Chemically Triggered Dopant Release from Surface-Modified Polypyrrole Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Electrochemical Polymerization of Py
2.2.1. Electrochemical Synthesis of DBSA-Doped Polypyrrole Films
2.2.2. Electrochemical Synthesis of Polypyrrole Films with Other Dopants
2.2.3. Surface Modification of Polypyrrole Films with Poly(ethylene glycol)
2.2.4. Exposure of Polypyrrole Films to Chemical Stimuli
3. Results and Discussion
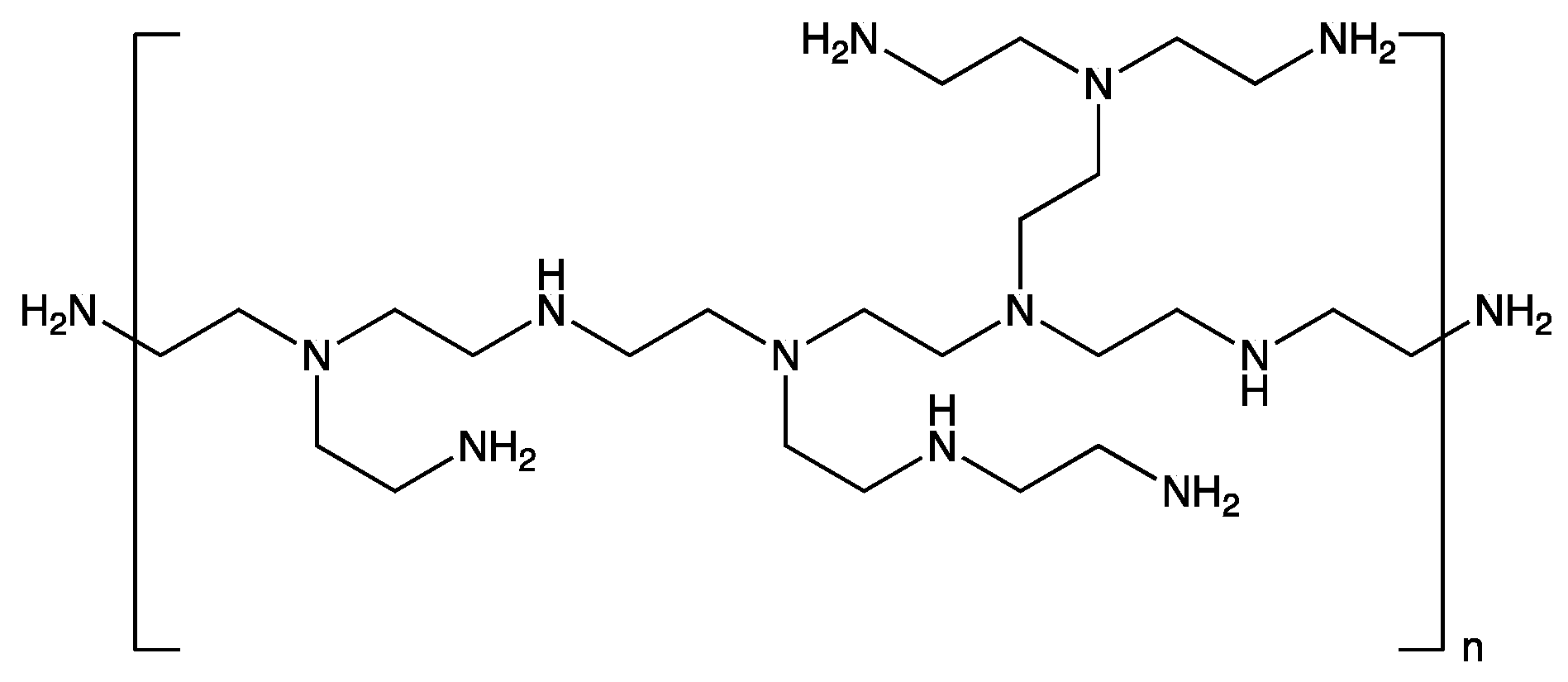
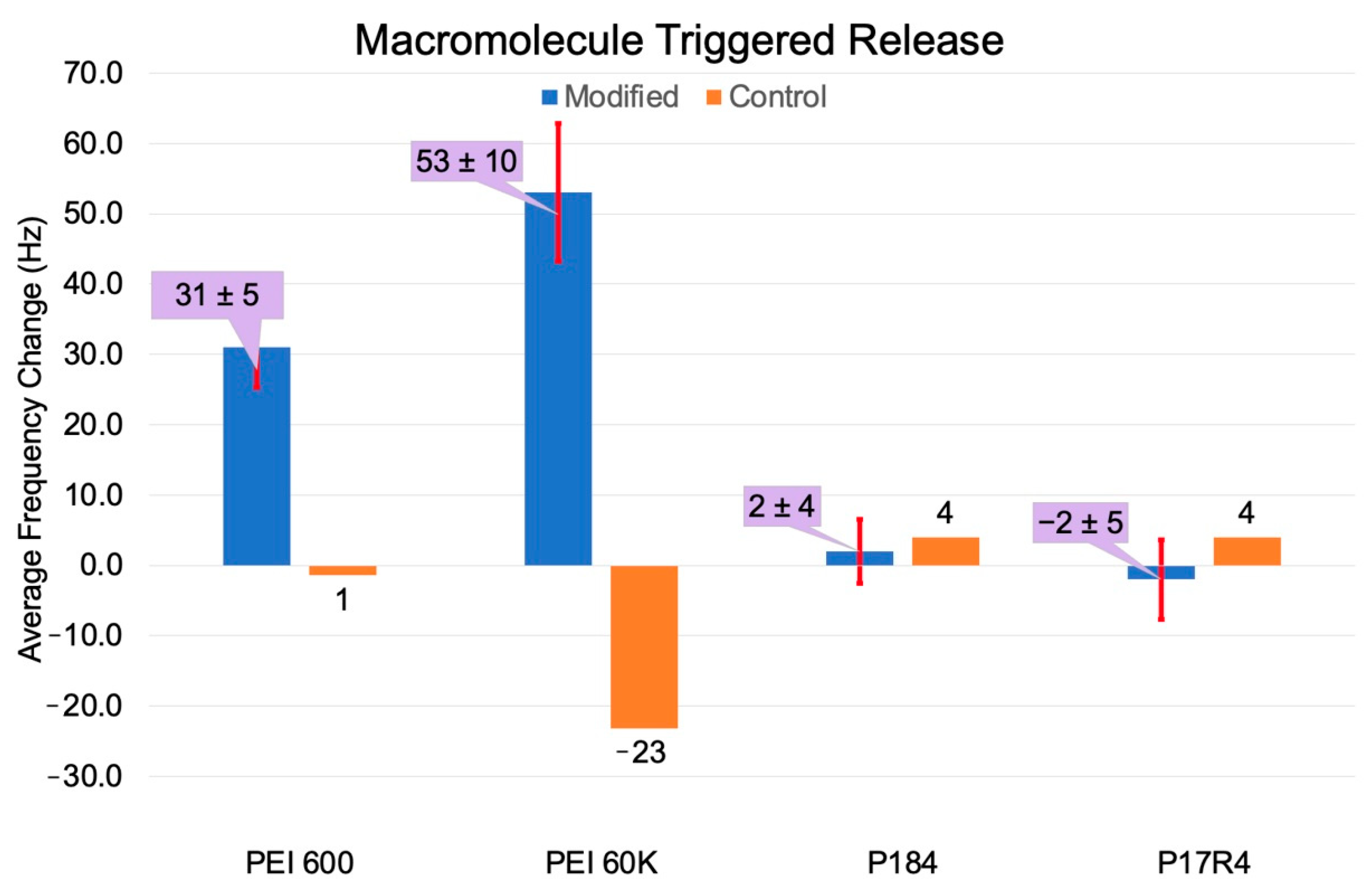
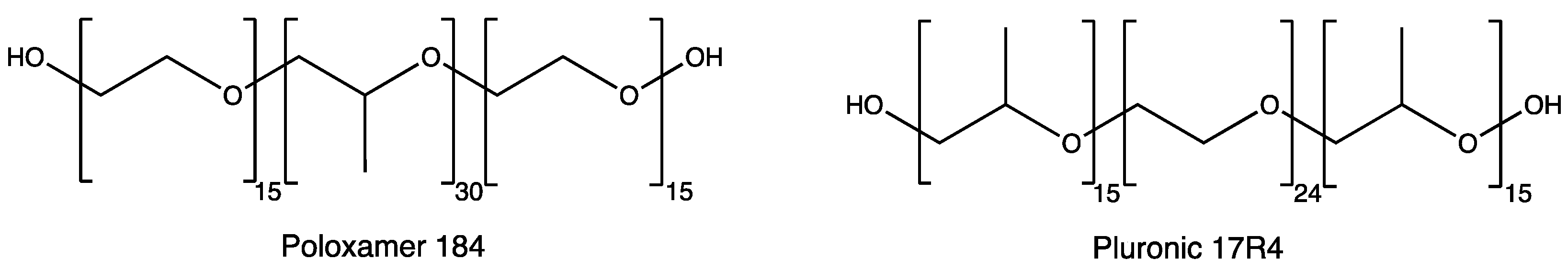
3.1. Dopant Extraction by Macromolecules
3.2. Dopant Extraction by Small Molecules
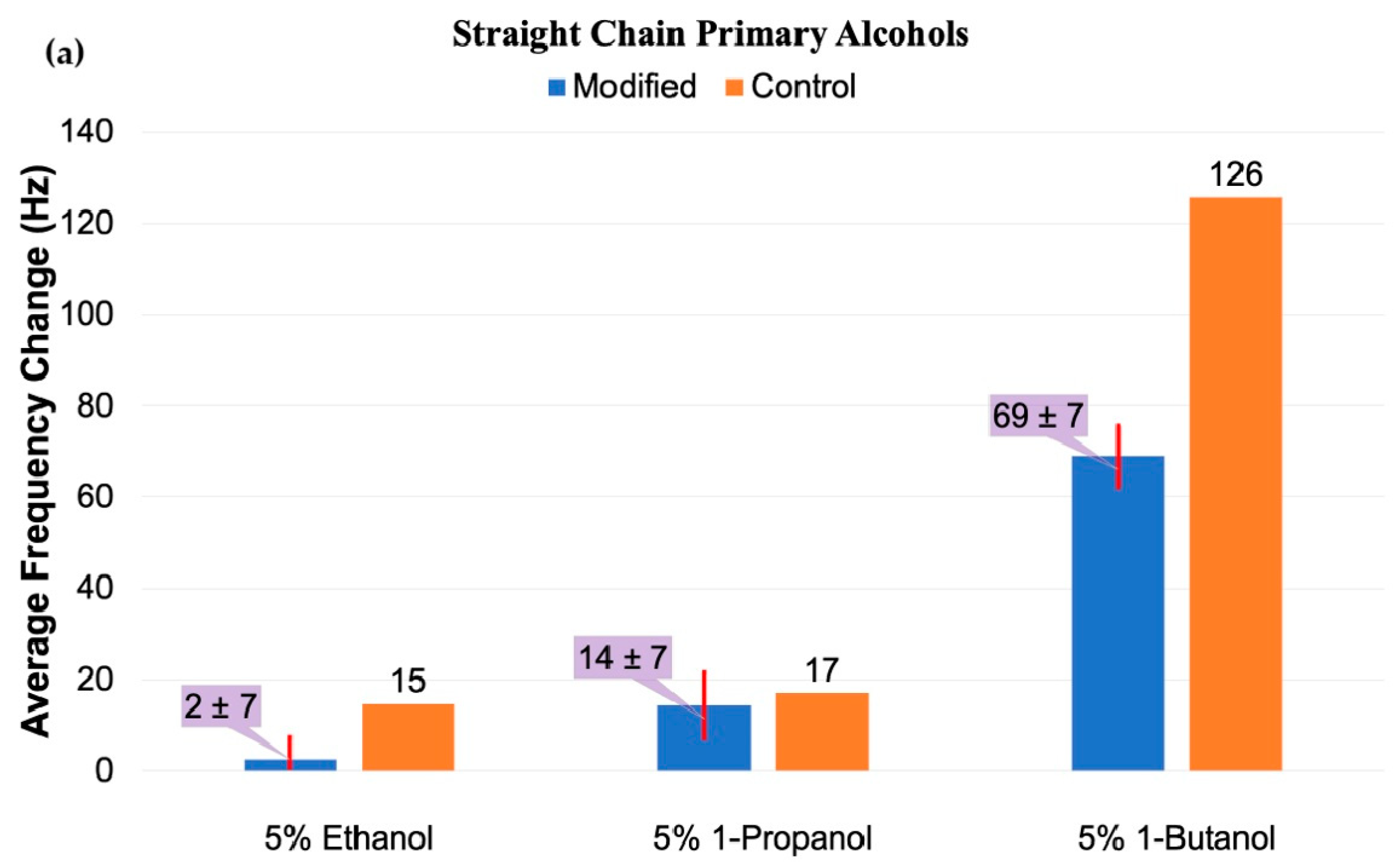
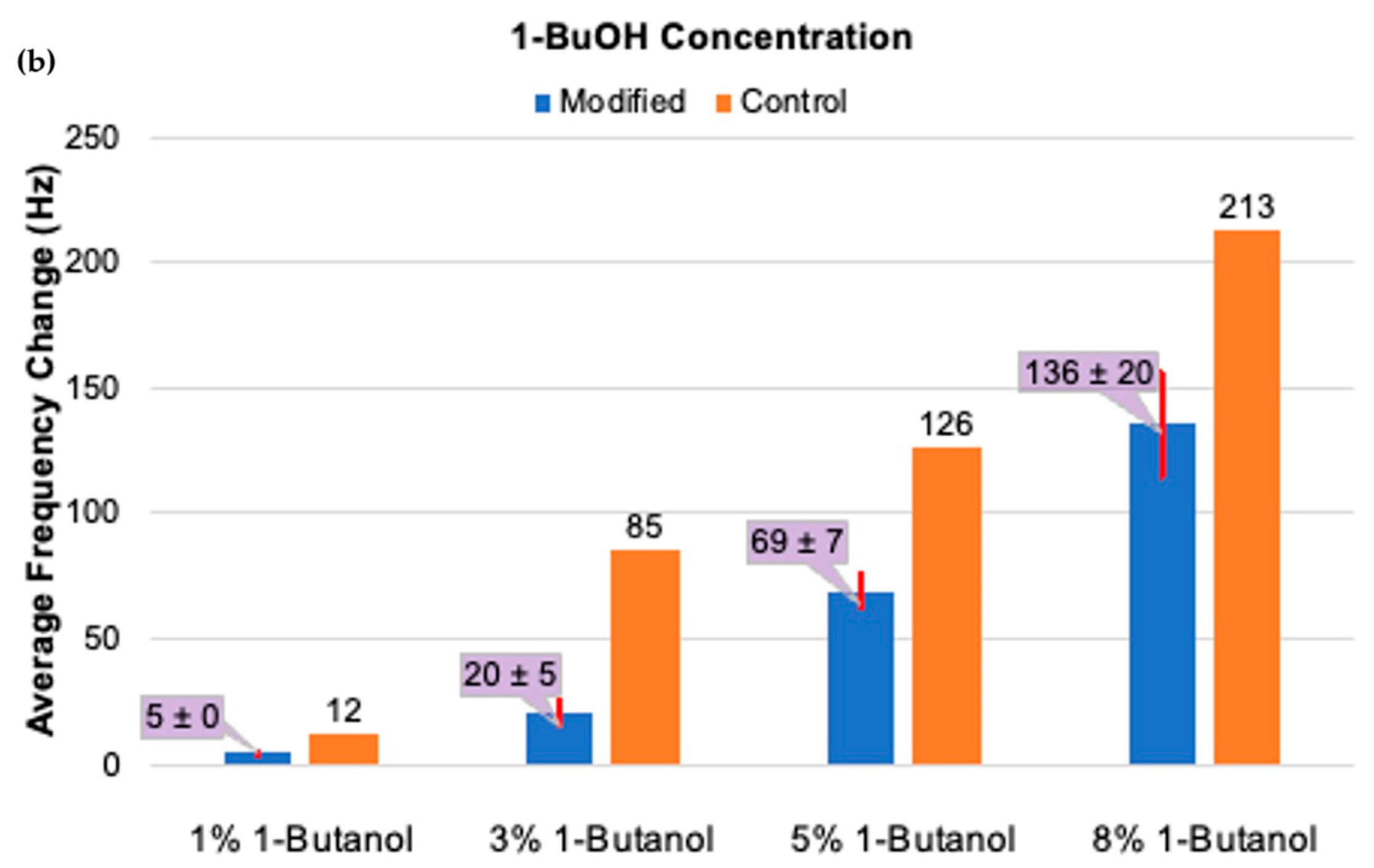
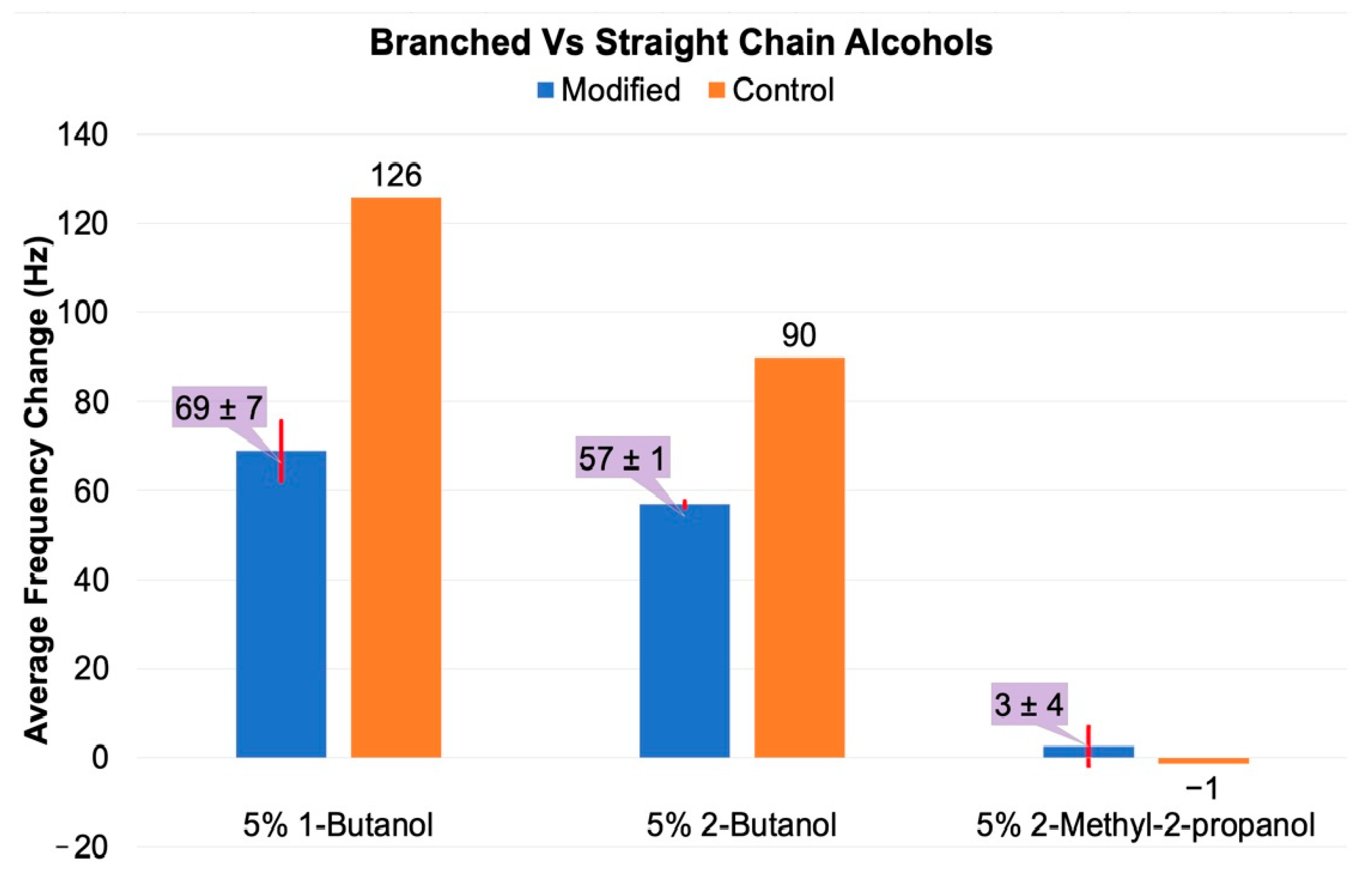
3.2.1. Small Alcohol Stimuli
3.2.2. Small Carboxylic Acid Stimuli
3.2.3. Small Amine Stimuli
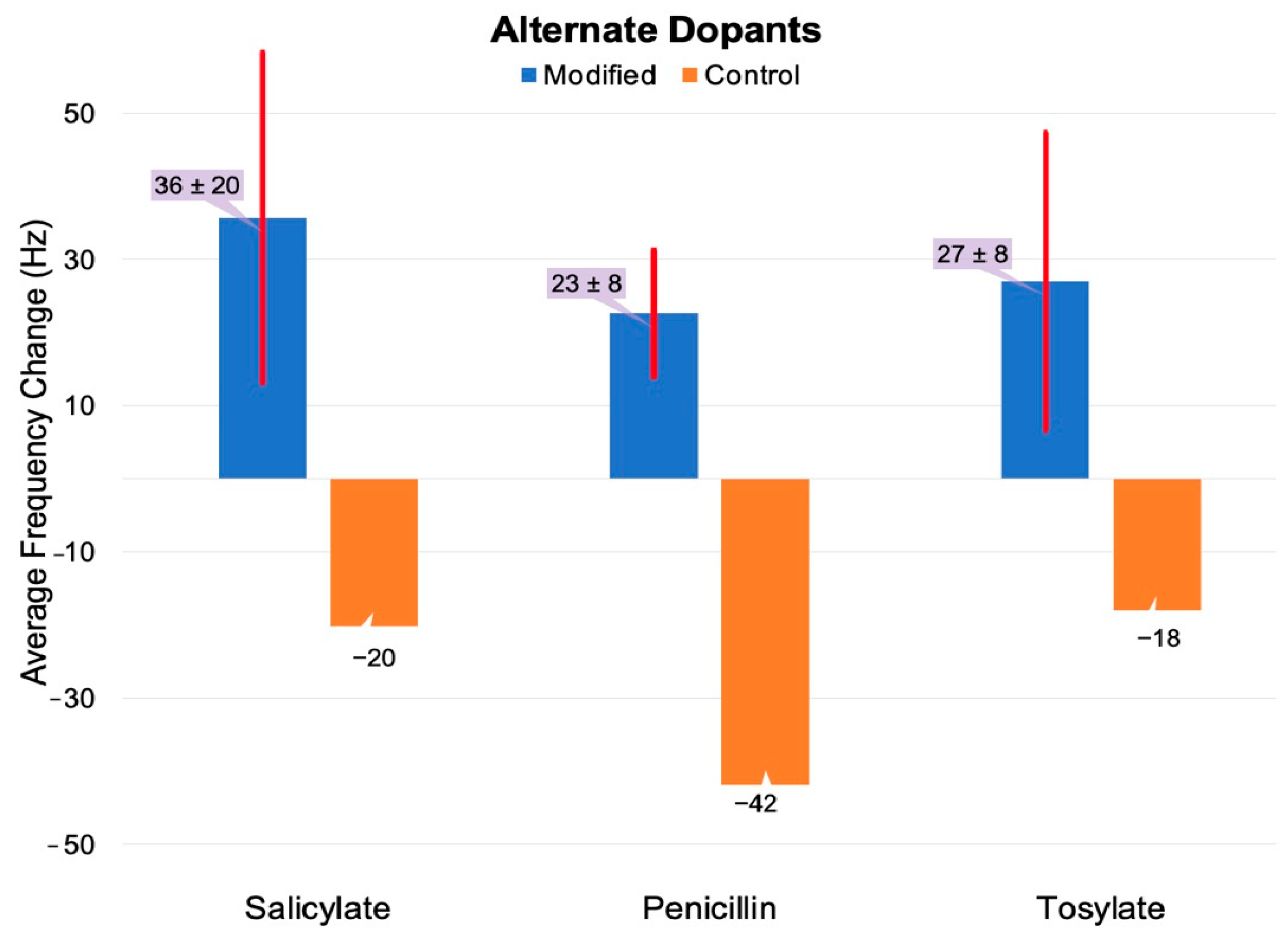
3.3. The Effect of PEG Adlayers on Alternative Dopants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dovzhenko, A.P.; Yapryntseva, O.A.; Sinyashin, K.O.; Doolotkeldievac, T.; Zairov, R.R. Recent progress in the development of encapsulated fertilizers for time-controlled release. