Abstract
Geopolymer mortars made from various waste products can appreciably reduce carbon dioxide emissions and landfill-related issues, making them viable substitutes for ordinary Portland cement, a workhorse in the concrete industry. Thus, a series of ternary geopolymer mortars were made and characterized to determine the effects of exposure to elevated temperatures (from room temperature up to 900 °C) on their engineered (residual compressive strength, weight loss, and slant shear bond strength) and microstructural properties. These mortars, which contain fly ash, ground blast furnace slag, and a high volume of palm oil fuel ash, were designed to activate via the incorporation of an alkali activator solution at a low concentration (molarity of 4). The elevated temperature-mediated deterioration of the ternary geopolymer mortar was quantified using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. The results revealed an improvement in the ternary geopolymer mortars’ resistance against elevated temperatures when the palm oil fuel ash level in the mortar matrix was raised from 50 to 70% and when slag was replaced by fly ash. It was asserted that the proposed ternary geopolymer mortars may contribute to the advancement of green concretes demanded by the construction sectors.
1. Introduction
Enormous amounts of palm oil fuel ash (POFA) are abandoned as waste materials by the agro-industrial sectors in countries such as Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand. The production of POFA has continually increased along with the increase in the rate of palm oil tree cultivation [1,2,3]. POFA is derived by burning empty fruit bunches, oil palm clinkers, and shells for electricity generation. A survey revealed that the annual production of POFA in Thailand and Malaysia in 2007 was nearly 100,000 tons and 300,000 tons, respectively. This trend continued to increase with the increase in palm tree plantations in these countries [4,5]. POFA, as a waste material, is generally discarded as a landfill product that poses serious environmental concerns [6]. Some studies [7,8] have shown that POFA (enriched with silica) can be suitably used in a manner similar to other wastes (including rice husk ash, RHA fly ash, FA, and GBFS) to design sustainable concretes or binders, thus making the construction sectors less dependent on ordinary Portland cement (OPC)-based concrete or binders. POFA, being a pozzolanic material, can be advantageous for the design of geopolymer mortars and binders (GPMs/GPBs) [9,10]. This advancement has added further research impetus in the construction industries worldwide, indicating the feasibility of making green concretes desirable for sustainable development. Many researchers have made partial substitutions of OPC by POFA in their newly designed concrete mixes to improve the durability and strength performance of conventional OPC-based concrete [1,6,11,12].
Salami et al. [13] evaluated the influence of POFA on the workability of GPMs and showed that the designed mortars, in their fresh state, can achieve reliability regarding their stiffness because POFA particles offer wide surface areas that are favorable for the development of resistance against flow. Furthermore, the workability of POFA mortar can be enhanced by increasing the content of the (NaOH + Na2SiO3) solution in the binder. This improvement can be attributed to the total amount of water increment in the specimen. Salih et al. [14] demonstrated that an improvement in the Na2SiO3-to-NaOH ratio from 1.0 to 3.0 could reduce the workability of POFA mortar. This was mainly attributed to a higher content of water in the lower ratio (1.0) than the higher one (3.0). The majority of the previous research [15,16,17,18,19] revealed that the compressive strength (CS) can vary between 28 and 66 MPa at low levels of POFA (roughly 30%) when supplemented with RHA, GBFS, and FA under curing temperatures of 65 and 75 °C for a period of one to two days. It was further shown that an increase in the POFA content of more than 30% can reduce the CS of the designed mortar.
Salih et al. [14,20,21] studied the effect of POFA (100%) on a comparatively large volume of calcium at a curing temperature of 60 °C for a period of 2 hr. The CS values of the mixes were increased up to 32 MPa, indicating that POFA can serve as a high-Ca-activated material when added to concrete. The observed enhanced CS of the mortars was mainly due to the generation of C–S–H gel from the elements Ca and Si, which exist in POFA, as well as the availability of silicates in the activator solution. Salih et al. [21] examined the influence of various curing temperatures on the alkaline solution activation of POFA. It was demonstrated that CS is enhanced and achieves a better rate when cured in an oven at an early stage. As the temperature increased from 60 to 80 °C, the values of CS remained unaffected. In addition, mortars subjected to curing at room temperature revealed roughly the same strength as those cured at higher temperatures at later ages of up to 90 days. This confirmed the effectiveness of curing at ambient temperature and the subsequent geopolymerization of POFA. Furthermore, the increase in the strength at ambient temperature for mortars aged between 7 and 90 days was higher than seen in those cured at oven temperatures. The optimum temperature for POFA activation by a solution of Na2SiO3 plus NaOH was observed to be 70 °C. Furthermore, the strength was shown to decrease for oven-cured (80 °C) samples, wherein further curing reduced the hardening time because of the increase in the rate of geopolymerization at higher temperatures. The micro-cracks were found to propagate with increasing curing time. Conversely, specimens that were cured at ambient temperature did not reveal any surface cracks.
Yusuf et al. [22,23] reported a reduction in the flexural and compressive strengths of a specimen containing 70% POFA, wherein the loss in strength increased with the increase in the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio, leading to the formation of reaction relics. The mortars’ CS was improved by as much as 50% with decreased metakaolin replacement; thereafter, the CS started to decrease when the level of POFA reached values of up to 80%. At 3 and 7 days of curing, the CS of the mortar made with 80% POFA was, correspondingly, 26.17 and 30.791 MPa, indicating the excellent performance of the mortars with low CS. It was established that the substitution of metakaolin by POFA can improve the workability of the GPMs via a reduction in water demand. GPBs show several notable attributes, such as high early CS, low creep, low drying shrinkage (DS), excellent resistance against acid and sulfate attacks, and environmental attributes [24,25]. Salmi et al. [13] displayed an increase in the weight loss of GPMs with an increase in NaOH molarity. The GPMs treated with the solution of MgSO4 (5%) and Na2SO4 (5%) corresponded to the lowest and highest weight loss. In addition, GPMs containing POFA exhibited a high resistance towards elevated temperatures and sulfate and acid attacks [16,26].
The influence of high calcium and C–S–H gel contents on the bond strengths (BSs) of GPMs made from FA and OPC was studied [27]. Four mixes were designed by replacing OPC using FA at different levels (0, 5, 10, and 15%) with changing NaOH molarity (at constant proportions of sodium silicate to NaOH content). With the increase in both OPC and NaOH contents, the values of the shear bonding strengths (SBSs) for the designed mixes were increased, which was ascribed to the development of more products from the resultant reactions. This result verified the earlier observation on the strength property enhancement of the FA-based GPs that contained high levels of Ca and produced more gels of C–S–H, C–A–S–H, and N–A–S–H [28]. This enhancement of various products at the boundary zone among cement and GPMs caused an enhancement in the strength properties [29]. Moreover, GPM made of OPC (15%) and NaOH (14 M) displayed a slight reduction in the BS [30]. This reduction at higher NaOH content was ascribed to the accelerated dissolution of silica and alumina and subsequent inhibition of the poly-condensation reaction [31]. The observed lower strength of GPMs at high NaOH contents was mainly due to the generation of excess OH ions that resulted in the alumina silicate gels’ precipitation at an early age [32]. Meanwhile, higher NaOH contents could inhibit the complete mixing of Ca, generating products with lower hydration.
