Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco
Abstract
:1. Introduction
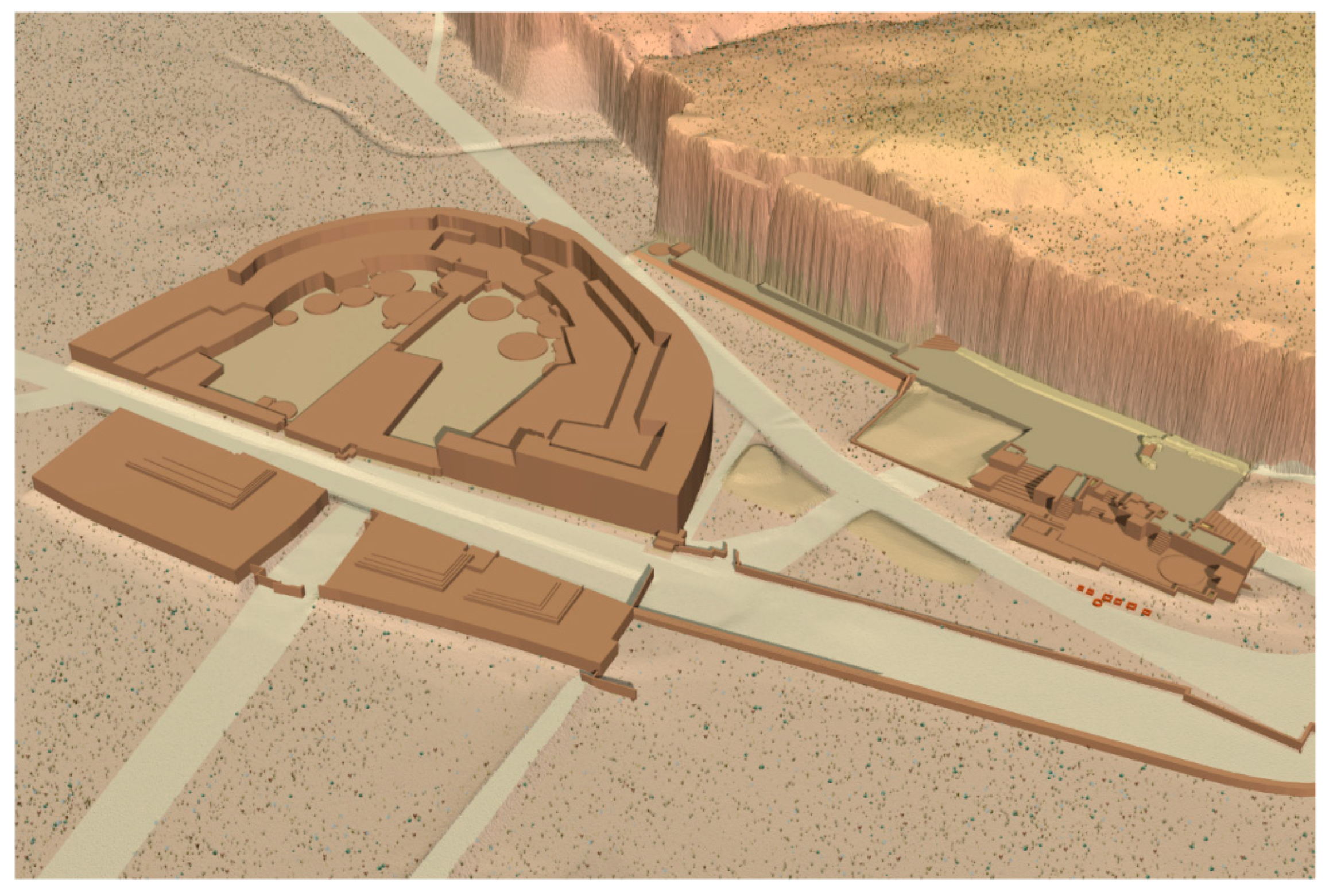
Background
2. Modeling Methods
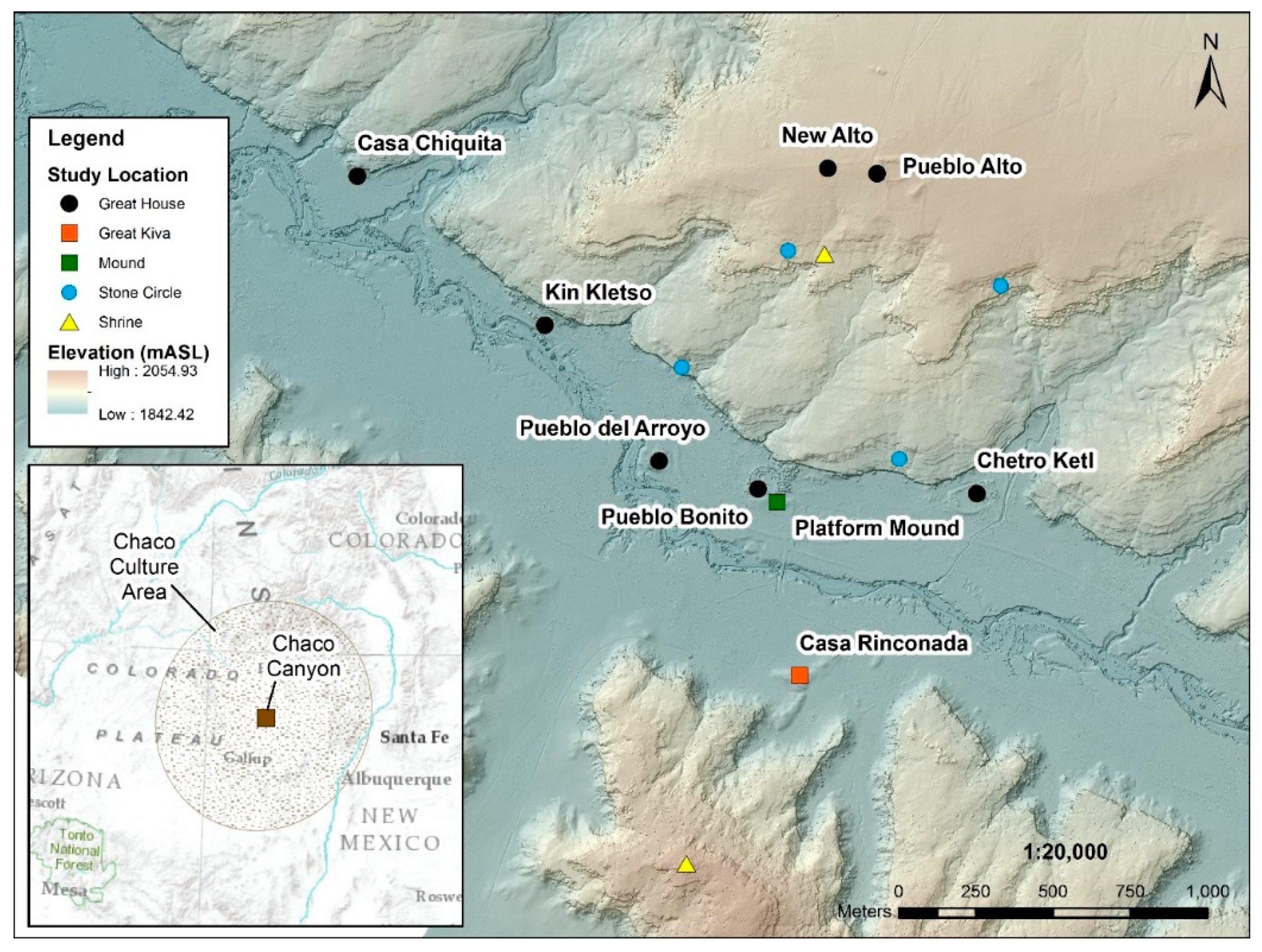
2.1. Model Inputs
2.2. Modeling Steps
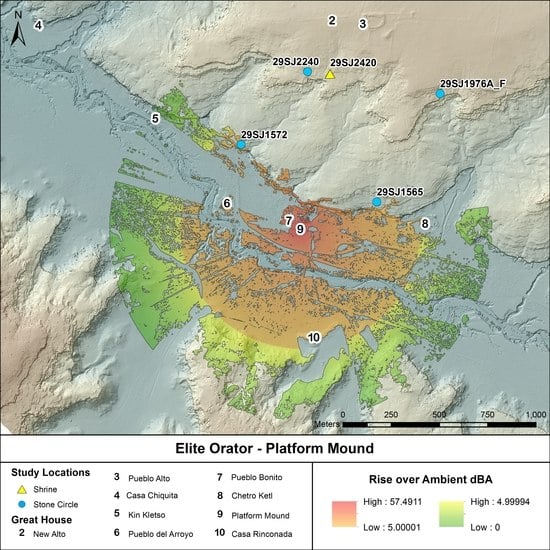
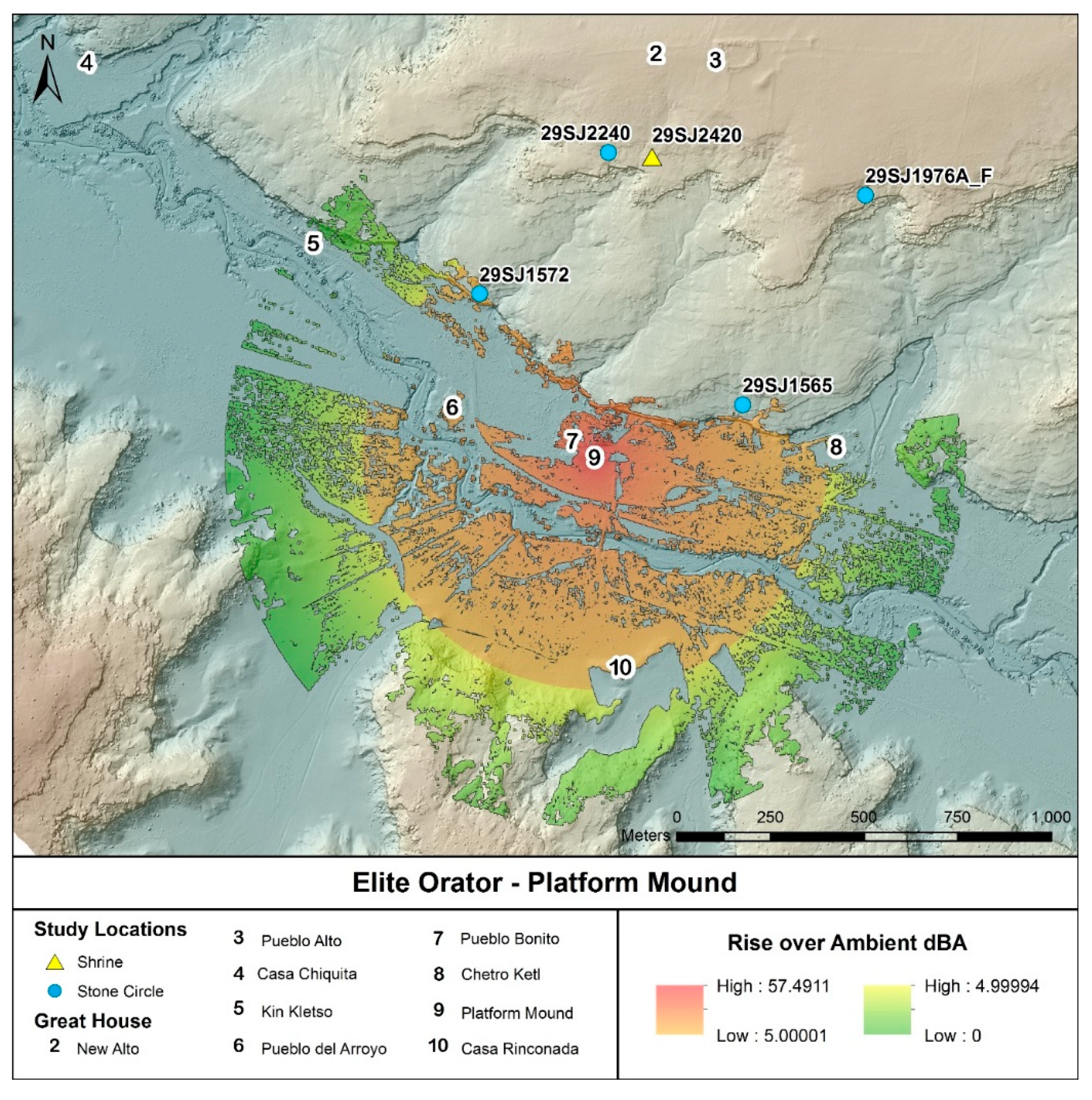
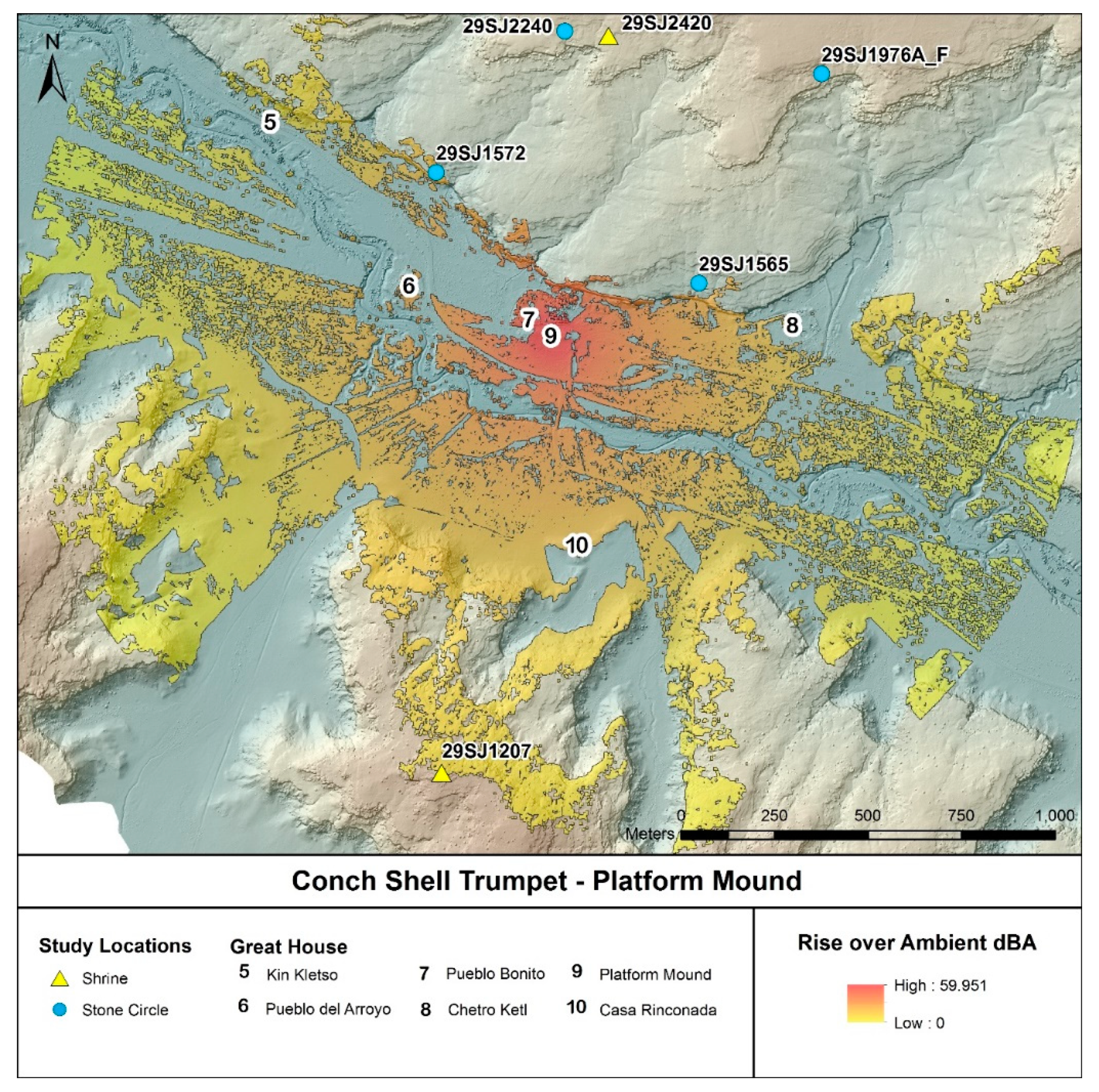
3. Modeling Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes in the Past: Towards a Phenomenology of Sound at the Landscape Level. Presented at the 81st Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–10 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes in the Past: A GIS Approach to Landscape Scale Archaeoacoustics. Presented at the Frontiers in Archaeological Sciences Symposium, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 23–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Witt, D.E.; Primeau, K.E. Soundscapes in the Past: Interaudibility in the Chacoan Built Landscape. Presented at the 82nd Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29 March–2 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes in the Past: Investigating Sound at the Landscape Level. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 19, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, T.; Coben, L.S. Overture: An Invitation to the Archaeological Theater. In Archaeology of Performance: Theaters of Power, Community, and Politics; Inomata, T., Coben, L.S., Eds.; Altamira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2006; pp. 11–44. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.C. Domination and the Arts of Resistance: Hidden Transcripts; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, I.; Zubrow, E.B.W.; Cowan, F. Musical behaviours and the archaeological record: A preliminary study. In Experimental Archaeology; Mathieu, J., Ed.; British Archaeological Reports: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, I.; Watson, A. Acoustics and the human experience of socially-organized sound. In Archaeoacoustics; Scarre, C., Lawson, G., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- D’Errico, F.; Lawson, G. The sound paradox: How to assess the acoustic significance of archaeological evidence? In Archaeoacoustics; Scarre, C., Lawson, G., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Devereux, P. Stone Age Soundtracks: The Acoustic Archaeology of Ancient Sites; Vega: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Eneix, L.C. (Ed.) Archaeoacoustics: The Archaeology of Sound; The OTS Foundation: Myakka City, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, R.; Till, R.; Howell, M. (Eds.) Music & Ritual: Bridging Material & Living Cultures; Ekho Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scarre, C. Sound, place and space: Towards an archaeology of acoustics. In Archaeoacoustics; Scarre, C., Lawson, G., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, A.; Keating, D. Architecture