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.; Santos, L. Delivery systems for cosmetics—From manufacturing to the skin of natural antioxidants. Powder Tech. 2017, 322, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Jamil, M.I.; Jiang, J.; Shoaib, M.; Amin, B.U.; Luo, S.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q. An overview of controlled-biocide-release coating based on polymer resin for marine antifouling applications. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, Z.; He, T.; Wang, Z.; Yao, S.; Qiu, H. Lubricant controlled release silicone fouling release coatings based on mesoporous molecular sieves. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2023, 20, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepu, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled drug delivery systems: Current status and future directions. Molecules 2021, 26, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, J.; Lee, D.; Rice, T.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Clinical translation of long-acting drug delivery formulations. Nature Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneaua, M.; Bennicia, S.; Brendlea, J.; Dutourniea, P.; Limousy, L.; Pluchon, S. Systems for stimuli-controlled release: Materials and applications. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, N.; Gopalan, G.P.; Eldho, J.; Francis, R. Conducting polymers: Biomedical applications. In Biomedical Applications of Polymeric Materials and Composites; Francis, R.D., Kumar, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Wiley Online Books: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K. Conducting Polymers Chemistries, Properties and Biomedical Applications; Gupta, R.K., Ed.; Taylor and Francis Online: Abingdon, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramshetti, S.; Angolkar, M.; Al Fatease, A.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Hani, U.; Garg, A.; Ravi, G.; Osmani, R.A.M. Revolutionizing drug delivery and therapeutics: The biomedical applications of conductive polymers and composites-based systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhuev, Y.O.; Shtil’man, M.I.; Artyukhov, A.A. The application of polyaniline and polypyrrolein medical and biological fields. Part 2. Tissue engineering, muscle simulation, and systems with controlled release of biologically active substances. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2021, 14, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzieliene, I.; Popov, A.; Vaiciuleviciute, R.; Kirdaite, G.; Bernotiene, E.; Ramanaviciene, A. Polypyrrole-based structures for activation of cellular functions under electrical stimulation. J. Bioelectrochem 2023, 155, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Patel, R.; Patel, K.D.; Bouchard, L.