The Effect of Dental Bleaching on Nanohybrid Composite Surface Roughness: A Comparative In Vitro Study of SEM and Profilometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size Calculation
2.2. Specimen Preparation
- Group 1: fresh composite (unstained, unbleached); this was the control group.
- Group 2: old composite (aged and stained, unbleached).
- Group 3: bleached fresh composite (unstained, bleached).
- Group 4: bleached old composite (aged and stained, bleached).
- Group 5: old repolished composite (aged and stained, unbleached, repolished).
- Group 6: old repolished bleached composite (aged and stained, bleached, repolished).
2.3. Simulated Staining and Aging Procedures
2.4. Bleaching Procedure
2.5. Repolishing
2.6. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results
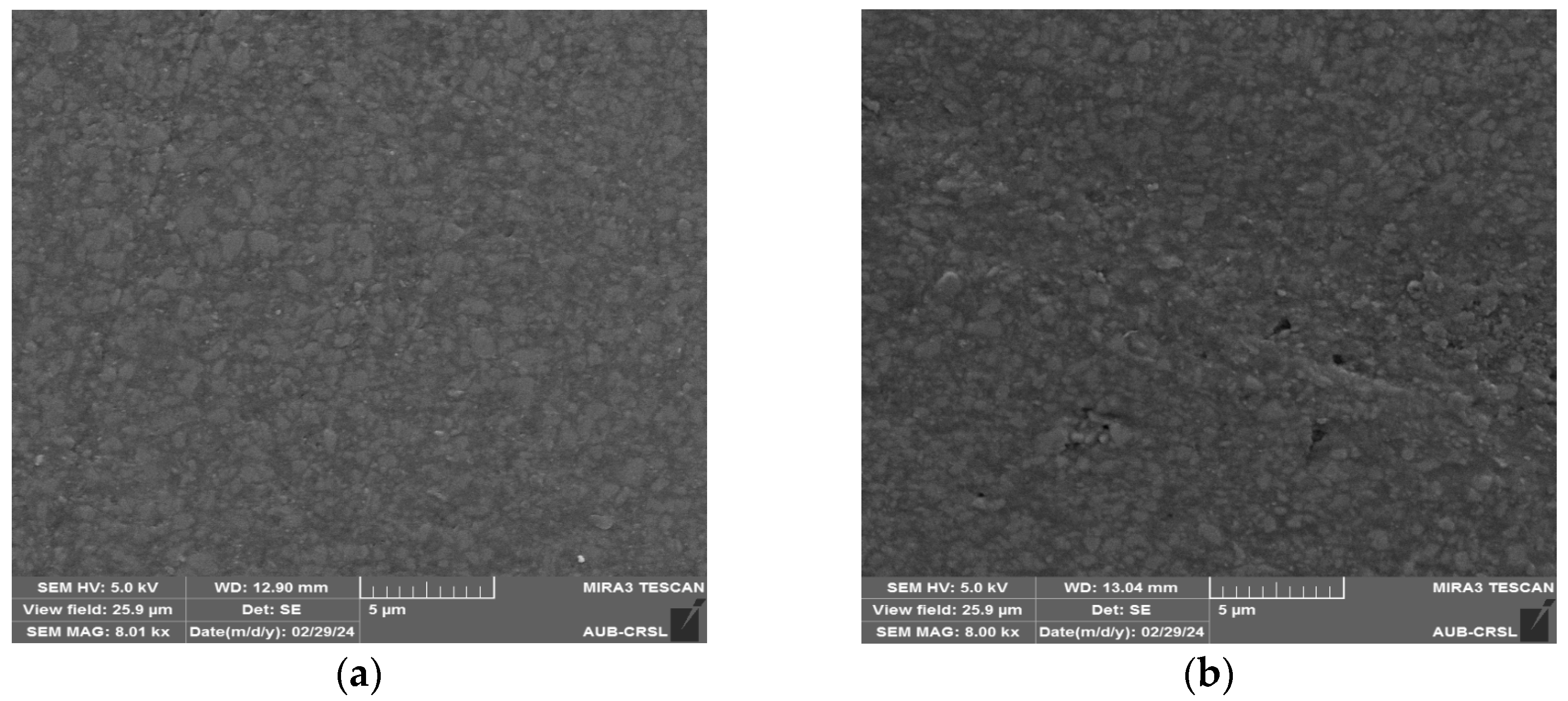
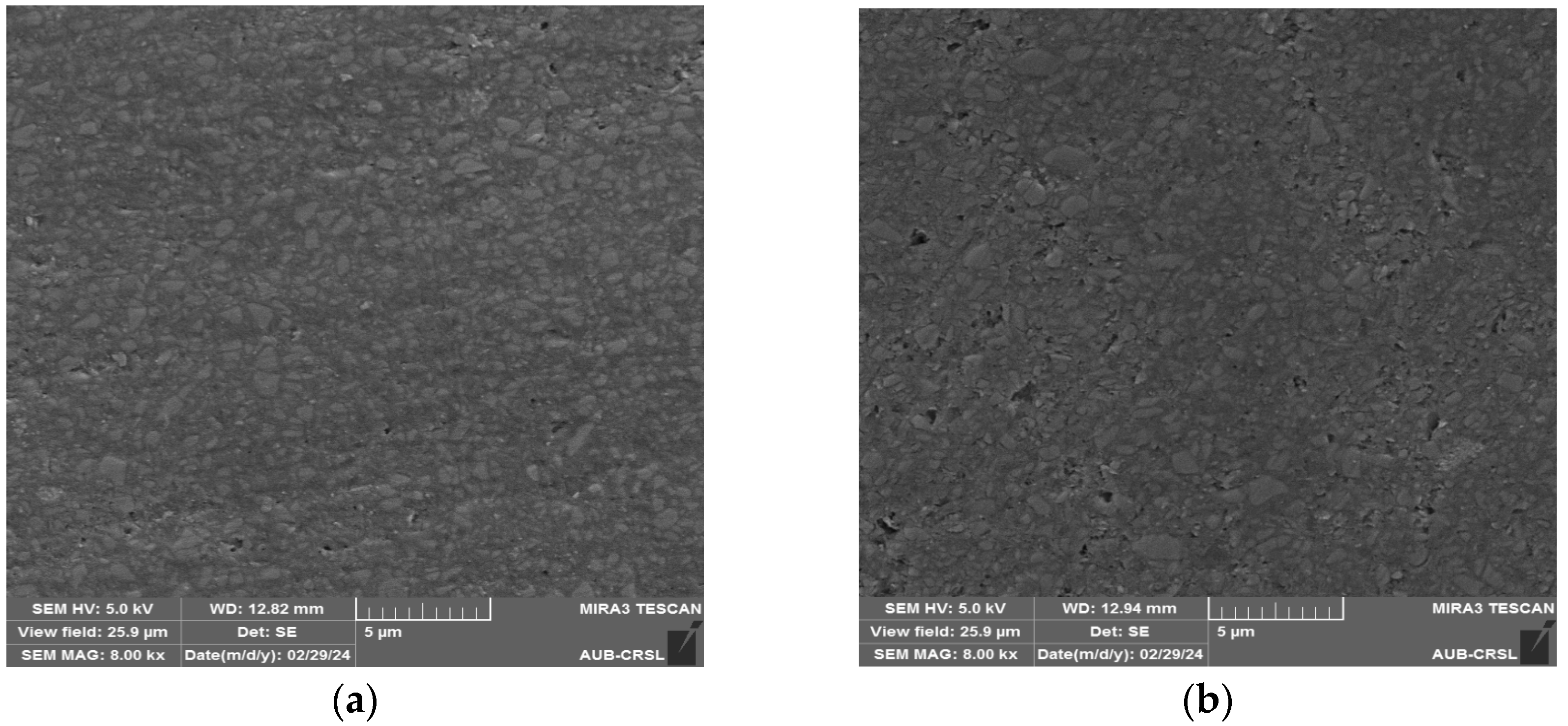
3.1. SEM Observations
3.2. Descriptive Statistics
3.3. Comparing Methods of Surface Roughness Measurement
3.4. Surface Roughness Comparison Across Treatment Groups: ANOVA Results
3.5. Three-Way ANOVA Analysis
3.6. Independent Samples T-Test Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newton, J.T.; Subramanian, S.S.; Westland, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Luo, W.; Joiner, A. The impact of tooth colour on the perceptions of age and social judgements. J. Dent. 2021, 112, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, C.; Nachabe, N.; El Osta, N.; Zogheib, C.M. Evaluation of dental parameters perception by Lebanese prosthodontists, orthodontists and aesthetic doctors. Int. Arab J. Dent. 2020, 11, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.R.; Wertz, P.W. Review of the mechanism of tooth whitening. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2015, 27, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.K.; Al-Abbasi, S.W.; Refaat, M.M.; Hussain, A.M. The effect of staining and bleaching on the color of two different types of composite restoration. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e1233–e1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preethy, N.A.; Jeevanandan, G.; Govindaraju, L.; Subramanian, E.M.G. Comparison of Shear Bond Strength of Three Commercially Available Esthetic Restorative Composite Materials: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2020, 13, 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Karademir, S.A.; Atasoy, S.; Yılmaz, B. Effect of bleaching and repolishing on whiteness change and staining susceptibility of resin-based materials. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerame, D.; Fanfoni, L.; De Biasi, M.; Bevilacqua, L.; Generali, L. Influence of Thickness and Shade on the Color of Layered Novel Nanohybrid Composite Systems. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2021, 41, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oja, J.; Lassila, L.; Vallittu, P.K.; Garoushi, S. Effect of Accelerated Aging on Some Mechanical Properties and Wear of Different Commercial Dental Resin Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Bektaş, Ö. Effect of in-office bleaching on the surface roughness of different composite resins. Cumhur. Dent. J. 2022, 25, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlukia, S.; Hammond, L.; Malik, K. Is surface roughness of direct resin composite restorations material and polisher-dependent? A systematic review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2023, 35, 947–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaboura, A.; Fragouli, M.; Rahiotis, C.; Silikas, N. Evaluation of surface characteristics of dental composites using profilometry, scanning electron, atomic force microscopy and gloss-meter. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Pham, K.; Vo, C.Q. A new method for assessment of nickel-titanium endodontic instrument surface roughness using field emission scanning electronic microscope. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, X.; Elsworth, D. Evolution of pore systems in low-maturity oil shales during thermal upgrading—Quantified by dynamic SEM and machine learning. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMarzooqi, F.A.; Bilad, M.R.; Mansoor, B.; Arafat, H.A. A comparative study of image analysis and porometry techniques for characterization of porous membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2017–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fátima Balderrama, Í.; de Toledo Stuani, V.; Cardoso, M.V.; Oliveira, R.C.; Lopes, M.M.; Greghi, S.L. The influence of implant surface roughness on decontamination by antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and chemical agents: A preliminary study in vitro. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 33, 102105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaal, G.; Daou, M.; Mahdi, S.S.; Ahmed, Z.; Maalouf, E.; Batteni, G.; Qasim, S.S.; Kassis, C.; Agha, D.; Haddad, H.; et al. In vitro evaluation of the color stability and surface roughness of a new composite flow. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2023, 15, e43–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, S.M.; Daou, M.; Najjar, G.; Zebouni, E. In vitro comparison of the color degradation of two computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing provisional materials: A 12-month simulation. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2023, 23, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, D.A.; Hallage, P.H.; Zebouni, E. In vitro evaluation of color changes of two different layering ceramics after thermocycling in coffee. Int. Arab J. Dent. (IAJD) 2021, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, A.D.; Tuculina, M.J.; Diaconu, O.A.; Gheorghiță, L.M.; Nicolicescu, C.; Cumpătă, C.N.; Petcu, C.; Abdul-Razzak, J.; Rîcă, A.M.; Voinea-Georgescu, R. Effects of Dental Bleaching Agents on the Surface Roughness of Dental Restoration Materials. Medicina 2023, 59, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Cartagena, R.; López-Galeano, E.J.; Latorre-Correa, F.; Agudelo-Suárez, A.A. Effect of polishing systems on the surface roughness of nano-hybrid and nano-filling composite resins: A systematic review. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.D.; Raisingani, D.; Jindal, D.; Mathur, R. A Comparative Analysis of Different Finishing and Polishing Devices on Nanofilled, Microfilled, and Hybrid Composite: A Scanning Electron Microscopy and Profilometric Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 9, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durner, J.; Stojanovic, M.; Urcan, E.; Spahl, W.; Haertel, U.; Hickel, R.; Reichl, F.X. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on the three-dimensional polymer network in composites. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.T.; Youssef, M.N.; Turbino, M.L. Effect of bleaching agents on the nanohardness of tooth enamel, composite resin, and the tooth-restoration interface. Oper. Dent. 2016, 41, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Yu, M.; Jin, C.; Huang, C. Effect of aging and bleaching on the color stability and surface roughness of a recently introduced single-shade composite resin. J. Dent. 2024, 143, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongpraparatana, I.; Matangkasombut, O.; Thanyasrisung, P.; Panich, M. Effect of Vital Tooth Bleaching on Surface Roughness and Streptococcal Biofilm Formation on Direct Tooth-Colored Restorative Materials. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Purayil, T.; Ginjupalli, K.; Pentapati, K.C.; Shenoy, N. Effect of in-office bleaching agent on the surface roughness and microhardness of nanofilled and nanohybrid composite resins. F1000Research 2023, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, N.; Topçu, F.T.; Karaoğlanoğlu, S.; Oktay, E.A.; Erdemir, U. Effect of finishing and polishing systems on the surface roughness and color change of composite resins. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e446–e454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, K.; Gupta, S.; Nikhil, V.; Jaiswal, S.; Jain, A.; Aggarwal, N. Effect of Different Finishing and Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Resin Composite and Enamel: An In vitro Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopy Study. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 2019, 9, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhyastha, P.S.; Hegde, S.; Srikant, N.; Kotian, R.; Iyer, S.S. Effect of finishing/polishing techniques and time on surface roughness of esthetic restorative materials. Dent. Res. J. 2017, 14, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Tuysuz, O.K.; Gurses, M. Changes in physical properties of universal composites and CAD/CAM materials after bleaching and antioxidant applications: Scanning electron microscope and atomic force microscope evaluation. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, A.A.; Shaalan, O.; Abdelraouf, R.M.; Habib, N.A. Effect of immersion and thermocycling in different beverages on the surface roughness of single- and multi-shade resin composites. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barac, R.; Gasic, J.; Trutic, N.; Sunaric, S.; Popovic, J.; Djekic, P.; Radenkovic, G.; Mitic, A. Erosive Effect of Different Soft Drinks on Enamel Surface in vitro: Application of Stylus Profilometry. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W. High-resolution imaging of the microbial cell surface. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.N.; Harbison, A.M. Scanning electron microscopy sample preparation and imaging. In Molecular Profiling: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Wang, X.Y. Surface roughness and gloss of polished nanofilled and nanohybrid resin composites. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, K.; Tekce, N.; Tuncer, S.; Serim, M.E.; Demirci, M. Evaluation of the surface hardness, roughness, gloss and color of composites after different finishing/polishing treatments and thermocycling using a multitechnique approach. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrabeah, G.; Shabib, S.; Almomen, R.; Alhedeithi, N.; Alotaibi, S.; Habib, S.R. Effect of Home Bleaching on the Optical Properties and Surface Roughness of Novel Aesthetic Dental Ceramics. Coatings 2023, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, I.; Bugshan, A. The role of salivary contents and modern technologies in the remineralization of dental enamel: A narrative review. F1000Research 2021, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Type | Composition | Filler Content (w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neo SpectraTM ST Effects E1 (Dentsply, Konstanz, Germany) | Nano-hybrid | Matrix: Methacrylate modified polysiloxane dimethacrylates, ethyl-4 (dimethylamino) benzoate, and bis(4-methyl-phenyl) iodonium hexafluorophosphate. | Weight: 78–80 wt.% Volume: 60–62 vol.% |
| Filler: Barium glass, Ytterbium fluoride, Inorganic fillers (0.1–3.0 μm), SphereTEC® fillers (d3, 50 ≈ 15 μm) |
| Group | N | Mean | Std. Error | Std. Deviation | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 141.57 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.09 |
| 2 | 10 | 222.72 | 1.58 | 4.98 | 24.81 |
| 3 | 10 | 212.40 | 1.22 | 3.87 | 14.98 |
| 4 | 10 | 254.90 | 0.61 | 1.93 | 3.73 |
| 5 | 10 | 167.33 | 1.64 | 5.18 | 26.80 |
| 6 | 10 | 159.81 | 2.18 | 6.91 | 47.70 |
| Group | N | Mean | Std. Error | Std. Deviation | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 10 | 19.59 | 1.58 | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| 3 | 10 | 19.63 | 1.22 | 0.89 | 0.79 |
| 4 | 10 | 21.39 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.40 |
| 5 | 10 | 19.75 | 1.64 | 0.54 | 0.29 |
| 6 | 10 | 22.61 | 2.18 | 0.43 | 0.19 |
| Surface Roughness (Nanometers) | Surface Roughness (Micrometers per Pixel) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group Comparison | Mean ± Standard Deviation | p-Value | Mean ± Standard Deviation | p-Value |
| Group 1 vs. Group 2 | −81.16 (141.57 ± 0.29 vs. 222.72 ± 4.98) | <0.001 | −19.50 (0.09 ± 0.003 vs. 19.59 ± 0.94) | <0.001 |
