Abstract
The present study focuses on the electrochemical sensing of amoxicillin (AMX, as a model antibiotic drug) and its interaction with Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) bacteria (as a model pathogen) under physiological conditions. The electrochemical sensor probe is formulated by nanostructured gold wires (AuNWs) embedded in a carbon nanofiber–chitosan (CNF-CHIT) matrix. The synthesis of AuNWs is characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-Visible spectrophotometry, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified system is characterized by SEM and XPS. Initially, the CNF-CHIT/AuNW electrode was utilized for the sensing of AMX; later, in the antibiotic drug-assisted sensing of UPEC, i.e., in the presence of AMX, the interaction of UPEC was studied. The modified electrode showed appreciable sensitivity for AMX sensing; also, the interaction of AMX with UPEC is studied at two different conditions. One, at a fixed concentration of AMX (100 µM) and different concentrations of UPEC bacteria (0.6–1.2 × 106 CFU/mL), and another with incubation time (1 h–1 h 35 min) for bacterial reaction. The electrochemical antimicrobial resistance developed by UPEC, which is inherent in the sensing of AMX, is the key concept for the detection of pathogens.
1. Introduction
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most commonly occurring infectious disease, yet it is not considered to be a serious condition. The fatality related to this condition is not as high as other fatal diseases but highly affects one’s quality of life in different ways. It affects almost 50% of the population [1], leading to an increased risk of bacteremia and septicemia. In a study with 500 patients, it was found that 76.80% reported having complicated UTIs, while 88.20% reported having community-acquired UTIs. It was also found that 8.40% accounted for catheter-related infections. From the study, it was evident that the most common infection-causing bacteria in the case of UTI was Escherichia coli, with an occurrence of 57.03% in complicated and 55.17% in uncomplicated UTIs [2,3,4]. The bacterial infection causes pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis leading to renal failure, tumors in the urinary tract, bacteremia (in the bloodstream), and septicemia (inflammatory response), which becomes a fatal condition for the female population [5]. This frequently occurring bacterial infection is reported to cause 150 million cases per year. Furthermore, 50–60% of women are estimated to be infected at least once in their lifetimes [6,7]. Even though this infectious condition is not considered to be serious and fatal, not treating it at the right time leads to a troubled lifestyle, leading to increased possibilities of fatality.
The conventional diagnostic method includes urine culture and dipstick urinalysis [8,9]. Dipstick analysis takes 1–2 min, but the accuracy is highly compromised. In this method, the presence of leukocyte esterase and nitrates are estimated. A urine culture is performed to culture the sample infected with bacterial strains. In this case, the specificity and accuracy are high, wherein the bacterial species causing the infection can be identified. Even though these methods are sensitive and selective, they require complex steps, skilled personnel, and time-consuming analysis (~48–72 h), which are not suitable for point-of-care diagnosis. The electrochemical detection method seems to be a convincing factor, with the ease of fabrication of electrodes and point-of-care devices [10,11]. Recently, a series of electrochemical immune/biosensors based on DNA [12,13,14], antibodies [15,16,17], aptamers [18,19,20,21], antimicrobial peptides [22], lectin [23], carbohydrates [24], and bacteriophages [25] for the detection of E. coli bacteria have been studied by using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) [12,13,17,18], electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) [15,16,19,20,21,22,23,24,25], amperometry [14], and quartz crystal microbalance [26]. However, the lifetime of DNA or antibodies in harsh conditions and their stability issues limit the practical application of these biosensors.
Nanomaterials are the leading cutting-edge research for the rapid development of point-of-care (POC) diagnostic tools due to their unique size-dependent properties, which make these materials superior and crucial in improving the patient’s quality of life [27,28,29]. In particular, the use of gold nanoparticles is commonly exploited in biosensing applications due to their improved conductivity, biocompatibility, comparatively low toxicity, and improved analytical signal-to-noise ratio [22,30,31,32,33]. Antibiotics are also known as antibacterial agents, which are commonly used for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections [34,35,36,37,38]. One of the frequently used antibiotics is amoxicillin trihydrate (AMX) for humans. The chemical structure of AMX is a form of β-lactam ring, which is purely responsible for the antibacterial, pharmacological, and chemical activities [34,35,36,37,38]. Recently, carbon nanomaterials and metal nanoparticle-modified carbon material-based electrochemical sensors and optical sensors for AMX have been extensively reviewed [34,36]. However, acute exposure to these antibiotics leaves residuals in the human body that can further increase resistant micro-organisms and antibiotic resistance. Thereby, the detection of AMX or residual AMX is important to understand the bacterial reaction, for instance, in one-step bulk construction of gold nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes using electroless deposition for the electrochemical sensing of AMX in bovine milk samples [37]. Likewise, gold nanoparticle-modified mesoporous carbon nanomaterials have been used for the detection of AMX in mineral water and environmental water samples [38].