-S.; Jha, A.; Perriman, A.W.; Patel, M. Conducting polymer-based scaffolds for neuronal tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 11006–11023. [Google Scholar]
- Alkahtani, M.E.; Elbadawi, M.; Chapman, C.A.; Green, R.A.; Gaisford, S.; Orlu, M.; Basit, A.W. Electroactive polymers for on-demand drug release. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2301759. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puiggalí-Jou, A.; del Valle, L.J.; Alemán, C. Drug delivery systems based on intrinsically conducting polymers. J. Control. Release 2019, 309, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Weng, W.; Cheng, K.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z. Electrochemical deposition of Ppy/Dex/ECM coatings and their regulation on cellular responses through electrical controlled drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 222, 113016. [Google Scholar]
- Boehler, C.; Oberueber, F.; Asplund, M. Tuning drug delivery from conducting polymer films for accurately controlled release of charged molecules. J. Control. Release 2019, 304, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.A.A.; Firlak, M.; Berrow, S.R.; Halcovich, N.R.; Baldock, S.J.; Yousafzai, B.M.; Hathout, R.M.; Hardy, J.G. Electrochemically enhanced drug delivery using polypyrrole films. Materials 2018, 11, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deike, M.; Asaumi, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Hirai, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujii, S. Morphological and chemical stabilities of polypyrrole in aqueous media for 1 year. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.P.; Hwang, T.I.; Oh, J.-M.; Maharjan, B.; Chun, S.; Kim, B.S.; Joshi, M.K.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. pH/NIR-responsive polypyrrole-functionalized fibrous localized drug-delivery platform for synergistic cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20256–20270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Torres, M.; Cruz-Cruz, G.J.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Gómez-Jiménez, L.M.; González-Salgado, F.; Mondragón-Lozano, R.; Olayo-González, M.G. Dapsone uptake and release from plasma polypyrrole for drug administration. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Pernaut, J.