; and (v) above the 4th CAC. The exact values of the concentrations used for each FIL are detailed in Table 2. These assays were executed by keeping the concentration of lysozyme constant at 0.2 mg/mL. The results are discussed to understand how the structural features of FILs affect the lysozyme conformation by analyzing the effect of cation and anion type and the functionalization of the cation with a hydroxyl group, and they can be found in Figure 2.
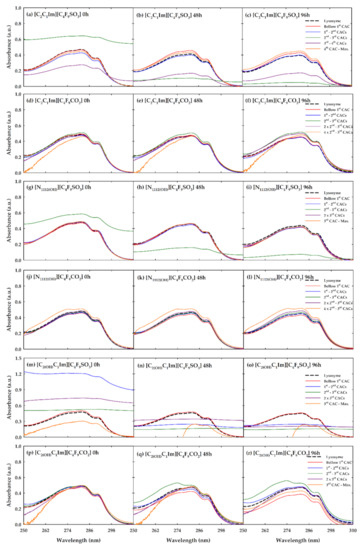
Figure 2.
UV–vis absorption spectra of lysozyme in the different concentrations of FILs studied in this work. The FILs and conditions of incubation are described in each graph.
Figure 2a–c illustrate the results of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3]–lysozyme assays. As in all the graphs of Figure 2, the lysozyme in solution is represented by a black dashed line and the colored solid lines correspond to the different concentrations of the tested FILs, as detailed in Table 2. The major variations of the lysozyme spectral profile are found for the two concentrations between the 2nd and 3rd and 3rd and 4th CACs. In Figure 2a–c, the green line (2nd and 3rd CACs) completely loses the conformation and becomes a flat line which, at time zero (0 h), has an increased intensity compared with the lysozyme reference and strongly decreases at 48 and 96 h. This result could be indication of the encapsulation of lysozyme by [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] due to the complete covering of the lysozyme curve profile. It is not attributed to unfolding because, as previously reported, this process is detected through a shift of the peak absorbance to values around 301 nm [40]. Moreover, the encapsulation of this protein was already proved by this FIL in other works at different concentrations and incubation times [26,27]. The decrement of absorbance intensity throughout the incubation may indicate a stabilization of the aggregates of FIL in the encapsulation of lysozyme. The same occurs for the concentration between the 3rd and 4th CACs (purple line) but the profile still has some similarities with the lysozyme reference, decreasing the intensity during the incubation. This behavior could indicate that in this concentration, the FIL does not totally encapsulate the enzyme. The other concentrations do show very slight differences compared with the lysozyme reference, which indicates the presence of the FIL in the local environment and subsequent interactions with the tryptophan residues at the protein surface. A surprising result is the fact that the highest concentration tested, after the 4th CAC, does not alter the lysozyme profile, indicating a turning point of the rearrangement of the FIL structure in these concentrations which does not allow the encapsulation of the protein.
In the case of [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2], the results are illustrated in Figure 2d–f. Only a slight increment of intensity is found for the 2nd and 3rd CACs at 48 and 96 h and for the 3rd and 4th CACs at 96 h. This behavior indicates that interactions between the surface of lysozyme and FIL are occurring but do not promote enzyme encapsulation or any modification in the overall conformation of the protein. Some spectral noise is found for the highest FIL concentration tested, which could be related to a saturation of the UV–vis signal and subsequently a bad discount of the FIL blank. For the [N1112(OH)][C4F9SO3] FIL (Figure 2g–i), only the concentration between the 2nd and 3rd CACs shows significant differences compared with the lysozyme reference, with a similar behavior found in the [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] case. This could be an indication of the encapsulation of lysozyme in this concentration of FIL. No alterations were found to the other concentrations studied. [N1112(OH)][C4F9CO2] (Figure 2j–l) shows slight alterations, as does the [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2] case, which could indicate interactions with the tryptophan residues at the surface without any significant modification of lysozyme conformation.
