Abstract
With accelerating urbanization and the exponential growth in vehicle populations, high-precision traffic monitoring has become indispensable for intelligent transportation systems (ITSs). Conventional sensing technologies—including inductive loops, cameras, and radar—suffer from inherent limitations: restrictive spatial coverage, prohibitive installation costs, and vulnerability to adverse weather. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS), leveraging Rayleigh backscattering to convert standard optical fibers into kilometer-scale, real-time vibration sensor networks, presents a transformative alternative. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the principles and system architecture of DAS for roadway traffic monitoring, with a focus on signal processing techniques, feature extraction methods, and recent advances in vehicle detection, classification, and speed/flow estimation. Special attention is given to the integration of deep learning approaches, which enhance noise suppression and feature recognition under complex, multi-lane traffic conditions. Real-world deployment cases on highways, urban roads, and bridges are analyzed to demonstrate DAS’s practical value. Finally, this paper delineates emerging research trends and technical hurdles, providing actionable insights for the scalable implementation of DAS-enhanced ITS infrastructures.
1. Introduction
With the rapid pace of urbanization and the dramatic increase in vehicle ownership, roadway traffic monitoring—an essential pillar of ITSs—has become ever more critical. Conventional sensing technologies such as inductive loops, cameras, radar, and magnetometers, while capable of vehicle detection and volume counting, exhibit notable limitations in terms of their long-distance coverage, adaptability to complex environments, and lifecycle maintenance costs [1]. In this context, Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS), which leverages the “fiber-as-sensor” paradigm and provides truly continuous spatial monitoring, has emerged as a promising alternative for traffic surveillance [2,3].
Originally developed for oil-and-gas pipeline integrity monitoring and seismic observation, DAS exploits the Rayleigh backscatter in an optical fiber: minute mechanical perturbations along the cable induce phase shifts in the returning light, which are detected coherently to yield high-resolution vibration profiles over tens of kilometers [4]. Recent research has successfully adapted this geophysical technique to roadway applications by capturing the subtle ground vibrations generated by passing vehicles, thereby enabling vehicle detection, localization, speed estimation, and even vehicle type classification—all without the need for discrete, on-roadside sensing nodes [5,6]. This cross-domain innovation not only broadens the functional scope of fiber-optic sensing but also offers a novel route to more precise and efficient traffic perception.
Compared with traditional monitoring systems, DAS affords several key advantages: its sensing capability leverages existing communication cables, allowing a low-cost, covert deployment that reuses installed infrastructure [4]; it maintains a robust performance under adverse weather or low-visibility conditions; and it delivers real-time, continuous coverage over tens to hundreds of kilometers with a meter-scale spatial resolution and high sensitivity [7]. Truong et al. demonstrated edge computing-driven real-time vehicle detection and tracking on Norway’s Åstfjorden Bridge: Hough transforms detected linear trajectory segments in DAS data, and DBSCAN clustering consolidated detections to enable low-latency, edge-based traffic monitoring [8]. Furthermore, ongoing advancements in optical instrumentation, signal processing algorithms, and machine learning techniques have substantially enhanced noise suppression, feature extraction, and pattern-recognition capabilities, positioning DAS as a powerful tool for complex traffic environments [9].
Despite these strengths, the practical deployment of DAS for traffic monitoring still faces challenges. Urban environments introduce a multitude of noise sources and signal overlap, complicating accurate interpretation and real-time processing [6]. Long-haul deployments must contend with attenuation and nonlinear effects that necessitate sophisticated compensation strategies. Moreover, the efficient modeling of such high-dimensional, time-varying signals demands advanced deep learning architectures. Recent studies have begun to address these hurdles by integrating self-supervised neural networks, edge-computing frameworks, and synthetic data generation to bolster system robustness and generalizability [6]. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology, primarily based on phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (Φ-OTDR) and coherent Rayleigh scattering, has evolved from its fundamental principles to diverse engineering applications, including oilfield geophysics and traffic monitoring, with ongoing research focused on enhancing system performance and expanding its sensing capabilities [10,11,12,13]. A schematic diagram of using DAS to monitor traffic information is shown in Figure 1.
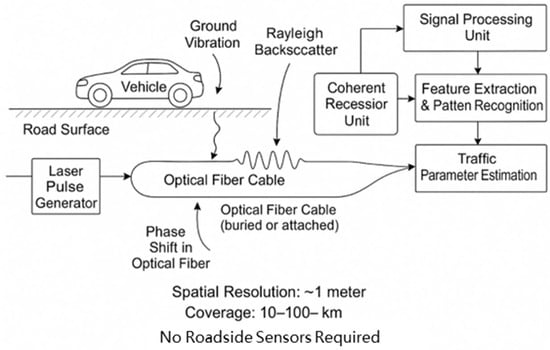
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of a Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system for roadway traffic monitoring.
This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of DAS applied in roadway traffic monitoring. This paper first presents the fundamental principles and system architecture of DAS, highlighting its unique advantages for traffic scenarios. Next, this paper examines the evolution of signal processing and feature extraction techniques, from classical filtering approaches to state-of-the-art deep learning models. This paper then surveys key applications in traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification, tracing the technological maturation through representative studies. Finally, this paper analyzes case studies in highway, urban roadway, and bridge monitoring, and offers perspectives on future research directions. Through this synthesis, this paper seeks to furnish both theoretical insights and practical guidance to accelerate the integration of DAS into next-generation smart transportation infrastructures.
2. Fundamental Principles and System Architecture
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) exploits the optical fiber itself as a continuous array of sensors by detecting acoustic and vibrational signals along its length. Applied across numerous practical domains—including roadway traffic monitoring—DAS offers real-time, continuous environmental surveillance at a low deployment cost and with minimal sensitivity to external conditions. These advantages stem directly from its underlying physical mechanisms and system architecture.
2.1. Principle of Rayleigh Scattering
In distributed fiber sensing, the sensing array consists of the fiber-optic cable itself. Physical perturbations imposed by the environment—such as mechanical vibrations, strain deformations, or temperature fluctuations—alter the fiber’s geometric parameters (e.g., length and diameter) and its refractive-index profile. These modifications induce Rayleigh backscattering of the incident light, detected at the receiver [10]. The backscattered spectrum comprises three scattering types—Rayleigh, Brillouin, and Raman—each corresponding to distinct interactions between light and the fiber medium [11]. Within the electromagnetic spectrum, optical scattering processes can be further categorized into Rayleigh, Stokes, and anti-Stokes scattering. Rayleigh scattering is an elastic process arising from random refractive-index inhomogeneities in the fiber core; as such, the scattered light retains the same frequency as the incident pulse. Importantly, the time delay of the Rayleigh backscatter permits spatially resolved sensing along the fiber’s length [12]. As Kimbell observed, the intensity of the Rayleigh scattering is directly linked to the laser source wavelength and exhibits a high sensitivity to the fiber strain induced by external vibrations.
Rayleigh scattering—being the primary mechanism of optical attenuation within the near-infrared transmission window—is central to distributed acoustic and vibration sensing. Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) techniques exploit the detection of Rayleigh backscatter to characterize fiber loss and identify defects. However, the advent of single-mode fibers revealed coherent interference effects in the backscattered Rayleigh signal, which can degrade attenuation measurements. To address this, coherent OTDR (C-OTDR) was developed, leveraging coherent detection to dramatically enhance the sensitivity for long-haul fiber communication links. Further advances in narrow-linewidth, single-frequency laser sources have given rise to phase-sensitive OTDR (Φ-OTDR), which capitalizes on phase information to achieve an even greater detection sensitivity and spatial resolution. The Rayleigh scattering and coherence detection principles in the DAS system are shown in Figure 2.
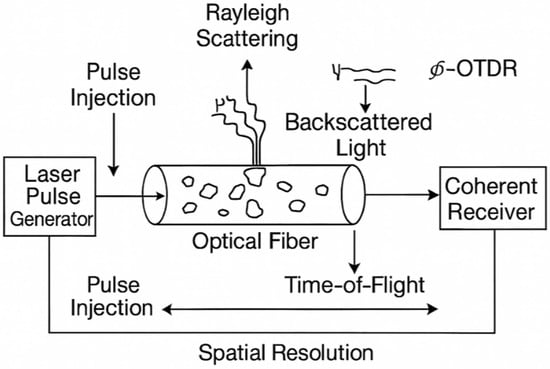
Figure 2.
Principle of Rayleigh scattering and coherent detection in DAS systems.
2.2. Mechanism and Function of C-OTDR
Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) underpins all distributed fiber-optic monitoring, yet modern DAS systems principally employ two variants of reflectometers: phase-sensitive OTDR (Φ-OTDR) and coherent OTDR (C-OTDR) [13]. When a pulse of light is launched into the fiber under test (FUT), Rayleigh backscattered signals (RBSs) arise from scattering centers at different positions along the fiber, each returning to the photodetector (PD) after a characteristic round-trip delay. By analyzing the PD’s electrical output, the intensity of the backscatter from each fiber location can be mapped in time: in an ideal uniform fiber, the RBS amplitude at any point is linearly proportional to the forward-propagating optical power at that location.
Whereas conventional Φ-OTDR extends OTDR by measuring phase variations induced by external disturbances, C-OTDR further incorporates coherent detection to vastly improve the sensitivity and dynamic range. The key advance of C-OTDR lies in its use of a narrow-linewidth laser with a coherence length far exceeding the FUT’s length, enabling the coherent interference of backscattered fields.
