Iron and Magnesium Impregnation of Avocado Seed Biochar for Aqueous Phosphate Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar Production
2.2. Metal-Loaded Biochar Preparation
2.3. Biochar Characterization
2.4. Initial pH Effect on Phosphate Adsorption
2.5. Phosphate Adsorption Isotherm
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochar Characterization
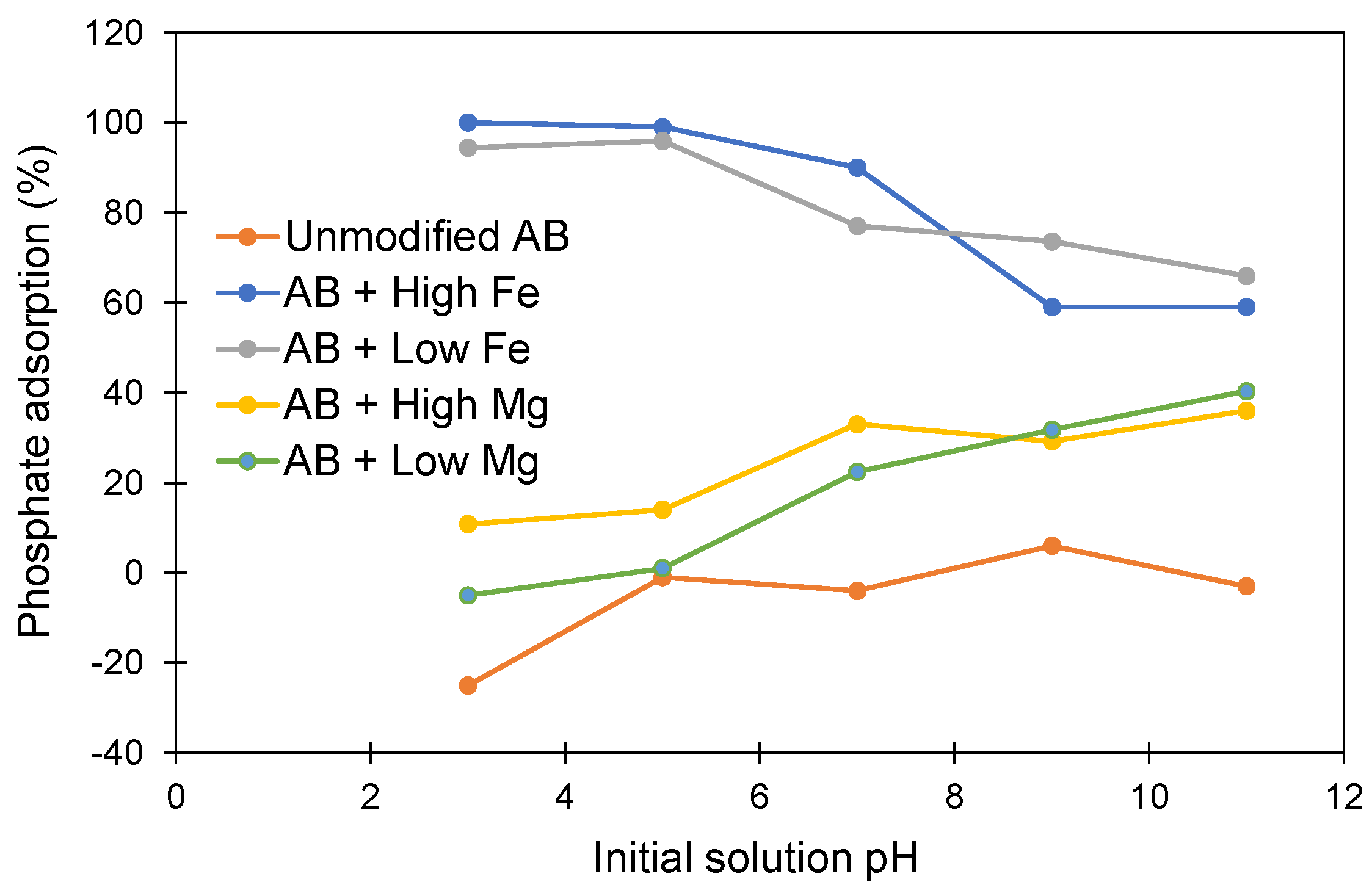
3.2. Intial pH Effect on Phosphate Adsorption
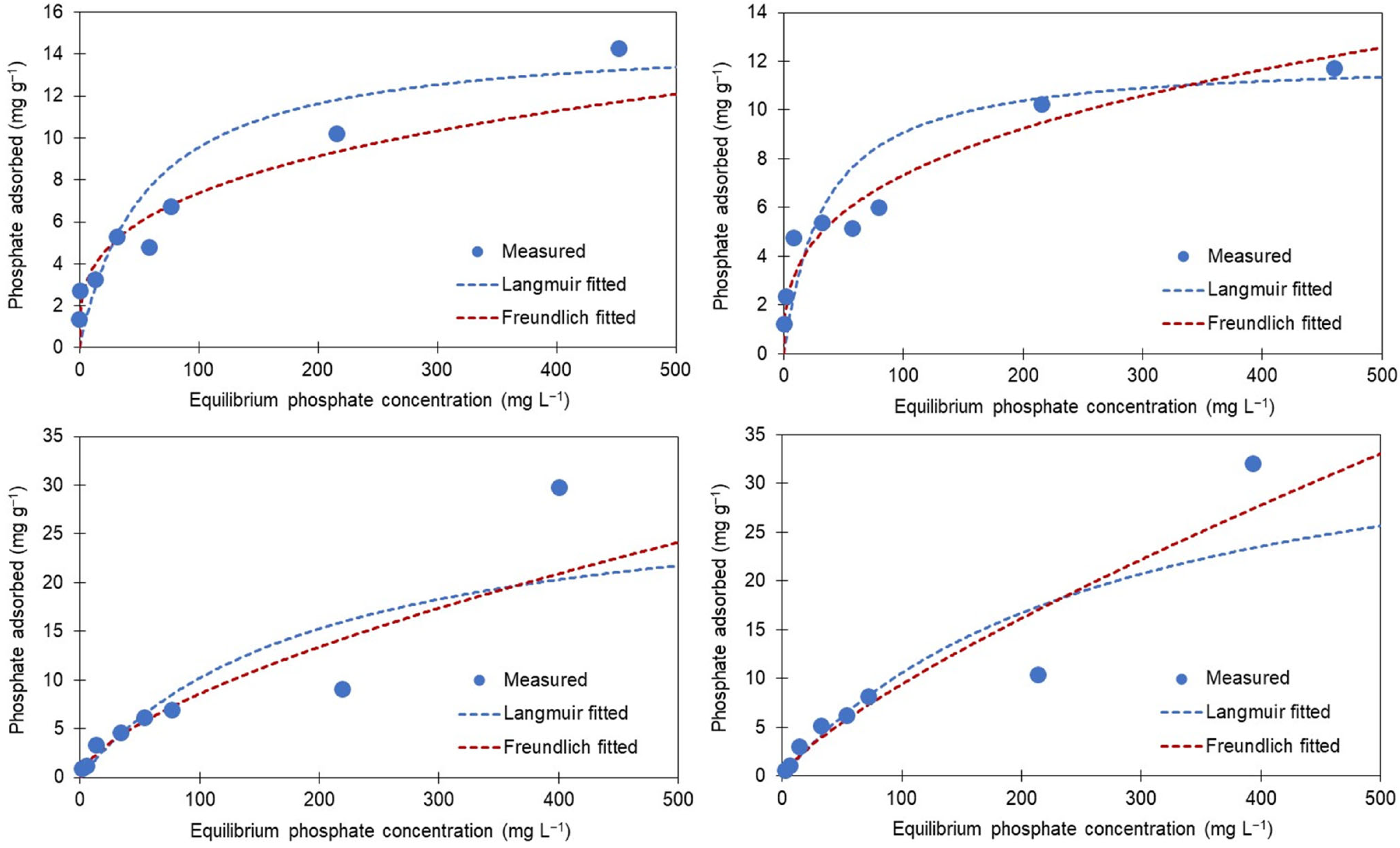
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharpley, A. Managing Agricultural Phosphorus to Minimize Water Quality Impacts. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D. Phosphorus: A Rate Limiting Nutrient in Surface Waters. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.R. Eutrophication of Aquatic Ecosystems: Bistability and Soil Phosphorus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10002–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litke, D.W. Review of Phosphorus Control Measures in the United States and Their Effects on Water Quality; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1999.
