Silent Neonatal Incubators, Prototype Nica+
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. From the Incubator
1.2. Regulation
1.3. Of the Advances
1.4. Interior Comfort
1.5. About the Environment
1.6. Of the Recommendations
1.7. Of the Prototype
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation Used
2.2. Measurement Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Background Noise (Incubators Stopped)
3.2. Incubator Working
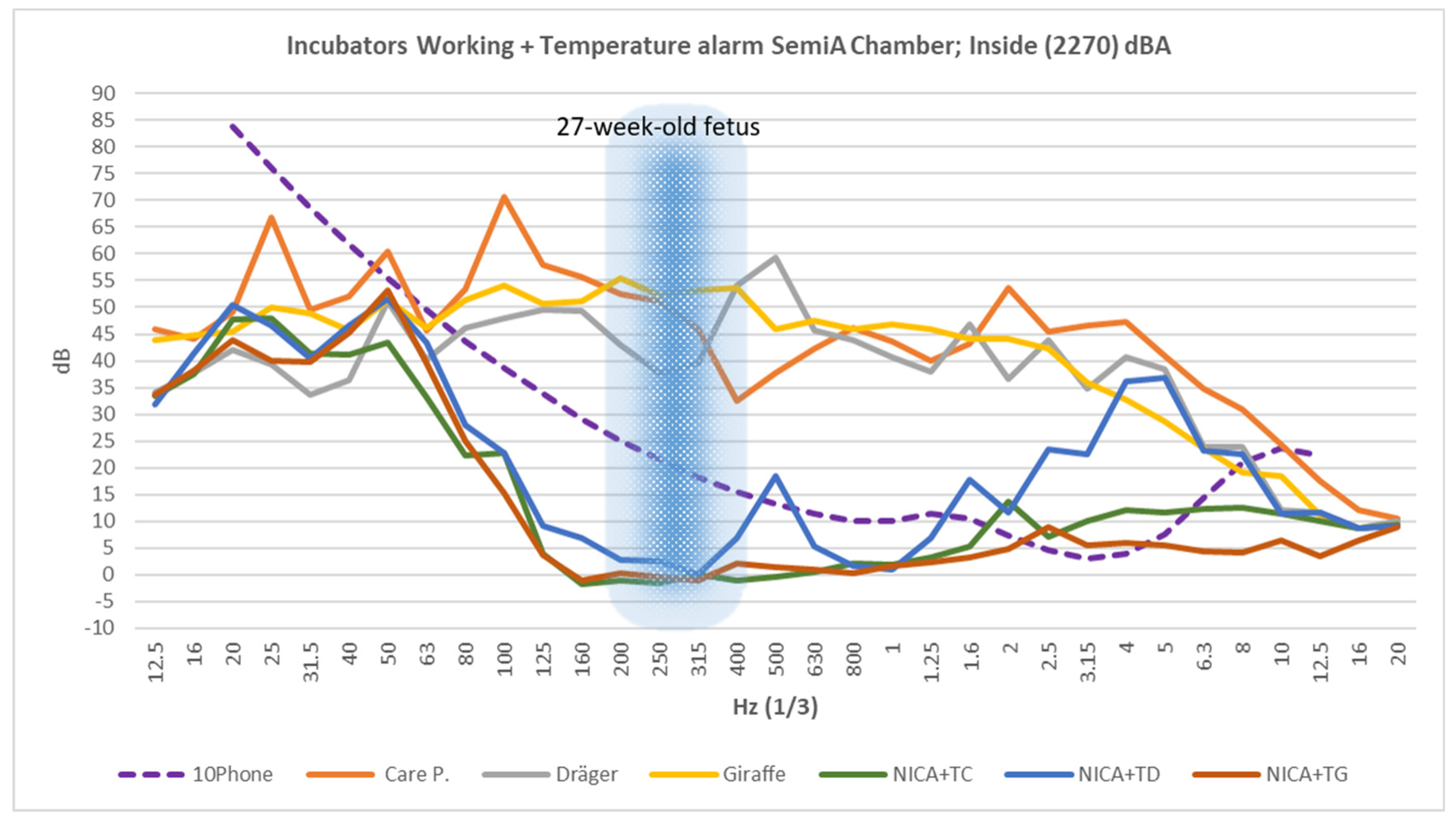
3.3. Incubator Running under the Influence of the Temperature Alarm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hess, J.H. Infant Incubator Filed 5 August 1929, Patented 7 March 1933, Patent Office Julius H. Hess, of Chicago, Illinois infant Incubator Application Filed 3 August 1929. Serial No. 383,403. Available online: https://neonatology.net/pdf/JuliusHessIncubatorPatent-1.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Grosholz, J.R.; Wallacel, J.D. 3,335,713. Infant Incubator mlm 3 November 1963, 8 Sheets-Sheet l 11111. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3335713A/en (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Xavier Pardel, Apuntes de Electromedicina: “Incubadora Neonatal. CENETEC; 21 September 2023. Available online: https://www.pardell.es/incubadora-neonatal.html (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Kuo, S.M.; Liu, L. Apparatus, System, and Method for Noise Cancellation and Communication for Incubators and Related Devices; Northern Illinois Research Foundation. 2013. US13/837,242. US20130204617A1. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US9542924B2/en (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Uri Rapoport; Incubator with a Noise Muffling Mechanism and Method Thereof. Application PCT/IL2014/050785 Events. 2014. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2015029044A3/en (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Ricardo, H.-M.; Zacarías, F.; Puyana, V.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Beira, J.L.; Luis, A.J.; Simón, L.L. “Análisis del ambiente sonoro en una Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos de Neonatología”, XI Congr. Iberoam. Acústica; X Congr. Ibérico Acústica; 49° Congr. Españ 23augustol Acústica-TECNIACUSTICA’18-. 2018. Available online: https://produccioncientifica.uca.es/documentos/625e8041552a9e6dec053328 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Almadhoob, A.; Ohlsson, A. Sound reduction management in the neonatal intensive care unit for preterm or very low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 1, CD010333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Montaño, V.M.; Beira-Jiménez, J.L.; Puyana-Romero, V.; Cueto-Ancela, J.L.; Hernández-Molina, R.; Fernández-Zacarías, F. Acoustic Conditioning of the Neonatal Incubator Compartment: Improvement Proposal. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 955553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stennert, E.; Schulte, F.; Vollrath, M. Incubator Noise and Hearing-Loss. Early Human Development. Early Hum. Dev. 1977, 1, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, E.D.; Morris, B.H.; Philbin, M.K.; Gray, L.C.; Lasky, R.E. Do former preterm infants remember and respond to neonatal intensive care unit noise? Early Hum. Dev. 2006, 82, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Rodarte, M.D.; Fujinaga, C.I.; Leite, A.M.; Salla, C.M.; da Silva, C.G.; Scochi, C.G.S. Exposure and Reactivity of the Preterm Infant to Noise in the Incubator. CoDAS 2019, 31, e20170233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, T.; Santos, U. Efeitos do ruído na audição. Rev. Ciência Elem. 2018, V6, 083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- da Silva Reis Santana, L.; Silva, L.; Silva, R.; Carvalho, J.; Santana, W.; Rossi-Barbosa, L.A.; Ruas, E. Measurement of Acoustic Noise Levels in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. REME Rev. Min. Enferm. 