Mitogenomic Architecture and Phylogenetic Relationship of European Barracuda, Sphyraena sphyraena (Teleostei: Sphyraenidae) from the Atlantic Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Species Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Assembly
2.3. Characterization and Comparative Analyses
2.4. Genetic Distance and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mitogenome Structure and Organization
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes
3.3. Ribosomal RNA and Transfer RNA Genes
3.4. Features of Control Region
3.5. Genetic Distances and Matrilineal Phylogeny
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballen, G.A. Nomenclature of the Sphyraenidae (Teleostei: Carangaria): A synthesis of fossil- and extant-based classification systems. Zootaxa 2019, 4686, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottfried, M.D.; Samonds, K.E.; Ostrowski, S.A.; Andrianavalona, T.H.; Ramihangihajason, T.N. New evidence indicates the presence of barracuda (Sphyraenidae) and supports a tropical marine environment in the Miocene of Madagascar. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Van der Laan, R. (Eds.) Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species. Electronic Version. 2022. Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Senou, H. Sphyraenidae. The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Pacific, Bony fishes part 4 (Labridae to Latimeriidae), estuarine crocodiles, sea turtles, sea snakes and marine mammals. In FAO Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes; Carpenter, K.E., Niem, V.H., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001; Volume 6, pp. 3685–3697. [Google Scholar]
- de Sylva, D.P. Barracudas (Pisces: Sphyraenidae) of the Indian Ocean and adjacent seas—A preliminary review of their systematics and ecology. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. India. 1975, 15, 74–94. [Google Scholar]
- Senou, H. Sphyraenidae. In Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species, 3rd ed.; Nakabo, T., Ed.; Tokai University Press: Hadano, Japan, 2013; pp. 1636–1639 + 2219–2221. [Google Scholar]
- Morishita, S.; Motomura, H. Sphyraena stellata, a new barracuda from the Indo-Pacific, with redescriptions of S. helleri Jenkins, 1901 and S. novaehollandiae Günther, 1860 (Perciformes: Sphyraenidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4772, zootaxa.4772.3.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadie, W.F.; Dowidar, N.M.; Rizkalla, S.I. Morphometric variations of the family Sphyraenidae from the South-eastern part of the Mediterranean Sea. Folia Morphol. 