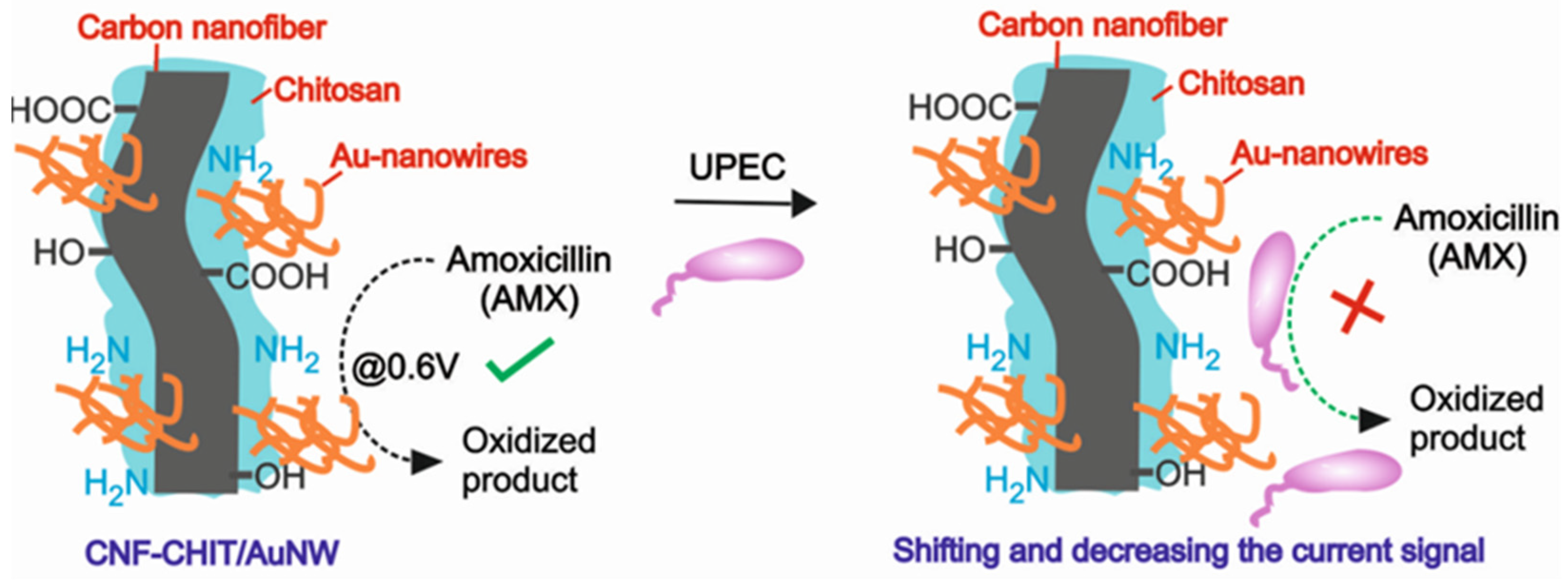
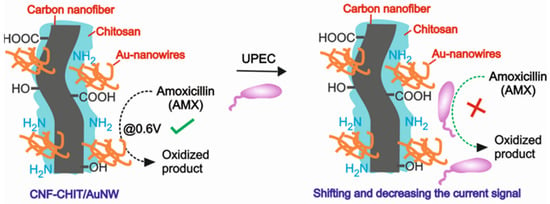
Among various carbon nanomaterials, carbon nanofibers (CNF) have the unique property of excellent conductivity, and its matrices with chitosan (CHIT) would make the hybrid composites more stable even in hydrodynamic conditions [31]. Likewise, gold nanostructures in hybrid with CHIT are highly stable for various electrocatalytic systems [31,32]. In this work, the interaction of amoxicillin (AMX, antibiotic drug) with Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) bacteria is monitored electrochemically for the first time. Nanostructured gold wires (AuNWs) are synthesized by using a chemical reduction method in which the morphology is controlled by appropriate gold nano seed and growth solutions in a suitable environment. The electrochemical antimicrobial resistance developed by UPEC on AMX sensing is taken as the key concept for the detection of pathogens by using a nanostructured gold wire (AuNW)-modified carbon nanofiber–chitosan (CNF-CHIT) matrix (Scheme 1). The synthesized AuNWs are characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-Visible spectrophotometry, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified system is also characterized by SEM and XPS to confirm the stability of the AuNWs.
Scheme 1.
Cartoon for the CNF-CHIT/AuNW nanostructures toward the electrochemical sensing of AMX and AMX-assisted UPEC bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All the chemicals, such as gold (III) chloride trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O), sodium citrate, sodium borohydride (NaBH4), ascorbic acid, and amoxicillin trihydrate (AMX) antibiotic drug, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA and Sisco Research Laboratories (SRL, Mumbai, India). Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) solution was purchased from SPECIALTY LAB & RESEARCH, Thanjavur, India, and stored in refrigerator at 4 °C. Bacteria chosen had inherent resistance towards amoxicillin, and the susceptibility was tested before purchase.
2.2. Instrumentations
The as-prepared AuNWs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (TESCAN VEGA3, SEM), UV-Visible spectrophotometry (Perkin Elmer Lambda 35 UV-Visible Spectrometer), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Thermo scientific K-Alpha, XPS, Waltham, MA, USA). The electrochemical experiments were performed in electrochemical workstation (CHI600, CH instrument, Bee Cave, TX, USA) equipped with corresponding software.