and sound: An acoustic analysis of megalithic monuments in prehistoric Britain. Antiquity 1999, 73, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, M.A. Sensing sonically at Andean Formative Chavín de Huántar, Perú. Time Mind 2017, 10, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.; Markham, B.; Wall, J.N. Acoustical archaeology—Recreating the soundscape of John Donne’s 1622 gunpowder plot sermon at Paul’s Cross. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2013, 19, 015133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, B.; Azevedo, M.; Wall, J.N. Recreating the soundscape of John Donne’s 1622 gunpowder plot sermon at Paul’s Cross. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.N. Transforming the Object of our Study: The Early Modern Sermon and the Virtual Paul’s Cross Project. Available online: http://journalofdigitalhumanities.org/3-1/transforming-the-object-of-our-study-by-john-n-wall/ (accessed on 24 December 2018).
- Reznikoff, I. Sound resonance in prehistoric times: A study of Paleolithic painted caves and rocks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, R.G.; Devereux, P.; Ibison, M. Acoustical resonances of assorted ancient structures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Trematerra, A.; Qandil, A. The Acoustics of the Catacombs. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 39, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Berardi, U. The Acoustic of Cumaean Sibyl. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2017, 30, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Marletta, L.; Sicurella, F.; Ianniello, E. Acoustic measurements in the Ear of Dionysius at Syracuse (Italy). In Proceedings of the 39th International Congress on Noise Control Engineering 2010, Lisbon, Portugal, 13–16 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kolar, M.A. Archaeological Psychoacoustics at Chavín de Huántar, Perú. Ph.D. Dissertation, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M.; de Smet, T. Chacoan Soundscapes. Archaeol. Southwest Mag. 2018, 32, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Andreu, M.; García Benito, C. Acoustics and Levantine rock art: Auditory perceptions in La Valltorta Gorge (Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 3591–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, T.; Farina, A.; Armelloni, E.; Hameau, P.; Díaz-Andreu, M. Echoing landscapes: Echolocation and the placement of rock art in the Central Mediterranean. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 83, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Andreu, M.; Atiénzar, G.G.; Benito, C.G.; Mattioli, T. Do You Hear What I See? Analyzing Visibility and Audibility in the Rock Art Landscape of the Alicante Mountains of Spain. J. Anthropol. Res. 2017, 73, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mileson, S. Sound and Landscape. In The Oxford Handbook of Later Medieval Archaeology in Britain; Christopher, G., Alejandra, G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 713–727. