Investigation of a Tuff Stone Church in Cappadocia via Acoustical Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
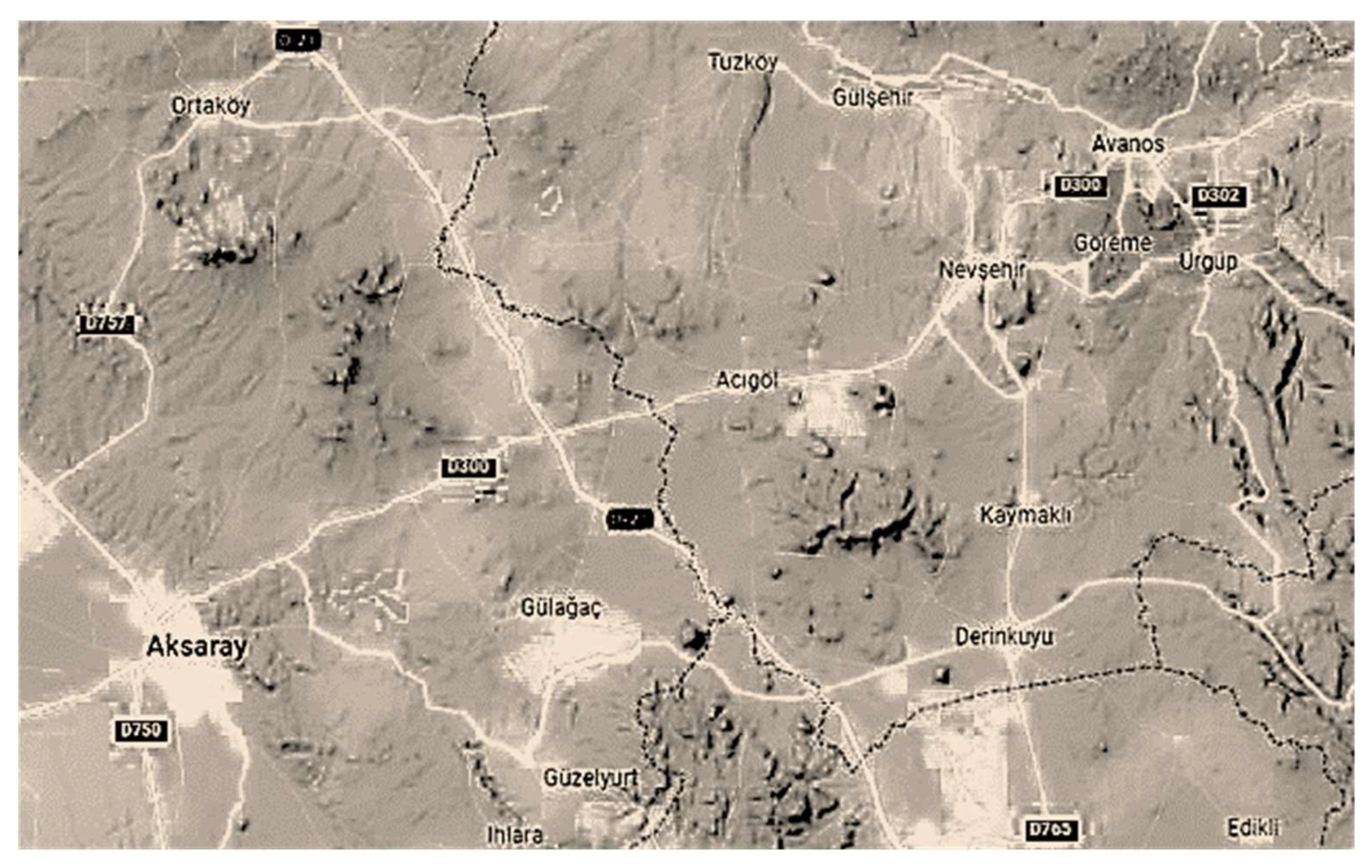
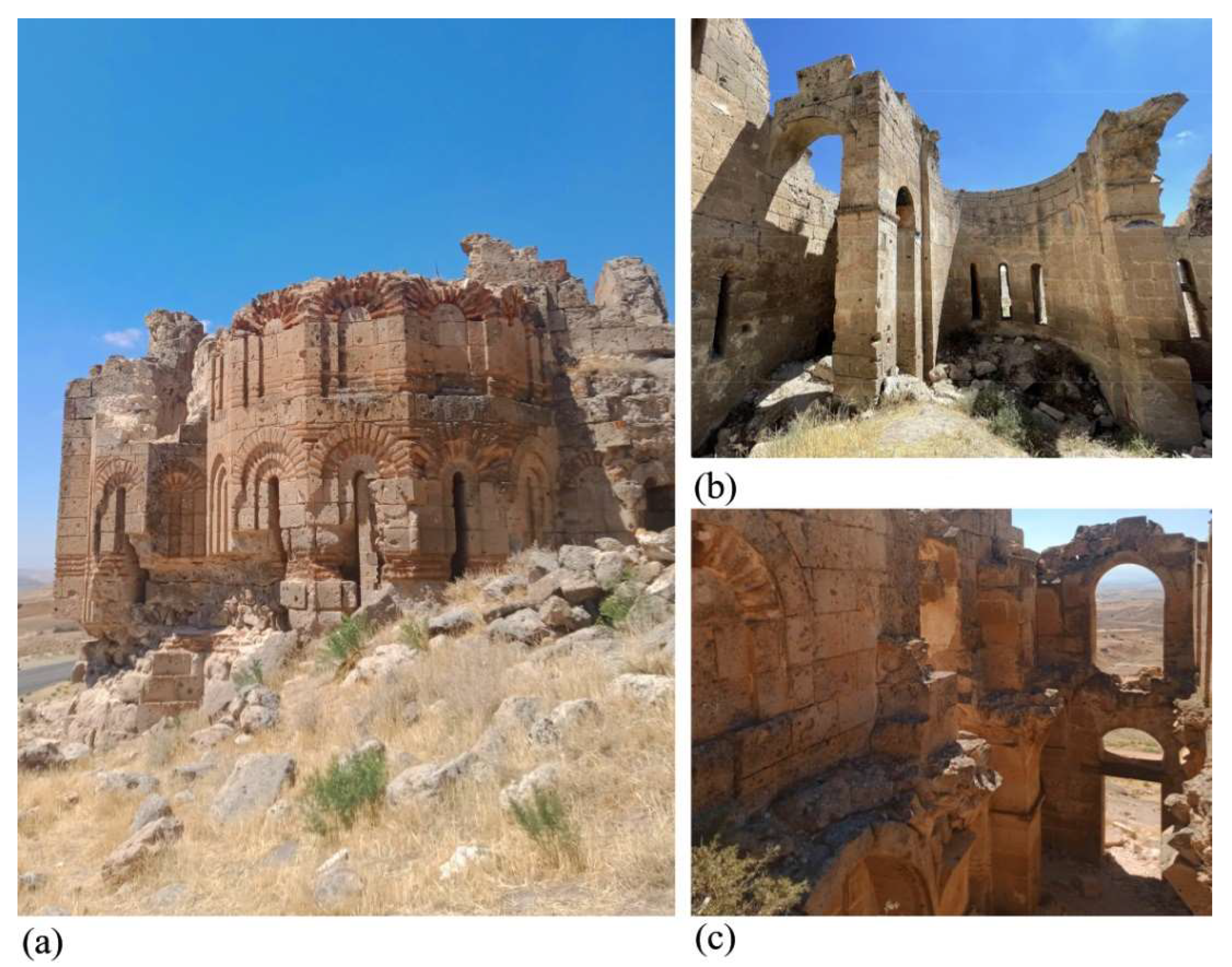
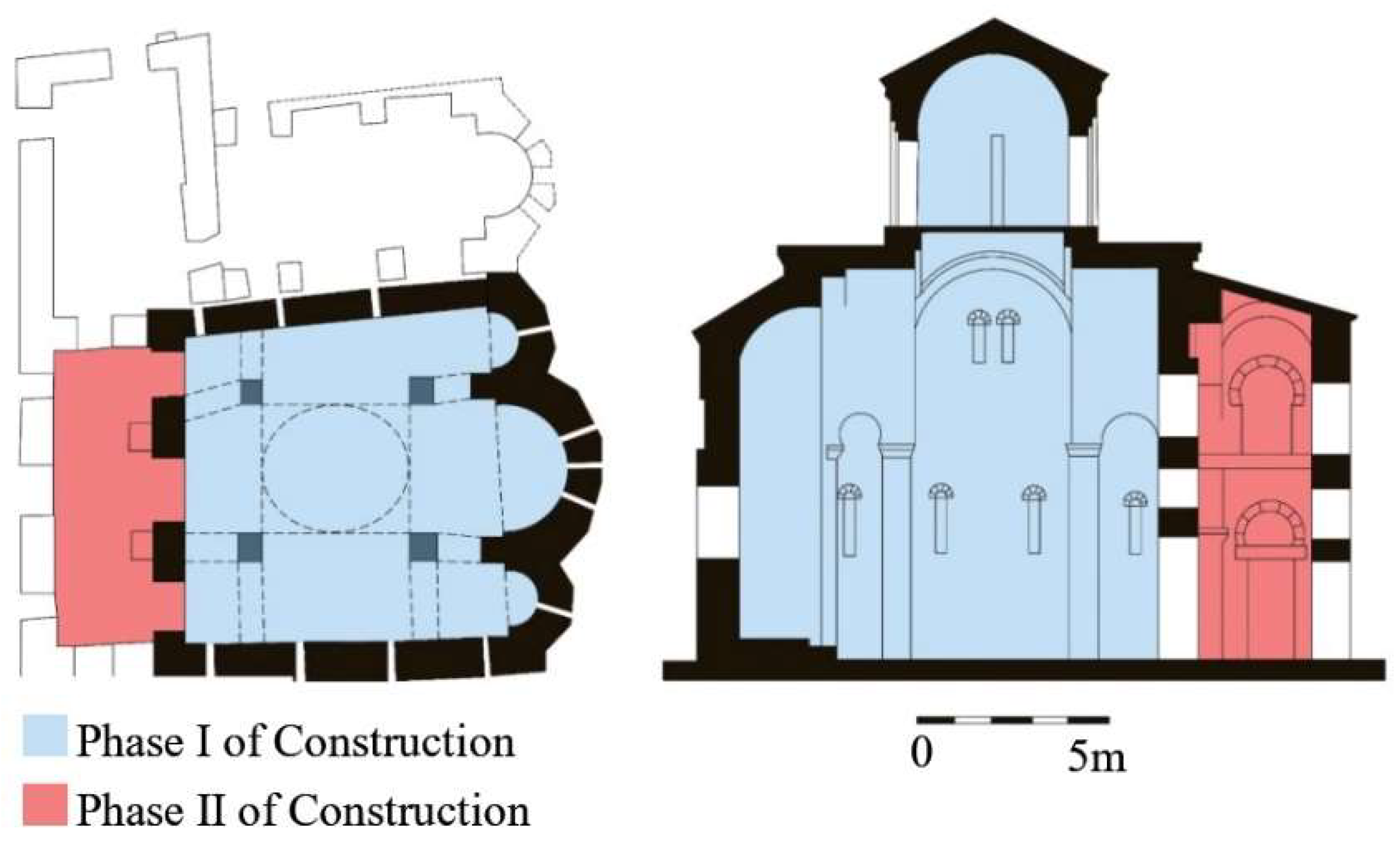
2. Historical and Architectural Description of Cappadocia and Bell Church (Çanlı Kilise)
3. Materials and Methods
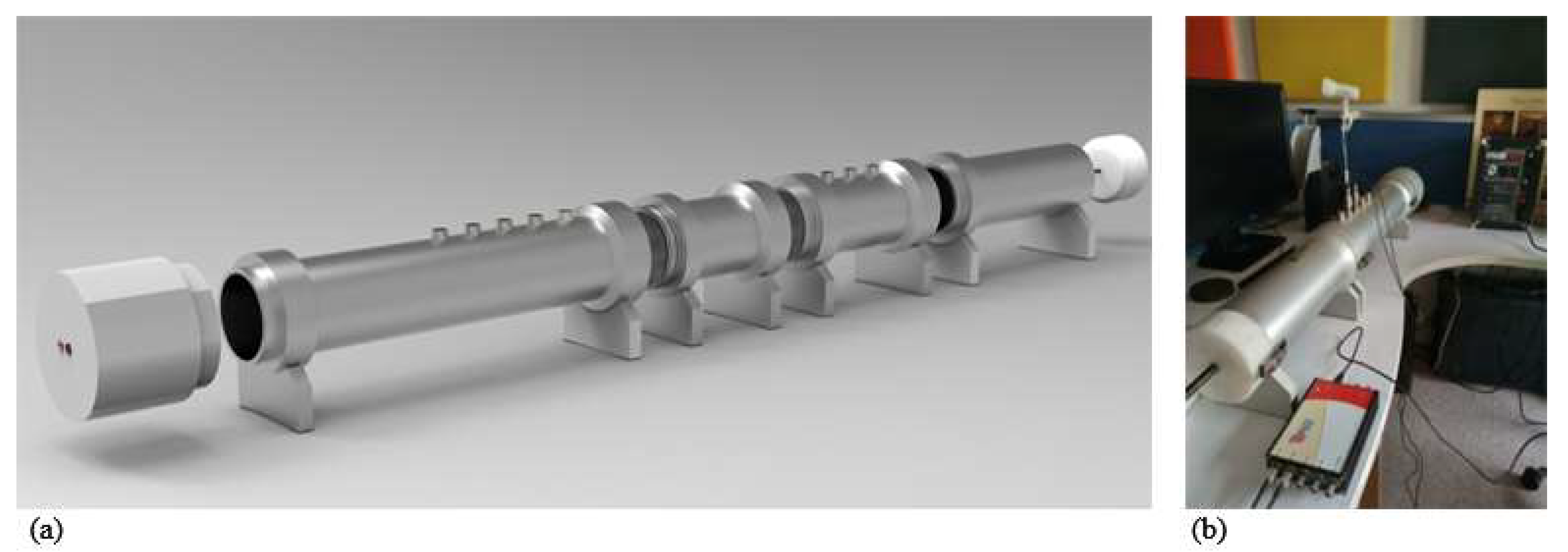
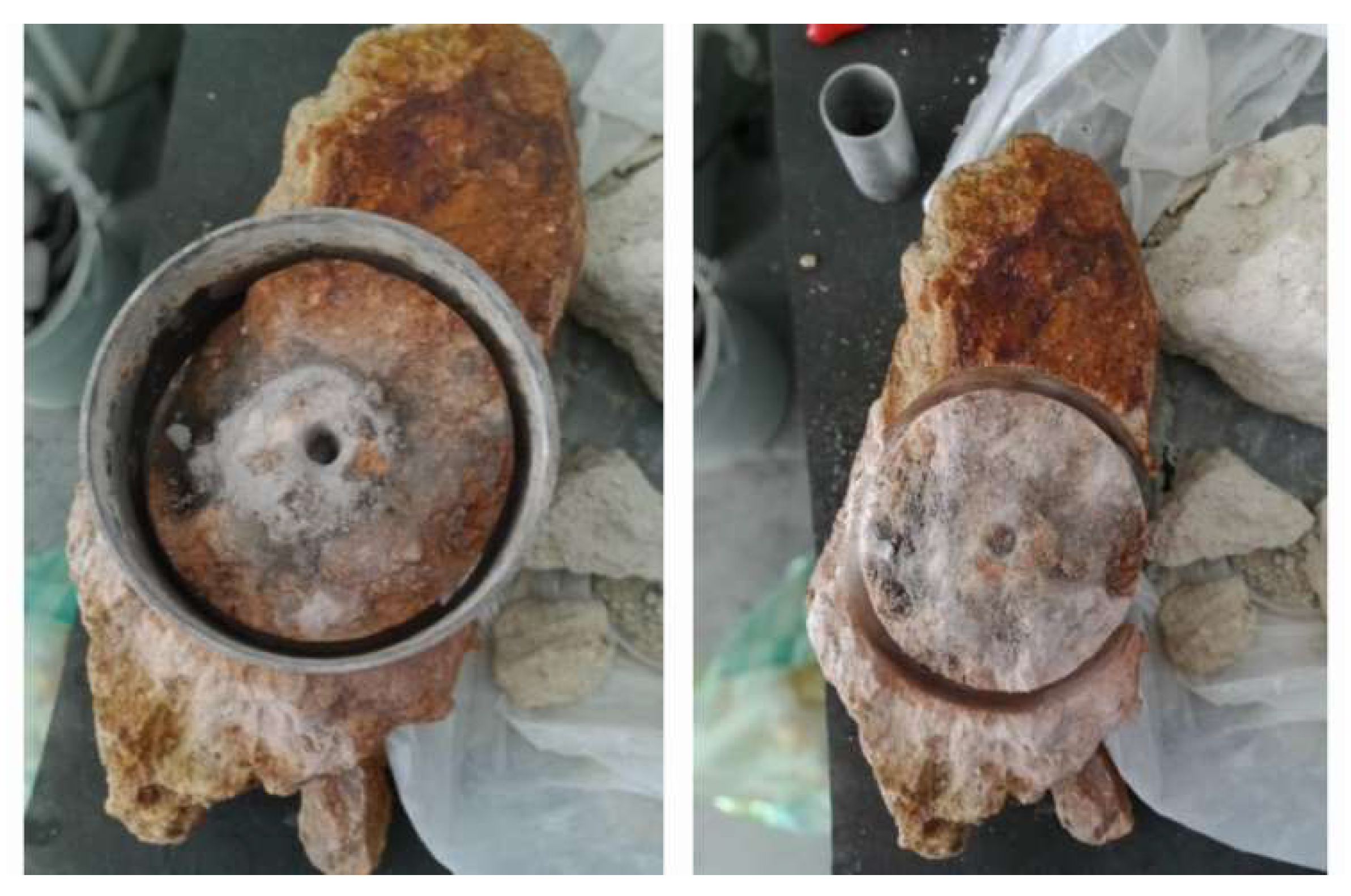
3.1. Impedance Measurements
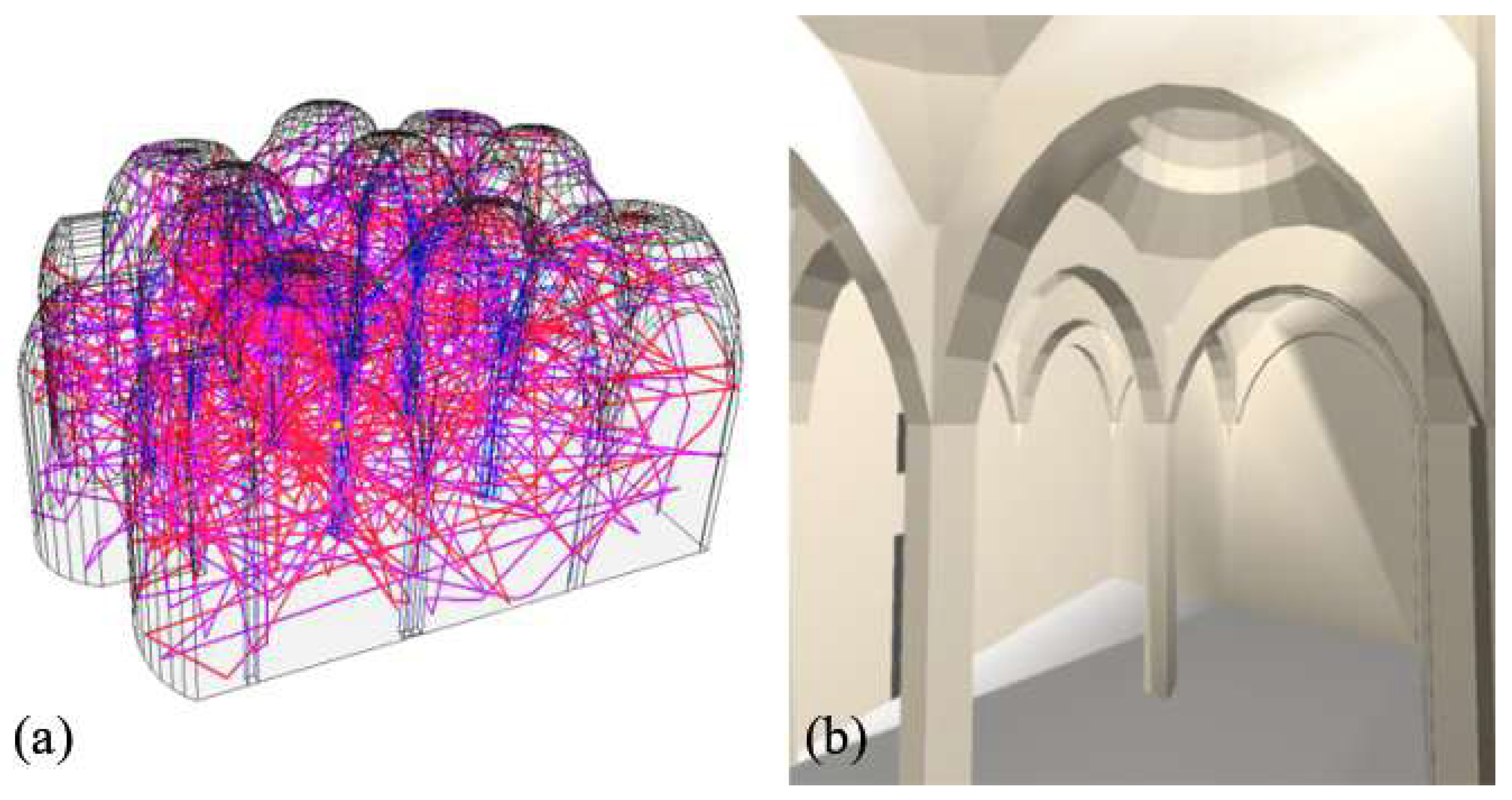
3.2. Acoustical Simulations
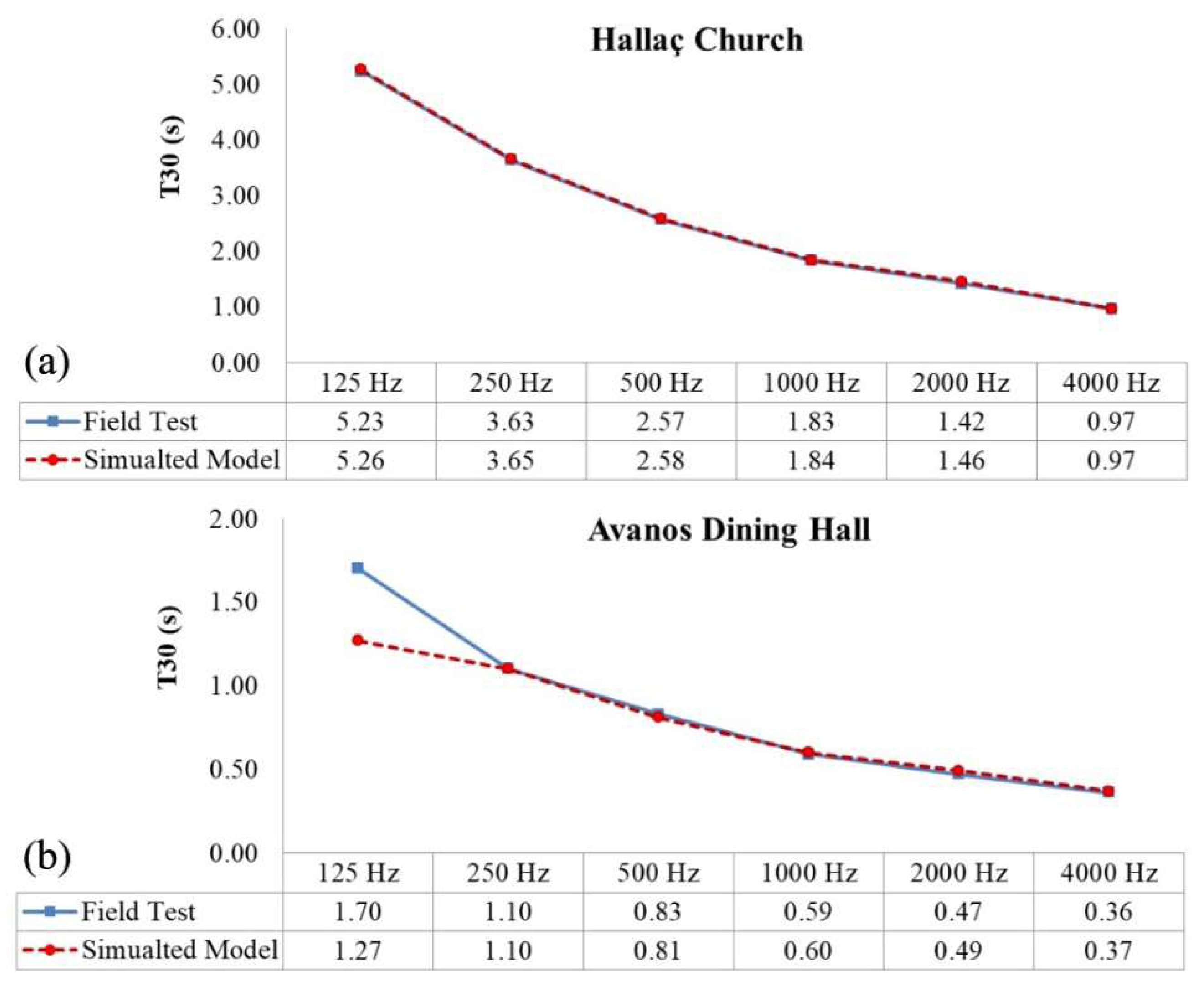
3.2.1. Simulations Based on Field Tests
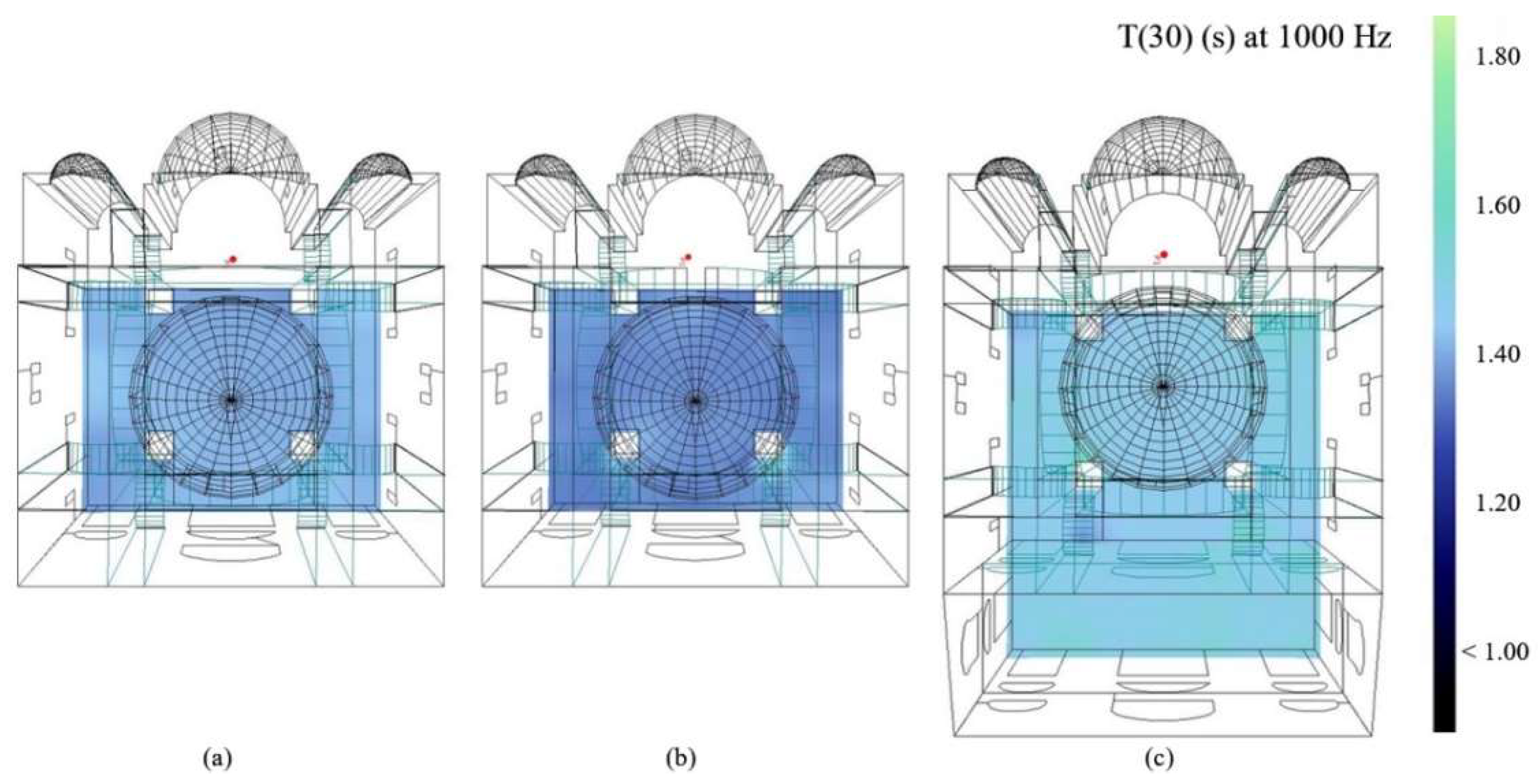
3.2.2. Acoustical Simulation Setup of Bell Church
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Acoustical Material Analysis
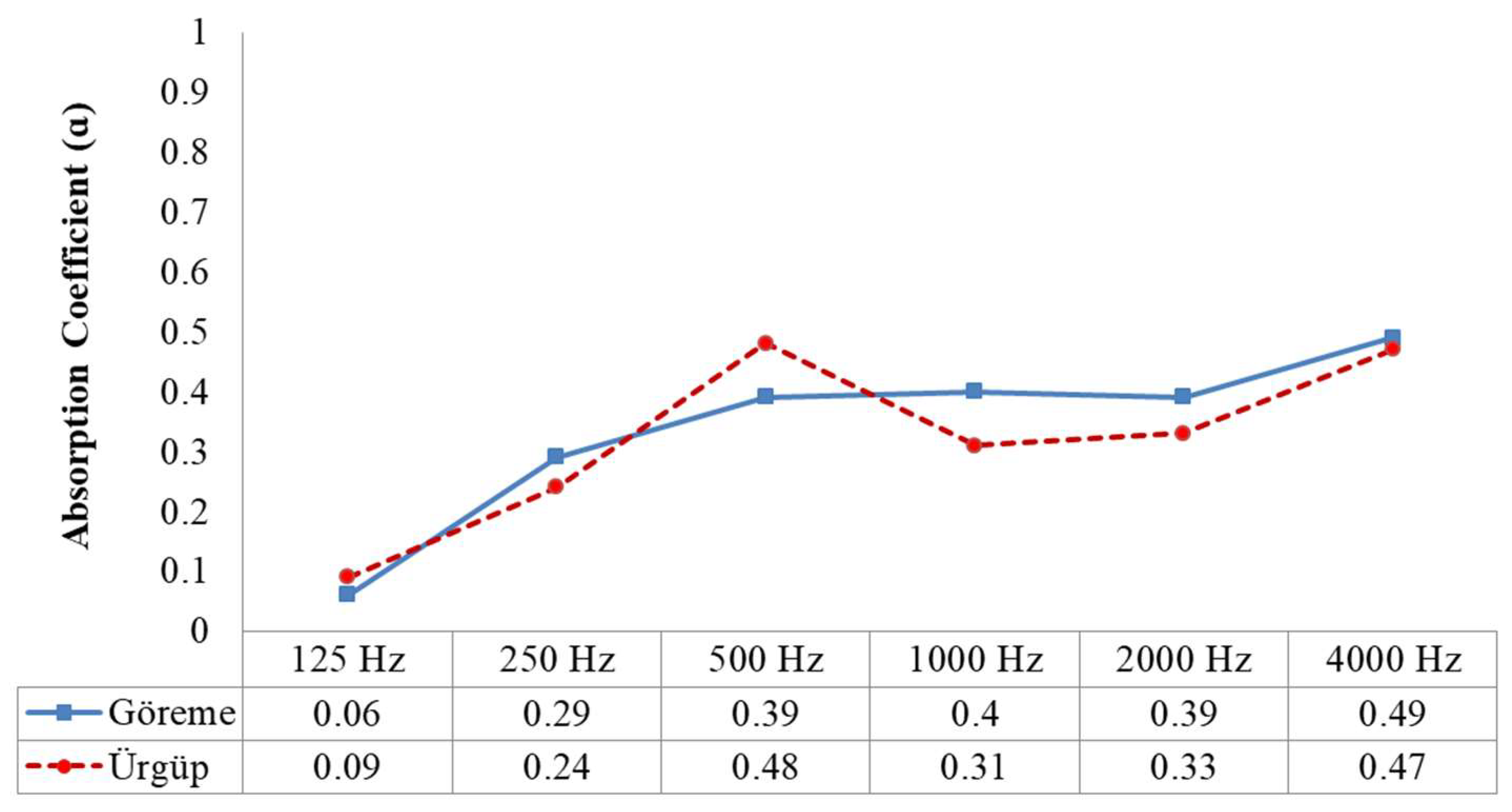
4.1.1. Impedance Test Results
4.1.2. Acoustical Simulation Results of the Hallaç Church and Avanos Dining Hall
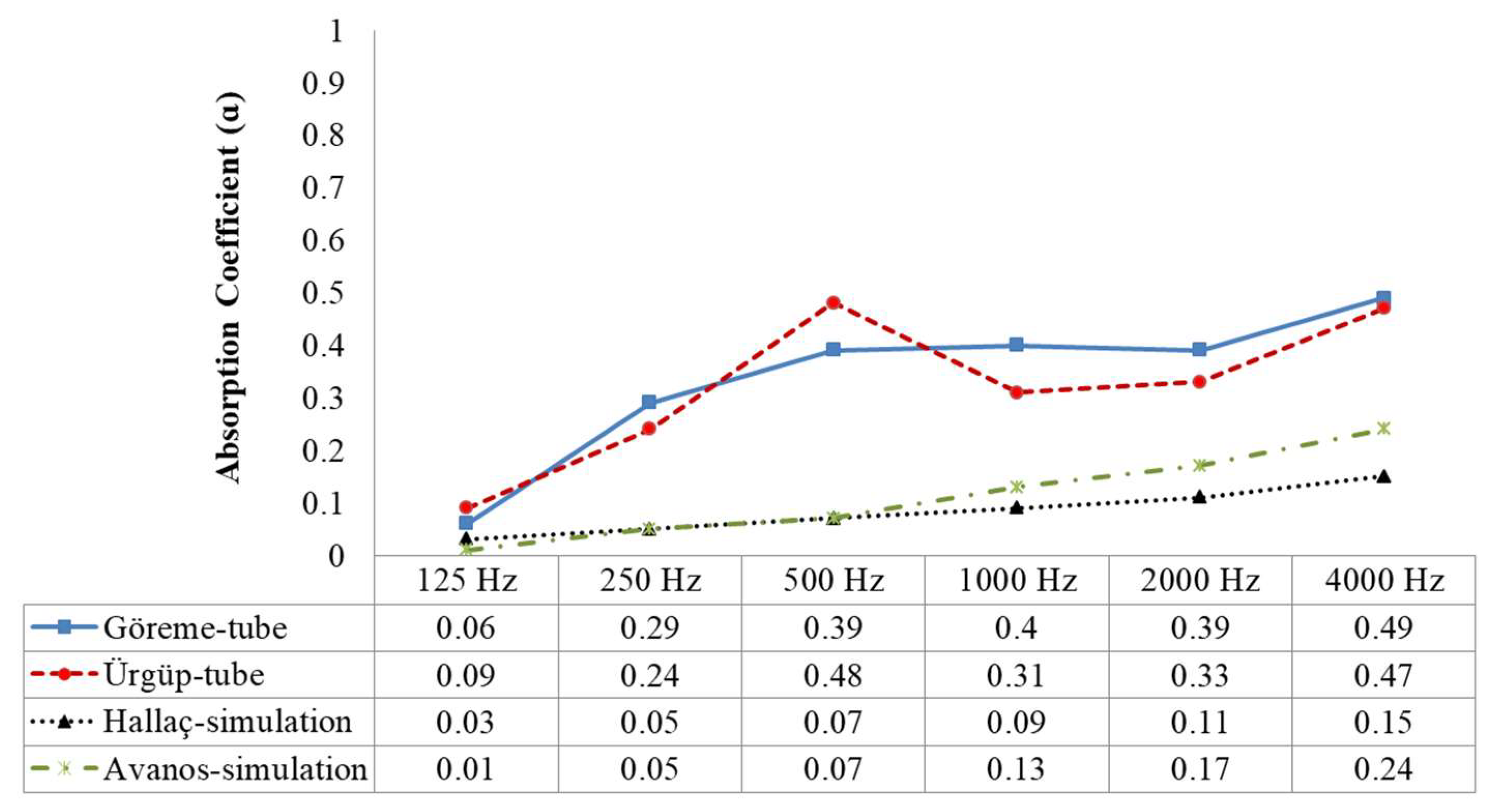
4.1.3. Comparison of Sound Absorption Coefficients Obtained by Simulations and Impedance Tests
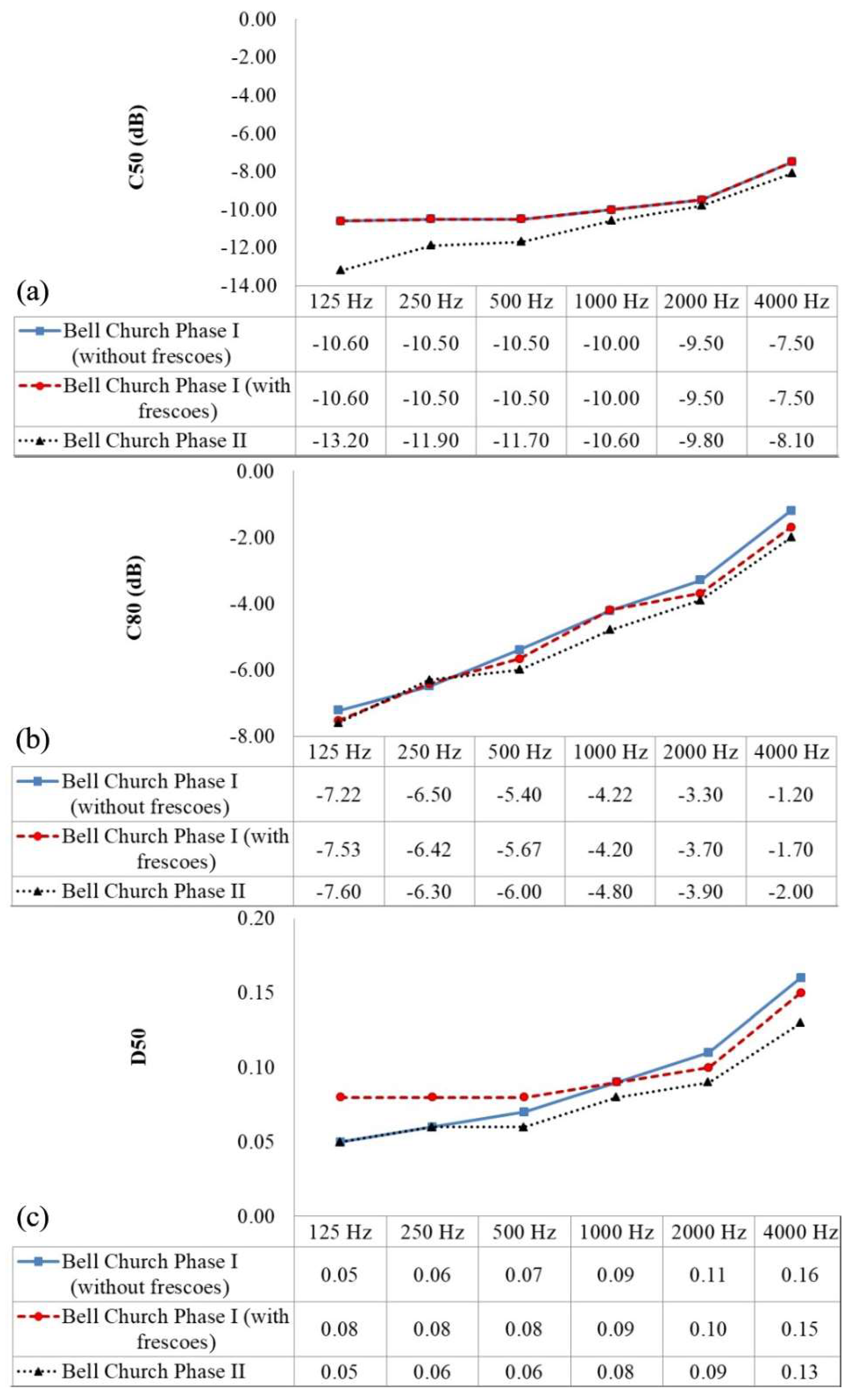
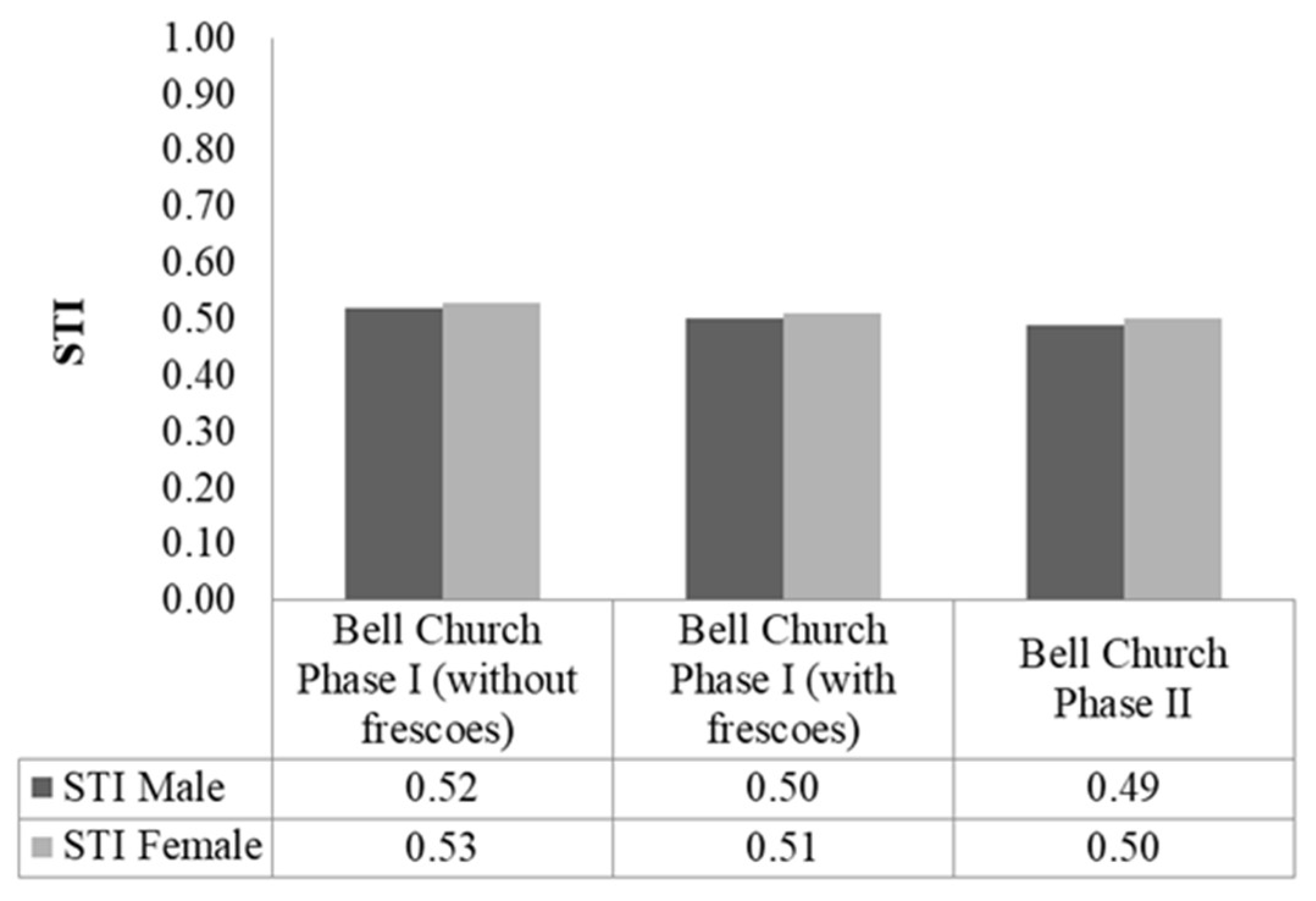
4.2. Acoustical Parameter Results and Comparisons of the Different Phases of Bell Church
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, A.L.; Gjestland, T.; Dubois, D. Acoustic environments and soundscapes. In Soundscape and the Built Environment, 1st ed.; Kang, J., Schulte-Fortkamp, B., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.J.; Carmichael, L. The Senses Considered as Perceptual Systems; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 