Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications: An Overview of Material Fabrication Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
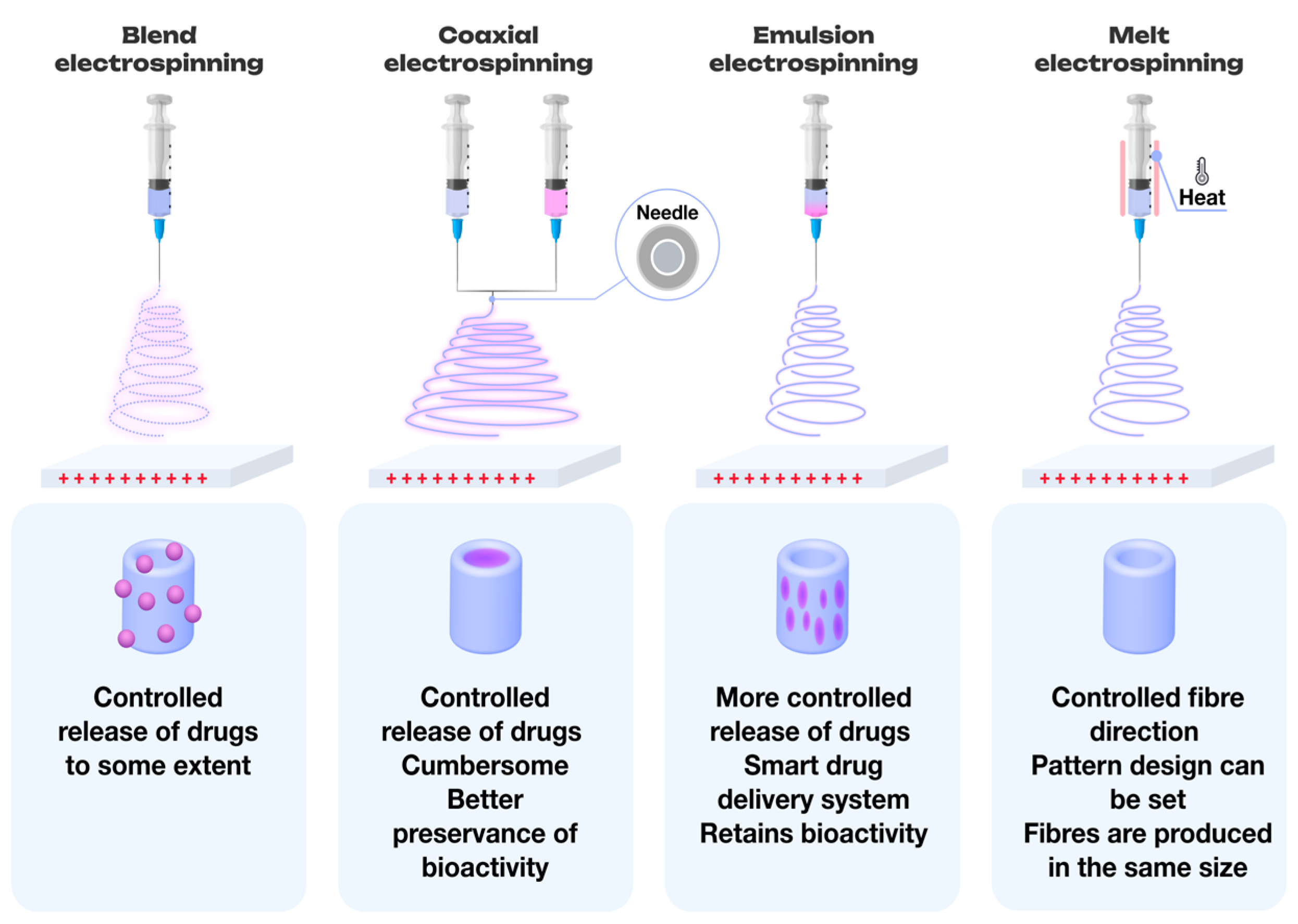
2. Methods for the Production of Polymer Nonwoven Materials
2.1. Melt Electrospinning
2.2. Electrospinning of Multicomponent Systems
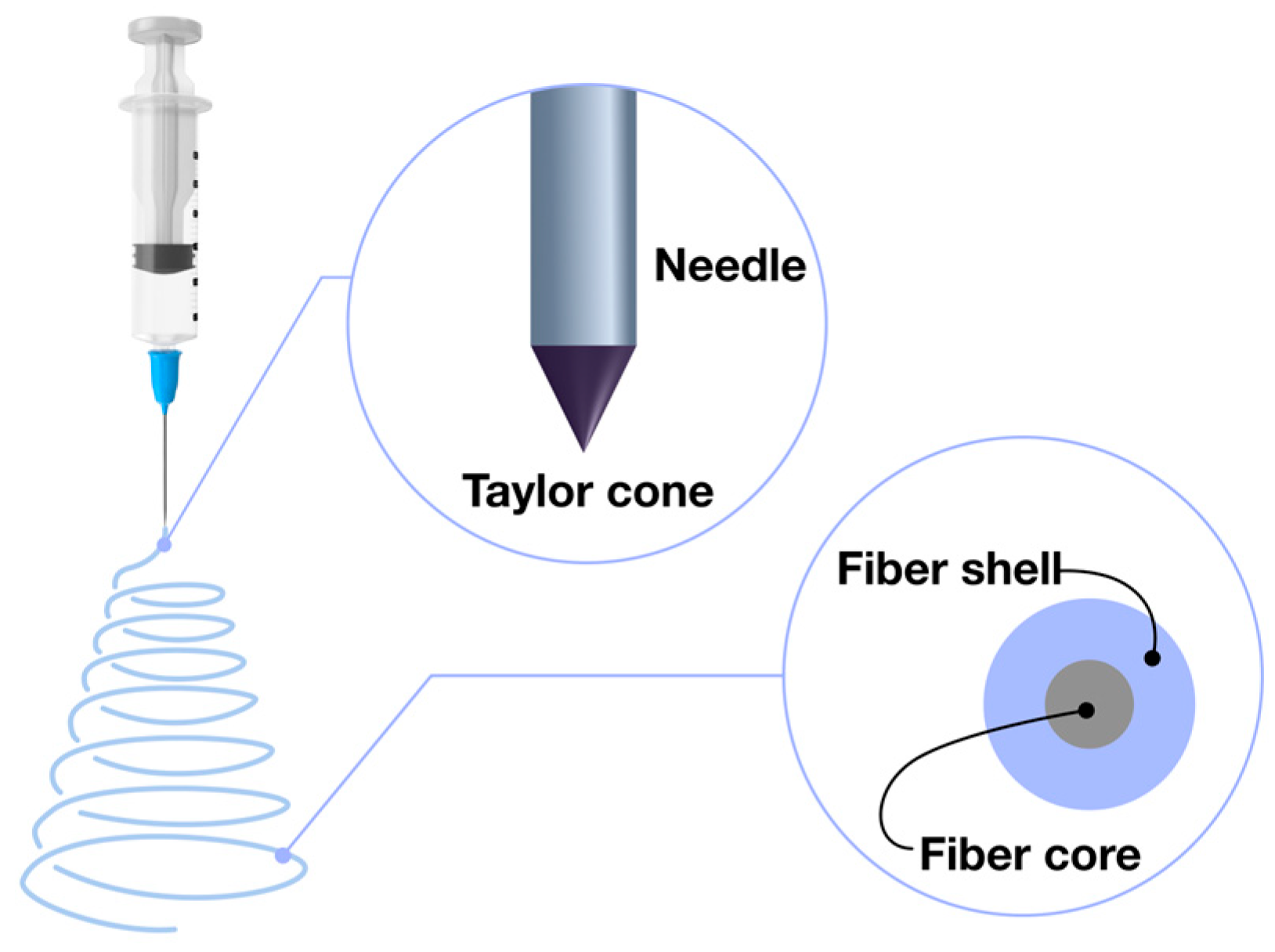
2.3. Coaxial Electrospinning: Advanced Fiber Formation Technique
2.4. Emulsion-Based Electrospinning Techniques
3. Polymers Utilized in Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications
3.1. Applications of Natural and Plant-Based Polymers in Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications
3.1.1. Silk Fibroin
3.1.2. Collagen
3.1.3. Gelatin
3.1.4. Chitosan
3.1.5. Alginate and Its Derivatives
3.2. Applications of Synthetic Polymers in Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering
3.2.1. Polylactic Acid (PLA)
3.2.2. Poly(ε–Caprolactone) (PCL)
3.2.3. Polyamide–6 (PA6)
3.2.4. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
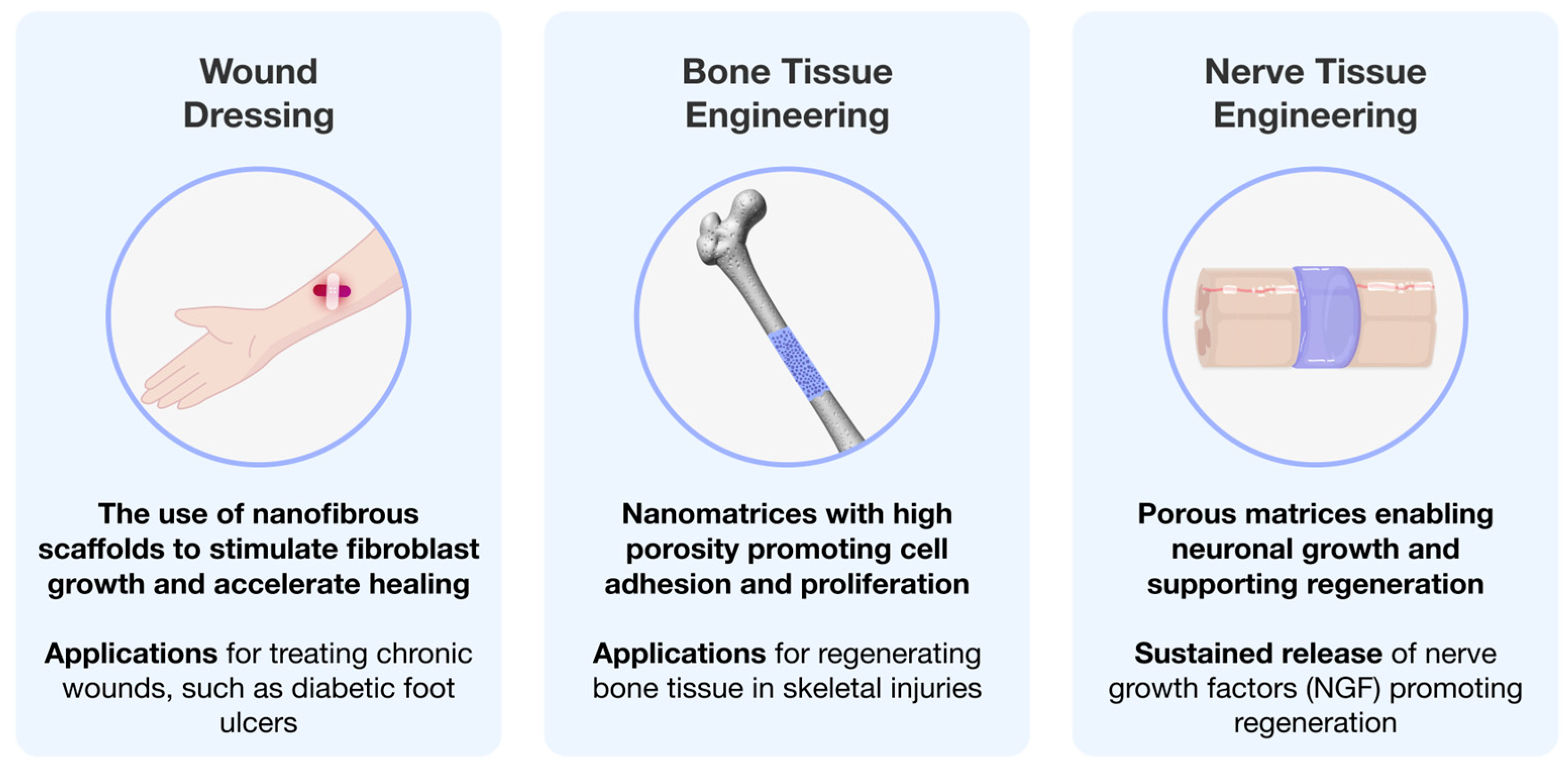
4. Tissue Engineering Using Electrospun Polymeric Matrices
4.1. Wound Healing
4.2. Nerve Tissue Engineering
4.3. Bone Tissue Engineering
5. Challenges and Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooley, J.F. Apparatus for Electrically Dispersing Fluids. U.S. Patent No. 692,631, 4 February 1902. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Cheng, Y.; Niu, X.; Hu, Y. Application of Electrospun Nanofibers in Bone, Cartilage and Osteochondral Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 32, 536–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiffrin, R.; Razak, S.I.A.; Jamaludin, M.I.; Hamzah, A.S.A.; Mazian, M.A.; Jaya, M.A.T.; Nasrullah, M.Z.; Majrashi, M.; Theyab, A.; Aldarmahi, A.A.; et al. Electrospun Nanofiber Composites for Drug Delivery: A Review on Current Progresses. Polymers 2022, 14, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, E.J. Electrospun Biomaterials in the Treatment and Prevention of Scars in Skin Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Recent Advances in Application of Electrospun Nanofiber Materials as Biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretov, E.I.; Zapolotsky, E.N.; Tarkova, A.R.; Prokhorikhin, A.A.; Boykov, A.A.; Malaev, D.U. Electrospinning for the Design of Medical Supplies. Bull. Sib. Med. 2020, 19, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Min, B.M.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. In Vitro Degradation Behavior of Electrospun Polyglycolide, Polylactide, and Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Shin, Y.M.; Terai, H.; Vacanti, J.P. A Biodegradable Nanofiber Scaffold by Electrospinning and Its Potential for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, S.K.; Prasath Mani, M.; Ayyar, M.; Rathanasamy, R. Biomimetic Electrospun Polyurethane Matrix Composites with Tailor Made Properties for Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, L.P.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Macedo, M.; Jardini, A.L.; Maciel Filho, R. Electrospun Polyurethane Membranes for Tissue Engineering Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, M.; Mills, D.K.; Urbanska, A.M.; Saeb, M.R.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, S.A.; Wolfe, P.S.; Garg, K.; McCool, J.M.; Rodriguez, I.A.; Bowlin, G.L. The Use of Natural Polymers in Tissue Engineering: A Focus on Electrospun Extracellular Matrix Analogues. Polymers 2010, 2, 522–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Huang, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Lannutti, J. Improved Cellular Infiltration in Electrospun Fiber via Engineered Porosity. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şimşek, M. Tuning Surface Texture of Electrospun Polycaprolactone Fibers: Effects of Solvent Systems and Relative Humidity. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannutti, J.; Reneker, D.; Ma, T.; Tomasko, D.; Farson, D. Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Y.; Suye, S.I.; Fujita, S. Cell Trapping via Migratory Inhibition within Density-Tuned Electrospun Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 7456–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.J. Drug Delivery Applications of Core-Sheath Nanofibers Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, K.; Gouma, P.; Simon, S. Electrospun Biocomposite Nanofibers for Urea Biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halicka, K.; Cabaj, J. Electrospun Nanofibers for Sensing and Biosensing Applications—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5726–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Bao, T.Q.; Park, I.; Lee, B.T. A Novel Fibrous Scaffold Composed of Electrospun Porous Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 28, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrigo, M.; McArthur, S.L.; Kingshott, P. Electrospun Nanofibers as Dressings for Chronic Wound Care: Advances, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzgo, M.; Mickova, A.; Doupnik, M.; Rampichova, M. Blend Electrospinning, Coaxial Electrospinning, and Emulsion Electrospinning Techniques. In Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics: Challenges, Strategies and Prospects for Novel Carrier Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 325–347. ISBN 9780081021989. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo Bravo, J.M.; Villarreal Gómez, L.J.; Serrano Medina, A. Electrospinning for Drug Delivery Systems: Drug Incorporation Techniques. In Electrospinning—Material, Techniques, and Biomedical Applications; InTech: Bronx, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voniatis, C.; Manikion, K.; Gyulai, G.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A. Synergistic properties of polysuccinimide/poly (lactic acid) co-electrospun and blended-electrospun nanofibers. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoraibi, I.; Alomari, S. Different Methods for Nanofiber Design and Fabrication. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, C.B.; Afghah, F.; Okan, B.S.; Yıldız, M.; Menceloglu, Y.; Culha, M.; Koc, B. Modeling 3D Melt Electrospinning Writing by Response Surface Methodology. Mater. Des. 2018, 148, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Duan, X.P.; Yan, X.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Y.Z. Recent Advances in Melt Electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53400–53414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt Electrospinning Today: An Opportune Time for an Emerging Polymer Process. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 56, 116–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachs-Herrera, A.; Yousefzade, O.; Del Valle, L.J.; Puiggali, J. Melt Electrospinning of Polymers: Blends, Nanocomposites, Additives and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Preparation and Properties of PET/SiO2 Composite Micro/Nanofibers by a Laser Melt-Electrospinning System. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengsawas Surasarang, S.; Keen, J.M.; Huang, S.; Zhang, F.; McGinity, J.W.; Williams, R.O. Hot Melt Extrusion versus Spray Drying: Hot Melt Extrusion Degrades Albendazole. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, E.; Mros, S.; McConnell, M.; Cabral, J.D.; Ali, A. Melt-Electrowriting with Novel Milk Protein/PCL Biomaterials for Skin Regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W.; Dalton, P.D. Melt Electrospinning. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, M.; Siamidi, A.; Kyriakou, S. Electrospinning and Drug Delivery. In Electrospinning and Electrospraying-Techniques and Applications; InTech: Bronx, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, S.; Senthil Ram, T.; Lakshmi, B.S.; Giridev, V.R. Herbal Drug Incorporated Antibacterial Nanofibrous Mat Fabricated by Electrospinning: An Excellent Matrix for Wound Dressings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 2893–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Du, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, D.G.; Bligh, S.W.A. Recent Progress of Electrospun Herbal Medicine Nanofibers. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Song, W.; Xu, L.; Yu, D.G.; Bligh, S.W.A. A Review on Electrospun Poly(Amino Acid) Nanofibers and Their Applications of Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aassar, M.R.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Fouda, M.M.G.; El-Beheri, N.G.; Agwa, M.M. Wound Healing of Nanofiber Comprising Polygalacturonic/Hyaluronic Acid Embedded Silver Nanoparticles: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehetmeyer, G.; Meira, S.; Scheibel, J.; Silva, C.; Rodembusch, F.; Brandelli, A.; Soares, R. Biodegradable and Antimicrobial Films Based on Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Electrospun Fibers. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 3243–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.T.G.; Rempel, S.P.; Agnol, L.D.; Bianchi, O. The Main Blow Spun Polymer Systems: Processing Conditions and Applications. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heseltine, P.L.; Hosken, J.; Agboh, C.; Farrar, D.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Fiber Formation from Silk Fibroin Using Pressurized Gyration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Compound Core-Shell Polymer Nanofibers by Co-Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Huang, C.; Ke, Q.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Mo, X. Preparation and Characterization of Coaxial Electrospun Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Collagen Compound Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalf, A.; Madihally, S.V. Recent Advances in Multiaxial Electrospinning for Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avossa, J.; Herwig, G.; Toncelli, C.; Itel, F.; Rossi, R.M. Electrospinning Based on Benign Solvents: Current Definitions, Implications and Strategies. Green. Chem. 2022, 24, 2347–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.J.; Zhu, K.J. Optimizing Double Emulsion Process to Decrease the Burst Release of Protein from Biodegradable Polymer Microspheres. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinatangkul, N.; Limmatvapirat, C.; Limmatvapirat, S. Electrospun Nanofibers from Natural Polymers and Their Application. Sci. Eng. Health Stud. 2021, 15, 21010005. [Google Scholar]
- Wray, L.S.; Hu, X.; Gallego, J.; Georgakoudi, I.; Omenetto, F.G.; Schmidt, D.; Kaplan, D.L. Effect of Processing on Silk-Based Biomaterials: Reproducibility and Biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 99B, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Baughman, C.B.; Kaplan, D.L. In Vitro Evaluation of Electrospun Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Vascular Cell Growth. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cao, C.; Ma, X.; Lin, J. Electrospinning of Silk Fibroin and Collagen for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y. Silk Fibroin for Vascular Regeneration. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çalamak, S.; Erdoǧdu, C.; Özalp, M.; Ulubayram, K. Silk Fibroin Based Antibacterial Bionanotextiles as Wound Dressing Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.P.; Reagan, M.R.; Bohara, R.A. Silk Fibroin and Silk-Based Biomaterial Derivatives for Ideal Wound Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4613–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.J.; Gogoi, D.; Chutia, J.; Kandimalla, R.; Kalita, S.; Kotoky, J.; Chaudhari, Y.B.; Khan, M.R.; Kalita, K. Controlled Antibiotic-Releasing Antheraea Assama Silk Fibroin Suture for Infection Prevention and Fast Wound Healing. Surgery 2016, 159, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuwalska, A.; Grabska-Zielińska, S.; Sionkowska, A. Chitosan/Silk Fibroin Materials for Biomedical Applications—A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesi, M.; Garcia-Nieto, M.; Guinea, G.V.; Panetsos, F.; Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; González-Nieto, D. Silk Fibroin: An Ancient Material for Repairing the Injured Nervous System. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadpour, S.; Kargozar, S.; Moradi, L.; Ai, A.; Nosrati, H.; Ai, J. Natural Biomacromolecule Based Composite Scaffolds from Silk Fibroin, Gelatin and Chitosan toward Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, M.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Samani, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Kundu, S.C.; Reis, R.L.; Fatahi, Y.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Fibroin/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 68–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Rather, A.H.; Wani, T.U.; Rather, S.; Abdal-hay, A.; Sheikh, F.A. A Comparative Review on Silk Fibroin Nanofibers Encasing the Silver Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents for Wound Healing Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 103914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phamornnak, C.; Han, B.; Spencer, B.F.; Ashton, M.D.; Blanford, C.F.; Hardy, J.G.; Blaker, J.J.; Cartmell, S.H. Instructive Electroactive Electrospun Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Peripheral Nerve Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 141, 213094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoulders, M.; Raines, R. Collagen Structure and Stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.O.; Levine, L.; Drake, M.P.; Rubin, A.L.; Pfahl, D.; Davison, P.F. The antigenicity of tropocollagen. Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol. 1964, 51, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, A.K.; Yannas, I.V.; Bonfield, W. Antigenicity and Immunogenicity of Collagen. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 71, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Singla, A.; Lee, Y. Biomedical Applications of Collagen. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.V.M.; Serricella, P.; Linhares, A.B.R.; Guerdes, R.M.; Borojevic, R.; Rossi, M.A.; Duarte, M.E.L.; Farina, M. Characterization of a Bovine Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4987–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A. Acellular collagen matrix as a possible “off the shelf” biomaterial for urethral repair. Urology 1999, 54, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Raines, R.T. Review Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Wound Healing. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doillon, C.J.; Whyne, C.F.; Brandwein, S.; Silver, F.H. Collagen-based Wound Dressings: Control of the Pore Structure and Morphology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1986, 20, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, D.W. A Review of Collagen and Collagen-Based Wound Dressings. Wounds 2008, 20, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kon, E.; Delcogliano, M.; Filardo, G.; Busacca, M.; Di Martino, A.; Marcacci, M. Novel Nano-Composite Multilayered Biomaterial for Osteochondral Regeneration: A Pilot Clinical Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankajakshan, D.; Voytik-Harbin, S.L.; Nör, J.E.; Bottino, M.C. Injectable Highly Tunable Oligomeric Collagen Matrices for Dental Tissue Regeneration. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, A.B.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Berdeja-Martínez, B.M.; Escamilla-García, M.; Salgado-Cruz, M.P.; Rentería-Ortega, M.; Farrera-Rebollo, R.R.; Vega-Cuellar, M.A.; Calderón-Domínguez, G. PVA-Based Electrospun Biomembranes with Hydrolyzed Collagen and Ethanolic Extract of Hypericum Perforatum for Potential Use as Wound Dressing: Fabrication and Characterization. Polymers 2022, 14, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djagny, K.B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Gelatin: A Valuable Protein for Food and Pharmaceutical Industries: Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 41, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O. Gelatin-Based Nanoparticles as Drug and Gene Delivery Systems: Reviewing Three Decades of Research. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echave, M.C.; Sánchez, P.; Pedraz, J.L.; Orive, G. Progress of Gelatin-Based 3D Approaches for Bone Regeneration. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, A.; Madjd, Z.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Khosrowpour, Z.; Farshi, P.; Eini, L.; Kiani, J.; Seifi, M.; Kundu, S.C.; Ghods, R.; et al. Bioengineering of Fibroblast-Conditioned Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Electrospun Scaffold for Skin Tissue Engineering. Artif. Organs 2022, 46, 1040–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.; Sharma, C.; Purohit, S.D.; Singh, H.; Dinda, A.K.; Potdar, P.D.; Chou, C.F.; Mishra, N.C. Gelatin-Polycaprolactone-Nanohydroxyapatite Electrospun Nanocomposite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; Shafiei, S.S.; Sabouni, F. Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds of Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Reinforced with Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoclay for Nerve Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 28351–28360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Chitosan-Based Materials: Preparation, Modification and Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K. Chitin, Chitosan, Oligosaccharides and Their Derivatives: Biological Activities and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, W.; Arbia, L.; Adour, L.; Amrane, A. Chitin Extraction from Crustacean Shells Using Biological Methods—A Review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavoni, J.M.F.; Luchese, C.L.; Tessaro, I.C. Impact of Acid Type for Chitosan Dissolution on the Characteristics and Biodegradability of Cornstarch/Chitosan Based Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, B.; Owczarek, A.; Nadolna, K.; Sionkowska, A. The Film-Forming Properties of Chitosan with Tannic Acid Addition. Mater. Lett. 2019, 245, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritchenkov, A.S.; Egorov, A.R.; Kurasova, M.N.; Volkova, O.V.; Meledina, T.V.; Lipkan, N.A.