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuz, D. Listening to landscapes: Modelling past soundscapes in GIS. Internet Archaeol. 2004, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwosz, C.R. Benchmarks: Ontological Considerations at Two Mojave Desert Petroglyph Labyrinths. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli, T.; Díaz-Andreu, M. Hearing rock art landscapes: A survey of the acoustical perception in the Sierra de San Serván area in Extremadura (Spain). Time Mind 2017, 10, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, J. Experiencing the past? The development of a phenomenological archaeology in British prehistory. Archaeol. Dialogues 2005, 12, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, V.; Whittle, A. Places of Special Virtue: Megaliths in the Neolithic Landscape of Wales; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.H. Phenomenological Approaches in Landscape Archaeology. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2012, 41, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, C. A Phenomenology of Landscape; Routledge: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C. The Materiality of Stone: Explorations in Landscape Phenomenology; Berg: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C. Body and Image: Explorations in Landscape Phenomenology 2; Left Coast Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C. Interpreting Landscapes: Geologies, Topographies, Identities; Explorations in Landscape Phenomenology 3; Left Coast Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M. Phenomenology in archaeology. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology; Smith, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 5909–5917. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilakis, Y. Archaeology and the Senses: Human Experience, Memory, and Affect; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Merleau-Ponty, M. Phenomenology of Perception; Routledge: London, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.; Whitehouse, R.; Brown, K.; Combes, P.; Herring, E.; Thomas, M.S. Phenomenology in practice: Towards a methodology for a ‘subjective’ approach. Eur. J. Archaeol. 2006, 9, 31–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eve, S. Augmenting Phenomenology: Using Augmented Reality to Aid Archaeological Phenomenology in the Landscape. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M. Landscape Phenomenology, GIS and the Role of Affordance. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobera, M. Life on a Pixel: Challenges in the Development of Digital Methods Within an “Interpretive” Landscape Archaeology Framework. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennell, R. Experience and GIS: Exploring the Potential for Methodological Dialogue. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigg, D. Place and Non-place: A Phenomenological Perspective. In Place, Space, and Hermeneutics; Janz, B.B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Trigger, B.G. A History of Archaeological Thought, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hacigüzeller, P. GIS, critique, representation and beyond. J. Soc. Archaeol. 2012, 12, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, D.Z. GIS and Urban Studies: Positivism, Post-Positivism, and Beyond. Urban Geogr. 1994, 15, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingold, T. The Perception of the Environment; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bunzel, R.L. Zuni Ceremonialism; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.N. The Distribution of Sound Instruments in the Prehistoric Southwestern United States. Ethnomusicology 1967, 11, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E. Instruments of Power: Musical Performance in Rituals of the Ancestral Puebloans of the American Southwest. Ph.D. Dissertation, Columbia University, University Microfilms, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E. Musical instruments in the pre-hispanic southwest. Park Sci. 2009, 26, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E. Music of the center place: The instruments of Chaco Canyon. In Flower World: Music Archaeology of the Americas; Stöckli, M., Howell, M., Eds.; Ekho Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.N. Ethnomusicology and the prehistoric southwest. Ethnomusicology 1971, 15, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, B.J.; Ferguson, T.J. Animate objects: Shell trumpets and ritual networks in the greater southwest. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2008, 15, 338–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, K. Gateways to Another World: The Symbolism of Supernatural Passageways in the Art and Ritual of Mesoamerican and the American Southwest. In Painting the Cosmos: Metaphor and Worldview in Images from the Southwest Pueblos and Mexico; Hays-Gilpin, K., Schaafsma, P., Eds.; Museum of Northern Arizona: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2010; pp. 73–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hays-Gilpin, K.; Sekaquaptewa, E.; Newsome, E.A. Sìitalpuva, “through the land brightened with flowers”: Ecology and cosmology in mural and pottery painting, Hopi and beyond. In Painting the Cosmos: Metaphor and Worldview in Images From the Southwest Pueblos and Mexico; Hays-Gilpin, K., Schaafsma, P., Eds.; Museum of Northern Arizona: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2010; pp. 