- Bunce, J.T.; Ndam, E.; Ofiteru, I.D.; Moore, A.; Graham, D.W. A Review of Phosphorus Removal Technologies and Their Applicability to Small-Scale Domestic Wastewater Treatment Systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vikrant, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Tsang, Y.F.; Giri, B.S.; Singh, R.S. Engineered/Designer Biochar for the Removal of Phosphate in Water and Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1242–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Mckay, G.; Kochkodan, V.; Atieh, M.A.; Al-Ansari, T. A State of the Art Review on Phosphate Removal from Water by Biochars. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Kochkodan, V.; Subeh, M.; Mckay, G.; Atieh, M.; Al-Ansari, T. Phosphate Removal from Synthetic and Treated Sewage Effluent by Carbide Derive Carbon. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauda, J.K.; Safferman, S.I.; Ghane, E. Adsorption Media for the Removal of Soluble Phosphorus from Subsurface Drainage Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, M.; Rodriguez, R.; Contrino, D.; Swenson, J.; Mazyck, D.W.; Suau, S. Impact of Inherent Magnesium in Biochar for Phosphate Removal from Reclaimed Water Streams. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 148, 04021085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireles, S.; Parsons, J.; Trad, T.; Cheng, C.-L.; Kang, J. Lead Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Biochars Derived from Corn Stover, Orange Peel, and Pistachio Shell. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 5817–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, D.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. Preparation and Reactivation of Magnetic Biochar by Molten Salt Method: Relevant Performance for Chlorine-Containing Pesticides Abatement. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizmur, T.; Fresno, T.; Akgül, G.; Frost, H.; Moreno-Jiménez, E. Biochar Modification to Enhance Sorption of Inorganics from Water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thines, K.R.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mubarak, N.M.; Ruthiraan, M. Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar from Agricultural Waste Biomass to Enhancing Route for Waste Water and Polymer Application: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.-S.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, X.-F.; Yuan, J.-P.; Bai, A.-Y.; Zhou, J.