Integrating Data Mining and Microsimulation Modelling to Reduce Traffic Congestion: A Case Study of Signalized Intersections in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Data Mining in Traffic Management: Video Analysis
2.2. Signal Time Optimizations Using Simulation Models
2.3. Studies on Dhaka’s Traffic Signals
3. Materials and Methods
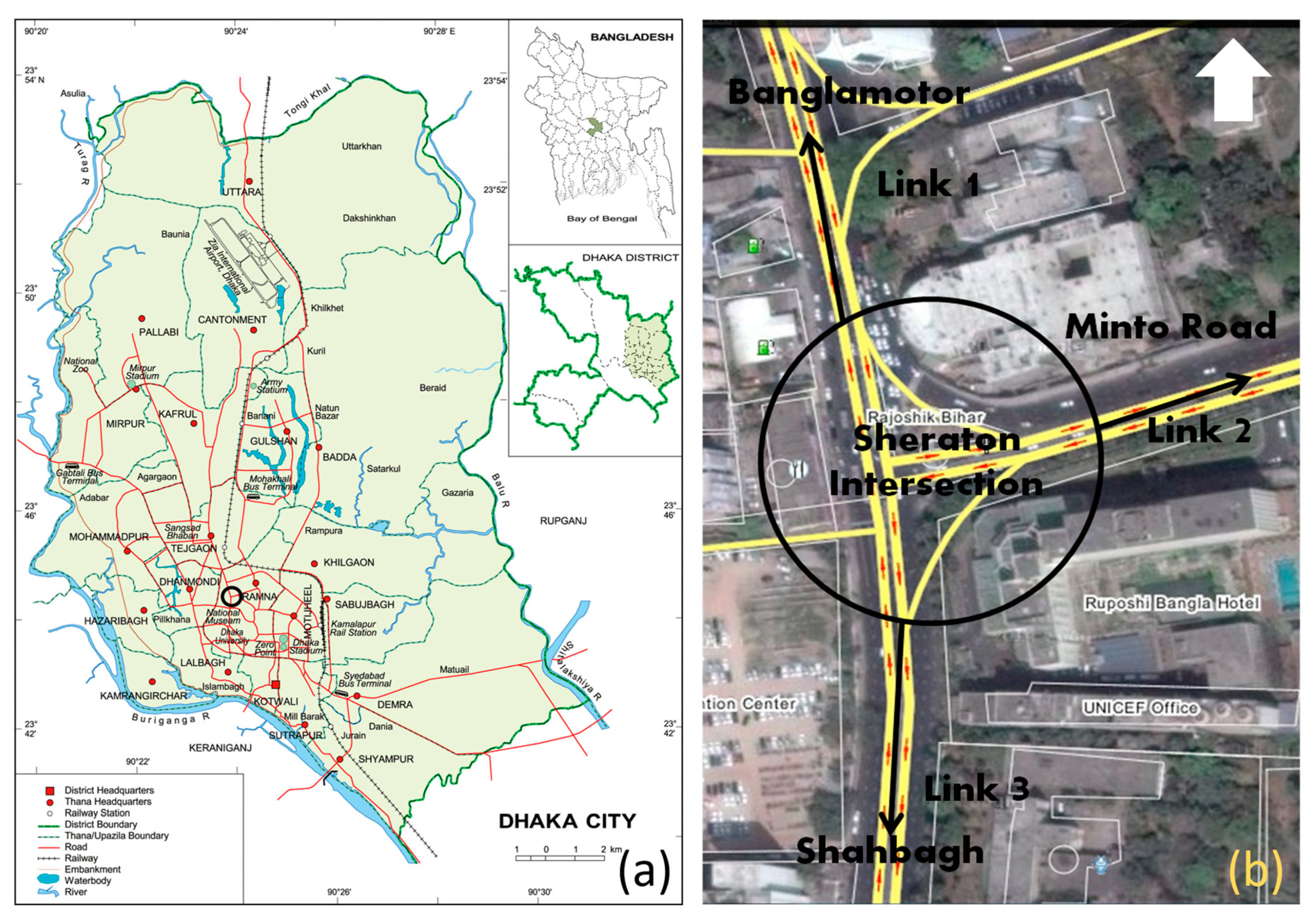
3.1. Case Study Area
3.2. Traffic Data Collection at Base Level
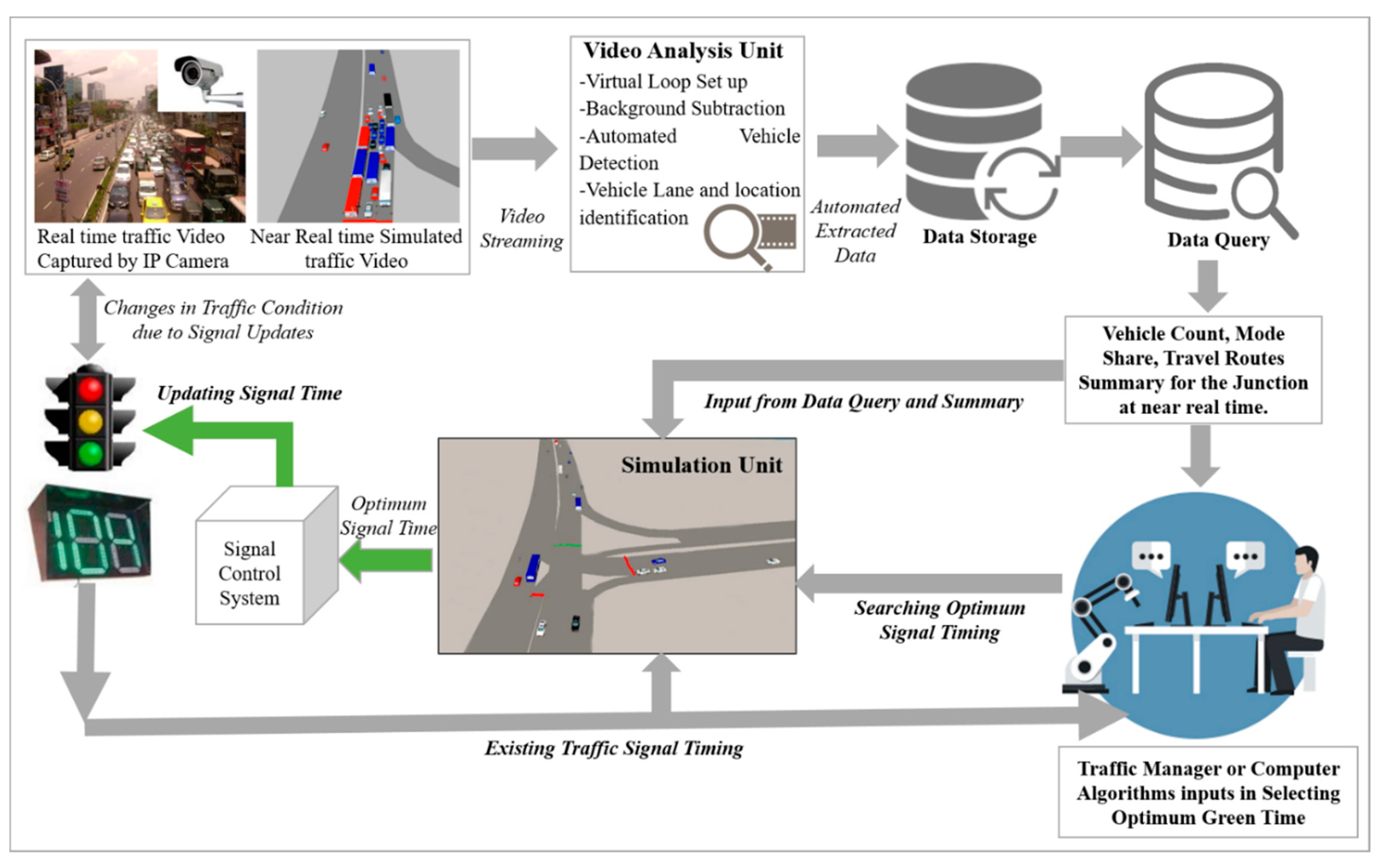
3.3. Overview of the Proposed System
3.4. Micro-Simulation Model
3.5. Video Analysis Unit
3.6. Data Mining: Running Automatic Query
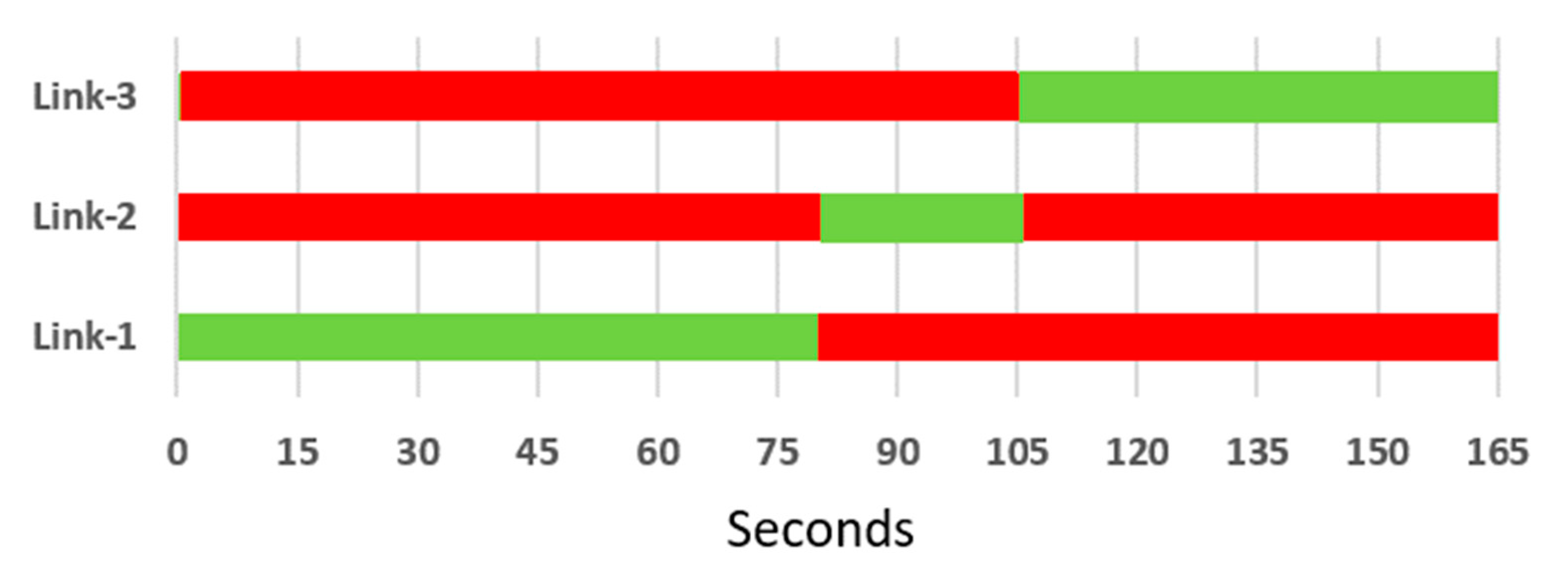
3.7. Signal Timing Updates (Tuning) and Related Changes
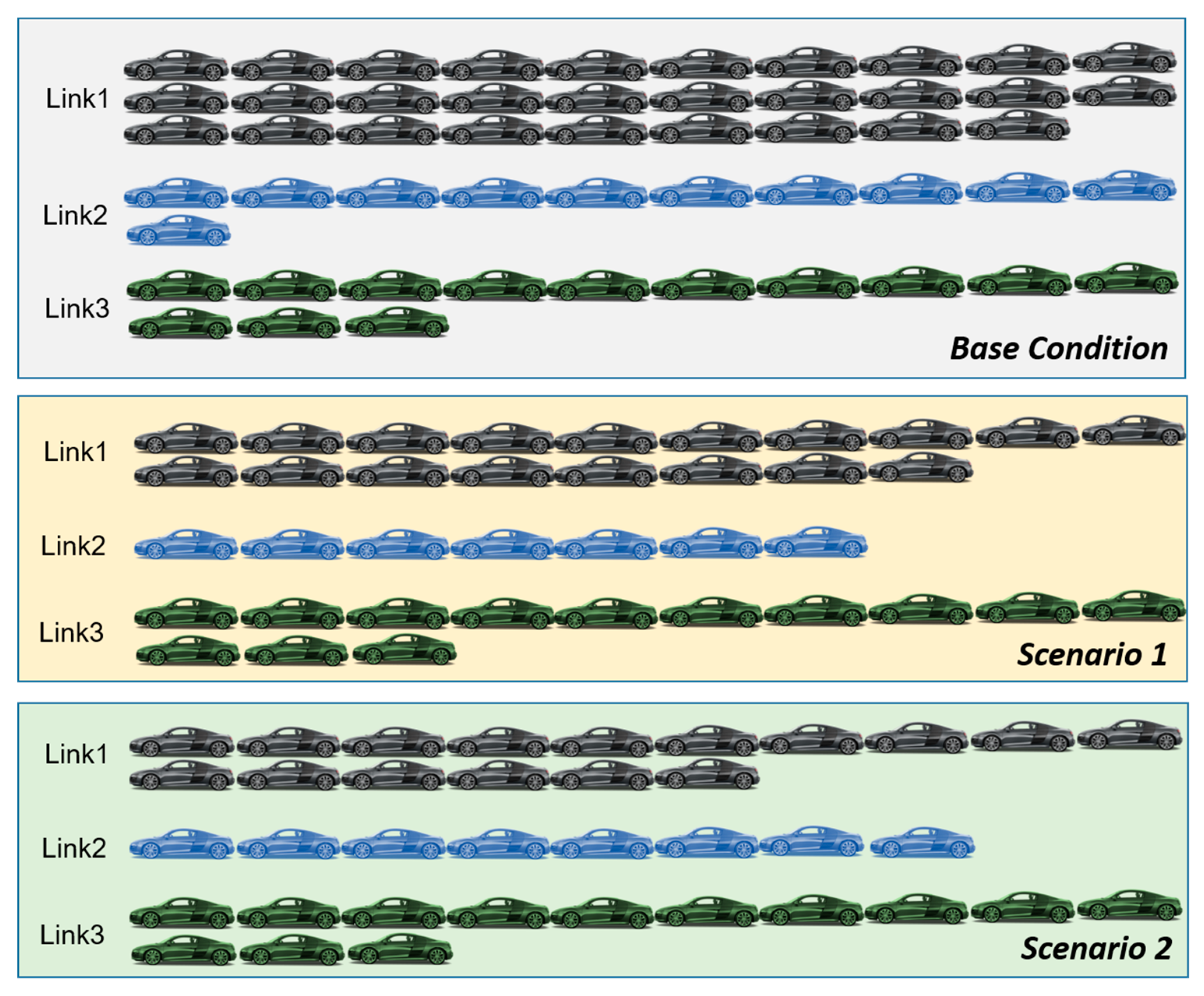
3.8. Evaluation of Tuned Signal Scenarios
4. Results
4.1. Overview of Existing Traffic Conditions
4.2. Results of Tuned Signal Timing
5. Discussion
5.1. Evatulation of Proposed Traffic Signal System and Solutions
5.2. Policy Implications
5.3. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Jin, J.; Lei, W. Multi-criteria analysis of optimal signal plans using microscopic traffic models. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.; Neema, M.; Rahaman, Z.; Patwary, S.; Shakil, S. Carbon dioxide emission and bio-capacity indexing for transportation activities: A methodological development in determining the sustainability of vehicular transportation systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, M.D. Traffic lights management using optimization tool. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2018, 238, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, A.; Garbo, A.; Loiacono, C.; Quer, S. Street viewer: An autonomous vision based traffic tracking system. Sensors 2016, 16, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Park, B.; Lee, J. Evaluating the impacts of urban corridor traffic signal optimization on vehicle emissions and fuel consumption. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2012, 35, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.B.; Malakorn, K.; So, J.J. Sustainability assessments of cooperative vehicle intersection control at an urban corridor. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2013, 32, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; Hao, H.; Long, C. An Adaptive Traffic Signal Control in a Connected Vehicle Environment: A Systematic Review. Information 2017, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Z. Computational intelligence in urban traffic signal control: A survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2012, 42, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J. Settings for fixed-cycle traffic signals. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1963, 14, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Head, K.L.; Khoshmagham, S.; Zamanipour, M. A real-time adaptive signal control in a connected vehicle environment. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R. Intelligent Transportation Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, R.; Zhang, X. Design and Evaluation of an Adaptive Traffic Signal Control System—A Case Study in Hefei, China. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 21, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shi, X.; Song, G.; Geng, Q.; Liu, Y. Towards improving quality of video-based vehicle counting method for traffic flow estimation. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, D. Vehicle Speed Control Based on GPS/MAP Matching of Posted Speeds. U.S. Patent 5,485,161, 16 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Moutakki, Z.; Ouloul, I.; Afdel, K.; Amghar, A. Real-Time Video Surveillance System for Traffic Management with Background Subtraction Using Codebook Model and Occlusion Handling. Transp. Telecommun. J. 2017, 18, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, R. Deficiency of Traffic Signal Control System in Dhaka City. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.; Barua, S.; Das, A. A Study on Feasible Traffic Operation Alternatives at Signalized Intersection in Dhaka City. In International Conference on Recent Innovation in Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development; Department of Civil Engineering, DUET: Gazipur, Bangladesh, 2015; pp. 656–660. [Google Scholar]
- Labib, S.; Mohiuddin, H.; Shakil, S. Transport Sustainability of Dhaka: A Measure of Ecological Footprint and Means for Sustainable Transportation System. J. Bangladesh Inst. Plan. 2013, 6, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, K.; Lin, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, C. Data-Driven Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 12, 1624–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barai, S.K. Data mining applications in transportation engineering. Transport 2003, 18, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.H.C.; Lee, W.C.; Tseng, V.S. Mining fastest path from trajectories with multiple destinations in road networks. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2011, 29, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, H.A. Review of Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) Techniques for Vehicles Traffic Management. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2014, 6, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrinaki, V.; Michalis, Z.; Kostas, K. A survey of video processing techniques for traffic applications. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Lam, W.H.; Zheng, C.; Li, Q. Integrated real-time vision-based preceding vehicle detection in urban roads. Neurocomputing 2013, 116, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, K. A vehicle detection algorithm based on three-frame differencing and background subtraction. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, Hangzhou, China, 28–29 October 2012; pp. 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ding, J. Optical flow based urban road vehicle tracking. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS), Leshan, China, 14–15 December 2013; pp. 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, S.; Kamath, C. Robust Background Subtraction with Foreground Validation for Urban Traffic Video. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2005, 14, 726261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragatto, T.A.; Ruas, G.I.; Benso, V.A.; Lamar, M.V.; Aldigueri, D.; Teixeira, G.L.; Yamashita, Y. A new approach to multiple vehicle tracking in intersections using harris corners and adaptive background subtraction. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 4–6 June 2008; pp. 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uke, N.; Thool, R. Moving vehicle detection for measuring traffic count using openCV. J. Autom. Control Eng. 2013, 1, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahim, K.; Salam, R.A. Traffic surveillance: A review of vision based vehicle detection, recognition and tracking. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 713–726. [Google Scholar]
- Barcellos, P.; Bouvié, C.; Escouto, F.; Scharcanski, J. A novel video based system for detecting and counting vehicles at user-defined virtual loops. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liang, B.; Zhang, W. Real-time moving vehicle detection, tracking, and counting system implemented with OpenCV. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), Shenzhen, China, 26–28 April 2014; pp. 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, A.; Stevanovic, J.; Zhang, K.; Batterman, S. Optimizing Traffic Control to Reduce Fuel Consumption and Vehicular Emissions. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2009, 2128, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.; Waterson, B.; Cherrett, T.; Robinson, A.; Snell, I. The evolution of urban traffic control: Changing policy and technology. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2013, 36, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, T.; Ho, T.; Fung, Y. Coordinated Road-Junction Traffic Control by Dynamic Programming. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 6, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulandi, J.; Stevanovic, A.; Martin, P. Cross-Evaluation of Signal Timing Optimized by Various Traffic Simulation and Signal Optimization Tools. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2192, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenekeci, G. A modelling technique for assessing linked MOVA. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Transp. 2007, 160, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.; Crabtree, M.; Kirkham, A.; Maxwell, A.; Robbins, R. Survey of MOVA and SCOOT Operation at M42 Junction 6; TRL Published Project Report; TRL limited: Wokingham, UK, 2008; Available online: https://trl.co.uk/sites/default/files/PPR252_secure.PDF (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- Cantarella, G.; de Luca, S.; Di Pace, R.; Memoli, S. Network Signal Setting Design: Meta-heuristic optimisation methods. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 55, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Schneeberger, J. Microscopic Simulation Model Calibration and Validation: Case Study of VISSIM Simulation Model for a Coordinated Actuated Signal System. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2003, 1856, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, B.; Adventaras, B.S.; Dyan, R.W.P. Analysis of signalized intersection performance using IHCM 1997 method and PTV Vistro software. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 195, 04012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gökçe, M.A.; Öner, E.; Işık, G. Traffic signal optimization with Particle Swarm Optimization for signalized roundabouts. Simulation 2015, 91, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Abu-Lebdeh, G. Real-Time Dynamic Transit Signal Priority Optimization for Coordinated Traffic Networks Using Genetic Algorithms and Artificial Neural Networks. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 19, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiuzzaman, M. Development of a Saturation Flow and Delay Models for Signalized Intersection in Dhaka City. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.A.; Khan, I.R.; Khan, M.R.M.; Rifaat, S.M. Optimizing signal timing: An efficient way to handle traffic congestion in developing countries. In Proceedings of the 5th Brunei International Conference on Engineering and Technology (BICET 2014), Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 1–3 November 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbes, M. Welcome to the Traffic Capital of the World. Available online: https://newrepublic.com/article/118416/what-dhaka-bangladesh-traffic-capital-world-can-teach-us (accessed on 29 December 2018).
- Labib, S.; Harris, A. The potentials of Sentinel-2 and LandSat-8 data in green infrastructure extraction, using object based image analysis (OBIA) method. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellendorf, M.; Peter, V. Fundamentals of Traffic Simulation; Barceló, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Chapter 2; pp. 63–93. [Google Scholar]
- OpenCV Template Matching—OpenCV 2.4.13.7 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/doc/tutorials/imgproc/histograms/template_matching/template_matching.html (accessed on 10 March 2018).
- Velazquez-Pupo, R.; Sierra-Romero, A.; Torres-Roman, D.; Shkvarko, Y.; Santiago-Paz, J.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, D.; Robles-Valdez, D.; Hermosillo-Reynoso, F.; Romero-Delgado, M. Vehicle Detection with Occlusion Handling, Tracking, and OC-SVM Classification: A High Performance Vision-Based System. Sensors 2018, 18, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycle Length Determination. Available online: https://www.webpages.uidaho.edu/niatt_labmanual/Chapters/signaltimingdesign/professionalpractice/CycleLengthDetermination.htm (accessed on 12 March 2018).