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, R.S. A Sensory Approach to Exotica, Ritual Practice, and Cosmology at Chaco Canyon. Kiva 2015, 81, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, R.M. The Chacoan past: Creative representations and sensory engagements. In Subjects and Narratives in Archaeology; Dyke, R.M.V., Bernbeck, R., Eds.; University Press of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015; pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Akins, N.J. The burials of Pueblo Bonito. In Pueblo Bonito: Center of the Chacoan World; Neitzel, J.E., Ed.; Smithsonian Books: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. Tse’Biinaholts’a Yalti (Curved Rock That Speaks). Time Mind 2008, 1, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loose, R.W. That old music: Reproduction of a shell trumpet from Pueblo Bonito. Pap. Archaeol. Soc. N. M. 2012, 38, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. Archaeoacoustics: Adding a Sound Track to Site Descriptions. Pap. Archaeol. Soc. N. M. 2010, 36, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. A Report on Tse Biinaholtsa’a Yałti (Curved Rock that Speaks): An Open-Air Public Performance Theater at Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Manuscript on File; Chaco Culture National Historical Park: New Mexico, NM, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, R.W. Computer Analysis of Sound Recordings from Two Anasazi Sites in Northwestern New Mexico. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.R.; Friedman, R.; Blackhorse, T.; Loose, R. Revisiting Downtown Chaco. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 199–223. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.E.; Mann, J.P.; Boggs, J.L. SPreAD-GIS: An ArcGIS Toolbox for Modeling the Propagation of Engine Noise in a Wildland Setting, version 1.2; The Wilderness Society: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.E.; Boggs, J.L.; Mann, J.P. SPreAD-GIS: An ArcGIS Toolbox for Modeling the Propagation of Engine Noise in a Wildland Setting, version 2.0; The Wilderness Society: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, G.; Richards-Rissetto, H.; Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Bringing Sound into the Picture: Experiencing Ancient Maya Landscapes with GIS and 3D Modeling. Presented at the Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology (CAA) International Conference, Tübingen, Germany, 19–23 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, G.; Richards-Rissetto, H.; Primeau, K.E.; Witt, D.E. Soundscapes and Visionscapes: Investigating Ancient Maya Cities with GIS and 3D Modeling. Presented at the 83rd Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Western Regional Climate Center. Chaco Canyon National Monument [sic], New Mexico, Monthly Climate Summary. Available online: http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?nm1647 (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Ambrose, S. Sound