2015, 19, 27–310. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282460547_Measurement_of_acoustic_noise_levels_in_a_neonatal_intensive_care_unit (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Wroblewska-Seniuk, K.; Greczka, G.; Dabrowski, P.; Szyfter-Harris, J.; Mazela, J. Hearing Impairment in Premature Newborns—Analysis Based on the National Hearing Screening Database in Poland. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes-Garrido, J.C.; Velez-Pereira, A.M.; Gázquez, M.; Hidalgo-Hidalgo, M.; Bolívar, J.P. The Characterization of Noise Levels in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and the Implications for Noise Management. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, A.E.; Hancock, L.E.; Ware, E.J. A descriptive study of noise in the neonatal intensive care unit. Ambient levels and perceptions of contributing factors. Adv. Neonatal Care 2008, 8, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, A.J. Acceptable Noise Levels for Neonates in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Indep. Stud. Capstones, p. Program in Audiology and Communication Sciences, W. 2012. Available online: https://digitalcommons.wustl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1643&context=pacs_capstones (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Environmental Health. Noise: A Hazard for the Fetus and Newborn. Pediatrics 1997, 100, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.D.M. Guidelines for Perinatal Care. Am. Acad. Pediatr. 1986. (Electromedical equipment. Part 2-19:2021: Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Operation of Baby Incubators). Available online: https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/physician-faqs/-/media/3a22e153b67446a6b31fb051e469187c.ashx (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- EN IEC 60601-2-2:2018; Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 2-2: Particular Requirements for the Basic Safety and Essential Performance of High Frequency Surgical Equipment and High Frequency Surgical Accessories. IEC: London, UK, 2018. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/clc/bd56ff83-1df5-41e8-89aa-f89f5abdf25d/en-iec-60601-2-2-2018 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- ANSI/AAMI/IEC 60601-2-19:2009; Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 2-19: Particular Requirements for the Basic Safety and Essential Performance of Infant Incubators. ANSI: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/64023 (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- NTP 270: Evaluación de la Exposición al Ruido. Determinación de Niveles Representativos; Instituto Nacional de Seguridad e Higiene en el Trabajo. 1991. Available online: https://www.insst.es/documents/94886/327166/ntp_270.pdf/9c674732-ce77-481f-8c38-ffc03579bb75 (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Waye, K.P. A caring sound environment in hospitals? Care Sound 2013, 11–26. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342834682_A_caring_sound_environment_in_hospitals (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Hernandez, R.; et al. Patent Technological Report: Incubator with a System to Improve the Acoustic Comfort of the Newborn. Spanish Patent and Trademark Office OEPM P202330766, Madrid. 12 September 2023. As it is protected by the Patent Law, it is only available through the Acoustic Engineering Laboratory of the University of Cádiz, with prior permission.