2.3. Synthesis of Gold Nanowires
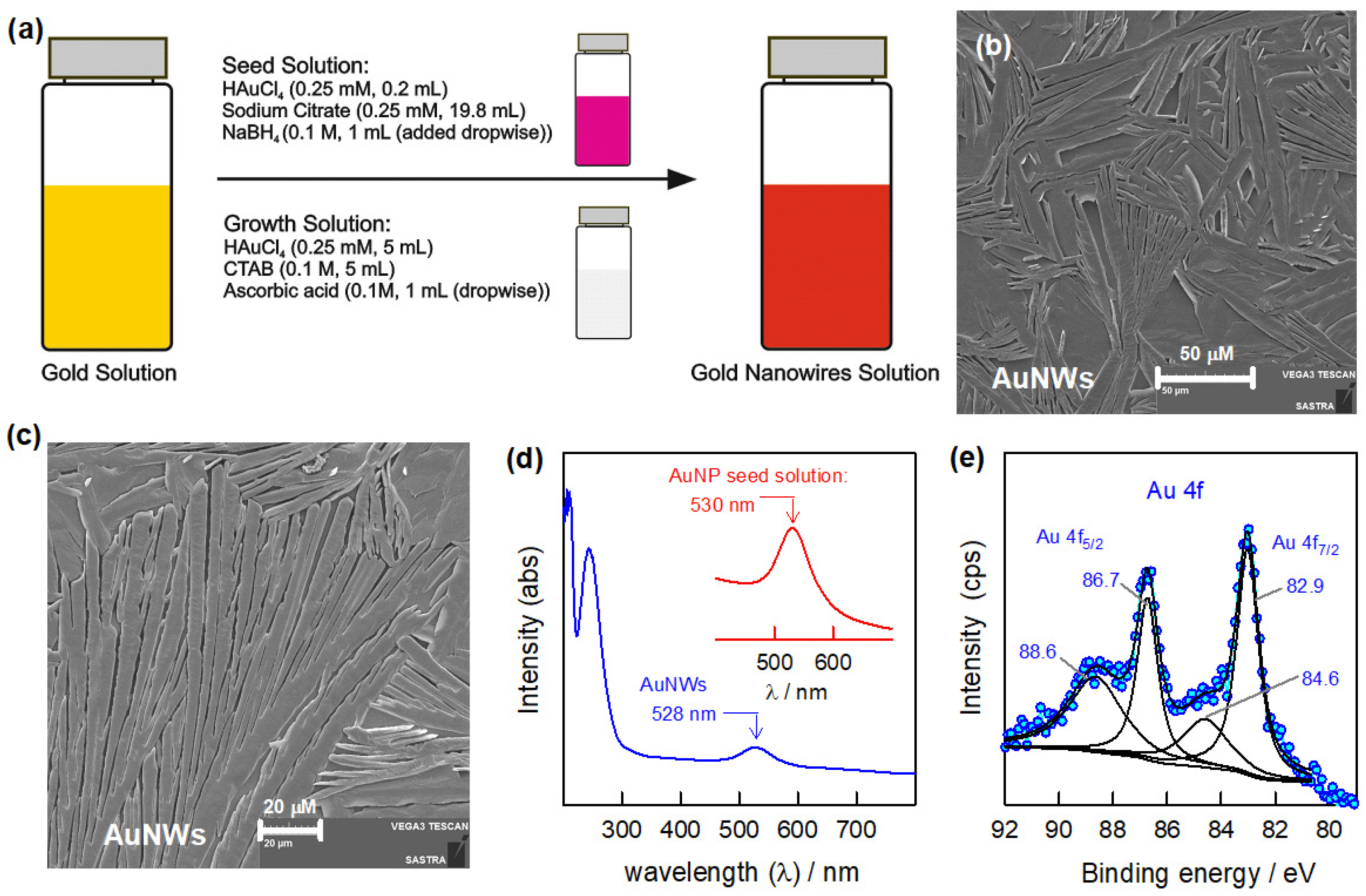
Gold nanowires (AuNWs) were synthesized using bottom-up approach by adopting the seeing method and appropriate aspect ratio-based growth solution (Figure 1a). Briefly, the seed solution was prepared by adding 0.2 mL of HAuCl4·3H2O (0.25 mM) to 19.8 mL of sodium citrate (0.25 mM) followed by dropwise addition of 1 mL NaBH4 (0.1 M) to obtain a pink-colored solution. The growth solution was synthesized by mixture of 5 mL of HAuCl4·3H2O (0.25 mM) with 5 mL of 0.1 M of CTAB, and 0.1 M of ascorbic acid was added dropwise to the solution until the color changed. Then, the size-controlled AuNWs were prepared by dropwise addition of seed solution (1 mL) to the 5 mL of stock solution until obtaining stable pink-colored solution.
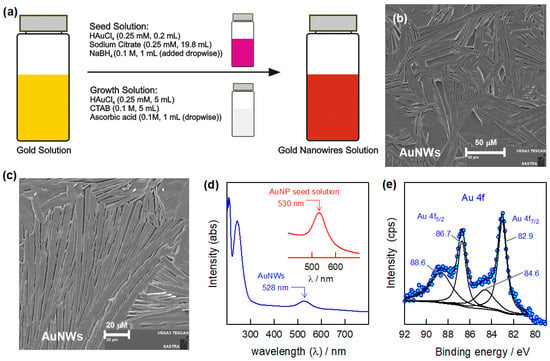
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the AuNW synthesis (a) along with characterizations: SEM images (b,c), UV-Visible spectroscopy (d), and XPS (e) analysis.
2.4. Electrochemical Experiments
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were performed in the conventional three-electrode cell. Glassy carbon electrode was used as working electrode, Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode, and a platinum wire as the counter electrode. The pH 7 phosphate-buffered solution (0.1 M PBS) was used as supporting electrolyte. For the preparation of GCE/CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified electrode, the cleaned GCE surface was functionalized using a composite mixture containing 400 µL of CNF-CHIT (50 mg of CNF in 400 µL of 5% chitosan) solution and 100 µL of the as-prepared AuNW solution. The whole mixture was shaken and mixed thoroughly, and then 5 µL of the final mixed composite solution was drop-casted onto the clean GCE surface and kept for drying at room temperature for 15 min. The as-obtained bacterial solution was added directly without dilution to the antibiotic-containing PB solution (10 mL) for their evaluation by DPV.
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterizations
The structural morphology was examined by SEM analysis (Figure 1b,c). The SEM images of the as-prepared AuNWs showed the long stretched wire-like structures of gold under different magnifications. It was further supported by UV-Visible analysis over the range of 200–800 nm (Figure 1d). The UV-Visible spectra of the gold seed solution and as-prepared AuNWs showed peaks at 530 nm and 528 nm, respectively [30,31]. The slight shift (~2 nm) in the observed peak indicates the formation of nanostructured gold particles with morphological changes. The presence of pure metallic gold nanostructures is confirmed by XPS studies (Figure 1e). As seen in the XPS spectra, the binding energies of the Au 4f7/2 and Au 4f5/2 peaks are clearly observed at 88.6 eV and 86.7 eV, and 84.6 eV and 82.9 eV, respectively, which corresponds to the pure metallic gold nanostructures [31]. The overall characterization studies confirm the formation of nanostructured gold wires is achieved successfully.