1987, 35, 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Grubich, J.R.; Rice, A.N.; Westneat, M.W. Functional morphology of bite mechanics in the great barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda). Zoology 2008, 111, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, A.; Kochanian, P.; Marammazi, J.; Yavari, V.; Savari, A.; Salari-Aliabadi, M.A. Length-weight relationship and spawning season of Sphyraena jello C., from Persian Gulf. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, B.G. Gross morphological and surface ultrastructural investigation on the gills of the European barracuda Sphyraena sphyraena. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Moschella, P.; Maynou, F. Tracking signals of change in Mediterranean fish diversity based on local ecological knowledge. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Mittermayer, F.; Pihl, L.; Wennhage, H. Feeding ecology of indigenous and non-indigenous fish species within the family Sphyraenidae. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 2528–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Hernández, H.; Muñoz, M.; Lloret, J. Life-history traits of temperate and thermophilic barracudas (Teleostei: Sphyraenidae) in the context of sea warming in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussellaa, W.; Neifar, L.; Goedknegt, M.A.; Thieltges, D.W. Lessepsian migration and parasitism: Richness, prevalence and intensity of parasites in the invasive fish Sphyraena chrysotaenia compared to its native congener Sphyraena sphyraena in Tunisian coastal waters. PeerJ 2018, 146, e5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corner, R.D.; Cribb, T.H.; Cutmore, S.C. A new genus of Bucephalidae Poche, 1907 (Trematoda: Digenea) for three new species infecting the yellowtail pike, Sphyraena obtusata Cuvier (Sphyraenidae), from Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Syst. Parasitol. 2020, 97, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguguah, N.M.; Onyekachi, M.; Ikegwu, J. Concentration and Human Health Implications of Trace Metals in Fish of Economic Importance in Lagos Lagoon, Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2017, 7, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyarko, E.; Boateng, C.M.; Asamoah, O.; Edusei, M.O.; Mahu, E. Potential human health risks associated with ingestion of heavy metals through fish consumption in the Gulf of Guinea. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanti, F.; Minelli, D.; Conte, G.L.; Miyashita, T. An exceptionally preserved Eocene shark and the rise of modern predator-prey interactions in the coral reef food web. Zool. Lett. 2016, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Near, T.J.; Eytan, R.I.; Dornburg, A.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Davis, M.P.; Wainwright, P.C.; Friedman, M.; Smith, W.L. Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13698–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, R.R.; Broughton, R.E.; Wiley, E.O.; Carpenter, K.; López, J.A.; Li, C.; Holcroft, N.I.; Arcila, D.; Sanciangco, M.; Cureton Ii, J.C.; et al. The tree of life and a new classification of bony fishes. PLoS Curr. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J.; Dornburg, A.; Eytan, R.I.; Keck, B.P.; Smith, W.L.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Price, S.A.; Burbrink, F.T.; Friedman, M.; et al. Phylogeny and tempo of diversification in the superradiation of spiny-rayed fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12738–12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Bonillo, C.; Lecointre, G. Repeatability of clades as a criterion of reliability: A case study for molecular phylogeny of Acanthomorpha (Teleostei) with larger number of taxa. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 262–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doiuchi, R.; Nakabo, T. Molecular evidence for the taxonomic status of three species of the Sphyraena obtusata group (Perciformes: Sphyraenidae) from East Asia. Ichthyol. Res. 2007, 54, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dettaï, A.; Cruaud, C.; Couloux, A.; Desoutter-Meniger, M.; Lecointre, G. RNF213, a new nuclear marker for acanthomorph phylogeny. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 50, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly-Engel, T.S.; Randall, J.E.; Bowen, B.W. Is the Great Barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) a reef fish or a pelagic fish? The phylogeographic perspective. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Milana, V.; Ciampoli, M.; Sola, L. mtDNA sequences of Sphyraena viridensis (Perciformes: Sphyraenidae) from Italy: Insights into historical events and the phylogeny of the genus. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 113, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakra, W.S.; Verma, M.S.; Goswami, M.; Lal, K.K.; Mohindra, V.; Punia, P.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Singh, K.V.; Ward, R.D.; Hebert, P. DNA barcoding Indian marine fishes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigt, L.A.; Baldwin, C.C.; Driskell, A.; Smith, D.G.; Ormos, A.; Reyier, E.A. Using DNA barcoding to assess Caribbean reef fish biodiversity: Expanding taxonomic and geographic coverage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, M.; Dimech, M.; Arculeo, M.; Biondo, G.; Martins, R.; Carneiro, M.; Carvalho, G.R.; Lo Brutto, S.; Costa, F.O. DNA barcoding for species assignment: The case of Mediterranean marine fishes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariche, M.; Torres, M.; Smith, C.; Sayar, N.; Azzurro, E.; Baker, R.; Bernardi, G. Red Sea fishes in the Mediterranean Sea: A preliminary investigation of a biological