Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Artocarpus heterophyllus L. Leaf Protein Concentrate: Solubility, Foaming, Emulsifying, and Antioxidant Properties of Protein Hydrolysates
Abstract
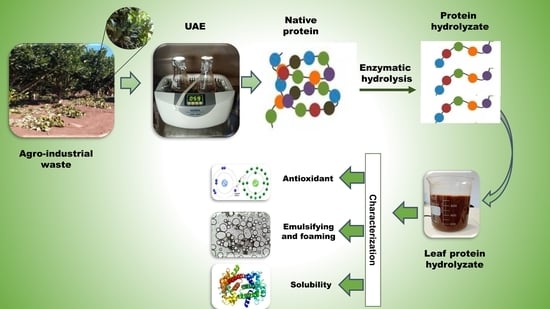
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vegetal Material
2.2. Chemical Substances
2.3. Preparation of Flour for Extraction Procedures
2.3.1. Maceration Extraction (M)
2.3.2. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
2.4. LPC Hydrolysis
2.5. Analysis of Amino Acids by Gas-Chromatography Mass-Spectrometry (GC-MS)
2.6. Techno-Functional Properties
2.6.1. Solubility
2.6.2. Foaming Properties
2.6.3. Emulsifying Properties
2.7. Antioxidant Properties
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yield and Amino Acid Composition
3.2. Techno-Functional Properties
3.2.1. Solubility
3.2.2. Foaming Properties
3.2.3. Emulsifying Properties
3.3. Antioxidant Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahergorabi, R.; Hosseini, S.V. Proteins, Peptides, and Amino Acids. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Components: Effects of Innovative Processing Techniques; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128052570. [Google Scholar]
- Deprá, M.C.; Dias, R.R.; Sartori, R.B.; de Menezes, C.R.; Zepka, L.Q.; Jacob-Lopes, E. Nexus on Animal Proteins and the Climate Change: The Plant-Based Proteins Are Part of the Solution? Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 133, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detzel, A.; Krüger, M.; Busch, M.; Blanco-Gutiérrez, I.; Varela, C.; Manners, R.; Bez, J.; Zannini, E. Life Cycle Assessment of Animal-Based Foods and Plant-Based Protein-Rich Alternatives: An Environmental Perspective. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 102, 5098–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estell, M.; Hughes, J.; Grafenauer, S. Plant Protein and Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Consumer and Nutrition Professional Attitudes and Perceptions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Varjani, S. Valorization of Agro-Industrial Wastes for Biorefinery Process and Circular Bioeconomy: A Critical Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Varjani, S.J.; Saravanan, A. Advances in Production and Application of Biochar from Lignocellulosic Feedstocks for Remediation of Environmental Pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 122030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion-Espinoza, I.A.; Iñiguez-Moreno, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Barros-Castillo, J.C.; Calderón-Chiu, C.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. Edible Pectin Film Added with Peptides from Jackfruit Leaves Obtained by High-Hydrostatic Pressure and Pepsin Hydrolysis. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadimu, G.J.; Gill, H.; Farahnaky, A.; Truong, T. Improving the Enzymolysis Efficiency of Lupin Protein by Ultrasound Pretreatment: Effect on Antihypertensive, Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Activities of the Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkouch, I.; Tabbene, O.; Gharbi, D.; Ben Mlouka, M.A.; Elkahoui, S.; Rihouey, C.; Coquet, L.; Cosette, P.; Jouenne, T.; Limam, F. Antioxidant, Antityrosinase and Antibiofilm Activities of Synthesized Peptides Derived from Vicia Faba Protein Hydrolysate: A Powerful Agents in Cosmetic Application. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.R.A.; Azlan, A.; Yusof, H.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Enzymatic Eel (Monopterus Sp) Protein Hydrolysate as Influenced by Different Molecular Weight. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Chiu, C.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Herman-Lara, E.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam) Leaf as a New Source to Obtain Protein Hydrolysates: Physicochemical Characterization, Techno-Functional Properties and Antioxidant Capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-González, Y.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. Characterization and Antifungal Activity of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) Leaf Extract Obtained Using Conventional and Emerging Technologies. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigliotti, J.C.; Jaczynski, J.; Tou, J.C. Determination of the Nutritional Value, Protein Quality and Safety of Krill Protein Concentrate Isolated Using an Isoelectric Solubilization/Precipitation Technique. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Potkule, J.; Verma, R.; Punia, S.; Mahapatra, A.; Belwal, T.; Dahuja, A.; Joshi, S.; Berwal, M.K.; et al. Advances in the Plant Protein Extraction: Mechanism and Recommendations. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Ren, J.; Zhao, M. Effects of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Soy Protein Isolates and on the Emulsifying Properties of Hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2600–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jia, J.; Kuang, C.; Yang, H. Effect of Ultrasonic Pretreatment on Whey Protein Hydrolysis by Alcalase: Thermodynamic Parameters, Physicochemical Properties and Bioactivities. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Food and Natural Products. Mechanisms, Techniques, Combinations, Protocols and Applications. A Review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Devi, L.M.; Badwaik, L.S. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Pumpkin Seeds Protein and Its Physicochemical and Functional Characterization. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.; Natarajan, V.; Modupalli, N.; Thangaraj, S.; Rawson, A. Pulsed Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Protein from Defatted Bitter Melon Seeds (Momardica charantia L.) Meal: Kinetics and Quality Measurements. LWT 2022, 115, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, K.; Azam, S.M.R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qu, W. Ultrasound Frequency Effect on Soybean Protein: Acoustic Field Simulation, Extraction Rate and Structure. LWT 2021, 145, 111320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-chiu, C.; Calderón-santoyo, M.; Damasceno-gomes, S.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Use of Jackfruit Leaf (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) Protein Hydrolysates as a Stabilizer of the Nanoemulsions Loaded with Extract-Rich in Pentacyclic Triterpenes Obtained from Coccoloba uvifera L. Leaf. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying Properties of Proteins: Evaluation of a Turbidimetric Technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingwascharapong, P.; Chaijan, M.; Karnjanapratum, S. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Protein from Bombay Locusts and Its Impact on Functional and Antioxidative Properties. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Nájera, L.C.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Gastón-Peña, C.R.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. Green Technologies for the Extraction of Proteins from Jackfruit Leaves (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/FAO World Health Organization/Food and Agricultural Organization. Protein and Amino Acid Requirement in Human Nutrition: Report of a Joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Acosta, L.; Serna-Saldivar, S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Escalante-Aburto, A.; Chuck-Hernández, C. Effect of Ultrasound Application on Protein Yield and Fate of Alkaloids during Lupin Alkaline Extraction Process. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Soltanzadeh, M.; Ebrahimi, A.R.; Hamishehkar, H. Spirulina Platensis Protein Hydrolysates: Techno-Functional, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties. Algal Res. 2022, 65, 102739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Li, P.P.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.H.; Sun, Z.L.; Sun, C.; Geng, Z.M.; Xu, W.M.; Wang, D.Y. Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Alkaline Extraction on the Physiochemical and Functional Characteristics of Chicken Liver Protein Isolate. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Tian, S.; Chen, F. Effect of Ultrasound-assisted Extraction on the Structure and Emulsifying Properties of Peanut Protein Isolate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wen, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction on the Structural, Functional and Antioxidant Properties of Dolichos lablab L. Protein. Process Biochem. 