- Murat, Y.; Gedizlioglu, E. A fuzzy logic multi-phased signal control model for isolated junctions. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2005, 13, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitturi, M.; Shaw, J.; Campbell, J.; Noyce, D. Validation of Origin–Destination Data from Bluetooth Reidentification and Aerial Observation. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2014, 2430, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, R.; Skabardonis, A.; Halkias, J.; McHale, G.; Zammit, G. Guidelines for Calibration of Microsimulation Models: Framework and Applications. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2004, 1876, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiang AT, G.; Lim, R. Type of vehicle recognition using template matching method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication and Information, Jakarta, Indonesia, 7–8 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, K.; Gope, K.; Chowdhury, S. Possible Causes & Solutions of Traffic Jam and Their Impact on the Economy of Dhaka City. J. Manag. Sustain. 2012, 2, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.; Rahaman, M.; Patwary, M. Green Transport Planning for Dhaka City: Measures for Environment Friendly Transportation System. Bachelor’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Department of Urban and Regional Planning, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, H.; Xiao, L. An Adaptive Signal Control Scheme to Prevent Intersection Traffic Blockage. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Oh, J.; Recker, W. Adaptive Signal Control System with Online Performance Measure for a Single Intersection. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2002, 1811, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.M.; Rahaman, Z.; Patwary, M.S.H. Comprehensive evaluation of urban public Non-Motorized Transportation Facility services in Dhaka. In Proceedings of the 8th Multidisciplinary Academic Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 October 2016; pp. 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Labib, S.M. Volunteer GIS (VGIS) based waste management: A conceptual design and use of web 2.0 for smart waste management in Dhaka City. In Proceedings of the 2017 Third International Conference on Research in Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (ICRCICN), Kolkata, India, 3–5 November 2017; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajzewicz, D.; Jakob, E.; Michael, B.; Laura, B. Recent development and applications of SUMO-Simulation of Urban MObility. Int. J. Adv. Syst. Meas. 2012, 5, 128–138. [Google Scholar]



| Traffic Behaviour | Parameters | Base Model Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Car following | Avg. Stand still | 2.00 (m) | |
| Additive part of safety | 2.00 (m) | ||
| Multiplic. Part of safety | 2.00 (m) | ||
| Lane changing | General Behaviour | Free lane selection | |
| Lateral Change | Desired Position | Middle of lane | |
| Consider Next turning direction | Not Marked | ||
| Over take on same lane | Not marked | ||
| Min. lateral distance | 1 at 0 km/h | 1 at 50 km/h | |
| Block | Code Snippet |
|---|---|
| Block-1 | # Libraries Import numpy, Computer Vision Library, Time # Import template, footage, and resize videos Bring in video footage with CV2. VideoCapture Bring in template image with CV2. Imread Resize video width to 20 Resize video height to 20 #setup and select a method of detection Methods [Coefficient, Coefficient Normalized, Correlation, Correlation Normalized, Square Difference, Square Difference Normalized] |
| Block-2 | # Select a Method Select Square Difference Normalized method CV2. FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX # Data Collection Create a CSV file with 5 points at (0,0), a at 300, b at 500 While Read footage Resize frame to (640, 480) Run matching algorithm with CV@, match template Remove the background Resize result of the matching algorithm Set 5 virtual loop frames Define 5 image moments to select objects Template match for different objects |
| Block-3 | Detect car if moment 1 is greater than threshold of 300 and less than threshold of 500 Record information Sleep for 0.09 Detect buses if moment 1 is greater than threshold of 500 Record information |
| Block | Code Snippet |
|---|---|