-B. Preconcentration and Determination of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Environmental Water Samples by Solid-Phase Microextraction with Fe3O4-Coated Bamboo Charcoal Fibers Prior to Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 769, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, B.-M.; Kim, Y.; Han, J.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, J.; Park, C.M. Preparation of Activated Biochar-Supported Magnetite Composite for Adsorption of Polychlorinated Phenols from Aqueous Solutions. Water 2019, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, L.; Liang, Q.; Wang, F. Mechanisms That Control the Adsorption–Desorption Behavior of Phosphate on Magnetite Nanoparticles: The Role of Particle Size and Surface Chemistry Characteristics. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Ge, W.; Liu, L.; Qiu, G. Preparation, Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of MgO-Loaded Biochar in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Luo, W.; Sun, J.; Xu, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Yao, F.; Wang, D.; et al. Effectiveness and Mechanisms of Phosphate Adsorption on Iron-Modified Biochars Derived from Waste Activated Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Cao, X.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Yang, L. Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by Biochar Derived from Anaerobically Digested Sugar Beet Tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Y. Application of Magnesium Modified Corn Biochar for Phosphorus Removal and Recovery from Swine Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9217–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, J.; Yang, L. Engineered Biochar Reclaiming Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions: Mechanisms and Potential Application as a Slow-Release Fertilizer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8700–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vargas, M.C.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Castro, E. Avocado-Derived Biomass as a Source of Bioenergy and Bioproducts. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, P.; Mireles, S.; Pereira, E.; Cheng, C.-L.; Kang, J.J. Effects of Biochar Production Methods and Biomass Types on Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, T.; Schultz, J.; Khan, M.; Zanoelo, E.; Mangrich, A.; Araújo, B.; Navickiene, S.; Romão, L. Using Magnetized (Fe3O4/Biochar Nanocomposites) and Activated Biochar as Adsorbents to Remove Two Neuro-Active Pesticides from Waters. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, Z.; Lv, S. A Novel Magnetic Biochar Efficiently Sorbs Organic Pollutants and Phosphate. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomin, O.; Yazdani, M.R. Production and Characterization of Porous Magnetic Biochar: Before and after Phosphate Adsorption Insights. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanithi, R.; Ok, Y.S.; Dharmarajan, R.; Ahmad, M.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Naidu, R. Sorption, Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Phosphate Sorption onto Soybean Stover Derived Biochar. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essington, M.E. Soil and Water Chemistry: An Integrative Approach, 2nd ed.; First Issued in Paperback; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-03-209869-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-12-656446-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.-K.; Shim, T.; Kim, Y.-S.; Hyun, S.; Ryu, C.; Park, Y.-K.; Jung, J. Characterization of Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solution by Biochar Produced from a Giant Miscanthus at Different Pyrolytic Temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eljamal, O.; Eljamal, R.; Maamoun, I.; Khalil, A.M.E.; Shubair, T.; Falyouna, O.; Sugihara, Y. Efficient Treatment of Ammonia-Nitrogen Contaminated Waters by Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Zeolite Composite. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maamoun, I.; Bensaida, K.; Eljamal, R.; Falyouna, O.; Tanaka, K.; Tosco, T.; Sugihara, Y.; Eljamal, O. Rapid and Efficient Chromium (VI) Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Nickel Hydroxide Nanoplates (NNiHs). J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 358, 119216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.-S.; Lee, Y.; Musa, A.; Salmah, A.; Zamri, I. Use of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Enhancement of Biosensor Response to the Herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid. Sensors 2008, 8, 5775–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiyas, A.P.A.; Vinod, E.M.; Joseph, J.; Ganesan, R.; Pandey, R.K. Dependence of PH and Surfactant Effect in the Synthesis of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles and Its Properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Ni, F.