Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, and Handgrip Strength in Overweight and Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
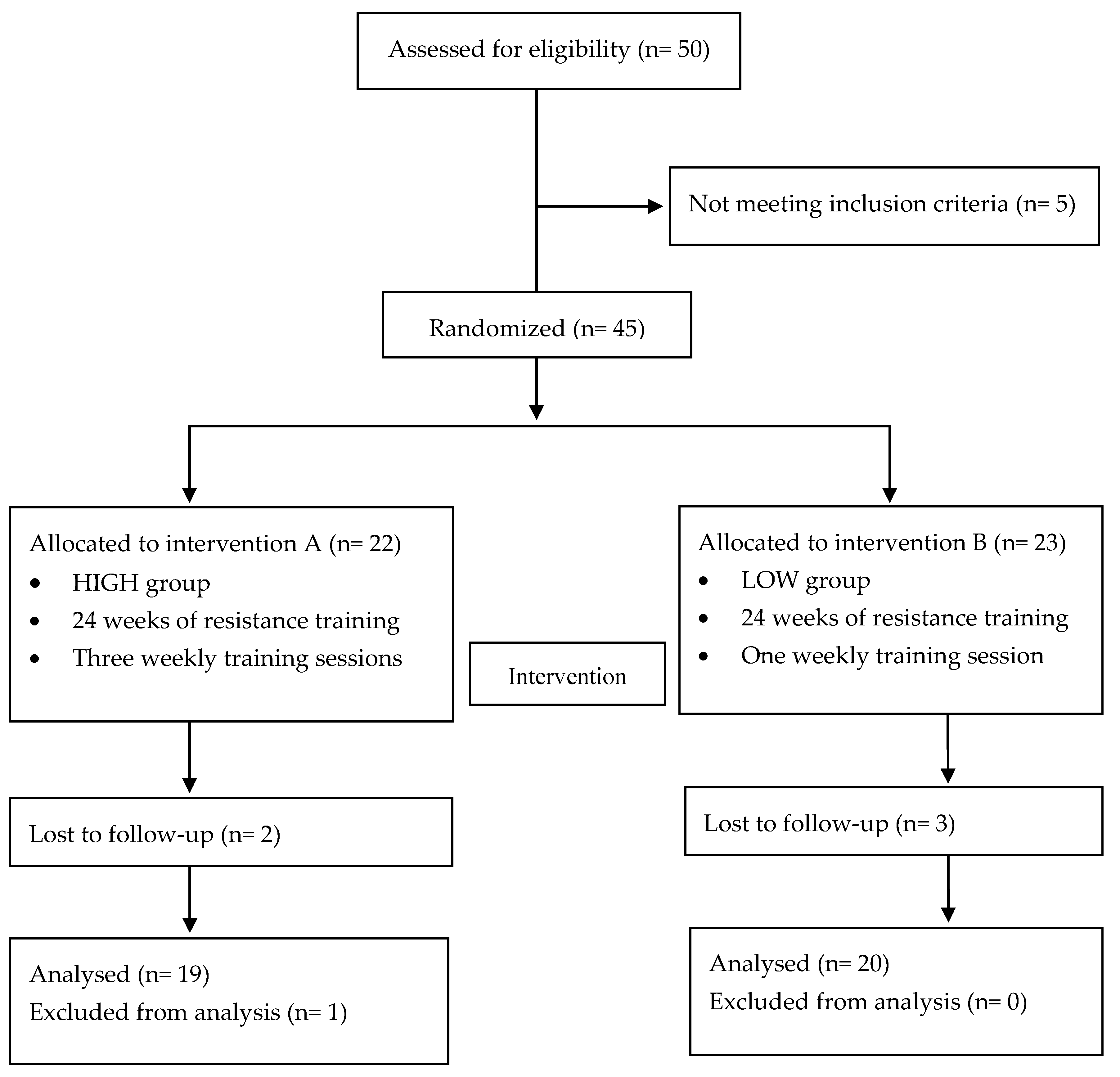
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Exercise Program
2.3. Anthropometry
2.4. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
2.5. Handgrip Strength
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ General Characteristics
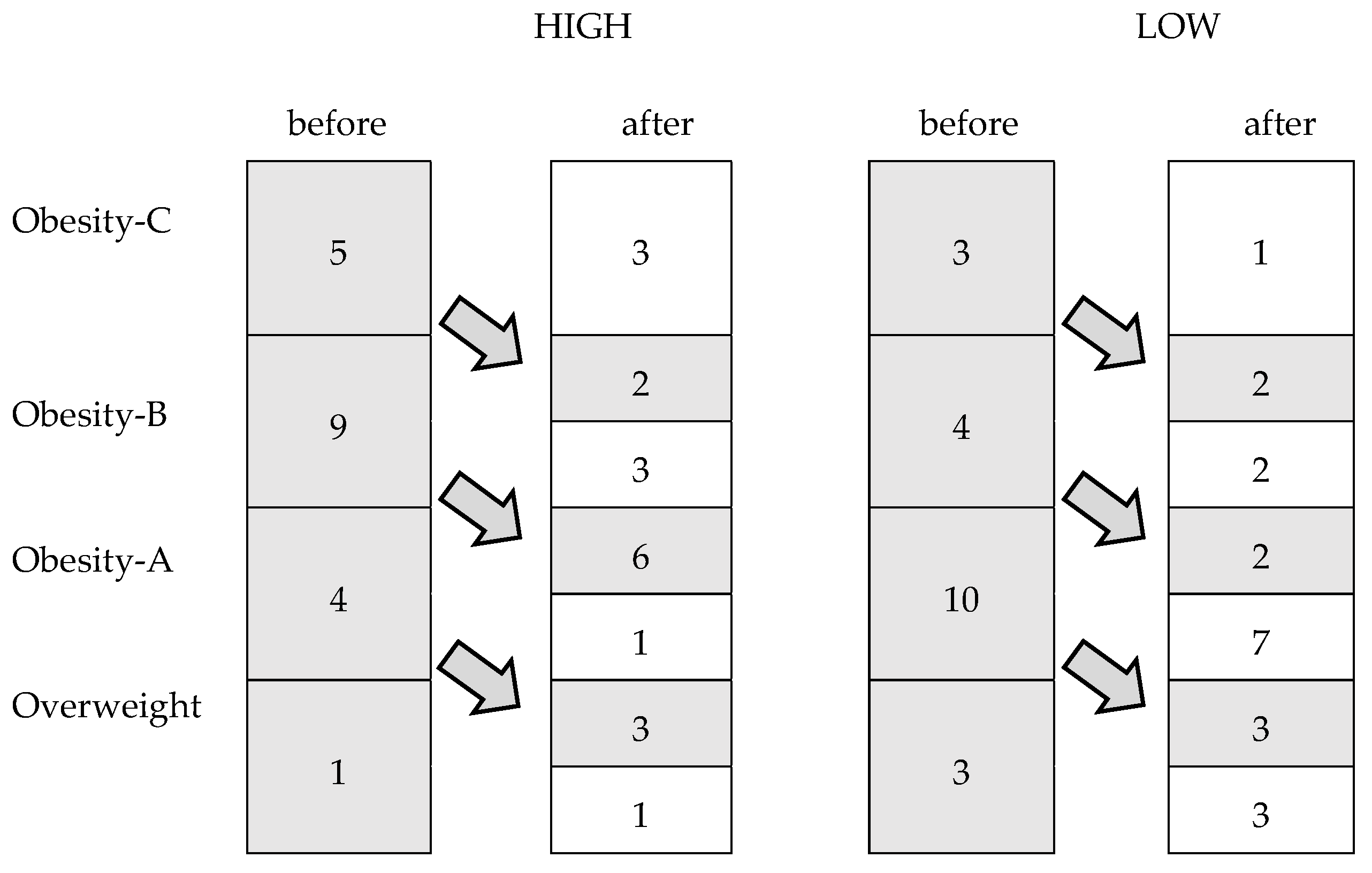
3.2. Anthropometry
3.3. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
3.4. Handgrip Strength
3.5. Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- National Institutes of Health. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report. National Institutes of Health. Obes. Res. 1998, 6, 51S–209S. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. In NCHS Data Brief; No. 360; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Statistic. Health Survey of England 2017. Overweight and Obesity in Adults and Children. Available online: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/health-survey-for-england/2017 (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Farrag, N.S.; Cheskin, L.J.; Farag, M.K. A systematic review of childhood obesity in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region: Health impact and management. Adv. Ped. Res. 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter Starr, K.N.; McDonald, S.R.; Bales, C.W. Obesity and physical frailty in older adults: A scoping review of lifestyle intervention trials. J. Am. Med. Direct. Assoc. 2014, 15, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huck, C.J. Effects of supervised resistance training on fitness and functional strength in patients succeeding bariatric surgery. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Gualdi-Russo, E.; Campa, F. Ethnic differences in body image perception in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 32, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Gualdi-Russo, E.; Mazzuca, P.; Campa, F. Ethnic differences in body composition, sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus living in Italy. Endocrine 2019, 65, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Avenell, A.; Bolland, M.; Hudson, J.; Stewart, F.; Robertson, C.; Sharma, P.; Fraser, C.; MacLennan, G. Effects of weight loss interventions for adults who are obese on mortality, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2017, 359, j4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Harrison, C.L.; Hutchison, S.; de Courten, B.; Stepto, N.K. Exploring factors related to changes in body composition, insulin sensitivity and aerobic capacity in response to a 12-week exercise intervention in overweight and obese women with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Managing Overweight and Obesity in Adults: Systematic Evidence Review from the Obesity Expert Panel. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/obesity-evidence-review.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2020).
