On the Dissolution of Metals in Ionic Liquids 1. Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, and Zinc
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Metallic Samples Preparation
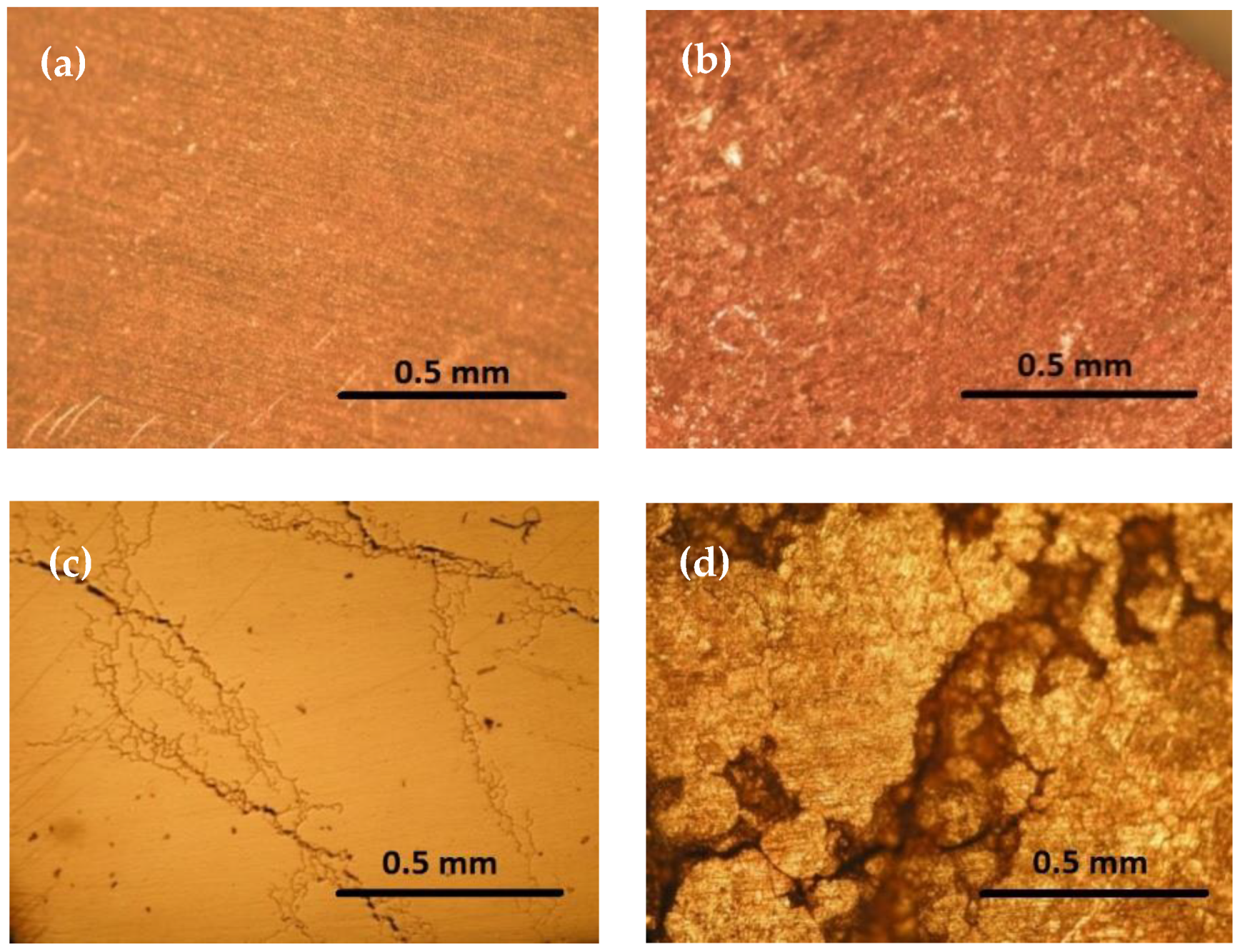
2.3. Dissolution Procedure for Visualization of the Dissolution
2.4. Dissolution Procedure for Rate Determination
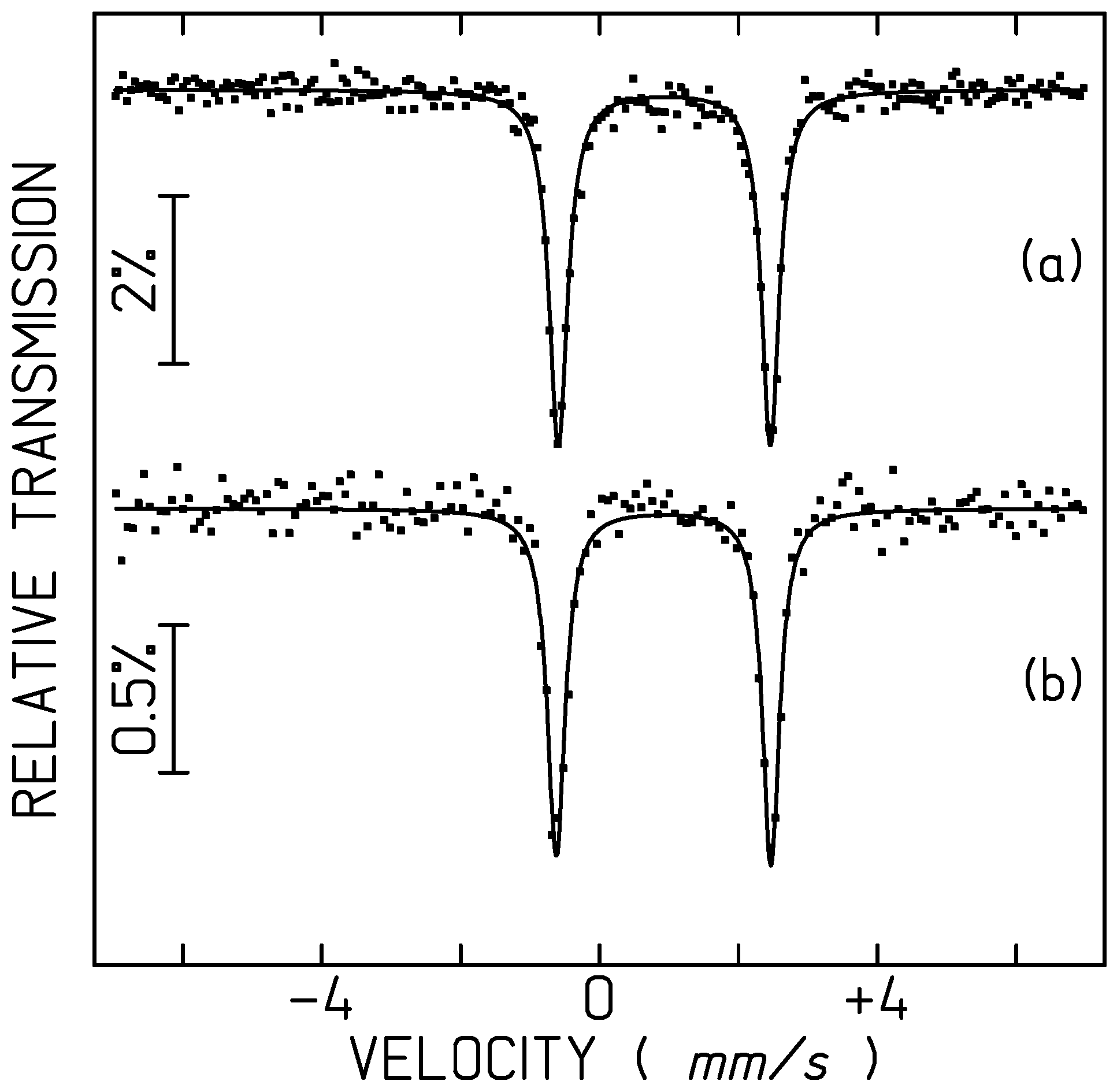
2.5. Mössbauer Spectrometry
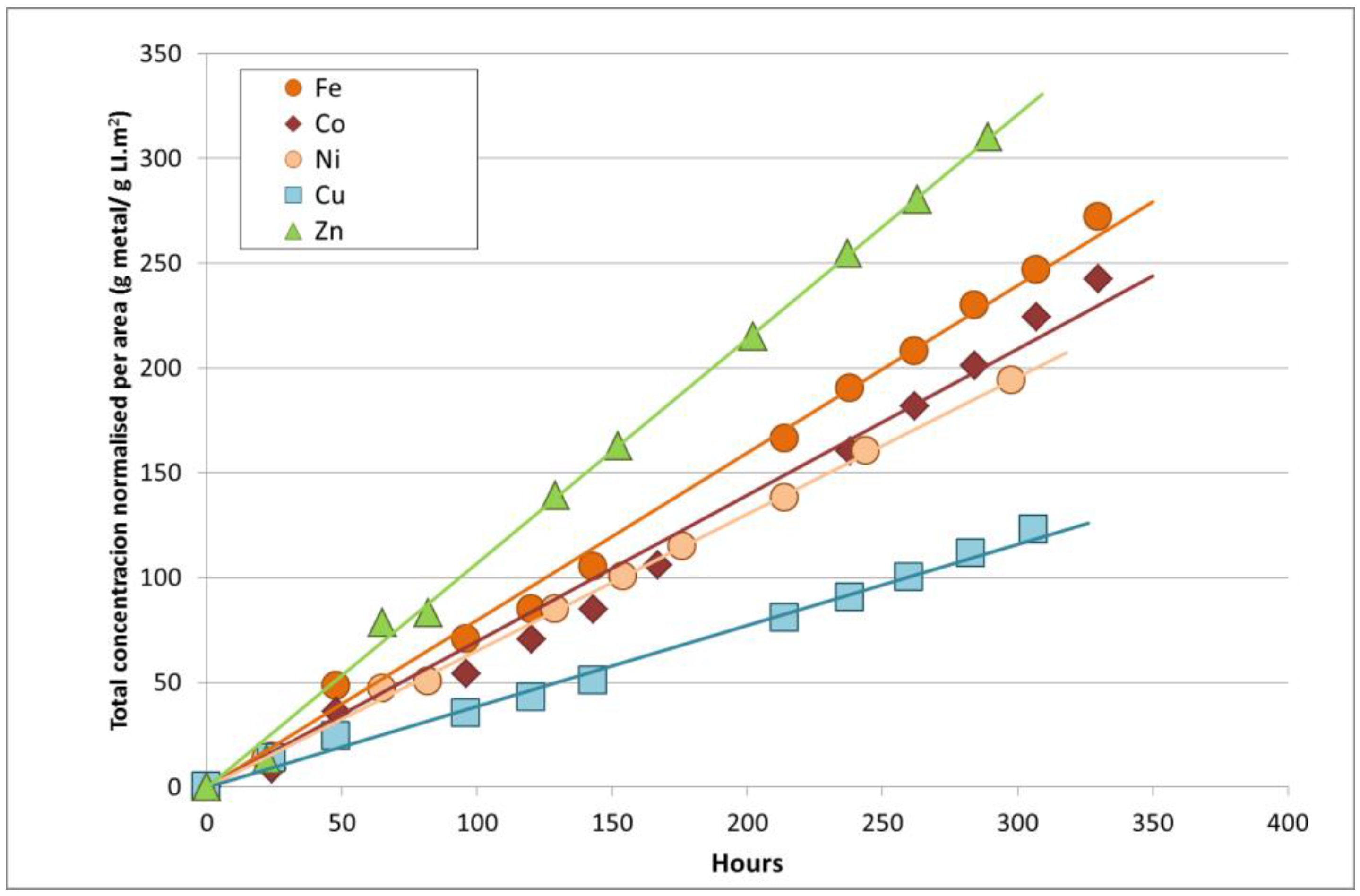
3. Results and Discussion
Dissolution of Metals in Imidazolium Chloride
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, K.E. What’s an Ionic Liquid? Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2007, 16, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T. Ionic Liquids as Tool to Improve Enzymatic Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10567–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirpour, N.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Heris, S.Z. Ionic liquids: Promising compounds for sustainable chemical processes and applications. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 264–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajan, M.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fontana, D.; Akcil, A.; Deveci, H.; Batinic, B.; Leal, J.P.; Gasche, T.A.; Kucuker, M.A.; Kuchta, K.; et al. Recent advances on hydrometallurgical recovery of critical and precious elements from end of life electronic wastes—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 212–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Hartley, J.; Ryder, K.S. Processing of metals and metal oxides using ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S.; König, U. Electrofinishing of metals using eutectic based ionic liquids. Trans. IMF 2008, 86, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Watkins, T.; Kumar, A.; Buttry, D.A. Designer Ionic Liquids for Reversible Electrochemical Deposition/Dissolution of Magnesium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Van den Bossche, A.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Binnemans, K. Ionic liquids with trichloride anions for oxidative dissolution of metals and alloys. Chem. Commun. 2017, 54, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Schwedtmann, K.; Weigand, J.J.; Doert, T.; Ruck, M. Dissolution behaviour and activation of selenium in phosphonium based ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7588–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Theron, R.; Scott, R.W.J. Redispersion of transition metal nanoparticle catalysts in tetraalkylphosphonium ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3227–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Yao, Y.; Durr, M.R.; Barrett, W.G.; Hu, Y.; Scott, R.W. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of iron nanoparticles as hydrogenation catalysts in alcohols and tetraalkylphosphonium ionic liquids: Do solvents matter? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5207–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luska, K.L.; Moores, A. Ruthenium nanoparticle catalysts stabilized in phosphonium and imidazolium ionic liquids: Dependence of catalyst stability and activity on the ionicity of the ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cui, G.; Wang, J.; Fan, M. Effects of Ionic Liquids on the Characteristics of Synthesized Nano Fe(0) Particles. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 10435–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Kamavaram, V.; Reddy, R.G. Thermodynamic properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (C(4)mim[CI]) ionic liquid. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2005, 26, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waerenborgh, J.C.; Salamakha, P.; Sologub, O.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Cardoso, C.; Sério, S.; Godinho, M.; Almeida, M. Influence of thermal treatment and crystal growth on the final composition and magnetic properties of the YFexAl12-x (4 ≤ x ≤ 4.2) intermetallics. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mu, T. Comprehensive Investigation on the Thermal Stability of 66 Ionic Liquids by Thermogravimetric Analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8651–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamavaram, V.; Reddy, R.G. Thermal stabilities of di-alkylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2008, 47, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Gibb, T.C. Mössbauer Spectroscopy; Chapman and Hall, Ltd. Publishers: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.W. Physical Chemistry, 6th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 9780716734659. [Google Scholar]
- Vanýsek, P. Electrochemical Series. In Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 93rd ed.; Haynes, W.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 5–80. ISBN 9781439880494. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Parsons, R.; Jordan, J. Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reported Density of the EMIMCl Ionic Liquid at 20 °C. Available online: http://synquestlabs.com/product/id/118549.html (accessed on 1 November 2020).
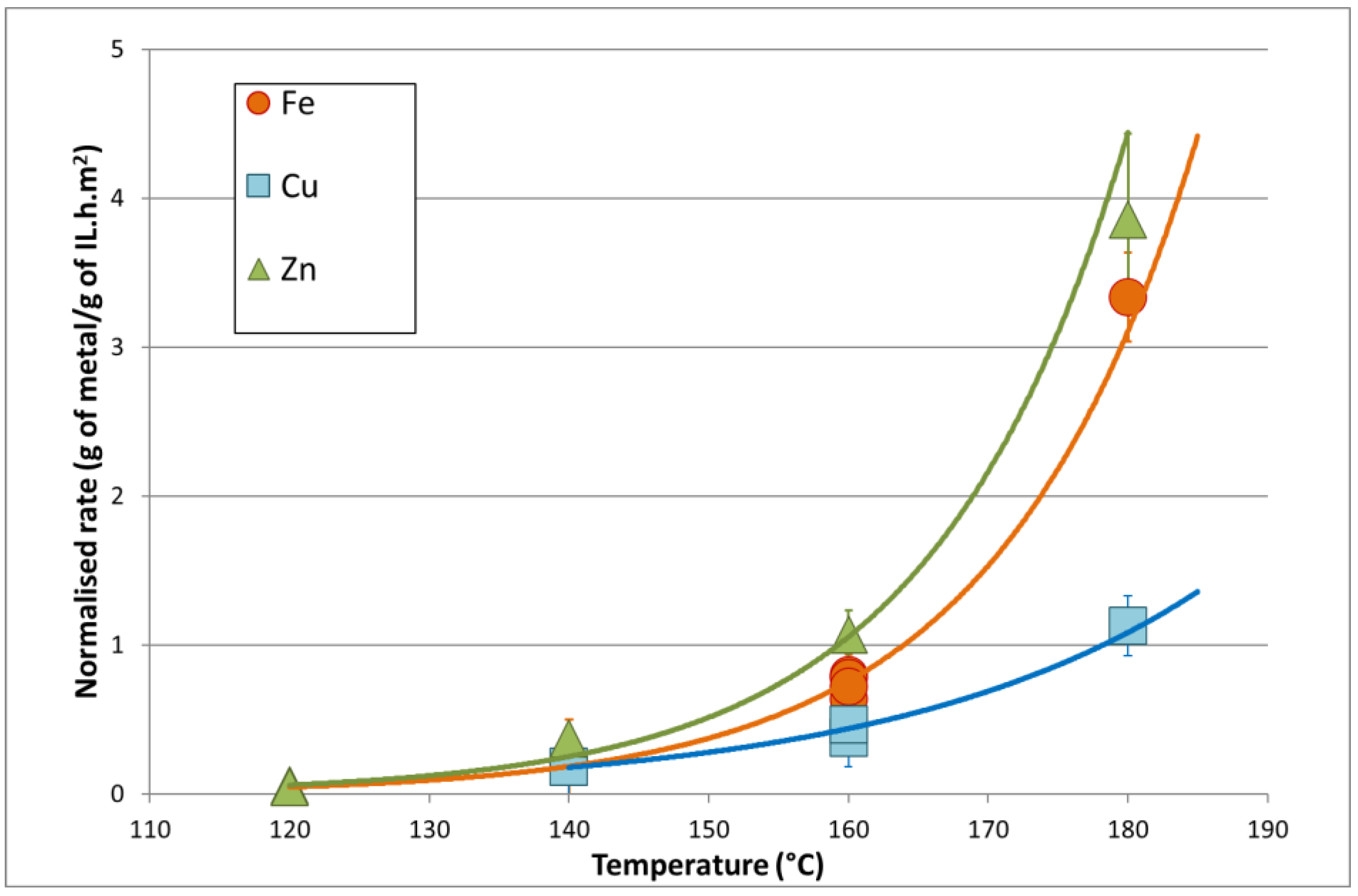
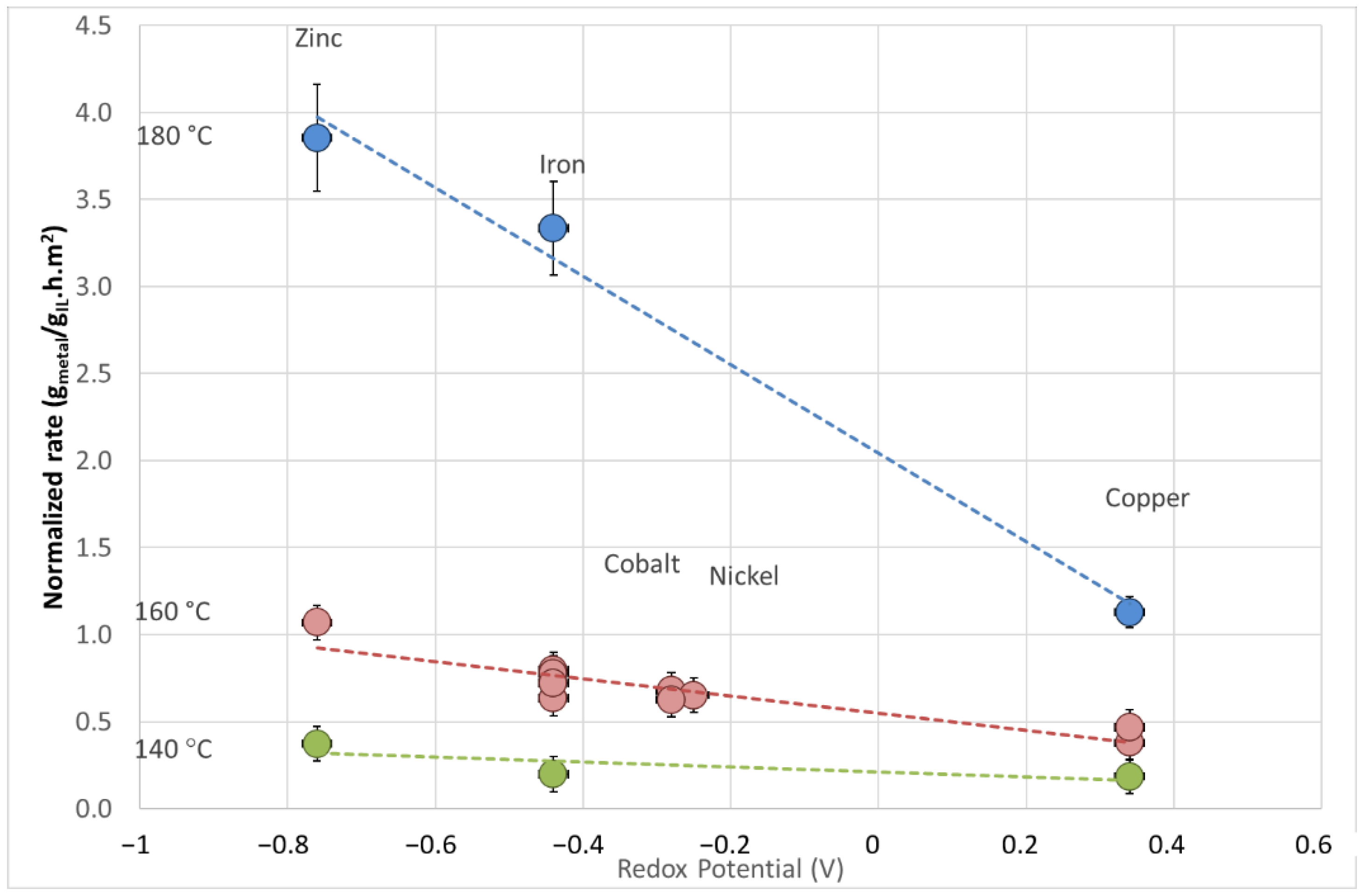
| Metal | Temperature (°C) | Area of Metal in Contact (m2) | Rate (gmetal/(gIL·h)) | Normalized Rate a (gmetal/(gIL·h·m2)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 140 | 2.38 × 10−5 | 4.710 × 10−6 | 0.198 |