invasion using DNA barcoding. J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzi, A.; Martinsohn, J.T. FishTrace: A genetic catalogue of European fishes. Database 2017, 2017, ax075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, P.T.; Huang, W.C.; Chou, T.K.; Van Quan, N.; Van Chien, P.; Li, F.; Shao, K.T.; Liao, T.Y. DNA barcoding of coastal ray-finned fishes in Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, Z.; Curd, E.E.; Goodwin, K.D.; Choi, E.S.; Frable, B.W.; Thompson, A.R.; Walker, H.J., Jr.; Burton, R.S.; Kacev, D.; Martz, L.D.; et al. Improving metabarcoding taxonomic assignment: A case study of fishes in a large marine ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2546–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal Abidin, D.H.; Mohd Nor, S.A.; Lavoué, S.; Rahim, M.A.; Jamaludin, N.A.; Mohammed Akib, N.A. DNA-based taxonomy of a mangrove-associated community of fishes in Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemis, K.E.; Girard, M.G.; Santos, M.D.; Carpenter, K.E.; Deeds, J.R.; Pitassy, D.E.; Flores, N.A.L.; Hunter, E.S.; Driskell, A.C.; Macdonald, K.S., 3rd; et al. Biodiversity of Philippine marine fishes: A DNA barcode reference library based on voucher specimens. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeros, V.J.; Pedraza-Marrón, C.D.R.; Betancourt-Resendes, I.; Calderón-Cortés, N.; Betancur, R.R.; Domínguez-Domínguez, O. Genome-wide species delimitation analyses of a silverside fish species complex in central Mexico indicate taxonomic over-splitting. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2022, 22, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Friedman, M.; Satoh, T.P.; Takeshima, H.; Sado, T.; Iwasaki, W.; Yamanoue, Y.; Nakatani, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Inoue, J.G.; et al. Evolutionary origin of the Scombridae (tunas and mackerels): Members of a paleogene adaptive radiation with 14 other pelagic fish families. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Cheng, Q.; Pang, J.; Zhang, H. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Sphyraena jello (Perciformes: Sphyraenidae) and its phylogenetic position. Mitochondrial DNA Part A–DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 4570–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, N.; Park, W.; Baek, H.J.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, H.-W. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of brown barracuda, Sphyraena pinguis (Perciformes: Sphyraenidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B–Resour. 