1966; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, F.G. Transformation of the ‘Sacred’ Image of a Byzantine Cappadocian Settlement. In Architecture and Landscape in Medieval Anatolia, 1100–1150, 1st ed.; Blessing, P., Goshgarian, R., Eds.; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 2017; pp. 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Sü Gül, Z.; Xiang, N.; Çalışkan, M. Investigations on sound energy decays and flows in a monumental mosque. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sü Gül, Z.; Xiang, N.; Çalışkan, M. Diffusion Equation-Based Finite Element Modeling of a Monumental Worship Space. J. Comput. Acoust. 2017, 25, 1750029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sü Gül, Z.; Çalıskan, M.; Tavukçuoğlu, A.; Xiang, N. Assessment of acoustical indicators in multi-domed historic structures by non-exponential energy decay analysis. Acoust. Aust. 2018, 46, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sü Gül, Z.; Odabaş, E.; Xiang, N.; Çalışkan, M. Diffusion equation modeling for sound energy flow analysis in multi domain structures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sü Gül, Z. Acoustical impact of architectonics and material features in the lifespan of two monumental sacred structures. Acoustics 2019, 1, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sü Gül, Z. Exploration of room acoustics coupling in Hagia Sophia of Istanbul for its different states. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilantonopoulos, S.L.; Mourjopoulos, J. Virtual acoustic reconstruction of ritual and public spaces of ancient Greece. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2001, 87, 604–609. [Google Scholar]
