Electrochemical Treatment of Arsenic in Drinking Water: Effect of Initial As3+ Concentration, pH, and Conductivity on the Kinetics of Oxidation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Solutions
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
- Initial As3+ concentration: 500 µg L−1–5000 µg L−1
- Conductivity: 700 µS cm−1–2000 µS cm−1
- pH: 5–10
2.3. Sampling Activities and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
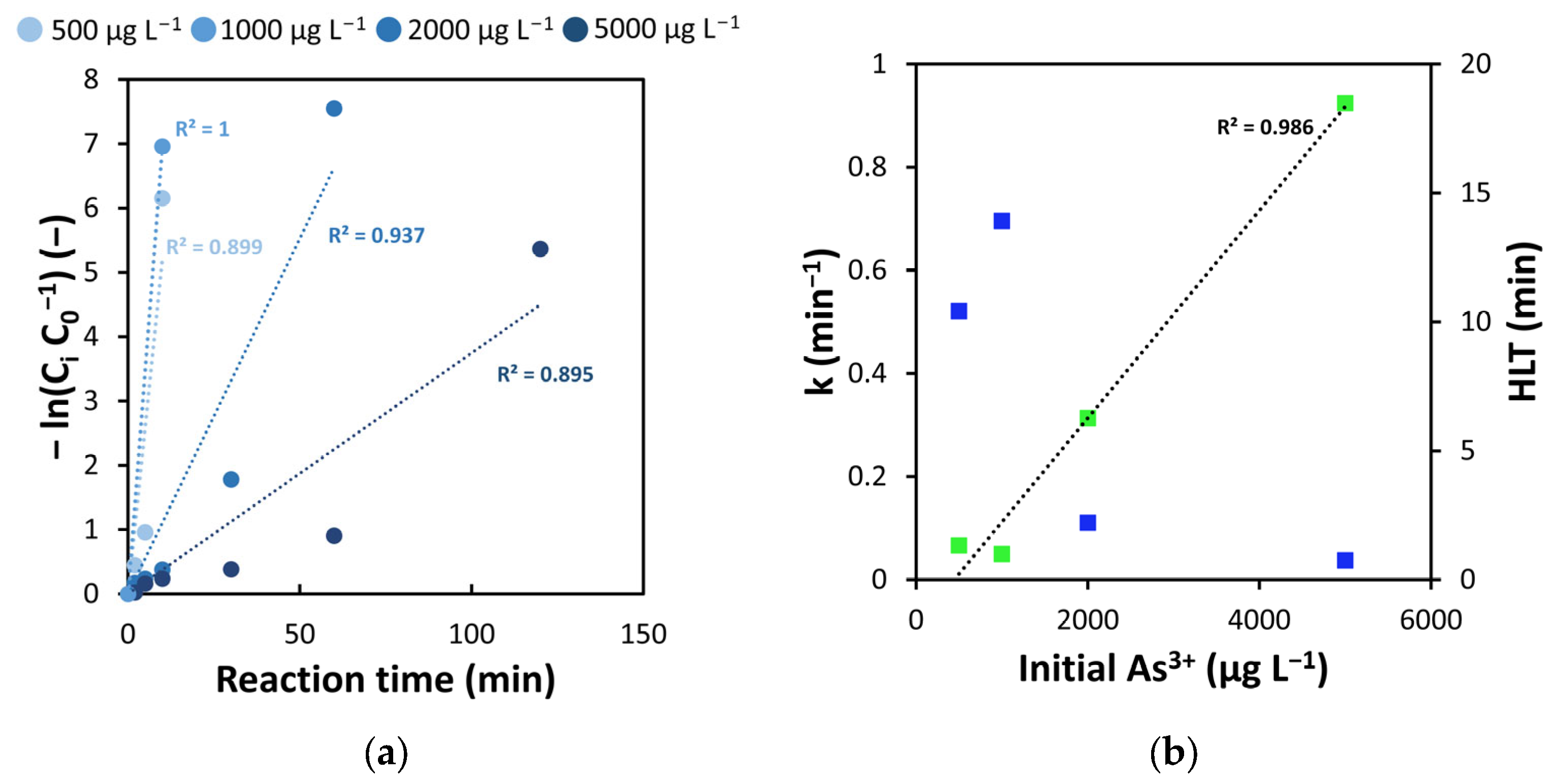
3.1. Influence of Initial As3+ Concentration
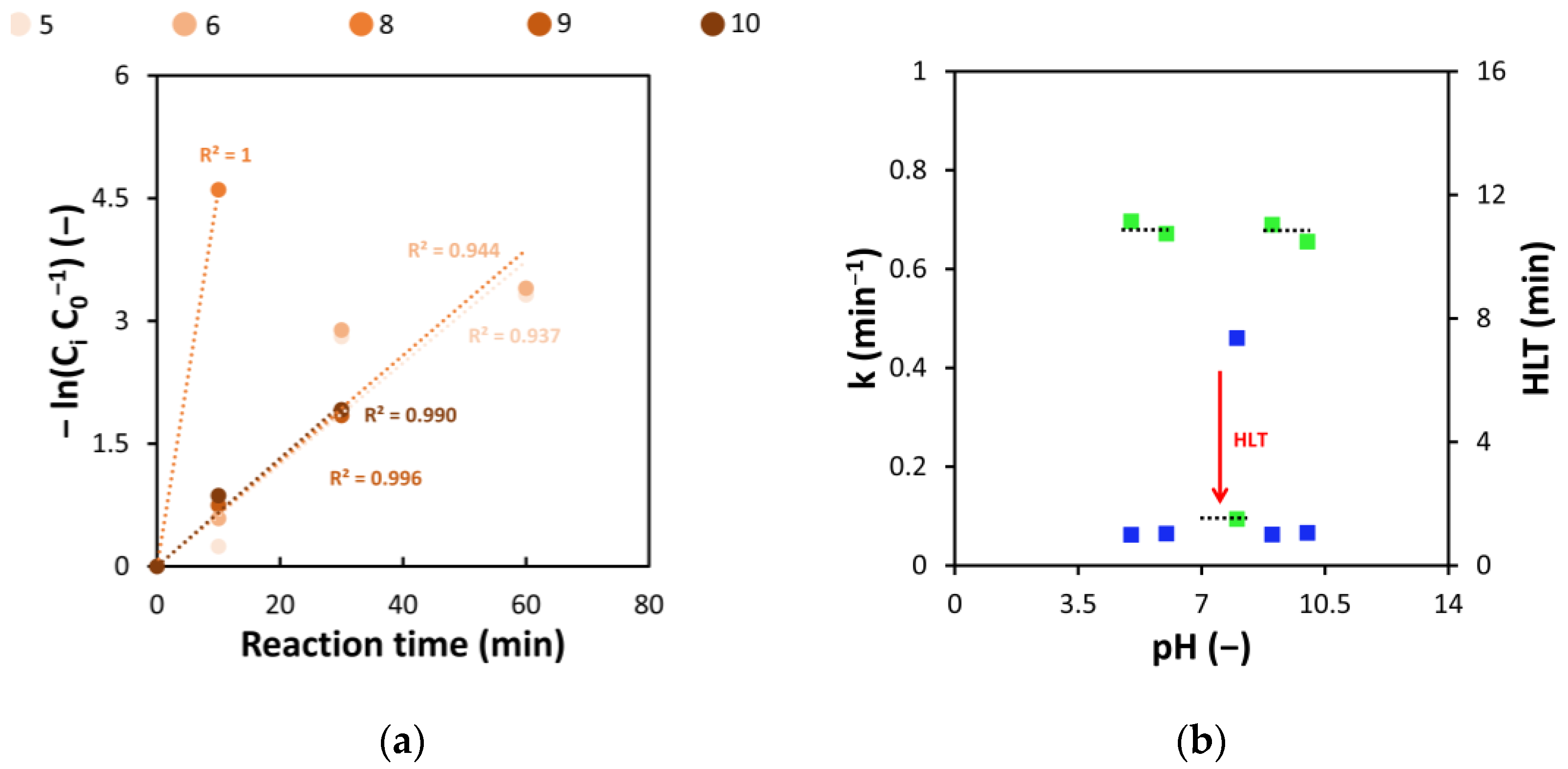
3.2. Influence of Initial PH
3.3. Influence of Initial Conductivity
3.4. Limitations of the Study and Tips for Future Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Upadhyay, S.K.; Devi, P.; Kumar, V.; Pathak, H.K.; Kumar, P.; Rajput, V.D.; Dwivedi, P. Efficient Removal of Total Arsenic (As3+/5+) from Contaminated Water by Novel Strategies Mediated Iron and Plant Extract Activated Waste Flowers of Marigold. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeloju, S.B.; Khan, S.; Patti, A.F. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater and Its Implications for Drinking Water Quality and Human Health in Under-Developed Countries and Remote Communities—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissen, M.; Frimmel, F.H. Arsenic—A Review. Part I: Occurrence, Toxicity, Speciation, Mobility. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2003, 31, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, J.S.; Zheng, Q.; Le, X.C. Arsenic in Drinking Water—Recent Examples and Updates from Southeast Asia. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Gutiérrez, M. Geogenic Arsenic in Groundwater: Challenges, Gaps, and Future Directions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 27, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.K.; Shukla, A.; Yadav, P.; Srivastava, S. A Review of Arsenic in Crops, Vegetables, Animals and Food Products. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Naidu, R. Consumption of Arsenic and Other Elements from Vegetables and Drinking Water from an Arsenic-Contaminated Area of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.-L.; Liu, H.-G.; Wang, Y.-Z. Arsenic Concentrations and Associated Health Risks in Laccaria Mushrooms from Yunnan (SW China). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 164, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Arsenic. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Khosravi-Darani, K.; Rehman, Y.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Kokkinos, E.; Zouboulis, A. Arsenic Exposure via Contaminated Water and Food Sources. Water 2022, 14, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; First Addendum to the Fourth Edition; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Council. EU Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; European Council: Bruxelles, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament. EU Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption (Recast); European Parliament: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Bhattacharya, P. Arsenic in Drinking Water: Is 10 Μg/L a Safe Limit? Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Patel, M.; Singh, P.; Bundschuh, J.; Pittman, C.U.; Trakal, L.; Mohan, D. Emerging Technologies for Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Rural and Peri-Urban Areas: Methods, Experience from, and Options for Latin America. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.-S.; Ujang, Z.; Le-Clech, P. Arsenic Removal Technologies for Drinking Water Treatment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Qu, J. Review on Heterogeneous Oxidation and Adsorption for Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 110, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhar, R.; Derco, J.; Čacho, F. An Overview of Main Arsenic Removal Technologies. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2018, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alka, S.; Shahir, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Ndejiko, M.J.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Manan, F.A. Arsenic Removal Technologies and Future Trends: A Mini Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, J. Arsenic Removal during Conventional Aluminium-Based Drinking-Water Treatment. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.S.; Srivastava, V.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Kumar, M.S. Detoxification of Water and Wastewater by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hasan, H.; Muhammad, M.H.; Ismail, N.I. A Review of Biological Drinking Water Treatment Technologies for Contaminants Removal from Polluted Water Resources. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, D.; Viraraghavan, T. Biological Filtration for Removal of Arsenic from Drinking Water. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1956–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorlini, S.; Gialdini, F.; Stefan, M. UV/H2O2 Oxidation of Arsenic and Terbuthylazine in Drinking Water. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, M.A.; Fuentes, R.; Thiam, A.; Salazar, R. Arsenic and Fluoride Removal by Electrocoagulation Process: A General Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Guzmán, M.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Irigoyen-Campuzano, J.R.; Torres-Castañón, L.A.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L. Simultaneous Removal of Fluoride and Arsenic from Well Water by Electrocoagulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrose, S.E.; Bandaru, S.R.S.; Delaire, C.; van Genuchten, C.M.; Dutta, A.; DebSarkar, A.; Orr, C.; Roy, J.; Das, A.; Gadgil, A.J. Electro-Chemical Arsenic Remediation: Field Trials in West Bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syam Babu, D.; Nidheesh, P.V. A Review on Electrochemical Treatment of Arsenic from Aqueous Medium. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2021, 208, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Simultaneous Removal of Arsenite and Fluoride via an Integrated Electro-Oxidation and Electrocoagulation Process. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkkä, H.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Recent Developments of Electro-Oxidation in Water Treatment—A Review. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 754, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for Wastewater Treatment: A General Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, Z.; Sorlini, S.; Buchheit, D. Treatment of Arsenic Containing Drinking Waters by Electrochemical Oxidation and Reverse Osmosis. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference METEAU, Cost 637, Kristianstad, Sweden, 13–15 October 2010; pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarova, Z. Removal of Toxic Metals from Drinking Water: A Review. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference METEAU, Cost 637, Antalya, Turkey, 24–26 October 2007; pp. 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Biesold, G.M.; Sewell, C.D.; Hao, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Lai, Y.; Lin, Z. Recent Advances in Silicon-Based Electrodes: From Fundamental Research toward Practical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Kong, W.; Ma, H. Electrochemical Treatment of Paper Mill Wastewater Using Three-Dimensional Electrodes with Ti/Co/SnO2-Sb2O5 Anode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacasa, E.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Fernández, F.J. Electro-Oxidation of As(III) with Dimensionally-Stable and Conductive-Diamond Anodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203–204, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Rashed, A.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Nagao, Y.; Hasnat, M.A. Electrochemical Oxidation of As(III) on Pd Immobilized Pt Surface: Kinetics and Sensing Performance. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8071–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Removal of Arsenite by Simultaneous Electro-Oxidation and Electro-Coagulation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, J.; Rivas, B.L. Arsenic Extraction from Aqueous Solution: Electrochemical Oxidation Combined with Ultrafiltration Membranes and Water-Soluble Polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Syam Babu, D.; Dasgupta, B.; Behara, P.; Ramasamy, B.; Suresh Kumar, M. Treatment of Arsenite-Contaminated Water by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 2418–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippoliti, D.; Santelli, E.; de Sario, M.; Scortichini, M.; Davoli, M.; Michelozzi, P. Arsenic in Drinking Water and Mortality for Cancer and Chronic Diseases in Central Italy, 1990-2010. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Charlet, L. A Review of Arsenic Presence in China Drinking Water. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, T.J.; Chen, A.S.C.; Wang, L. Arsenic Species in Drinking Water Wells in the USA with High Arsenic Concentrations. Water Res. 2014, 48, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuigan, C.F.; Hamula, C.L.A.; Huang, S.; Gabos, S.; Le, X.C. A Review on Arsenic Concentrations in Canadian Drinking Water. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmipathiraj, P.; Prabhakar, S.; Raju, G.B. Studies on the Electrochemical Decontamination of Wastewater Containing Arsenic. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J. Electrocatalytical Oxidation of Arsenite by Reduced Graphene Oxide via In-Situ Electrocatalytic Generation of H2O2. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, B.Z.; Boncukcuoglu, R.; Yilmaz, A.E.; Fil, B.A. Effect of Some Operational Parameters on the Arsenic Removal by Electrocoagulation Using Iron Electrodes. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, P.; Dubey, B.K.; Gupta, A.K. Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment by Electrochemical Oxidation: Drawbacks, Challenges and Future Scope. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 250–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ün, Ü.T.; Koparal, A.S.; Ögütveren, Ü.B.; Durucan, A. Electrochemical Process for the Treatment of Drinking Water. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Lebik-Elhadi, H.; Frontistis, Z.; Ait-Amar, H.; Amrani, S.; Mantzavinos, D. Electrochemical Oxidation of Pesticide Thiamethoxam on Boron Doped Diamond Anode: Role of Operating Parameters and Matrix Effect. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, S.; Muthuchamy, M. Electrochemical Oxidation of Paracetamol in Water by Graphite Anode: Effect of PH, Electrolyte Concentration and Current Density. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7358–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Dai, Q.; Ma, X. Electrochemical Oxidation of Acid Orange 7 Azo Dye Using a PbO2 Electrode: Parameter Optimization, Reaction Mechanism and Toxicity Evaluation. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Pepping, T.J.; Banerji, T.; Chaudhari, S.; Giammar, D.E. Effects of Water Chemistry on Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water by Electrocoagulation. Water Res. 2011, 45, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa, Z.H.; Othman, M.R.; Abdullah, M.P. Electrochemical Oxidation of Landfill Leachate: Investigation of Operational Parameters and Kinetics Using Graphite-PVC Composite Electrode as Anode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Concentration ± C.I. (mg L−1) | Parameter | Concentration ± C.I. (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium | 0.015 ± 0.003 | Molybdenum | 0.0016 ± 0.005 |
| Calcium | 80.46 ± 1.2 | Sodium | 14.21 ± 1.8 |
| Cadmium | <0.001 | Nickel | 0.0008 ± 0.0001 |
| Chromium | 0.0003 ± 0.0001 | Lead | 0.0010 ± 0.002 |
| Copper | 0.0003 ± 0.0001 | Zinc | 0.0251 ± 0.007 |
| Iron | 0.0078 ± 0.0010 | Fluoride | <0.1 |
| Potassium | 1.276 ± 0.3 | Chloride | 35.6 ± 1.1 |
| Lithium | 0.0044 ± 0.001 | Nitrate | 34.8 ± 3.4 |
| Magnesium | 31.86 ± 2.7 | Sulphates | 101 ± 9.2 |
| Manganese | <0.001 | HCO3− | 280 ± 12.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorlini, S.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Lazarova, Z.; Collivignarelli, M.C. Electrochemical Treatment of Arsenic in Drinking Water: Effect of Initial As3+ Concentration, pH, and Conductivity on the Kinetics of Oxidation. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 203-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5010012
Sorlini S, Carnevale Miino M, Lazarova Z, Collivignarelli MC. Electrochemical Treatment of Arsenic in Drinking Water: Effect of Initial As3+ Concentration, pH, and Conductivity on the Kinetics of Oxidation. Clean Technologies. 2023; 5(1):203-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorlini, Sabrina, Marco Carnevale Miino, Zdravka Lazarova, and Maria Cristina Collivignarelli. 2023. "Electrochemical Treatment of Arsenic in Drinking Water: Effect of Initial As3+ Concentration, pH, and Conductivity on the Kinetics of Oxidation" Clean Technologies 5, no. 1: 203-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5010012
APA StyleSorlini, S., Carnevale Miino, M., Lazarova, Z., & Collivignarelli, M. C. (2023). Electrochemical Treatment of Arsenic in Drinking Water: Effect of Initial As3+ Concentration, pH, and Conductivity on the Kinetics of Oxidation. Clean Technologies, 5(1), 203-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol5010012









