Estimation of Sound Transmission Loss for Elastic Closed-Cell Porous Material in Mass Control Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Modeling
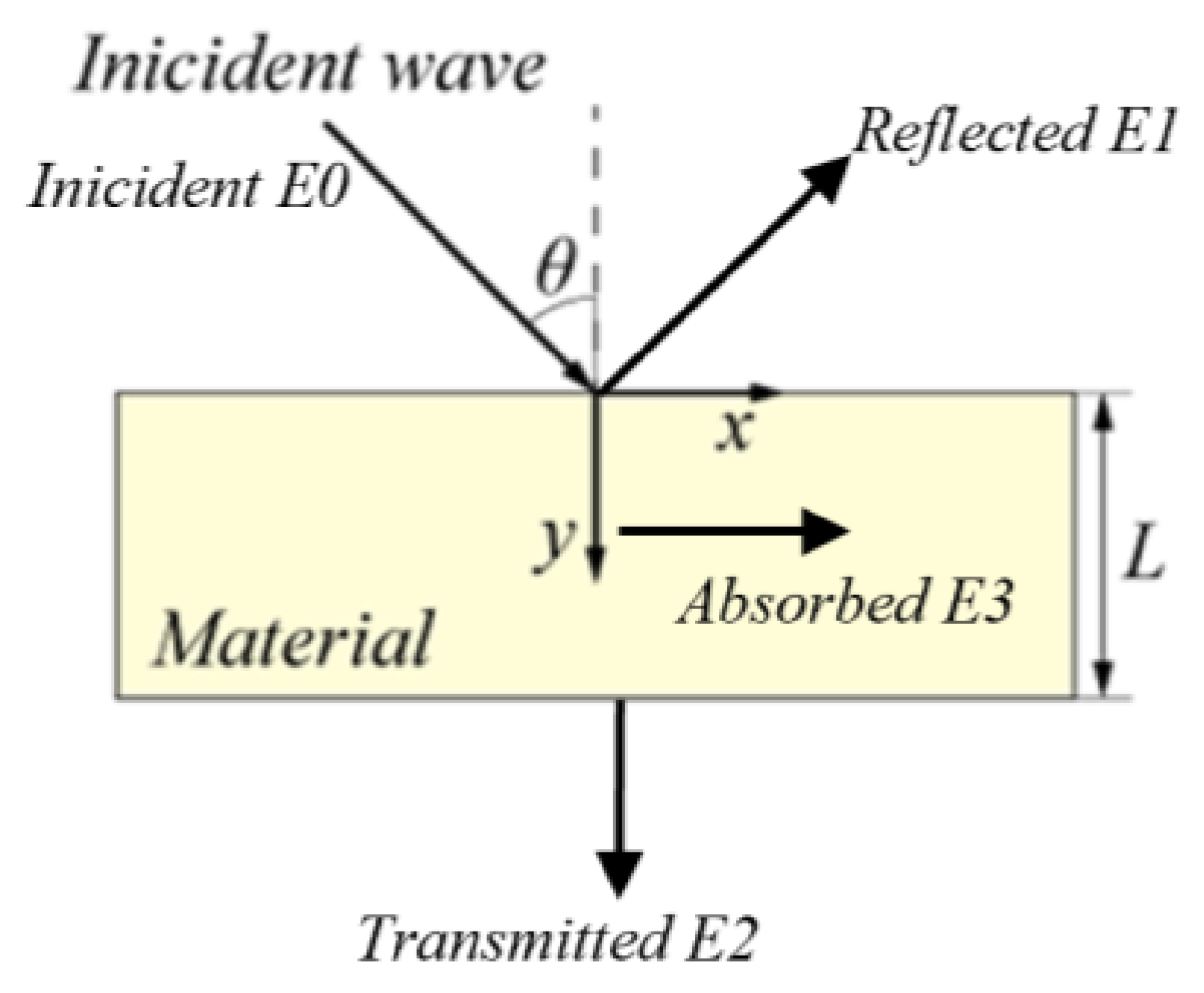
2.1.1. Acoustic Field Equations
2.1.2. Elastic Porous Model
2.1.3. Solution for the Parameters
2.1.4. Boundary Conditions
- The mean pressure acting on the fluid phase satisfies the following:
- 2.
- The normal pressure acting on the solid phase satisfies the following:
- 3.
- The normal volume velocity satisfies the continuity as follows:
- 4.