2021, 101, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdar, S.N.; Rajalakshmi, V.; Pednekar, M.D.; Juan, F.; Yardi, V.; Sharma, A. Influence of Degree of Hydrolysis on Functional Properties, Antioxidant Activity and ACE Inhibitory Activity of Peanut Protein Hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Luo, L.; Chen, J.; Luo, S.; McClements, D.J.; Wu, L. Effect of Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Structure and Emulsifying Properties of Rice Glutelin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural, Physical and Emulsifying Properties of Animal and Vegetable Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; He, J.; Dang, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhou, C. Insight into Ultrasound-Assisted Phosphorylation on the Structural and Emulsifying Properties of Goose Liver Protein. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Tu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Yu, C.; Battino, M.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Du, M. Biological and Conventional Food Processing Modifications on Food Proteins: Structure, Functionality, and Bioactivity. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 40, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, B.; Dia, V.P. Alcalase and Bromelain Hydrolysis Affected Physicochemical and Functional Properties and Biological Activities of Legume Proteins. Food Struct. 2021, 27, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayas, J.F. Foaming Properties of Proteins. In Functionality of Proteins in Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 260–309. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, P.; Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, D. Effect of Ultrasound Assisted Extraction on the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Collagen from Soft-Shelled Turtle Calipash. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Protein. In Fennema’s Food Chemistry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 235–356. ISBN 9781315372914. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, T.H.; Ren, H.; Quek, S.Y. Effects of Ultrasonic Pretreatment on the Structure and Functionality of Chicken Bone Protein Prepared by Enzymatic Method. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Taha, A.; Hu, H.; Lu, Q.; Pan, S. Effects of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction on the Physicochemical Properties of Different Walnut Proteins. Molecules 2019, 24, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liang, Q.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Zhou, C.; Mahunu, G.K. Effects of Ultrasound and Ultrasound Assisted Alkaline Pretreatments on the Enzymolysis and Structural Characteristics of Rice Protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Hayat, K.; Kurtz, N.C.; Wu, X.; Ahmad, M.; Zheng, F. Ultrasound-Assisted Alkaline Proteinase Extraction Enhances the Yield of Pecan Protein and Modifies Its Functional Properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 80, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, N.; Mohammadzadeh Milani, J.; Biparva, P. Functional and Conformational Properties of Proteolytic Enzyme-modified Potato Protein Isolate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Effects of Divergent Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Structure of Watermelon Seed Protein and the Antioxidant Activity of Its Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, S.U.; Álvarez, C.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C.P. Extraction and Characterization of Protein from Irish Brown Seaweed Ascophyllum Nodosum. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, R.E. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins as Antioxidants for Food Preservation; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9781782420972. [Google Scholar]
- Fadimu, G.J.; Gill, H.; Farahnaky, A.; Truong, T. Investigating the Impact of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Antioxidant Properties of Lupin Protein Hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 2004–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Amino Acid (mg/100 g Protein) | Leaf Protein Concentrate (LPC) | Hydrolysate (H) | Suggested Intake (%) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maceration (M) | Ultrasound (U) | Maceration (M) | Ultrasound (U) | ||
| Yield (%) | 6.76 ± 0.60 a | 7.04 ± 0.29 a | 38.80 ± 0.92 b | 41.38 ± 4.14 b | NA |
| Alanine | 2.06 ± 0.12 a | 1.89 ± 0.45 a | 3.78 ± 0.48 b | 3.16 ± 0.07 ab | NA |
| Glycine | 2.10 ± 0.11 a | 1.67 ± 0.53 a | 3.70 ± 0.39 b | 3.79 ± 0.19 b | NA |
| Valine | 2.15 ± 0.14 a | 2.26 ± 0.46 a | 4.72 ± 0.0 b | 3.67 ± 0.02 c | 3.9 |