- Theodorakopoulos, C.; Jones, J.; Bannerman, E.; Greig, C.A. Effectiveness of nutritional and exercise interventions to improve body composition and muscle strength or function in sarcopenic obese older adults: A systematic review. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Buscemi, J.; Milsom, V.; Malcolm, R.; O’Neil, P.M. Effects on cardiovascular risk factors of weight losses limited to 5–10. Transl. Behav. Med. 2016, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Weight Management: Lifestyle Services for Overweight or Obese Adults (NICE guidance PH53); National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2014; Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph53/chapter/Introduction-scope-and-purpose-of-this-guidance (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Etemad, Z.; Moradiani, H.; Aziz-Beigi, K. Adiponectin is associated with inflammatory markers and insulin resistance following moderate-intensity circuit weight training in healthy overweight and obese men. Med. Sport 2015, 68, 627–638. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan, P.; Dixit, S.; Alahmari, K.; Devenesan, C.S.; Rengaramanujam, K.; Zaman, G.S.; Ali Asiri, H.; Chandramoorthy, C.H. Resistance training influences Adipokines and various biochemical factors altering the risk of metabolic syndrome in young male obese students. Med. Sport 2018, 71, 561–578. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Kuk, J.L. What Is the Role of Resistance Exercise in Improving the Cardiometabolic Health of Adolescents with Obesity? J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 28, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, T.; Paulsen, S.K.; Bruun, J.M.; Pedersen, S.B.; Richelsen, B. Exercise training versus diet-induced weight-loss on metabolic risk factors and inflammatory markers in obese subjects: A 12-week randomized intervention study. American journal of physiology. Endoc. Met. 2010, 298, E824–E831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straight, C.R.; Dorfman, L.R.; Cottell, K.E.; Krol, J.M.; Lofgren, I.E.; Delmonico, M.J. Effects of resistance training and dietary changes on physical function and body composition in overweight and obese older adults. J. Phys. Act. Health 2012, 9, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Campa, F.; Spiga, F.; Grigoletto, A.; Simonelli, I.; Gualdi-Russo, E. The association between body composition and quality of life among elderly Italians. Endocrine 2020, 68, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shreef, F.M.; Al-Jiffri, O.H.; Abd El-Kader, S.M. Bone metabolism and hand grip strength response to aerobic versus resistance exercise training in non-insulin dependent diabetic patients. Afr. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fazelifar, S.; Ebrahim, K.; Sarkisian, V. Effect of exercise training and detraining on serum leptin levels in obese young boys. Med. Sport 2013, 66, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Campa, F.; Silva, A.M.; Toselli, S. Changes in Phase Angle and Handgrip Strength Induced by Suspension Training in Older Women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; So, B.; Son, J.S.; Yoon, D.; Song, W. Effect of aerobic training and resistance training on circulating irisin level and their association with change of body composition in overweight/obese adults: A pilot study. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, J.C.; Gobbi, L.T.; Gurjão, A.L.; Gonçalves, R.; Prado, A.K.; Gobbi, S. Effect of different rest intervals, between sets, on muscle performance during leg press exercise, in trained older women. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2013, 12, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, E.F.; Ribeiro, A.S.; do Nascimento, M.A.; Silva, A.M.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nabuco, H.; Pina, F.; Mayhew, J.L.; Da Silva-Grigoletto, M.E.; da Silva, D.; et al. Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Fat in Overweight/Obese Older Women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C.; DeBeliso, M.A.; Spitzer-Gibson, T.A.; Adams, K.J. The effect of resistance-training intensity on strength-gain response in the older adult. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2004, 18, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Sayers, S.P.; Gibson, K. Effects of high-speed power training on muscle performance and braking speed in older adults. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 426278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murlasits, Z.; Reed, J.; Wells, K. Effect of resistance training frequency on physiological adaptations in older adults. J. Exer. Sci. Fit. 2012, 10, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. J. Clin. Epidem. 2010, 63, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Badicu, G.; Bragonzoni, L.; Spiga, F.; Mazzuca, P.; Campa, F. Comparison of the Effect of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Phase Angle and Handgrip Strength in Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. IJERPH 2020, 17, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrman, K.J.; Gordon, M.P.; Visich, S.P.; Keteyian, J.S. Clinical Exercise Physiology, 4th ed.; Human Kinetics Books: Champaign, IL, USA, 2019; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A. Fundamentals of resistance training: Progression and exercise prescription. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G.; Roche, A.F.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics Books: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Durnin, J.V.; Womersley, J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: Measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Brit. J. Nutr. 1974, 32, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri, W.E. Body composition from fluid spaces and density: Analyses of methods. In Techniques for Measuring Body Composition; The National Academies National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; pp. 223–244. [Google Scholar]
