Eco-Friendly Cement Mortar with Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Upcycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical Methods
2.2. Sludge Preparation
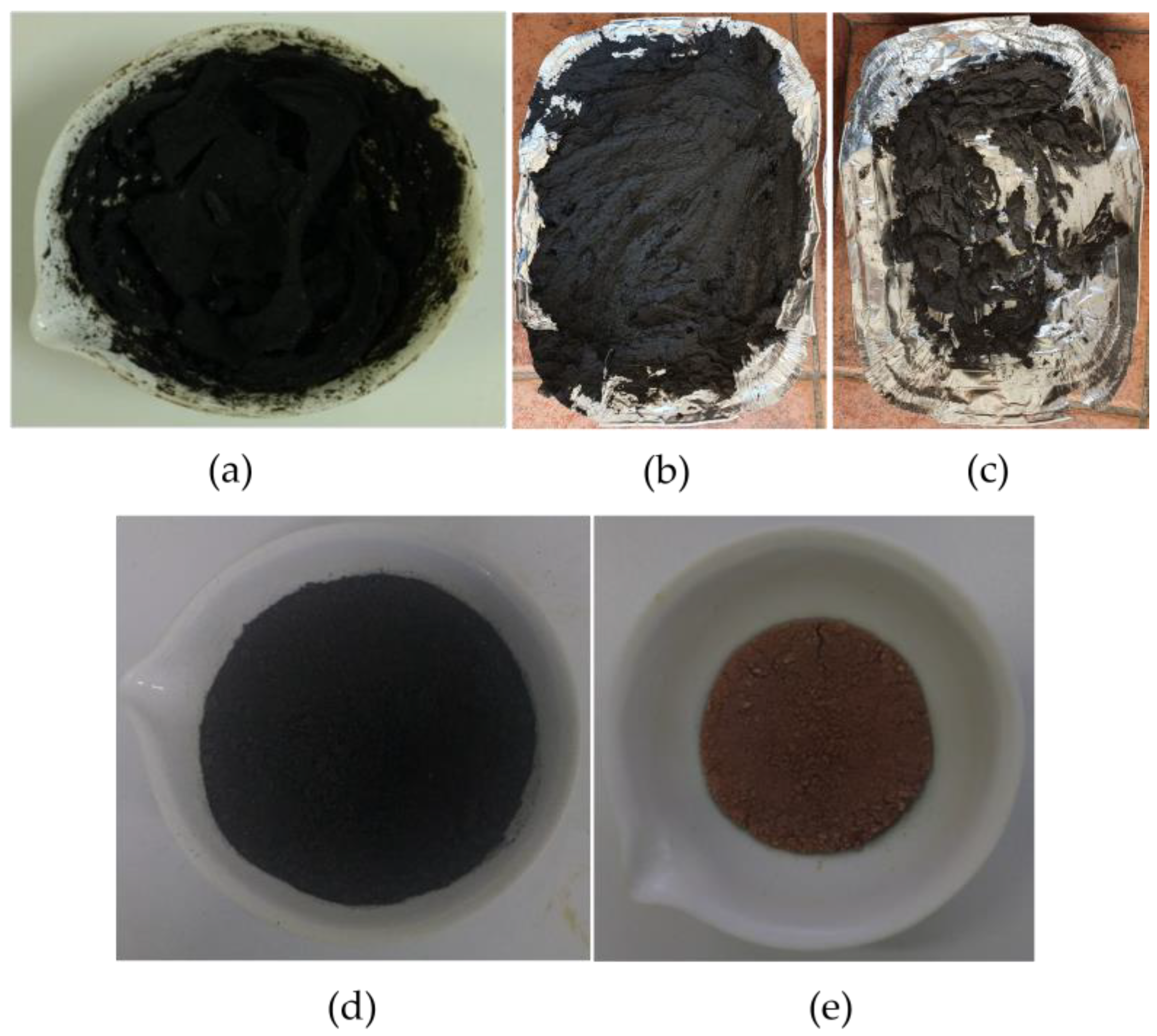
2.2.1. Method 1: Dry Sludge
2.2.2. Method 2 and 3: Dry Sludge in the Sun
2.2.3. Method 4: Incineration
2.3. Mortar Specimens
2.4. Mechanical Tests
2.5. Economic Viability
3. Results
3.1. Sludge Preparation
3.2. Mechanical Tests
4. Discussion
4.1. Dry Sludge (M1–M2)
4.2. Sludge Ash (M4)
4.3. Economic Viability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sistema FIEP (Sistema Federação das Indústrias do Estado do Paraná). Circular Economy Elements (Elementos de Economia Circular); Sistema FIEP: Curitiba, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AdP (Águas de Portugal). Sustainability Reports (Relatórios de Sustentabilidade); Águas de Portugal: Águas Santas, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Águas do Algarve. Do Lamas de ETAR; Águas do Algarve: Faro, Portugal. Available online: https://www.aguasdoalgarve.pt/content/lamas-de-etar (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- AdP (Águas de Portugal). Annual Report and Accounts. 2020. Available online: https://www.resultadosadp2020.pt/en/ (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Gherghel, A.; Teodosiu, C.; De Gisi, S. A review on wastewater sludge valorisation and its challenges in the context of circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.d.C.; Zhou, J.L.; Li, W.; Long, G. Progress in manufacture and properties of construction materials incorporating water treatment sludge: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczek, L.; Cieślik, B.M.; Konieczka, P. The potential of raw sewage sludge in construction industry—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgal, F.P.; Jalali, S. Eco-efficient concrete: The future of the ready-mixed concrete industry (Betão eco-eficiente: O futuro da indústria do betão pronto). Betão 2011, 26, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, R.T. Características de Pastas de Cimento Portland com Adição de Cinza de Lodo de Eta. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, Santa Maria, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, J.M.; Roessler, J.G.; Ferraro, C.C.; Deford, H.D.; Townsend, T.G. A review of waste products utilized as supplements to Portland cement in concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.T. Concrete folder features with Portland WTP sludge ash addition. In Proceedings of the 5th Fórum Internacional Ecoinovar, Santa Maria, Brazil, 9–12 August 2016; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Isaia, G.C. Materiais de Construção Civil e Princípios de Ciência e Engenharia de Materiais, 3rd ed.; Isaia, G.C., Ed.; Arte Interativa: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- EN 998-1:2017; Specification for Mortar for Masonry; Part 1: Rendering and Plastering Mortar. (CEN) European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; p. 25.
- EN 197-1:2012; Cement—Part 1: Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. (CEN) European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2012; p. 39.
- EN 13139:2005; Aggregates for Mortar. (CEN) European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005; p. 45.