The influence of various solid-to-liquid (S:L) proportions (0.5–1.1) on the SBS of GPMs at ambient conditions was evaluated by Zhang et al. [33]. A very small (0.5) or highly elevated (1.1) proportion of S:L was observed to be detrimental to the SBS development of GPMs, making the failure of bonds more vulnerable. However, S:L ratios of 0.6 and 0.8 produced an excellent SBS and optimal workability. The effects of curing temperature and humidity level on the SBS performance of GPs were evaluated under different conditions, wherein two kinds of mixes (Group A and B) with identical constituents were made. For the specimen in Group A, the curing temperature and humidity were 20 °C and 90%, respectively, whereas for the Group B specimen, these values were 20 °C and 50%, respectively. At the age of 7 days, the SBS values of the Group A and B specimens were, correspondingly, 2.83 and 2.43 MPa. The observed lower SBS for the Group B mixes was mainly due to a higher water loss at lower humidity levels [33].
Compared to the traditional OPC, the geopolymer has a higher resistance to elevated temperatures [34]. Several studies [35,36,37] reported that an increase in the aluminum silicate content with a reduction in calcium oxide level can significantly improve the thermal resistance of the designed geopolymer. Rickard et al. [38] showed that the geopolymer resistance to elevated temperatures can be influenced by the ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3. In addition, an increase in this ratio was observed to reduce the geopolymer performance due to the swelling of silica-rich secondary phases. In another study [39], it was found that the reduction in the ratio of CaO to SiO2 via the replacement of slag by a waste tile ceramic and an increase in the ratio of AL2O3 to SiO2 via the inclusion of fly ash as a slag replacement can lead to an enhancement in the durability of the geopolymer, which was mainly due to an increase in the thermal resistance of the designed ternary binder.
Based on the abovementioned factors, the proposed new types of GPMs were obtained by mixing high volumes of POFA, FA, and GBFS at proper ratios. The impacts of different proportions of CaO to SiO2, CaO to Al2O3, and SiO2 to Al2O3 on the engineering properties, such as the CS and SBS of the proposed GPMs exposed to elevated temperatures, were investigated. Various tests and measurements were carried out for the thorough characterizations (physical, morphological, structural, chemical, mineralogy, and composition) and composition optimization of GPMs. The optimum specimen was observed to be the one made from 50% POFA (by weight) and 0.4 alkali solution-to-binder ratio. The NaOH molarity and Na2SiO3 to NaOH ratio were correspondingly fixed as 4 M and 0.75. The bond strength values of the proposed GPMs were evaluated using the slant shear (SS), splitting tensile strength (STS), flexural strength (FS), and residual compressive strength (RCS) tests after exposing them to 200, 600, and 900 °C. The obtained optimum GPMs were analyzed in-depth to determine their hardened and microstructural characteristics as well as their permanence. Additionally, various ratios of SiO2 to Al2O3, CaO to SiO2, and CaO to Al2O3 were implemented to produce the best sustainable mortar beneficial for practical applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
As aforementioned, POFA is a waste material produced from the palm oil fibers, bunches, and shells used as fuel for power generation in mills. In this work, POFA was obtained from Kilang Sawit PPNJ Kahang factory located in Johor (Malaysia). It was collected from an ash outlet kept away from the boiler burning chamber. It was first sieved with 600 µm to remove the large particles and then dried in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h to eliminate free water. Next, POFA was sieved with 300 µm to screen out the larger particles, thus increasing its effectiveness. Later, it was ground to fine particles for 6 h (Loss Angelos Abrasion instrument equipped with fifteen stainless balls of 50 mm diameter) at a drum speed in the range of 32–35 rpm (Figure 1). The particles’ refinement was found to be strongly affected by the grinding duration that was recorded repeatedly after each 1 h interval. The particles’ percentage preserved on the 45 µm sieve was decreased with the increasing period of grinding. After the grinding was complete, all POFA was passed through the sieve (45 µm), as depicted in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
POFA treatment and processing, including collection, sieving, drying, and grinding [40,41].
To make the proposed GPMs, FA with low CaO contents (a source of aluminosilicate) was collected from a power plant in Malaysia. It satisfied the ASTM C618 requisites for N class pozzolan and F class FA that appeared gray in color. In the present work, pristine GBFS was obtained from Ipoh (Malaysia) and used as it is to free the binder of cement. It showed both cementitious and pozzolanic characteristics and was different from other cementitious supplements. Figure 2 shows the off-white appearance of GBFS that was due to the hydraulic reaction during the mixing process in water. GBFS, being a pozzolanic material comprising Ca-silicate and alumina (approximately 90%), could meet the requisite of ASTM C618.

Figure 2.
The utilized ground blast furnace slag (GBFS).
The chemical compositions of POFA, FA, and GBFS were determined using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy. In this measurement, the incident X-ray photons excited the atoms in the powder specimen wherein the tightly bound inner shell electrons were detached, followed by the relaxation into the ground state, emitting fluorescent X-rays. An energy dispersive detector was used to record the emitted energies, thus identifying the trace elements present in the specimen. In addition, the emitted intensity of X-rays was analyzed to quantify the amount of elements that exist in the specimen under study. Table 1 displays the XRF results of FA, POFA, and GBFS. The oxides of Si and Al were the main compositions, amounting to 86% in FA, 68.45% in POFA, and 41.7% in GBFS. In comparison to FA and POFA, GBFS was composed of very high amounts of CaO (about 51.8%). In essence, such high contents of silicate, Al, and CaO played a vital role in the formulation of TGPMs, wherein the development of enhanced geopolymerization led to the production of excess N–A–S–H, C–A–S–H, and C–S–H gels as essential components for achieving high-performance mortars and binders. Meanwhile, FA and GBFS showed very low concentrations of K2O, but POFA revealed high contents of K2O (8.6%). The loss on ignition (LOI) was discerned to be insignificant in FA and GBFS. Furthermore, POFA showed high LOI (1.73%) that was consistent with the ASTM C618 standard.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of POFA, FA, and GBFS.
To make the proposed GPMs, the natural siliceous river sand was utilized as fine aggregates. First, the collected sand was cleaned using tap water in accordance with the ASTM C117 standard, thereby reducing the silts and impurities. Then, the obtained clean sand was dried in an oven at 60 °C for 24 h to control the moisture content. Next, it was graded according to the ASTM C33-33M requirement, as depicted in Figure 3. The values of the estimated fineness modulus and specific gravity of the resultant aggregates were 2.9 and 2.6, respectively.
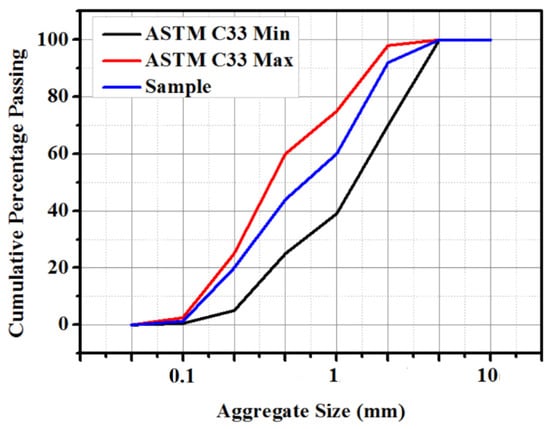
Figure 3.
Particle size analysis of fine aggregates [2].
The alkaline solution composed of high-purity NaOH (NH) and Na2SiO3 (NS) (98%, QREC, Malaysia) was utilized for the activation of alumina and silica in various wastes, including FA, POFA, and GBFS. Figure 4 illustrates the alkali solution preparation procedure, wherein an analytical grade sodium silicate solution was made from SiO2 (29.5 wt.%), Na2O (14.70 wt.%), and H2O (55.80 wt.%) (QREC, Malaysia). The pellets were mixed in water to make the required NH solution of molarity 4. The resultant mixture was cooled down for 24 h following the addition of NS solution, achieving the desired alkali mixture with a SiO2 to Na2O ratio of 1.02. For all alkali mixes, the NS to NH ratio was kept fixed at 0.75.