In 2005, Kashiwagi and Hotate demonstrated that by synthesizing the optical coherence function over regions exceeding the source’s intrinsic coherence length, one could achieve a dynamic range of 45 dB in reflectometric measurements [14]. A decade later, Liu et al. introduced a digitally enhanced optical frequency domain reflectometry technique, mapping the frequency to the distance in the digital domain and attaining a spatial resolution over 56 km spans [15]. In 2019, Zheng and colleagues devised a novel C-OTDR length calibration method by circulating light continually within a fiber loop, enabling the precise fiber length measurement critical for long-haul traffic monitoring [16]. Jiang et al. analyzed noise floor limitations in C-OTDR and experimentally validated its high-precision acoustic vibration sensing capabilities, underscoring its relevance for extended-range traffic applications [17].
More recently, Fernandez-Ruiz et al. presented a time-stretched phase-sensitive OTDR using two mutually coherent optical frequency combs to achieve an ultrahigh resolution [18], while Wang et al. demonstrated that bidirectional linear frequency-modulated pulses can expand C-OTDR’s dynamic range and enhance sensitivity in complex traffic environments [19]. In 2024, Liu and co-workers detailed how optical pulse coding schemes in C-OTDR improve both the signal-to-noise ratio and spatial resolution, further optimizing the technique for traffic-monitoring deployments [20].
These innovations collectively illustrate the ongoing evolution of C-OTDR in the time domain, driving a greater sensitivity, resolution, and measurement accuracy for long-distance Distributed Acoustic Sensing in roadway applications.
2.3. Fiber Deployment
Unlike conventional roadside sensors (e.g., inductive loops or cameras), DAS transforms the optical fiber into a ubiquitous, low-maintenance sensor array.
Conventional roadside sensing technologies—such as inductive loop detectors, magnetometers, cameras, and radar—suffer from significant limitations. Sensors that must be embedded in the pavement or mounted on lampposts entail high installation and maintenance costs and are vulnerable to road damage and construction activities [21]. Inductive loops and magnetometers are fixed to discrete locations and cannot achieve a fine-grained coverage over large areas, while cameras and radar, despite their extended detection ranges, remain constrained by line-of-sight requirements and have difficulty reliably detecting small or slow-moving vehicles under adverse environmental conditions [22,23]. In contrast, DAS-based vehicle detection leverages the optical fiber itself as the sensor, obviating the need for additional roadside hardware and offering an inherent immunity to electromagnetic interference, corrosion resistance, and a high-temperature tolerance [24,25]. Moreover, DAS delivers a meter-scale spatial resolution and enables ultra-long-range monitoring—single DAS units routinely cover in excess of 100 km of roadways [26,27].
In practical deployments, Peng et al. demonstrated that reusing existing telecommunications cables provides considerable logistical and economic benefits for DAS installation [28]. Subsequent studies have shown that embedding the fiber either in the roadway sub-surface or alongside the shoulder can reliably capture the strong vibration signatures generated by passing vehicles [29,30]. Recent advances in DAS hardware—with low backscatter noise and a high dynamic range—now allow standard telecom fibers to achieve a robust vehicle detection performance [31,32]. Consequently, leveraging pre-installed communication cables not only reduces both capital and operational expenditures, but also accelerates the widespread adoption of DAS systems for traffic monitoring.
2.4. Detector Parameters
The DAS performance hinges on four optimized parameters, each refined through recent research.
The performance of a DAS detector is characterized by four key parameters—the sensitivity and signal quality, dynamic performance, spatial and frequency response, and system stability—all of which have seen continual improvement and innovative applications in recent years.
Sensitivity and Signal Quality. Sensitivity denotes the detector’s ability to resolve minute signal variations; in traffic monitoring, a higher sensitivity allows the system to pick up the faint vibrations generated by lightweight or distant vehicles, thereby enhancing the overall detection capability and accuracy. Zhao et al. [33] showed that by optimizing the sampling rate, ADC bit depth, and EDFA gain, the DAS sensitivity can be dramatically increased—an essential advancement for capturing the weak vibration signatures of light vehicles. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), a measure of the signal integrity relative to background noise, is likewise vital for distinguishing true traffic signals from environmental interference. The same study demonstrated that enhancements to the IQ-demodulation algorithm significantly boost the SNR, improving the detection reliability in noisy traffic environments.
Dynamic Performance. The dynamic range—the ratio between the smallest and largest signals the detector can faithfully record—must be broad enough to handle the wide amplitude variations encountered in traffic vibrations. Gorshkov et al. [34] explored how tailoring the system’s response bandwidth and signal processing algorithms can expand the dynamic range, a critical factor when simultaneously observing both subtle and robust vibration events on the roadway. The sampling rate determines how frequently the system records data; higher rates ensure rapid vibration changes are captured in real time, which is particularly important in fast-changing traffic scenarios. Via distributed affine-projection algorithms, Ferrer et al. [35] demonstrated that adjusting the sampling frequency can markedly improve the system’s responsiveness and accuracy across diverse conditions.
Spatial and Frequency Response. The spatial resolution—the minimum physical separation at which two events can be distinguished—directly affects the ability to localize vehicles and other moving objects, underpinning flow analysis and obstacle detection. Cai et al. [36] discussed how fine-tuning fiber sensor parameters can enhance the spatial resolution, enabling the precise geolocation of traffic features. They also noted that expanding the frequency bandwidth allows the DAS system to capture a broader spectrum of vibration frequencies, ensuring the comprehensive detection of multi-frequency traffic signals.
System Stability. Linearity, which describes the proportionality between the measured output and actual environmental change, is crucial for accurate and consistent readings; nonlinearity can introduce significant measurement errors, especially in complex traffic settings. He et al. [37] emphasized improvements in signal processing algorithms to bolster both the linearity and overall system stability under varying field conditions. Ferrer et al.’s work further showed that by optimizing hardware parameters and processing routines, DAS can maintain a high stability and adaptability even in high-noise, dynamically complex traffic environments, thereby improving the reliability of long-term monitoring.
3. Signal Processing
Recent advances in DAS denoising span traditional filters, machine learning, and hybrid methods. Cascaded filters and hardware improvements enable real-time noise suppression, while deep learning models like DAS-N2N and GANs offer powerful, data-driven denoising. Hybrid techniques, such as wavelet–f–x filtering, balance precision and efficiency. These approaches collectively enhance the signal clarity, reduce fading noise, and improve the SNR across diverse DAS applications.
3.1. Denoising Algorithms
3.1.1. Advanced Denoising Techniques
Denoising represents a critical preprocessing stage where advanced algorithms combat diverse noise types—high-frequency interference, fading, and coherent distortions—to extract meaningful vibrational signatures.
To address high-frequency noise, fading, and coherent interference in DAS data, Chen et al. [38] proposed a novel cascaded denoising framework. First, an Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter in the time domain suppresses high-frequency components; next, a Structure-Oriented Median Filter (SOMF), adapted from seismic reflection processing, removes random noise. Finally, a dip filter in the frequency–wavenumber domain eliminates vertical and horizontal coherent disturbances. When tested on the FORGE geothermal DAS dataset, this cascaded approach yielded a substantial SNR improvement.
He et al. [39] introduced a “trajectory-sorted averaging” (SAOT) algorithm to combat fading noise. By sorting and averaging simulated DAS traces, SAOT effectively mitigates large-amplitude dropouts. Orsuti et al. [40] investigated the relationship between the phase variation and strain in multimode fibers and developed a coherent averaging technique for multimode DAS. This method greatly reduces background noise and lowers the probability of coherent fade events.
While these studies employ traditional filtering and statistical methods, recent work has increasingly leveraged machine learning for denoising. Lapins et al. [41] developed DAS-N2N, a weakly supervised denoising model that fuses two noise-corrupted replicas recorded on adjacent fibers within the same cable. By training a deep network on these natural noise pairs—with no need for manual labels—they elevated the SNR of ambient microseismic signals to meet microseismic detection requirements. Yuan et al. [42] proposed a self-supervised U-Net with spatial deconvolution, incorporating wavelet features of vehicle signatures and an L2-norm regularization term in the loss function to enhance sensitivity to distant signals. Their model significantly improved the spatiotemporal resolution of vehicle signals, effectively separating closely spaced, parallel traffic.
Xie et al. [6] introduced a two-stage deep learning pipeline: first, a convolutional neural network detects fragmented vehicle trajectories in DAS data; then, Hough transform clustering reconstructs complete trajectories by mapping geometric shapes in the image domain to accumulations in the parameter space. This approach demonstrated real-time applicability for traffic monitoring. Most recently, Dong’s group at Jilin University [43] employed a generative adversarial network (GAN) to reconstruct clean DAS signals and suppress fading noise. Their data-driven model reduced the root-mean-square error to 0.0097, effectively addressing noise issues in phase-sensitive DAS systems.
Several researchers have also explored hybrid signal processing schemes to enhance DAS denoising. Sun et al. [44] combined f–x deconvolution with wavelet transforms to suppress phase noise “jump” edges in DAS records: by decomposing the signal into scaled and shifted wavelet bases, they preserved local event features while stabilizing phase sensitivity in seismic wave measurements. Tabjula et al. [45] developed a low-computational-cost, real-time denoising pipeline that employs adaptive frequency–wavenumber filtering to both compress the data volume and extract gas slug signatures in a 1573 m deep well under high background noise. Isken et al. [46] likewise leveraged DAS’s dense spatiotemporal sampling to design an adaptive f–k filter that attenuates incoherent seismic noise while enhancing coherent wavefields.