- Hernández-Molina, R.; Rodríguez-Montaño, V.M.; Jiménez, J.L.B.; Puyana-Romero, V.; Cueto-Ancela, J.L.; Zacarías, F.F. Diagnosis del Ruido en el Interior de Incubadoras Neonatales en Condiciones de Campo Libre. 53° Congreso Español de Acústica -Tecniacústica 2022; ID-13 SEA. Available online: https://documentacion.sea-acustica.es/publicaciones/Elche22/ID-13.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Fernández-Zacarías, F.; Beira-Jiménez, J.L.; Puyana-Romero, V.; Hernández-Molina, R. Diagnosis of Noise Inside Neonatal Incubators under Free-Field Conditions. Acoustics 2023, 5, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgami, N.; Oshino, R.; Ninomiya, H.; Li, X.; Kato, M.; Yajima, I. Risk Assessment of Neonatal Exposure to Low Frequency Noise Based on Balance in Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leventhall, G.; Pelmear, P.; Benton, S. A Review of Published Research on Low Frequency Noise and its Effects. UK Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. 2003. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237245317_A_Review_of_Published_Research_on_Low_Frequency_Noise_and_its_Effects (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Gerhardt, K.J.; Abrams, R.M. Fetal Exposures to Sound and Vibroacoustic Stimulation. J. Perinatol. 2000, 20, S21–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepper, P.G.; Shahidullah, B.S. Development of fetal hearing. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1994, 71, F81–F87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, A. Questionable sound exposure outside of the womb: Frequency analysis of environmental noise in the neonatal intensive care unit. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 104, e14–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, G.B.; Fletcher, M.A.; MacDonald, M.G. Neonatología: Fisiopatología y Manejo del Recién Nacido; Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schust, M. Effects of low frequency noise up to 100 Hz. Noise Health 2004, 6, 73–85. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15273025/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Harrison, L.L.; Roane, C.; Weaver, M. The Relationship Between Physiological and Behavioral Measures of Stress in Preterm Infants. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2004, 33, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
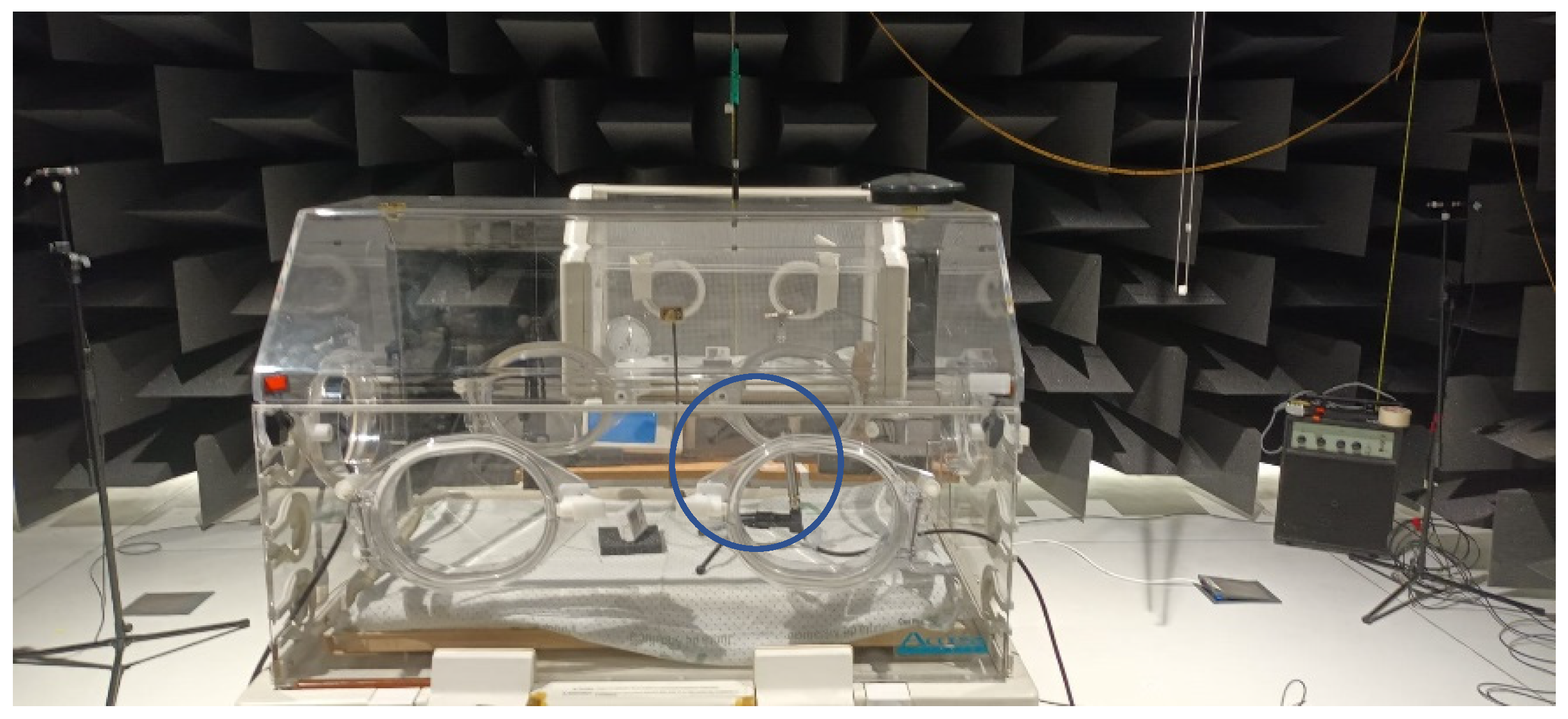
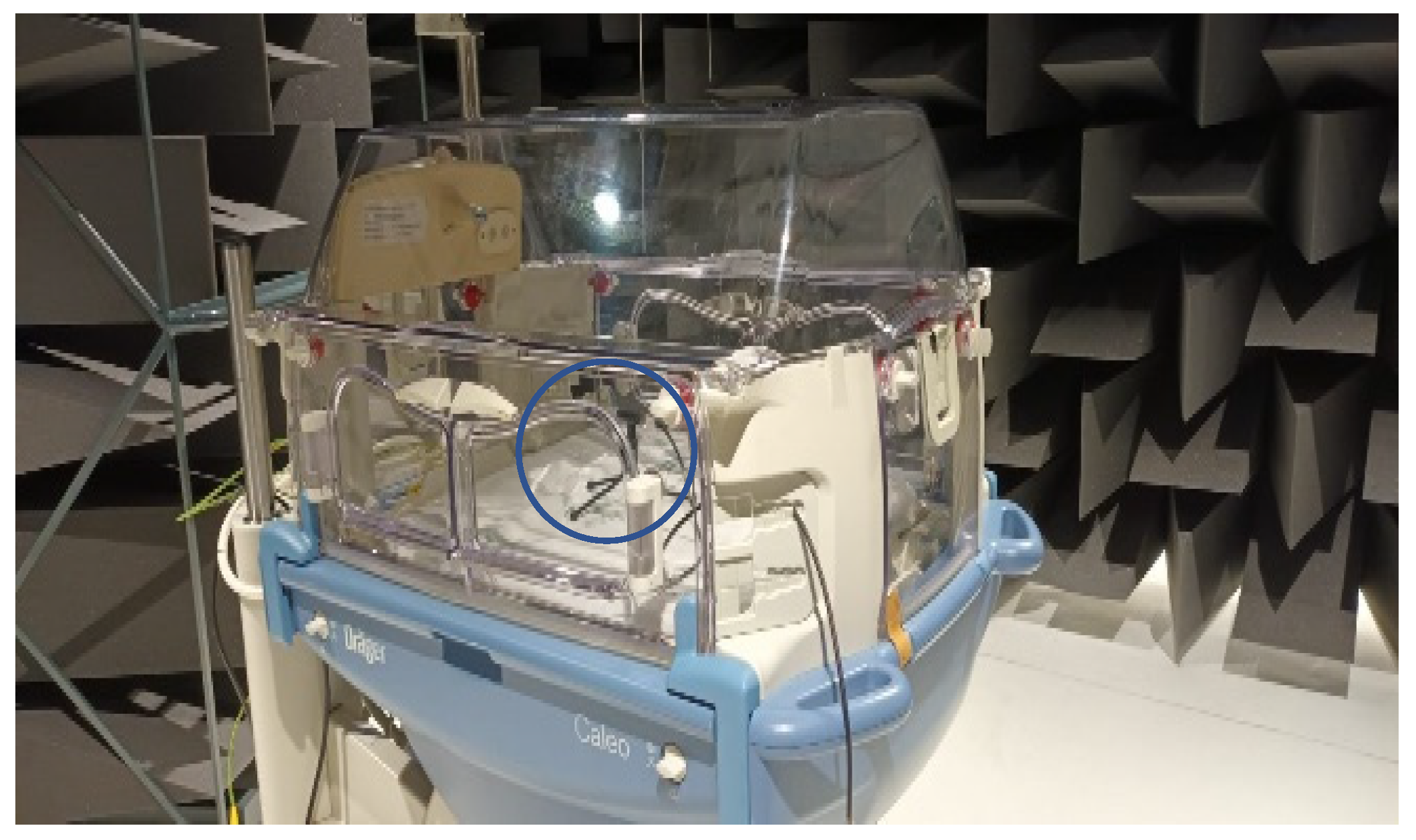
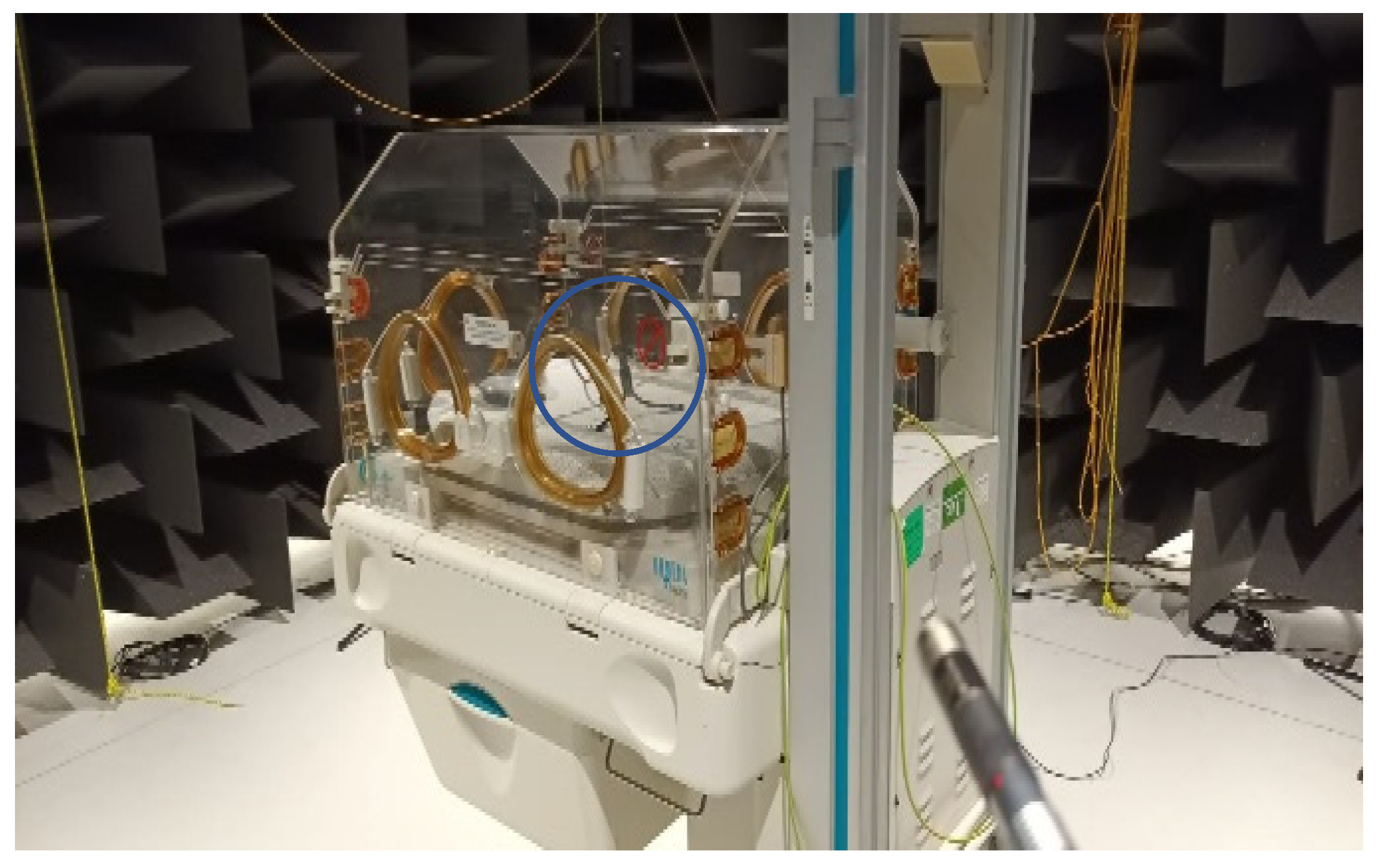

| Incubator Model | Outdoor (2250) [dBA] | |||||||
| LAeq,Ti | LCeq,Ti | LAIeq,Ti | LAFmax | LAFmin | L10 | L50 | L90 | |
| 01 Care Plus Rever | 17.8 | 35 | 17.8 | 18.2 | 17.5 | 17.9 | 17.5 | 17.1 |
| 02 Dräger Medical | 17.8 | 35.7 | 17.8 | 18.8 | 17.5 | 18.0 | 17.8 | 17.6 |
| 03 Giraffe | 17.8 | 34.0 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 17.5 | 18.0 | 17.8 | 17.6 |
| Prototype (NICA+) | 17.75 | 32 | 17.77 | 18.42 | 17.46 | 17.94 | 17.74 | 17.62 |
| Incubator Model | Indoor (2270) [dBA] | |||||||
| LAeq,Ti | LCeq,Ti | LAIeq,Ti | LAFmax | LAFmin | L10 | L50 | L90 | |