The [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] is the FIL that has more impact on the spectral profile of lysozyme, as can be seen in Figure 2m–o. The behavior of the lysozyme profile in the concentrations between the 1st and 2nd CACs, 2nd and 3rd CACs, and twice the concentration of the 3rd CAC indicates an encapsulation of the enzyme, which seems to stabilize with time. The highest concentration seems to alter the profile in a different way, which could be related to a conformational change of the lysozyme in the presence of FIL. For [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2] (Figure 2p–r), significant differences are only found after 48 and 96 h of incubation, and could have been triggered by the changes in the local environment of the protein without significant modifications in its conformation. Only the 2nd and 3rd CAC concentrations have a change in the maximum of absorbance, which is shifted to around 270 nm, possibly indicating a change in lysozyme conformation.
All these results markedly indicate that in terms of anion influence, the FILs based on [C4F9SO3]‾ anion have a greater effect on the spectral profile of lysozyme, with a great indication of encapsulation of the protein due to the completely loss of the conformation of the characteristic band. This behavior is emphasized as the time of incubation increases, possibly indicating a stabilization of the FIL aggregates with the protein. The same is not found for [C4F9CO2]‾ anion, which only shows slight increments or decrements of absorbance intensity. Then, there are some interactions between the tryptophan residues on the surface of the protein, but the overall conformation is not highly affected. Looking at the results in terms of cation comparisons, the encapsulation ability grows in the following order: [N1112(OH)][C4F9SO3] > [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] > [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3]. The results indicate that the functionalization of the cation with a hydroxyl group improves the ability to encapsulate the lysozyme. This is a surprising result because, as proven in other work [23], the aggregation behavior of FILs is weakened by the addition of the hydroxyl group. However, they seem to have a higher power of enzyme encapsulation, meaning that the increment of polarity strengthens this mechanism. For the FILs conjugated with the [C4F9CO2]‾ anion, the same trend is found, with greater significant difference in the profile of lysozyme in the presence of [C2(OH)C1Im]+ cation.
With the aim to verify how the concentration of lysozyme affects the encapsulation ability of the FILs, two concentrations of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] were selected. One between the 1st and 2nd CACs, where a low influence on the spectral profile was found, and the other between the 2nd and 3rd CACs, where encapsulation of the lysozyme seems to occur. The influence of lysozyme was studied in a range of concentrations between 0.005 and 0.5 mg/mL. The results are depicted in Figure 3, except for the lowest concentration tested (0.005 mg/L), whose result was not reproducible within the error.

Figure 3.
UV–vis absorption spectra of lysozyme in different concentrations (red, 0.5 mg/mL; gray, 0.3763 mg/mL; blue, 0.2525 mg/mL; green, 0.2000 mg/mL; and yellow, 0.1288 mg/mL) in the presence of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], where (a–c) are the concentrations between 1st and 2nd CAC and (d–f) between 2nd and 3rd CACs. The solid lines are the lysozyme refence in each concentration studied and the dashed lines the solutions with lysozyme and FIL. The duration of incubation is described in each graph.
In Figure 3a–c, the effect of varying the concentration of lysozyme in the presence of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] between the 1st and 2nd CACs is shown. The lysozyme profile is slightly altered by the presence of FIL in the concentrations of 0.3763 (gray) and 0.2525 (blue) mg/mL of lysozyme, evidenced by a small decrease in absorbance intensity. This behavior can be indicative that in these two concentrations of lysozyme, some interactions within the FIL–lysozyme system are promoted but do not lead to substantial modifications of lysozyme conformation. The duration of incubation does not have a meaningful effect. Figure 3d–f show the assays where the concentration of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] was fixed at a value between the 2nd and 3rd CAC, in which, in the previous results (Figure 2a–c), encapsulation of the protein was found. The lowest concentration of lysozyme (yellow, 0.1288 mg/mL) does not allow the FIL to encapsulate the enzyme, since any significant alterations compared with the reference are found in all incubation times. As explained in the results of Figure 2a–c, lysozyme at a concentration of 0.2 mg/mL (green lines in Figure 3d–f) seems to be fully encapsulated by the FIL due to the modification of the characteristic absorbance band to a flat line. If the lysozyme concentration increases, the absorbance band starts to broaden, and some similarities to the shape of the lysozyme reference are visible. This behavior could mean that the encapsulation of lysozyme by the FIL reaches a level of saturation, and some enzyme is free in the solution. As expected, there is a stabilization of this mechanism throughout the incubation time.
