Automated IoT-Based Monitoring of Industrial Hemp in Greenhouses Using Open-Source Systems and Computer Vision
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
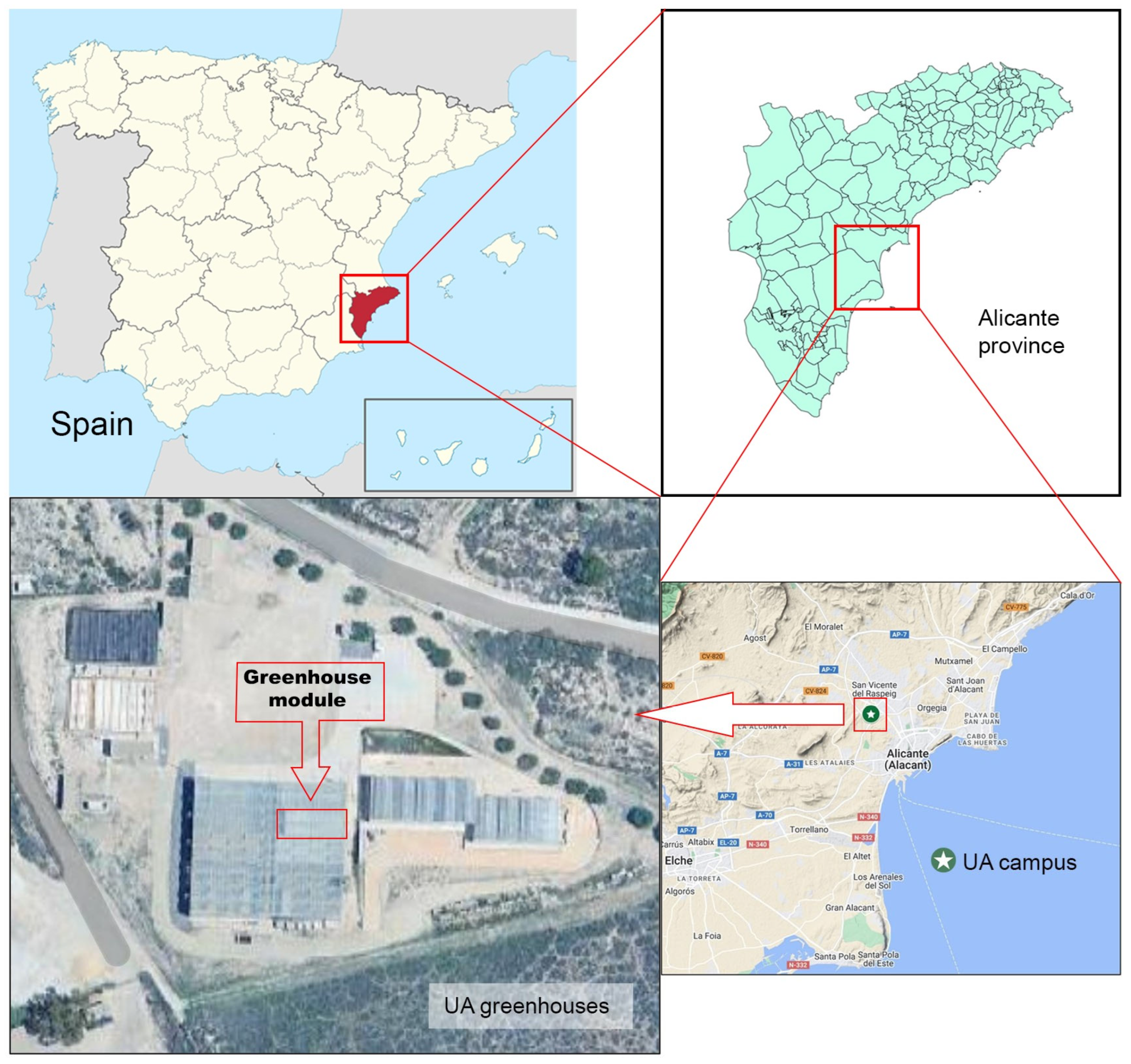
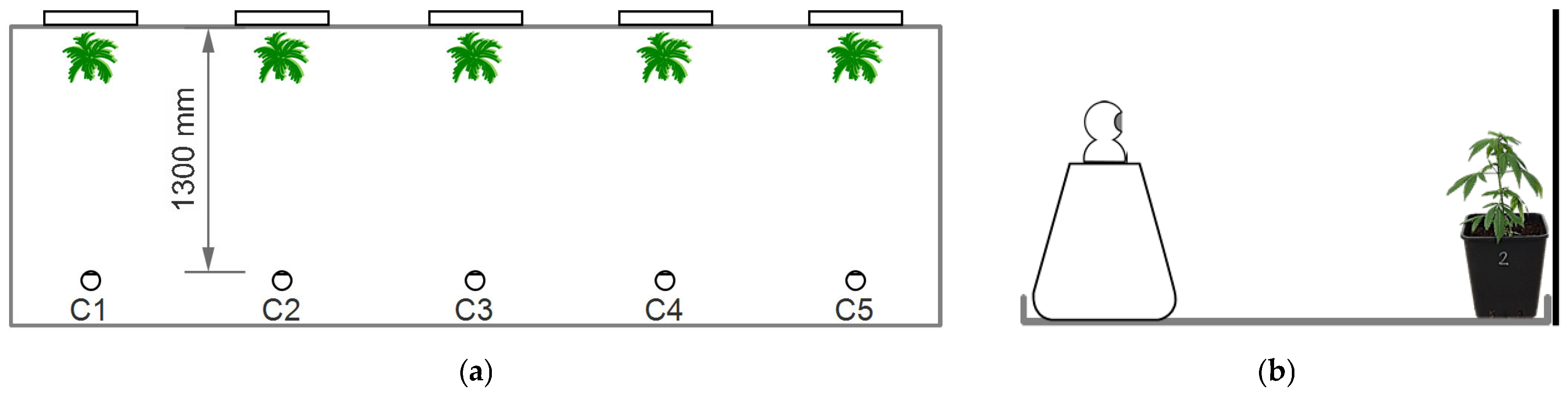
2.1. Experimental Setting and Plant Material
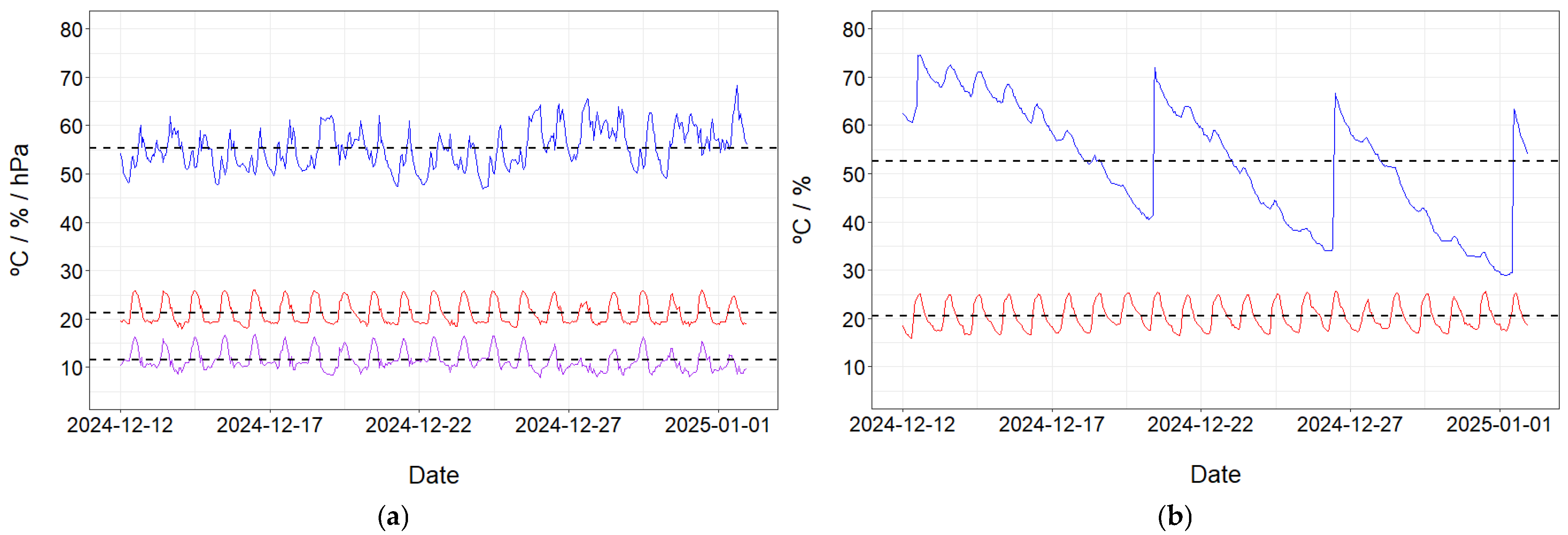
2.2. Architecture and Communications
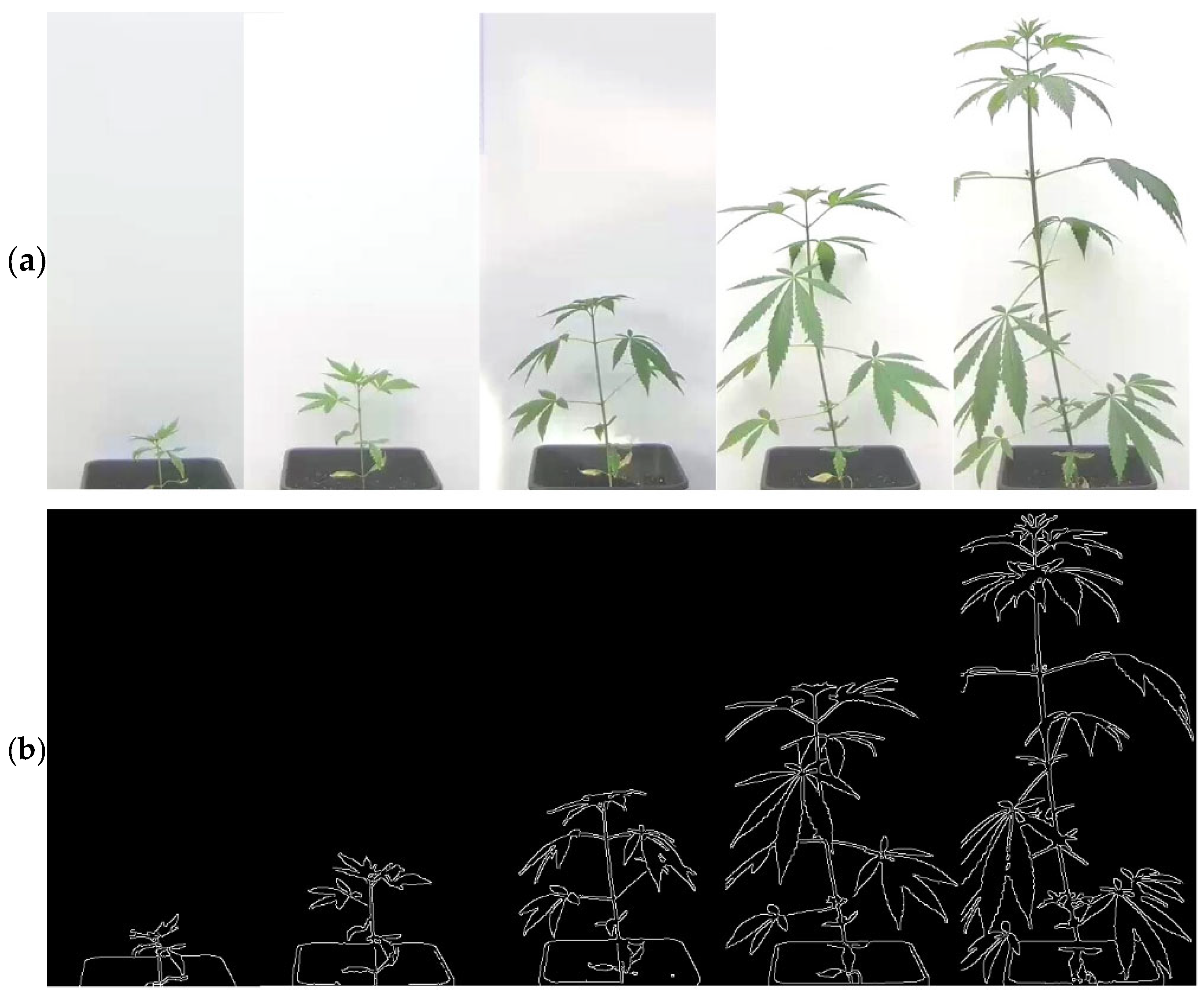
2.3. Image Acquisition
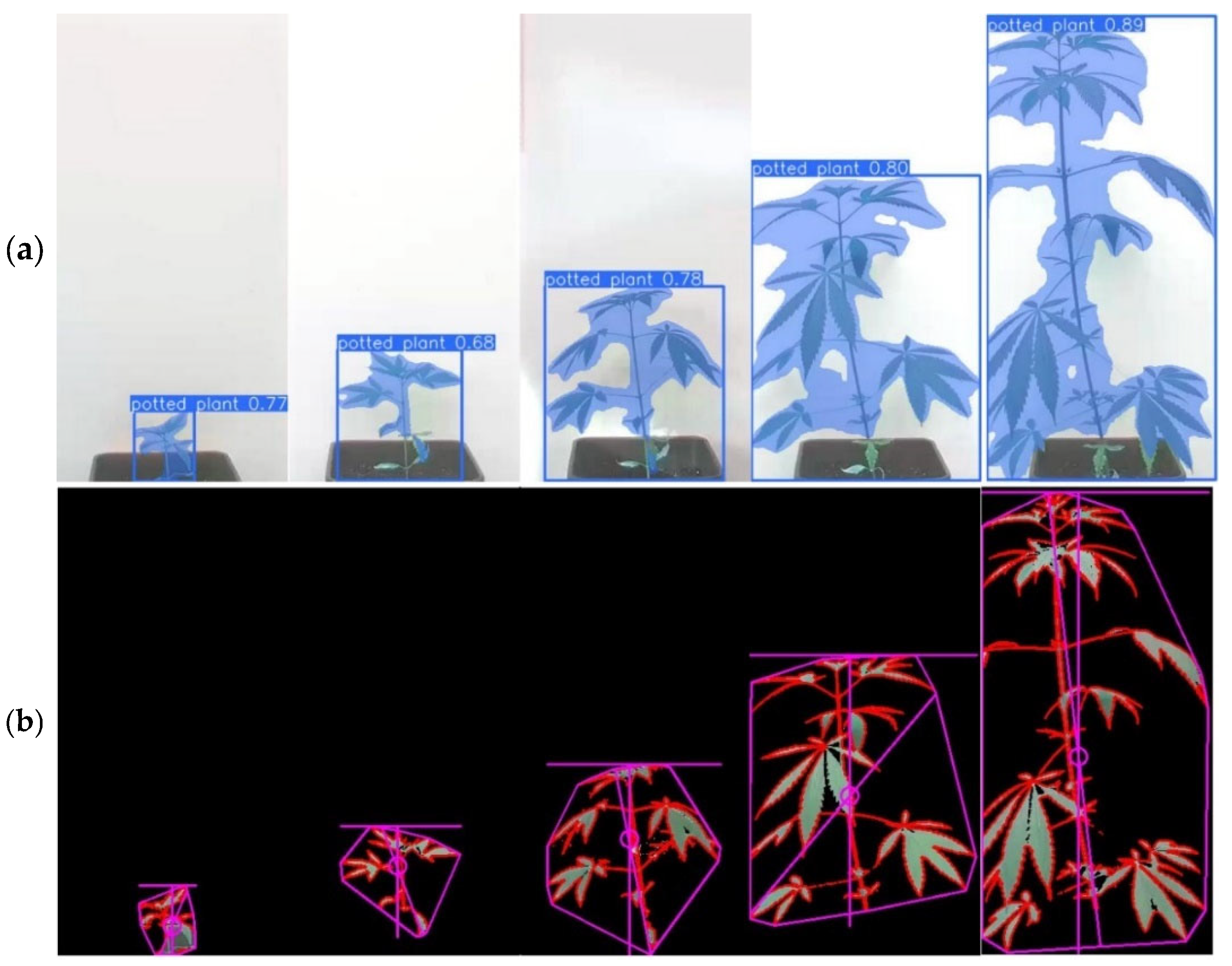
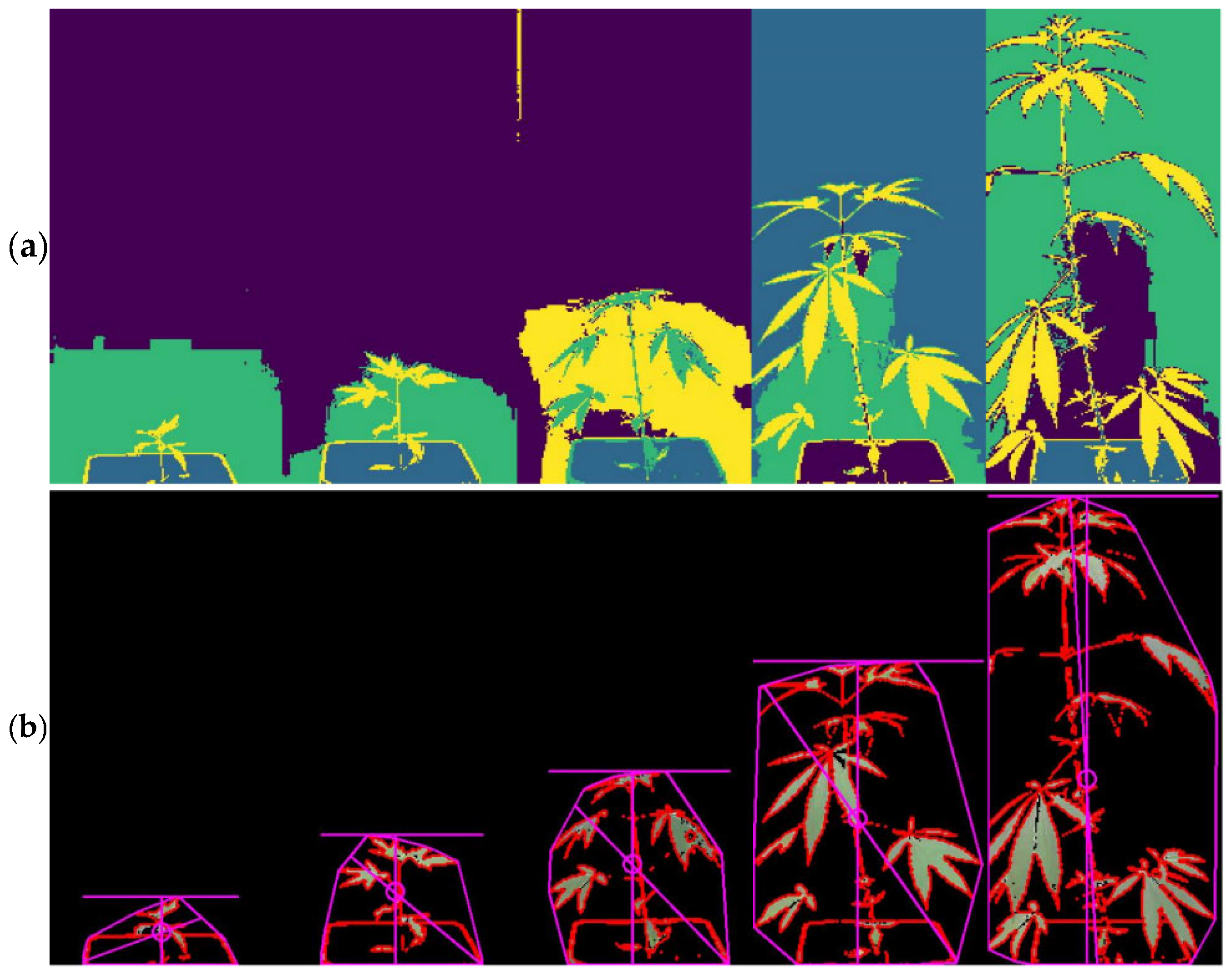
2.4. Image Processing and Growth Assessment
- Convex hull area: Area of the smallest convex shape completely containing an object.
- Solidity: The ratio of the plant area to the convex hull area.
- RMSE (Root Mean-Squared Error): This measures the root mean-squared difference between the predicted values and the real values. It is calculated according to Equation (1):
- MAE (Mean Absolute Error): This calculates the average of the absolute errors between the actual and predicted values. It is calculated according to Equation (2):
2.5. Water Stress Assessment
- 81 images of healthy plants for training and 20 for testing;
- 90 images corresponding to 3 days of stress for training and 20 images for testing;
- 70 images with 6 days of stress for training and 17 for testing;
- 64 images of plants with 9 days of stress for training and 16 for testing.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth Determination
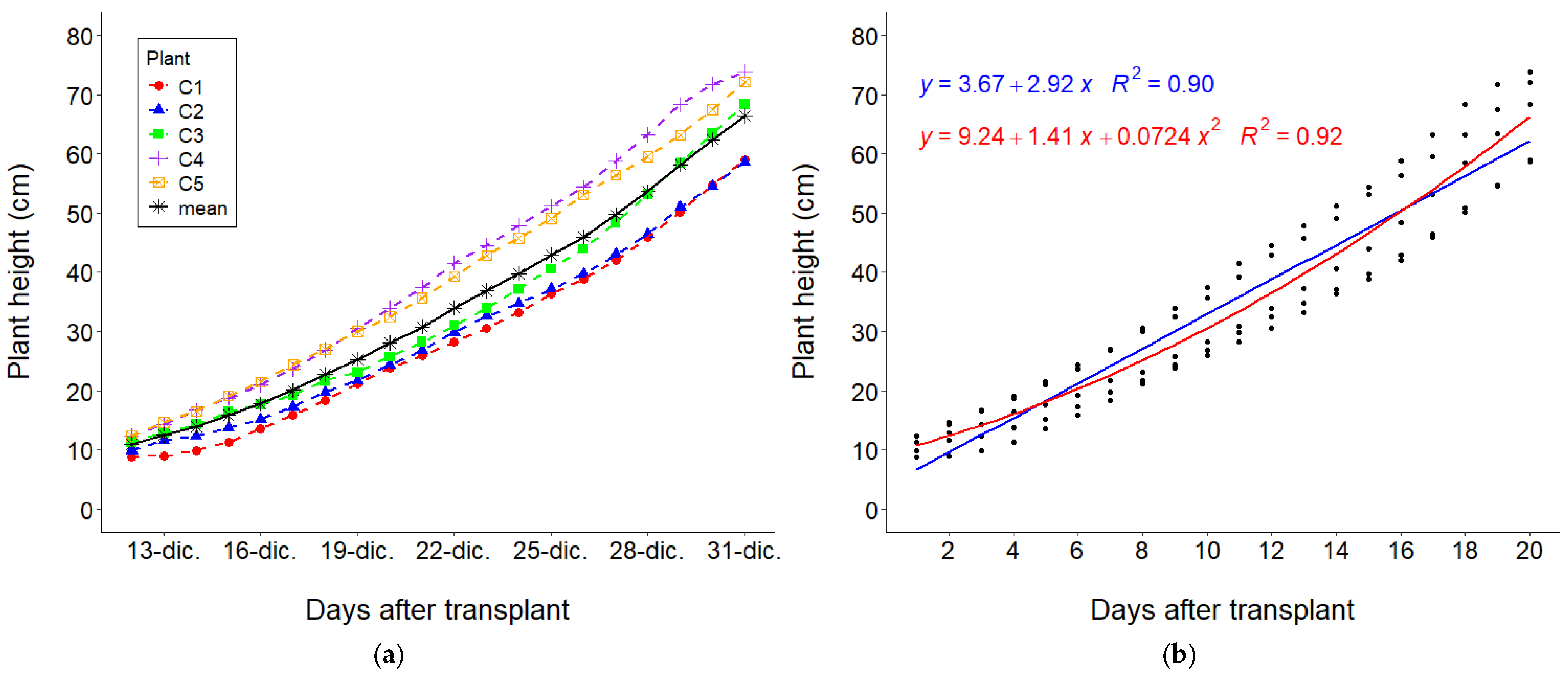
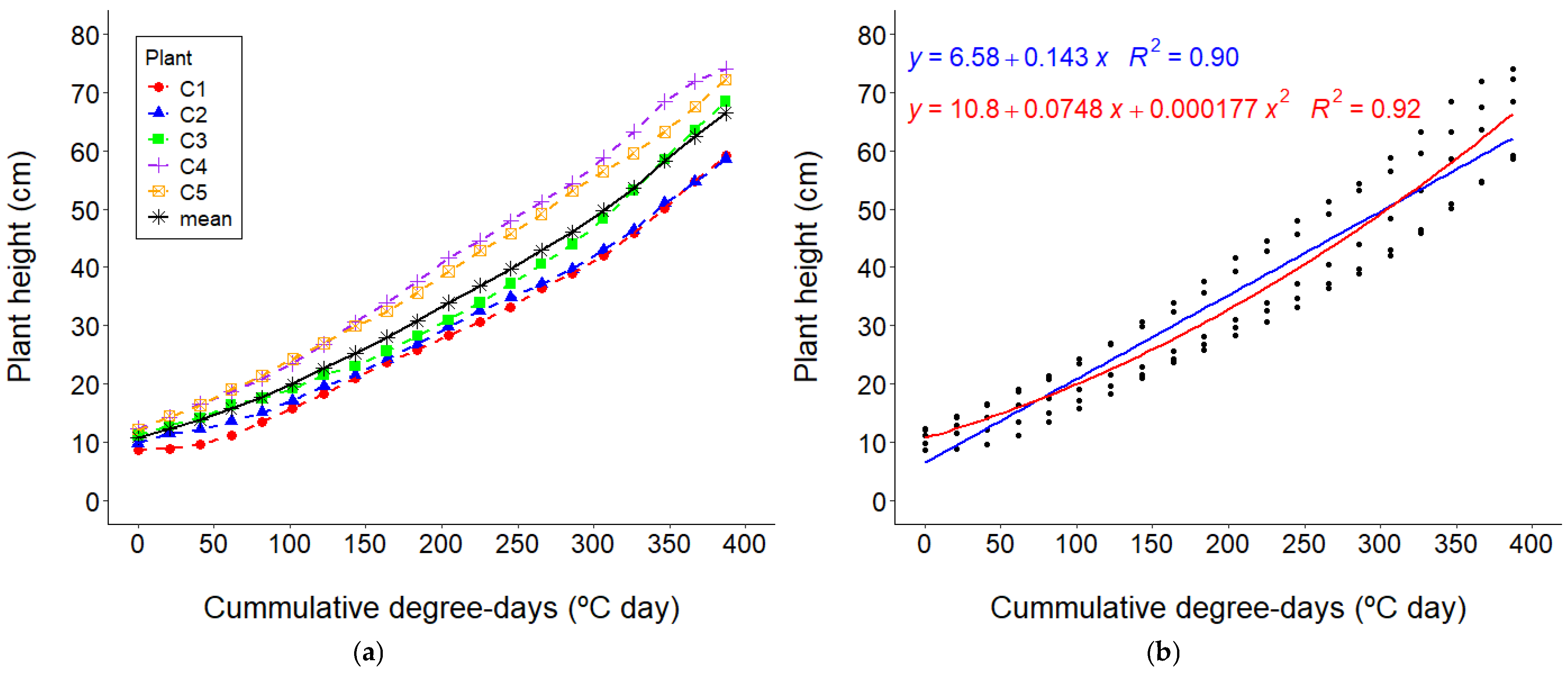
3.2. Growth Curves
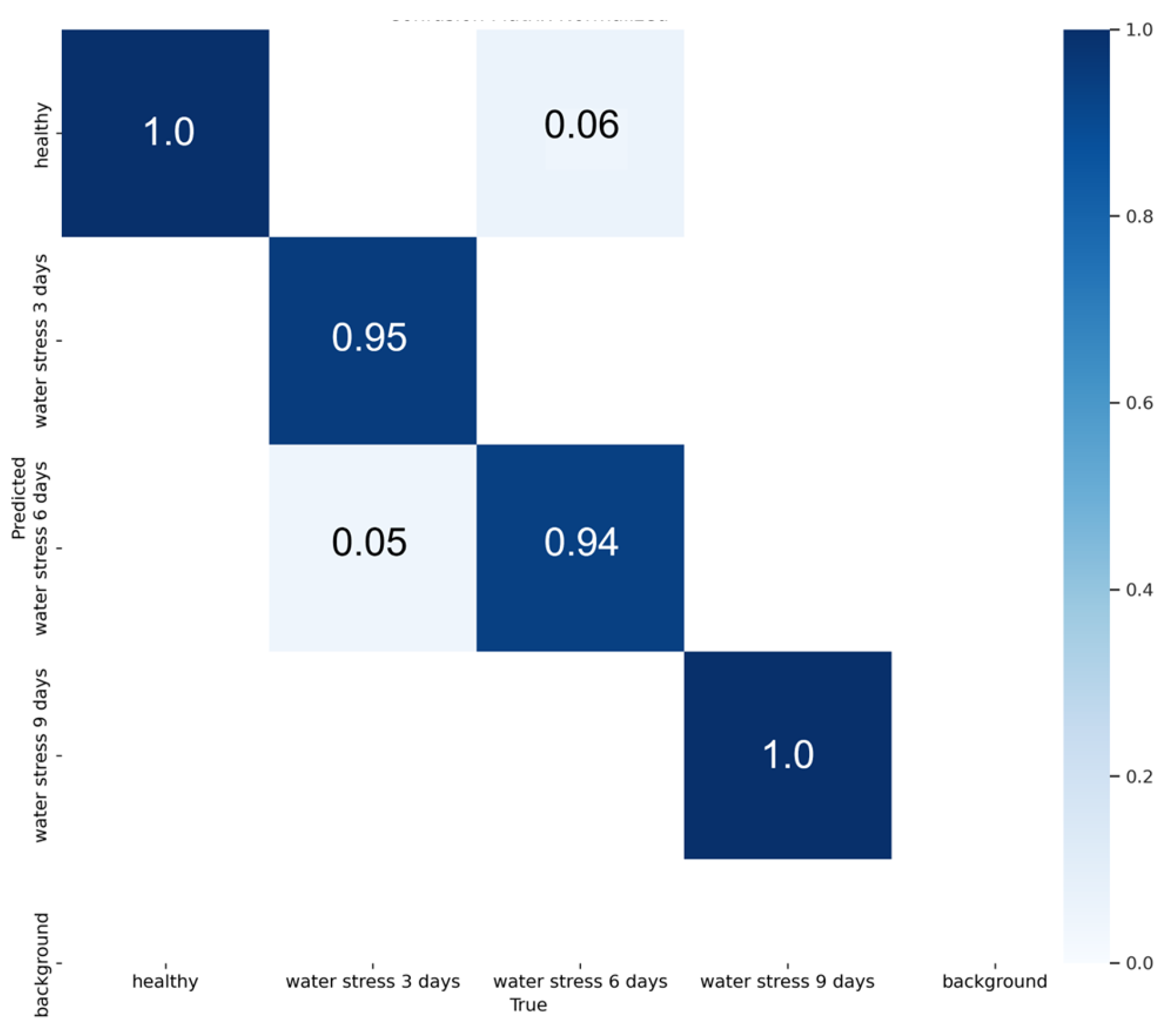
3.3. Water Stress Detection
3.4. The Potential of Internet of Things (IoT) Systems and Low-Cost Platforms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guillevic, P.; Aouizerats, B.; Burger, R.; Besten, D.; Jackson, D.; Ridderikhoff, M.; Zajdband, A.; Houborg, R.; Franz, T.; Robertson, G.; et al. Planet’s Biomass Proxy for monitoring aboveground agricultural biomass and estimating crop yield. Field Crop. Res. 2024, 316, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Hong, S.; Kang, S. Improving remotely-sensed crop monitoring by NDVI-based crop phenology estimators for corn and soybeans in Iowa and Illinois, USA. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 238, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, Q. A heterogeneous access metamodel for efficient IoT remote sensing observation management: Taking precision agriculture as an example. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 8616–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behmann, J.; Acebron, K.; Emin, D.; Bennertz, S.; Matsubara, S.; Thomas, S.; Bohnenkamp, D.; Kuska, M.T.; Jussila, J.; Salo, H.; et al. Specim IQ: Evaluation of a New, Miniaturized Handheld Hyperspectral Camera and Its Application for Plant Phenotyping and Disease Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Koh, S.; Teo, M.; Bi, R.; Zhang, S.; Dev, K.; Urano, D.; Dinish, U.; Olivo, M. Handheld Multifunctional Fluorescence Imager for Non-invasive Plant Phenotyping. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 822634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirilli, M.; Bellincontro, A.; Urbani, S.; Servili, M.; Esposto, S.; Mencarelli, F.; Muleo, R. On-field monitoring of fruit ripening evolution and quality parameters in olive mutants using a portable NIR-AOTF device. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, J.; Digman, M.; Cherney, D. Handheld NIRS for forage evaluation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 190, 106469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykas, D.; Ball, C.; Sia, A.; Zhu, K.; Shotts, M.; Schmenk, A.; Rodriguez-Saona, L. In-Situ Screening of Soybean Quality with a Novel Handheld Near-Infrared Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, S.; Vibhute, A.; Kale, K.; Mehrotra, S. An innovative IoT based system for precision farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtasim, S.; Khan, J.; Islam, M.; Sarker, M.; Uddin, M.; Hasan, M. IoT-based Crop Monitoring and Disease Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 5.0 (STI), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 9–10 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushma, Y.; Lakshmi Ch, J.; Rajesh, K.; Hemanth, V.; Sowmyarao, V. IoT Based Soil Nutrient Monitoring and Analysis System. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on IoT Based Control Networks and Intelligent Systems (ICICNIS), Bengaluru, India, 17–18 December 2024; pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.; Srilakshmi, V.; Reddy, B.; Thatha, V.N.; Sanapala, S. Image Processing Techniques in Computer Vision; IIP Series: Chikkamagaluru, India, 2024; pp. 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, V.; Subeesh, A.; Kushwaha, N.; Vishwakarma, D.; Kumar, N.; Ritika, G.; Singh, A. Deep learning based computer vision approaches for smart agricultural applications. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2022, 6, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, S.; Munir, A.; Qureshi, W. Computer vision in smart agriculture and precision farming: Techniques and applications. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2024, 13, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Li, Y. Computer vision technology in agricultural automation—A review. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO11 (11.0.0) 2024 [Computer Software]. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Wu, D.; Lv, S.; Jiang, M.; Song, H. Using channel pruning-based YOLO v4 deep learning algorithm for the real-time and accurate detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Nouaze, J.C.; Touko Mbouembe, P.L.; Kim, J.H. YOLO-tomato: A robust algorithm for tomato detection based on YOLOv3. Sensors 2020, 20, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Gerbino, S.; Akbari Sekehravani, E.; Russo, M.B.; Carillo, P. Crop Growth Analysis Using Automatic Annotations and Transfer Learning in Multi-Date Aerial Images and Ortho-Mosaics. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi Goharrizi, K.; Wilde, H.D.; Amirmahani, F.; Moemeni, M.M.; Zaboli, M.; Nazari, M.; Moosavi, S.S.; Jamalvandi, M. Selection and validation of reference genes for normalization of qRT-PCR gene expression in wheat (Triticum durum L.) under drought and salt stresses. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, M.; Goharrizi, K.J.; Moosavi, S.S.; Maleki, M. Expression changes in the TaNAC2 and TaNAC69-1 transcription factors in drought stress tolerant and susceptible accessions of Triticum boeoticum. Plant Genet. Resour. 2019, 17, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Moosavi, S.S.; Maleki, M.; Jamshidi Goharrizi, K. Chloroplastic acyl carrier protein synthase I and chloroplastic 20 kDa chaperonin proteins are involved in wheat (Triticum aestivum) in response to moisture stress. J. Plant Interact. 2020, 15, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirbalouti, A.G.; Malekpoor, F.; Salimi, A.; Golparvar, A.; Hamedi, B. Effects of foliar of the application chitosan and reduced irrigation on essential oil yield, total phenol content and antioxidant activity of extracts from green and purple basil. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2017, 16, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, K.; Moghaddam, M.; Farhadi, N.; Pirbalouti, A.G. Morphological, physiological and phytochemical responses of Mexican marigold (Tagetes minuta L.) to drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 284, 110116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Guzmán, H.A.; Padilla-Medina, J.A.; Martínez-Nolasco, C.; Martinez-Nolasco, J.J.; Barranco-Gutiérrez, A.I.; Contreras-Medina, L.M.; Leon-Rodriguez, M. IoT-Based Monitoring System Applied to Aeroponics Greenhouse. Sensors 2022, 22, 5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohabuth, A.; Nem, D. An IoT-Based Model for Monitoring Plant Growth in Greenhouses. J. Inf. Syst. Inform. 2023, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, M.; Rinku, D.; Swapna, P.; Jyothi, V.; Athiraja, A.; Prasannakumar, G. An IoT Based Greenhouse Remote Monitoring System for Automation of Supervision for Optimal Plant Growth. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 14–15 March 2024; pp. 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, P.; Rane, T.; Rawale, N.; Jadhav, A. Greenhouse Monitoring System Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, A.; Mohamed, N.; Ahmad, R.; Rahim, A.; Ani, N. Improved Internet of Things (IoT) monitoring system for growth optimization of Brassica chinensis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 164, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.; Pahadsingh, S.; Giri, N.; Kuziakin, O.; Leliuk, S.; Bilyk, S. Smart Plant Monitoring and Controlling System for Greenhouse Application Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 5th International Conference on Modern Electrical and Energy System (MEES), Kremenchuk, Ukraine, 27–30 September 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabay, G.S.; Çavaş, M. Artificial Intelligence Based Smart Agriculture Applications in Greenhouses. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th International Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing Symposium (IDAP), Malatya, Turkiye, 21–22 September 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G.; Liang, R. Review of the internet of things communication technologies in smart agriculture and challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yin, H. Camera-based plant growth monitoring for automated plant cultivation with controlled environment agriculture. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.; Lai, T.; Liu, T.; Liu, C.; Chung, W.; Lin, T. An automated growth measurement system for leafy vegetables. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 117, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijanarko, A.; Nugroho, A.; Sutiarso, L.; Okayasu, T. Development of mobile RoboVision with stereo camera for automatic crop growth monitoring in plant factory. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2202, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetedjo, A.; Hendriarianti, E. Plant Leaf Detection and Counting in a Greenhouse during Day and Nighttime Using a Raspberry Pi NoIR Camera. Sensors 2021, 21, 6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Reza, M.; Samsuzzaman, S.; Ahmed, S.; Cho, Y.; Noh, D.; Chung, S.; Hong, S. Machine vision and artificial intelligence for plant growth stress detection and monitoring: A review. Precis. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Bartzanas, T. Application of Internet of Things (IoT) for Optimized Greenhouse Environments. AgriEngineering 2021, 3, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Riaz, S.; Helou, M.; Khan, F.; Abid, A.; Alvi, A. A Survey on IoT in Agriculture for the Implementation of Greenhouse Farming. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53374–53397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lee, W.; Kim, Y. A Review of the Applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) for Agricultural Automation. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 45, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayılmış, C.; Ebleme, M.A.; Çavuşoğlu, Ü.; Küçük, K.; Sevin, A. A survey on communication protocols and performance evaluations for Internet of Things. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Home Foundation. Home Assistant. Available online: https://www.home-assistant.io/ (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Hüwe, P.; Hüwe, S. IoT at Home; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Setz, B.; Graef, S.; Ivanova, D.; Tiessen, A.; Aiello, M. A Comparison of Open-Source Home Automation Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 167332–167352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspberry Pi Foundation. Raspberry Pi, 2024. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.org/ (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- GitHub. GitHub: Where the World Builds Software. Available online: https://github.com/ (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- De Prato, L.; Ansari, O.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Howieson, J.; O’Hara, G.; Ruthrof, K.X. The cannabinoid profile and growth of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is influenced by tropical daylengths and temperatures, genotype and nitrogen nutrition. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 178, 114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisson, S.N.; Mendham, N.J.; Carberry, P.S. Development of a hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) simulation model 2. The flowering response of two hemp cultivars to photoperiod. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2000, 40, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiponi, S.; Bernstein, N. Response of medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) genotypes to P supply under long photoperiod: Functional phenotyping and the ionome. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 161, 113154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, N.; Campbell, S.; Carvalho, A.; Harapanahalli, S.; Hernandez, G.V.; Krpalkova, L.; Riordan, D.; Walsh, J. Deep learning vs. traditional computer vision. In Advances in Computer Vision, Proceedings of the Computer Vision Conference (CVC 2019), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–3 May 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 128–144. [Google Scholar]
- Neha, F.; Bhati, D.; Shukla, D.K.; Amiruzzaman, M. From classical techniques to convolution-based models: A review of object detection algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 6th International Conference on Image Processing, Applications and Systems (IPAS), Lyon, France, 9–11 January 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014. ECCV 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehan, M.A.; Fahlgren, N.; Abbasi, A.; Berry, J.C.; Callen, S.T.; Chavez, L.; Doust, A.N.; Feldman, M.J.; Gilbert, K.B.; Hodge, J.G.; et al. PlantCV v2: Image analysis software for high-throughput plant phenotyping. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Du, W.; Ma, C.; Gu, Z. Gradient Color Leaf Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Meanshift and Kmeans. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 March 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1609–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sachar, S. Swarm Intelligence for Segmentation of Leaf Images. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2023, 46, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Fruit detection and positioning technology for a Camellia oleifera C. Abel orchard based on improved YOLOv4-tiny model and binocular stereo vision. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2023, 211, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, J.U.M.; Kamarulzaman, S.F.; Muzahid, A.J.