| 01 Care Plus Rever | 17.7 | 42.7 | 18.9 | 27.6 | 16.5 | 17.8 | 17 | 16.2 |
| 02 Dräger Medical | 16.9 | 36.6 | 17.1 | 19.9 | 16.5 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 16.6 |
| 03 Giraffe | 17.0 | 34.3 | 17.1 | 19.1 | 15.8 | 17.2 | 17.0 | 16.8 |
| Prototype (NICA+) | 16.87 | 35.87 | 17.08 | 19.16 | 16.38 | 17.19 | 16.79 | 16.61 |
| Incubator Model | Outdoor (2250) [dBA] | |||||||
| LAeq,Ti | LCeq,Ti | LAIeq,Ti | LAFmax | LAFmin | L10 | L50 | L90 | |
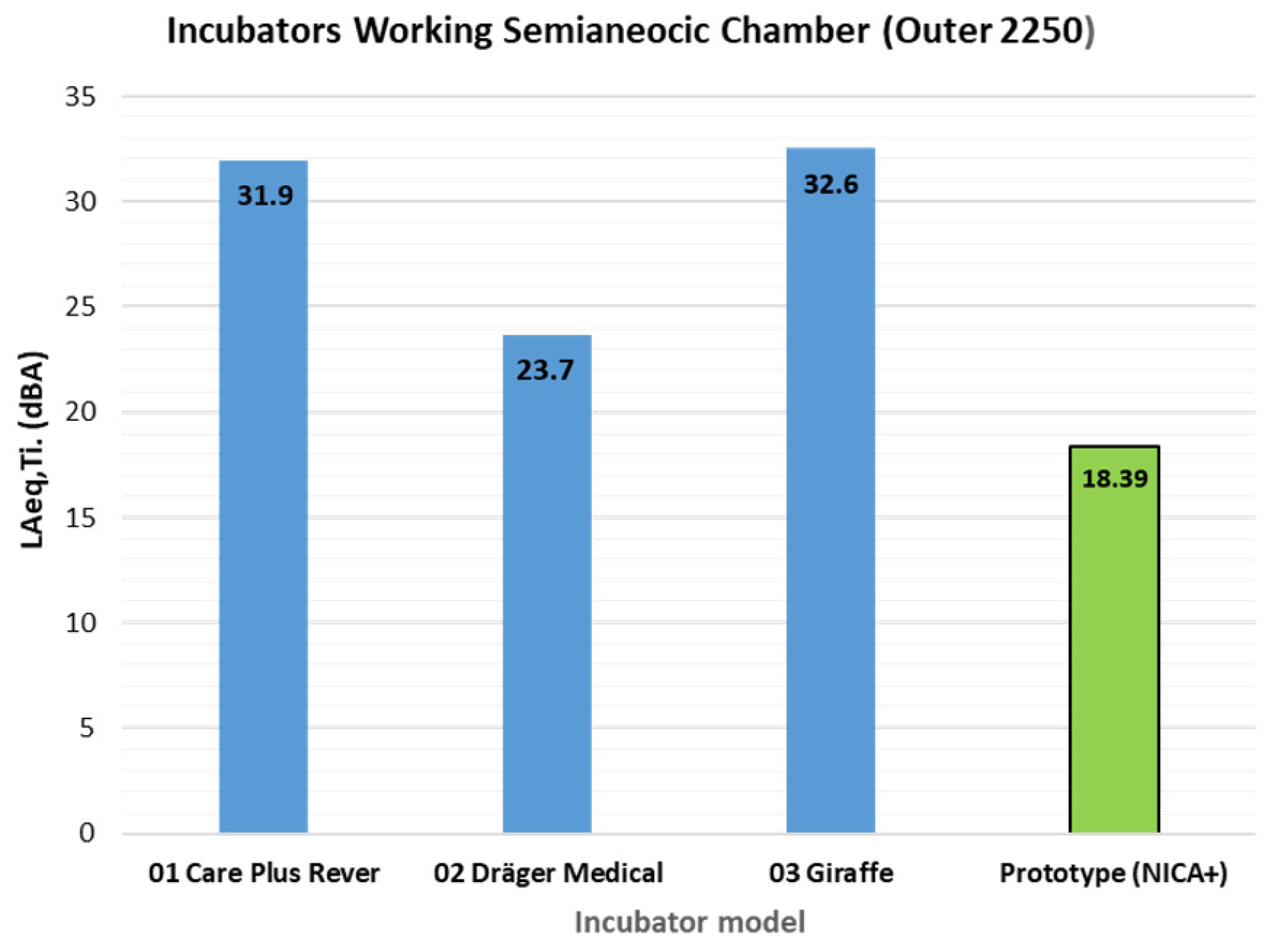
| 01 Care Plus Rever | 31.9 | 44.3 | 32.9 | 33.3 | 30.4 | 32.8 | 32.0 | 31.2 |
| 02 Dräger Medical | 23.7 | 38.6 | 24.3 | 24.8 | 22.8 | 24.1 | 23.7 | 23.3 |
| 03 Giraffe | 32.6 | 40.1 | 33.3 | 33.6 | 32.1 | 33.0 | 32.6 | 32.1 |
| Prototype (NICA+) | 18.4 | 43.32 | 18.66 | 20.88 | 17.66 | 19.11 | 18.21 | 17.89 |
| Incubator Model | Indoor (2270) [dBA] | |||||||
| LAeq,Ti | LCeq,Ti | LAIeq,Ti | LAFmax | LAFmin | L10 | L50 | L90 | |
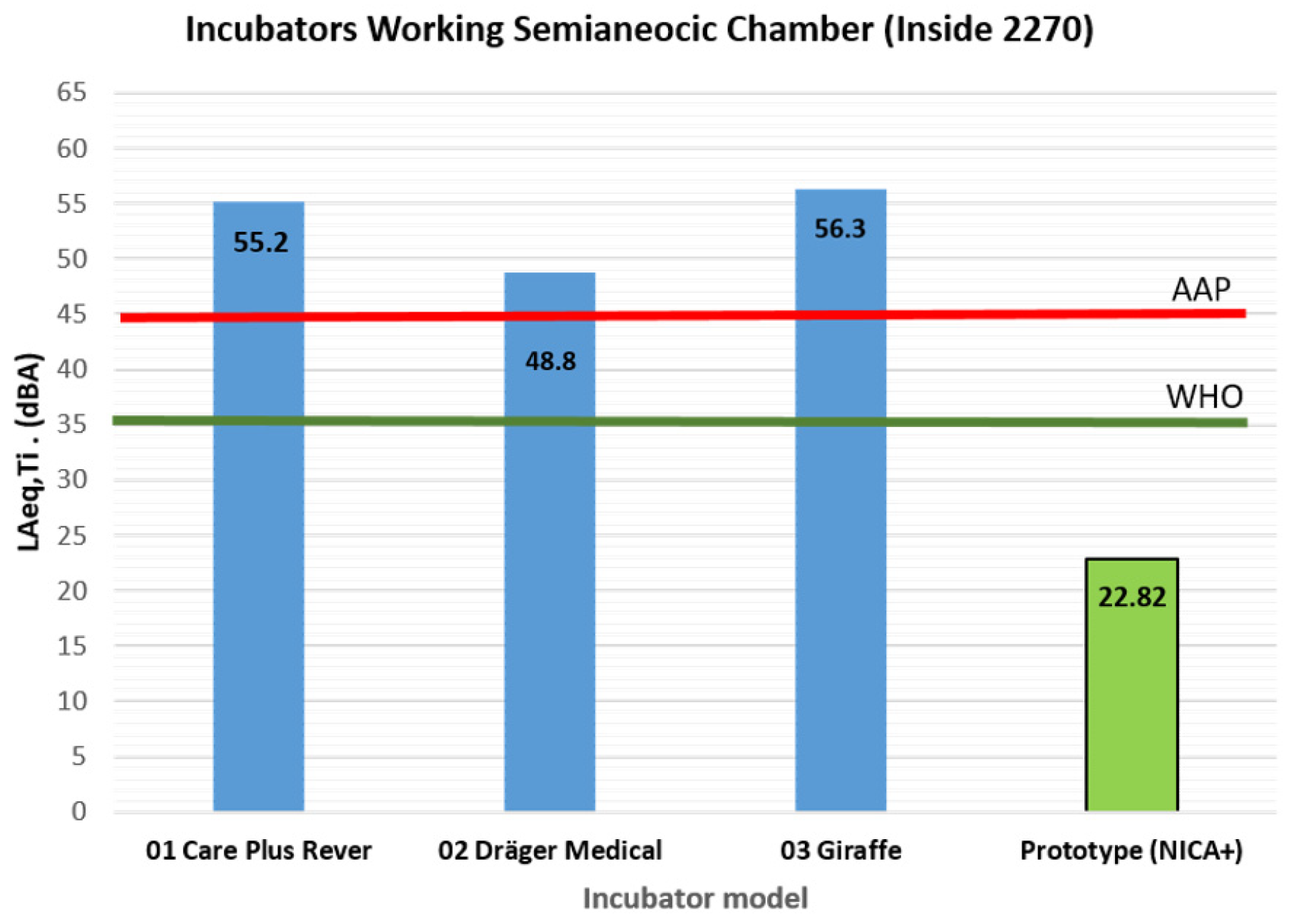