| 160 | 1.07 × 10−4 | 8.560 × 10−5 | 0.798 | |
| 160 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 6.885 × 10−5 | 0.777 | |
| 160 | 7.15 × 10−5 | 4.536 × 10−5 | 0.634 | |
| 160 | 6.00 × 10−6 | 4.329 × 10−6 | 0.722 | |
| 180 | 1.88 × 10−5 | 6.256 × 10−5 | 3.335 | |
| Co | 160 | 3.68 × 10−5 | 2.506 × 10−5 | 0.681 |
| 160 | 1.86 × 10−5 | 1.164 × 10−5 | 0.626 | |
| Ni | 160 | 1.49 × 10−4 | 9.679 × 10−5 | 0.651 |
| Cu | 140 | 2.88 × 10−5 | 5.319 × 10−6 | 0.185 |
| 160 | 1.40 × 10−5 | 6.534 × 10−6 | 0.467 | |
| 160 | 2.28 × 10−4 | 8.644 × 10−5 | 0.379 | |
| 180 | 2.80 × 10−5 | 3.160 × 10−5 | 1.129 | |
| Zn | 120 | 9.50 × 10−5 | 5.286 × 10−6 | 0.056 |
| 120 | 8.61 × 10−5 | 4.174 × 10−6 | 0.048 | |
| 140 | 3.32 × 10−4 | 1.236 × 10−4 | 0.372 | |
| 160 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 1.482 × 10−4 | 1.069 | |
| 180 | 2.98 × 10−4 | 1.149 × 10−3 | 3.854 |
| Sample | T | IS | QS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe dissolved in the ionic liquid in air | 20 K | 1.05 | 3.05 |
| 4 K | 1.05 | 3.09 | |