- The shear pressure acting on the solid surface satisfies the following:
2.1.5. Sound Transmission Loss
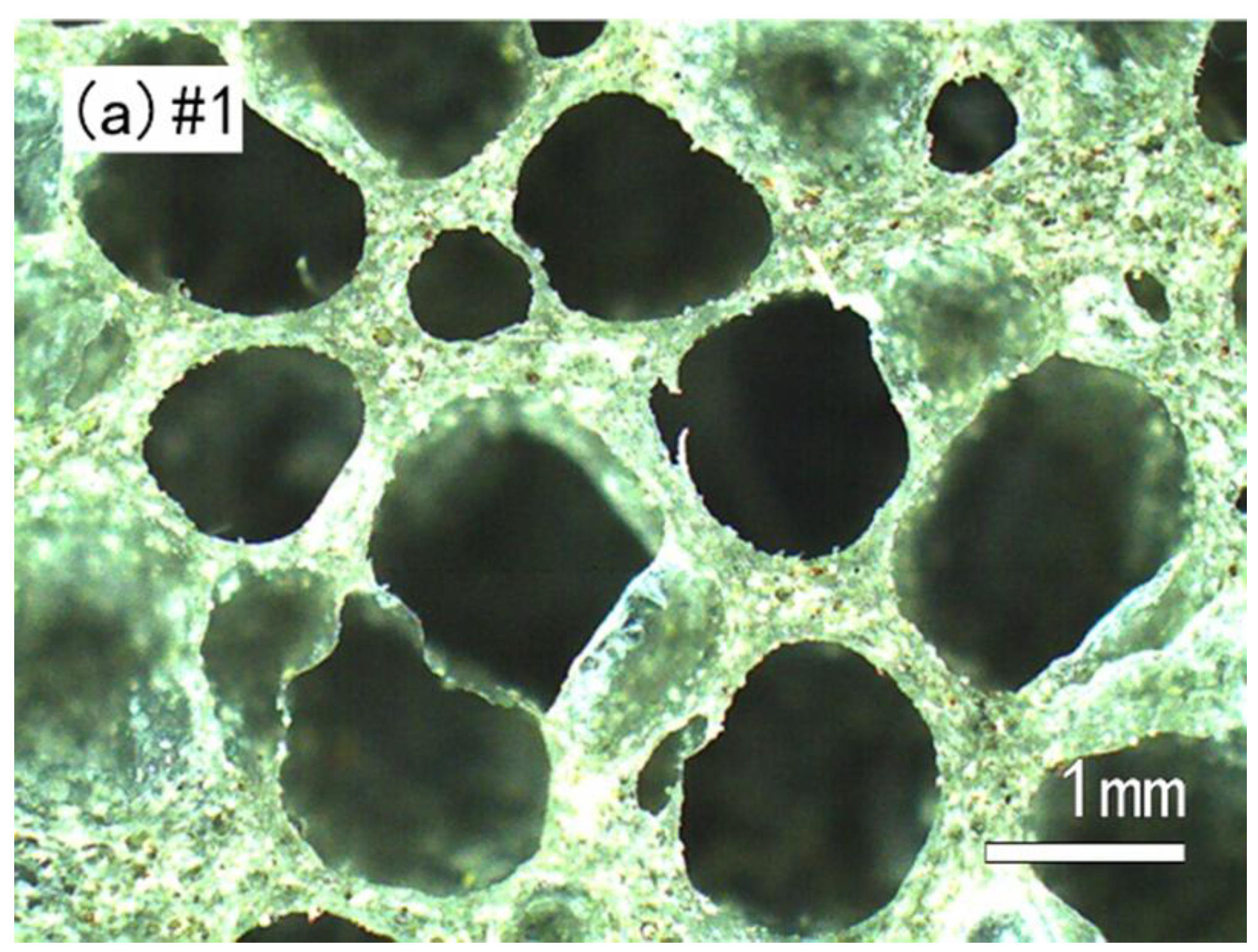
2.2. The Elastic Closed-Cell Porous Samples
2.2.1. Measurements
2.2.2. Model Calculation Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
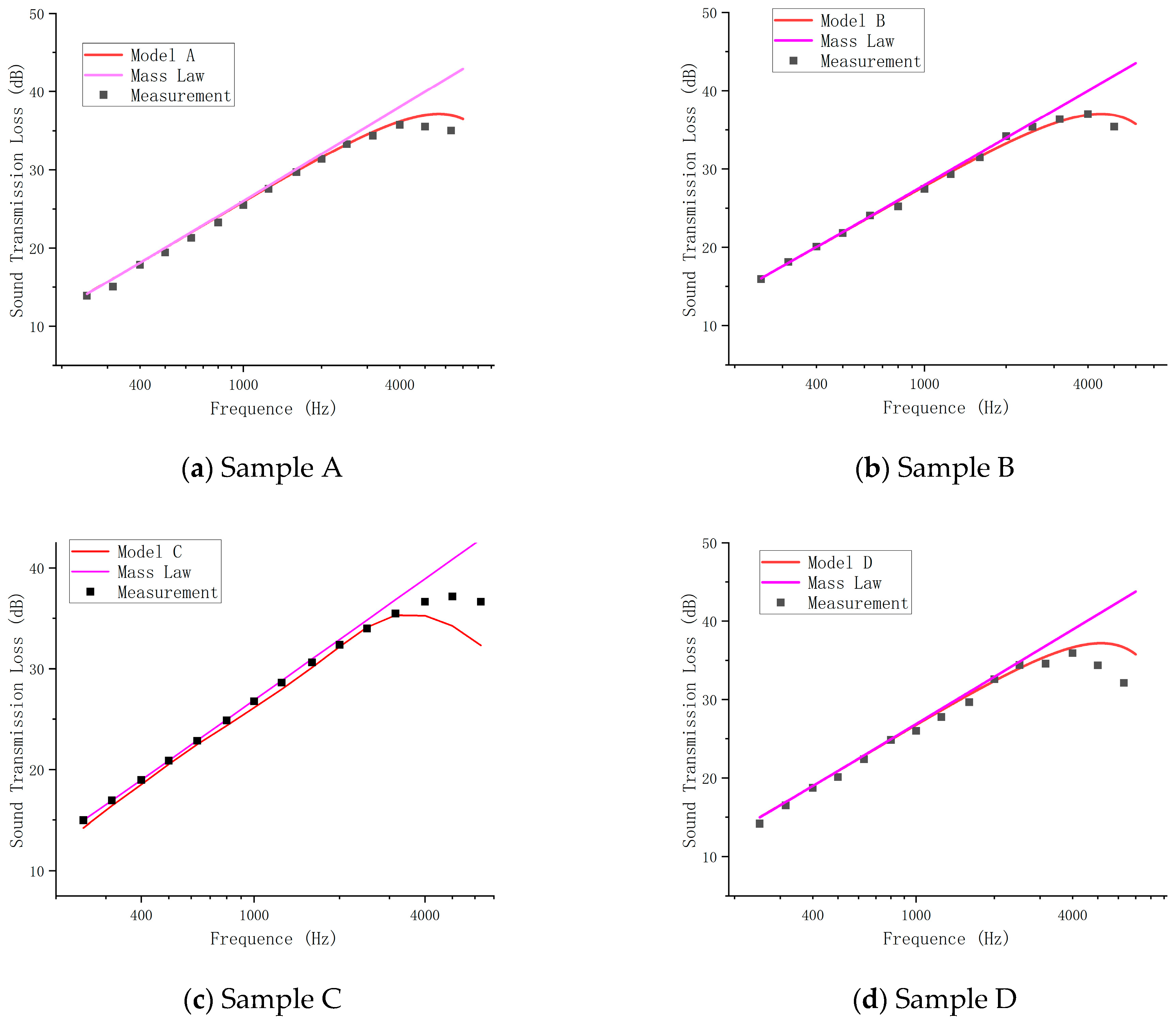
3.1. Comparison Between Calculations and STL Measurement Under the Normal Incidence
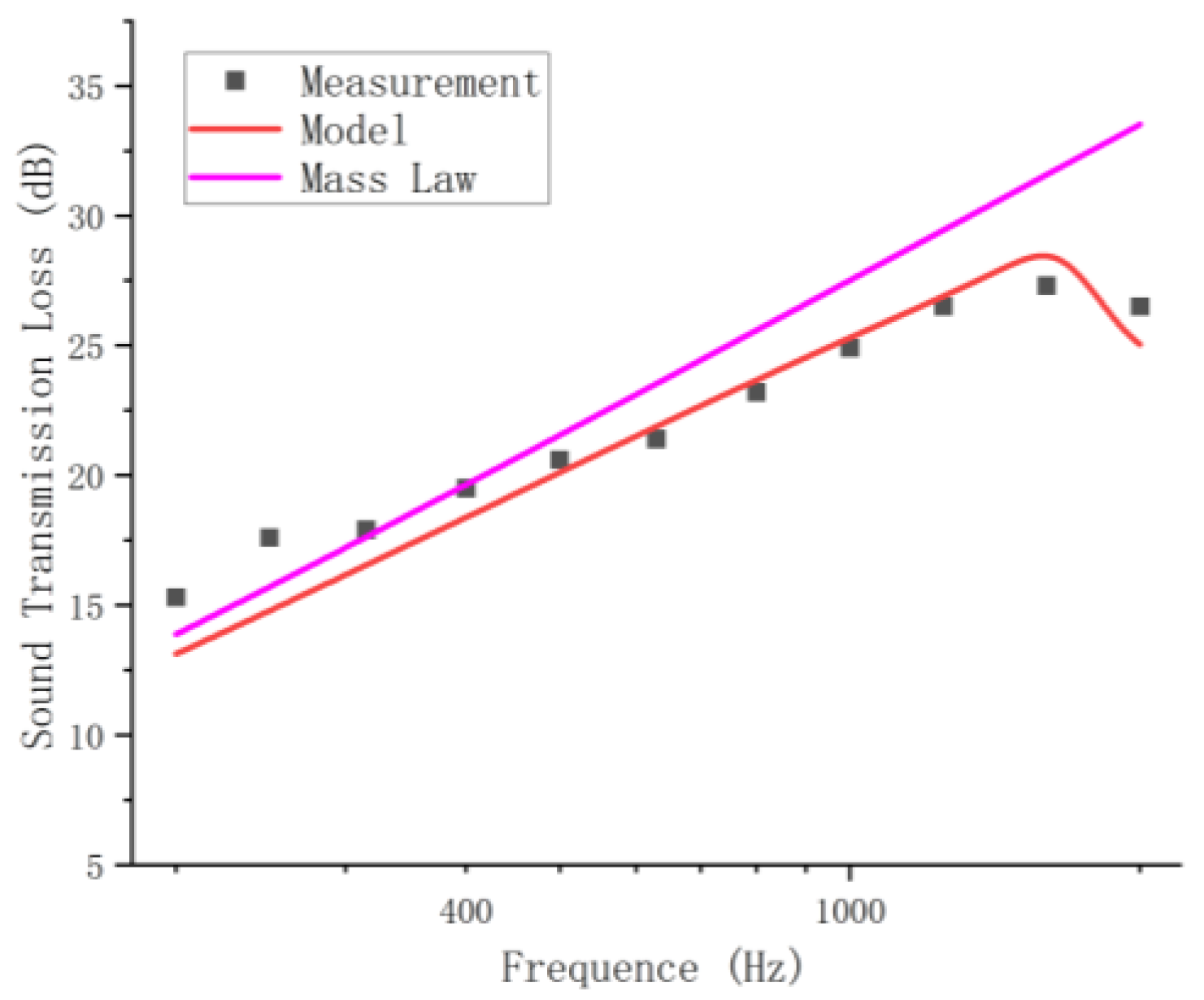
3.2. Comparison Between Calculations and STL Measurement Under the Random Incidence
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
| , | , |
References
- Cai, J.; Fu, Q.; Long, M.; Liao, G.; Xu, Z. The sound insulation property of composite from waste printed circuit board and unsaturated polyester. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 145, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navacerrada, M.A.; Fernandez, P.; Diaz, C.; Pedrero, A. Thermal and acoustic properties of aluminium foams manufactured by the infiltration process. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Wu, J.H.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, W. Acoustic performance of aluminum foams with semiopen cells. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 87, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yao, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Sound insulation property of Al-Si closed-cell aluminum foam sandwich panels. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 68, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, W.; Shi, L.; Zuo, B.; Gao, W. General regression neural network for prediction of sound absorption coefficients of sandwich structure nonwoven absorbers. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-J.; Yao, G.-C.; Wang, X.-L.; Li, B.; Yin, Y.; Liu, K. Sound insulation property of Al-Si closed-cell aluminum foam bare board material. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doutres, O.; Atalla, N.; Brouillette, M.; Hebert, C. Using shock waves to improve the sound absorbing efficiency of closed-cell foams. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 79, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, H.; Song, C.