In a more event-driven approach, AT et al. [47] proposed a multi-stage noise suppression framework for DAS data in which bandpass and median filters are selectively applied to different classes of impact events, achieving a 13.1 dB SNR boost with minimal processing overhead. On the hardware front, Masoudi et al. [48] engineered a high-resolution DAS system featuring an electro-optic modulator (EOM) and fiber Bragg grating (FBG) in the optical path to reduce intrinsic noise; their prototype achieved a 5 km sensing range and a 0.5 m spatial resolution with markedly lower background noise.
Purely signal-based enhancements have also progressed: As shown in Figure 3, Liu et al. [49] combined improved wavelet thresholding with dual-threshold detection in the time–frequency domain to robustly isolate vehicle vibration signatures, while Li’s team [50] employed variational mode decomposition optimized via genetic algorithms to adaptively suppress fading noise, raising the SNR by 11.26 dB and lowering the RMS error from 1.10 to 0.30. Finally, Kishida et al. [51] addressed coherent fading in Φ-OTDR by synthesizing complementary phase signals: by decomposing the detected waveform and applying a phase correction from the complementary channel, they reduced intensity fluctuations by 45 dB and achieved a phase noise standard deviation of just 0.0224.
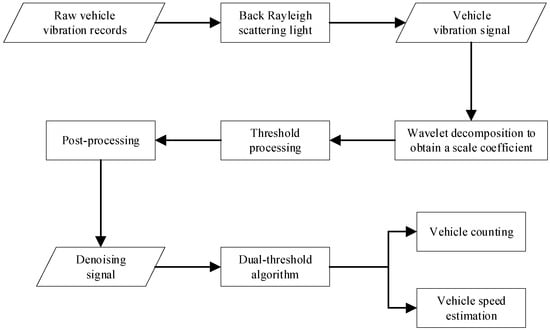
Figure 3.
The workflow of traffic flow detection for vehicle vibration data.
Overall, mature cascaded filter and hardware optimization methods excel in their real-time operation and ease of integration, while machine learning approaches such as DAS-N2N and GANs offer a powerful performance against complex noise patterns, though at the expense of higher computational demands. Hybrid techniques like f–x deconvolution and wavelet-based filtering strike a practical balance between accuracy and efficiency, though their ultimate precision remains an area for further improvement.
3.1.2. Data Augmentation
Data augmentation techniques have been increasingly applied to enhance the robustness and effectiveness of DAS-based monitoring. Khacef et al. [52] introduced a self-supervised DAS data alignment model that integrates a non-uniform temporal registration module with a deep learning backbone, achieving sequence alignment accuracy improvements of nearly 80% and a 16-fold increase in computation speed compared to traditional dynamic time warping (DTW). This advancement lays a solid foundation for deep traffic information mining, such as automated accident detection. Tan X. et al. [53] proposed an anomaly detection framework combining Incremental Principal Component Analysis (IPCA) with the Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN). By reducing dimensionality via the IPCA and clustering in the residual space, their IPCA–DBSCAN method optimizes the extraction of anomalous acoustic features, achieving an AUC of 0.84 in benchmark tests.
In the realm of seismic applications, Atterholt et al. [54] leveraged the dense linear geometry of DAS arrays to develop a curved-wave transform for wavefield decomposition, exploiting anisotropic wave propagation to separate seismic signals from noise. Applied to DAS data collected following the Mw 7.1 Ridgecrest earthquake in California, this method enhanced structured representations of aftershocks and increased detected aftershock counts by 30% over conventional approaches. Shragge et al. [55] analyzed low-frequency environmental wavefields using DAS data from a curved fiber installation in Perth, Australia, transforming virtual source gathers into dispersion images via phase-shift and high-resolution linear Radon transforms and inverting them with a particle swarm global optimization algorithm to identify sub-surface interfaces beyond a 0.5 km depth.
Aslangul et al. [56] demonstrated a cost-effective, equipment-free solution that clusters spatiotemporal alarm data from an existing database to suppress false positives, reducing misreports by 60% in long-distance subterranean tunnel surveillance scenarios. Carri et al. [57] validated the efficacy of DBSCAN for acoustic emission signals in structural health monitoring at bonded joints, showing that noise points can be identified without predefining cluster counts, thus offering a novel approach to parameter optimization.
As summarized in Table 1, these studies illustrate a progression from single-domain, manually parameterized augmentation techniques toward multimodal fusion and adaptive, learning-based methods—heralding a new era of data-centric signal enhancement in DAS applications.

Table 1.
Comparison of signal processing methods.
4. Feature Extraction
Recent advancements in DAS signal feature extraction focus on both traditional and deep learning techniques. While earlier methods used hand-crafted time, frequency, and spatial features, newer approaches leverage deep learning, such as CNNs and 3D attention networks, to automatically capture complex spatiotemporal patterns. These data-driven strategies achieve higher accuracy in vehicle detection and classification, marking a shift towards multimodal, efficient feature extraction for smart transportation.
Feature extraction is the core step in DAS signal interpretation, and researchers worldwide have investigated techniques spanning temporal, spectral, and spatial domains, as well as multidimensional feature selection. The time–frequency–space analysis enables the simultaneous characterization of non-stationary or multidimensional signals across all three axes. As shown in Figure 4, Min et al. [58] extracted 62 one-dimensional time domain features and 128 two-dimensional time–frequency features from vehicle-induced vibrations. After the random forest selection, 31 salient features were retained and classified via a support vector machine (SVM), yielding an 80% accuracy in distinguishing vehicles from noise. Wiesmeyr et al. [59] applied DAS to traffic monitoring by measuring the mechanical strain induced by passing vehicles in a buried fiber, estimating metrics such as the traffic flow and mean velocity on an actual highway test site. He et al. [3] developed an image processing approach based on the Hough transform to extract vehicle trajectories from spatiotemporal DAS data and compute related traffic parameters.
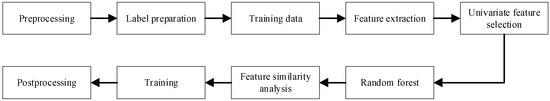
Figure 4.
The flowchart of the ML-based vehicle signal framework.
Moving beyond hand-crafted features, Chiang et al. [60] employed a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) directly on raw DAS traces, with a Softmax classification layer to discriminate between five vehicle classes; they achieved a 94% classification accuracy and revealed that large vehicles exhibit distinct low-frequency energy signatures. Wu et al. [61] introduced an end-to-end three-dimensional attention-augmented CNN (3D-CNN) that concurrently learns time–frequency–space features. Their 3D attention mechanism focuses on critical frequency bands, boosting the recognition accuracy to 99.33% while processing each spatial channel in just 0.22 ms—171× faster than equivalent 2D architectures with time–frequency inputs.
Van et al. [62] leveraged a deconvolutional autoencoder (DAE) to derive high-resolution impulse responses of vehicle signatures from continuous DAS streams, achieving near-real-time feature extraction over 24 h traffic cycles. Truong et al. [9] demonstrated edge computing-driven real-time vehicle detection and tracking on Norway’s Åstfjorden Bridge: Hough transforms detected linear trajectory segments in DAS data, and DBSCAN clustering consolidated detections to enable low-latency, edge-based traffic monitoring.
In complex and heterogeneous environments, hybrid strategies have also proven effective. Wu et al. [63] applied a 1D-CNN directly to raw DAS signals to obviate manual feature design, pairing it with an SVM classifier for innovative vehicle recognition. Liu et al. [64] optimized wavelet decomposition depth and threshold functions to jointly denoise in the time–frequency domain, extracting temporal, spectral, and statistical features; this approach achieved an over 80% vehicle detection accuracy, a <5% speed estimation error, and a >70% vehicle type classification accuracy. Liu et al. [32] further decomposed DAS signals into sub-bands to compute the energy entropy for each band, enabling vehicle localization via dual-thresholding and attaining a <6% speed error in single-vehicle scenarios on mining roadways.
Ye et al. [65] contrasted traditional time–frequency features with a classifier performance, evaluating neural networks (NNs) versus SVMs for vehicle identification. In a campus traffic study, Liu et al. refined vehicle impact features using adaptive wavelet thresholding, achieving classification accuracies of 78% for large vehicles, 73% for medium vehicles, and 68% for small vehicles.
Table 2 reflects the shift from manual, single-domain feature design toward data-driven, multimodal extraction strategies. The progression from the 1D-CNN to attention-based 3D-CNN architectures underscores deep learning’s superior ability to capture complex spatiotemporal patterns in DAS signals, marking a new paradigm for feature extraction in smart transportation applications.

Table 2.
Comparison of feature extraction methods.
5. Traffic Parameter Estimation and Vehicle Classification
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology, with its advantages of high sensitivity, fully distributed perception, and long-distance monitoring, demonstrates significant application potential in the field of road traffic monitoring. By utilizing optical fiber networks, DAS enables real-time acquisition of traffic-induced vibration signals, providing continuous and high-resolution acoustic data. This offers a novel technical approach for traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification.
However, the road traffic environment is complex and dynamic, characterized by diverse vehicle types, high traffic volumes, and significant environmental noise interference. These factors result in DAS signals containing substantial noise and complex signal characteristics, posing challenges for traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification. Effectively extracting meaningful traffic features from complex DAS signals, mitigating environmental noise interference, and achieving high-accuracy traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification have become key objectives in current research.
This section systematically reviews the latest developments in applying Distributed Acoustic Sensing technology to traffic monitoring, focusing on core aspects of traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification5.1. Vehicle Detection and Classification Based on DAS Signals
DAS-based vehicle classification leverages Rayleigh backscattering to transform optical fibers into vibration-sensing arrays, enabling long-range monitoring with a meter-scale resolution.
