Ceramic Filters for the Efficient Removal of Azo Dyes and Pathogens in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
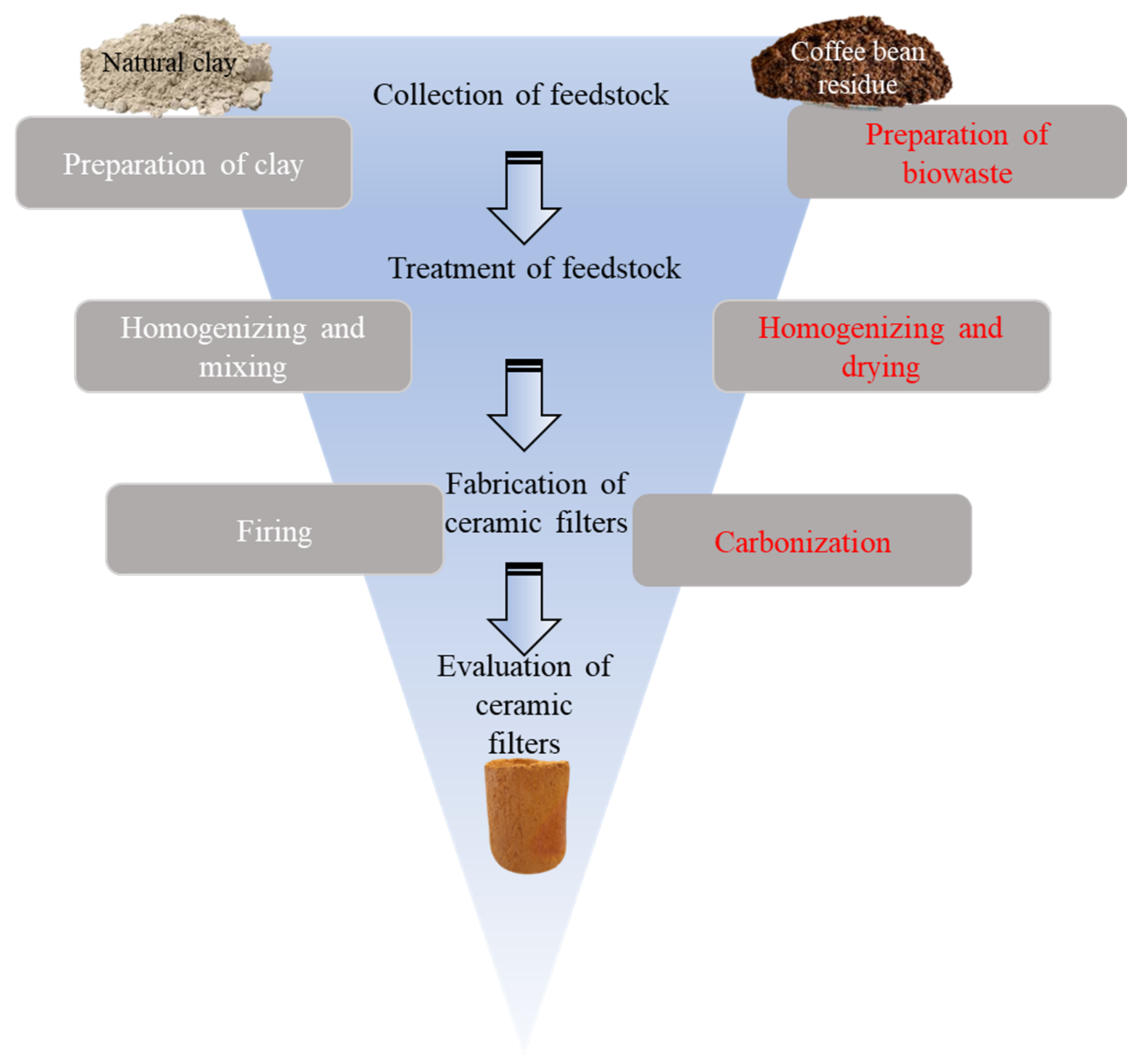
2.2. Fabrication of Ceramic Filters
2.3. Characterization of Feedstock and Ceramic Filters
2.4. Physical Characterization of Ceramic Filters
2.4.1. Apparent Porosity
2.4.2. Water Absorption and Water Flow Rate
2.5. Evaluation of the Capacity of CFs to Remove Methylene Blue and Ortho-Toluidine Blue
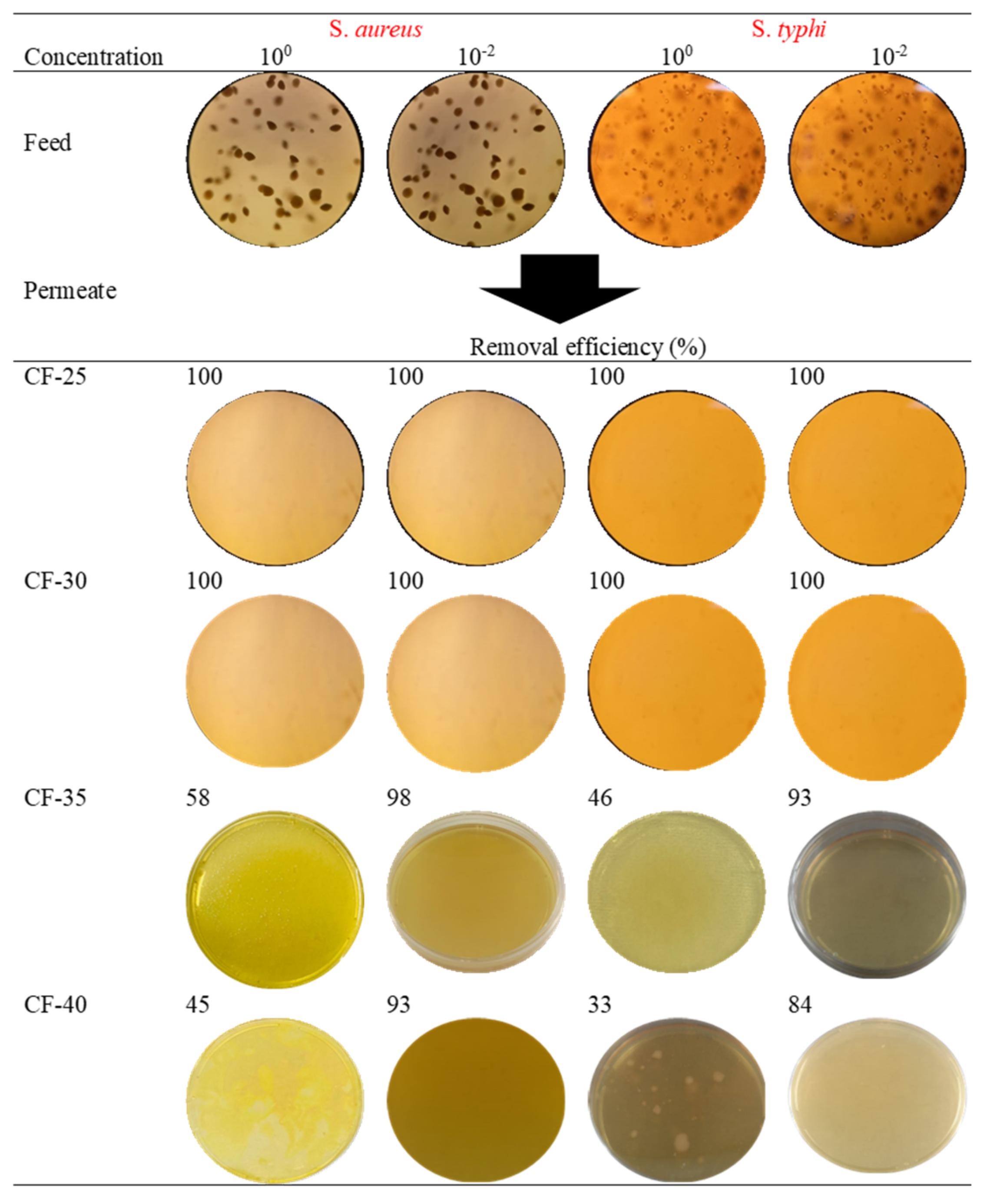
2.6. Evaluation of the Ceramic Filters for Pathogens Removal
2.7. Evaluation of Recyclability of CFs for Repeated Use
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Clay, Coffee Bean Waste, and Ceramic Filters
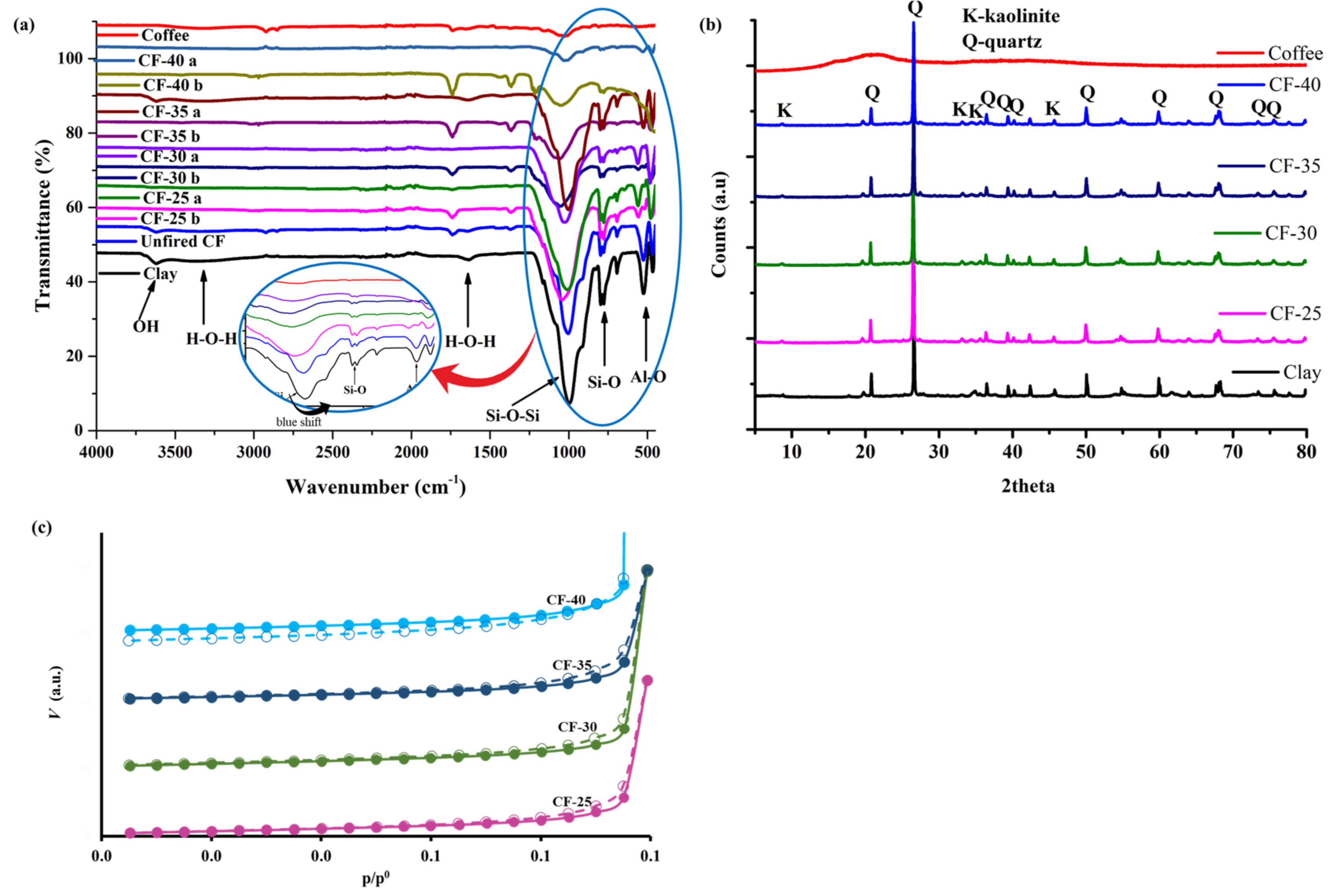
3.1.1. Surface Functional Groups
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
3.1.3. Textural Properties of the Ceramic Filters
3.1.4. Surface Morphology of Ceramic Filters
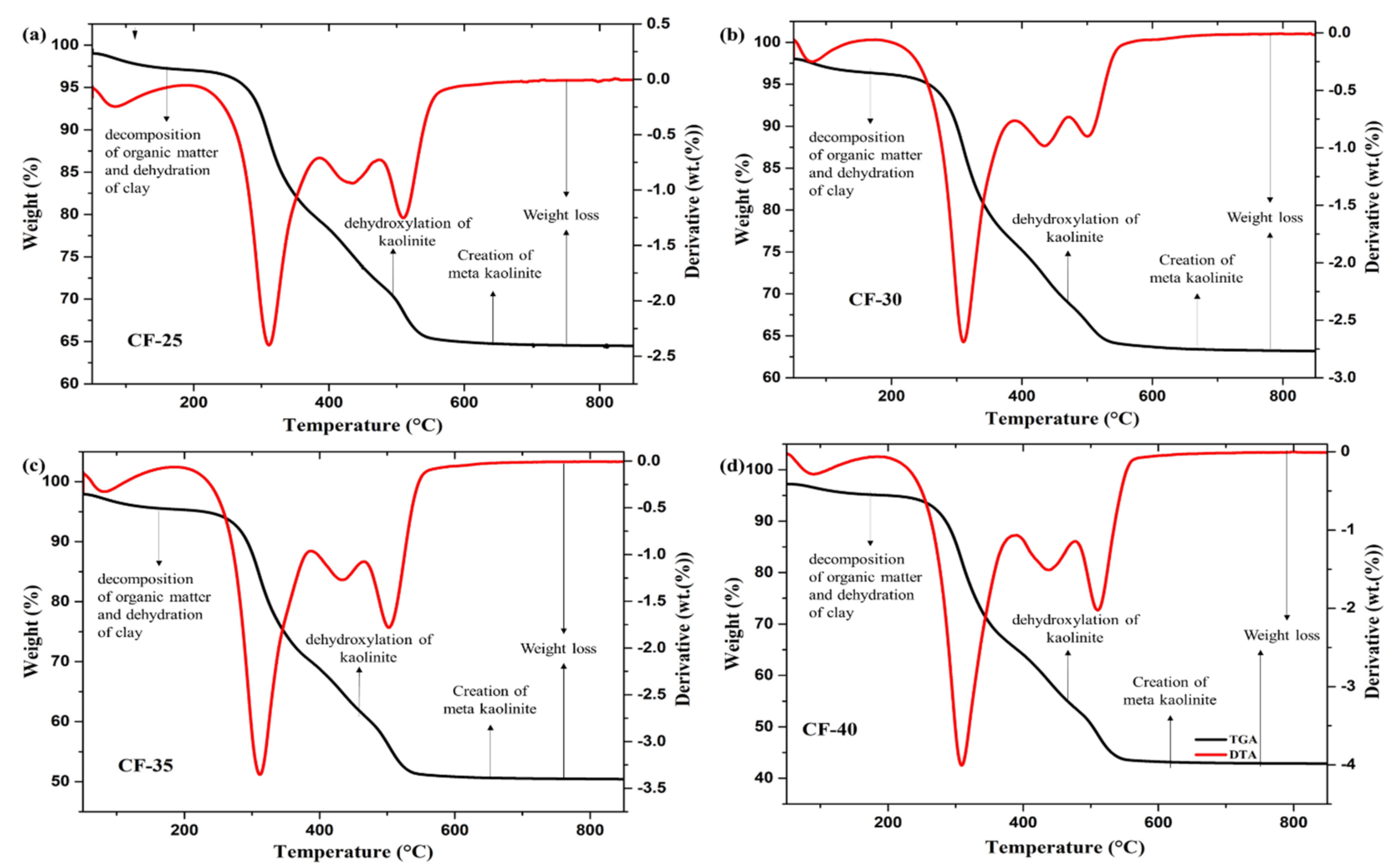
3.1.5. The Thermal Stability of Ceramic Filters
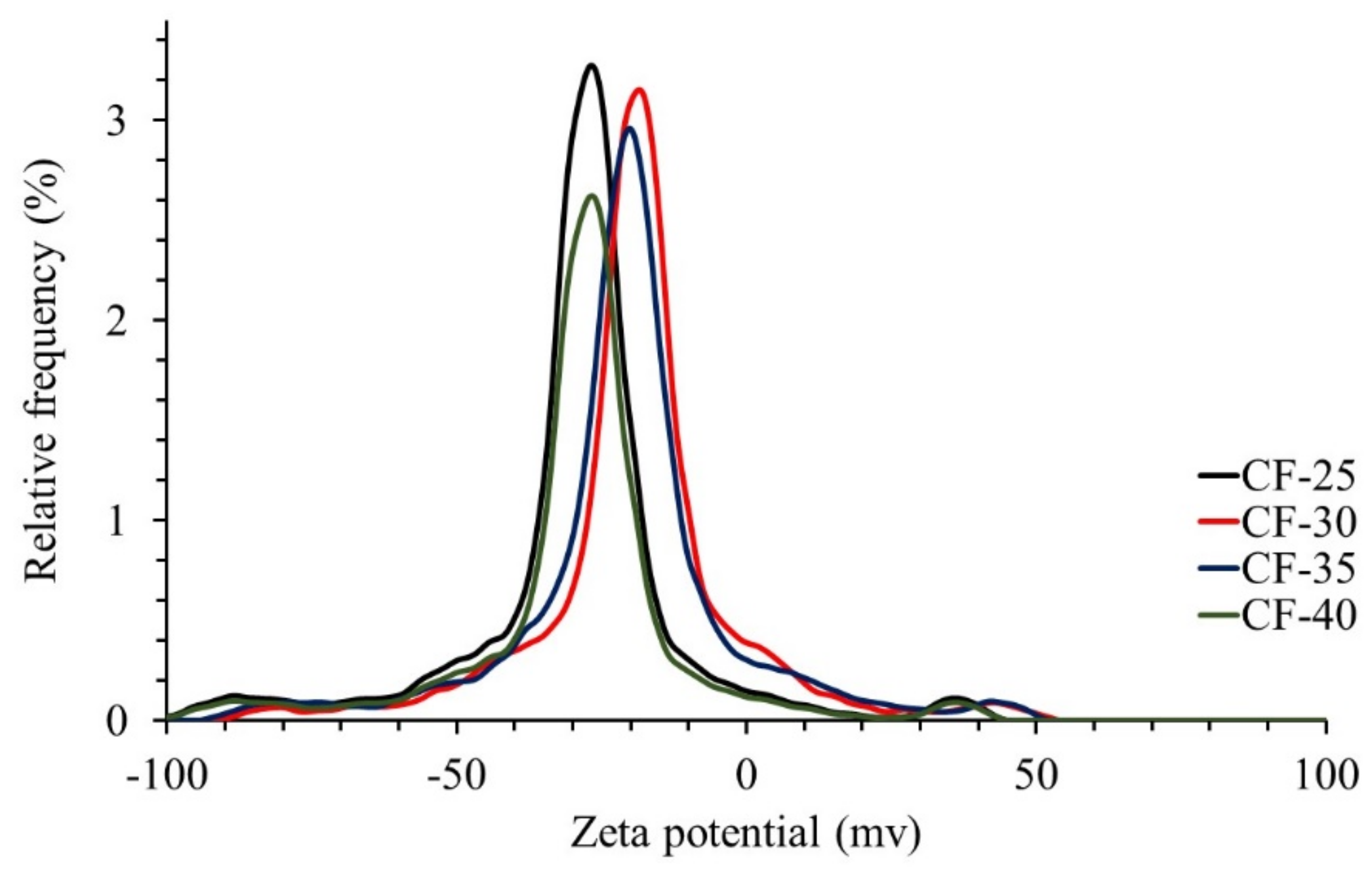
3.1.6. Surface Charge of the Ceramic Filters
3.1.7. Apparent Porosity, Water Adsorption, and Water Flow Rate of Ceramic Filters
3.2. Evaluation of Ceramic Filters in Removing Azo Dyes and Pathogens
3.2.1. Dye Removal Efficiency of the Ceramic Filters
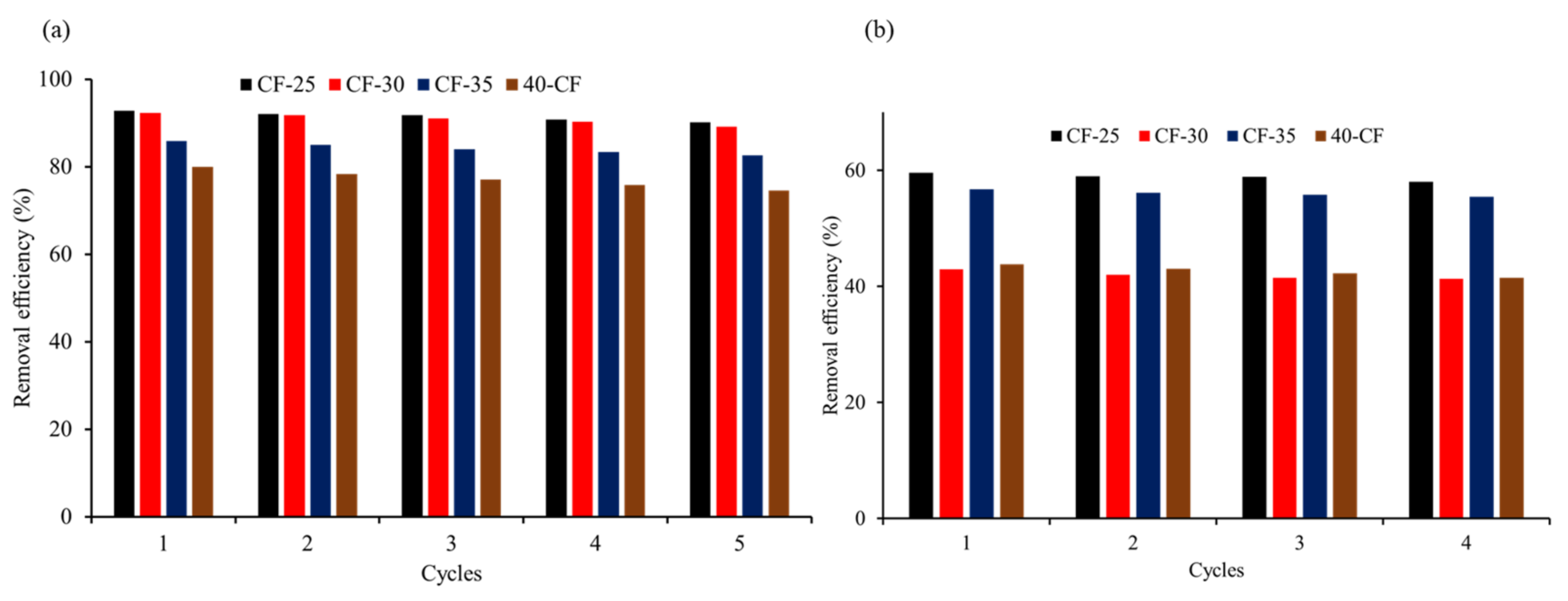
3.2.2. Recyclability of Ceramic Filters
3.2.3. Removal of Pathogens
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ekpunobi, U.; Agbo, S.; Ajiwe, V. Evaluation of the mixtures of clay, diatomite, and sawdust for production of ceramic pot filters for water treatment interventions using locally sourced materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, K.; Yin, J. Low-Cost ceramic disk filters coated with Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for