Quantum-Based Maximum Likelihood Detection in MIMO-NOMA Systems for 6G Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access
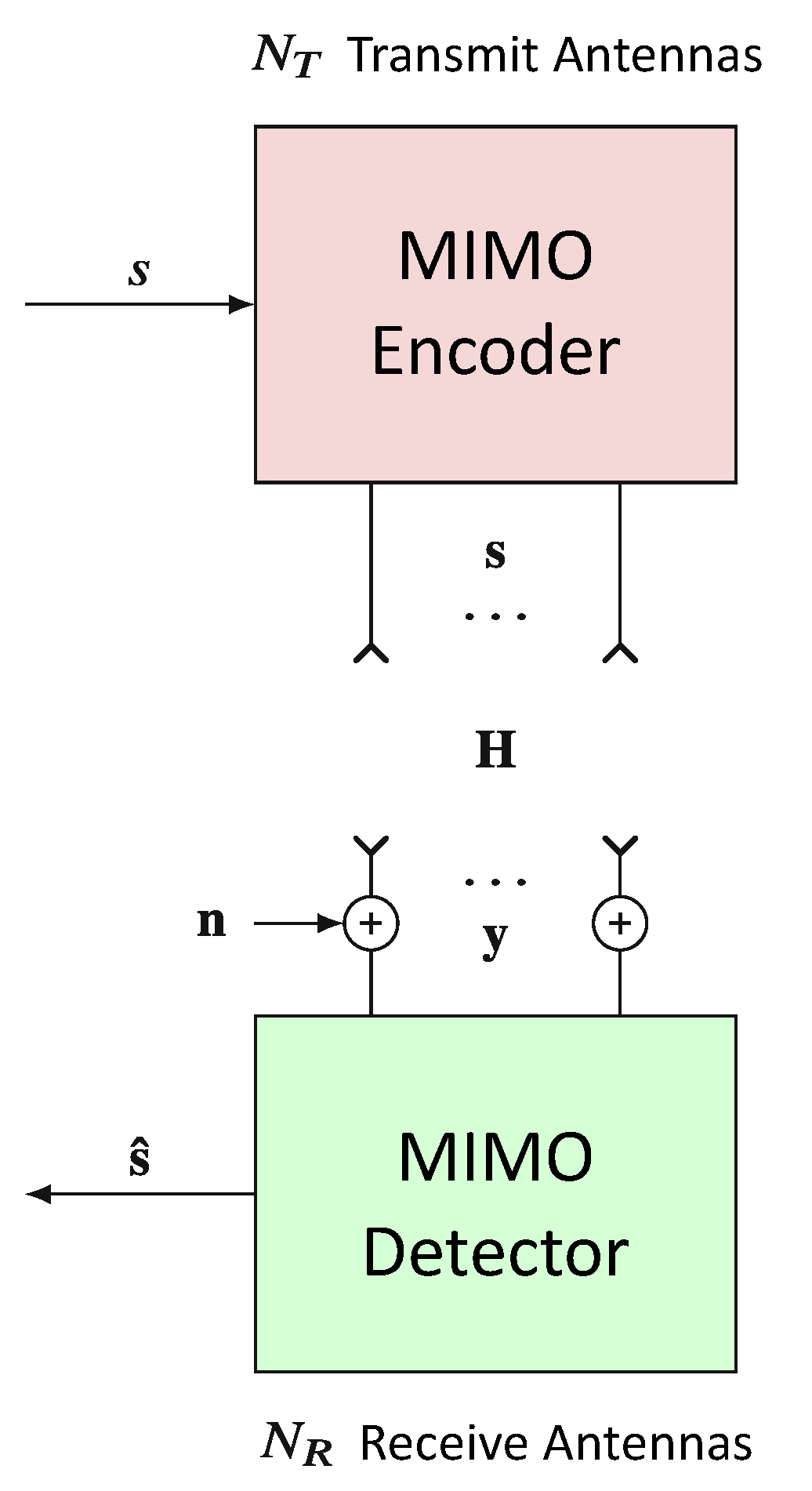
2.2. Multiple-Input Multiple-Output
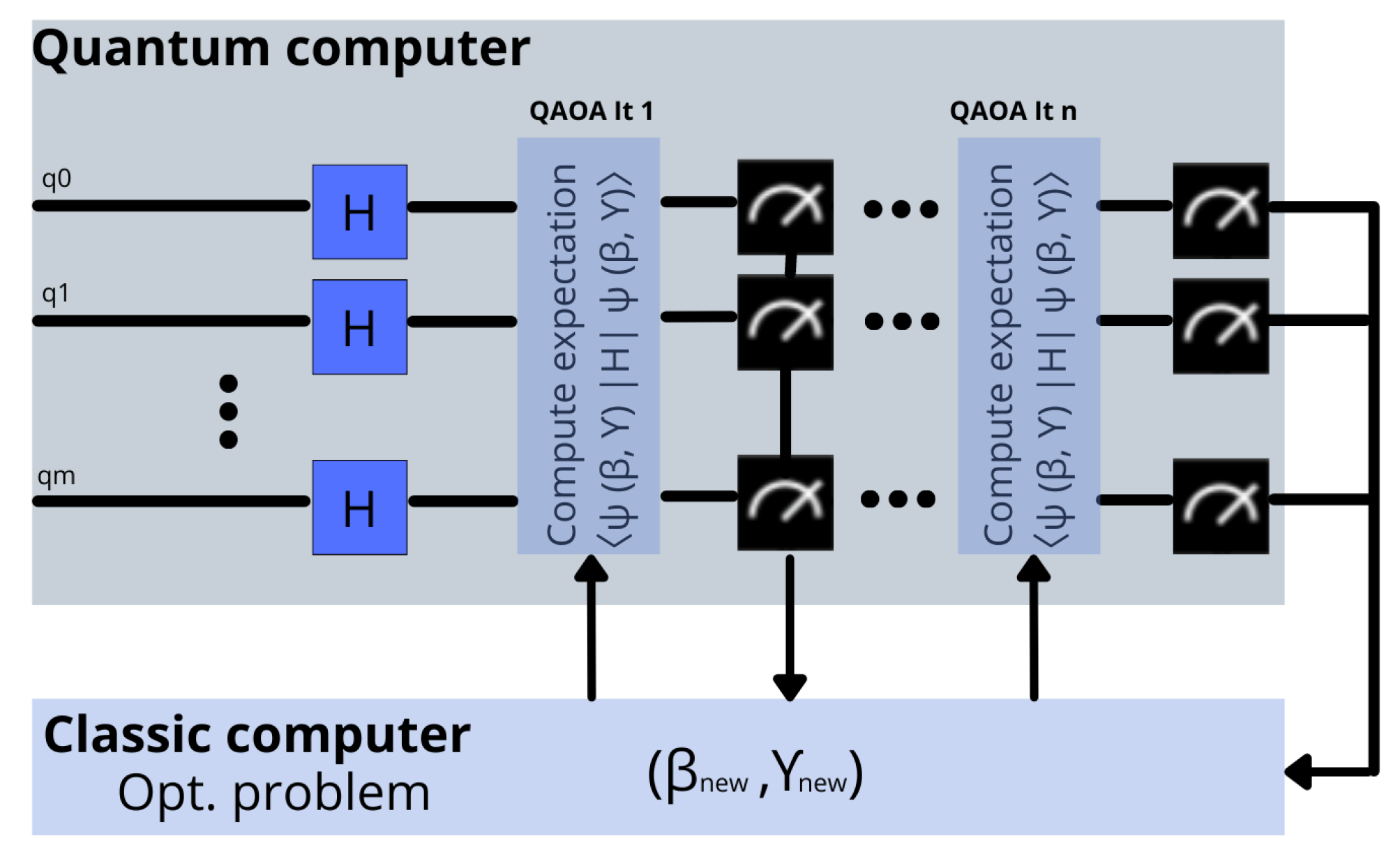
3. Quantum Computing
4. Quantum Maximum-Likelihood Detector for MIMO-NOMA
- If an error is made while decoding one iteration, it propagates through other successive ones.
- All the channel information should be known at the receiver to equalize.
- Since the decoding is iterative, complexity increases with the number of users, causing latency problems in some cases.
- Differences in the power levels of each signal should be large enough for successful detection.