- Aruga, M.; Tokita, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Kamachi, K.; Tanaka, A. The effect of combined diet and exercise intervention on body weight and the serum GPIHBP1 concentration in overweight/obese middle-aged women. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2017, 475, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquette, S.; Bouchard, D.R.; Doyon, C.Y.; Sénéchal, M.; Brochu, M.; Dionne, I.J. Relative strength as a determinant of mobility in elders 67–84 years of age. a nuage study: Nutrition as a determinant of successful aging. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronne, L.J.; Isoldi, K.K. Overweight and obesity: Key components of cardiometabolic risk. Clin. Cornerstone 2007, 8, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, L.; Cyrino, E.S.; Antunes, M.; Santos, D.A.; Sardinha, L.B. Changes in phase angle and body composition induced by resistance training in older women. Europ. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.; Dendale, P.; Berger, J.; van Loon, L.J.; Meeusen, R. The effects of exercise training on fat-mass loss in obese patients during energy intake restriction. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavers, K.M.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Rejeski, W.J.; Burdette, J.H.; Walkup, M.P.; Sheedy, J.L.; Nesbit, B.A.; Gaukstern, J.E.; Nicklas, B.J.; Marsh, A.P. Effect of Exercise Type During Intentional Weight Loss on Body Composition in Older Adults with Obesity. Obesity 2017, 25, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, L.H.; Slentz, C.A.; Bateman, L.A.; Shields, A.T.; Piner, L.W.; Bales, C.W.; Houmard, J.A.; Kraus, W.E. Effects of aerobic and/or resistance training on body mass and fat mass in overweight or obese adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberga, A.S.; Farnesi, B.C.; Lafleche, A.; Legault, L.; Komorowski, J. The effects of resistance exercise training on body composition and strength in obese prepubertal children. Physic. Sportsmed. 2013, 41, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; Parker, H.M.; Way, K.L.; O’Connor, H.T.; Sainsbury, A.; Baker, M.K.; Chuter, V.H.; Caterson, I.D.; George, J.; et al. Effect of resistance training on liver fat and visceral adiposity in adults with obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2017, 47, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.D.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Huang, S.W.; Ku, J.W.; Hsiao, D.J.; Liou, T.H. Effects of elastic band exercise on lean mass and physical capacity in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Scient. Rep. 2018, 8, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, P.D.; Silva, A.G.; Ferreira, P.G.; DA Silva, A.; Salge, J.M.; Carvalho-Pinto, R.M.; Cukier, A.; Brito, C.M.; Mancini, M.C.; Carvalho, C. Exercise Improves Physical Activity and Comorbidities in Obese Adults with Asthma. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villareal, D.T.; Aguirre, L.; Gurney, A.B.; Waters, D.L.; Sinacore, D.R.; Colombo, E.; Armamento-Villareal, R.; Qualls, C. Aerobic or resistance exercise, or both, in dieting obese older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.C.; Franklin, B.A.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Stewart, K.J. Effects of single bout resistance exercise on glucose levels, insulin action, and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes: A narrative review. J. Diab. Complic. 