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ao, T.; Chen, W. Synthesis of Magnesium Modified Biochar for Removing Copper, Lead and Cadmium in Single and Binary Systems from Aqueous Solutions: Adsorption Mechanism. Water 2021, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, W.; Jansson, S.; Mašek, O. Unexplored Potential of Novel Biochar-Ash Composites for Use as Organo-Mineral Fertilizers. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sima, J.; Zhao, L.; Mašek, O.; Cao, X. Indispensable Role of Biochar-Inherent Mineral Constituents in Its Environmental Applications: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ajmal, Z.; Muhmood, A.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. Probing the Efficiency of Magnetically Modified Biomass-Derived Biochar for Effective Phosphate Removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Jiao, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, G.; Li, G. Synthesis of a Novel Magnetic Caragana Korshinskii Biochar/Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide Composite and Its Strong Adsorption of Phosphate in Aqueous Solutions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18641–18651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karunanayake, A.G.; Navarathna, C.M.; Gunatilake, S.R.; Crowley, M.; Anderson, R.; Mohan, D.; Perez, F.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Dispersed on Douglas Fir Biochar for Phosphate Sorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3467–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U. Cadmium and Lead Remediation Using Magnetic Oak Wood and Oak Bark Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.A.; Zhu, J.; Muhammad, N.; Sheng, T.; Xu, X. Effect of Synthesis Methods on Magnetic Kans Grass Biochar for Enhanced As(III, V) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 71, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic Molecular Structure of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahir, M.H.; Rahman, M.M.; Irshad, K.; Rahman, M.M. Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Materials for Solar Energy Storage: MgO and Mg(OH)2 Mixed with Polyethylene Glycol. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchimiya, M.; Wartelle, L.H.; Klasson, K.T.; Fortier, C.A.; Lima, I.M. Influence of Pyrolysis Temperature on Biochar Property and Function as a Heavy Metal Sorbent in Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2501–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Sorption and Leaching of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Phosphate in a Sandy Soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Tan, X.