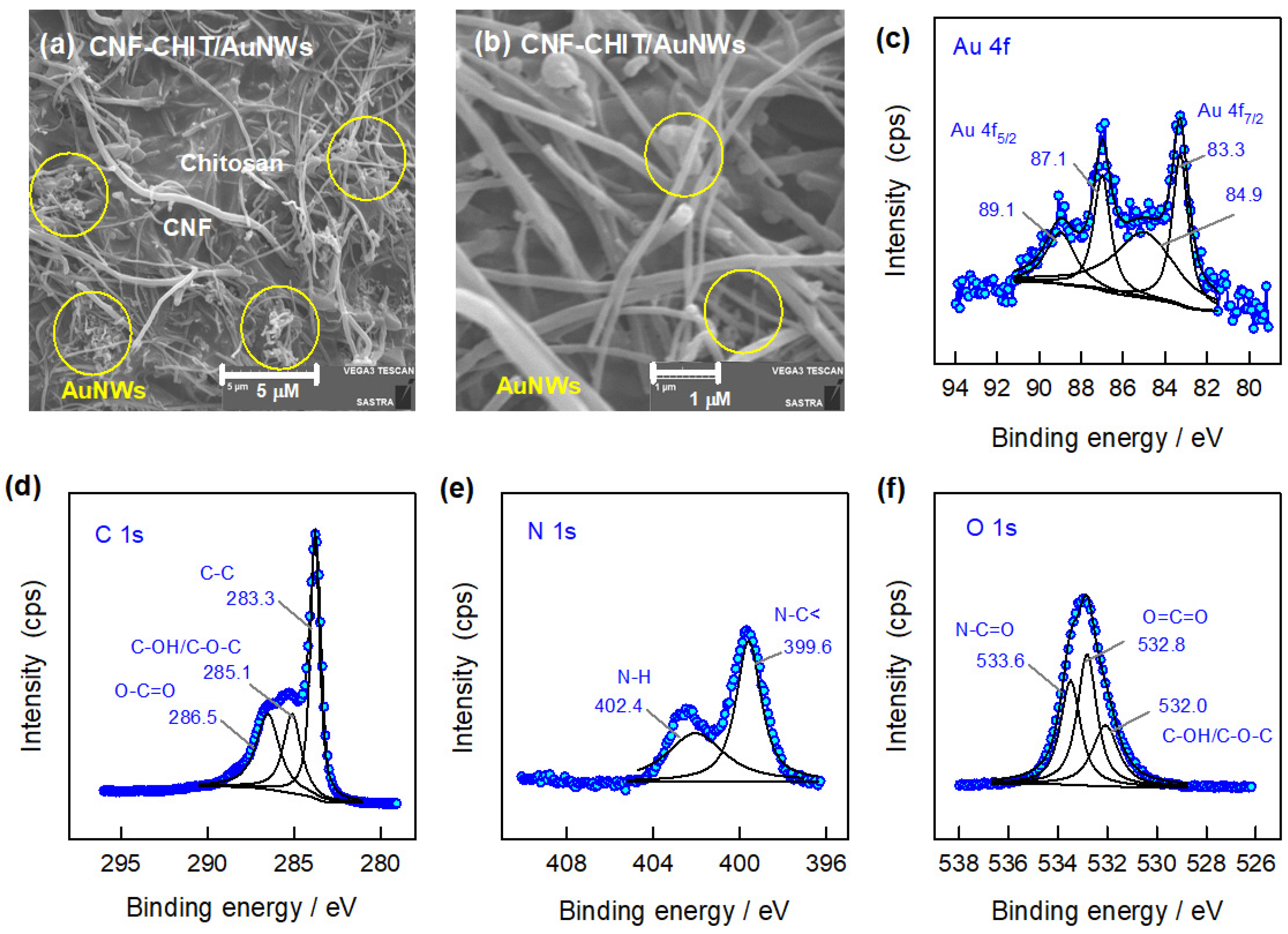
Further, the as-prepared AuNWs are mixed with CNF-CHIT matrices to improve the conductivity and stabilization of AuNWs for electrochemical sensing of AMX. The prepared mixture solution is also characterized by SEM analysis. The SEM images of the CNF-CHIT/AuNW mixture with two different magnifications are shown in Figure 2a,b. It is noticed that the AuNWs are dispersed randomly on the CNF-CHIT matrix, which helps to retain the nature as well as the activities of each component. Furthermore, the core energy level XPS spectra of Au 4f, C 1s, N 1s, and O 1s of the CNF-CHIT/AuNWs system are displayed in Figure 2c–f. The observed binding energies of the Au 4f7/2 and Au 4f5/2 peaks at 89.1 eV and 87.1 eV, and 84.9 eV and 83.3 eV indicate the existence of metallic gold nanostructures [28]. The shift in the binding energies represents the interaction and stabilization of AuNWs within the CNF-CHIT matrices. The binding energies of C 1s are observed at 286.5 eV, 285.1 eV, and 283.3 eV, related to the O-C=O, C-OH/C-O-C, and C-C functional groups [28]. Likewise, the binding energies of the N 1s at 402.4 eV and 399.6 eV represent N-H and N-C < functionalities, while the O 1s at 533.6 eV, 532.8 eV, and 532.0 eV corresponds to the N-C=O, O=C=O, and C-OH/C-O-C functional groups present in the CNF-CHIT matrices [31]. From the SEM and XPS analysis, the as-synthesized AuNWs are well mixed and stabilized by CNF-CHIT functionalities purely in the presence of COOH and NH2 functional groups. Furthermore, the CNF-CHIT/AuNWs are utilized for the electrochemical sensing of AMX and evaluating the antibacterial activities of UPEC bacteria.
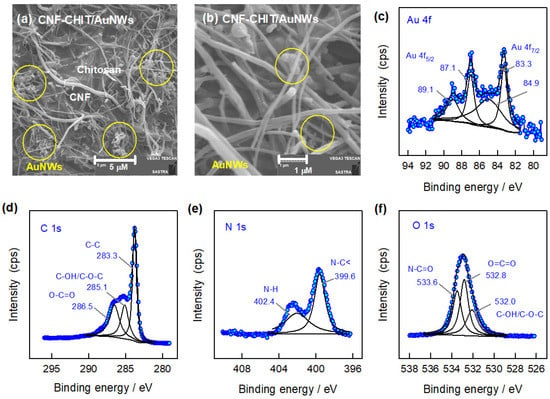
Figure 2.