4.1. MIMO-NOMA Detector
4.2. Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm
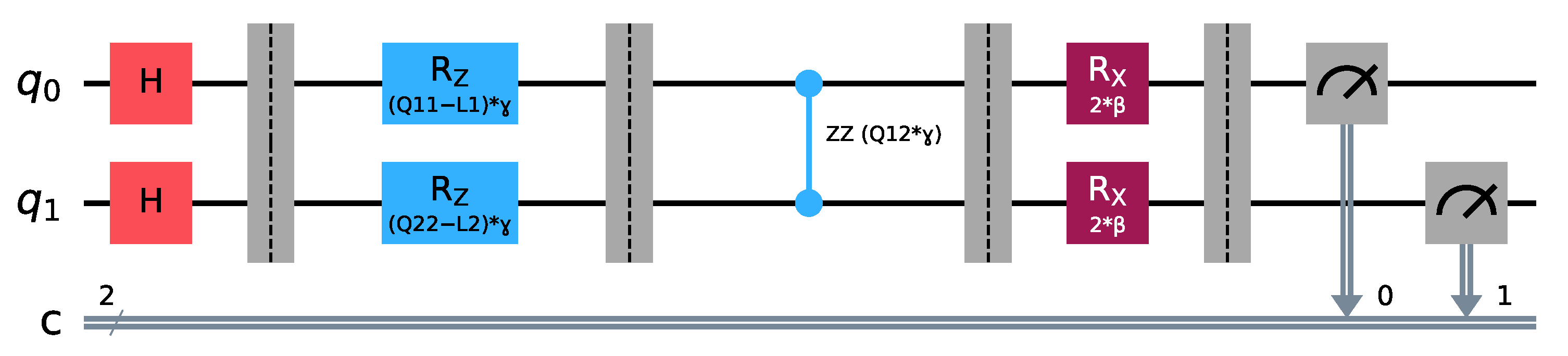
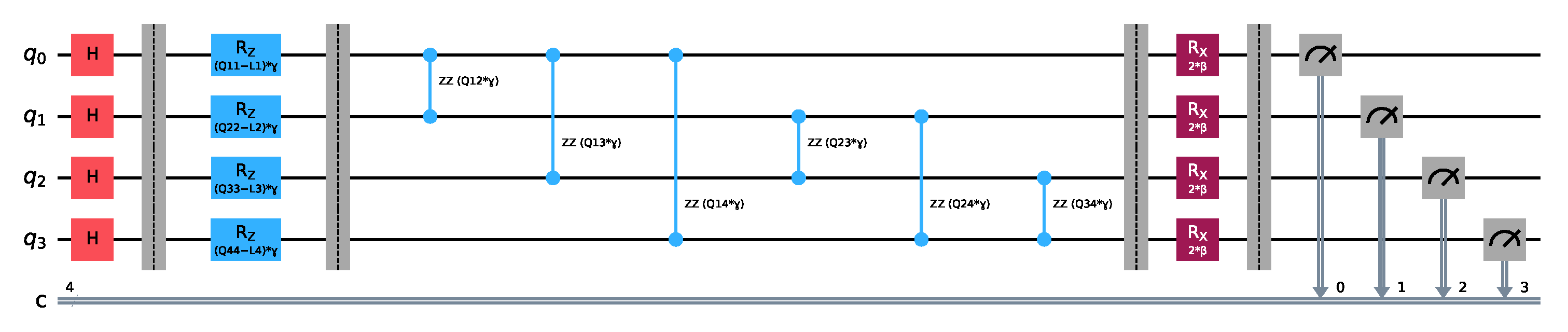
4.3. Quantum MIMO-NOMA Detection
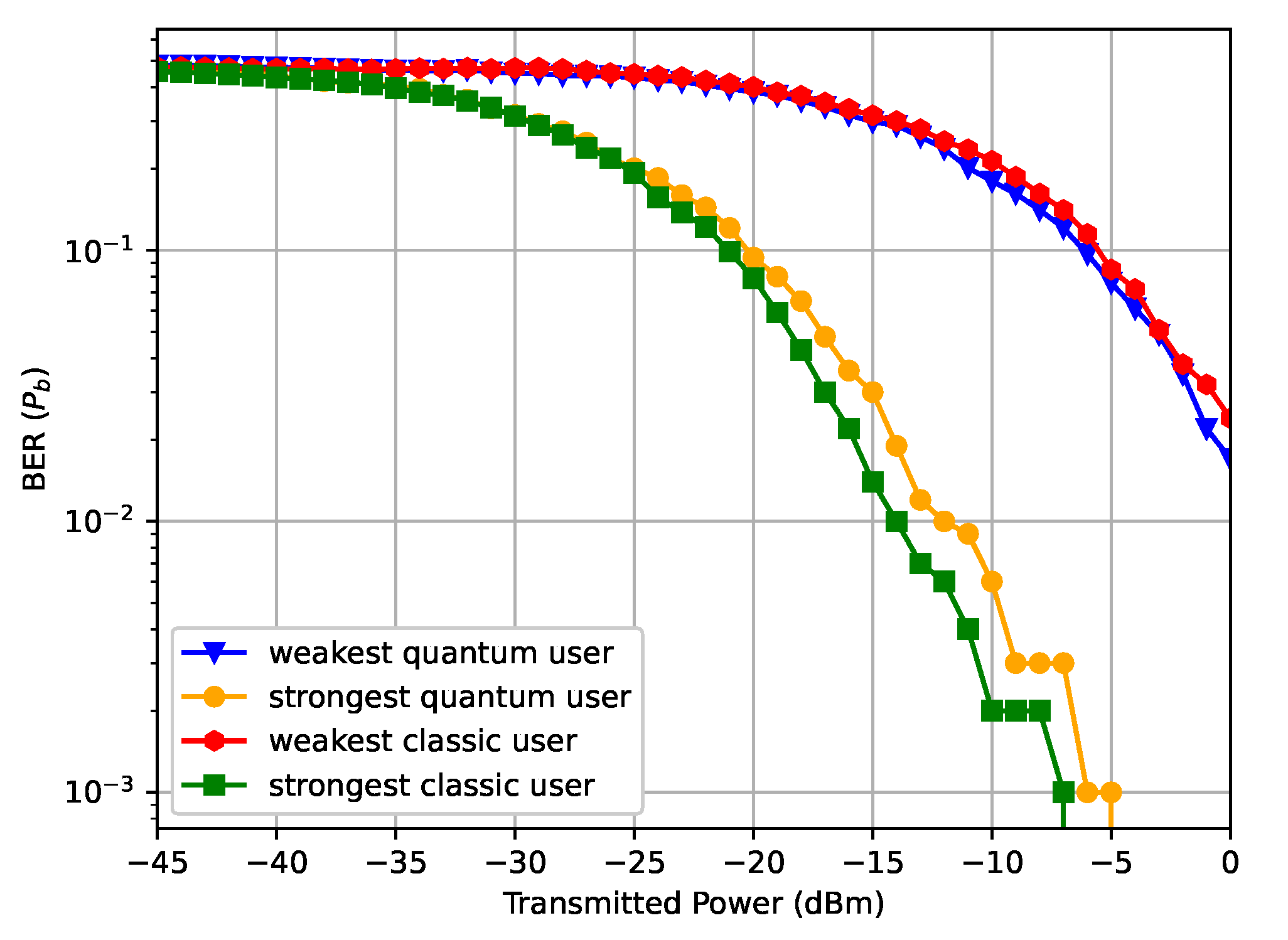
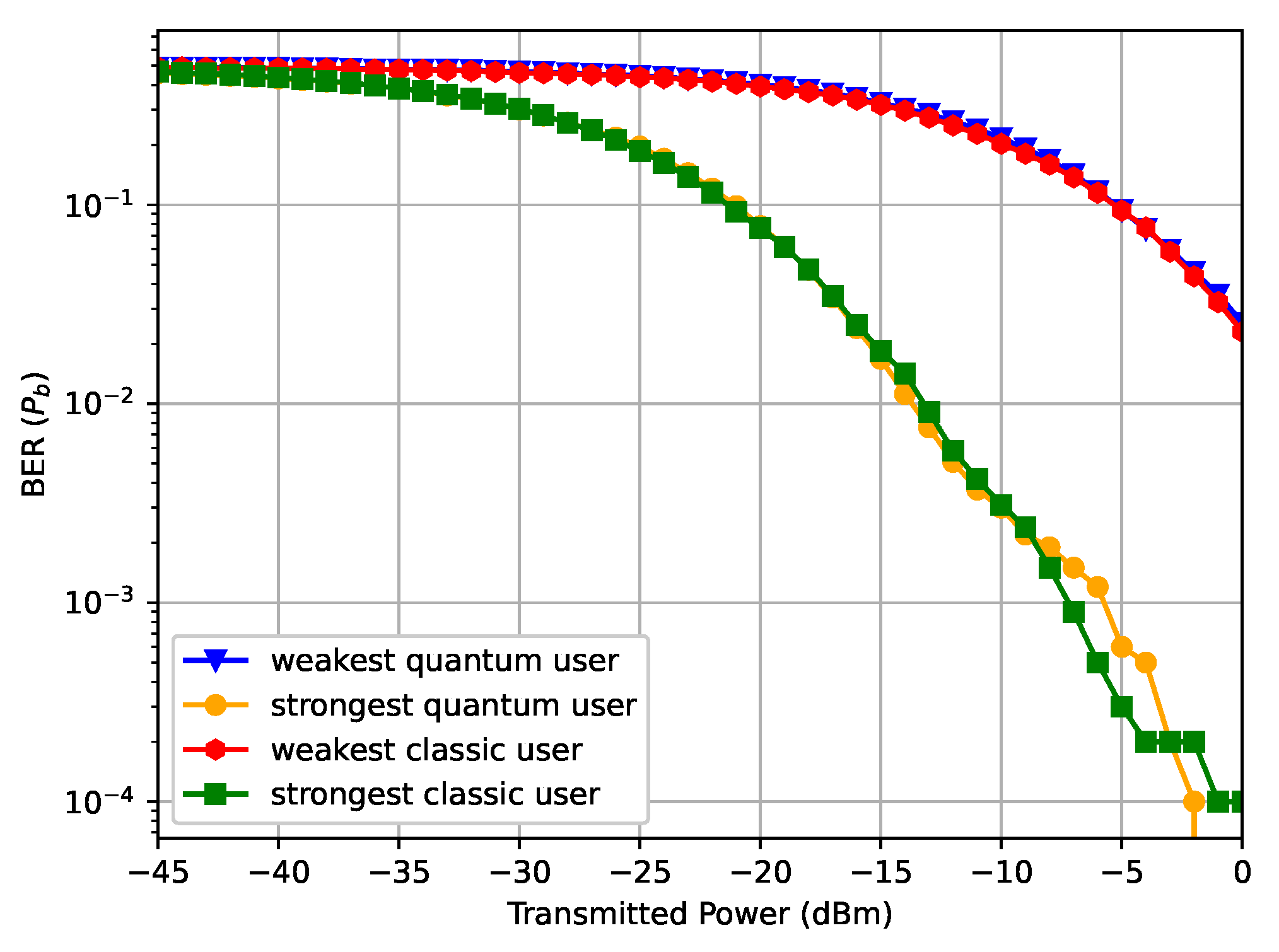
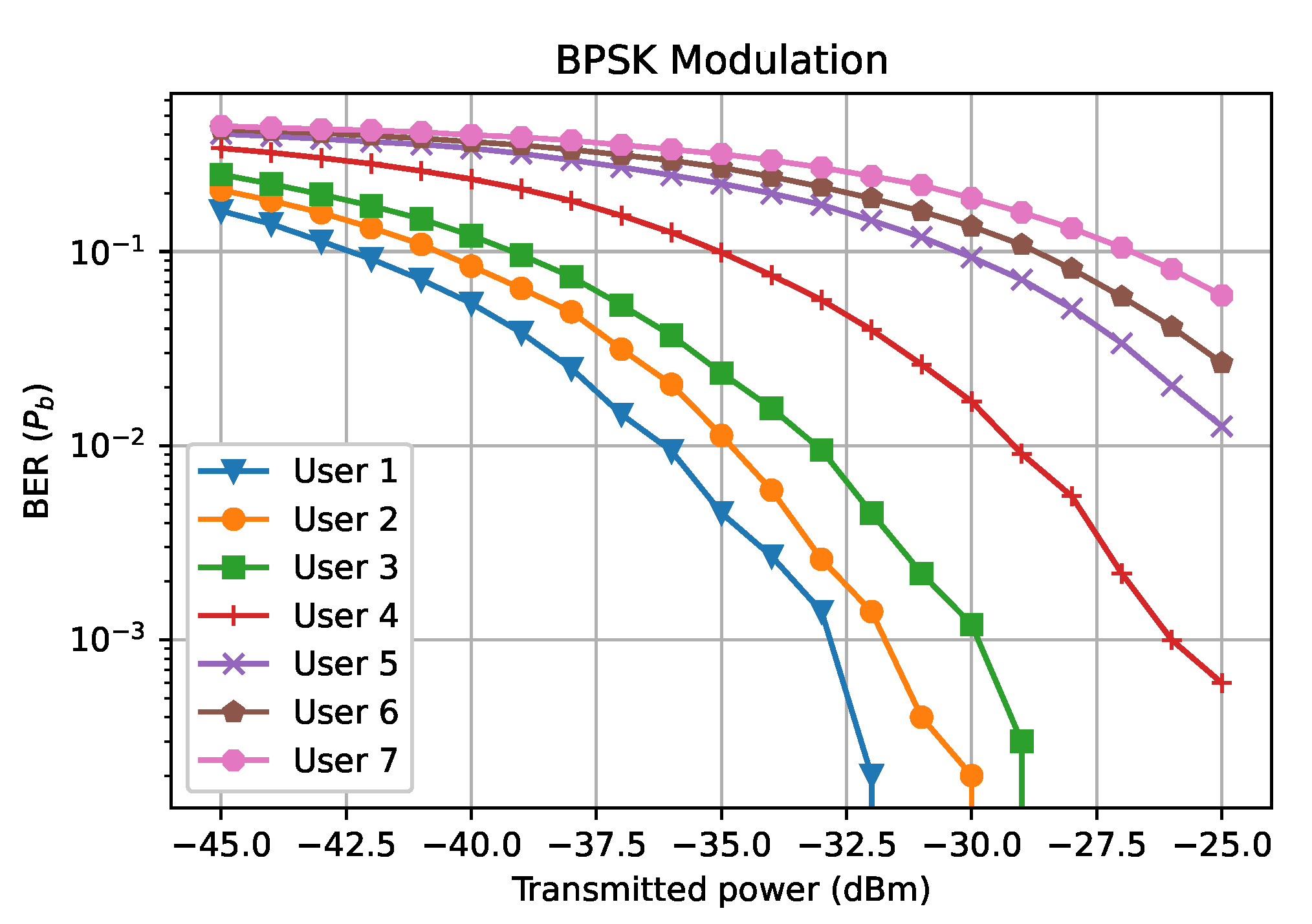
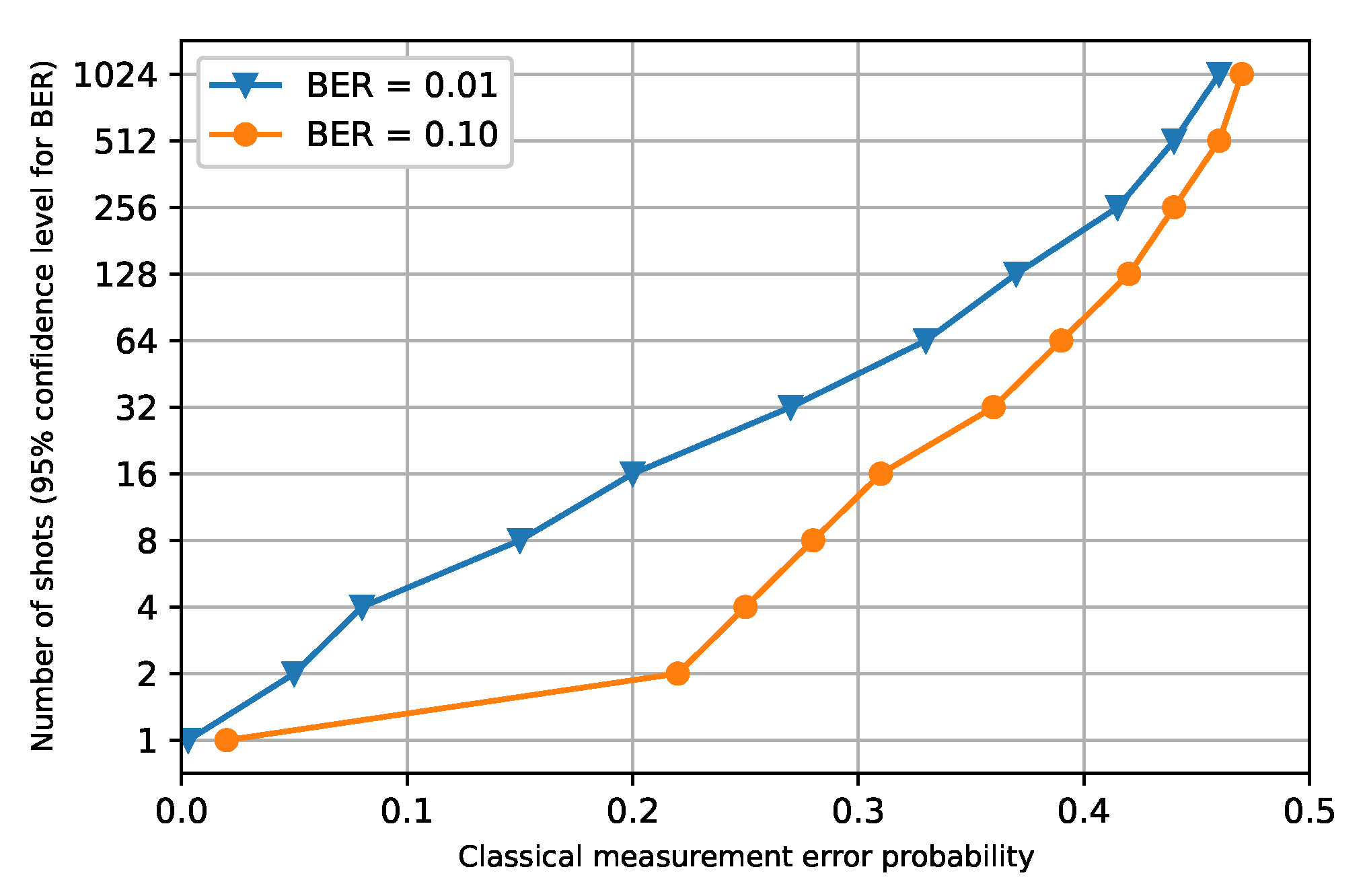
5. Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, X.; Wang, C.-X.; Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Towards 6G wireless communication networks: Vision, enabling technologies, and new paradigm shifts. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 64, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriya, M. Machine learning and quantum computing for 5G/6G communication networks—A survey. Int. J. Intell. Netw. 2022, 3, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Li, G.Y.; Swindlehurst, A.L.; Ashikhmin, A.; Zhang, R. An Overview of Massive MIMO: Benefits and Challenges. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2014, 8, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauch, G.; Alexiou, A. MIMO technologies for the wireless future. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Cannes, France, 15–18 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dogra, A.; Jha, R.K.; Jain, S. A Survey on beyond 5G Network with the Advent of 6G: Architecture and Emerging Technologies. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 67512–67547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucur, O.; Karabulut Kurt, G.; Shakir, M.Z.; Ansari, I.S. Nonorthogonal Multiple Access for 5G and Beyond. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 1907506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, B.; Chitti, K.; Behravan, A.; Alouini, M.S. A Survey of NOMA: Current Status and Open Research Challenges. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2020, 1, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.; Aruma Baduge, G.A.; Liu, Y.; Arafa, A.; Fang, F.; Ding, Z. Interplay Between NOMA and Other Emerging Technologies: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2019, 5, 900–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhiraja, I.; Kumar, N.; Tyagi, S.; Tanwar, S.; Han, Z.; Piran, M.J.; Suh, D.Y. A Systematic Review on NOMA Variants for 5G and Beyond. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 85573–85644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, G.; Ma, S.; Hou, F.; Tsiftsis, T.A. Zero-Forcing-Based Downlink Virtual MIMO–NOMA Communications in IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 2716–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yuen, C.; Guan, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Huang, C. Gaussian Message Passing Iterative Detection for MIMO-NOMA Systems with Massive Access. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sena, A.S.; Lima, F.R.M.; da Costa, D.B.; Ding, Z.; Nardelli, P.H.J.; Dias, U.S.; Papadias, C.B. Massive MIMO-NOMA Networks With Imperfect SIC: Design and Fairness Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 6100–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micciancio, D. The hardness of the closest vector problem with preprocessing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2001, 47, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Sugiura, S.; Ng, S.X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Hanzo, L. Two Decades of MIMO Design Tradeoffs and Reduced-Complexity MIMO Detection in Near-Capacity Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18564–18632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, I.M.; Hu, W.C.; Chiueh, T.D. Limited search sphere decoder and adaptive detector for NOMA with SU-MIMO. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chi, Y.; Yuen, C.; Guan, Y.L.; Li, Y. Capacity-Achieving MIMO-NOMA: Iterative LMMSE Detection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Leung, S.H.; Song, R. Precoding Design for Two-Cell MIMO-NOMA Uplink With CoMP Reception. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 2607–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Jing, Y.; Yang, L.; You, X. Signal Processing for MIMO-NOMA: Present and Future Challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2018, 25, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albreem, M.A.; Juntti, M.; Shahabuddin, S. Massive MIMO Detection Techniques: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 3109–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.R.; Avazov, N.; Dobre, O.A.; Kwak, K.S. Power-Domain Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) in 5G Systems: Potentials and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 721–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Rahman, A. Quantum-Enabled 6G Wireless Networks: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2022, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilirmak, R.C. Quantum Annealing Approach to NOMA Signal Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Porto, Portugal, 20–22 July 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narottama, B.; Hendraningrat, D.K.; Shin, S.Y. Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithms for NOMA user pairing. ICT Express 2022, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabdulsattarov, E.; Rabie, K.; Li, X.; Nauryzbayev, G. Towards Quantum Annealing for Multi-user NOMA-based Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 96th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2022-Fall), London, UK, 26–29 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, M.; Arnon, S. Quantum key distribution by a free-space MIMO system. J. Light. Technol. 