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, W.; Song, Q.; Ren, F. Preparation and performance of melamine-formaldehyde rigid foams with high closed cell content. Cell. Polym. 2021, 40, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, W.; Ren, F.; Yang, X. Preparation and properties of melamine-formaldehyde rigid closed-cell foam toughened by ethylene glycol/carbon fiber. Cell. Polym. 2021, 40, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, A.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Yang, S. Closed-Cell Rigid Polyimide Foams for High-Temperature Applications: The Effect of Structure on Combined Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, W.; Uhlirova, T.; Gregorova, E.; Wiegmann, A. Young’s modulus and thermal conductivity of closed-cell, open-cell and inverse ceramic foams model-based predictions, cross-property predictions and numerical calculations. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, P.; Cui, C.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Thermal Conductivity of Closed Cell Aluminum Foam. ASME J. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 147, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, T.; Kim, T. Effective Thermal Conductivity Modelling for Closed-Cell Porous Media with Analytical Shape Factors. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 100, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.F. Principles of Composite Material Mechanics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chevillotte, F.; Panneton, R. Elastic characterization of closed cell foams from impedance tube absorption tests. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 2653–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazel, O.; Tournat, V. Nonlinear Biot waves in porous media with application to unconsolidated granular media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Huang, Q. Resonance Variation of Double-Layer Structure Composed of Porous Material and Air Layer Based on Biot Theory. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablonik, L.R. A Simplified Method for Calculating Multilayer Sound Insulation with Layers of Fibrous Porous Material. Acoust. Phys. 2018, 64, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Effect of physical and subsequent processing parameters of glass fiber felts on sound insulation. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low-frequency range. Repr. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. II. Higher frequency range. Repr. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.S.; Shiau, N.M.; Kang, Y.J. Sound transmission through multi-panel structures lined with elastic porous materials. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 191, 317–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakooti, S.; Churu, H.G.; Lee, A.; Xu, T.; Luo, H.; Xiang, N.; Sotiriou-Leventis, C.; Leventis, N.; Lu, H. Sound insulation properties in low-density, mechanically strong and ductile nanoporous polyurea aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 476, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.F. Propagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Attenborough, K. Acoustical characteristics of porous materials. Phys. Rep. 1982, 82, 179–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Cai, J.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, N.; Lian, Y. Preparation of high-density metal/NBR-PVC microporous damping composite and its sound insulation performance. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2018, 35, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10140-2; Acoustics-Laboratory Measurement of Sound Insulation of Building Elements. Part 2 Measurement of Airborne Sound Insulation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Ma, D. Acoustics Handbook, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, J.; Yu, N. Sound Insulation Property of Elastic Closed-cell Foams. Noise Vib. Control. 2020, 5, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
| Samples | Value |
|---|---|
| Air fluid density (,) | 1.29 |
| Sound speed (,) | 343 |
| Prandtl number () | 0.71 |
| Ratio of specific heats () | 1.402 |
| Samples | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (, ) | 11.4 | 13.0 | 17.6 | 13.2 | 16 |