SEM images (a,b) and core energy level XPS spectra of Au 4f (c), C 1s (d), N 1s (e), and O 1s (f) of the CNF-CHIT/AuNWs system.
3.2. Electrochemical Sensing of AMX on GCE/CNF-CHIT/AuNWs
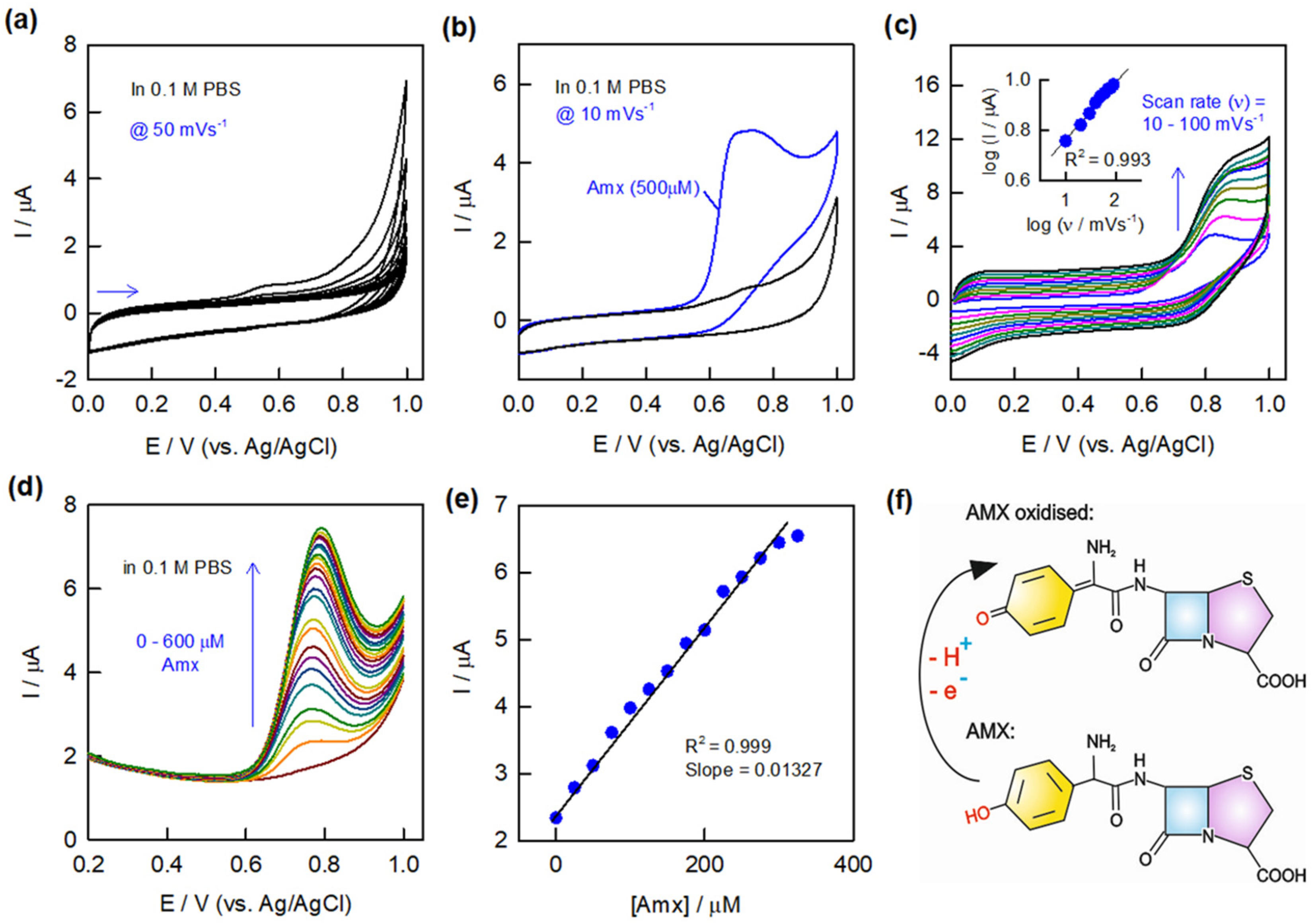
The electrochemical sensing of the AMX drug is studied by using CV and DPV techniques in pH 7 PBS (Figure 3). In order to understand the stability of the GCE/CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified electrode, a continuous CV experiment was performed in blank pH 7 PBS at a scan rate of 50 mV s−1 in 0 to 1 V potential window (Figure 3a). Furthermore, the CV experiments are performed on the GCE/CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified electrode in the presence and absence of amoxicillin (500 µM AMX) at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1 in the 0 to 1 V potential window (Figure 3b). The modified electrode showed an oxidation peak at 0.65 V vs. Ag/AgCl in the presence of the AMX drug. This observation confirms the electrochemical sensing of AMX in neutral pH conditions. Figure 3c represents the effect of various scan rates from 10 to 100 mV s−1 in the AMX solution resulting in the increasing current values (I) with respect to scan rates (v). The double logarithmic plot of log I vs. Log v showed good linearity (inset of Figure 3c). Furthermore, DPV experiments on AMX sensing were performed under the same conditions. As seen in Figure 3d, the DPV current responses on the GCE/CNF-CHIT/AuNW electrode showed a linear increase with respect to the increase in the concentration of AMX. The concentration range of AMX is 25–600 µM. From the current values vs. concentration, a linear calibration plot was drawn (Figure 3e). The obtained calibration plot for AMX looks linear with a good regression value. There are two linear ranges, and the one from 25 to 325 μM is considered, probably due to the fact that it has a higher sensitivity. The calculated sensitivity value is 13.27 nA µM−1. This observation reveals that the present CNF-CHIT/AuNWs is a model system for the electrochemical sensing of AMX. Once the system is working for a good linear range of AMX, it was preceded for further experiment. Figure 3f represents the possible electrochemical oxidation of AMX on the present CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified electrode. From this conclusion, the UPEC bacterial reaction is preceded by monitoring the interaction of bacteria with AMX at a fixed concentration.