- Sukaj, S.; Ciaburro, G.; Iannace, G.; Lombardi, I.; Trematerra, A. The Acoustics of the Benevento Roman Theatre. Buildings 2021, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe, C.; Iannace, G.; Lombardi, I.; Trematerra, A. Acoustic design of ancient buildings: The odea of Pompeii and Posillipo. Buildings 2020, 10, 224. [Google Scholar]
- Gino, I.; Berardi, U. Acoustic virtual reconstruction of the Roman theater of Posillipo, Naples. Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics 173EAA. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, R.; Sendra, J.J.; Alonso, A. Acoustics, Liturgy and Architecture in the Early Christian Church. From the domus ecclesiae to the basilica. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2013, 99, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, R.; Alonso, A.; Sendra, J.J. Intangible cultural heritage: The sound of the Romanesque cathedral of Santiago de Compostela. J. Cult. Herit. 2015, 16, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, R.; Alonso, A.; Sendra, J.J. Archaeoacoustics of intangible cultural heritage: The sound of the Maior Ecclesia of Cluny. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 19, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Suarez, R.; Sendra, J.J. Virtual reconstruction of indoor acoustics in cathedrals: The case of the Cathedral of Granada. Build. Simul. 2016, 4, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, M.C.; Planells, A.; Perelló, R.R.; Segura, J.G.; Giménez, A. Virtual acoustic reconstruction of a lost church: Application to an Order of Saint Jerome monastery in Alzira, Spain. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2018, 11, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesco, M.; Cirillo, E.; Della Crociata, S.; Gasparini, E.; Preziuso, D. Acoustical reconstruction of San Petronio Basilica in Bologna during the Baroque period: The effect of festive decorations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3607. [Google Scholar]
- Adeeb, A.H.; Sü-Gül, Z.; Henry, A.B. Characterizing the Indoor Acoustical Climate of the Religious and Secular Rock-Cut Structures of Cappadocia. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, T.F.; Daskalakis Mathews, A.C. Islamic-style mansions in Byzantine Cappadocia and the development of the inverted T-plan. J. Soc. Archit. Hist. 1997, 56, 294–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousterhout, R.G. Visualizing Community: Art, Material Culture, and Settlement in Byzantine Cappadocia; Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ousterhout, R.G. A Byzantine Settlement in Cappadocia; Dumbarton Oaks: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, W.M.; Bell, G.L. The Thousand and One Churches (London, 1909); Reprint, with a new foreword; Outsterhout, R.G., Jackson, M.P.C., Eds.; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rodley, L. Cave Monasteries of Byzantine Cappadocia; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Krautheimer, R.; Ćurčić, S. Early Christian and Byzantine