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. Biochar Synthesized via Pyrolysis of Broussonetia Papyrifera Leaves: Mechanisms and Potential Applications for Phosphate Removal. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6565–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milonjić, S.K.; Kopečni, M.M.; Ilić, Z.E. The Point of Zero Charge and Adsorption Properties of Natural Magnetite. J. Radioanal. Chem. 1983, 78, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.X.; Wang, L. Adsorption of Dyes Using Magnesium Hydroxide-Modified Diatomite. Desalination Water Treat. 2009, 8, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, X.; Huang, T.; Lv, B. Synthesis of Fe/Mg-Biochar Nanocomposites for Phosphate Removal. Materials 2020, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; He, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, Y. Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by a Novel Mg(OH)2/ZrO2 Composite: Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 561, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, S.; Zhou, J. Magnetic Fe0/Iron Oxide-Coated Diatomite as a Highly Efficient Adsorbent for Recovering Phosphorus from Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xian, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Qi, H.; Ma, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Adsorption Characteristics of Pb(II) Using Biochar Derived from Spent Mushroom Substrate. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alves, B.S.Q.; Fernandes, L.A.; Southard, R.J. Biochar-Cadmium Retention and Its Effects after Aging with Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2). Heliyon 2021, 7, e08476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshgar, S.; Buttafava, A.; Capsoni, D.; Callegari, A.; Capodaglio, A. Impact of PH and Ionic Molar Ratios on Phosphorous Forms Precipitation and Recovery from Different Wastewater Sludges. Resources 2018, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
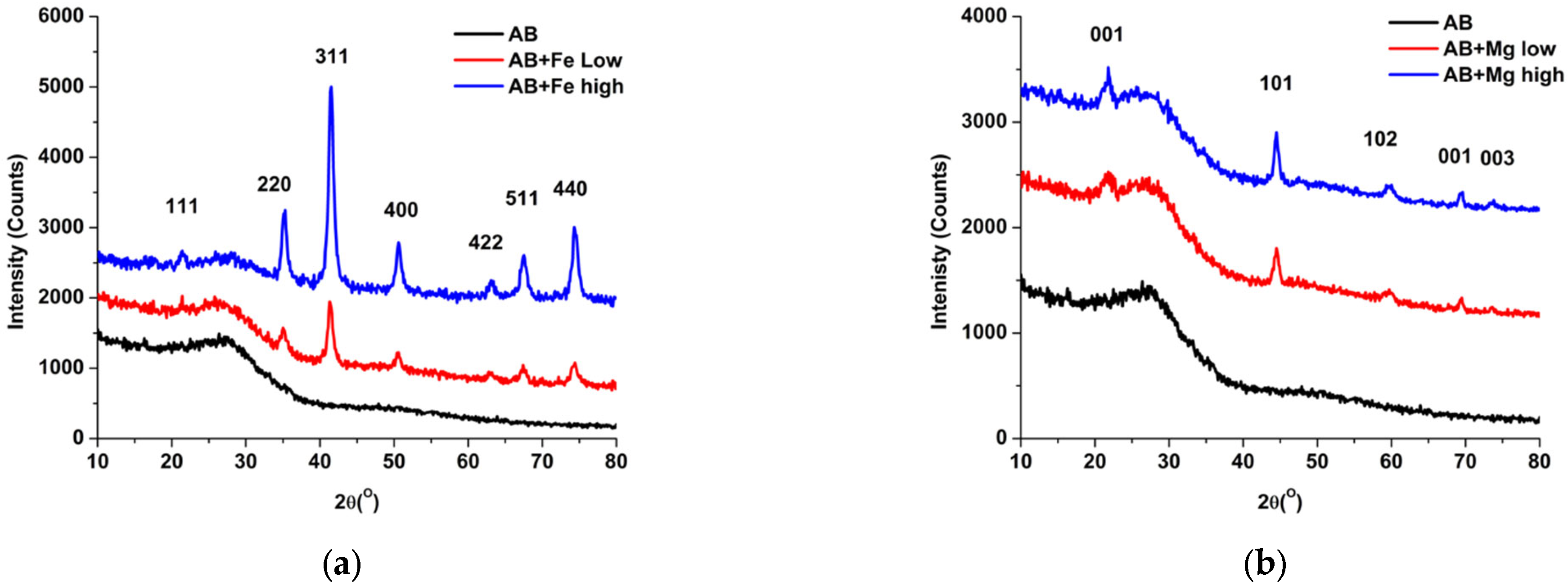
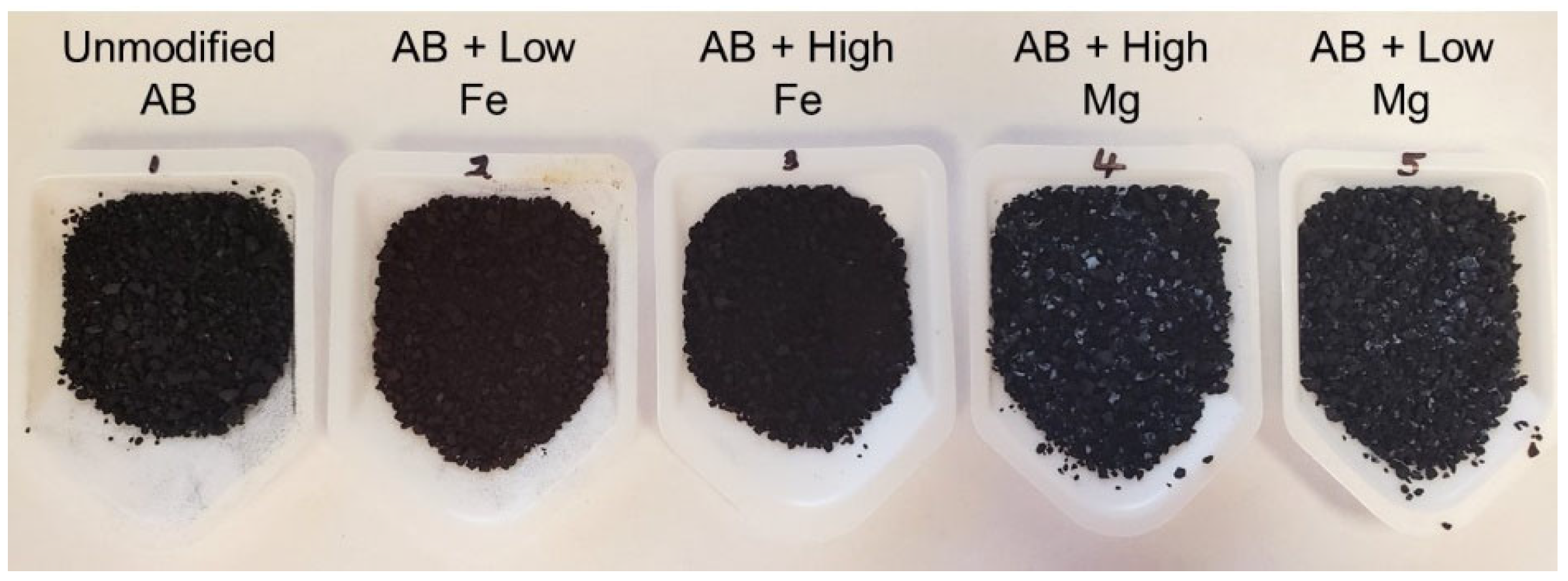

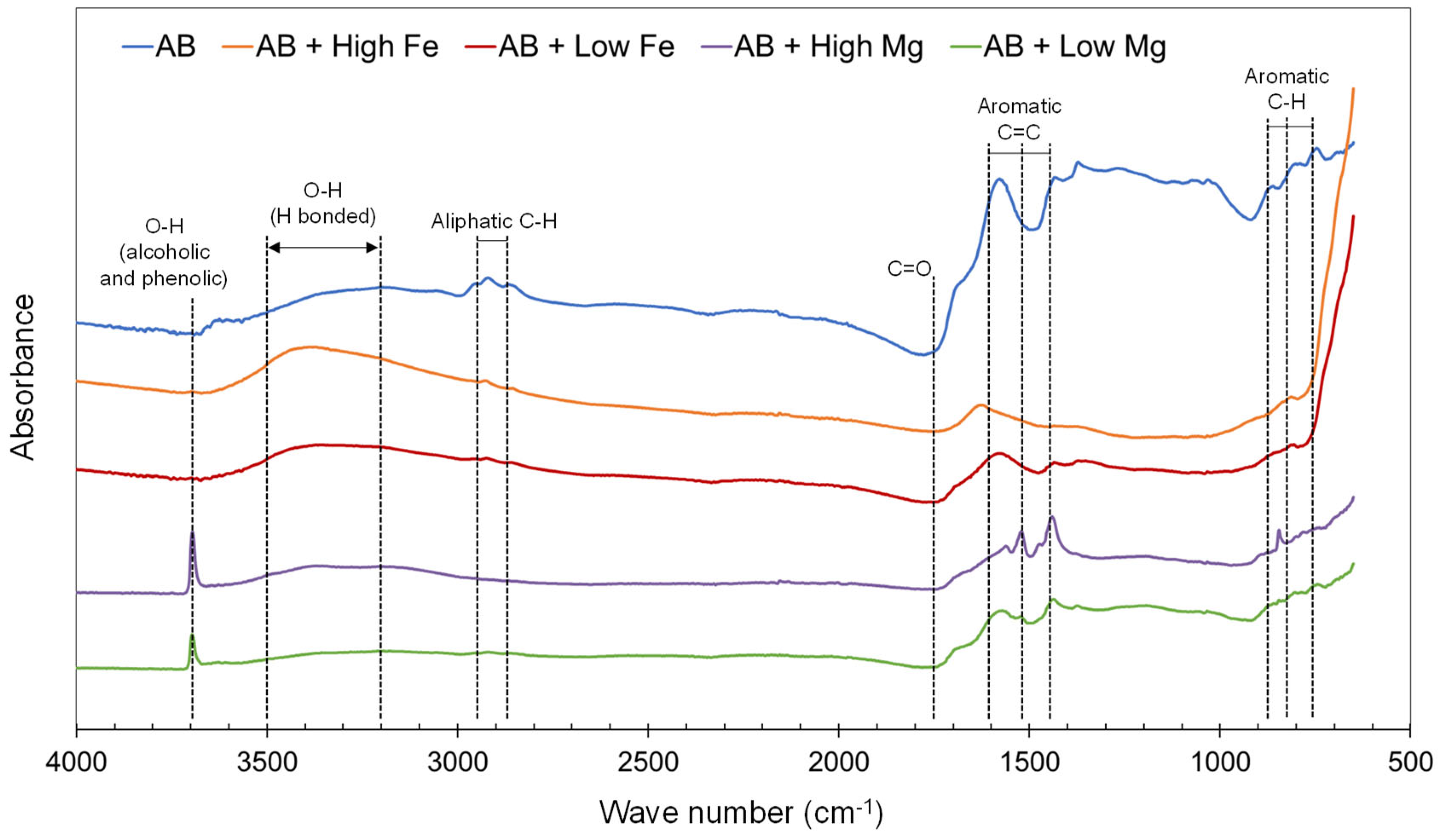
| Metal Loaded AB | Constituents Added to 0.5 L of Deionized Water | Mass (g) | Metal Chloride (mmol L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AB + High Fe | Raw avocado seed biochar (AB) | 5 | |
| Fe (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O) | 20 | 148 | |
| Fe (II) chloride tetrahydrate (FeCl2·4H2O) | 20 | 200 | |
| AB + Low Fe | Raw avocado seed biochar (AB) | 5 | |
| Fe (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl2 6H2O) | 5 | 37 | |