Summarizing, the results point out that a mechanism of encapsulation of lysozyme can occur in the presence of FIL, which is predominantly promoted by the presence of [C4F9SO3]‾ anion. It was also found that the functionalization of the imidazolium cation with a hydroxyl group enhances this mechanism of encapsulation of the protein by the FILs. A longer time of incubation facilitates the stabilization of the FIL aggregates, showing higher capacity to completely suppress the lysozyme UV–vis band. It was also found that the loading of lysozyme by the FIL self-assembled structures can reach a maximum. With the aim to obtain better knowledge on this mechanism, the encapsulation efficiency of lysozyme was studied in this work, along with the effect of FILs on its activity and thermal stability and the results are discussed.
3.3. Encapsulation of Lysozyme by FILs
The results regarding the UV–vis spectroscopy assays reveal that some of the FILs seem to have the ability of lysozyme encapsulation. Therefore, [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] were selected to study the encapsulation efficiency of lysozyme due to the larger number of concentrations with this ability. [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2] were also selected as “negative” controls due to the absence of the same behavior of [C4F9SO3]‾-based FILs regarding the spectroscopy results. The same five concentrations of each FIL (Table 2) were selected to study the encapsulation efficiency of lysozyme. The encapsulation efficiency was evaluated through the centrifugation of the solutions, with the aim to separate the lysozyme encapsulated by the FILs, with the formation of a pellet, from the free lysozyme in solution that remained in the supernatant. When a pellet was detected, both pellet and supernatant were separated, and the pellet was resuspended in the same volume of buffer solution. The concentration of protein was then measured in both phases, as well as in the solutions where no pellet was detected. The amount of lysozyme in the pellet and supernatant always corresponded to the amount of protein used for the sample preparation. This indicated that the lysozyme in the pellet was what was entrapped in the self-assembled structures of FILs. The lysozyme in solution at 0.2 mg/mL was also measured by this method and used as a reference to allow the determination of the lysozyme encapsulated by the FILs and for comparison purposes. There was no formation of a pellet after centrifugation of the reference, which emphasizes that the pellet is formed by lysozyme encapsulated in the self-assembled structures. The encapsulation efficiency of each protein concentration was calculated for each FIL-based system and is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Encapsulation efficiency (%) of lysozyme in the different concentrations of FILs.
The results indicate that for the [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] FIL, the formation of a pellet occurs in the concentration between the 2nd and 3rd CACs at the three incubation times. The results are in concordance with the UV–vis spectroscopy data, where a flat line was found for concentrations between the 2nd and 3rd CACs. The encapsulation efficiency of lysozyme by [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] is slightly higher after an incubation time of 48 h. The formation of a pellet was also found between the 3rd and 4th CACs, but only at time zero of incubation and was very difficult to reproduce within the experimental error. These results indicate that the aggregates of FIL in this concentration are not stable enough to maintain the encapsulation of the protein during the incubation. Surprisingly, the formation of a pellet in the solutions with the [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] FIL only arises between the 2nd and 3rd CAC. This was expected to happen in the concentrations between the 1st and 2nd CACs, 2nd and 3rd CACs, and twice the concentration of the 3rd CAC, as shown by the results of UV spectroscopy. However, these results are not reflected by the encapsulation efficiency assay, which probably indicates that the aggregates formed by this FIL in the concentration between the 1st and 2nd CACs, and twice the concentration of the 3rd CAC, have a lower stability which does not promote an efficient encapsulation of lysozyme. Regarding the encapsulation efficiency values of the concentration between the 2nd and 3rd CACs, represented in Table 3, a slight increment is shown with the increment of time. However, the values are within the experimental error, which means no significant relevance. As expected, the two FILs based on [C4F9CO2]‾ anion do not encapsulate the lysozyme in any of the studied concentrations.