Levels in the Primary Vegetation Types in Grand Canyon National Park, July 2005; NPS Report No. GRCA-05-02; Sandhill Company: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hayne, M.J.; Rumble, R.H.; Mee, D.J. Prediction of crowd noise. In Proceedings of the Acoustics 2006, Christchurch, New Zealand, 20–22 November 2006; pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Van Heusden, E.; Plomp, R.; Pols, L.C.W. Effect of ambient noise on the vocal output and the preferred listening level of conversational speech. Appl. Acoust. 1979, 12, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organización Internacional de Normalización. ISO 9613-2:1996, Acoustics: Attenuation of Sound during Propagation Outdors. General Method of Calculation; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI). ANSI S1.26-1995 Method for Calculation of the Absorption of Sound by the Atmosphere; Acoustical Society of America: New York City, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa, Z. Noise reduction by screens. Appl. Acoust. 1968, 1, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamancusa, J.S. Outdoor sound propagation. In Noise Control, ME 458 Engineering Noise Control; Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Primeau, K.E. Methodological Improvements in Landscape Archaeoacoustics: Exploring the Effects of Vegetation and Ground Cover. Presented at the 84th Annual Meeting of the Society for American Archaeology, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 10–14 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, N.M. The Architecture of Pueblo Bonito; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; Volume 147. [Google Scholar]
- Windes, T.C. Investigations at the Pueblo Alto Complex, Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, 1975–1979; National Park Service: Sante Fe, NM, USA, 1987; Volume II, Pt. 2: Architecture and Stratigraphy. [Google Scholar]
- Lekson, S.H. Great House Form. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 7–44. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.R.; Lekson, S.H. Anasazi Ritual Landscapes. In Anasazi Regional Organization and the Chaco System; Doyel, D.E., Ed.; University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1992; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Crown, P.L. (Ed.) The Pueblo Bonito Mounds of Chaco Canyon; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Toll, H.W. Making and Breaking Pots in the Chaco World. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, C.M. Pink Chert, Projectile Points, and the Chacoan Regional System. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, W. Building Social History at Pueblo Bonito: Footnotes to a Biography of Place. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, M.P. The Chacoan Roads: A Cosmological Interpretation. In Anasazi Architecture and American Design; Morrow, B.H., Price, V.B., Eds.; University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1997; pp. 