- Jamshidi, A.; Kurumisawa, K.; Nawa, T.; Hamzah, M.O. Analysis of structural performance and sustainability of airport concrete pavements incorporating blast furnace slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaish, A.B.M.A.; Breesem, K.M.; Abood, M.M. Influence of pre-treated alum sludge on properties of high-strength self-compacting concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Esteves, A.M.; Carvalho, M.; Machado, Â.; Correira, E. Incoporation of sludge from a water treatment plant in cement mortars. In Proceedings of the International RILEM Conference on the Use of Recycled Mareirals in Buildings and Structures, Barcelona, Spain, 8–11 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, D.J.R. Análise da Viabilidade Técnica da Utilização de Lama de ETA para Substituição Parcial de Cimento na Produção de Betão. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Samolada, M.C.; Zabaniotou, A.A. Comparative assessment of municipal sewage sludge incineration, gasification and pyrolysis for a sustainable sludge-to-energy management in Greece. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, C.J.; Dhir, R.K.; Ghataora, G.S.; West, R.P. Sewage sludge ash characteristics and potential for use in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrapa. Manual of Soil Analysis Methods (Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo); no. 1; Embrapa: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Clescerl, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, T.F.; Fernandes, D.M.; Guerrini, A.; Bogiani, J.C.; Backes, C. Comparison between methods of organic matter determination in soil samples based on volume or mass. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2011, 36, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakic, D. Environmental evaluation of concrete with sewage sludge ash based on LCA. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2018, 16, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.M.; Quaresma, D.S.; Santos, L.S.; Pereira, L.F.S.; Neves, A.S.S. Process development for the production of synthetic aggregate from flying ash and biomass in fixed-bed vertical reactor (Desenvolvimento de processo para produção de agregado sintético a partir de cinza volante e biomassa em reator vertical de leito fixo). In Proceedings of the Anais do I Congresso Brasil Norte de Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental, Belém, PA, Brasil, 24–26 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Awere, E.; Bonoli, A.; Obeng, P.A. Solids-liquid separation and solar drying of palm oil mill wastewater sludge: Potential for sludge reuse. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2020, 2, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, S.E.; Gastaldini, A.L.G.; Cocco, M.; Jahn, S.L.; Terra, L.M. Synergic effects of the substitution of Portland cement for water treatment plant sludge ash and ground limestone: Technical and economic evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.C.A.; Silva, C.A.; de Oliveira Dias, B. Characterization of the organic matrix of residues of diverse origins (Caracterização da matriz orgânica de resíduos de origens diversificadas). Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2008, 32, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 5738; Concreto—Procedimento para Moldagem e Cura de Corpos de Prova (Concrete—Procedure for Molding and Curing Concrete Test Specimens). Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015; pp. 1–12.