3.4. Effect of FILs on the Bioactivity of Lysozyme
The bioactivity of the lysozyme in the presence of FILs was also evaluated in this work. This evaluation has the main objective of understanding the effects of lysozyme encapsulation by FILs on the activity of the enzyme. Furthermore, we want to understand if the FILs that do not encapsulate the protein have an influence on the bioactivity. [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] were selected to study the influence of lysozyme encapsulation, while [C2C1Im][C4F9CO2] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2] were chosen as “negative” controls, as in the case of the encapsulation efficiency results. The solutions studied for the encapsulation efficiency at the same incubation times were submitted to the enzymatic activity assays. The activity of the lysozyme without FIL was used as a reference, considered as 100% of lysozyme activity. In this assay, the samples were also submitted to the centrifugation step, as in the case of encapsulation efficiency, to separate the encapsulated and the free lysozyme in the solutions. The activity of all solutions was measured before and after (samples without formation of pellet; pellet resuspended; supernatant) the step of centrifugation.
Figure 4 shows the results of the lysozyme activity before the step of centrifugation at the different times of incubation. The most significant alterations of lysozyme activity can be seen in the case of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] at the concentration between the 3rd and 4th CACs. Surprisingly, a great decrease in activity is found for incubation times of 48 and 96 h. This result indicates that the interactions with the IL in this range of concentrations affect the activity. This behavior can be translated to a change of the protein conformation that does not enable the protein to reach the substrate. The encapsulation of the protein may not be an explanation for this result since it was concluded that this concentration at both 48 and 96 h of incubation time does not form a pellet. For the other concentrations of this FIL and for the other FILs studied, the activity of lysozyme is slightly superior compared with the reference solution. This result is emphasized in the case of [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2] at the time zero, where an increment of lysozyme activity to 150% is found. This could indicate that this FIL contributes to a better stabilization of the protein, which is reflected in an enhanced activity performance. This behavior was also found in previous works for other families of ILs [13,14]. The increment of lysozyme activity was attributed to conformational changes in the enzyme structure induced by ILs, stabilizing the integrity of the active site [13,14].
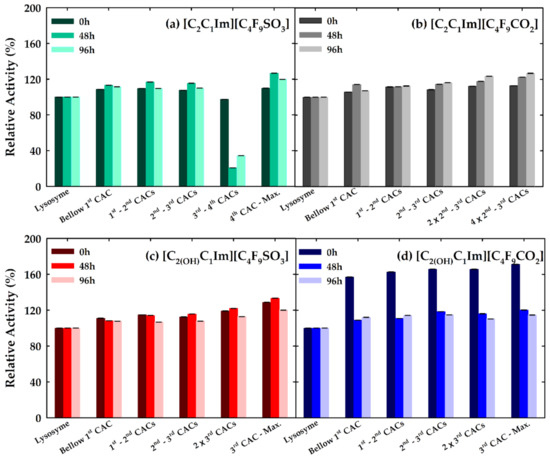
Figure 4.
Relative enzyme activity (%) of lysozyme at different concentrations of FILs before the encapsulation efficiency assays. The FILs and conditions of incubation are described in each graph.
Figure 5 presents the results regarding the lysozyme activity after the centrifugation of the solutions. As explained in the previous section, only [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] FILs showed the formation of a pellet. In all concentrations where encapsulation occurs, the activity of lysozyme is preserved and is slightly higher compared with the reference. Therefore, it can be concluded that the encapsulation of lysozyme by the studied FILs can preserve the enzyme bioactivity. Lysozyme, in the presence of the FILs based on [C4F9CO2]‾ anion, also shows good activity values, which are still enhanced by the presence of [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9CO2].