-M.; Reynolds, J.R. Use of conducting electroactive polymers for drug delivery and sensing of bioactive molecules. A redox chemistry approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 4080–4090. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, R.; Lundstrom, I. The effect of ammonia on the physical properties of polypyrrole. Synth. Met. 1987, 20, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist, M.; Babacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Levon, K. Electrochemical and spectroscopic study on thiolation of polyaniline. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 604–614. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, B.; Hanks, T. Spectroscopic, microscopic, and surface analysis of alkanethiol- and fuoroalkanethiol- modified conducting polymer thin films. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8035–8042. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Nagle, A.; Wallace, G.G.; Hanks, T.W.; Molino, P.J. Functionalised inherently conducting polymers as low biofouling materials. Biofouling 2015, 31, 493–502. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ma, M.; Yao, S. Preparation of thiolated polymeric nanocomposite for sensitive electroanalysis of dopamine. Biosen. Bioelect. 2012, 36, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Ryu, C.; Lee, J.Y. Enzymatically stable, non-cell adhesive, implantable polypyrrole/thiolated hyaluronic acid bioelectrodes for in vivo signal recording. Int. J. Biomacromol. 2024, 276, 133770. [Google Scholar]
- Molino, P.J.; Wetherill, R.E.; Knepper, A.; Trupia, D.; Hayes, P.; Molino, B.Z.; Hanks, T.W. Biofouling resistant electroactive polymer composites for protein triggered counterion delivery. Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6294–6302. [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbrey, G. The use of quarts oscillators for weighing thin layers and for microweighing. Z. Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Fuentes-Hernández, C.; Shim, J.; Meyer, J.; Giordano, A.J.; Li, H.; Winget, P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Cheun, H.; Kim, J.; et al. A universal method to produce low-work function electrodes for organic electronics. Science 2012, 336, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-G.; Kim, S.Y. Increase in interfacial adhesion and electrochemical charge storage capacity of polypyrrole on Au electrodes using polyethyleneimine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2169. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Ramsey, J.D.; Samadi, A.; Atoufi, Z.; Yazdi, M.K.; Ganjali, M.R.; Amirabad, L.M.; Zagnene, E.; Farokhi, M.; Formela, K.; et al. Poloxamer: A versatile tri-block copolymer for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 110, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seike, M.; Hirai, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujii, S. Alcohol as hydrophobizer for polypyrrole. Chem. Lett. 2022, 51, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Richter, G.; Knepper, A.; Molino, P.J.; Hanks, T.W. Chemically Triggered Dopant Release from Surface-Modified Polypyrrole Films. Surfaces 2025, 8, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8020023
Richter G, Knepper A, Molino PJ, Hanks TW. Chemically Triggered Dopant Release from Surface-Modified Polypyrrole Films. Surfaces. 2025; 8(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleRichter, Grant, Allen Knepper, Paul J. Molino, and Timothy W. Hanks. 2025. "Chemically Triggered Dopant Release from Surface-Modified Polypyrrole Films" Surfaces 8, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8020023
APA StyleRichter, G., Knepper, A., Molino, P. J., & Hanks, T. W. (2025). Chemically Triggered Dopant Release from Surface-Modified Polypyrrole Films. Surfaces, 8(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8020023