| Fe dissolved in the ionic liquid in nonoxidizing atmosphere | 4 K | 1.04 | 3.09 |
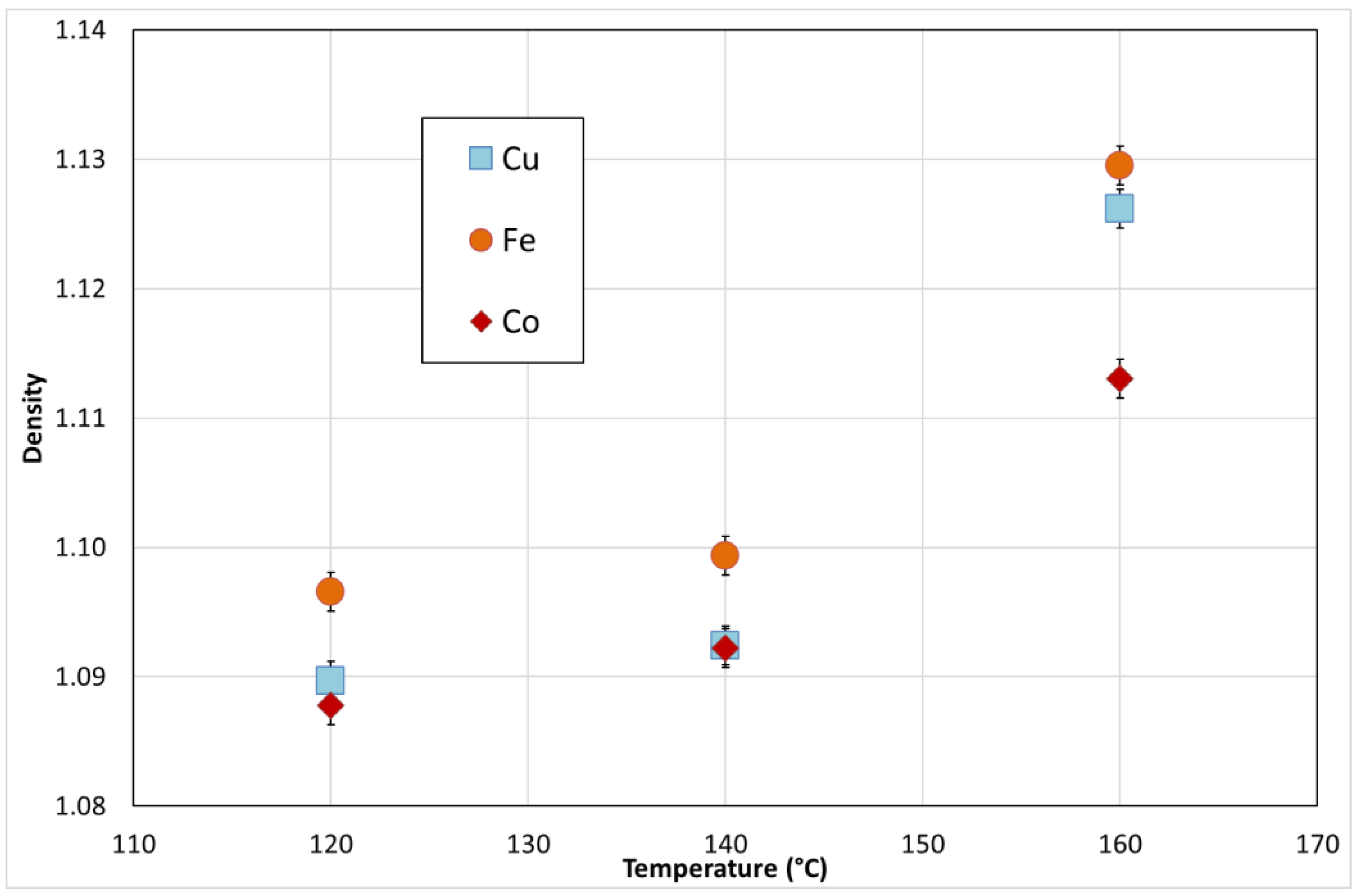
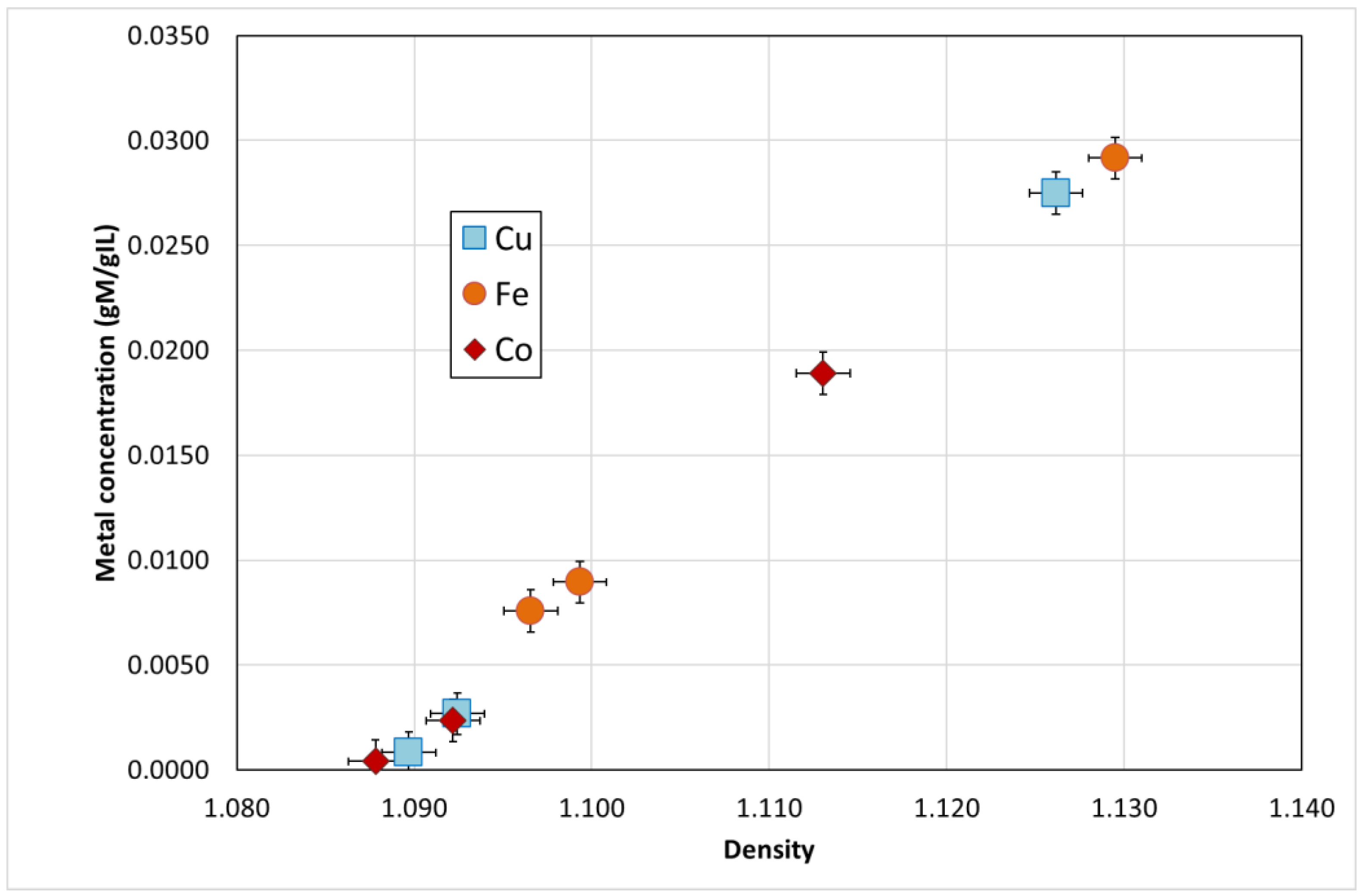
| Temperature (°C) | Metal | Density (g/mL) | Metal in Solution (gMetal/gIL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | Cu | 1.0897 | 0.00082 |
| Fe | 1.0966 | 0.00758 | |
| Co | 1.0878 | 0.00041 | |
| 140 | Cu | 1.0924 | 0.00268 |
| Fe | 1.0993 | 0.00895 | |
| Co | 1.0939 | 0.00234 | |
| 160 | Cu | 1.1261 | 0.02749 |
| Fe | 1.1295 | 0.02915 | |
| Co | 1.1130 | 0.01890 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicente, J.D.S.; Miguel, D.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.P.; Cabrita, D.M.; Carretas, J.M.; Vieira, B.J.C.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Belo, D.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Leal, J.P. On the Dissolution of Metals in Ionic Liquids 1. Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, and Zinc. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 2, 63-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010005
Vicente JDS, Miguel DC, Gonçalves AMP, Cabrita DM, Carretas JM, Vieira BJC, Waerenborgh JC, Belo D, Gonçalves AP, Leal JP. On the Dissolution of Metals in Ionic Liquids 1. Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, and Zinc. Sustainable Chemistry. 2021; 2(1):63-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicente, Jéssica D. S., Domingas C. Miguel, Afonso M. P. Gonçalves, Diogo M. Cabrita, José M. Carretas, Bruno J. C. Vieira, João C. Waerenborgh, Dulce Belo, António P. Gonçalves, and João Paulo Leal. 2021. "On the Dissolution of Metals in Ionic Liquids 1. Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, and Zinc" Sustainable Chemistry 2, no. 1: 63-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010005
APA StyleVicente, J. D. S., Miguel, D. C., Gonçalves, A. M. P., Cabrita, D. M., Carretas, J. M., Vieira, B. J. C., Waerenborgh, J. C., Belo, D., Gonçalves, A. P., & Leal, J. P. (2021). On the Dissolution of Metals in Ionic Liquids 1. Iron, Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, and Zinc. Sustainable Chemistry, 2(1), 63-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem2010005