| 01 Care Plus Rever | 55.2 | 69.7 | 56.2 | 56.9 | 53.7 | 55.9 | 55.5 | 55.1 |
| 02 Dräger Medical | 48.8 | 54.8 | 49.8 | 50.3 | 47.5 | 49.3 | 48.8 | 48.3 |
| 03 Giraffe | 56.3 | 63.2 | 56.9 | 57.2 | 55.2 | 56.7 | 56.3 | 55.9 |
| Prototype (NICA+) | 22.82 | 51.25 | 26.3 | 35.22 | 16.8 | 25.78 | 20.68 | 17.37 |
| Incubator Model OUTER | LAeq,Ti dBA | Incubator Model INSIDE | LAeq,Ti dBA |
|---|---|---|---|
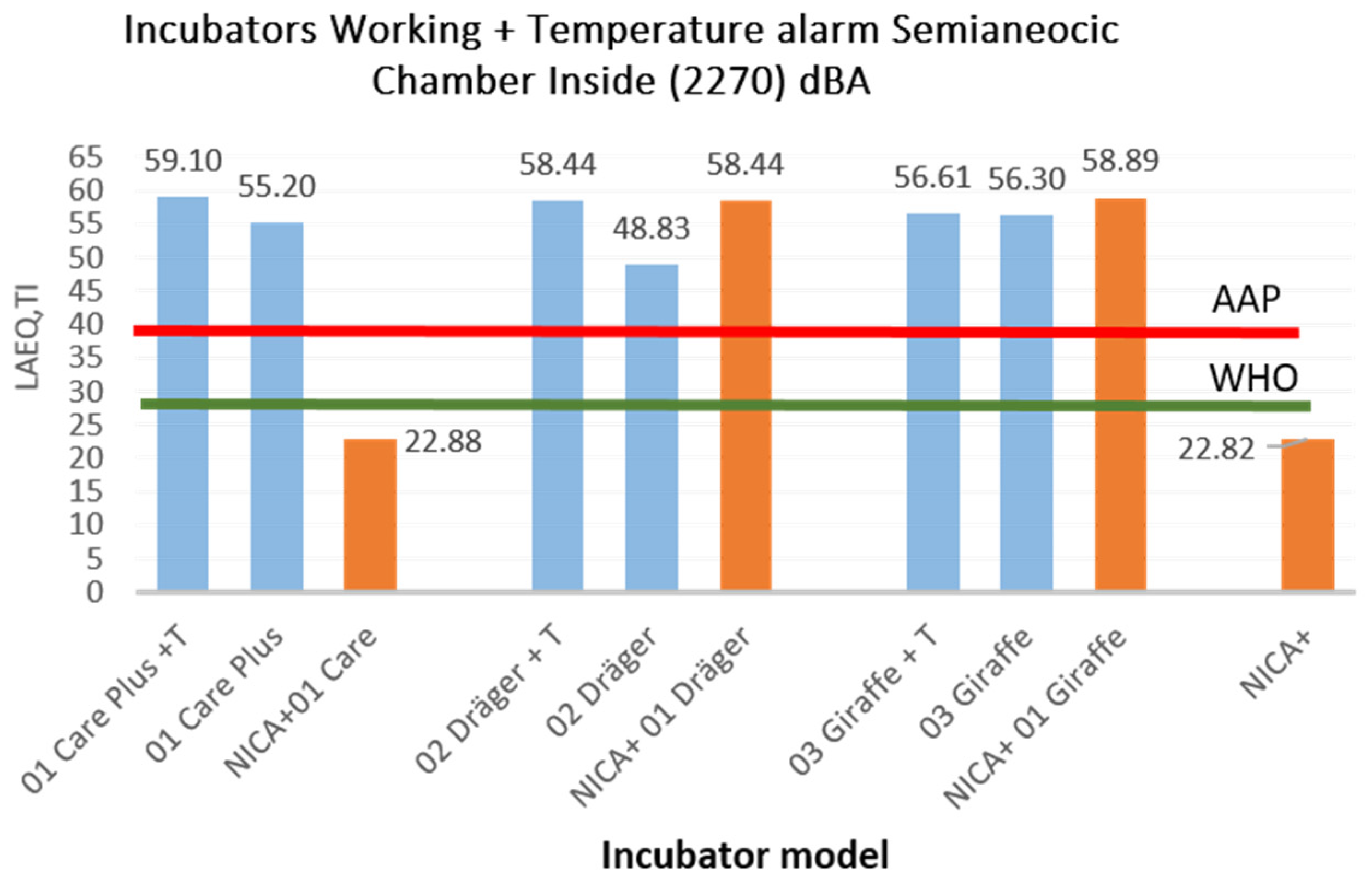
| 01 Care Plus +T | 56.60 | 01 Care Plus +T | 59.10 |
| 01 Care Plus | 31.90 | 01 Care Plus | 55.20 |
| NICA+ 01 Care | 25.61 | NICA+ 01 Care | 22.88 |
| 02 Dräger + T | 72.55 | 02 Dräger + T | 58.44 |
| 02 Dräger | 23.68 | 02 Dräger | 48.83 |
| NICA+ 01 Dräger | 48.87 | NICA+ 01 Dräger | 58.44 |
| 03 Giraffe + T | 58.01 | 03 Giraffe + T | 56.61 |
| 03 Giraffe | 32.55 | 03 Giraffe | 56.30 |
| NICA+ 01 Giraffe | 26.24 | NICA+ 01 Giraffe | 58.89 |