drinking water disinfection and purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diarrhoeal-disease (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- WHO (World Health Organization). Preventing Diarrhoea through Better Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: Exposures and Impacts in Low- and Middle-Income Countries; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Muduli, M.; Choudhary, M.; Haldar, S.; Ray, S. Monitoring and assessment of Dracaena-based constructed vertical flow wetlands treating textile dye wastewater. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Mosteo, R.; Gómez, J.; Rubio, E.; Goñi, P.; Ormad, M.P. How does urban wastewater treatment affect the microbial quality of treated wastewater? Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 130, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Singh, M.K.; Kumar, S. Biofiltration technique for removal of waterborne pathogens. In Waterborne Pathogens; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 123–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ajala, O.; Tijani, J.; Salau, R.; Abdulkareem, A.; Aremu, O. A review of emerging micro-pollutants in hospital wastewater: Environmental fate and remediation options. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solayman, H.; Hossen, M.A.; Abd Aziz, A.; Yahya, N.Y.; Hon, L.K.; Ching, S.L.; Monir, M.U.; Zoh, K.-D. Performance Evaluation Of Dye Wastewater Treatment Technologies: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, A.; Amar, A.; Loulidi, I.; Hadey, C.; Jabri, M.; Alrashdi, A.A.; Lgaz, H.; Sadoq, M.; El-kordy, A.; Boukhlifi, F. Efficient adsorption removal of an anionic azo dye by lignocellulosic waste material and sludge recycling into combustible briquettes. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Ahmad, H.; Drioli, E.; Rehan, Z.A.; Rashid, A.; Akram, S.; Khalid, T. Role of polymeric nanocomposite membranes for the removal of textile dyes from wastewater. In Aquananotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, V.; Sasidharan, A. Seafood industry effluents: Environmental hazards, treatment and resource recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, L.; Elgamouz, A.; Kawde, A.N. An insight to the filtration mechanism of Pb (II) at the surface of a clay ceramic membrane through its preconcentration at the surface of a graphite/clay composite working electrode. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hube, S.; Eskafi, M.; Hrafnkelsdóttir, K.F.; Bjarnadóttir, B.; Bjarnadóttir M, Á.; Axelsdóttir, S.; Wu, B. Direct membrane filtration for wastewater treatment and resource recovery: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrow, C.; McBean, E.; Huang, G.; Yang, A.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Fu, H.; Cawte, T.; Li, Y. Ceramic water filters: A point-of-use water treatment technology to remove bacteria from drinking water in Longhai City, Fujian Province, China. J. Environ. Inform. 2018, 32, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Vidal, A.; Rivera-Sanchez, S.P.; Florez-Elvira, L.J.; Silva-Leal, J.A.; Diaz-Gomez, J.; Herrera-Cuero, L.F.; Botero, L.P.L. Removal of E. coli and Salmonella in pot ceramic filters operating at different filtration rates. Water Res. 2019, 159, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, C.; Tenebe, I.; Omole, D.; Ngene, B.U.; Oniemayin, B.I.; Maxwell, O.; Onoka, B. Accessing safe drinking water in sub-Saharan Africa: Issues and challenges in South–West Nigeria. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 30, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavoshani, A.; Hashemi, M.; Amin, M.M.; Ameta, S.C. Micropollutants and Challenges: Emerging in the Aquatic Environments and Treatment Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chaukura, N.; Katengeza, G.; Gwenzi, W.; Mbiriri, C.I.; Nkambule, T.T.; Moyo, M.; Kuvarega, A.T. Development and evaluation of a low-cost ceramic filter for the removal of methyl orange, hexavalent chromium, and Escherichia coli from water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 249, 122965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, D.; Amin, S.K.; Mansour, M.; Abdallah, H. Fabrication of low-cost antibacterial microfiltration tubular ceramic membranes. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 11489–11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Xin, X. Reduction of Escherichia coli using ceramic disk filter decorated by nano-TiO2: A low-cost solution for household water purification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, B.A.; Desta, A.F.; Assefa, F. Evaluating the efficacy of household filters used for the removal of bacterial contaminants from drinking water. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 14, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Min, X.; Xu, S.; Bender, J.; Wang, Y. Development of effective and fast-flow ceramic porous media for point-of-use water treatment: Effect of pore size distribution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, P.; Ziegler, D.; Rovere, M.; Tulliani, J.M.; Tagliaferro, A. Waste coffee ground biochar: A material for humidity sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.N.; Mahy, J.G.; Calberg, C.; Farcy, A.; Caucheteux, J.; Fagel, N.; Lambert, S.D. Influence of thermal and acidic treatments on the morphology of a natural kaolinitic clay mineral. Results