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS)-based vehicle detection and classification technology is a traffic perception method that monitors fiber-optic vibration signals. It leverages Rayleigh backscattering in optical fibers—wherein a DAS interrogator injects pulsed laser light into the fiber and receives the backscattered light—thus transforming the fiber into a vibration sensor array. When vehicles pass by, the resulting vibration signals are analyzed using signal processing algorithms to achieve vehicle detection and classification.
This technology offers advantages such as long-distance monitoring, a high resolution, cost-effectiveness, and privacy protection, making it suitable for traffic flow monitoring and vehicle classification statistics. In the future, further development is expected in algorithm optimization and multi-sensor data fusion, providing more efficient support for ITSs.
- (1)
- Early Studies (2019–2021)
In 2019, Huiyong Liu et al. [65] were the first to propose the use of DAS technology for vehicle detection and classification. Their research, based on Rayleigh backscattered light, employed wavelet denoising and a dual-threshold algorithm to process signals, extract vibration features caused by vehicles, and estimate vehicle counts and categories.
In 2021, Wiesmeyr et al. [59] further explored vehicle detection and classification based on DAS signals. They combined wavelet transform and deep learning models (such as convolutional neural networks, CNNs). The wavelet transform was used to extract characteristic frequencies, which were then input into a deep learning model for high-accuracy vehicle classification.
Hubbard et al. [66] proposed that DAS technology can also be applied to road deformation monitoring and event detection. By analyzing the signal features when vehicles pass, they estimated the traffic flow and speed, highlighting DAS’s multi-scenario application potential.
- (2)
- Recent Studies (2023–2025)
In 2025, Chiang et al. [67] proposed DAS as a novel data source for ITSs, used for vehicle detection and classification. Based on real-world DAS data, they revealed the presence of unique vehicle signatures in the signal and applied a 1D-CNN model to extract and classify vehicle features. Their extensive experiments confirmed the effectiveness of the 1D-CNN in vehicle classification tasks.
Xiao et al. [68] studied the performance of DAS in tracking vehicle movement on roads. They found that a vehicle’s mass and the contact area between tires and the road significantly affect the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of DAS signals.
Despite recent advances, challenges remain—such as an increased complexity in analyzing multi-lane traffic and the lack of publicly available datasets.
5.1. Deep Learning-Based Vehicle Detection and Classification
Contemporary DAS systems increasingly leverage specialized neural architectures to balance resolution requirements with real-time processing constraints.
Deep learning-based vehicle detection and classification using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) leverages fiber-optic sensors to capture vehicle-induced vibration signals. Deep learning models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are then used to automatically extract features and learn the distinctions between different vehicle types, enabling high-precision vehicle detection and classification. This approach combines the long-range monitoring capability of DAS with the powerful feature extraction abilities of deep learning, effectively coping with complex traffic scenarios, reducing false detection rates, and providing essential support for intelligent traffic management and autonomous driving. As such, it holds significant promise for future applications.
In DAS-based sensing systems, the spatial decoding capabilities of the U-Net architecture and the real-time detection efficiency of YOLOv8 represent two important technical directions. U-Net, a classic encoder–decoder network, features a decoder that gradually restores the spatial resolution, enabling the generation of high-resolution prediction maps. This makes it suitable for the accurate segmentation and localization of objects like vehicles and pedestrians in traffic monitoring, thus supporting traffic flow analysis and autonomous driving.
YOLOv8, by contrast, is renowned for its exceptional real-time detection performance. It introduces several innovations in real-time object detection, including anchor-free decoupled detection heads and an advanced backbone architecture, which significantly improve both the accuracy and speed. Compared to its predecessor YOLOv3, YOLOv8 achieves much faster detection speeds, meeting the demands of urban traffic monitoring and pedestrian safety applications. Additionally, YOLOv8 supports multiple tasks—such as object detection, segmentation, and classification—making it adaptable to complex traffic environments.
In 2023, Van Den Ende et al. [69] proposed using a spatial deep deconvolution U-Net model to detect vehicles and estimate the traffic flow from DAS signals. This model uses CNNs to automatically extract spatiotemporal features from DAS signals and employs deconvolution operations to reconstruct high-resolution signals, thereby enhancing the vehicle detection accuracy.
Zhipeng Ye et al. [70] introduced a deep learning technique based on a unified real-time object detection algorithm for estimating the traffic flow and vehicle speed from DAS data. In their study, DAS records were reconstructed into spatiotemporal images of the fiber cross-section, and a large number of images were manually labeled for model training, demonstrating the strong potential of deep learning in traffic parameter estimation.
In 2025, Jen Aldwayne B. Delmo [71] developed a deep learning-based system using the YOLOv8 model to estimate the vehicle speed in bidirectional traffic. The study utilized the existing camera infrastructure and advanced image processing techniques, focusing on regions of interest (ROIs) for more accurate speed calculations and evaluating the performance of the YOLOv8 model.
The application of deep learning models has significantly improved the performance of DAS-based traffic monitoring. The U-Net model excels in high-resolution signal reconstruction, making it suitable for scenarios requiring high-precision detection. YOLOv8, with its advantage in real-time detection, enables the rapid adaptation to traffic changes and is ideal for dynamic traffic environments. However, training deep learning models requires large volumes of labeled data, which can be a practical challenge in real-world deployments.
While U-Net excels in resolution-intensive tasks and YOLOv8 excels in dynamic environments, both face practical deployment challenges, including labeled data scarcity and computational resource demands.
5.2. Vehicle Speed Estimation Techniques
Early speed estimations rely on a physics-based signal analysis, where vehicle trajectories manifest as linear features in spatiotemporal domains.
Vehicle speed estimation using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology leverages fiber-optic sensors to capture vibrations generated by moving vehicles. By analyzing the temporal and spatial characteristics of these vibration signals, vehicle speeds can be estimated. Specifically, the DAS system deploys optical fibers along roadways, and when a vehicle passes, the resulting vibrations propagate along the fiber and are detected. Since a vehicle’s trajectory appears as a straight line in the two-dimensional spatiotemporal vibration signal, and the slope of that line correlates with the vehicle’s speed, the speed can be calculated by analyzing the trajectory of the signal.
Moreover, DAS technology can extract vibration signal features using enhanced wavelet denoising and dual-threshold algorithms to further determine the vehicle speed. In real-world applications, DAS systems can effectively monitor traffic flow and, when combined with traffic models, provide more accurate estimates of both the vehicle speed and traffic volume. This technology is highly resistant to electromagnetic interference, cost-effective, and discreet, making it suitable for a wide range of traffic monitoring scenarios.
- (1)
- Traditional Signal Processing Methods
In 2020, Liu et al. [72] proposed that vehicle speed estimation based on DAS signals could be achieved with high accuracy using wavelet denoising and a dual-threshold algorithm. Their study experimentally validated the effectiveness of wavelet denoising in removing environmental noise, as well as the ability of the dual-threshold algorithm to accurately detect signal features associated with passing vehicles. In 2021, Narisetty et al. [73] further improved both the wavelet denoising and dual-threshold algorithms to extract features from DAS signals, achieving a high-accuracy estimation of the traffic flow and vehicle speed. Deep learning models can also be used to automatically extract signal features from DAS data and optimize parameters through training, enabling a precise traffic flow estimation.
- (2)
- Deep Learning Methods
In 2025, Xiao et al. [68] studied the performance of DAS technology in tracking vehicle movements on roadways. Their research found that the vehicle mass and the contact area between tires and the road surface significantly impact the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of DAS signals. Based on these findings, they proposed a deep learning model that analyzes the frequency and intensity of DAS signals to achieve high-accuracy speed estimation.
Jen Aldwayne B. Delmo [71] introduced a deep learning-based system that utilizes the YOLOv8 model to estimate vehicle speeds in bidirectional traffic. This study employed image processing techniques to extract spatiotemporal features of vehicles and leveraged the real-time detection capabilities of YOLOv8 to enhance the accuracy of the speed estimation.
5.3. Traffic Flow Estimation Techniques
Traffic flow estimation is a critical component of ITSs, aiming to monitor and predict the volume of vehicles on roadways in real time using various methods and data sources. It primarily includes sensor-based monitoring approaches—such as inductive loop detectors, microwave radar, video detection systems, and the emerging Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology—as well as data-driven prediction methods like time series analysis, machine learning, and deep learning models.
These techniques are widely applied in urban traffic management, highway flow monitoring, and ITS development. With the integration of multi-source data and the increasing use of deep learning, the accuracy and real-time performance of traffic flow estimation continue to improve, providing essential support for traffic management and travel planning.
5.3.1. Traffic Flow Estimation Based on DAS Signals
- (1)
- Traditional Signal Processing Methods
In 2020, Narisetty et al. [73] proposed that DAS technology can achieve a high-accuracy traffic flow and speed estimation through improved wavelet denoising and dual-threshold algorithms. Their study experimentally verified the effectiveness of these signal processing algorithms in enhancing the DAS signal quality.
- (2)
- Deep Learning Methods
In 2022, Chiang et al. [67] proposed a deep learning-based approach for accurate traffic flow estimation by analyzing DAS signals. Their method uses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to automatically extract features from DAS signals and optimizes model parameters through training data to improve the estimation accuracy.
Chen et al. [74] proposed a deep learning-based traffic parameter estimation method that achieves high-precision traffic flow and speed estimation through the image representation of DAS signals. In this study, DAS signals are converted into image data, and deep learning models are used to extract spatiotemporal features, further enhancing the estimation accuracy.