Figure 5.
Relative enzyme activity (%) of lysozyme at different concentrations of FILs after the encapsulation efficiency assays. The FILs and conditions of incubation are described in each graph.
3.5. Influence of FILs in the Thermal Stability of Lysozyme
The thermal stability of lysozyme was studied in this work in the presence and absence of the FILs. The influence of the enzyme encapsulation by FILs was evaluated by the determination of lysozyme melting temperature (Tm), measured in the presence of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3]. In this study, the concentration of lysozyme was increased to 1 mg/mL due to the apparatus sensitivity. The solutions below the 1st CAC of both FILs were selected to infer the influence of FIL without aggregation behavior in the lysozyme stability. The concentrations of both FILs that evidenced lysozyme encapsulation in the UV–vis methodology were selected to study the effect of encapsulation on the stability of the enzyme. The solutions were prepared and left to equilibrate for 30 min. After that, the solutions were centrifugated and in the cases where the formation of a pellet occurs, it was separated from the supernatant and resuspended in the same volume of buffer. The determined Tm values and the enthalpy (ΔH) of the process of each solution can be found in Table 4. The Tm characterizes the equilibrium between folded and unfolded states of the protein and is marked by a two-state transition [11,41].

Table 4.
Melting temperature (Tm) and enthalpy (ΔH) of lysozyme in buffer and in the presence of different concentrations of FILs.
For the case of [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3], the concentrations between the 2nd and 3rd and 3rd and 4th CACs were selected to infer their influence on the thermal stability of encapsulated lysozyme. As can be seen in Table 4, the results indicate that both concentrations maintain the values of lysozyme Tm very close to the reference. However, in the case of the solution below the 1st CAC, where no aggregation of FIL is found, a decrease greater than 3 °C in the Tm and a high decline of the enthalpy is found. This indicates that the encapsulation of the lysozyme by FIL is a favorable mechanism for the enzyme thermal stability. The same behavior was found for [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3], with a difference of almost 7 °C between the Tm of the reference and of the concentration below the 1st CAC. Surprisingly, the increment of lysozyme to 1 mg/mL promoted the formation of a pellet in the concentration between the 1st and 2nd CAC, which was not detected in the efficiency encapsulation assays. The concentration between the 2nd and 3rd CAC was also included. For both concentrations, the melting temperature remained very close to the values of the lysozyme reference, indicating a thermal stabilization of the protein by the encapsulation platform. In conclusion, both [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] show that the encapsulation of lysozyme is useful to thermally stabilize the protein, compared with the case of the concentration of FIL where the aggregation behavior is not found.