Figure 4.
Preparation process of alkali activator solution Sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate bottles supplied by QREC [42].
2.2. Mix Design
In this process, NH and NS were first weighed to make the mixture and then cooled down to room temperature. The proposed TGPMs were made via the alkali solution activation of the ternary blend composed of POFA, FA, and GBFS. The mixture was blended in a mortar mixer for 2 min under a dry state to obtain a uniform mix of these fine aggregates, followed by the alkali solution activation. The resultant mixture was blended in a device operated at intermediate speed for an extra 4 min. Next, the fresh mortar mixes were cast in the mold in 2 layers, wherein every layer was strengthened by a vibration table for 15 s to eliminate the air voids. A total of 9 mortar mixes enclosing high contents of POFA were obtained using the same procedure (Table 2). The POFA contents in the TGPMs were increased up to 70% through the substitution of FA and GBFS (varied in the range of 20 to 50%). It was observed that with the increase in POFA level from 50 to 70%, the concentration of silicate in the TGPMs was considerably increased (Figure 5). In addition, the contents of CaO and Al2O3 were increased with the increase in GBFS and FA levels, respectively. After the casting, the designed TGPM specimens were cured for 24 h at (27 ± 1.5) °C and 75% of humidity. Then, the mortar mixes were left in ambient atmosphere for further characterization.

Table 2.
Constituents in TGPMs.
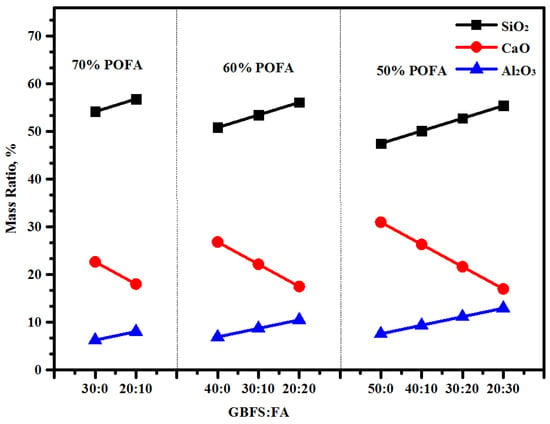
Figure 5.
Effect of high POFA content as FA and GBFS replacement on SiO2, CaO, and Al2O3 content of TGPMs.
2.3. Tests Procedure
Following the ASTM C109-109M requirement, the CS test was performed on the adequately cured mortars at 28 days, which served as a control sample. At each curing age, 3 sets of mortars were tested to obtain the average value. During the CS test, the mortar was duly prepared and positioned accurately between the upper and lower metal bearing plates as specified by the relevant standard. The specimen was subjected to a steady load rate (2.5 kN/s) till failure occurred. The density and CS of TGPMs were produced automatically depending on their imputed weights and dimensions.
The compression machine was used for the slant–shear test of the produced TGPMs, wherein the hardened specimen was slanted diagonally at 30° (that corresponded to the lowest failure stress of a smooth surface from the vertical) following the ASTM C882 standard. The specimen was cut and formed in a cylindrical shape with a diameter of 75 mm and a length of 150 mm. Then, it was divided into halves following the half-slanted dimension and then placed into a cylindrical mold before being poured with fresh TGPM. The mortars were tested after 28 days of curing following a systematic protocol.
The ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV) test of the studied TGPMs was carried out using Proceq brand of UPV machine in accordance with ASTM C597 (2009). In this test, adequately cured cubic samples with dimensions (50 mm × 50 mm × 50 mm) were used, wherein three sets of specimens were tested after each curing age. The mortar mixes were dried in the air for 24 hr at 27 °C before being tested, facilitating an efficient blending between the transducers and mortar mixes. The mean path length of the cubic specimen was obtained from the measured length across 4 faces (longitudinal to the direction of the transducers). At the beginning of the test, the pundit unit was calibrated to standard transit time of 42.5 µs using a Plexiglass cylinder. The transducers were calibrated to zero reading via the face-to-face placement with water-soluble coupling gel. In this procedure, the transducers were tied firmly to the mortar, in which the Pundit unit displayed both transit time and UPV based on the specified path length of the specimen. The average reading of three specimens was recorded to determine the transit time and UPV value.
The resistance of the TGPMs against elevated temperatures was evaluated using an automatic electrical furnace (Figure 6). Herein, 3 mortar mixes, each with dimensions (50 mm × 50 mm × 50 mm), were prepared and tested after 28 days of curing. Each specimen was subjected to the temperature of 200, 400, 700, and 900 °C at various time periods (Figure 7). The hot mixes were cooled by water spray and blown air. The specimens’ weights before and after high-temperature exposure were recorded for the weight loss estimation. Then, these TGPMs were subjected to the CS test to determine the RCS, strength loss percentage, and UPV in accordance with the ASTM C597 requirement. At last, the relative quality of the mortar mixes was assessed after heating at high temperatures. In addition, the microstructural characteristics of the designed TGPMs were determined by the FTIR, SEM, DTG, and TGA measurements.
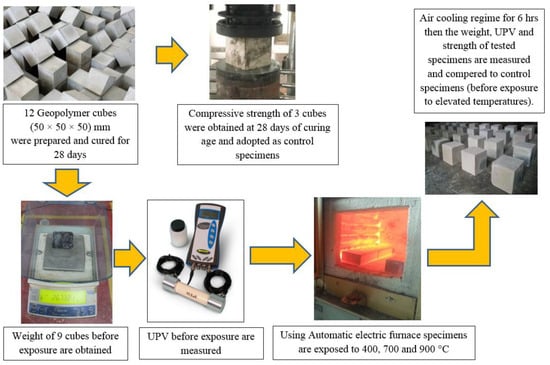
Figure 6.
Procedure to determine the GPMs’ resistance to elevated temperature.
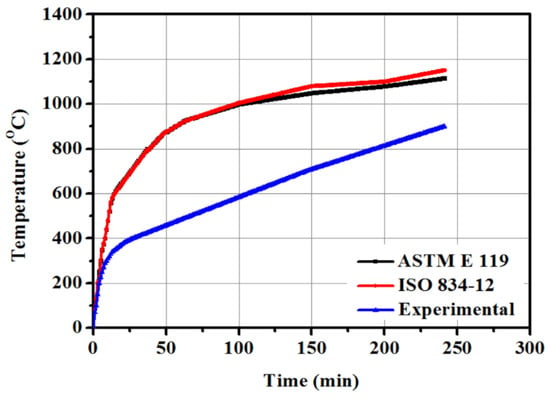
Figure 7.
A comparison of experimental time against temperature curve between ASTM E119 and ISO 834-12 standard [35].