Surf. Interfaces 2023, 12, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, D.; Li, L.; Lin, M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of magnesium salt contamination on the microstructures and properties of metakaolinitebased geopolymer: The role of MgCl2 and MgSO4. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 4500–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, S.O.; Kengara, F.O.; Kemmegne-Mbouguen, J.C.; Langmi, H.W.; Kowenje, C.B.O.; Mokaya, R. The effects of metakaolinization and fused-metakaolinization on zeolites synthesized from quartz rich natural clays. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 290, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, J.; Koutnik, P.; Bezucha, P.; Kwocznski, Z. Leachability of the metakaolinite-rich materials in different alkaline solutions. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung TT, N.; Nam, V.N.; Nhan, T.T.; Hoang, B.N.; Hung DL, T.; Quang, D.V. Utilization of Rice Husk, an Abundant and Inexpensive Biomass in Porous Ceramic Membrane Preparation: A Crucial Role of Firing Temperature. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 8688238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, S.; Zhu, C.; Wang, B.; Du, B.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, L. Study of the denitration performance of a ceramic filter using a manganese-based catalyst. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saja, S.; Bouazizi, A.; Achiou, B.; Ouaddari, H.; Karim, A.; Ouammou, M.; Aaddane, A.; Bennazha, J.; Younssi, S.A. Fabrication of low-cost ceramic ultrafiltration membrane made from bentonite clay and its application for soluble dyes removal. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Aslam, M.; Park, E.; Chang, S.; Kwon, D.; Kim, J. Submerged low-cost pyrophyllite ceramic membrane filtration combined with GAC as fluidized particles for industrial wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangtam, A.R.; Saikia, P.; Goswamee, R.L.; Sinha, D.; Sinha, U.B. Green synthesis of mesoporous Ni-Co layered double hydroxide and its application for removal of 2, 4-dinitrophenol from water: A theoretical study complemented by the first principle density functional theory-Monte-Carlo approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, A.E.; Shibeshi, N.T.; Tizazu, B.Z. Kinetic analysis of dehydroxylation of Ethiopian kaolinite during calcination. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 12837–12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, A.; El Haddar, A.; El Hassani, I.-E.E.A.; El Bouari, A.; Sadik, C. Valorization of coffee waste with Moroccan clay to produce a porous red ceramics (class BIII). Boletín Soc. Española Cerámica Vidr. 2019, 58, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Miller, C.A. Characterization of kaolinite ζ potential for interpretation of wettability alteration in diluted bitumen emulsion separation. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2350–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.; Nyström, M. Fouling phenomena. In Membranes in Bioprocessing: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 203–241. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, I.H.; Trägårdh, G.; Trägårdh, C.; Pihlajamäki, A. Determining the zeta-potential of ceramic microfiltration membranes using the electroviscous effect. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 147, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulta, A.L.; Micheal, G.A.W. Evaluation of the efficiency of ceramic filters for water treatment in Kambata Tabaro zone, southern Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2019, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, A.; Sharma, R.; Singh, A.; Upadhyay, N.K.; Shandilya, P. Direct dual-Z-scheme PANI/Ag2O/Cu2O heterojunction with broad absorption range for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, E.; Pla, L.; Lozano-Torres, B.; El Sayed, S.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Chromogenic and fluorogenic probes for the detection of illicit drugs. ChemistryOpen 2018, 7, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, H.; Ajmal, M.; Qureshi, R.B.; Muntha, S.T.; Farooq, M.; Siddiq, M. Facile synthesis of graphene oxide–silver nanocomposite for decontamination of water from multiple pollutants by adsorption, catalysis and antibacterial activity. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, C.; Golder, A.K. Utilizing Bioinspired AgNPs as an Antibacterial Agent to Enhance Ceramic Membrane Performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Wu, M. High antibacterial and antioxidant cotton fabric based on AgNPs@ HTCS and hyaluronic acid via lay by lay self-assembly. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 52, 15280837221140922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Oladejo, T.J.; Muhammed, N.M.; Saka, A.A.; Oluwabunmi, A.A.; Abdulkabir, M.; Joel, O.O. Fabrication of porous ceramic pot filters for adsorptive removal of pollutants in tannery wastewater. Sci. Afr. 2021, 11, e00705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Olufemi, A.F.; Qanungo, K. Development of green geo-adsorbent pellets from low fire clay for possible use in methylene blue removal in aquaculture. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ceramic Filters | Coffee Bean Residues (w/w%) | Clay (w/w%) |
|---|---|---|
| CF-25 | 25 | 75 |
| CF-30 | 30 | 70 |