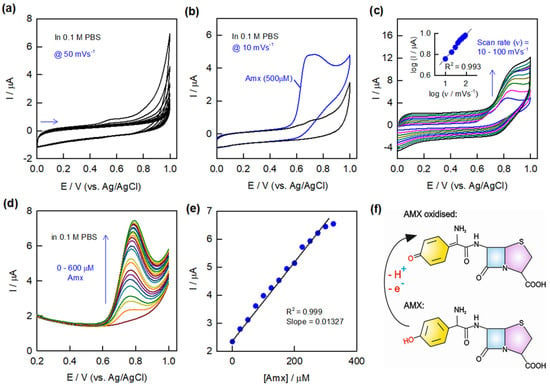
Figure 3.
Continuous CV responses of GCE/CNF–CHIT/AuNWs in blank pH 7 PBS at a scan rate of 50 mV s−1 (a). CV responses of the stabilized modified electrode in the presence and absence of AMX (500 µM) at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1 (b) and effect of various CV scan rates along with double logarithmic plot (c) in pH 7 PBS. DPV responses of AMX in the range of 25–600 µM (d) along with the calibration plot (e). Possible mechanism for the electrochemical oxidation of AMX on the AuNW-modified electrode (f).
3.3. Electrochemical Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
The bacterial species used in the experiment had inherent resistance to antibiotics [39]. The bacteria render the antibiotic ineffective by several mechanisms, and one of them is enzymatic activation, wherein the β-lactamase enzyme is released, which cleaves the β-lactam ring in the antibiotic [39,40]. The bacterial cell wall has peptidoglycans that give integrity to the cell and is maintained by two main enzymes: transglycosylase and transpeptidase. These enzymes help in cross-linking the peptidoglycan layers. The antibiotics containing β-lactam interfere with cell wall synthesis, which ultimately results in lysis of the cell. Penicillin derivative antibiotic is an analog of the D-alanyl-D-alanine dipeptide of peptidoglycan, which acts as a substrate for transpeptidase. The cross-linking of the peptidoglycans is inhibited by preventing the transpeptidase enzyme catalyzes. Thereby, it reduces the mechanical strength of the bacterial cell and hinders the cell wall synthesis process. In response to the stress, a few bacterial species release β-lactamase, which is an enzyme that recognizes the β-lactam ring present in the antibiotics and hydrolyzes the peptide bond present in the ring. Once the ring is open, the antibiotic becomes ineffective, and the bacterial species thrives. By taking advantage of this principle, the present work is designed for the evaluation of drug interaction on bacteria by electrochemical sensing of AMX.
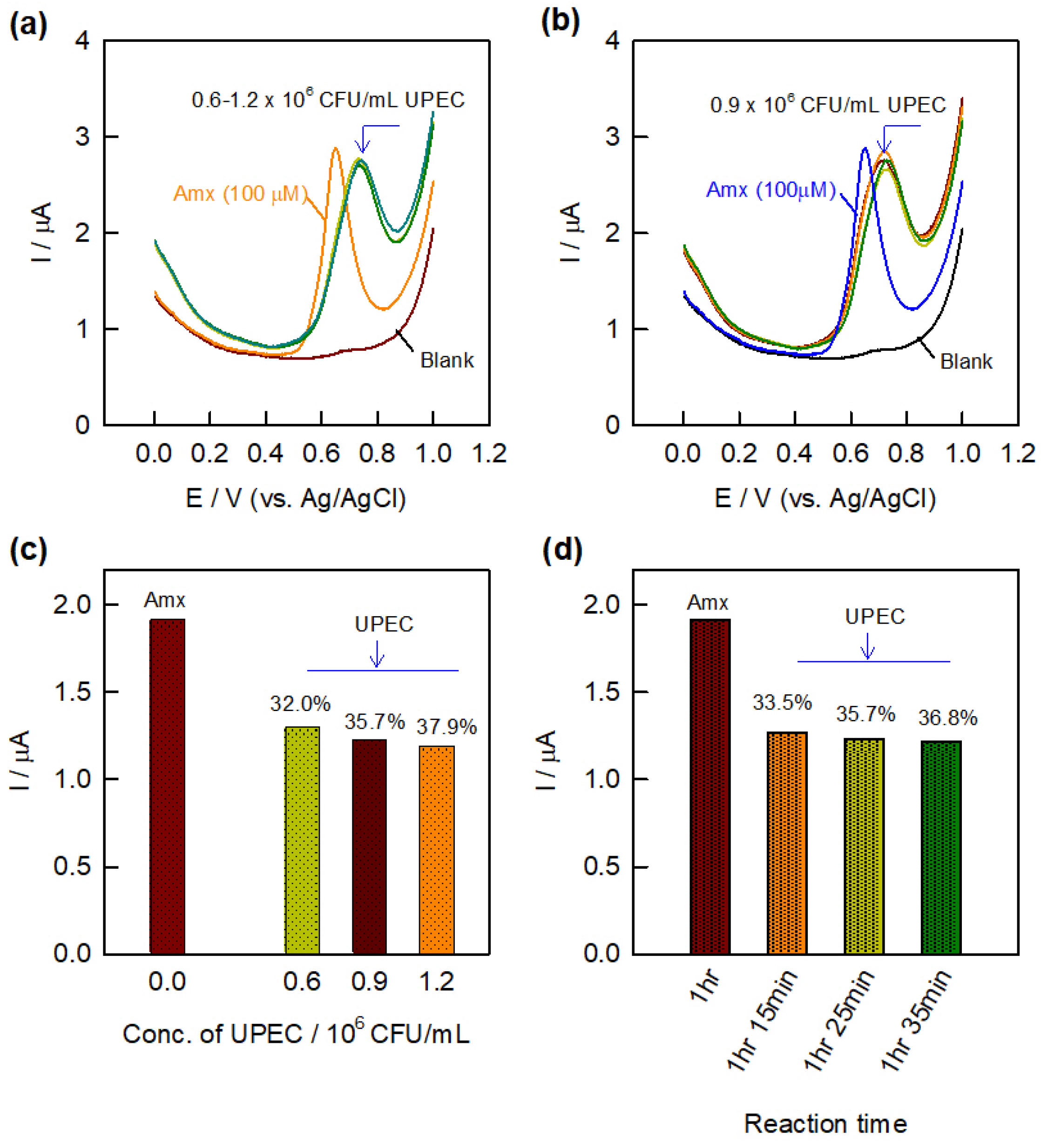
The electrochemical evaluation of the antibacterial activity of the AMX antibiotic drug is shown, with respect to Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) bacteria, by the interaction of the drug with UPEC and the resistance developed by the bacteria towards the AMX antibiotic drug (Figure 4). The as-obtained bacterial solution was added directly in a specified quantity to the antibiotic solution, and the corresponding electrochemical activity was studied by DPV. At a fixed concentration of AMX (100 µM), different concentrations (0.6–1.2 × 106 CFU/mL) and different incubation times (1 h–1 h 35 min) were analyzed for bacterial reactions (Figure 4a,b). Prior to the bacterial reaction, the DPV experiment was performed for 100 µM AMX in 0.1 M PBS. After the addition of bacterial solution, the whole setup was left undisturbed for 1 h for incubation at room temperature in PBS, and then DPV was recorded. As seen in Figure 4a, the current response for the AMX decreased incrementally, and a prominent peak shift is also