The XRD measurement was performed to confirm the crystallinity and mineral composition of the studied TGPMs. The XRD patterns were analyzed to determine the crystal structure, phase, lattice orientation, and cell parameters of the TGPMs. After performing the CS test at 28 days of curing, a small portion of TGPMs was collected and ground into fine powder. The powder specimen was used for the XRD analysis (2θ range, step size, and scan speed were 5–90°, 0.020°, and 15.4 s, respectively). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), being a very adaptable tool, was utilized to study the microstructures, interfacial transition zone, hydration progress, and elemental compositions of the designed TGPMs. In this work, various specimens were prepared for the test. For each required batch, the samples were tested before and after exposure to the elevated temperatures. Before testing, the specimens were coated with gold to achieve the desired surface structure. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) were carried out using an automatic thermal analyzer to evaluate the thermal behavior of various TGPM specimens (each weighing 5 mg). The test was designed deliberately to ensure the possibility of high-temperature withstanding capacity of the proposed TGPMs. These measurements were conducted (under nitrogen gas ambiance) in the range of 29 to 950 °C at 10 °C/min of heating rate. The room temperature FTIR spectra of the produced TGPMs in the range of 400–4000 cm−1 were recorded for the identification of the functional chemical bonds or groups that existed in the organic and inorganic components. A similar procedure was followed to test all TGPM specimens using the XRD and TGA.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Materials Properties
Figure 8 shows the XRD profiles of POFA, FA, and GBFS materials. The results of the POFA and FA showed many intense diffraction peaks around 16 to 30° that corresponded to the crystalline phase of silica and alumina compound. Other intense XRD peaks signified the existence of crystalline phases of quartz and mullite structures. Conversely, the XRD profile of GBFS in the presence of a broad hump indicated its glassy nature, wherein the high content of reactive silica and Ca played a significant role in the formation of GBFS, indicating its immense potential for the design of sustainable TGPMs. The main reason for FA inclusion in the proposed mortars was to surmount the low concentration of Al2O3 (10.49 wt.%) in the GBFS.
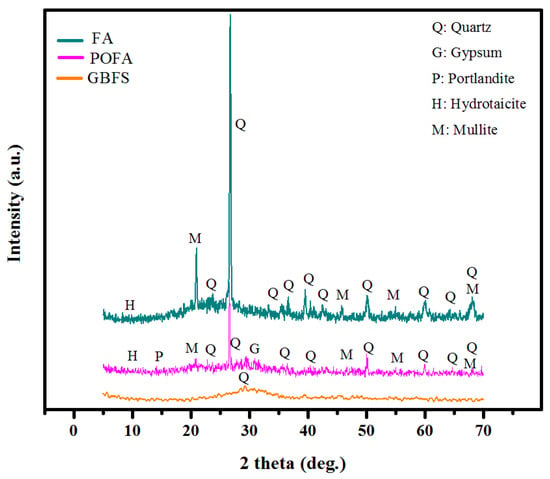
Figure 8.
X-ray diffraction profiles of FA, POFA, and GBFS.
Figure 9 displays the SEM micrographs of the POFA, FA, and GBFS. The morphologies showed spherical particles of FA (Figure 9b) with smooth surfaces. The POFA consisted of spherical and irregularly shaped particles (Figure 9a). The morphology of the GBFS (Figure 9c) comprised irregular and angular particles that agreed with the previous report [43].
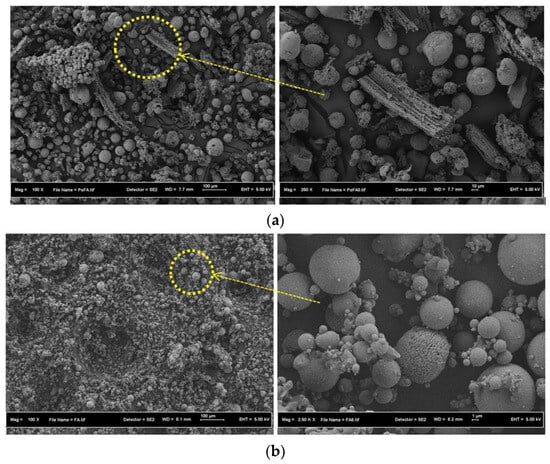
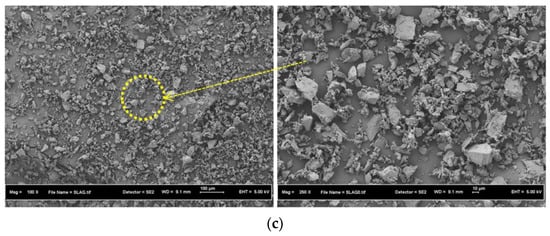
Figure 9.
SEM of raw materials (a) POFA (b) FA (c) GBFS.
Figure 10 displays the TGA results of the FA, POFA, and GBFS, which indicate the weight changes at different temperatures. The FA was found to be more stable at high temperatures than others. Furthermore, the FA showed the desorption/drying (rerun) stage only and had a lower weight loss of about 0.32% compared to the others. The weight losses of the FA, POFA, and GBFS were 1.27, 3.4, and 2.31%, respectively.
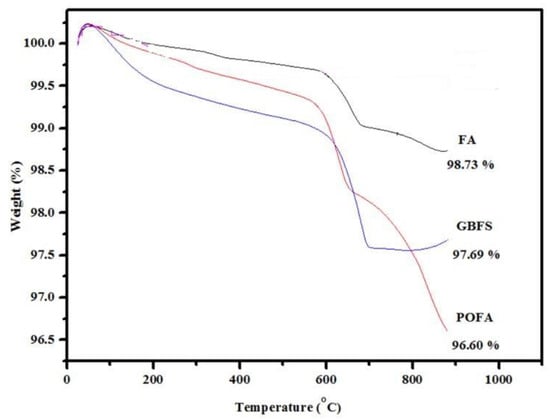
Figure 10.
TGA curves of POFA, FA, and GBFS.
Figure 11 displays the DTG results of the FA, POFA, and GBFS, which was carried out to determine the mass loss during the specimens’ heating, indicating their physical alterations. The DTG curves of the POFA showed early weight change with temperature and decomposition at 680 °C with a ratio of 0.0176%/°C. The decomposition peak of the FA started after 700 °C, indicating a lower weight loss (0.0078%/°C) than the POFA and GBFS. The highest weight loss of 0.02%/°C of GBFS occurred at 718 °C. Generally, POFA exhibited lower stability than FA and GBFS at higher temperatures.
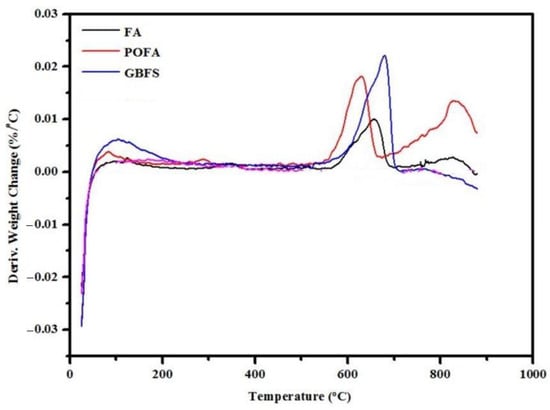
Figure 11.
DTG curves for FA, POFA, and GBFS.