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Kurliuk, A.V.; Shakola, T.V.; Dysin, A.P.; et al. Novel Non-Toxic High Efficient Antibacterial Azido Chitosan Derivatives with Potential Application in Food Coatings. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagangadharan, K.; Dhivya, S.; Selvamurugan, N. Chitosan Based Nanofibers in Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Biswas, S.; Nurus Sakib, M.; Rashid, T.U. Chitosan Based Bioactive Materials in Tissue Engineering Applications—A Review. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Qiao, X.; Liu, T.; Sun, K. Silk Fibroin Microfibers and Chitosan Modified Poly (Glycerol Sebacate) Composite Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, V.; Pramanik, K.; Biswas, A. Optimization and Evaluation of Silk Fibroin-Chitosan Freeze-Dried Porous Scaffolds for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Application. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Zandi, M.; Rajabi, S. Tailoring the Gelatin/Chitosan Electrospun Scaffold for Application in Skin Tissue Engineering: An in Vitro Study. Prog. Biomater. 2018, 7, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, D.R.; Biswal, T. Alginate and Its Application to Tissue Engineering. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsan, S.; Franklin, D.S.; Guhanathan, S. Imbibed Salts and PH-Responsive Behaviours of Sodium Alginate Based Eco-Friendly Biopolymeric Hydrogels-A Solventless Approach. MMAIJ 2015, 11, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, F. Alginate Production by Azotobacter Vinelandii. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 1997, 17, 327–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govan, J.R.W.; Fyfe, J.A.M.; Jarman, T.R. Isolation of Alginate-Producing Mutants of Pseudomonas Fluorescens, Pseudomonas Putida and Pseudomonas Mendocina. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1981, 125, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, M.Y.; Shafiq, M.; Li, H.Y.; Hashim, R.; EL-Newehy, M.; EL-Hamshary, H.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Synthesis of Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Its Electrospun Bio-Hybrids with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles to Promote Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajiabbas, M.; Alemzadeh, I.; Vossoughi, M. A Porous Hydrogel-Electrospun Composite Scaffold Made of Oxidized Alginate/Gelatin/Silk Fibroin for Tissue Engineering Application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing Technologies for Poly(Lactic Acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.P.; Tekale, S.U.; Shisodia, S.U.; Totre, J.T.; Domb, A.J. Biomedical Applications of Poly(Lactic Acid). Recent. Pat. Regen. Med. 2014, 4, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Zhang, J.X.; Song, Z.; Varshney, S.K. Thermal Properties of Polylactides: Effect of Molecular Mass and Nature of Lactide Isomer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 95, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Wan, J.; Cui, L. Effect of Mixed Solvents on the Structure and Properties of PLLA/PDLA Electrospun Fibers. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Huang, X.B.; Cai, X.M.; Lu, J.; Yuan, J.; Shen, J. The Influence of Fiber Diameter of Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid) on Drug Delivery. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mele, E. Effect of Antibacterial Plant Extracts on the Morphology of Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid) Fibres. Materials 2018, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; López, J.; López, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Development of Flexible Materials Based on Plasticized Electrospun PLA-PHB Blends: Structural, Thermal, Mechanical and Disintegration Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.; New, J.; Dasari, A.; Yu, S.; Manan, M.A. Surface Morphology of Electrospun PLA Fibers: Mechanisms of Pore Formation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44082–44088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xu, L.; Ahmed, A. Batch Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Porous Polylactic Acid-Based Nanofiber Membranes for Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Ghosh, C.; Hwang, S.G.; Chanunpanich, N.; Park, J.S. Porous Core/Sheath Composite Nanofibers Fabricated by Coaxial Electrospinning as a Potential Mat for Drug Release System. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasola, R.; Thomas, N.L.; Trybala, A.; Georgiadou, S. Electrospun Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Fibres: Effect of Different Solvent Systems on Fibre Morphology and Diameter. Polymer 2014, 55, 4728–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, F.S.; Khoddami, A.; Avinc, O. Poly (Lactic Acid) Nano-Fibers as Drug-Delivery Systems: Opportunities and Challenges. Nanomed. Res. J. 2019, 4, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumine, H.; Sasaki, R.; Yamato, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, H. A Polylactic Acid Non-Woven Nerve Conduit for Facial Nerve Regeneration in Rats. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 8, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, D.; Mauceri, R.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Advance on Resveratrol Application in Bone Regeneration: Progress and Perspectives for Use in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, H.; Azimi, B.; Ismaeilimoghadam, S.; Danti, S. Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Electrospun Fibrous Structures for Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samokhin, Y.; Varava, Y.; Diedkova, K.; Yanko, I.; Husak, Y.; Radwan-Pragłowska, J.; Pogorielova, O.; Janus, Ł.; Pogorielov, M.; Korniienko, V. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Chitosan/Polylactic Acid (CH/PLA) Nanofiber Scaffolds for Biomedical Application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.F.; Andriyana, A.; Muhamad, F.; Ang, B.C. Fabrication of Poly(Lactic Acid)-Cellulose Acetate Core-Shell Electrospun Fibers with Improved Tensile Strength and Biocompatibility for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Qiao, T.; Rawlinson, S.C.F.; Almeida, F.V.; Li, W.Q.; Cattell, M.; Barber, A.H. 3D Imaging of Cell Interactions with Electrospun PLGA Nanofiber Membranes for Bone Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2015, 27, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, A.L.; Ekinci, D.; Lendlein, A. The Contemporary Role of ε-Caprolactone Chemistry to Create Advanced Polymer Architectures. Polymer 2013, 54, 4333–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppalli, R.; Marega, C.; Marigo, A.; Bajgai, M.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Causin, V. Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Filled with Electrospun Nylon Fibres: A Model for a Facile Composite Fabrication. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, E.R.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Chellappan, V.; Verma, N.K.; Chinnappan, A.; Neisiany, R.E.; Amuthavalli, K.; Poh, Z.S.; Wong, B.H.S.; Dubey, N.; et al. Electrospun Aligned PCL/Gelatin Scaffolds Mimicking the Skin ECM for Effective Antimicrobial Wound Dressings. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie Karizmeh, M.; Poursamar, S.A.; Kefayat, A.; Farahbakhsh, Z.; Rafienia, M. An in Vitro and in Vivo Study of PCL/Chitosan Electrospun Mat on Polyurethane/Propolis Foam as a Bilayer Wound Dressing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 135, 112667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Xia, D.; Liang, C.; Li, N.; Xu, R. Synergistic Effect of Co-Delivering Ciprofloxacin and Tetracycline Hydrochloride for Promoted Wound Healing by Utilizing Coaxial PCL/Gelatin Nanofiber Membrane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitxelena-Iribarren, O.; Riera-Pons, M.; Pereira, S.; Calero-Castro, F.J.; Castillo Tuñón, J.M.; Padillo-Ruiz, J.; Mujika, M.; Arana, S. Drug-Loaded PCL Electrospun Nanofibers as Anti-Pancreatic Cancer Drug Delivery Systems. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7763–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroosh, H.J.; Dong, Y.; Jasim, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Morphological Structures and Drug Release Effect of Multiple Electrospun Nanofibre Membrane Systems Based on PLA, PCL, and PCL/Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites. J. Nanomater. 2022, 1, 5190163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskitoros-Togay, M.; Bulbul, Y.E.; Tort, S.; Demirtaş Korkmaz, F.; Acartürk, F.; Dilsiz, N. Fabrication of Doxycycline-Loaded Electrospun PCL/PEO Membranes for a Potential Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbasizadeh, B.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Kobarfard, F.; Jaafari, M.R.; Hashemi, A.; Farhadnejad, H.; Feyzi-barnaji, B. Electrospun Doxorubicin-Loaded PEO/PCL Core/Sheath Nanofibers for Chemopreventive Action against Breast Cancer Cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, Z.; Mohebbi-Kalhori, D.; Afarani, M.S. Engineered Electrospun Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Octacalcium Phosphate (OCP) Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 81, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Ullah, I.; Cheng, P. Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers Using H2O as Benign Additive in Polycaprolactone/Glacial Acetic Acid Solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsogiannis, K.A.G.; Vladisavljević, G.T.; Georgiadou, S. Porous Electrospun Polycaprolactone (PCL) Fibres by Phase Separation. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 69, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Callanan, A. Influence of Surface Topography on PCL Electrospun Scaffolds for Liver Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 8081–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, P.; Harlin, A. Parameter Study of Electrospinning of Polyamide-6. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 3067–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, S.Y.; Lin, H.S.; Cheng, P.J.; Huang, C.L.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, C. Rheological Aspect on Electrospinning of Polyamide 6 Solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3619–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, M.; Qin, M.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lian, X.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; et al. Electrospun Polyamide-6/Chitosan Nanofibers Reinforced Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polyamide-6 Composite Bilayered Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatma Nur, P.; Pınar, T.; Uğur, P.; Ayşenur, Y.; Murat, E.; Kenan, Y. Fabrication of Polyamide 6/Honey/Boric Acid Mats by Electrohydrodynamic Processes for Wound Healing Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Preparation of Polyamide 6/CeO2 Composite Nanofibers through Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 2019, 2494586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.S.; Sandeep, K.; Singh, M.; Singh, G.P.; Lee, J.K.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kalia, V.C. Biotechnological Application of Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Their Composites as Anti-Microbials Agents. In Biotechnological Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtuvia, V.; Villegas, P.; Fuentes, S.; González, M.; Seeger, M. Burkholderia Xenovorans LB400 Possesses a Functional Polyhydroxyalkanoate Anabolic Pathway Encoded by the Pha Genes and Synthesizes Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) under Nitrogen-Limiting Conditions. Int. Microbiol. 2018, 21, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Cao, R.; Hua, D.H.; Li, P. Study of Class i and Class III Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Synthases with Substrates Containing a Modified Side Chain. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Sharma, S.K. A Handbook of Applied Biopolymer Technology: Synthesis, Degradation and Applications; RSC Green Chemistry: College Park, MD, USA, 2011; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Q.; Wu, Q. The Application of Polyhydroxyalkanoates as Tissue Engineering Materials. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6565–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.; Keshavarz, T.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Roy, I. Medium Chain Length Polyhydroxyalkanoates, Promising New Biomedical Materials for the Future. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2011, 72, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudesh, K.; Lee, Y.-F.; Sridewi, N.; Ramanathan, S. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters and Drug Loading on Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Nanofibers for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biotechnol. Wellness Ind. 2016, 4, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cicek, N.; Levin, D.B.; Logsetty, S.; Liu, S. Bacteria-Triggered Release of a Potent Biocide from Core-Shell Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-Based Nanofibers for Wound Dressing Applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandayuthapani, B.