| Fe (II) chloride tetrahydrate (FeCl2·4H2O) | 5 | 50 | |
| AB + High Mg | Raw avocado seed biochar (AB) | 5 | |
| Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2 6H2O) | 10 | 394 | |
| AB + Low Mg | Raw avocado seed biochar (AB) | 5 | |
| Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2 6H2O) | 40 | 98 |
| Unmodified AB | AB + High Fe | AB + Low Fe | AB + High Mg | AB + Low Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile matter (%) | 19.6 | 16.0 | 9.7 | 14.4 | 23.8 |
| Ash (%) | 6.8 | 42.1 | 75.0 | 8.1 | 8.5 |
| Fixed matter (%) | 71.6 | 38.5 | 12.6 | 71.7 | 62.3 |
| Surface area (m2 g−1) | 1.8 | 49.9 | 17.1 | 1.4 | 2.2 |
| pH | 8.8 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 9.9 | 9.7 |
| Model | Parameter | AB + High Fe | AB + Low Fe | AB + High Mg | AB + Low Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Linearized equation | y = 0.0763x + 3.7393 (R2 = 0.91) | y = 0.0825x + 2.7632 (R2 = 0.96) | y = 0.033x + 6.4971 (R2 = 0.45) | y = 0.0251x + 6.9383 (R2 = 0.46) |
| Smax (mg g−1) | 14.86 | 12.12 | 30.29 | 39.79 | |
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| CIA | 32 | 24 | 145 | 127 | |
| Freundlich | Linearized equation | y = 0.2846x + 0.2691 (R2 = 0.88) | y = 0.3408x + 0.1908 (R2 = 0.90) | y = 0.6422x + 2.6492 (R2 = 0.94) | y = 0.7797x + 2.4147 (R2 = 0.96) |
| KF | 1.80 | 1.57 | 446 | 260 | |
| n | 3.26 | 2.99 | 1.56 | 1.28 | |
| 1/n | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.78 | |
| CIA | 16 | 9 | 79 | 86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Parsons, J.; Gunukula, S.; Tran, D.T. Iron and Magnesium Impregnation of Avocado Seed Biochar for Aqueous Phosphate Removal. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 690-702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4030042
Kang J, Parsons J, Gunukula S, Tran DT. Iron and Magnesium Impregnation of Avocado Seed Biochar for Aqueous Phosphate Removal. Clean Technologies. 2022; 4(3):690-702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jihoon, Jason Parsons, Sampath Gunukula, and Dat T. Tran. 2022. "Iron and Magnesium Impregnation of Avocado Seed Biochar for Aqueous Phosphate Removal" Clean Technologies 4, no. 3: 690-702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4030042
APA StyleKang, J., Parsons, J., Gunukula, S., & Tran, D. T. (2022). Iron and Magnesium Impregnation of Avocado Seed Biochar for Aqueous Phosphate Removal. Clean Technologies, 4(3), 690-702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4030042