Figure 12 illustrates the FTIR spectrum of the FA, POFA, and GBFS, which consists of various chemical bonds and functional groups originating from the constituent raw materials of TGPMs. In addition, with varying temperatures, the conversion of the materials from the crystalline to glassy phases was also observed. The stretching vibration modes related to Si–Al linkage showed a shift toward the lower frequency, implying an increase in the number of tetrahedral Al atoms [44]. It was reported [45] that the presence of silicate and aluminosilicate glassy phases shows a broad band in the range of 500–650 cm−1. In the current work, the studied material constituents revealed some short-range structural ordering with the tetrahedral or octahedral rings. The significant band around 460 cm−1 corresponded to the in-plane and bending vibration modes of Al–O/Si–O bonds. The band at 730 cm−1 was due to the vibration modes of the octahedral sites of Al, and the band at 820 cm−1 was due to the stretching vibration of the tetrahedral Al–O bond [46]. The IR band at 1400 cm−1 was due to the Al–O/Si–O bonds’ asymmetric stretching vibration [47]. Essentially, the FA and POFA showed various broad bands of C=O vibration modes with intermediate intensity in the range of 1460–1600 cm−1. In addition, the IR band intensity of the FA was higher than that of the POFA. However, no characteristic vibration modes of GBFS were evidenced in this region. For all the waste materials, the IR bands around 3500 cm−1 were due to the bending and stretching vibration modes of the C = O–H and –OH groups, respectively. The presence of hydroxyl ions was mainly due to the adsorption or trapping of moisture/water at the materials’ surface cavities that formed many weak bonds/ligaments.
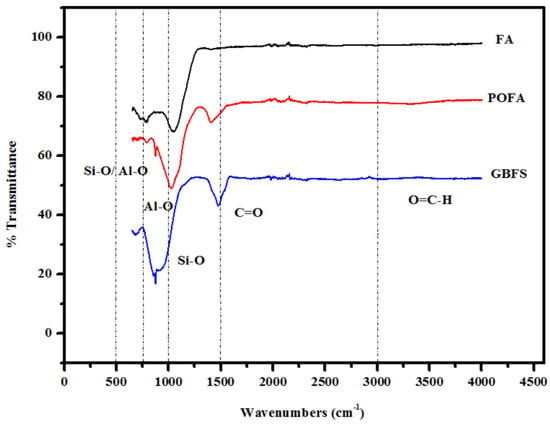
Figure 12.
FTIR spectra of FA, POFA, and GBFS.
3.2. Residual Compressive Strength
Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15 illustrate the influence of POFA at high content on the development of the RCS, degree of internal cracks (DIC), and weight loss percentage (WLP) of the proposed TGPMs exposed to elevated temperatures. The value of RCS was enhanced from 15 to 32.4% with the increase in the POFA level in place of GBFS from 50 to 70% (Figure 13). A similar trend in the development of RCS values of TGPMs was observed with the increase in FA level from 50 to 70% in place of GBFS. Initially, the UPV results revealed an increase in the DIC with the increase in temperatures, and then the readings were dropped at higher temperatures (Figure 14). The WLP was found to be directly proportional to the POFA concentration in the mixes. When the POFA level was increased from 50 to 70%, the value of WLP was increased from 19.8 to 21.8% (Figure 15). A linear relationship between RCS and WLP was observed (Figure 16). These results showed an improvement in the RCS values with the increase in WLP. The following relation was used to calculate the RCS development (with an R2 value of 0.72) for all samples:
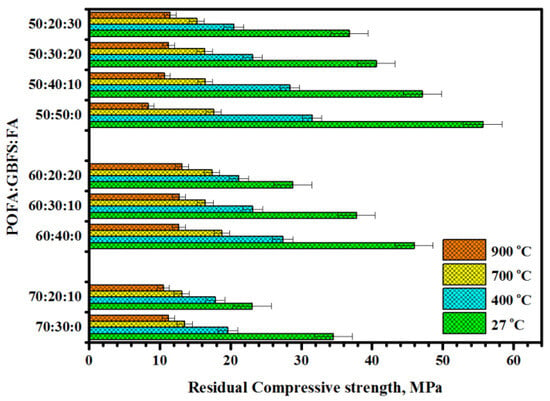
Figure 13.
Effect of elevated temperatures on RCS of TGPMs containing high volume of POFA.
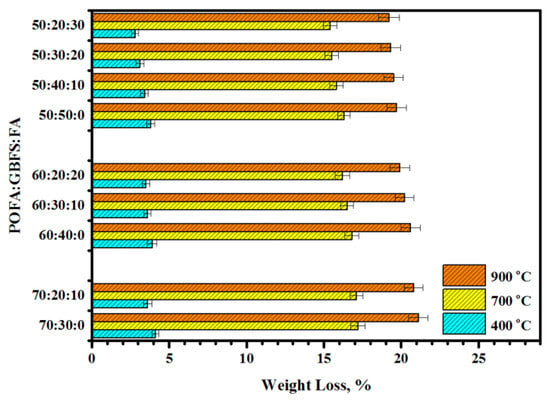
Figure 14.
Effect of elevated temperatures on WLP of TGPMs containing high volume of POFA.
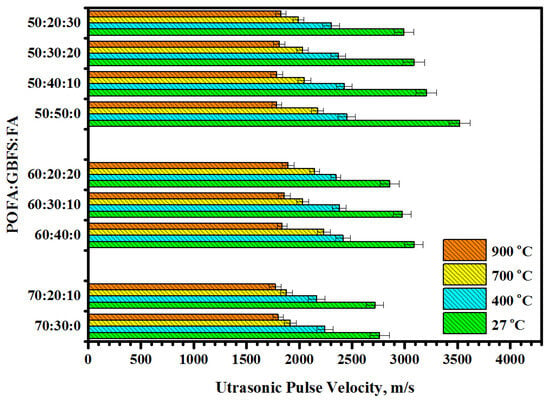
Figure 15.
Effect of elevated temperatures on UPV (DIC) of TGPMs containing high volume of POFA.
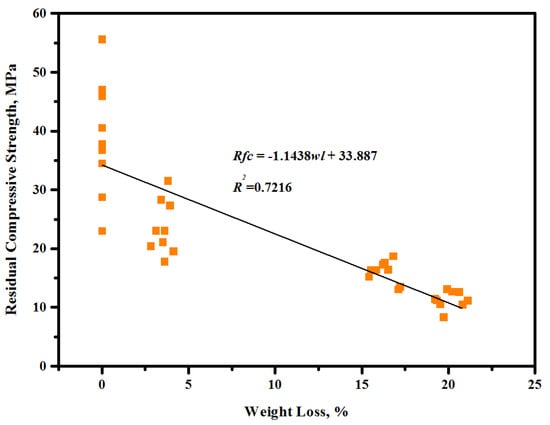
Figure 16.
Relationship between RCS and WLP of TGPMs containing high volume of POFA exposed to elevated temperatures.
At elevated temperatures, more bonds were observed to break in the alkali-activated mortar matrix, wherein the TGPMs containing higher levels of calcium showed a higher degree of damage, implying a higher loss of strength. This higher loss was mainly due to the development of more calcium carbonate decomposition-mediated product generation that led to the expansion of the mortar matrix volume, producing more internal cracks. This observation can be ascribed to two competitive mechanisms that occurred in the mortar matrix with the increase in temperatures. First, the continued geopolymerization process led to the mortars gaining strength. Second, the lack of capacity of the mortars to resist the high temperatures led to a reduction in the strength values. For each elevated temperature, the average values of the RCS of the three tested cubes, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance were calculated using Equations (2) and (3), and the obtained results are presented in Table 3.
where n is the number of cubes (n= 3), Ave. is the average of the RCS of three specimens (in MPa), Xi is the RCS of each specimen (in MPa), SD is the standard deviation, and CV is the coefficient of variance.

Table 3.
The average, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance of obtained residual compressive strength.