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Polymeric Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering Application: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 2011, 290602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdil, D.; Aydin, H.M. Polymers for Medical and Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 1793–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Chantre, C.O.; Gannon, A.R.; Lind, J.U.; Campbell, P.H.; Grevesse, T.; O’Connor, B.B.; Parker, K.K. Soy Protein/Cellulose Nanofiber Scaffolds Mimicking Skin Extracellular Matrix for Enhanced Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, D.; Janani, G.; Chakraborty, B.; Nandi, S.K.; Mandal, B.B. Functionalized PVA-Silk Blended Nanofibrous Mats Promote Diabetic Wound Healing via Regulation of Extracellular Matrix and Tissue Remodelling. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e1559–e1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Tian, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Ding, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of Nerve Growth Factor Encapsulated Aligned Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Nanofibers and Their Assessment as a Potential Neural Tissue Engineering Scaffold. Polymers 2016, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijeńska, E.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Swieszkowski, W.; Kurzydlowski, K.J.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Bio-Composite P(LLA-CL)/Collagen I/Collagen III Scaffolds for Nerve Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100B, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Tang, D.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Wei, W.; Gong, R.H.; Li, J. Heterogeneous Porous PLLA/PCL Fibrous Scaffold for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethinam, S.; Basaran, B.; Vijayan, S.; Mert, A.; Bayraktar, O.; Aruni, A.W. Electrospun Nano-Bio Membrane for Bone Tissue Engineering Application—A New Approach. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 249, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Wang, B.; Yu, D.G.; Zhu, Y. Integrating Chinese herbs and western medicine for new wound dressings through handheld electrospin-ning. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersanli, C.; Voidarou, C.; Tzora, A.; Fotou, K.; Zeugolis, D.I.; Skoufos, I. Electrospun Scaffolds as Antimicrobial Herbal Extract Delivery Vehicles for Wound Healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, S. Electrospun herbal extract-loaded poly (3-hydroxy butyric acid-co-3-hydroxy valeric acid) nanofiber mats as potential wound dressing materials. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Doostan, M.; Khoshnevisan, K.; Baharifar, H.; Maleki, S.A.; Fatahi, M.A. Zingiber officinale and thymus vulgaris extracts co-loaded polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan electrospun nanofibers for tackling infection and wound healing promotion. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, R.; Andra, S.; Balu, S.K.; Damiri, F.; Krishnan, G.; Andiappan, M.; Muthalagu, M.; Berrada, M. Flavonoids, phenolics, and tannins loaded polycaprolactone nanofibers (NF) for wound dressing applications. Results Mater. 2023, 18, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owida, H.; Moh’d, B.A.; Al-Naimat, F. Fabricating orientated nanofibrous meshes with a bespoke ultra-cost-effective electrospinning machine. HardwareX 2023, 16, e00483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switz, A.; Mishra, A.; Jabech, K.; Prasad, A. Affordable lab-scale electrospinning setup with interchangeable collectors for targeted fiber formation. HardwareX 2024, 17, e00501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
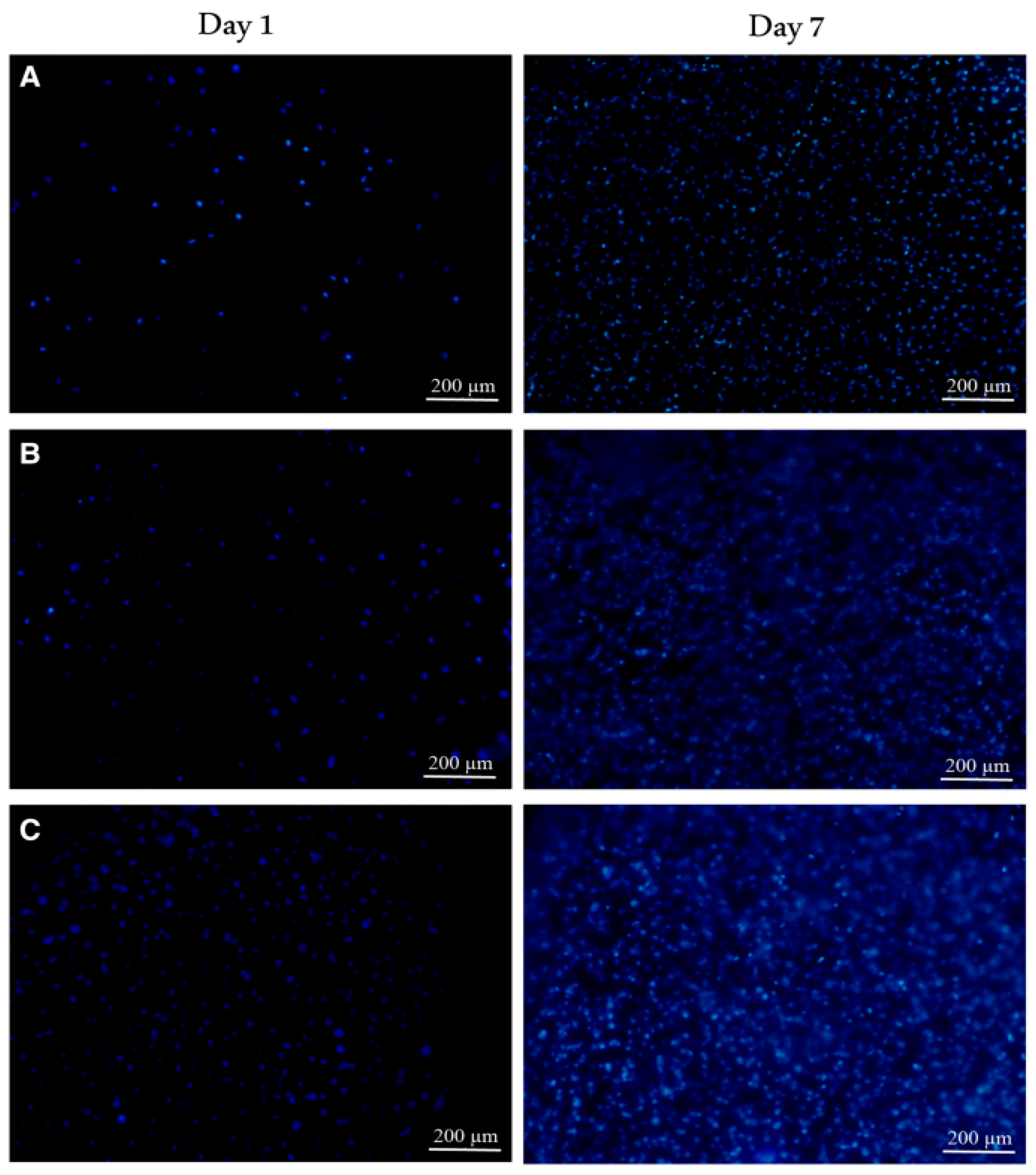
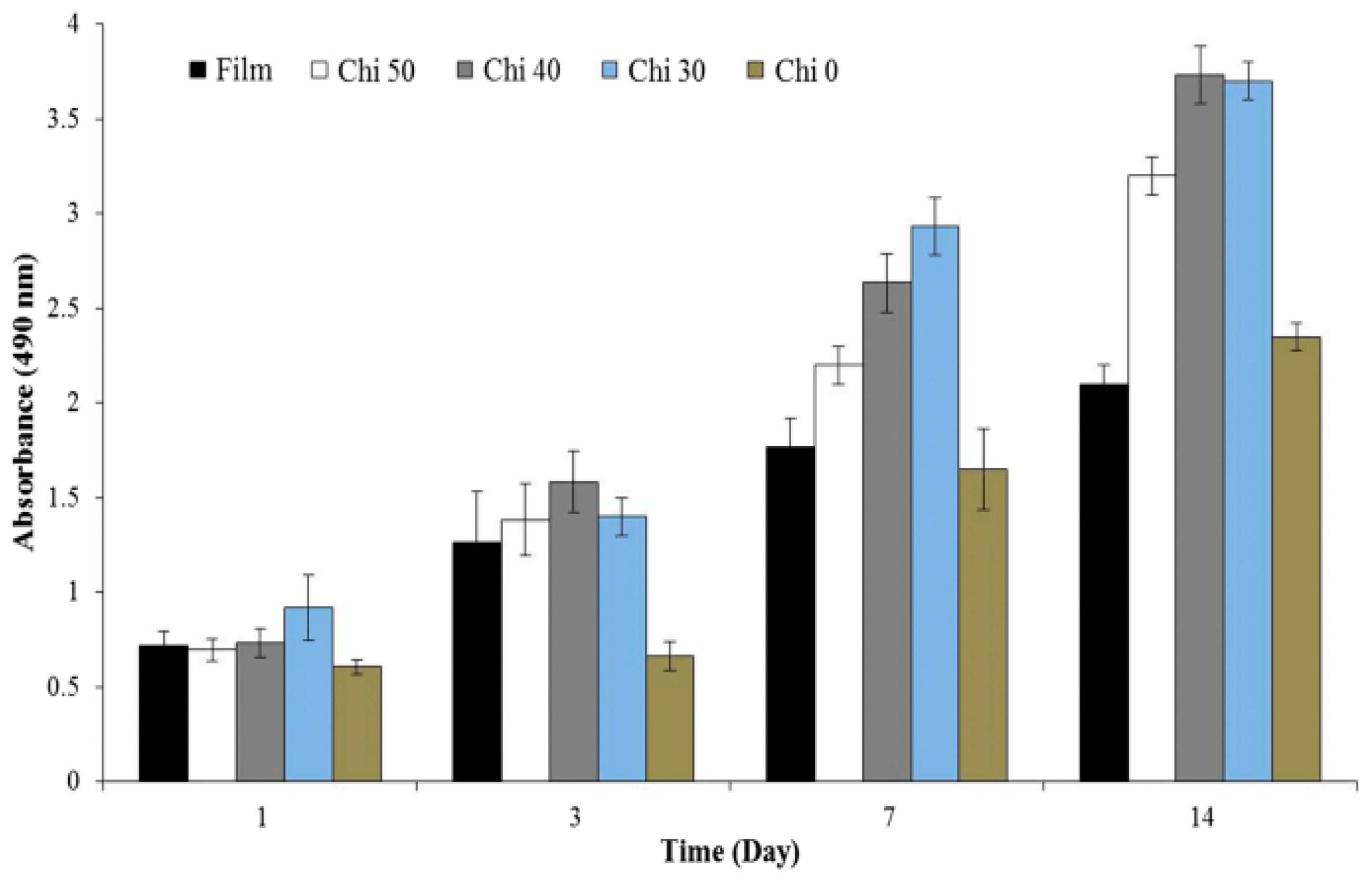
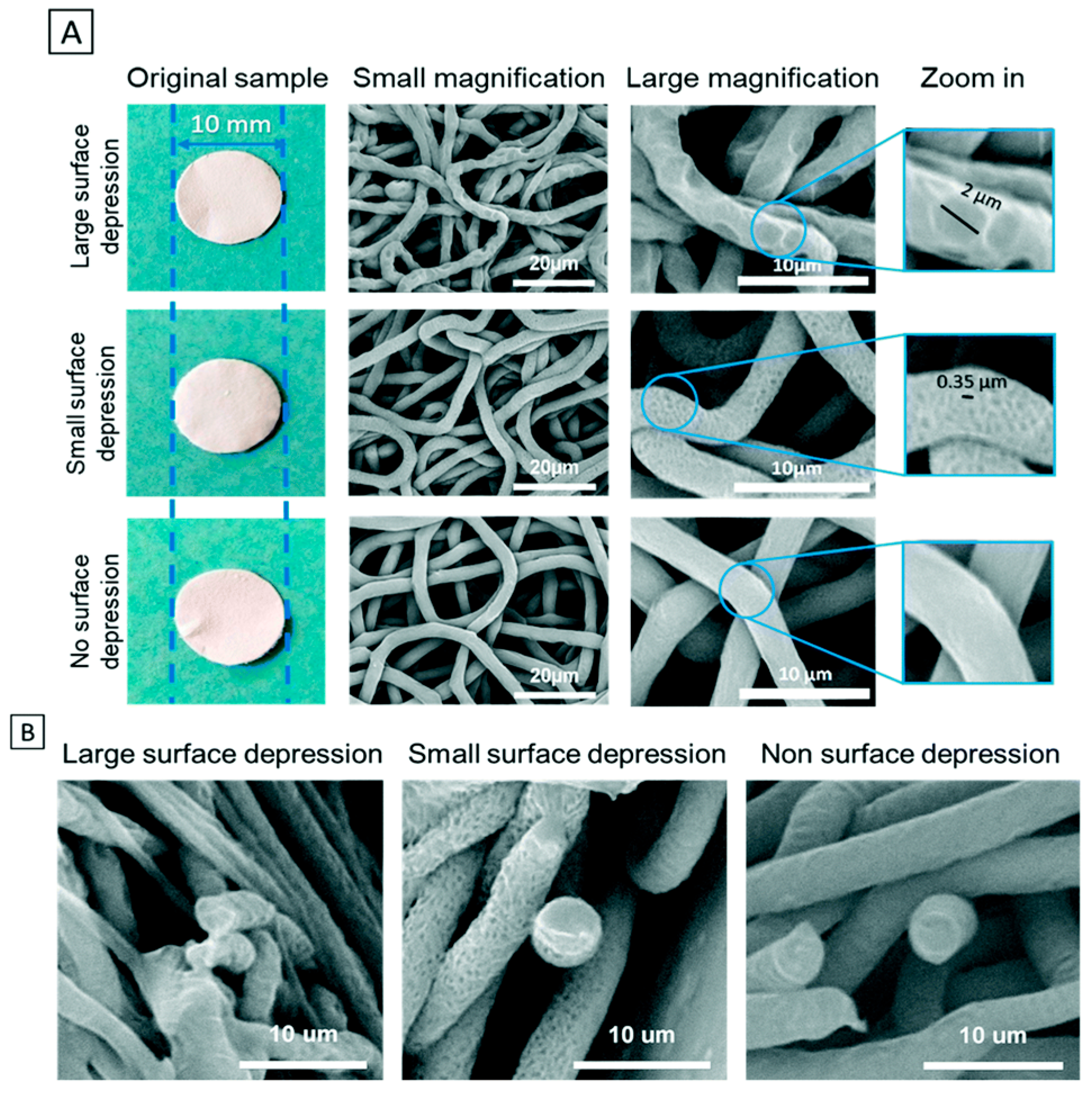

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsareva, A.D.; Shtol, V.S.; Klinov, D.V.; Ivanov, D.A. Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications: An Overview of Material Fabrication Techniques. Surfaces 2025, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8010007
Tsareva AD, Shtol VS, Klinov DV, Ivanov DA. Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications: An Overview of Material Fabrication Techniques. Surfaces. 2025; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsareva, Anastasiia D., Valeriia S. Shtol, Dmitriy V. Klinov, and Dimitri A. Ivanov. 2025. "Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications: An Overview of Material Fabrication Techniques" Surfaces 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8010007
APA StyleTsareva, A. D., Shtol, V. S., Klinov, D. V., & Ivanov, D. A. (2025). Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications: An Overview of Material Fabrication Techniques. Surfaces, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8010007