2020, 34, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fock, K.M.; Khoo, J. Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. J. Gastroent. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.J.; VanWormer, J.J.; Crain, A.L.; Boucher, J.L.; Histon, T.; Caplan, W.; Bowman, J.D.; Pronk, N.P. Weight-loss outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of weight-loss clinical trials with a minimum 1-year follow-up. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, R.J.; Kenny, G.P.; Boulé, N.G.; Wells, G.A.; Prud’homme, D.; Fortier, M.; Reid, R.D.; Tulloch, H.; Coyle, D.; Phillips, P.; et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann. Int. Med. 2007, 147, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Peng, L.N.; Chiou, S.T.; Chen, L.K. Relative Handgrip Strength Is a Simple Indicator of Cardiometabolic Risk among Middle-Aged and Older People: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | HIGH (n = 22) | LOW (n = 23) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | a | 55.51 ± 9.16 | 57.50 ± 8.44 | 0.46 |
| b | 40–69 | 40–68 | ||
| Weight (kg) | a | 97.43 ± 17.41 | 88.76 ± 16.00 | 0.10 |
| b | 73.50–137.10 | 73.20–139.30 | ||
| Height (cm) | a | 158.51 ± 6.12 | 158.05 ± 6.60 | 0.81 |
| b | 146.80–170.70 | 146.00–168.90 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | a | 38.70 ± 6.18 | 35.58 ± 6.35 | 0.11 |
| b | 28.10–52.10 | 27.50–51.00 |
| Variable | HIGH (n = 19) | LOW (n = 20) | ES | Interaction p-Value | SP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | ||||
| Anthropometry | |||||||
| Weight (kg) | 97.43 ± 17.41 | 88.73 ± 18.52 * | 88.76 ± 16.00 | 84.02 ± 13.20 * | −0.31 | <0.01 | 0.80 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 38.70 ± 6.18 | 35.25 ± 6.85 * | 35.58 ± 6.35 | 33.66 ± 5.05 * | −0.19 | <0.01 | 0.77 |
| WC (cm) | 110.31 ± 13.68 | 100.49 ± 14.66 * | 106.69 ± 12.26 | 101.46 ± 11.24 * | −0.41 | <0.01 | 0.89 |
| FM (%) | 40.17 ± 3.29 | 36.26 ± 3.73 * | 39.36 ± 3.36 | 37.24 ± 3.70 * | −5.60 | <0.01 | 0.94 |
| Blood pressure | |||||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 130.48 ±13.77 | 125.24 ± 17.78 | 127.62 ± 11.46 | 121.43 ± 25.93 | 0.04 | 0.89 | 0.05 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81.43 ± 9.10 | 77.57 ± 9.66 | 78.81 ± 6.69 | 78.33 ± 10.16 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Lipid profile | |||||||
| TC (mg/dl) | 204.50 ± 49.16 | 196.14 ± 44.08 * | 209.85 ± 32.42 | 202.36 ± 27.87 | −0.05 | 0.87 | 0.05 |
| TG (mg/dl) | 143.35 ± 52.90 | 120.18 ± 50.28 * | 138.54 ± 54.25 | 127.69 ± 50.44 * | −0.31 | 0.30 | 0.17 |
| HDL-C(mg/dl) | 54.30 ± 15.16 | 59.43 ± 16.24 * | 53.04 ± 13.74 | 54.35 ± 13.96 * | 0.58 | 0.06 | 0.45 |
| LDL-C (mg/dl) | 133.58 ± 27.76 | 121.29 ± 25.00 * | 122.98 ± 41.62 | 120.33 ± 48.75 | −0.60 | 0.05 | 0.58 |
| Insulin resistance | |||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 6.05 ± 0.65 | 5.68 ± 0.67 * | 6.56 ± 1.36 | 6.31 ± 1.22 * | −0.39 | 0.20 | 0.23 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 97.48 ± 13.77 | 88.82 ± 12.89 * | 94.98 ± 7.83 | 92.43 ± 7.54 * | −1.33 | <0.01 | 0.98 |