3.3. SEM Images and TGA Curves
The SEM micrographs and TGA curves of the studied TGPMs are presented in Figure 17 and Figure 18, respectively. The SEM images indicated the structural deterioration and development of more porosity with the increase in temperature. This, in turn, destroyed the interlocking among the particles in the mortar matrix. The TGA results revealed a strong influence of high-volume POFA content on the residual weights of TGPMs. When the POFA level was increased from 50 to 70%, the residual weight was decreased from 81.8 to 78.7%, respectively. The observed improvement in the resistance of TGPMs against elevated temperatures with the increase in POFA and FA contents was due to the boost of Al2O3 and SiO2 concentration that made the mortar matrix more thermally compatible than that of the GPMs designed to have high contents of GBFS. In addition, FA contained a considerable amount of hollow sphere-like particles wherein the partial dissolution of these particles generated highly dispersed tiny pores in the mortar matrix, thus causing an improvement in the thermal resistance against high temperatures. The residual free space created by the dissolved FA particles, in turn, produced several unreacted particles within the hollow cavities, a major factor in the improvement of the thermal compatibility of TGPMs. In contrast, TGPMs formulated to have 70% POFA content showed more stable surface morphology at elevated temperatures than the specimens designed to have a lower content of POFA.
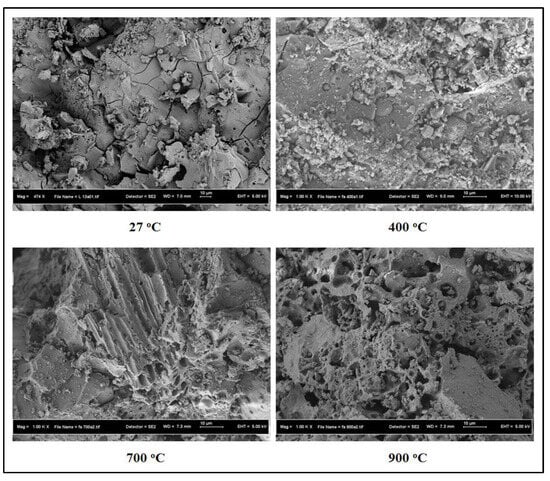
Figure 17.
SEM micrographs of 70% POFA replaced by GBFS at various temperatures.
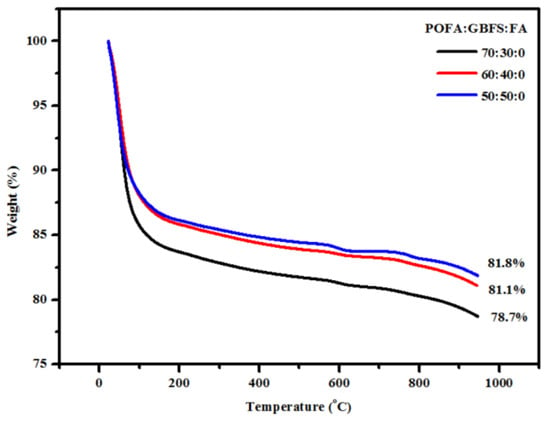
Figure 18.
Effect of elevated temperatures on the weight loss of TGPMs containing high volume of POFA.
3.4. XRD Analysis
Figure 19a–b illustrate the XRD profiles of TGPMs before and after the increase in temperatures from 27 to 900 °C. XRD profiles of TGPMs before and after high-temperature exposure (below 400 °C) showed the presence of semi-crystalline aluminosilicate gel and quartz (Q). Several intense broad peaks were observed in the range of 25–30°. XRD results of TGPMs exposed to elevated temperatures (700 and 900 °C) showed the formation of crystalline zeolites as the secondary reaction products. TGPMs made with a high volume of POFA when heated at 700 °C showed intense XRD peaks of Q, mullite (M), and nepheline (N), wherein M is the only stable crystalline phase of Al2O3 and SiO2. This clearly indicated that M maintained its room temperature strength even at high temperatures, showing high temperature stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent oxidation resistance. After the exposure at 700 °C, the Q peaks were still stable, and the M peaks became increasingly intense. When the TGPM specimen was heated at 400 °C, crystalline goethite was transformed into a hematite phase, wherein most of the constituent water molecules from the mortar matrix were released. Consequently, it caused a local buildup of internal stress due to the outgoing -OH flux and synchronized diffusion in the grain structures. In addition, it could even cause fractures in the hematite grains, thus increasing the DIC of the TGPM matrix. At such high temperatures, the grain morphology (shape and size) was completely reorganized, forming a new crystalline hematite phase by largely retaining the stable phase of the original goethite structures. XRD profiles of the studied TGPMs exposed to 900 °C displayed the disappearance of the hematite phase and preservation of the crystalline sodium aluminum silicate (nepheline, AlNaSiO4) with Q and M as the crystalline phases. In comparison to other TGPM mixes, the specimen designed to have 70% POFA revealed stable XRD peaks at high temperatures.
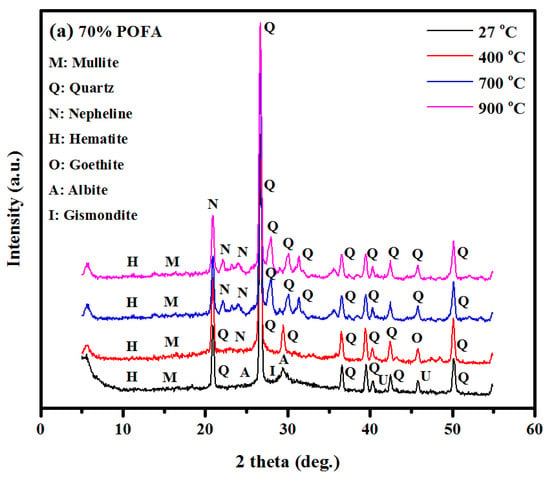
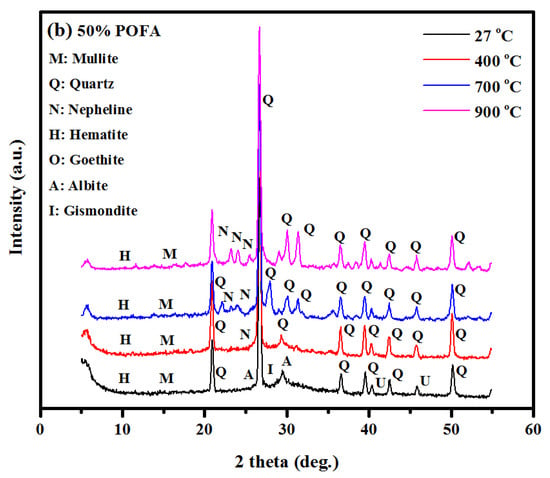
Figure 19.
XRD of GPMs after heated at (a) 70% POFA to 30% GBFS and (b) 50% POFA to 50% GBFS.
3.5. Visual Appearance
Figure 20 shows the impact of high temperature (900 °C) on the surface of TGPMs. The surface presented in Figure 20b,d clearly indicated the development of surface cracks in the studied TGPMs containing a high volume of POFA after being exposed to 900 °C. The specimen containing 50% POFA revealed the development of wider cracks (Figure 20d) compared to the mortars made with 70% POFA (Figure 20b). The specimen containing a high volume of POFA showed a slight decrease in surface deterioration at higher temperatures. However, the resistance of TGPMs against elevated temperatures was improved due to the inclusion of POFA, manifesting fewer cracks on the mortar surface. Generally, the exposure of the specimens to higher temperatures can be accompanied by many alterations, such as an increase in the moisture evaporation and internal vapor pressures, expansion of the fine aggregates, contractions of the geopolymer paste, and decompositions of various chemicals in the mortar matrix. In the early phase of heating, such changes might not produce a significant number of cracks. However, if the heating rate is quite fast and the mortar is very dense or encloses a sufficient amount of moisture, then spalling can happen within the first 30 min of the heat exposure, which is detrimental for the applications.