2020, 5, 3042–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relini, M.; Relini, L.O. The two species of barracuda (Sphyraenidae) in the western Mediterranean. Cybium 1997, 21, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Vaniz, W.F.; Collette, B.B.; Luckhurst, B.E. Fishes of Bermuda: History, Zoogeography, Annotated Checklist, and Identification Keys; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1999; Volume 4, pp. i–x + 1–424, Pls. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A Mitochondrial Genome Database of Fish with an Accurate and Automatic Annotation Pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE6: New tools for microbial genomics, phylogenetics and molecular evolution. J. Hered. 2017, 108, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D.; Canbäck, B. ARWEN: A program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2007, 24, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vences, M.; Miralles, A.; Brouillet, S.; Ducasse, J.; Fedosov, A.; Kharchev, V.; Kostadinov, I.; Kumari, S.; Patmanidis, S.; Scherz, M.D. iTaxoTools 0.1: Kickstarting a specimen-based software toolkit for taxonomists. Megataxa 2021, 6, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Peng, X.; Ai, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, S. The complete mitochondrial genome of Polydactylus sextarius (Teleostei, Mugiliformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part A–DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 3344–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Schwartz, T.; Pickett, B.E.; He, S.; Klem, E.B.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Passarotti, M.; Kaufman, S.; O’Leary, M.A. A RESTful API for Access to Phylogenetic Tools via the CIPRES Science Gateway. Evol. Bioinform. 2015, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Binarao, J.D.; De Alwis, P.S.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Andriyono, S.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Kim, H.-W. First Mitogenome of Endangered Enteromius thysi (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) from Africa: Characterization and Phylogeny. Fishes 2023, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, P.S.; Kundu, S.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Amin, M.H.F.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, A.R. Mitochondriomics of Clarias Fishes (Siluriformes: Clariidae) with a New Assembly of Clarias camerunensis: Insights into the Genetic Characterization and Diversification. Life 2023, 13, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Tong, J. Evolutionary analysis of cyprinid mitochondrial genomes: Remarkable variation and strong adaptive evolution. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Quirós, J.L.; Hernández-Muñoz, S.; Baeza, J.A. The complete mitochondrial genome of the roosterfish Nematistius pectoralis Gill 1862: Purifying selection in protein coding genes, organization of the control region, and insights into family-level phylogenomic relationships in the recently erected order Carangiformes. Gene 2022, 845, 146847. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, N.S.; Hirabayashi, N.; Agmon, I.; Yonath, A.; Suzuki, T. Comprehensive genetic selection revealed essential bases in the peptidyl-transferase center. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15386–15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Palimirmo, F.S.; Kang, H.-E.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Song, S.H.; Kim, H.-W. Insights into the Mitochondrial Genetic Makeup and Miocene Colonization of Primitive Flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes: Psettodidae) in the East Atlantic and Indo-West Pacific Ocean. Biology 2023, 12, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.P.; Miya, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Nishida, M. Structure and variation of the mitochondrial genome of fishes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Kumar, V.; Tyagi, K.; Chandra, K. The complete mitochondrial genome of the endangered Assam Roofed Turtle, Pangshura sylhetensis (Testudines: Geoemydidae): Genomic features and phylogeny. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; De Alwis, P.S.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Kang, H.-E.; Go, Y.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Wibowo, A.; Kim, H.-W. Mitogenomic Characterization of Cameroonian Endemic Coptodon camerunensis (Cichliformes: Cichlidae) and Matrilineal Phylogeny of Old-World Cichlids. Genes 2023, 14, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, F.; Carnevale, G.; Sorenson, L. First timetree of Sphyraenidae (Percomorpha) reveals a Middle Eocene crown age and an Oligo–Miocene radiation of barracudas. Ital. J. Zool. 2015, 82, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
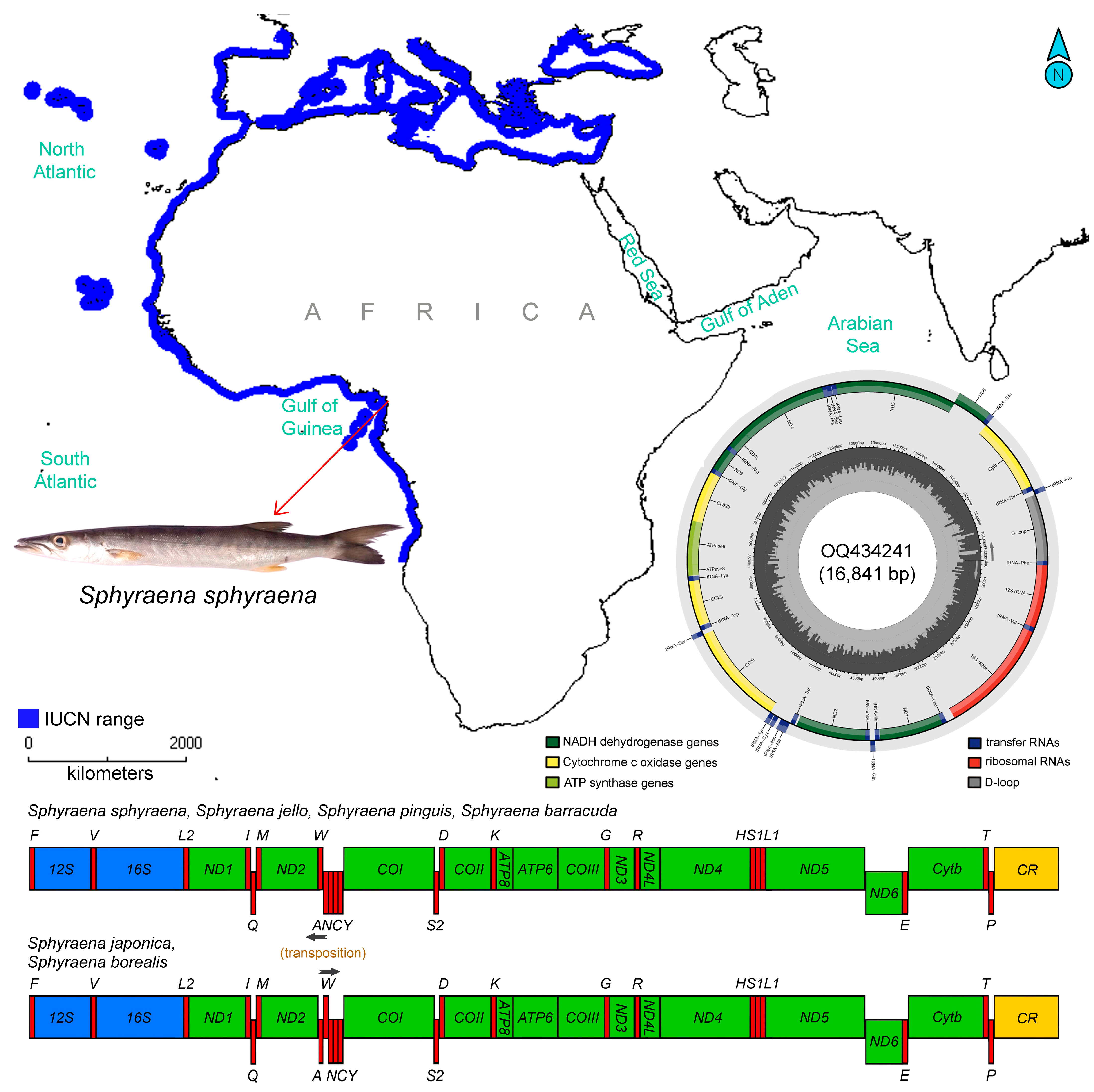
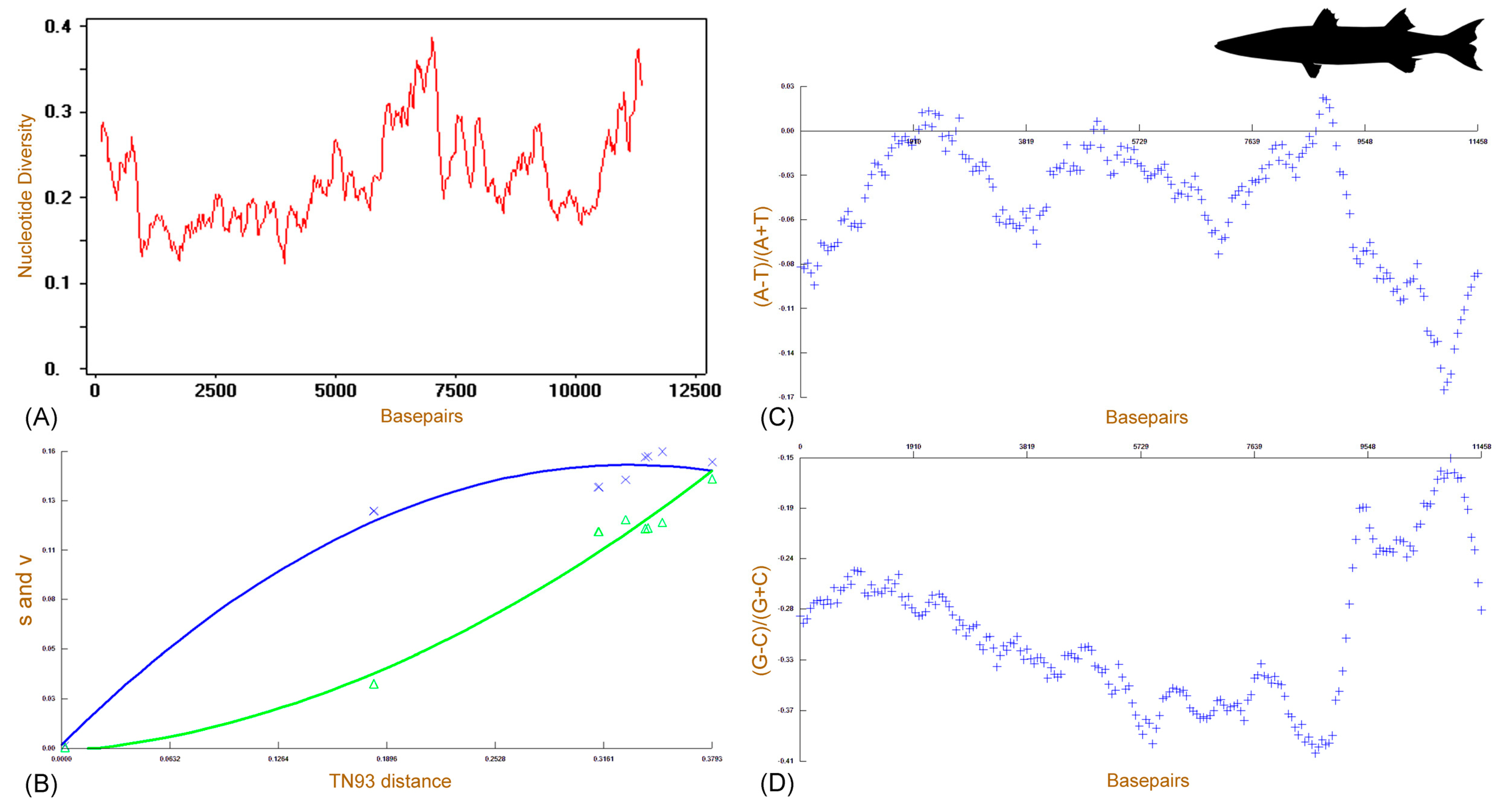
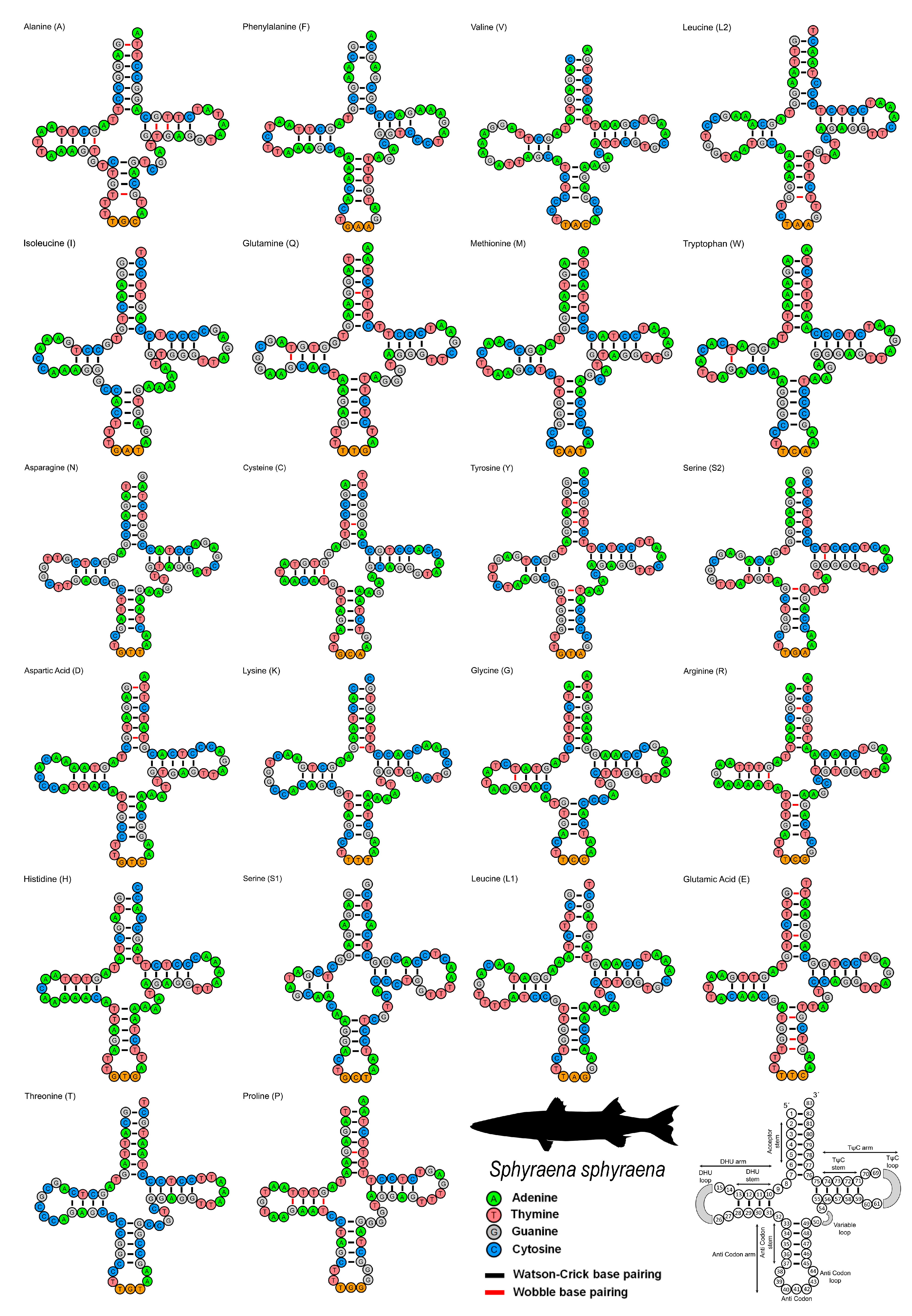

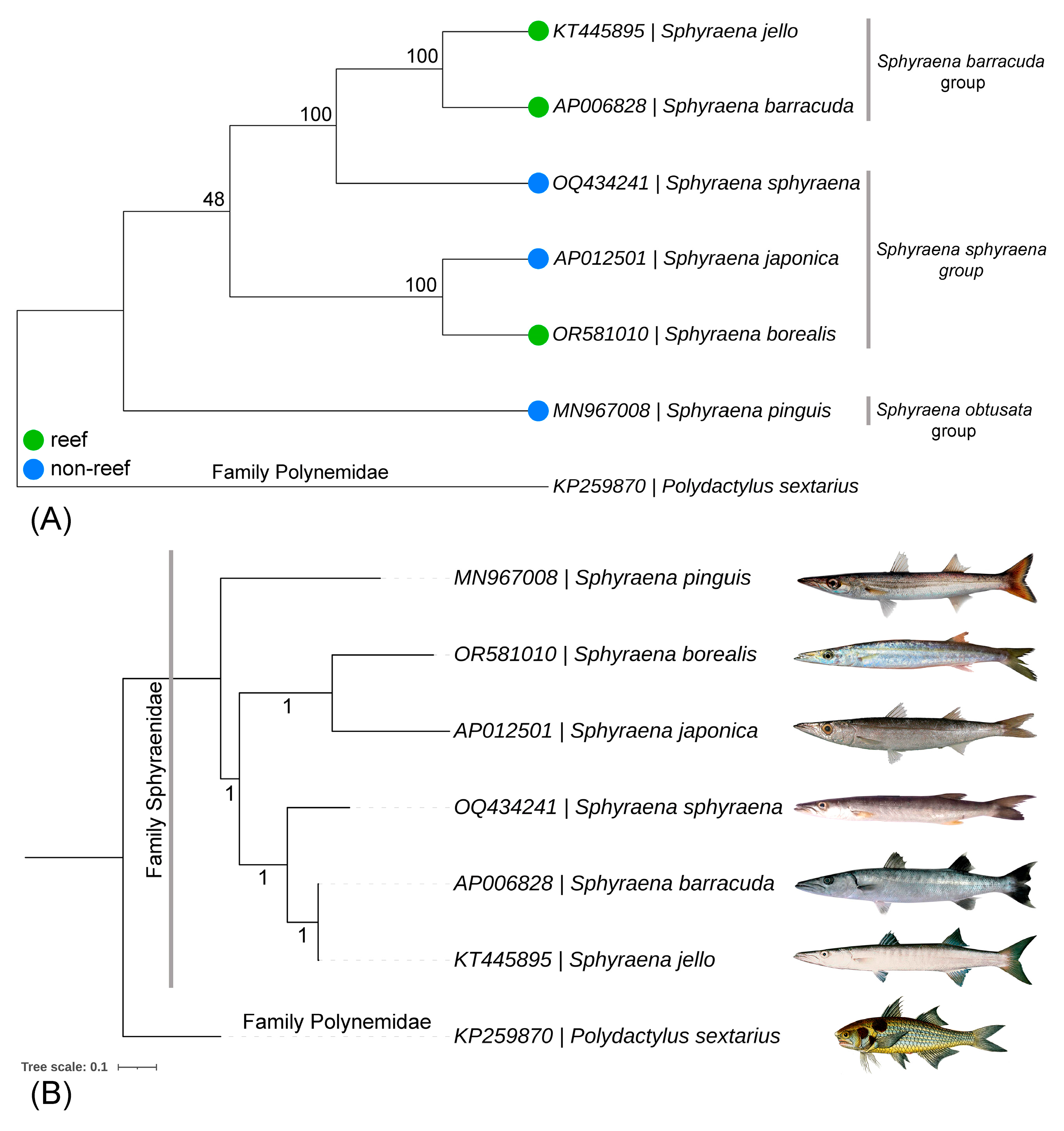
| Name | Start | End | Strand | Size (bp) | Intergenic Nucleotide | Anticodon | Start Codon | Stop Codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRNA-Phe (F) | 1 | 70 | H | 70 | 0 | AAG | ||
| 12S rRNA | 71 | 1035 | H | 965 | 0 | |||
| tRNA-Val (V) | 1036 | 1108 | H | 73 | 0 | CAU | ||
| 16S rRNA | 1109 | 2889 | H | 1781 | 127 | |||
| tRNA-Leu (L2) | 3017 | 3090 | H | 74 | 0 | AAU | ||
| ND1 | 3091 | 4065 | H | 975 | 5 | ATG | TAA | |
| tRNA-Ile (I) | 4071 | 4141 | H | 71 | −1 | UAG | ||
| tRNA-Gln (Q) | 4141 | 4211 | L | 71 | 8 | GUU | ||
| tRNA-Met (M) | 4220 | 4289 | H | 70 | 0 | UAC | ||
| ND2 | 4290 | 5351 | H | 1062 | 30 | ATG | TAA | |
| tRNA-Trp (W) | 5382 | 5452 | H | 71 | 3 | ACU | ||
| tRNA-Ala (A) | 5456 | 5524 | L | 69 | 1 | CGU | ||
| tRNA-Asn (N) | 5526 | 5598 | L | 73 | 47 | UUG | ||