| Leucine | 2.81 ± 0.10 a | 2.89 ± 0.61 a | 6.76 ± 0.23 c | 4.48 ± 0.04 b | 5.9 |
| Isoleucine | 1.60 ± 0.08 a | 1.80 ± 0.33 a | 3.52 ± 0.13 c | 2.71 ± 0.07 b | 3.0 |
| Proline | 1.54 ± 0.06 a | 2.23 ± 0.36 ab | 4.40 ± 0.67 c | 3.96 ± 0.59 bc | NA |
| Methionine | 0.37 ± 0.02 a | 0.55 ± 0.08 ab | 0.71 ± 0.06 b | 0.61 ± 0.08 ab | 2.2 |
| Serine | 1.15 ± 0.03 a | 1.46 ± 0.28 ab | 1.54 ± 0.48 ab | 2.35 ± 0.10 c | NA |
| Threonine | 1.12 ± 0.04 a | 1.44 ± 0.26 a | 1.88 ± 0.05 a | 2.16 ± 0.23 b | 2.3 |
| Phenylalanine | 1.56 ± 0.08 a | 2.01 ± 0.41 ab | 3.20 ± 0.32 c | 2.83 ± 0.22 bc | 3.8 |
| Aspartic acid | 2.99 ± 0.08 a | 3.11 ± 0.84 a | 3.18 ± 0.58 a | 5.68 ± 0.40 b | NA |
| Glutamic acid | 3.19 ± 0.26 a | 4.45 ± 1.01 a | 3.19 ± 0.56 a | 6.69 ± 0.77 b | NA |
| Lysine | 2.02 ± 0.31 ab | 9.03 ± 0.30 b | nd | 7.02 ± 1.12 c | 4.5 |
| HAA | 12.09 ± 0.61 a | 13.63 ± 1.69 a | 27.10 ± 1.11 b | 21.42 ± 0.22 c | NA |
| AAA | 1.56 ± 0.08 a | 2.01 ± 0.41 ab | 3.20 ± 0.32 c | 2.83 ± 0.22 bc | NA |
| EAA | 10.51 ± 0.73 a | 18.54 ± 1.18 ab | 18.91 ± 0.96 ab | 21.32 ± 2.56 b | NA |
| NCAA | 6.18 ± 0.34 a | 7.56 ± 0.86 a | 6.36 ± 0.14 a | 12.37 ± 1.17 b | NA |
| TAA | 24.65 ± 1.44 a | 34.78 ± 2.93 ab | 40.58 ± 2.16 b | 49.11 ± 2.55 c | NA |
| pH | Leaf Protein Concentrate | Hydrolysate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maceration | Ultrasound | Maceration | Ultrasound | |
| 2 | 0 ± 0 a | 0 ± 0 a | 1.00 ± 0.02 b,A | 3.83 ± 0.23 c,B |
| 4 | 0 ± 0 a | 0 ± 0 a | 60.14 ± 0.10 d,A | 72.12 ± 3.05 ab,B |
| 6 | 0.97 ± 0.18 ab,A | 2.59 ± 0.1 a,A | 67.8 ± 0.98 a,B | 77.39 ± 0.43 b,C |
| 8 | 2.95 ± 0.18 b,A | 2.89 ± 0.91 a,A | 65.27 ± 1.35 a,B | 66.26 ± 1.70 a,B |
| 10 | 0 ± 0 a | 0 ± 0 a | 52.74 ± 0.10 c,A | 66.16 ± 0.14 a,B |
| Functionals Properties | Leaf Protein Concentrate | Hydrolysate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maceration | Ultrasound | Maceration | Ultrasound | |
| Foaming capacity (FC, %) | 0 ± 0 a | 0 ± 0 a | 15.56 ± 2.55 b | 35 ± 1.67 c |
| Foaming stability (FS, %) | 0 ± 0 a | 0 ± 0 a | 0 ± 0 a | 21.11 ± 4.19 b |
| Emulsifying activity index (EAI, m2/g) | 9.59 ± 1.10 a | 33.99 ± 0.91 b | 67.57 ± 1.31 c | 78.28 ± 0.03 d |
| Emulsion stability index (ESI, min) | 32.74 ± 3.7 a | 46.19 ± 4.81 b | 200.34 ± 11.44 c | 480.89 ± 10.77 d |
| Concentration (mg/mL) | Leaf Protein Concentrate | Hydrolysate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maceration | Ultrasound | Maceration | Ultrasound | |
| 0.3 | 11.52 ± 0.59 a,A | 18.09 ± 2.44 a,B | 13.88 ± 0.42 a,AB | 12.21 ± 0.83 a,A |
| 0.5 | 11.97 ± 0.14 a,B | 23.38 ± 1.06 a,A | 54.58 ± 1.02 b,C | 59.41 ± 3.04 b,C |
| 0.8 | 21.25 ± 2.61 b,B | 30.91 ± 0.17 b,A | 75.28 ± 3.62 c,D | 85.59 ± 1.37 c,C |
| 1.0 | 20.37 ± 0.69 b,B | 38.15 ± 0.39 c,A | 99.68 ± 0.23 d,C | 99.63 ± 0.26 d,C |
| IC50 | nd | nd | 0.32 ± 0.01 B | 0.29 ± 0.01 A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vera-Salgado, J.; Calderón-Chiu, C.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Barros-Castillo, J.C.; López-García, U.M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Artocarpus heterophyllus L. Leaf Protein Concentrate: Solubility, Foaming, Emulsifying, and Antioxidant Properties of Protein Hydrolysates. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6040050
Vera-Salgado J, Calderón-Chiu C, Calderón-Santoyo M, Barros-Castillo JC, López-García UM, Ragazzo-Sánchez JA. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Artocarpus heterophyllus L. Leaf Protein Concentrate: Solubility, Foaming, Emulsifying, and Antioxidant Properties of Protein Hydrolysates. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleVera-Salgado, Julián, Carolina Calderón-Chiu, Montserrat Calderón-Santoyo, Julio César Barros-Castillo, Ulises Miguel López-García, and Juan Arturo Ragazzo-Sánchez. 2022. "Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Artocarpus heterophyllus L. Leaf Protein Concentrate: Solubility, Foaming, Emulsifying, and Antioxidant Properties of Protein Hydrolysates" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6040050
APA StyleVera-Salgado, J., Calderón-Chiu, C., Calderón-Santoyo, M., Barros-Castillo, J. C., López-García, U. M., & Ragazzo-Sánchez, J. A. (2022). Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Artocarpus heterophyllus L. Leaf Protein Concentrate: Solubility, Foaming, Emulsifying, and Antioxidant Properties of Protein Hydrolysates. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6040050