| Group 1 vs. Group 3 | −70.83 (141.57 ± 0.29 vs. 212.40 ± 3.87) | <0.001 | −19.53 (0.09 ± 0.003 vs. 19.63 ± 0.89) | <0.001 |
| Group 1 vs. Group 4 | −113.34 (141.57 ± 0.29 vs. 254.90 ± 1.93) | <0.001 | −21.30 (0.09 ± 0.003 vs. 21.39 ± 0.63) | <0.001 |
| Group 1 vs. Group 5 | −25.76 (141.57 ± 0.29 vs. 167.33 ± 5.18) | <0.001 | −19.65 (0.09 ± 0.003 vs. 19.75 ± 0.54) | <0.001 |
| Group 1 vs. Group 6 | −18.24 (141.57 ± 0.29 vs. 159.81 ± 6.91) | <0.001 | −22.52 (0.09 ± 0.003 vs. 22.61 ± 0.43) | <0.001 |
| Group 2 vs. Group 3 | 10.32 (222.72 ± 4.98 vs. 212.40 ± 3.87) | <0.001 | −0.03 (19.59 ± 0.94 vs. 19.63 ± 0.89) | 0.939 * |
| Group 2 vs. Group 4 | −32.18 (222.72 ± 4.98 vs. 254.90 ± 1.93) | <0.001 | −1.79 (19.59 ± 0.94 vs. 21.39 ± 0.63) | <0.001 |
| Group 2 vs. Group 5 | 55.39 (222.72 ± 4.98 vs. 167.33 ± 5.18) | <0.001 | −0.15 (19.59 ± 0.94 vs. 19.75 ± 0.54) | 0.67 * |
| Group 2 vs. Group 6 | 62.91 (222.72 ± 4.98 vs. 159.81 ± 6.91) | <0.001 | −3.02 (19.59 ± 0.94 vs. 22.61 ± 0.43) | <0.001 * |
| Group 3 vs. Group 4 | −42.50 (212.40 ± 3.87 vs. 254.90 ± 1.93) | <0.001 | −1.76 (19.63 ± 0.89 vs. 21.39 ± 0.63) | <0.001 |
| Group 3 vs. Group 5 | 45.07 (212.40 ± 3.87 vs. 167.33 ± 5.18) | <0.001 | −0.12 (19.63 ± 0.89 vs. 19.75 ± 0.54) | 0.722 * |
| Group 3 vs. Group 6 | 52.59 (212.40 ± 3.87 vs. 159.81 ± 6.91) | <0.001 | 2.99 (19.63 ± 0.89 vs. 22.61 ± 0.43) | <0.001 * |
| Group 4 vs. Group 5 | 87.57 (254.90 ± 1.93 vs. 167.33 ± 5.18) | <0.001 | 1.64 (21.39 ± 0.63 vs. 19.75 ± 0.54) | <0.001 |
| Group 4 vs. Group 6 | 95.09 (254.90 ± 1.93 vs. 159.81 ± 6.91) | <0.001 | −1.22 (21.39 ± 0.63 vs. 22.61 ± 0.43) | <0.001 * |
| Group 5 vs. Group 6 | 7.52 (167.33 ± 5.18 vs. 159.81 ± 6.91) | 0.013 | −2.87 (19.75 ± 0.54 vs. 22.61 ± 0.43) | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saad, D.A.; Shatila, R.; Khazaal, G.; Abboud, M.; Kharouf, N.; Zogheib, C.M. The Effect of Dental Bleaching on Nanohybrid Composite Surface Roughness: A Comparative In Vitro Study of SEM and Profilometry. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060313
Saad DA, Shatila R, Khazaal G, Abboud M, Kharouf N, Zogheib CM. The Effect of Dental Bleaching on Nanohybrid Composite Surface Roughness: A Comparative In Vitro Study of SEM and Profilometry. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(6):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaad, Dalia Abou, Rania Shatila, Gina Khazaal, Marie Abboud, Naji Kharouf, and Carina Mehanna Zogheib. 2025. "The Effect of Dental Bleaching on Nanohybrid Composite Surface Roughness: A Comparative In Vitro Study of SEM and Profilometry" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 6: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060313
APA StyleSaad, D. A., Shatila, R., Khazaal, G., Abboud, M., Kharouf, N., & Zogheib, C. M. (2025). The Effect of Dental Bleaching on Nanohybrid Composite Surface Roughness: A Comparative In Vitro Study of SEM and Profilometry. Journal of Composites Science, 9(6), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9060313