| Insulin (u/l) | 13.07 ± 2.61 | 11.01 ± 2.90 * | 11.63 ± 2.85 | 10.79 ± 2.71 * | −0.76 | 0.01 | 0.68 |
| HOMAIR | 3.12 ± 0.68 | 2.40 ± 0.67 * | 2.72 ± 0.69 | 2.45 ± 0.58 * | −1.07 | <0.01 | 0.92 |
| Strength | |||||||
| DHS (kg) | 22.76 ± 4.92 | 27.04 ± 5.29 * | 24.50 ± 5.66 | 25.45 ± 5.77 | 1.34 | <0.01 | 0.99 |
| AHS (kg) | 42.81 ± 9.39 | 50.35 ± 9.13 * | 46.88 ± 11.18 | 48.83 ± 11.71 | 1.36 | <0.01 | 0.99 |
| RHS (kg) | 1.12 ± 0.27 | 1.47 ± 0.36 * | 1.34 ± 0.36 | 1.47 ± 0.39 * | 1.53 | <0.01 | 0.98 |
| BMI | WC | FM | HDL-C | LDL-C | HbA1c | GLU | INS | HOMAIR | AHS | RHS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 1.00 † | 0.54 † | 0.39 * | −0.24 | 0.20 | 0.68 | 0.47 † | 0.29 | 0.35 * | −0.07 | −0.45 * |
| BMI | 1.00 | 0.53 † | 0.38 * | −0.24 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.47 † | 0.29 | 0.35 * | −0.06 | −0.45 * |
| WC | - | 1.00 | 0.29 | −0.41 * | 0.42 * | 0.25 | 0.40 * | 0.30 * | 0.36 * | −0.21 | −0.38 * |
| FM | - | - | 1.00 | −0.08 | 0.36 * | 0.24 | 0.53 † | 0.45 * | 0.47 † | −0.39 * | −0.47 † |
| HDL-C | - | - | - | 1.00 | −0.32 * | −0.01 | −0.28 | −0.09 | −0.16 | 0.10 | 0.18 |
| LDL-C | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 0.40 * | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.23 | −0.23 | −0.27 |
| HbA1c | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 0.07 | −0.05 | −0.07 | −0.32 * | −0.29 |
| GLU | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 0.41 * | 0.60 † | −0.31 * | −0.47 † |
| INS | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 0.95 † | −0.36 * | −0.42 * |
| HOMAIR | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | −0.40 * | −0.47 † |
| AHS | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 0.88 † |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campa, F.; Maietta Latessa, P.; Greco, G.; Mauro, M.; Mazzuca, P.; Spiga, F.; Toselli, S. Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, and Handgrip Strength in Overweight and Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030051
Campa F, Maietta Latessa P, Greco G, Mauro M, Mazzuca P, Spiga F, Toselli S. Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, and Handgrip Strength in Overweight and Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2020; 5(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampa, Francesco, Pasqualino Maietta Latessa, Gianpiero Greco, Mario Mauro, Paolo Mazzuca, Federico Spiga, and Stefania Toselli. 2020. "Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, and Handgrip Strength in Overweight and Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 5, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030051
APA StyleCampa, F., Maietta Latessa, P., Greco, G., Mauro, M., Mazzuca, P., Spiga, F., & Toselli, S. (2020). Effects of Different Resistance Training Frequencies on Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, and Handgrip Strength in Overweight and Obese Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 5(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk5030051