| Bulk density (, ) | 246.7 | 270.7 | 158.6 | 235.4 | 143 |
| Skeletal density (, ) | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 | 350 |
| Porosity () | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 0.59 |
| Static Young’s modulus (, ) | 11.28 | 9.98 | 4.22 | 12.02 | 5.19 |
| Poisson’s ratio () | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Loss factor () | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Flow resistivity (, ) | Exponentially large number | ||||
| Tortuosity () | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Model | Mass Law | Theoretical Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Deviation ) | Deviation of 250–2500 Hz ) | Deviation of 2500–6300 Hz ) | Average Deviation Rate ) | Average Deviation ) | Deviation of 250–2500 Hz ) | Deviation of 2500–6300 Hz ) | Average Deviation Rate ) | |
| A | 1.44 | 0.57 | 3.83 | 5.41% | 0.59 | 0.42 | 1.08 | 2.23% |
| B | 1.56 | 0.24 | 5.18 | 5.71% | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.49 | 1.47% |
| C | 3.62 | 2.57 | 10.57 | 15.22% | 0.41 | 0.40 | 1.05 | 3.20% |
| D | 1.95 | 0.61 | 5.62 | 7.23% | 0.91 | 0.42 | 2.24 | 3.69% |
| Average | 2.14 | 1.00 | 6.30 | 0.49 | 0.32 | 0.97 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J. Estimation of Sound Transmission Loss for Elastic Closed-Cell Porous Material in Mass Control Region. Acoustics 2025, 7, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040078
Cai J, Yang Y, Xu L, Zhou J. Estimation of Sound Transmission Loss for Elastic Closed-Cell Porous Material in Mass Control Region. Acoustics. 2025; 7(4):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040078
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Jun, Yining Yang, Lin Xu, and Junyu Zhou. 2025. "Estimation of Sound Transmission Loss for Elastic Closed-Cell Porous Material in Mass Control Region" Acoustics 7, no. 4: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040078
APA StyleCai, J., Yang, Y., Xu, L., & Zhou, J. (2025). Estimation of Sound Transmission Loss for Elastic Closed-Cell Porous Material in Mass Control Region. Acoustics, 7(4), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040078