Architecture; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1992; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sukaj, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Iannace, G.; Lombardi, I.; Parente, R.; Trematerra, A. Byzantine Churches in Albania: How Geometry and Architectural Composition Influence the Acoustics. Buildings 2022, 12, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Nicholas (Mesopotam) Monastery. Available online: https://www.intoalbania.com/attraction/st-nicholas-mesopotam-monastery (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Vasileios, M. Architecture and Ritual in the Churches of Constantinople: Ninth to Fifteenth Centuries; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teteriatnikov, N.B. The Liturgical Planning of Byzantine Churches in Cappadocia. In Orientalia Christiana Analecta; Pontificio Istituto Orientale: Rome, Italy, 1996; p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 10534-2; Acoustics–Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes-Part 2: Transfer-Function Method.; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McGrory, M.; Castro Cirac, D.; Gaussen, O.; Cabrera, D. Sound Absorption Coefficient Measurement: Re-Examining the Relationship between Impedance Tube and Reverberant Room Methods. In Proceedings of the Acoustics, Fremantle, Australia, 21–23 November 2012; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.Y.; Blaser, D.A. Transfer function method of measuring in-duct acoustic properties. II. Experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindel, J.H. The use of computer modeling in room acoustics. J. Vibroengineering 2000, 3, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). In ISO. ISO 3382-1; Acoustics: Measurement of the Reverberation Time of Rooms with Reference to Other Acoustical Parameters; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Martellotta, F. The just noticeable difference of center time and clarity index in large reverberant spaces. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, I. A comparison of room simulation software-the 2nd round robin on room acoustical computer simulation. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2000, 86, 943–956. [Google Scholar]
- Ousterhout, R. Survey of the Byzantine Settlement at Çanlı Kilise in Cappadocia: Results of the 1995 and 1996 Seasons; Dumbarton Oaks Papers: Wahington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Beranek, L.L. Acoustical Measurements; Acoustical Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, M. Auditorium Acoustics and Architectural Design; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Giron, S.; Alvarez-Morales, L.; Zamarreno, T. Church acoustics: A state-of-the-art review after several decades of research. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 411, 378–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrinenko, L.I. Acoustics of Auditoriums in Public Buildings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Templeton, D. Acoustics in the Built Environment: Advice for the Design Team; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Steeneken, H.J.; Houtgast, T. A physical method for measuring speech-transmission quality. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 67, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | Mineral Composition |