2006, 24, 3114–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, G. A new scheme for quantum key distribution in free-space. In Proceedings of the 15th Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications, Shanghai, China, 8–10 October 2009; pp. 637–640. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Shi, J.; Guo, Y.; Peng, X.; Lee, M.H. Quantum MIMO Communication Scheme Based on Quantum Teleportation with Triplet States. Int. J. Theor. Phys 2011, 50, 2334–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikki, S. A Quantum MIMO Architecture for Antenna Wireless Digital Communications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2019, 93, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaawi, A.M.A.; Almasaoodi, M.R.; Gaily, S.E.; Imre, S. New Constrained Quantum Optimization Algorithm for Power Allocation in MIMO. In Proceedings of the 2022 45th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 13–15 July 2022; pp. 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sabaawi, A.M.A.; Almasaoodi, M.R.; Gaily, S.E.; Imre, S. MIMO System Based-Constrained Quantum optimization Solution. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing, Porto, Portugal, 20–22 July 2022; pp. 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Venturelli, D.; Jamieson, K. Leveraging quantum annealing for large MIMO processing in centralized radio access networks. In Proceedings of the the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication (SIGCOMM ’19), Beijing China, 19–23 August 2019; pp. 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Tabi, Z.I.; Marosits, A.; Kallus, Z.; Vaderna, P.; Gódor, I.; Zimborás, Z. Evaluation of Quantum Annealer Performance via the Massive MIMO Problem. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 131658–131671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Nishimori, H.; Katzgraber, H.G. Quantum annealing for problems with ground-state degeneracy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 143, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, L.T.; Baldwin, C.L.; Bapat, A.; Kharkov, Y.; Gorshkov, A.V. Optimal Protocols in Quantum Annealing and Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm Problems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 070505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chen, Y.W.; Zhou, Q.; Finkelstein, J.; Chang, G.K. Demonstration of Pattern Division Multiple Access with Message Passing Algorithm for Multi-Channel mmWave Uplinks via RoF Mobile Fronthaul. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 5908–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Peng, K.; Pan, C.; Yang, F.; Jin, H. Scalable Video Broadcasting Using Bit Division Multiplexing. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2014, 60, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotobas, B.; Nafkha, A.; Louët, Y. A Review to Massive MIMO Detection Algorithms: Theory and Implementation. In Advanced Radio Frequency Antennas for Modern Communication and Medical Systems; Sabban, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, E.; Harrow, A.W. Quantum Supremacy through the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1602.07674. [Google Scholar]
- Blekos, K.; Brand, D.; Ceschini, A.; Chou, C.H.; Li, R.H.; Pandya, K.; Summer, A. A Review on Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm and its Variants. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.09198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgelles, H.; Picazo-Martinez, P.; Garcia-Roger, D.; Monserrat, J.F. Multi-Objective Routing Optimization for 6G Communication Networks Using a Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, F.; Kochenberger, G.; Hennig, R.; Du, Y. Quantum Bridge Analytics I: A tutorial on formulating and using Qubo Models. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 314, 141–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Quantum Learning—Solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems Using QAOA. Available online: https://learning.quantum.ibm.com/ (accessed on 31 August 2024).
- Pellow-Jarman, A.; Sinayskiy, I.; Pillay, A.; Petruccione, F. A comparison of various classical optimizers for a variational quantum linear solver. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Quantum. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/quantum (accessed on 31 March 2023).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urgelles, H.; Garcia-Roger, D.; Monserrat, J.F. Quantum-Based Maximum Likelihood Detection in MIMO-NOMA Systems for 6G Networks. Quantum Rep. 2024, 6, 533-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6040036
Urgelles H, Garcia-Roger D, Monserrat JF. Quantum-Based Maximum Likelihood Detection in MIMO-NOMA Systems for 6G Networks. Quantum Reports. 2024; 6(4):533-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrgelles, Helen, David Garcia-Roger, and Jose F. Monserrat. 2024. "Quantum-Based Maximum Likelihood Detection in MIMO-NOMA Systems for 6G Networks" Quantum Reports 6, no. 4: 533-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6040036
APA StyleUrgelles, H., Garcia-Roger, D., & Monserrat, J. F. (2024). Quantum-Based Maximum Likelihood Detection in MIMO-NOMA Systems for 6G Networks. Quantum Reports, 6(4), 533-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6040036