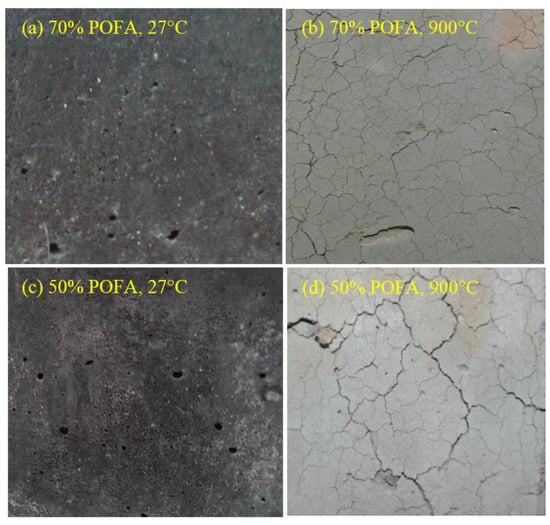
Figure 20.
Crack development in GPMs containing various levels of POFA when heated at 900 °C.
The variations in the color of TGPMs as a function of temperatures were determined. It showed a dark grey appearance at 27 °C and then transformed to light dark (up to 400 °C) with the increase in the substitution of GBFS content by FA. Then, the color of TGPMs was somewhat transformed to vanilla and light grey when the temperature was further increased from 400 to 700 °C. The color of TGPMs appeared whitish at 900 °C irrespective of the POFA contents. The impact of burning appeared more severe at the outer planes of the mortar specimens. This effect was further reduced toward the interiors of the mortars. A close inspection of the crushed mortar specimen indicated that at a specific temperature, the surface color could penetrate into the interior of the mortar depending on the internal heat intensity, while a clear surface appearance was observed to last up to approximately 10 mm deep, especially for the mortar heated at 700 °C or below. However, the penetration depth differed when the mortar was heated at 900 °C. Overall, all the proposed TGPMs showed more or less similar color appearances and variations due to exposure to high temperatures.
3.6. Slant Shear Bond Strength
Figure 21 presents the effect of heat exposure at different temperatures on the slant shear bond strength (SSBS) of the mortar substrate prepared at 30°. The values of the SSBS of all TGPMs were enhanced with the increase in temperature from 27 to 900 °C. Generally, with the increase in temperature, the values of the SSBS of TGPMs were increased. All the studied mortars showed somewhat stronger bonding at 27 °C compared to other temperatures. The SSBS values were reduced with the increase in POFA in place of GBFS. The loss percentage of the TGPMs at 27 °C was reduced from 3.72 to 2.69% with the increase in POFA level from 50 to 70%, respectively. However, the SSBS values of the proposed GPMs were significantly influenced when the temperature was increased from 27 to 900 °C. The specimens containing a higher amount of POFA as a GBFS replacement were discerned to achieve better performance under elevated temperature exposure. The residual SSBS value of TGPMs showed an increase from 0.52 to 0.61 MPa with an increase in POFA level from 50% to 70%, respectively. The SSBS of the TGPMs were improved when FA was substituted by GBFS, irrespective of the POFA content. In addition, with the increase in FA concentration, the SSBS values of the specimens were enhanced. The specimens prepared with 50% POFA as a GBFS replacement displayed a drop in the percentage of loss on bond strength from 86% to 77%, with the corresponding rise from 0 to 30% for FA replacement of GBFS. The mortars containing 60 and 70% POFA, when exposed to 900 °C, showed a similar trend in the loss of bond strength values. However, the mortars made using high levels of POFA and FA exhibited lesser loss of bond strength than other mortar mixes. TGPMs containing 50% POFA and GBFS displayed a maximum loss in bond strength (86%) compared to other specimens when exposed to 900 °C.
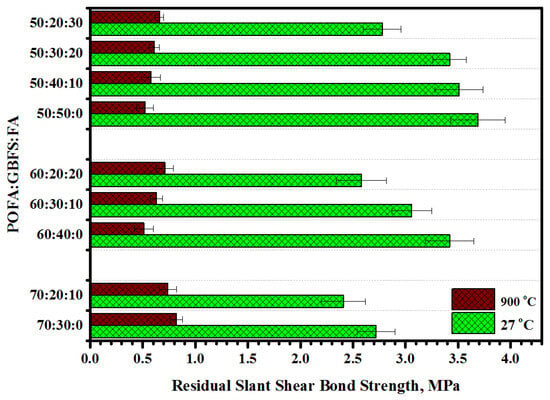
Figure 21.
Effect of elevated temperatures on residual slant shear bond strength of geopolymer mortars containing high volume of POFA.
4. Conclusions
The effects of elevated temperatures on the engineering properties of TGPMs containing various levels of high-volume POFA, GBFS, and FA were determined in terms of durability, residual strength, microstructures, crystallinity, degree of internal cracks, weight loss percentage, and bond strength performance. Based on the observed results, the following conclusions can be made:
- The proposed geopolymers made with a high volume of POFA (enriched in silica and alumina) showed high durability performance against elevated temperature exposure;
- The thermal resistance of TGPMs made with various POFA contents (50 to 70%) was significantly improved when exposed to high temperatures up to 900 °C;
- The existence of the crystalline phases, porosity, wide surface area of the tiny spherical particles, formation of various gels due to enhanced geopolymerization, and less water demand were the main factors for such improvement in the engineering characteristics of the designed TGPMs;
- TGPMs made using a high volume of POFA and FA as slag replacement showed considerable improvement in the residual strength and UPV values at elevated temperatures;
- The microstructure results of TGPM containing 70% POFA at high temperature exposure displayed an increase in thermal stability;
- The loss of bond strength of the TGPM mixes enclosing high levels of POFA, FA, and GBFS was remarkably reduced when heated up to 900 °C;
- The effects of heat intensity on the color appearance of the studied TGPMs at elevated temperatures were quantified in terms of surface discoloration, indicating their practical benefits under fire hazards;
- It is asserted that POFA (an eco-friendly and sustainable agricultural waste material) can suitably be recycled to make high-performance sustainable TGPMs demanded by the construction industries, providing immense benefits to the economy due to their durability in civil structures, high strength performance, and resistance to elevated heat exposure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.F.H. and Z.K.; methodology, G.F.H.; software, Z.K.; validation, S.K.G., Z.K. and G.F.H.; formal analysis, G.F.H.; investigation, S.K.G.; resources, G.F.H.; data curation, Z.K.; writing—original draft preparation, G.F.H.; writing—review and editing, S.K.G.; visualization, S.K.G.; supervision, S.K.G.; project administration, Z.K.; funding acquisition, G.F.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| GPMs | geopolymer mortars |
| TGPMs | ternary geopolymer mortars |
| GPBs | geopolymer binders |
| OPC | ordinary Portland cement |
| FA | fly ash |
| POFA | palm oil fuel ash |
| GBFS | ground blast furnace slag |
| AS | aluminum silicate |
| LOI | loss in ignition |
| FS | flexural strength |
| STS | splitting tensile strength |
| CS | compressive strength |
| RCS | residual compressive strength |
| SSBS | slant shear bond strength |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Tangchirapat, W.; Saeting, T.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Kiattikomol, K.; Siripanichgorn, A. Use of waste ash from palm oil industry in concrete. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huseien, G.F.; Ismail, M.; Tahir, M.M.; Mirza, J.; Khalid, N.H.A.; Asaad, M.A.; Husein, A.A.; Sarbini, N.N. Synergism between palm oil fuel ash and slag: Production of environmental-friendly alkali activated mortars with enhanced properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Mirza, J.; Ismail, M.; Ghoshal, S.; Hussein, A.A. Geopolymer mortars as sustainable repair material: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Behnia, A.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. Compressive strength and microstructural analysis of fly ash/palm oil fuel ash based geopolymer mortar. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Jumaat, M.Z. Compressive strength and microstructural analysis of fly ash/palm oil fuel ash based geopolymer mortar under elevated temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, A.A.; Hussin, M.W. The effectiveness of palm oil fuel ash in preventing expansion due to alkali-silica reaction. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1997, 19, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengaram, U.J.; Mahmud, H.; Jumaat, M.Z. Enhancement and prediction of modulus of elasticity of palm kernel shell concrete. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. A review on the use of agriculture waste material as lightweight aggregate for reinforced concrete structural members. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 365197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiso, E.M.; Tabelin, C.B.; Maestre, C.V.; Aseniero, J.P.J.; Park, I.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M. Synthesis and characterization of coal fly ash and palm oil fuel ash modified artisanal and small-scale gold mine (ASGM) tailings based geopolymer using sugar mill lime sludge as Ca-based activator. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.J.; Alengaram, U.J.; Santhanam, M.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Mo, K.H. Microstructural investigations of palm oil fuel ash and fly ash based binders in lightweight aggregate foamed geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, A.A.; Hussin, M.W. Effect of palm oil fuel ash in controlling heat of hydration of concrete. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 2650–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rukzon, S.; Sirivivatnanon, V. Resistance to chloride penetration of blended Portland cement mortar containing palm oil fuel ash, rice husk ash and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, B.A.; Johari, M.A.M.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Maslehuddin, M. Durability performance of Palm Oil Fuel Ash-based Engineered Alkaline-activated Cementitious Composite (POFA-EACC) mortar in sulfate environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.A.; Ali, A.A.A.; Farzadnia, N. Characterization of mechanical and microstructural properties of palm oil fuel ash geopolymer cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Bashar, I.I. The development of compressive strength of ground granulated blast furnace slag-palm oil fuel ash-fly ash based geopolymer mortar. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, M.; Bhutta, M.; Hussin, M.; Tahir, M.M.; Aziah, N. Sulfuric acid resistance of blended ash geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Zain, M.F.M.; Jamil, M.; Lai, F. Fabrication of a non-cement binder using slag, palm oil fuel ash and rice husk ash with sodium hydroxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.O.; Johari, M.A.M.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Maslehuddin, M. Evolution of alkaline activated ground blast furnace slag–ultrafine palm oil fuel ash based concrete. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.O.; Johari, M.A.M.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Maslehuddin, M. Effects of H2O/Na2O molar ratio on the strength of alkaline activated ground blast furnace slag-ultrafine palm oil fuel ash based concrete. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.A.; Farzadnia, N.; Ali, A.A.A.; Demirboga, R. Development of high strength alkali activated binder using palm oil fuel ash and GGBS at ambient temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.A.; Farzadnia, N.; Ali, A.A.A.; Demirboga, R. Effect of different curing temperatures on alkali activated palm oil fuel ash paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, T.O.; Ismail, M.; Usman, J.; Noruzman, A.H. Impact of blending on strength distribution of ambient cured metakaolin and palm oil fuel ash based geopolymer mortar. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2014, 2014, 658067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Yusuf, T.O.; Noruzman, A.H.; Hassan, I. Early strength characteristics of palm oil fuel ash and metakaolin blended geopolymer mortar. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 690, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T. Durability of geopolymer materials in sodium and magnesium sulfate solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; van Riessen, A.; MacKenzie, K. Preparation and characterisation of fly ash based geopolymer mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, M.; Bhutta, M.; Azreen, M.; Ramadhansyah, P.; Mirza, J. Performance of blended ash geopolymer concrete at elevated temperatures. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoo-ngernkham, T.; Sata, V.; Hanjitsuwan, S.; Ridtirud, C.; Hatanaka, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. High calcium fly ash geopolymer mortar containing Portland cement for use as repair material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, K.; Buchwald, A.; Weil, M. The influence of calcium content on the structure and thermal performance of fly ash based geopolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Jalali, S. Adhesion characterization of tungsten mine waste geopolymeric binder. Influence of OPC concrete substrate surface treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somna, K.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Kajitvichyanukul, P.; Chindaprasirt, P. NaOH-activated ground fly ash geopolymer cured at ambient temperature. Fuel 2011, 90, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhua, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Huajun, Z.; Yue, C. Role of water in the synthesis of calcined kaolin-based geopolymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Van Deventer, J. The effects of inorganic salt contamination on the strength and durability of geopolymers. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 211, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Kodur, V.; Qi, S.L.; Wu, B. Characterizing the bond strength of geopolymers at ambient and elevated temperatures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 58, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Huang, S.-S.; Debbarma, S.; Rashid, R.S. Fire resistance of geopolymer concrete: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Sam, A.R.M.; Mirza, J.; Tahir, M.M.; Asaad, M.A.; Ismail, M.; Shah, K.W. Waste ceramic powder incorporated alkali activated mortars exposed to elevated Temperatures: Performance evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, K.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.; Yu, Q. Thermal and fire resistance of Class F fly ash based geopolymers–A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoti, M.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.-H. A critical review of geopolymer properties for structural fire-resistance applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, W.D.; Temuujin, J.; van Riessen, A. Thermal analysis of geopolymer pastes synthesised from five fly ashes of variable composition. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.W.; Huseien, G.F. Bond strength performance of ceramic, fly ash and GBFS ternary wastes combined alkali-activated mortars exposed to aggressive environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 119088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaya, A.M.; Shahidan, S.; Zuki, S.S.M.; Huseien, G.F.; Azmi, M.A.M.; Ismail, M.; Mirza, J. Durability and Acoustic Performance of Rubberized Concrete Containing POFA as Cement Replacement. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Asaad, M.A.; Abadel, A.A.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Hamzah, H.K.; Benjeddou, O.; Mirza, J. Drying shrinkage, sulphuric acid and sulphate resistance of high-volume palm oil fuel ash-included alkali-activated mortars. Sustainability 2022, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, H.K.; Huseien, G.F.; Asaad, M.A.; Georgescu, D.P.; Ghoshal, S.; Alrshoudi, F. Effect of waste glass bottles-derived nanopowder as slag replacement on mortars with alkali activation: Durability characteristics. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Lo, T.Y.; Barbhuiya, S.; Xu, W. Development of form-stable composite phase change material by incorporation of dodecyl alcohol into ground granulated blast furnace slag. Energy Build. 2013, 62, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yan, C.; Duan, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, X.; Li, D. A comparative study of high-and low-Al2O3 fly ash based-geopolymers: The role of mix proportion factors and curing temperature. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Mozgawa, W.; Handke, M. Vibrational spectra of complex ring silicate anions—Method of recognition. J. Mol. Struct. 1997, 404, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.W.; Van Deventer, J.; Smith, J. Mechanism of polysialation in the incorporation of zirconia into fly ash-based geopolymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shi, H.; Dick, W.A. Compressive strength and microstructural characteristics of class C fly ash geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).