observed with different concentrations of bacterial solution. The potential peak shift may possibly be due to the immediate reaction of AMX with UPEC, whereas the incremental decrease in the current response is purely due to the interaction between them. Similarly, the effect of incubation time for the bacterial reaction was also studied under the same conditions (Figure 4b). It is observed that the increase in the incubation time leads to a further decrement in the AMX sensing current. This observation confirms the interaction of bacteria with the drug is still possible with respect to the changes in the peak potential followed by the decrease in the current responses. Figure 4c,d display the respective bar diagrams for the results obtained in the different concentrations of bacteria and the incubation time for the bacterial reaction with respect to the baseline corrected current values. The percentage value represents the decremental current values of the antibacterial reaction with respect to the AMX current value. As seen in the bar diagrams, the known concentration of AMX showed a constant current, which decreased gradually upon the addition of bacterial solution in terms of concentration and incubation time. Table 1 represents the summarized information about the versatile electrochemical sensing probes for the detection of the pathogen. From Table 1, we can conclude that the electrochemical sensing of pathogens was mainly demonstrated by DNA, antibody, aptamer, and peptide-based systems, unlike the antibacterial drug interaction-based detection system.
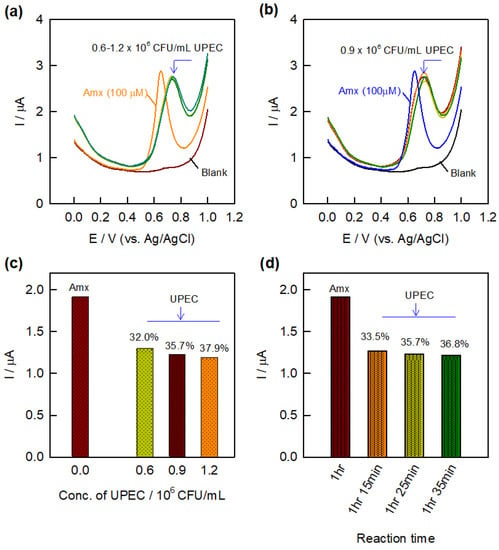
Figure 4.
DPV response of different concentrations of UPEC bacteria (0.6–1.2 106 CFU/mL) (a) and different incubation times (1 h–1 h 35 min) (b) on GCE/CNF–CHIT/AuNWs in the presence of AMX (100 µM) along with respective bar diagrams (c,d).

Table 1.
Various electrochemical methodologies for sensing E. coli bacteria.
4. Conclusions
The resistant behavior of bacterial species toward antibiotic drugs is the driving force for all the electrochemical experimental studies in this work. The present ‘AMX and AMX-assisted UPEC’ detection was demonstrated as a model system that can be extended to achieve more specific and selective ‘drug-pathogen’ interaction studies. The developed CNF-CHIT/AuNW-modified electrode showed the current responses for sensing AMX in a linear range of 25–600 μM with a sensitivity value of 13.27 nA μM−1. The conclusions arising from the present preliminary study are (i) after a specified incubation time, the bacteria begin to produce the enzyme which cleaves the antibiotic, thereby affecting the electron flow between the AMX and CNF-CHIT/AuNWs system, and (ii) after a particular incubation time, the electrochemical activity of the AMX is decreased due to the influence of β-lactamase enzyme. The more the bacterial concentration, the greater its impact, and hence, the current decreases with an increase in bacterial concentration as well as the incubation time. The present studies are helpful for the development of various specific and selective pathogen sensors with the aid of computational and theoretical approaches.