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sofaer, A. The Primary Architecture of the Chacoan Culture: A Cosmological Expression. In Anasazi Architecture and American Design; Morrow, B.H., Price, V.B., Eds.; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1997; pp. 88–132. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M. Sacred Landscapes: The Chaco-Totah Connection. In Chaco’s Northern Prodigies: Salmon, Aztec, and the Ascendancy of the Middle San Juan Region after AD 1100; Reed, P.F., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2008; pp. 334–348. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, W.H. Ritual and Mound Formation during the Bonito Phase in Chaco Canyon. Am. Antiq. 2001, 66, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windes, T.C. Gearing Up and Piling On: Early Great Houses in the Interior San Juan Basin. In The Architecture of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico; Lekson, S.H., Ed.; The University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 45–92. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, R.M. The Chaco Experience: Landscape and Ideology at the Center Place; School for Advanced Research Press: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, C.M. Sacred Earthen Architecture in the Northern Southwest: The Bluff Great House Berm. Am. Antiq. 2002, 67, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekson, S.H. A History of the Ancient Southwest; School for Advanced Research Press: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin, M.A. Plazas, Performance, and Symbolic Power in Ancestral Pueblo Religion. In Religious Transformation in the Late Pre-Hispanic Pueblo World; Glowacki, D.M., Keuren, S.V., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, ZA, USA, 2012; pp. 130–152. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarsson, J.J.; Nordström, H.; Lundén, P.; Nilsson, M.E. Aircraft noise and speech intelligibility in an outdoor living space. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boren, B. Whitefield’s Voice. In George Whitefield; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 167–189. [Google Scholar]
- Boren, B. The Maximum Intelligible Range of the Human Voice. Ph.D. Dissertation, New York University, New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boren, B.; Roginska, A.; Gill, B. Maximum Averaged and Peak Levels of Vocal Sound Pressure. In Proceedings of the 135th Audio Engineering Society Convention, New York, NY, USA, 17–20 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Larm, P.; Hongisto, V. Experimental comparison between speech transmission index, rapid speech transmission index, and speech intelligibility index. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, H. Prediction of Verbal Communication is Noise—A review: Part 1. Appl. Acoust. 1986, 19, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovičić, S.T. A relation between speech intelligibility and distribution of speech pressure about the head. Appl. Acoust. 1991, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, N.M. The Material Culture of Pueblo Bonito; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 124. [Google Scholar]
- Luckman, T. Comments on Legitimation. Curr. Sociol. 1987, 35, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, R. Legitimating Identities: The Self-Presentations of Rulers and Subjects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Elliot, J.H. A Palace for a King: The Buen Retiro and the Court of Philip IV; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley, P.M. Deliberate Acts: Changing Hopi Culture through the Oraibi Split; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yoffee, N. The Chaco “Rituality” Revisited. In Chaco Society and Polity: Papers from the 1999 Conference; Cordell, L.S., Judge, W.J., Piper, J.-E., Eds.; New Mexico Archaeological Council: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2001; pp. 63–78. [Google Scholar]


| Environmental Inputs | Cultural Inputs |
|---|---|
| Percentage of Relative Humidity | Location of Sound Source |
| Air Temperature (°F) | Height of Sound Source (ft) |
| Ambient Sound Pressure Level (dB(A)) | Sound Pressure Level of Source (dB(A)) |
| LiDAR-based DEM | Measurement Distance of Source (ft) |
| Frequency of Source (Hz) |
| Modeling Inputs | Elite Orator with a Raised Voice: Afternoon in June | Conch Shell Trumpet: Dawn in June | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Inputs | Percentage of Relative Humidity | 30% | 30% |
| Air Temperature | 89.6 °F (32 °C) | 55.4 °F (13 °C) | |
| Ambient Sound Pressure Level | 20.7 dB(A) | 20.7 dB(A) | |
| Cultural Inputs | Height of Sound Source | 5 ft (1.5 m) | 6 ft (1.8 m) |
| Sound Pressure Level of Source | 84 dB(A) | 96 dB(A) | |
| Measurement Distance of Source | 3 ft (0.9 m) | 4 ft (1.2 m) | |
| Frequency of Source | 325 Hz | 330 Hz | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Witt, D.E.; Primeau, K.E. Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco. Acoustics 2019, 1, 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007
Witt DE, Primeau KE. Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco. Acoustics. 2019; 1(1):78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleWitt, David E., and Kristy E. Primeau. 2019. "Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco" Acoustics 1, no. 1: 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007
APA StyleWitt, D. E., & Primeau, K. E. (2019). Performance Space, Political Theater, and Audibility in Downtown Chaco. Acoustics, 1(1), 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics1010007