| Block-1 | :establish Connection With Database (host, user); If file Open (fileName) == TRUE then: while get Data From CSV(fileName) !== FALSE: If validate Data(type, position, lane) == TRUE then: :sql = Insert into table (type, position, lane) values (data [0], data [1], data [2]); :query = mysql_query(sql); file Close(fileName); |
| Block-2 | : establish Connection With Database (host, user); If connection Establish With Database == FALSE then: Kill Session With Database(); break; :user Input Of Lane = user Input Of Lane From Web; :user Input Of Type = user Input Of Type From Web; :sqlQuery = select * from table where lane= ‘user Input Of Lane’ and type = ‘user Input Of Type’; If (fetch Result (sqlQuery) == TRUE) then: If (num Of Row Fetch > 0) then: show Type Position Lane And Number Of Vehicle Count (type, position, lane, count); else: show No Data Found(); close Database ConnectionConnection(); |
| Traffic Behaviour | Parameters | Base Model Values | Different Scenarios Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car following | Avg. Stand still | 2.00 (m) | 1.30 (m) | ||
| Additive part of safety | 2.00 (m) | 1.00 (m) | |||
| Multiplic. Part of safety | 2.00 (m) | 1.00 (m) | |||
| Lane changing | General Behaviour | Free lane selection | Free lane selection | ||
| Lateral change | Desired Position | Middle of lane | Any Position | ||
| Consider next turning direction | Not marked | Marked | |||
| Over take on same lane | Not marked | Marked (Left and Right) | |||
| Min. lateral distance | 1 at 0 km/h | 1 at 50 km/h | 0.3 at 0 km/h | 0.3 at 50 km/h | |
| Mode | Link-1 | Link-2 | Link-3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume Count | Volume % | Volume Count | Volume % | Volume Count | Volume % | |
| Car | 877 | 50 | 359 | 69 | 343 | 50 |
| HGV | 53 | 3 | 10 | 2 | 34 | 5 |
| Bus | 316 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 123 | 18 |
| Motor cycle | 508 | 29 | 146 | 28 | 178 | 26 |
| Total | 1753 | 100 | 516 | 100 | 678 | 100 |
| Link | Field Survey Volume | Base Model Simulated Volume | GEH Value | Queue Length (m) | No. of Stops | Speed (km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Link-1 | 1753 | 1716 | 0.888 | 131 | 616 | 26.1 |
| Link-2 | 521 | 480 | 1.833 | 50 | 345 | 29.6 |
| Link-3 | 685 | 697 | 0.457 | 61 | 134 | 25.2 |
| Link | Simulated Volume (Base Model 3D Video) | Video Analysis Volume | GHE Value | Error Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Link-1 | 1716 | 1598 | 2.898 | 6.731 |
| Link-2 | 480 | 415 | 3.072 | 3.707 |
| Link-3 | 697 | 596 | 3.397 | 5.761 |
| Scenario | Link | Video Analysis Volume | New Simulated Volume | GEH Value | Queue Length (m) | No. of Stops | Speed (km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario-1 | Link-1 | 1598 | 1707 | 2.681 | 81 | 278 | 26.2 |
| Link-2 | 415 | 483 | 3.209 | 31 | 318 | 29.8 | |
| Link-3 | 596 | 688 | 3.630 | 58 | 134 | 25.5 | |
| Scenario-2 | Link-1 | 1598 | 1717 | 2.922 | 75 | 272 | 27.3 |
| Link-2 | 415 | 484 | 3.254 | 36 | 318 | 29.8 | |
| Link-3 | 596 | 691 | 3.744 | 59 | 134 | 25.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labib, S.M.; Mohiuddin, H.; Hasib, I.M.A.; Sabuj, S.H.; Hira, S. Integrating Data Mining and Microsimulation Modelling to Reduce Traffic Congestion: A Case Study of Signalized Intersections in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Urban Sci. 2019, 3, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci3020041
Labib SM, Mohiuddin H, Hasib IMA, Sabuj SH, Hira S. Integrating Data Mining and Microsimulation Modelling to Reduce Traffic Congestion: A Case Study of Signalized Intersections in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Urban Science. 2019; 3(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci3020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabib, S.M., Hossain Mohiuddin, Irfan Mohammad Al Hasib, Shariful Hasnine Sabuj, and Shrabanti Hira. 2019. "Integrating Data Mining and Microsimulation Modelling to Reduce Traffic Congestion: A Case Study of Signalized Intersections in Dhaka, Bangladesh" Urban Science 3, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci3020041
APA StyleLabib, S. M., Mohiuddin, H., Hasib, I. M. A., Sabuj, S. H., & Hira, S. (2019). Integrating Data Mining and Microsimulation Modelling to Reduce Traffic Congestion: A Case Study of Signalized Intersections in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Urban Science, 3(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci3020041