Author Contributions
J.S. performed the synthesis, characterizations, and experiments and prepared the first draft of the manuscript. S.N. conceptualized the idea, supervised, prepared the original draft, and corrected and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the SASTRA Deemed University for the infrastructure and characterization facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Foxman, B. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karishetti, M.S.; Shaik, H.B. Clinicomicrobial assessment of urinary tract infections in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J. Health Sci. Biomed. Res. (KLEU) 2019, 12, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, R.; Murt, A. Epidemiology of urological infections: A global burden. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoglu, S. Toilet-based continuous health monitoring using urine. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2022, 19, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dospinescu, V.M.; Tiele, A.; Covington, J.A. Sniffing out urinary tract infection—Diagnosis based on volatile organic compounds and smell profile. Biosensors 2020, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: Epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chlebicki, M.P. Urinary tract infections in adults. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, S.; Munir, T.; Rehman, S.; Hafiz, A.; Gilani, M.; Latif, M. Comparison of urine dipstick test with conventional urine culture in diagnosis of urinary tract infection. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2015, 25, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gennifer, T.S.; Dwork, N.; Khan, S.A.; Millet, M.; Magar, K.; Javanmard, M.; Bowden, A.K.E. Robust dipstick urinalysis using a low-cost, micro-volume slipping manifold and mobile phone platform. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Nellaiappan, S.; Mandali, P.K.; Prabakaran, A.; Krishnan, U.M. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Quantification of Procalcitonin: Progress and Prospects. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtugyn, G.; Porfireva, A.; Shamagsumova, R.; Hianik, T. Advances in Electrochemical Aptasensors Based on Carbon Nanomaterials. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, J. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of E. coli and S. typhimurium based on target recycling amplification using self-assembled hairpin probes on a gold electrode. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Marugan, J.; Petit-Dominguez, M.; Casero, E.; Vázquez, L.; García, T.; Parra-Alfambra, A.; Lorenzo, E. Sol–gel derived gold nanoparticles biosensing platform for Escherichia coli detection. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 182, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.C.; Mastali, M.; Gau, V.; Suchard, M.A.; Møller, A.K.; Bruckner, D.A.; Babbitt, J.T.; Li, Y.; Gornbein, J.; Landaw, E.M.; et al. Use of electrochemical DNA biosensors for rapid molecular identification of uropathogens in clinical urine specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chee, G.; Yamada, K.; Jun, S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic technique with a functionalized microwire sensor for rapid detection of foodbornepathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Erf, G.F. Interdigitated Array Microelectrode-Based Electrochemical Impedance Immunosensor for Detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Alocilja, E.C. Gold nanoparticle-labeled biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of bacterial pathogens. J. Biol. Eng. 2015, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J. Label-free and highly sensitive electrochemical detection of E. coli based on rolling circle amplifications coupled peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosel-Oliu, S.; Ferreira, R.; Uria, N.; Abramova, N.; Gargallo, R.; Muñoz-Pascual, F.-X.; Bratov, A. Novel impedimetric aptasensor for label-free detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrs, S.; Bhargava, M.; Sidhu, R.; Kiernan-Lewis, J.; Gomes, C.; Claussen, J.; McLamore, E. A paper based graphene-nanocauliflower hybrid composite for point of care biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Shorie, M.; Sharma, M.; Ganguli, A.K.; Sabherwal, P. Bridged Rebar Graphene functionalized aptasensor for pathogenic E. coli O78:K80:H11 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Afrasiabi, R.; Fathi, F.; Wang, N.; Xiang, C.; Love, R.; She, Z.; Kraatz, H.-B. Impedance based detection of pathogenic E. coli O157: H7 using a ferrocene-antimicrobial peptide modified biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; Hao, H.; Gong, Q.; Nie, K. Detection of Escherichia coli with a label-free impedimetric biosensor based on lectin functionalized mixed self-assembled monolayer. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 229, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Marar, A.; Kner, P.; Ramasamy, R.P. Charge-directed immobilization of bacteriophage on nanostructured electrode for wholecell electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5734–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Rehman, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, X. Glycosylation of quinone-fused polythiophene for reagentless and labelfree detection of E. coli. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.X.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Ying, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Evaluation of different micro/nanobeads used as amplifiers in QCM immunosensor for more sensitive detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumpano, R.; Polli, F.; D’Agostino, C.; Antiochia, R.; Favero, G.; Mazzei, F. Nanostructure-Based Electrochemical Immunosensors as Diagnostic Tools. Electrochem 2021, 2, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facure, M.H.M.; Schneider, R.; Lima, J.B.S.; Mercante, L.A.; Correa, D.S. Graphene Quantum Dots-Based Nanocomposites Applied in Electrochemical Sensors: A Recent Survey. Electrochem 2021, 2, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, J.H.; González-García, L.; Reiser, B.; Kanelidis, I.; Kraus, T. Templated self-assembly of ultrathin gold nanowires by nanoimprinting for transparent flexible electronics. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellaiappan, S.; Kumar, A.S.; Nisha, S.; Pillai, K.C. In-situ preparation of Au(111) oriented nanoparticles trapped carbon nanofiber-chitosan modified electrode for enhanced bifunctional electrocatalysis and sensing of formaldehyde and hydrogen peroxide in neutral pH solution. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 249, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.A.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Balogh, D.T.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Mercante, L.A.; Frade-Barros, A.F.; Pavinatto, A. Chitosan/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite Film for Bisphenol A Electrochemical Sensing. Electrochem 2022, 3, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Chang, T.-F.M.; Chien, Y.-A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chakraborty, P.; Nakamoto, T.; Sone, M. Catalytic Activity of Atomic Gold-Decorated Polyaniline Support in Glucose Oxidation. Electrochem 2020, 1, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrioua, A.; Loudiki, A.; Farahi, A.; Bakasse, M.; Lahrich, S.; Saqrane, S.; El Mhammedi, M.A. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for amoxicillin detection in biological and environmental samples. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 137, 107687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihaiti, A.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, X.; Huangfu, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhang, M. Construction of electrochemical sensors for antibiotic detection based on carbon nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, Q.A.; Luo, Z.; Ali, R.; Khan, M.I.; Li, F.; Qiu, B. advances in gold nanoparticles-based colorimetric aptasensors for the detection of antibiotics: An overview of the past decade. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Yusof, N.A.; Hajian, R.; Abdullah, J. Construction of an electrochemical sensor based on carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles for trace determination of amoxicillin in bovine milk. Sensors 2016, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollap, A.; Knihnicki, P.; Kus’trowski, P.; Kozak, J.; Cezpa, M.G.; Kotarba, A.; Kochana, J. Sensitive voltammetric amoxicillin sensor based on tio2 sol modified by cmk-3-type mesoporous carbon and gold ganoparticles. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Khalid, H.; Mushtaq, M.; Basha, S.; Rabaan, A.A.; Garout, M.; Halwani, M.A.; Mutair, A.A.; Alhumaid, S.; Alawi, Z.A.; et al. The molecular characterization of virulence determinants and antibiotic resistance patterns in human bacterial uropathogens. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Bhadelia, N. Management of urinary tract infections from multidrug-resistant organisms. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2014, 28, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).