| CF-35 | 35 | 65 |
| CF-40 | 40 | 60 |
| Ceramic Filter | Zeta Potential (mV) | Electrophoretic Mobility (µm·cm/V·s) | Conductivity (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CF-25 | −26.8 | −2.09 | 0.068 |
| CF-30 | −25.1 | −1.95 | 0.072 |
| CF-35 | −27.8 | −2.16 | 0.149 |
| CF-40 | −28.0 | −2.28 | 0.180 |
| Ceramic Filters | Water Absorption (%) | Flow Rate (L/h) | Apparent Porosity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CF-25 | 41.00 ± 0.82 | 1.28 ± 0.06 | 1.12 ± 0.03 |
| CF-30 | 54.40 ± 1.02 | 1.50 ± 0.08 | 1.24 ± 0.08 |
| CF-35 | 62.70 ± 1.92 | 2.20 ± 0.08 | 1.13 ± 0.02 |
| CF-40 | 81.80 ± 1.99 | 3.93 ± 0.12 | 1.25 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oaikhena, M.; Oluwalana-Sanusi, A.E.; Mokoena, P.P.; Mabuba, N.; Tshabalala, T.; Chaukura, N. Ceramic Filters for the Efficient Removal of Azo Dyes and Pathogens in Water. Ceramics 2023, 6, 2134-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6040131
Oaikhena M, Oluwalana-Sanusi AE, Mokoena PP, Mabuba N, Tshabalala T, Chaukura N. Ceramic Filters for the Efficient Removal of Azo Dyes and Pathogens in Water. Ceramics. 2023; 6(4):2134-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6040131
Chicago/Turabian StyleOaikhena, Marvellous, Abimbola E. Oluwalana-Sanusi, Puseletso P. Mokoena, Nonhlangabezo Mabuba, Themba Tshabalala, and Nhamo Chaukura. 2023. "Ceramic Filters for the Efficient Removal of Azo Dyes and Pathogens in Water" Ceramics 6, no. 4: 2134-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6040131
APA StyleOaikhena, M., Oluwalana-Sanusi, A. E., Mokoena, P. P., Mabuba, N., Tshabalala, T., & Chaukura, N. (2023). Ceramic Filters for the Efficient Removal of Azo Dyes and Pathogens in Water. Ceramics, 6(4), 2134-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics6040131