| tRNA-Cys (C) | 5646 | 5712 | L | 67 | 12 | ACG | ||
| tRNA-Tyr (Y) | 5725 | 5794 | L | 70 | 1 | AUG | ||
| COI | 5796 | 7352 | H | 1557 | −5 | GTG | AGA | |
| tRNA-Ser (S2) | 7348 | 7418 | L | 71 | 3 | AGU | ||
| tRNA-Asp (D) | 7422 | 7493 | H | 72 | 10 | CUG | ||
| COII | 7504 | 8194 | H | 691 | 0 | ATG | T-- | |
| tRNA-Lys (K) | 8195 | 8268 | H | 74 | 8 | UUU | ||
| ATP8 | 8277 | 8444 | H | 168 | −10 | ATG | TAA | |
| ATP6 | 8435 | 9117 | H | 683 | 0 | TTG | TA- | |
| COIII | 9118 | 9902 | H | 785 | 0 | ATG | TA- | |
| tRNA-Gly (G) | 9903 | 9972 | H | 70 | 1 | CCU | ||
| ND3 | 9974 | 10,322 | H | 349 | 0 | ATG | T-- | |
| tRNA-Arg (R) | 10,323 | 10,391 | H | 69 | 0 | GCU | ||
| ND4L | 10,392 | 10,688 | H | 297 | −7 | ATG | TAA | |
| ND4 | 10,682 | 12,062 | H | 1381 | 0 | ATG | T-- | |
| tRNA-His (H) | 12,063 | 12,131 | H | 69 | 0 | GUG | ||
| tRNA-Ser (S1) | 12,132 | 12,199 | H | 68 | 5 | UCG | ||
| tRNA-Leu (L1) | 12,205 | 12,278 | H | 74 | 0 | GAU | ||
| ND5 | 12,279 | 14,117 | H | 1839 | −4 | ATG | TAA | |
| ND6 | 14,114 | 14,635 | L | 522 | 0 | ATG | TAA | |
| tRNA-Glu (E) | 14,636 | 14,704 | L | 69 | 3 | CUU | ||
| Cyt b | 14,708 | 15,848 | H | 1141 | 0 | ATG | T-- | |
| tRNA-Thr (T) | 15,849 | 15,921 | H | 73 | −1 | UGU | ||
| tRNA-Pro (P) | 15,921 | 15,991 | L | 71 | 0 | GGU | ||
| D-loop | 15,992 | 16,841 | H | 850 |
| Species Name | Size (bp) | A% | T% | G% | C% | A + T% | AT-Skew | GC-Skew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete mitogenome | ||||||||
| Sphyraena sphyraena | 16,841 | 28.63 | 26.43 | 16.29 | 28.65 | 55.06 | 0.040 | −0.275 |
| Sphyraena japonica | 16,760 | 25.99 | 27.42 | 18.74 | 27.85 | 53.41 | −0.027 | −0.196 |
| Sphyraena jello | 16,699 | 28.97 | 25.25 | 16.14 | 29.64 | 54.22 | 0.068 | −0.295 |
| Sphyraena pinguis | 16,620 | 26.03 | 26.35 | 18.80 | 28.81 | 52.38 | −0.006 | −0.210 |
| Sphyraena barracuda | 16,707 | 28.90 | 25.23 | 16.18 | 29.68 | 54.13 | 0.068 | −0.294 |
| Sphyraena borealis | 16,739 | 26.42 | 26.39 | 18.9 | 28.29 | 52.81 | 0.001 | −0.199 |
| PCGs | ||||||||
| Sphyraena sphyraena | 11,450 | 25.8 | 28.6 | 15.9 | 29.7 | 54.41 | −0.052 | −0.303 |
| Sphyraena japonica | 11,453 | 23.64 | 29.31 | 17.88 | 29.17 | 52.95 | −0.107 | −0.240 |
| Sphyraena jello | 11,445 | 26.67 | 27.12 | 15.38 | 30.83 | 53.79 | −0.008 | −0.334 |
| Sphyraena pinguis | 11,439 | 23.46 | 28.18 | 18.37 | 29.99 | 51.64 | −0.091 | −0.240 |
| Sphyraena barracuda | 11,444 | 26.64 | 27.13 | 15.38 | 30.85 | 53.77 | −0.009 | −0.335 |
| Sphyraena borealis | 11,443 | 23.65 | 28.29 | 18.65 | 29.42 | 51.94 | −0.089 | −0.224 |
| rRNAs | ||||||||
| Sphyraena sphyraena | 2746 | 31.32 | 22.61 | 20.9 | 25.16 | 53.93 | 0.161 | −0.092 |
| Sphyraena japonica | 2772 | 29.94 | 22.87 | 22.22 | 24.96 | 52.81 | 0.134 | −0.058 |