4. Conclusions
In this work, several FILs were selected to study the influence of their structural features (cation, anion, and functionalization of cation) in the mechanisms of the encapsulation and stabilization of lysozyme. The cytotoxicity of those FILs was studied to ensure biocompatibility with the human body, by selecting two human cell lines (HepG2 and Caco-2), representative of oral and rectal administration routes. The results have indicated that all the studied compounds have negligible cytotoxicity and are appropriate tools to be used in biological field. UV–visible spectrophotometry was used to infer the different interactions of the FIL–lysozyme system, and the results highlighted that the major differences are found in FIL concentrations able to encapsulate the protein, which is clearly promoted by the presence of [C4F9SO3]‾ anion. Some FILs were selected and the encapsulation efficiency was studied, concluding that [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] efficiently encapsulate the lysozyme at the concentration between the 2nd and 3rd CACs. The activity and thermal stability of lysozyme were determined to understand how the encapsulation can affect both properties. The results indicate that the encapsulation by [C2C1Im][C4F9SO3] and [C2(OH)C1Im][C4F9SO3] promotes the activity and thermal stability of lysozyme. Therefore, it was possible to design biocompatible FILs with improved aggregation properties, which enabled the encapsulation of lysozyme, granting enhanced properties to the lysozyme. This makes them promising candidates to be used as stabilizers/additives and/or nanoencapsulation platforms able to preserve the protein stability and activity, and consequently can be used in potential applications as therapeutic biopharmaceuticals or biocatalysts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.P.; methodology, M.L.F. and N.S.M.V.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.F.; writing—review and editing, A.B.P. and J.M.M.A.; supervision, A.B.P. and J.M.M.A.; project administration, A.B.P. and J.M.M.A.; funding acquisition, A.B.P. and J.M.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from FCT/MCTES (Portugal), through grant SFRH/BD/130965/2017 and project PTDC/EQU-EQU/29737/2017. This work was also supported by the Associate Laboratory for Green Chemistry—LAQV which is financed by national funds from FCT/MCTES (UIDB/50006/2020).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Balcão, V.M.; Vila, M.M.D.C. Structural and functional stabilization of protein entities: State-of-the-art. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 93, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Bisht, M.; Venkatesu, P. Biocompatibility of ionic liquids towards protein stability: A comprehensive overview on the current understanding and their implications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 611–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, C. Proteins in ionic liquids: Current status of experiments and simulations. Top Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, L.K.; Pereira, J.F.B.; Campos, W.F.; Silva, E.C.; Moutinho, C.G.; Vila, M.M.D.C.; Oliveira, J.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Balcão, V.M.; Tubino, M. Insights into protein-ionic liquid interactions aiming at macromolecule delivery systems. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 1983–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P.V.; Ananthanarayan, L. Enzyme stability and stabilization—Aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Process. Biochem. 2008, 43, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callewaert, L.; Michiels, C.W. Lysozymes in the animal kingdom. J. Biosci. 2010, 35, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kaur, M.; Singh, D.; Kesavan, A.K.; Kang, T.S. Antimicrobial colloidal complexes of lysozyme with bio-based surface active ionic liquids in aqueous medium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 3791–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindl, A.; Hagen, M.L.; Muzammal, S.; Gunasekera, H.A.D.; Croft, A.K. Proteins in ionic liquids: Reactions, applications, and futures. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, M.; Kumar, A.; Venkatesu, P. Analysis of the driving force that rule the stability of lysozyme in alkylammonium-based ionic liquids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, L.; Rana, S.; Arakha, M.; Rout, L.; Ekka, B.; Jha, S.; Dash, P.; Sahoo, H. Impact of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on the structure and stability of lysozyme. Spectrosc. Lett. 2016, 49, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Mondal, S.; Pan, A.; Moulik, S.P.; Ghosh, S. Physicochemical study of the interaction of lysozyme with surface active ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium octylsulfate [BMIM] [OS] in aqueous and buffer media. Coll. Surf. A 2015, 484, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Dohare, N.; Maurya, N.; Dohare, R.; Patel, R. Effect of 1-methyl-3-octyleimmidazolium chloride on the stability and activity of lysozyme: A spectroscopic and molecular dynamics studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 2016–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, M.; Singh, U.K.; Beg, I.; Alanazi, A.M.; Khan, A.A.; Patel, R. Effect of cations and anions of ionic liquids on the stability and activity of lysozyme: Concentration and temperature effect. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Dar, T.A.; Singh, L.R.; Rather, G.M.; Bhat, M.A. Structural-functional integrity of lysozyme in imidazolium based surface active ionic liquids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, H.; Kang, T.S. Synthesis and complexation of a new caffeine based surface active ionic liquid with lysozyme in aqueous medium: Physicochemical, computational and antimicrobial studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Martinho, S.; Alves, F.; Nunes, S.; Matias, A.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Fluorinated ionic liquids: Properties and applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.L.