- EN 1015-11:2019; Methods of Test for Mortar for Masonry; Part 11: Determination of Flexural and Compressive Strength of Hardened Mortar. (CEN) European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; p. 18.
- ECRA. Improving Energy Efficiency: The Main Daily Objective; NEWSLETTER 1/2020; European Cement Research Academy: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schnell, M.; Horst, T.; Quicker, P. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, W.; Hong, J. Life-cycle environmental and economic assessment of sewage sludge treatment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 67, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, M.; Olofsson, M.; Pettersson, G.J.; Zetterlund, H. Environmental and economic assessment of sewage sludge handling options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 41, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, S.A.C. Study of Mortars with Sludge Introduction from WWTP (ESTUDO de Argamassas com Introdução de Lamas de ETAR). Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Durante Ingunza, M.d.P.; Camarini, G.; Silva da Costa, F.M. Performance of mortars with the addition of septic tank sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoalino, M.P.; da Silva Alfaya, A.A.; Santos Yabe, M.J.; Nobre Gimenez, S.M. Incorporation of residual CuSO4 in mortar, as a final disposal method (Incorporação de CuSO4 residual em argamassa, como método de disposição final). Quim. Nova 2006, 29, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochez, E.; Nijs, W. Cement production. Energy Technol. Syst. Anal. Program 2010, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Process | Electricity Demand |
|---|---|
| Cement production | 102 kWh t−1 cement [33] |
| Drum or fluidized bed dryers | 0.07 kWh kg−1H2O [34] |
| Drying operation | 39 kWh t−1 dry sludge [35] |
| Dry sludge and incineration | 275 kWh t−1 dry sludge −1024.5 kWh t−1 dry sludge (recovery) [35] |
| Co-incineration | −250 kWh t−1 of dry sludge (recovery) [36] |
| Treatment | Average (MPa) | Concentration (%) | Average (Mpa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M3 | 10.81 a | 10 | 12.52 a |
| M1 | 11.00 a | 5 | 14.50 ab |
| M2 | 12.26 a | 7 | 14.80 ab |
| M4 | 23.70 b | 3 | 16.02 ab |
| 0 | 22.45 b |
| Energy Saving (kWh t−1 Cement) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Electricity Demand | 3% | 10% |
| Drum or fluidized bed dryers | 0.07 kWh kg−1H2O [34] | 2.6 | 8.6 |
| Drying operation | 39 kWh t−1 dry sludge [35] | 1.9 | 6.3 |
| Sun-drying | 0 | 3.1 | 10.2 |
| Dry sludge and incineration | −749.5 kWh t−1 dry sludge [35] | 25.5 | 85.2 |
| Co-incineration | −250 kWh t−1 dry sludge [36] | 10.6 | 35.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grabowski, T.T.; Pietrobelli, J.M.T.d.A.; Martins, R.J.E. Eco-Friendly Cement Mortar with Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Upcycling. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 961-972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030048
Grabowski TT, Pietrobelli JMTdA, Martins RJE. Eco-Friendly Cement Mortar with Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Upcycling. Clean Technologies. 2023; 5(3):961-972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrabowski, Thais Theomaris, Juliana Martins Teixeira de Abreu Pietrobelli, and Ramiro José Espinheira Martins. 2023. "Eco-Friendly Cement Mortar with Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Upcycling" Clean Technologies 5, no. 3: 961-972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030048
APA StyleGrabowski, T. T., Pietrobelli, J. M. T. d. A., & Martins, R. J. E. (2023). Eco-Friendly Cement Mortar with Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Upcycling. Clean Technologies, 5(3), 961-972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5030048