In 2023, Van Den Ende et al. [69] introduced a spatial deep deconvolution U-Net model to detect vehicles and estimate the traffic flow from DAS signals. This model uses CNNs to automatically extract spatiotemporal features from DAS signals and reconstructs high-resolution signals through deconvolution, improving the traffic flow estimation accuracy.
In 2025, Zheng Wang et al. [75] proposed a novel method combining DAS with YOLOv8-based deep learning object detection for traffic flow estimation. Their approach extracts features from DAS signals using deep learning models and leverages the real-time detection capability of YOLOv8 to enhance the accuracy and robustness of traffic flow estimation. The comparative study of DAS technology for traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification in recent years is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparative studies on DAS technology for traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification.
5.3.2. Traffic Flow Estimation Based on Multi-Model Fusion
In 2022, Shuling Wang [76] and colleagues proposed a traffic parameter estimation method based on trajectory data from arterial corridors with multiple signalized intersections. They developed a general framework that integrates various traffic flow models with Bayesian Networks (BNs) to estimate overall traffic parameters using partially observed vehicle trajectory data with unknown penetration rates. This study established probabilistic relationships among traffic processes, traffic states, traffic flow model parameters, and observed vehicle trajectories through Bayesian Networks, providing a novel approach to traffic parameter estimation.
Alfonso Navarro-Espinoza [77] and others proposed a traffic flow estimation method based on machine learning and deep learning algorithms to support intelligent traffic signal control frameworks. Their research automatically extracts features from DAS signals using machine learning and deep learning techniques and optimizes model parameters through training data, thereby achieving high-accuracy traffic flow estimation.
5.4. Traffic Monitoring and Event Detection Technology
DAS technology uses optical fibers as sensors to capture vibration signals generated by passing vehicles, enabling the real-time monitoring of traffic conditions and event detection. It can be covertly deployed over long distances without a destructive installation on roads, offering advantages such as a strong interference resistance and low maintenance costs. DAS systems can accurately detect the traffic flow, vehicle speed, and vehicle types and leverage intelligent algorithms to identify abnormal events such as traffic accidents and congestion, providing efficient support for traffic management and emergency response, significantly enhancing road safety and operational efficiency.
- (1)
- Road Deformation Monitoring and Event Detection
In 2021, Hubbard [78] and colleagues proposed embedding DAS technology into asphalt for road deformation monitoring and event detection. By analyzing DAS signals, they estimated the traffic flow and vehicle speed. This study demonstrated DAS’s potential in road health monitoring and traffic event detection. Corera [79] and others developed a long-distance high-resolution traffic monitoring method based on pulse-compressed DAS and advanced vehicle tracking algorithms, enabling the real-time monitoring of the traffic flow and speed. Pulse compression technology improved the resolution of DAS signals, further enhancing the monitoring accuracy and coverage. In 2025, Wiesmeyr [80] proposed using DAS for real-time train tracking, developing a Kalman filter-based tracking algorithm tested across various vehicle types and speeds. This research provided theoretical support for applying DAS in railway traffic monitoring.
- (2)
- Urban Traffic Pattern Monitoring
In 2022, Chambers et al. [81] proposed that DAS technology could be used for monitoring urban traffic patterns by analyzing acoustic signals generated when vehicles pass over optical fibers, achieving real-time traffic flow monitoring. This study showcased the potential of DAS technology in urban traffic management.
5.5. Current Research Landscape
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology has garnered increasing attention in the field of ITSs, with various research institutions and universities actively engaged in related studies.
The Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences [82], proposed a digital coherent phase demodulation technique combined with a multidimensional comprehensive analysis and deep learning methods for railway safety monitoring. One affiliated unit conducted a study titled “Localization error analysis for near-field hydro-acoustic detection with distributed fiber acoustic sensing,” which investigated the error mechanisms in near-field underwater acoustic target localization using DAS technology within the context of optical phased array antennas and related optical techniques. The research revealed the impacts of detection aperture integration effects and Acoustic Sensitive Optical Cable (ASOC) deformation on the localization accuracy and proposed an error compensation model. These techniques share common principles with DAS optical signal processing.
Significant advancements have also been made by academic teams specializing in DAS technology. Professor He Zuyuan’s group [83] achieved notable progress particularly in Time-Gated Optical Frequency Domain Reflectometry (TGD-OFDR). This approach employs innovations such as pulse compression and matched filtering to simultaneously achieve a high spatial resolution and a high signal-to-noise ratio, overcoming inherent limitations of conventional DAS techniques and substantially enhancing the performance of distributed acoustic sensors. This technology demonstrates broad application potential not only in perimeter security, oil and gas exploration, and seismic waveform detection but also offers efficient solutions for traffic flow monitoring, vehicle speed measurement, and event detection in intelligent transportation systems, laying a solid foundation for the further expansion of DAS applications in complex scenarios.
The application of DAS technology in intelligent transportation systems has seen remarkable progress. From early signal processing methods to recent advances in deep learning, DAS has demonstrated a strong performance in vehicle detection, speed estimation, traffic flow estimation, and event detection. The incorporation of deep learning models has significantly enhanced DAS capabilities in complex traffic environments, particularly in handling intricate signal features and noise interference. Nonetheless, the training and deployment of these models require substantial labeled datasets and computational resources, which may pose practical challenges. Additionally, the further optimization of the DAS performance under complex noise conditions is necessary to improve the accuracy and reliability of event detection.
Overall, DAS technology holds great promise for intelligent transportation applications, although further integration with ITSs remains an important direction for development. As the technology continues to mature and application scenarios expand, DAS is expected to play an increasingly significant role in traffic monitoring and event detection.
6. Field Deployment and Typical Cases
Thanks to the innovative principle of “fiber as a sensor,” Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology enables large-scale, high-precision, and real-time distributed monitoring. DAS has been applied in fields such as road and bridge monitoring, transforming traditional monitoring methods. This section summarizes the development of DAS technology in monitoring applications and elaborates on its use in highways, urban roads, and bridges.
6.1. Application on Highways
DAS technology enables the continuous monitoring of vehicles on highways, including vehicle entry points, trajectory extraction, and speed estimation. Kou, Xue-Wei et al. employed the out-of-bag error criterion of random forests to select multiple features from vibration signals, extracting key features best representing road vibration. Then, they calculated and compared the root-mean-square values of signals after matched filtering, using set thresholds to distinguish vehicle vibration signals from noise. Finally, an optimized trajectory initiation algorithm was applied to accurately detect vehicles on highways and obtain real-time information [84].
Wang et al. proposed an attention-based convolutional neural network (CNN) structure with an extremely short signal window that learns and approximates classical denoising methods. Experiments conducted on real highway field data showed that existing denoising algorithms lacked sufficient time to process signals collected within a 100 ms window, whereas their proposed structure achieved satisfactory denoising results [85].
Fontana et al. introduced a novel method derived from a harmonic analysis to estimate vehicle trajectories from DAS data. This method iteratively segments estimated lines to detect closely spaced trajectories. Compared to the Hough transform, this method demonstrated a significantly better performance and validated the potential of notch filter dynamic vehicle detectors under high noise levels [86].
Wang et al. developed a new approach combining DAS with YOLOv8 deep learning object detection. Preprocessed and labeled DAS data collected over two weeks on highways were used to train the YOLOv8 network, achieving a 92% classification accuracy. The trained model revealed detailed hourly traffic patterns and vehicle compositions, demonstrating the potential of DAS for stable and cost-effective ITSs. These results highlight the effectiveness of integrating DAS with deep learning for noise reduction in traffic monitoring [87].
Khacef, Y et al. presented a neural network-based model capable of producing accurate and high-resolution vehicle localization and speed tracking. Their model outperformed existing dynamic time warping-based solutions and reduced the processing time by an order of magnitude [88].
Another team proposed a vehicle detection and classification system using DAS technology. They described a comprehensive classification approach involving signal processing and feature extraction. Traffic vibration signals were collected via distributed sensing fibers, from which multiple features were extracted to estimate the vehicle count and classify vehicle types. Based on the characteristics of vehicle vibration signals, an optimized wavelet denoising algorithm and dual-threshold algorithm were employed. After the feature extraction, a support vector machine (SVM) classifier was used to categorize vehicle types [89].
6.2. Urban Roads
In addition to its extensive experimentation and application on highways, Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology has also been employed for vehicle detection and traffic flow analysis on urban roads by leveraging existing fiber-optic cables and other infrastructure. This positions DAS as a technology with great potential in the development of future “smart cities.”
Van den Ende et al. investigated the potential of roadside DAS for simultaneously detecting and characterizing vehicle speeds on urban roads. They proposed a self-supervised deep learning approach called deconvolutional autoencoder (DAE), which performs deconvolution on the characteristic impulse response of vehicles from DAS data. Their results demonstrated that the DAE significantly improves the temporal resolution and detection performance of DAS signals [62].
Liu et al. utilized DAS to collect traffic-induced vibration signals via distributed optical fibers, from which various features were extracted to estimate vehicle counts and classify vehicle types. To enhance the signal clarity, they optimized wavelet-based denoising and dual-threshold algorithms, reconstructing the signals and extracting features such as the vehicle quantity and velocity [32].
Lindsey et al. successfully monitored traffic over a two-month period using DAS connected to buried telecommunications cables in Palo Alto, California. Over 450,000 individual vehicle events were analyzed using an automatic template-matching detection algorithm based on subgrade strain signatures [90].