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Shimizu, K.; Pereiro, A.B. Influence of nanosegregation on the phase behavior of fluorinated ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 5415–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Shimizu, K.; Marrucho, I.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. On the formation of a third, nanostructured domain in ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 10826–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.S.; Vieira, N.S.M.; Cortes, O.A.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Marrucho, I.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereiro, A.B. Phase equilibria and surfactant behavior of fluorinated ionic liquids with water. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 82, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Teixeira, F.S.; Marrucho, I.M.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aggregation behavior and total miscibility of fluorinated ionic liquids in water. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Bastos, J.C.; Hermida-Merino, C.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Aggregation and phase equilibria of fluorinated ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.L.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Vega, L.F.; Llovell, F.; Pereiro, A.B. Functionalization of fluorinated ionic liquids: A combined experimental-theoretical study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 112489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Stolte, S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereiro, A.B.; Markiewicz, M. Acute aquatic toxicity and biodegradability of fluorinated ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Bastos, J.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Matias, A.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Human cytotoxicity and octanol/water partition coefficients of fluorinated ionic liquids. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.; Vieira, N.S.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B.; Archer, M. Fluorinated ionic liquids for protein drug delivery systems: Investigating their impact on the structure and function of lysozyme. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2017, 526, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Castro, P.J.; Marques, D.F.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Tailor-made fluorinated ionic liquids for protein delivery. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, M.M.S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Martins, I.C.; Pereiro, A.B.; Archer, M. Insights into the interaction of bovine serum albumin with surface-active ionic liquids in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Yoshizawa, M.; Ohno, H. Room temperature ionic liquids from 20 natural amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2398–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Reis, P.M.; Shimizu, K.; Cortes, O.A.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Pereiro, A.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N. A thermophysical and structural characterization of ionic liquids with alkyl and perfluoroalkyl side chains. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65337–65350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.M.M.; Florindo, C.; Pereiro, A.B.; Vieira, N.S.M.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Cholinium-based ionic liquids with pharmaceutically active anions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 28126–28132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Luís, A.; Reis, P.M.; Carvalho, P.J.; Lopes da Silva, J.A.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Freire, M.G.; Pereiro, A.B. Fluorination effects on the thermodynamic, thermophysical and surface properties of ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 97, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereira, C.S. Ionic liquids: A pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patinha, D.J.S.; Tomé, L.C.; Florindo, C.; Soares, H.R.; Coroadinha, A.S.; Marrucho, I.M. New low-toxicity cholinium-based ionic liquids with perfluoroalkanoate anions for aqueous biphasic system implementation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2670–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lorenzo, A.; Tojo, E.; Tojo, J.; Teijeira, M.; Rodríguez-Berrocal, F.J.; González, M.P.; Martínez-Zorzano, V.S. Cytotoxicity of selected imidazolium-derived ionic liquids in the human Caco-2 cell line. Sub-structural toxicological interpretation through a QSAR study. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, A.; Nunes, S.L.; Poejo, J.; Mecha, E.; Serra, A.T.; Madeira, P.J.A.; Bronze, M.R.; Duarte, C.M.M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of a flavonoid-rich concentrate recovered from Opuntia ficus-indica juice. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 3269–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkening, S.; Stahl, F.; Bader, A. Comparison of primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hepg2 with regard to their biotransformation properties. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrochategui, E.; Pérez-Albaladejo, E.; Casas, J.; Lacorte, S.; Porte, C. Perfluorinated chemicals: Differential toxicity, inhibition of aromatase activity and alteration of cellular lipids in human placental cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2014, 277, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, X. Tainted water: The scientists tracing thousands of fluorinated chemicals in our environment. Nature 2019, 566, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, S.I.; Sugihara, M. Characterization of the transition state of lysozyme unfolding. II. Effects of the intrachain crosslinking and the inhibitor binding on the transition state. Biopolymers 1984, 23, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrikkis, R.M.; Fraser, K.J.; Fujita, K.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Elliott, G.D. Biocompatible ionic liquids: A new approach for stabilizing proteins in liquid formulation. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 074514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).