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, M. A comprehensive review on deep learning assisted computer vision techniques for smart greenhouse agriculture. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 4485–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.H.; Stack, G.M.; Jiang, Y.; Taşkıran, B.; Cala, A.R.; Philippe, G.; Rose, J.K.C.; Smart, C.D.; Smart, L.B. Morphometric relationships and their contribution to biomass and cannabinoid yield in hybrids of hemp (Cannabis sativa). J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 7694–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Yu, T.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, H. Low-cost lettuce height measurement based on depth vision and lightweight instance segmentation model. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarianakis, Z.; Perdikakis, S.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Papadimitriou, D.M.; Panagiotakis, S. Design and Implementation of a Low-Cost, Linear Robotic Camera System, Targeting Greenhouse Plant Growth Monitoring. Future Internet 2024, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, D.; Kacira, M. Design and implementation of a computer vision-guided greenhouse crop diagnostics system. Mach. Vision Appl. 2015, 26, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoj, S.; Igathinathane, C.; Saliendra, N.; Hendrickson, J.; Archer, D.; Liebig, M. PhenoCam Guidelines for Phenological Measurement and Analysis in an Agricultural Cropping Environment: A Case Study of Soybean. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.T.; Gilani, H.; Ashraf, M.; Iqbal, M.S.; Munir, S. Field validation of NDVI to identify crop phenological signatures. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 2245–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.L.; Pearson, B.; Kjelgren, R.; Brym, Z. Response of essential oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) growth, biomass, and cannabinoid profiles to varying fertigation rates. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, L. Optimizing plant density for fiber and seed production in industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramkale, V.; Andze, L.; Cernova, L.; Teirumnieka, E.; Filipova, I.; Stramkalis, A.; Teirumnieks, E.; Andzs, M. Industrial Hemp Variety Performance in Latvia Under Baltic Sea Climate. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliyanny, H.; Thinakaran, R.; Jalari, S.; Neerugatti, V.; Nalluri, M.R.; Cholla, R.R. Smart Agriculture: Enhancing Crop Management through IoT-Based Real-Time Monitoring and Automation. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Information Technology and Digital Applications (ICITDA), Nilai, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia, 7–8 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, S.L.; Testa, G.; Scordia, D.; Copani, V. Sowing time and prediction of flowering of different hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) genotypes in southern Europe. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2012, 37, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Carvalho, M.E.; Azevedo, R.A.; Fidalgo, F. Plants facing oxidative challenges—A little help from the antioxidant networks. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharrizi, K.J.; Amirmahani, F.; Salehi, F. Assessment of changes in physiological and biochemical traits in four pistachio rootstocks under drought, salinity and drought+ salinity stresses. Physiol. Plant 2020, 168, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Approach | Algorithm/Model | RMSE (cm) | MAE (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Canny | 1.47 (0.57) 1,2 a | 1.39 (0.59) a |
| K-means | 1.54 (0.70) a | 1.41 (0.70) a | |
| Deep learning | YOLO v11 | 1.41 (0.58) a | 1.29 (0.54) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocamora-Osorio, C.; Aragon-Rodriguez, F.; Codes-Alcaraz, A.M.; Ferrández-Pastor, F.-J. Automated IoT-Based Monitoring of Industrial Hemp in Greenhouses Using Open-Source Systems and Computer Vision. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090272
Rocamora-Osorio C, Aragon-Rodriguez F, Codes-Alcaraz AM, Ferrández-Pastor F-J. Automated IoT-Based Monitoring of Industrial Hemp in Greenhouses Using Open-Source Systems and Computer Vision. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(9):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090272
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocamora-Osorio, Carmen, Fernando Aragon-Rodriguez, Ana María Codes-Alcaraz, and Francisco-Javier Ferrández-Pastor. 2025. "Automated IoT-Based Monitoring of Industrial Hemp in Greenhouses Using Open-Source Systems and Computer Vision" AgriEngineering 7, no. 9: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090272
APA StyleRocamora-Osorio, C., Aragon-Rodriguez, F., Codes-Alcaraz, A. M., & Ferrández-Pastor, F.-J. (2025). Automated IoT-Based Monitoring of Industrial Hemp in Greenhouses Using Open-Source Systems and Computer Vision. AgriEngineering, 7(9), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090272