Hubbard et al. embedded fiber-optic strain-sensing cables in an asphalt concrete test road to measure the spatially distributed dynamic road strain under different load types. Their findings confirmed that DAS can quantitatively and accurately measure road deformation [29].
Yuan et al. introduced a self-supervised U-Net model capable of suppressing background noise and spatially deconvolving vehicle-induced DAS signals into high-resolution pulses. Their approach incorporated spatial vehicle wavelets into the U-Net to maintain the output consistency under varying vehicle speeds. Furthermore, L2-norm regularization in the loss function enhanced the model’s sensitivity to weak signals from distant lanes. Their model not only improved the spatiotemporal resolution but also enabled the identification of the vehicle axle count and length [42].
Robles-Urquijo et al. buried a fiber-optic cable along the shoulder of a westbound urban road (with some segments offset from the curb), training multiple U-Net convolutional neural networks to improve the spatial resolution. Their work offered a novel tool for developing and evaluating DAS signal processing, optimizing cable layouts, and advancing DAS applications in complex urban monitoring scenarios [91].
Ferguson et al. connected a DAS system to an existing telecommunication fiber-optic line along the Calgary Light Rail Transit (LRT) Red Line. By monitoring intensity peaks, they estimated the DAS path distances of trains between City Hall and Tuscany stations. The study suggested DAS-based tracking as either an alternative or a supplementary system to GPS-based train monitoring, asserting that so long as the fiber placement and rail infrastructure remain fixed, DAS measurements will consistently correspond to unique geographic coordinates [92].
Corera and colleagues conducted vehicle detection measurements using dark fibers within telecom cables buried in a 40 km stretch of open urban road. Each trajectory detected by DAS was considered a vehicle passing event. The vehicle classification achieved an overall accuracy of 97.7%, with car and truck detection rates of 99.6% and 85.7%, respectively [26].
Zhong et al. developed an intelligent vehicle monitoring system supported by DAS for vehicle type and passenger number estimation in ITSs. They introduced a novel Sparse Residual (SR) block neural network structure and designed several deep learning models based on DAS signals. Experimental results showed that (1) their proposed SR-Net and Alex-SR networks achieved a detection accuracy above 90%; (2) their models outperformed the traditional ResNet in terms of convergence, stability, and accuracy; and (3) the proposed solutions were more efficient in terms of complexity and model size [93].
Martínez et al. proposed a method for generating urban traffic flow pattern databases using DAS, along with an automated labeling procedure to create accessible datasets for future machine learning applications. Continuous monitoring on a field platform enabled the detection of three event types: buses, cars, and pedestrians [94].
Zhong, R. et al. explored a novel DAS-based sensing approach for smart transportation systems. Utilizing fiber-optic cables as continuous-length virtual sensors, they collected DAS data from urban roads, applied various vehicle feature extraction techniques, and achieved a vehicle type recognition rate of 94% and a vehicle size recognition rate of 95% [93].
6.3. Bridges
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) systems offer distinct advantages for bridge monitoring by enabling the real-time assessment of structural conditions, environmental disturbances, and abnormal events. Rodet et al. extracted dynamic responses from five bridges using a 24 km long fiber-optic cable deployed across the Lyon metropolitan area in France. Based on the characteristic signals, three physical parameters influencing structural health—vibration frequency, damping, and the modal shape—were identified. The study demonstrated that the spatial and temporal variation in bridge dynamic responses can be effectively evaluated using existing fiber-optic infrastructure and DAS data [95].
Parajuli et al. introduced an ongoing investigation into the feasibility of using DAS-based distributed optical fiber (DOF) systems for rail support condition monitoring. During testing, a DAS system was used to monitor a 50 m section of track. Results showed that the system successfully captured strain variations in the rails caused by changes in support conditions under various loading speeds. This marked the first successful application of DAS for directly monitoring rail support states via track-mounted fiber-optic cables [96].
Kishida et al. conducted a field study on an elevated high-speed railway bridge in Taiwan. Multiple fiber-optic strain sensors were installed along a bullet train bridge with a span of up to 1 km. By integrating the data collected from these sensors, the three-dimensional deformation of the bridge was calculated. The installed system, equipped with continuous monitoring capabilities, allowed the rapid assessment of structural safety following two earthquakes with magnitudes of 6.4 and 6.8. In addition, the DAS system enabled the dynamic monitoring of the bullet train itself, further demonstrating the superior capabilities of fiber-optic sensing in both static and dynamic structural measurement contexts [97].
7. Conclusions
7.1. Key Method Comparison
In the realm of traffic monitoring using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS), a variety of signal processing and feature extraction methods have been developed and compared to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification. This section provides a comprehensive comparison of these methods, focusing on traditional signal processing techniques versus machine learning approaches and the application of deep learning for feature extraction.
7.1.1. Traditional Signal Processing Methods
Traditional signal processing methods have been widely used in DAS for traffic monitoring due to their simplicity and computational efficiency. These methods typically involve filtering techniques such as Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filters, Structure-Oriented Median Filters (SOMFs), and frequency–wavenumber (f–k) dip filters. These filters are effective in suppressing high-frequency noise and random disturbances, making them suitable for real-time applications where a quick response is crucial. For instance, the cascaded denoising framework proposed by Chen et al. combines IIR filters in the time domain and SOMFs and dip filters in the frequency–wavenumber domain to achieve significant improvements in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). However, these methods often struggle with complex noise patterns and may require the manual tuning of parameters to adapt to different environmental conditions.
7.1.2. Machine Learning Methods
Machine learning methods, particularly deep learning models, have gained increasing attention for their ability to automatically learn complex patterns from data. The DAS-N2N model, for example, uses a hybrid deep learning network that combines an autoencoder for denoising and a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network for sequential processing. This self-supervised network does not require annotated data or time-consuming labeling, making it more practical for large-scale applications. Another example is the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for feature extraction, which can automatically identify relevant features from raw DAS signals. These methods have shown a superior performance in handling complex traffic scenarios and improving the accuracy of vehicle detection and classification. However, they typically require substantial computational resources and large datasets for training, which can be a limitation in some practical deployments.
7.1.3. Deep Learning Feature Extraction
Deep learning has also been applied to feature extraction in DAS for traffic monitoring. Methods such as the 1D-CNN and 3D-CNN have been used to extract temporal, spectral, and spatial features from DAS signals. These models can capture complex spatiotemporal patterns, which are essential for an accurate traffic parameter estimation and vehicle classification. For example, a 3D-CNN with attention mechanisms can focus on critical frequency bands, improving the recognition accuracy while maintaining fast processing times. Additionally, techniques like spatial deconvolutional U-Nets have been employed to reconstruct high-resolution signals, enhancing the detection of vehicle trajectories. These deep learning approaches offer significant advantages in terms of accuracy and robustness but may face challenges related to model complexity and computational efficiency.
7.1.4. Comparison and Practical Implications
When comparing traditional signal processing methods with machine learning approaches, it is evident that traditional methods excel in their real-time performance and computational efficiency. They are particularly suitable for applications where an immediate response is required and computational resources are limited. On the other hand, machine learning methods, especially deep learning models, outperform traditional methods in terms of their accuracy and adaptability to complex scenarios. They can handle intricate signal patterns and improve the overall performance of traffic monitoring systems. However, the deployment of these models requires the careful consideration of computational resources and data availability.
In practice, the choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the traffic monitoring application. For real-time applications with limited computational resources, traditional signal processing methods may be preferred. For applications that prioritize accuracy and can accommodate the computational overhead, machine learning methods, particularly deep learning, are recommended. Future research may focus on developing hybrid approaches that combine the strengths of both traditional and machine learning methods to achieve a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency.
In conclusion, the comparison of key methods in DAS signal processing and feature extraction highlights the trade-offs between traditional and machine learning approaches. By understanding these trade-offs, researchers and practitioners can make informed decisions to optimize traffic monitoring systems for specific applications.
7.2. Limitations of Usage Method
In the realm of Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) for traffic monitoring, various signal processing methods exhibit distinct limitations under specific conditions. For instance, Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filters, while effective in certain applications, struggle with edge preservation due to their tendency to smooth high-frequency components, which can blur critical signal transitions. This smoothing effect is particularly problematic in scenarios requiring the meticulous preservation of abrupt signal changes, such as detecting sudden vibrations from vehicles. Additionally, IIR filters may face stability issues, especially when their coefficients are not carefully designed and quantized. On the other hand, while machine learning methods, including deep learning models, offer a superior performance in handling complex signals and improving accuracy, they demand substantial computational resources and large datasets for training, which can be impractical for real-time applications. Moreover, these advanced methods may encounter challenges in generalizing across different environments and maintaining their performance in dynamic conditions. Therefore, when selecting signal processing methods for DAS in traffic monitoring, it is crucial to weigh the trade-offs between computational efficiency, signal fidelity, and the adaptability to specific traffic conditions.
7.3. Summarization and Prospects
7.3.1. Main Research Topics and Unresolved Issues
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology has made significant advancements in recent years, with deep learning methods, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer-based architectures, outperforming traditional models such as logistic regression and support vector machines (SVMs) in terms of accuracy and robustness. These advancements have been crucial in various applications, including traffic monitoring, seismic event detection, and environmental sensing. For instance, in traffic monitoring, DAS has shown potential in detecting and classifying vehicles with high precision, even in complex scenarios with multiple sources of noise. Similarly, in seismic monitoring, DAS has been effective in recording seismic waveforms with a high spatial resolution, providing valuable data for earthquake detection and characterization.