| NICA+ | 18.39 | NICA+ | 22.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Molina, R.; Puyana-Romero, V.; Beira-Jiménez, J.L.; Morgado-Estévez, A.; Bienvenido-Bárcena, R.; Fernández-Zacarías, F. Silent Neonatal Incubators, Prototype Nica+. Acoustics 2024, 6, 638-650. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6030035
Hernández-Molina R, Puyana-Romero V, Beira-Jiménez JL, Morgado-Estévez A, Bienvenido-Bárcena R, Fernández-Zacarías F. Silent Neonatal Incubators, Prototype Nica+. Acoustics. 2024; 6(3):638-650. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Molina, Ricardo, Virginia Puyana-Romero, Juan Luis Beira-Jiménez, Arturo Morgado-Estévez, Rafael Bienvenido-Bárcena, and Francisco Fernández-Zacarías. 2024. "Silent Neonatal Incubators, Prototype Nica+" Acoustics 6, no. 3: 638-650. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6030035
APA StyleHernández-Molina, R., Puyana-Romero, V., Beira-Jiménez, J. L., Morgado-Estévez, A., Bienvenido-Bárcena, R., & Fernández-Zacarías, F. (2024). Silent Neonatal Incubators, Prototype Nica+. Acoustics, 6(3), 638-650. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6030035