|---|---|
| Göreme | Gypsum, kaolinite, clay, calcite, quartz, plagioclase, cristobalite, alkali feldspar, mica, zeolite, amphibole |
| Ürgüp | Plagioclase, clay, quartz, cristobalite, dolomite, zeolite, alkali feldspar, mica, calcite |
| Hallaç | Quartz, plagioclase, clay, mica, alkali feldspar, cristobalite, tridymite, amphibole (little traces) |
| Sample | Chemical Compounds (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A.Za | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | K2O | MgO | MnO | Na2O | P2O5 | SiO2 | TiO2 | |
| Göreme | 8.9 | 10.0 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 3.2 | 0.2 | <0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 70.9 | 0.1 |
| Ürgüp | 6.7 | 11.3 | 1.3 | 3.0 | 3.9 | 0.5 | <0.1 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 71.7 | 0.1 |
| Hallaç | 4.2 | 10.9 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 3.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.6 | <0.1 | 74.2 | 0.2 |
| Materials/Locations | Frequency (Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | |
| Stone (marble)/Floor | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 100% open to outdoor | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Hallaç church (tuff stone type I)/Walls & ceiling | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
| Materials/Locations | Frequency (Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | |
| Stone (marble)/Floor | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 50% Absorbent (open door to kitchen) | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Avanos dining hall (tuff stone type II)/Walls & ceiling vault | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.24 |
| Materials/Locations | Frequency Band (Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | |
| Stone (marble)/Floor | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 100% open to outdoor | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tuff stone type I/Walls & ceiling | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
| Fresco paintings | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Wooden screen & narthex roof | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adeeb, A.H.; Sü Gül, Z. Investigation of a Tuff Stone Church in Cappadocia via Acoustical Reconstruction. Acoustics 2022, 4, 419-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics4020026
Adeeb AH, Sü Gül Z. Investigation of a Tuff Stone Church in Cappadocia via Acoustical Reconstruction. Acoustics. 2022; 4(2):419-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics4020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdeeb, Ali Haider, and Zühre Sü Gül. 2022. "Investigation of a Tuff Stone Church in Cappadocia via Acoustical Reconstruction" Acoustics 4, no. 2: 419-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics4020026
APA StyleAdeeb, A. H., & Sü Gül, Z. (2022). Investigation of a Tuff Stone Church in Cappadocia via Acoustical Reconstruction. Acoustics, 4(2), 419-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics4020026