Despite these advancements, several challenges remain. One of the primary issues is the need for computationally efficient models capable of real-time processing, especially in applications requiring immediate responses, such as traffic monitoring and seismic event detection. Additionally, the scarcity of labeled data in specific regions and the sensitivity of models to environmental and seasonal variations pose significant hurdles. For example, in traffic monitoring, DAS systems often struggle with the vast quantities of data and the diverse shapes of targets, which complicate signal extraction and object detection. In seismic monitoring, DAS data can be noisy, and traditional data processing algorithms may fail to effectively handle the high spatial resolution and complex waveforms.
7.3.2. Future Prospects
Future research directions may focus on addressing these challenges through the development of more efficient data processing techniques and machine learning models. This includes exploring transfer learning and domain adaptation methods to improve the model performance with limited labeled data. Additionally, enhancing the model interpretability and developing strategies for handling class imbalances could improve the deployment of DAS systems in real-world applications. In the context of seismic monitoring, further research is needed to develop algorithms that can effectively process the large volumes of data generated by DAS and accurately detect and locate seismic events. Overall, these research directions aim to make DAS technology more robust, scalable, and efficient for a wide range of applications.
8. Literature Search Methods and Screening Process
In conducting a systematic literature review, the process of the literature retrieval and screening is crucial to ensure the scientific rigor and reliability of the research. The following is a detailed description of the literature retrieval and screening process.
Initially, the databases for the literature retrieval were determined, including Scopus, IEEE Xplore, Web of Science, SCI-HUB, and Google Scholar. These databases cover a wide range of academic fields and can provide high-quality academic literature, ensuring the comprehensiveness and authority of the research.
The search keywords were centered around Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) and its applications in traffic monitoring. Specific keywords included Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS), traffic monitoring, signal processing, vehicle detection, classification, speed estimation, and traffic flow. These keywords and their variants were used to construct search strings to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the results.
The publication date range for the included literature was 2019 to 2025. This period covers the entire process from the initial application to the latest developments of DAS technology in traffic monitoring.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria for literature are as follows:
- (1)
- Inclusion criteria
Only peer-reviewed academic articles were included to ensure the quality and academic value of the research. To maintain uniformity and readability, only English-language literature was included. The literature had to be related to the application of DAS in traffic monitoring, including vehicle detection, classification, speed estimation, and traffic flow.
- (2)
- Exclusion criteria
Meeting abstracts, commentaries, editorials, and letters were excluded. Duplicate entries were removed using tools such as Excel. The literature that did not pertain to the research topic was excluded.
The literature screening and filtering process was as follows:
- (1)
- Number of search results
The initial search yielded a substantial number of results, the exact count of which was not specified. However, after screening, a number of highly relevant articles were finally included.
- (2)
- Screening process:
The first round of screening was based on titles, keywords, and abstracts to eliminate the literature that clearly did not meet the inclusion criteria. The remaining literature was then subjected to a full-text evaluation to further confirm its relevance to the study.
- (3)
- Screening tools
Literature management tools such as EndNote and de-duplication tools like Excel were used for the screening and management of the literature.
In summary, a systematic approach to the literature retrieval and screening was employed to ensure the scientific rigor and reliability of the research.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, J.D.; Investigation, L.J. and H.W.; Writing—original draft, Z.Z.; Formal analysis, Y.L. and F.M.; Validation, J.W. (Jikai Wang); Writing—review & editing, Z.L.; Resources, J.W. (Jianqing Wu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the City–University Integration Development Strategy Project of Jinan under Grant No. JNSX2024008.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the City–University Integration Development Strategy Project of Jinan under Grant No. JNSX2024008. All individuals included in this section have consented to the acknowledgement.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jingxiang Deng, Long Jin and Hongzhi Wang was employed by Gezhouba Group Transportation Investment Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Cai, H.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Z. Progress in research of distributed fiber acoustic sensing techniques. J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 36, 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Vehicle trajectory extraction method based on distributed optical fiber sensing system. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2021, 53, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Online Monitoring Method of Highway Operation Status Based on Distributed Optical Fiber Acoustic Sensing; University of Electronic Science and Technology of China: Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, M.; Yamada, T.; Akuhara, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Sakai, S. Performance of seismic observation by distributed acoustic sensing technology using a seafloor cable off Sanriku, Japan. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, A.; Newson, T.P. Contributed Review: Distributed optical fibre dynamic strain sensing. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 011501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Wu, X.; Guo, Z. Intelligent traffic monitoring with distributed acoustic sensing. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2025, 96, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, S. Fiber Signal Denoising Algorithm using Hybrid Deep Learning Networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.15125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, K.; Eidsvik, J.; Rørstadbotnen, R.A. Edge computing in distributed acoustic sensing: An application in traffic monitoring. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.16278. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yamagishi, J. Investigating self-supervised front ends for speech spoofing countermeasures. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.07725. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.W.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, B. Distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing technology based on coherent Rayleigh scattering. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 050001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M. Distributed Optical Fiber Vibration Sensor Based on Phase-Sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometry. Doctoral Dissertation, Université d’Ottawa/University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Cannada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Miah, K.; Potter, D.K. A review of hybrid fiber-optic distributed simultaneous vibration and temperature sensing technology and its geophysical applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Du, Y.; Yi, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, J. Research progress in distributed acoustic sensing techniques. Sensors 2022, 22, 6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwgi, M.; Hotate, K. Improvement of dynamic range in reflectometry by synthesis of optical coherence function at region beyond the coherence length. In Proceedings of the 2005 Pacific Rim Conference on Lasers & Electro-Optics, Tokyo, Japan, 14 July 2005; pp. 1584–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Fan, X.; Du, J.; Ma, L.; He, Z. Digitally enhanced optical frequency domain reflectometry with long measurement range. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 22–26 March 2015; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. W4I–2. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F. Study on length calibration method of coherent optical time domain reflectometer. In Proceedings of the AOPC 2019: Optoelectronic Devices and Integration; and Terahertz Technology and Applications, Beijing, China, 18 December 2019; Volume 11334, pp. 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. The noise lower-bound of Rayleigh-scattering-patten-based distributed acoustic sensing with coherent detection. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 40, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Ruiz, M.R.; Soriano-Amat, M.; Durán, V.; Martins, H.F.; Martin-Lopez, S.; Gonzalez-Herraez, M. Time expansion in distributed optical fiber sensing. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wu, H.; Huang, D.; Yu, C.; Lu, C. Coherent OTDR with large dynamic range based on double-sideband linear frequency modulation pulse. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 17165–17174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, F.; Hong, R.; Xu, W.; Shao, L.; Wang, F. Advances in phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2022, 5, 200078. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, E.; Coscetta, A.; Cerri, E.; Cennamo, N.; Zeni, L.; Minardo, A. Automatic traffic monitoring by ϕ-OTDR data and Hough transform in a real-field environment. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 3579–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, M.F. Detection of road surface anomaly using distributed fiber optic sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 22127–22134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeyr, C.; Coronel, C.; Litzenberger, M.; Döller, H.J.; Schweiger, H.B.; Calbris, G. Distributed acoustic sensing for vehicle speed and traffic flow estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 2596–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, A.J.; Minto, C. Using fibre optic cables to deliver intelligent traffic management in smart cities. In International Conference on Smart Infrastructure and Construction 2019 (ICSIC) Driving Data-Informed Decision-Making; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2019; pp. 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Ding, H.; Liu, M.; Zhu, Z.; Rui, D.; Chen, Y.; Xu, F. Vehicle operation status monitoring based on distributed acoustic sensor. Sensors 2023, 23, 8799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corera, I.; Piñeiro, E.; Navallas, J.; Sagues, M.; Loayssa, A. Long-range traffic monitoring based on pulse-compression distributed acoustic sensing and advanced vehicle tracking and classification algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 3127. [Google Scholar]
- Ip, E.; Huang, Y.K.; Huang, M.F.; Yaman, F.; Wellbrock, G.; Xia, T.; Wang, T.; Asahi, K.; Aono, Y. DAS over 1,007-km hybrid link with 10-Tb/s DP-16QAM co-propagation using frequency-diverse chirped pulses. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 41, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Q. A Deep Learning Image Segmentation Model for Detection of Weak Vehicle-Generated Quasi-Static Strain in Distributed Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 8933–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, P.G.; Ou, R.; Xu, T.; Luo, L.; Nonaka, H.; Karrenbach, M.; Soga, K. Road deformation monitoring and event detection using asphalt-embedded distributed acoustic sensing (DAS). Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2022, 29, e3067. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Zhao, H.; Gao, D.; Bian, Z.; Wu, D. Reconstruction of vehicle-induced vibration on concrete pavement using distributed fiber optic. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 24305–24317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, E.; Ravet, F.; Martins, H.; Huang, M.F.; Okamoto, T.; Han, S.; Narisetty, C.; Fang, J.; Huang, Y.K.; Salemi, M.; et al. Using global existing fiber networks for environmental sensing. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1853–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Xu, T.; Yan, W.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X. Vehicle detection and classification using distributed fiber optic acoustic sensing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, S.; Dong, Y.; Biondi, B.; Noh, H.Y. TelecomTM: A fine-grained and ubiquitous traffic monitoring system using pre-existing telecommunication fiber-optic cables as sensors. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2023, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.J.; Zhang, X.Z.; Xu, Z.N.; Chen, Y.H. Influencing factors of IQ demodulation method in distributed acoustic sensors. Acta Opt. Sin. 2023, 43, 1428001. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkov, B.G.; Yüksel, K.; Fotiadi, A.A.; Wuilpart, M.; Korobko, D.A.; Zhirnov, A.A.; Stepanov, K.V.; Turov, A.T.; Konstantinov, Y.A.; Lobach, I.A. Scientific applications of distributed acoustic sensing: State-of-the-art review and perspective. Sensors 2022, 22, 1033. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, M.; Gonzalez, A.; de Diego, M. Distributed affine projection algorithm over acoustically coupled sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 6423–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Gao, M.; Yiu, K.F.; Nordholm, S. Distributed Microphone Array Localization Problem via SDP-SOCP Method. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 31, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Savvaidis, A.; Fomel, S.; Pinero, G. Denoising of distributed acoustic sensing seismic data using an integrated framework. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2023, 94, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Cao, Z.; Ji, P.; Gu, L.; Wei, S.; Fan, B. Eliminating the Fading Noise in Distributed Acoustic Sensing Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5906510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsuti, D.; Marcon, G.; Turolla, A.; Santagiustina, M.; Galtarossa, A.; Zampato, M. DAS over Multimode Fibers with Reduced Fading by Coherent Averaging of Spatial Modes. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2023, 35, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapins, S.; Butcher, A.; Kendall, J.M.; Hudson, T.S.; Stork, A.L.; Werner, M.J. DAS-N2N: Machine learning distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) signal denoising without clean data. Geophys. J. Int. 2024, 236, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; van Den Ende, M.; Liu, J.; Noh, H.Y.; Clapp, R.; Richard, C.; Biondi, B. Spatial deep deconvolution u-net for traffic analyses with distributed acoustic sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, Y. Denoising the optical fiber seismic data by using convolutional adversarial network based on loss balance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 10544–10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Zhu, N. Noise Suppression of Distributed Acoustic Sensing Based on f-x Deconvolution and Wavelet Transform. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 7800208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabjula, J.; Sharma, J. Feature extraction techniques for noisy distributed acoustic sensor data acquired in a wellbore. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, E51–E61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isken, M.P.; Vasyura-Bathke, H.; Dahm, T.; Heimann, S. De-noising distributed acoustic sensing data using an adaptive frequency–wavenumber filter. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 231, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turov, A.T.; Konstantinov, Y.A.; Barkov, F.L.; Korobko, D.A.; Zolotovskii, I.O.; Lopez-Mercado, C.A.; Fotiadi, A.A. Enhancing the distributed acoustic sensors’(das) performance by the simple noise reduction algorithms sequential application. Algorithms 2023, 16, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, A.; Newson, T.P. High spatial resolution distributed optical fiber dynamic strain sensor with enhanced frequency and strain resolution. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Traffic flow detection using distributed fiber optic acoustic sensing. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 68968–68980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.X.; Zhang, F.D.; Lin, J.; Bai, X.Y.; Liu, H.Z. Fading Noise Suppression Method of Φ-OTDR System Based on GA-VMD Algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 22608–22619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Guzik, A.; Nishiguchi, K.; Li, C.H.; Azuma, D.; Liu, Q.; He, Z. Development of real-time time gated digital (TGD) OFDR method and its performance verification. Sensors 2021, 21, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khacef, Y. Advanced Road Traffic Monitoring with Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Deep Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Côte d’Azur, Nice, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Yiu, S.M. Self-Adaptive Incremental PCA-Based DBSCAN of Acoustic Features for Anomalous Sound Detection. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atterholt, J.; Zhan, Z.; Shen, Z.; Li, Z. A unified wavefield-partitioning approach for distributed acoustic sensing. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 228, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shragge, J.; Yang, J.; Issa, N.; Roelens, M.; Dentith, M.; Schediwy, S. Low-frequency ambient distributed acoustic sensing (DAS): Case study from Perth, Australia. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 226, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslangul, S. Detecting Tunnels for Border Security based on Fiber Optical Distributed Acoustic Sensor Data using DBSCAN. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Sensor Networks, Valleta, Malta, 28–29 February 2020; pp. 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delli Carri, S. A DBscan Clustering Approach of Acoustic Emission Signals of Adhesively Bonded Joints Under Mode I Fatigue Loading. POLITECNICO MILANO 1863. 2023. Available online: https://www.politesi.polimi.it/handle/10589/215801 (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Min, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. DAS vehicle signal extraction using machine learning in urban traffic monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5908510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeyr, C.; Bamberger, J.; Höfler, M. Vehicle Detection and Classification Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 3456–3467. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.Y.; Jaber, M.; Chai, K.K.; Loo, J. Distributed acoustic sensor systems for vehicle detection and classification. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 31293–31303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rao, Y. Multi-Dimensional Information Extraction and Utilization in Smart Fiber-Optic Distributed Acoustic Sensor (sDAS). J. Light. Technol. 2024, 42, 6967–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ende, M.; Ferrari, A.; Sladen, A.; Richard, C. Deep deconvolution for traffic analysis with distributed acoustic sensing data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Rao, Y. One-dimensional CNN-based intelligent recognition of vibrations in pipeline monitoring with DAS. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 4359–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Savvaidis, A.; Fomel, S. Vehicle Detection and Classification Using Distributed Fiber Optic Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B. Research on Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing for Vehicle Identification and Speed Measurement. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, S.; Biondi, B.; Fomel, S. Road Deformation Monitoring and Traffic Event Detection Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2021, 27, 4567–4578. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Vehicle Feature Extraction and Classification Using 1D-CNN for Distributed Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 5678–5689. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Vehicle Speed Estimation Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 6789–6790. [Google Scholar]
- n Ende, D.; Wiesmeyr, C.; Bamberger, J. Traffic Flow Estimation Using U-Net for Distributed Acoustic Sensing Signals. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 7890–7891. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Real-Time Traffic Flow and Speed Estimation Using YOLOv8 and Distributed Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 8901–8902. [Google Scholar]
- Delmo, J.A.B.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Speed Estimation in Bidirectional Traffic Using YOLOv8 and Distributed Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 9012–9013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Savvaidis, A.; Fomel, S. Speed Estimation Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Wavelet Denoising. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Narisetty, S.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Improved Wavelet Denoising and Dual-Threshold Algorithms for Traffic Flow and Speed Estimation Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Traffic Flow and Speed Estimation Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Traffic Flow Estimation Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing and YOLOv8. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Traffic Parameter Estimation Using Bayesian Networks and Traffic Flow Models. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Espinoza, A.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Traffic Flow Estimation Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms for Intelligent Traffic Signal Control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, S.; Biondi, B.; Fomel, S. Road Deformation Monitoring and Event Detection Using Embedded DAS Technology. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2021, 27, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Corera, J.; Wiesmeyr, C.; Bamberger, J. Long-Range High-Resolution Traffic Monitoring Using Pulse Compression DAS and Advanced Vehicle Tracking Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 1789–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmeyr, C.; Bamberger, J.; Höfler, M. Real-Time Train Tracking Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Kalman Filtering. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 1890–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.; Liu, H.; Fomel, S. Urban Traffic Pattern Monitoring Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1901–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Song, F.; Gao, K.; Cai, H.; Qu, R.; Ye, Q. Localization error analysis for near-field hydro-acoustic detection with distributed fiber acoustic sensing. Opt. Express 2025, 33, 11901–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, Q.W. Principles and applications of distributed fiber acoustic sensors. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 58, 1306001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kou, X.W.; Du, Q.G.; Huang, L.T.; Wang, H.H.; Li, Z.Y. Highway vehicle detection based on distributed acoustic sensing. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 27068–27080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, F. Rapid response DAS denoising method based on deep learning. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; García-Fernández, Á.F.; Maskell, S. A vehicle detector based on notched power for distributed acoustic sensing. In Proceedings of the 2022 25th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Linköping, Sweden, 4–7 July 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.C.; Shi, B. Enhancing traffic monitoring with noise-robust distributed acoustic sensing and deep learning. J. Appl. Geophys. 2025, 233, 105616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khacef, Y.; van den Ende, M.; Richard, C.; Ferrari, A.; Sladen, A. Precision Traffic Monitoring: Leveraging Distributed Acoustic Sensing and Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 7678–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarizadehasl, S.; Jiménez, M.A.G.; Casas, J.M.P.; Lozano-Galant, J.A.; Turmo, J. Eigenfrequency analysis using fiber optic sensors and low-cost accelerometers for structural damage detection. Eng. Struct. 2024, 318, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, N.J.; Yuan, S.; Lellouch, A.; Gualtieri, L.; Lecocq, T. City-scale dark fiber DAS measurements of infrastructure use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Urquijo, I.; Benavente, J.; Blanco García, J.; Diego Gonzalez, P.; Loayssa, A.; Sagues, M. Method to Use Transport Microsimulation Models to Create Synthetic Distributed Acoustic Sensing Datasets. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.J.; McDonald, M.A.D.; Basto, D.J. Take the Eh? train: Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) of commuter trains in a Canadian City. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 183, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Chiang, C.Y.; Jaber, M. Intelligent Vehicle Monitoring: Distributed Acoustic Sensors Enabled Smart Road Infrastructure. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 15211–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; García, L.; Titos, M. Generating a Mobility-Pattern Database for Urban Traffic Monitoring Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 2382–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Rodet, J.; Tauzin, B.; Amin Panah, M.; Pittet, R. Urban dark fiber distributed acoustic sensing for bridge monitoring. Struct. Health Monit. 2025, 24, 636–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, B.; Gharizadehvarnosefaderani, M.; Damm, D.; Rabbi, M.F.; Drapp, B.; Pooch, A.; Mishra, D. Rail track support condition monitoring with distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2025, 239, 09544097251338449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Aung, T.L.; Lin, R. Monitoring a Railway Bridge with Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing Using Specially Installed Fibers. Sensors 2024, 25, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).