| Sphyraena jello | 2696 | 31.49 | 22.07 | 20.73 | 25.7 | 53.56 | 0.176 | −0.107 |
| Sphyraena pinguis | 2699 | 30.57 | 22.23 | 21.9 | 25.31 | 52.80 | 0.158 | −0.072 |
| Sphyraena barracuda | 2696 | 31.45 | 22 | 20.77 | 25.78 | 53.45 | 0.177 | −0.108 |
| Sphyraena borealis | 2772 | 30.56 | 22.22 | 22.29 | 24.93 | 52.78 | 0.158 | −0.056 |
| tRNAs | ||||||||
| Sphyraena sphyraena | 1559 | 28.48 | 27.13 | 23.16 | 21.23 | 55.61 | 0.024 | 0.043 |
| Sphyraena japonica | 1561 | 28.12 | 27.99 | 23.96 | 19.92 | 56.11 | 0.002 | 0.092 |
| Sphyraena jello | 1562 | 27.98 | 27.14 | 23.88 | 21.00 | 55.12 | 0.015 | 0.064 |
| Sphyraena pinguis | 1552 | 27.06 | 26.29 | 24.48 | 22.16 | 53.35 | 0.014 | 0.050 |
| Sphyraena barracuda | 1559 | 28.03 | 27.26 | 23.93 | 20.78 | 55.29 | 0.014 | 0.070 |
| Sphyraena borealis | 1551 | 27.92 | 27.08 | 24.24 | 20.76 | 55.00 | 0.015 | 0.077 |
| CRs | ||||||||
| Sphyraena sphyraena | 850 | 36.71 | 27.06 | 12.82 | 23.41 | 63.77 | 0.151 | −0.292 |
| Sphyraena japonica | 859 | 28.21 | 30.42 | 17.6 | 23.78 | 58.63 | −0.038 | −0.149 |
| Sphyraena jello | 799 | 31.79 | 28.79 | 18.15 | 21.28 | 60.58 | 0.050 | −0.079 |
| Sphyraena pinguis | 832 | 29.69 | 29.45 | 16.71 | 24.16 | 59.14 | 0.004 | −0.182 |
| Sphyraena barracuda | 809 | 30.41 | 28.68 | 19.28 | 21.63 | 59.09 | 0.029 | −0.057 |
| Sphyraena borealis | 839 | 32.54 | 29.2 | 16.33 | 21.93 | 61.74 | 0.054 | −0.146 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kundu, S.; Kim, H.-W.; Lee, J.; Chung, S.; Lee, S.R.; Gietbong, F.Z.; Wibowo, A.; Kang, K. Mitogenomic Architecture and Phylogenetic Relationship of European Barracuda, Sphyraena sphyraena (Teleostei: Sphyraenidae) from the Atlantic Ocean. Fishes 2023, 8, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120573
Kundu S, Kim H-W, Lee J, Chung S, Lee SR, Gietbong FZ, Wibowo A, Kang K. Mitogenomic Architecture and Phylogenetic Relationship of European Barracuda, Sphyraena sphyraena (Teleostei: Sphyraenidae) from the Atlantic Ocean. Fishes. 2023; 8(12):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120573
Chicago/Turabian StyleKundu, Shantanu, Hyun-Woo Kim, Jaebong Lee, Sangdeok Chung, Soo Rin Lee, Fantong Zealous Gietbong, Arif Wibowo, and Kyoungmi Kang. 2023. "Mitogenomic Architecture and Phylogenetic Relationship of European Barracuda, Sphyraena sphyraena (Teleostei: Sphyraenidae) from the Atlantic Ocean" Fishes 8, no. 12: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120573
APA StyleKundu, S., Kim, H.-W., Lee, J., Chung, S., Lee, S. R., Gietbong, F. Z., Wibowo, A., & Kang, K. (2023). Mitogenomic Architecture and Phylogenetic Relationship of European Barracuda, Sphyraena sphyraena (Teleostei: Sphyraenidae) from the Atlantic Ocean. Fishes, 8(12), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8120573









