No Sex-Specific Effects of Artificial Selection for Relative Telencephalon Size during Detour Learning and Spatial Discrimination in Guppies (Poecilia reticulata)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Guppy Telencephalon Size Selection Lines
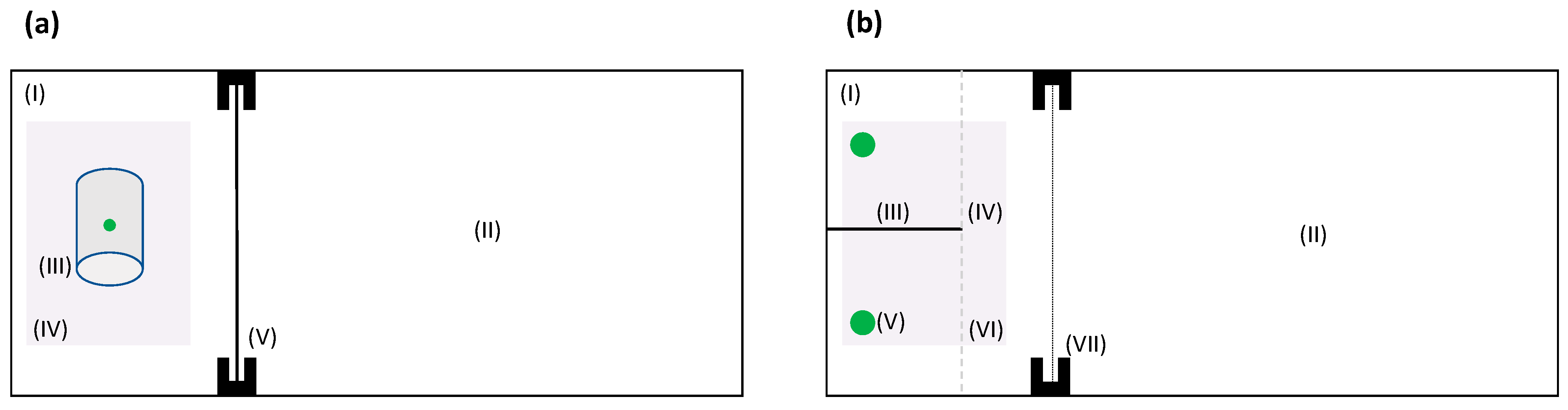
2.2. Detour Learning Test
2.3. Binary Spatial Discrimination Test
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Detour Learning
2.4.2. Spatial Discrimination
3. Results
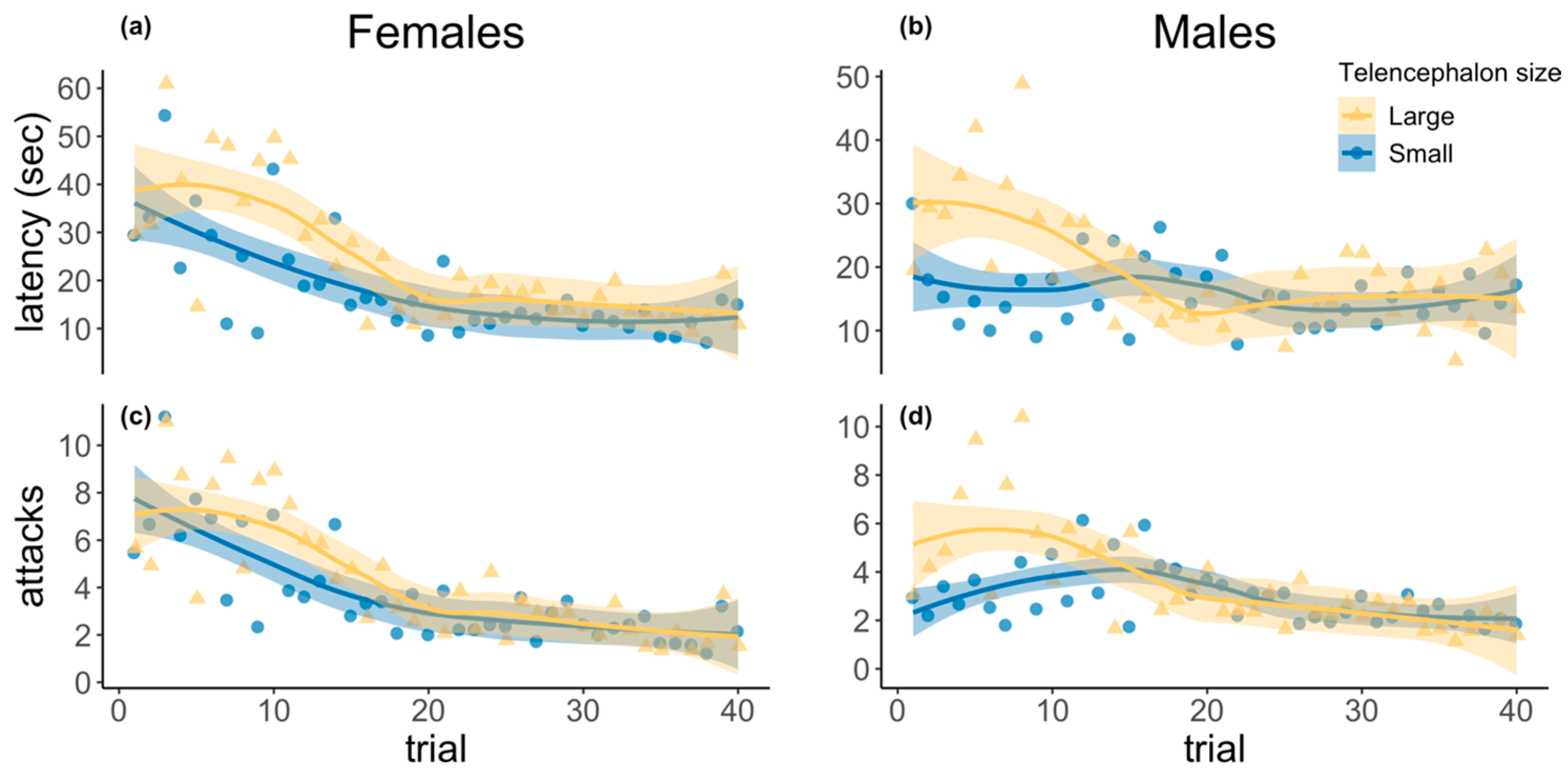
3.1. Detour Learning Assay
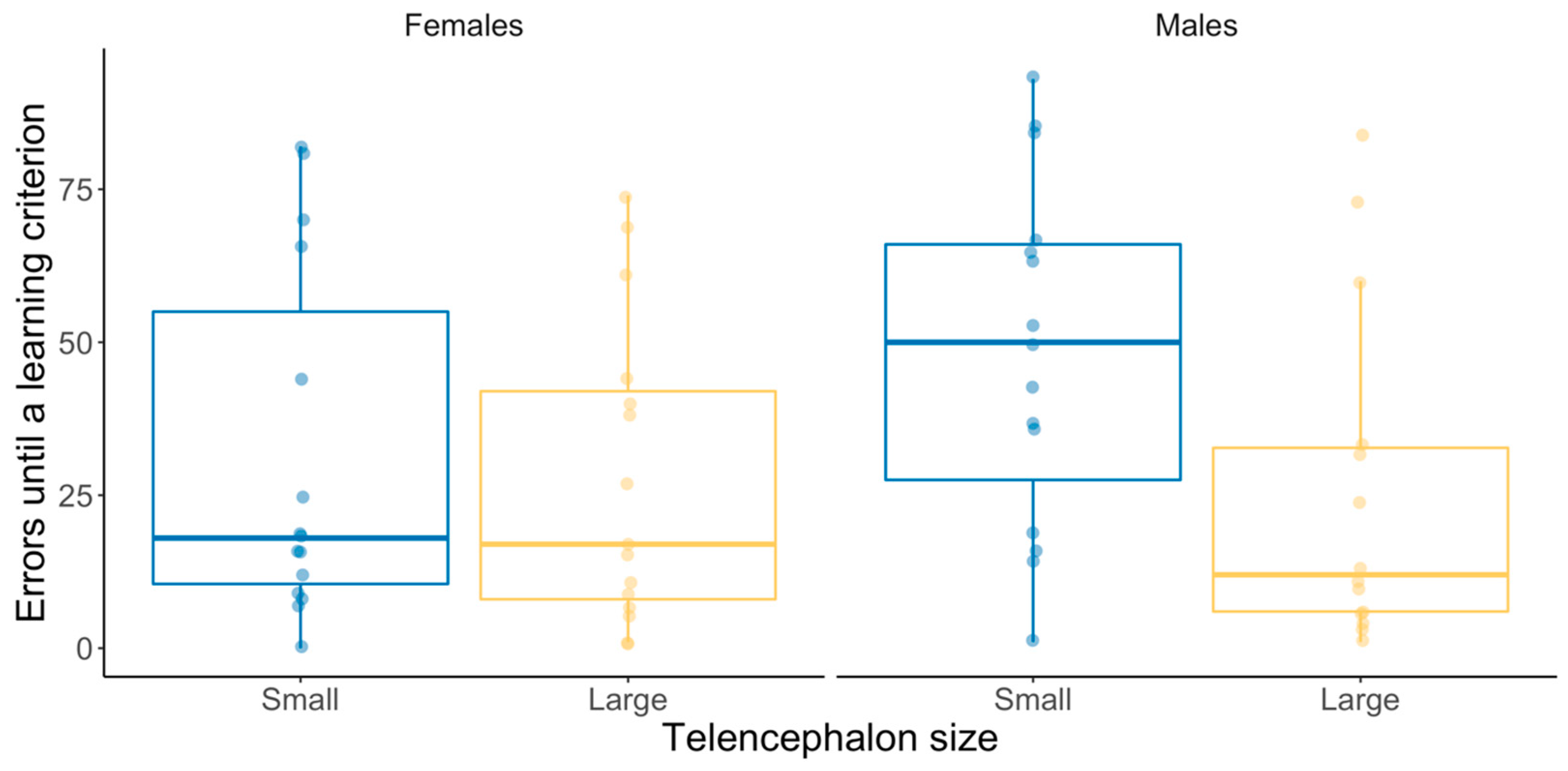
3.2. Binary Spatial Discrimination Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, C.; Laland, J.; Karuse, J. Fish Cognition and Behavior; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bshary, R.; Brown, C. Fish Cognition. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R947–R950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bshary, R.; Gingins, S.; Vail, A.L. Social cognition in fishes. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2014, 18, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bshary, R.; Wickler, W.; Fricke, H. Fish cognition: A primate´s eye view. Anim. Cogn. 2002, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouca, C.V.; Brown, C. Contemporary topics in fish cognition and behaviour. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 16, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salena, M.G.; Turko, A.J.; Singh, A.; Pathak, A.; Hughes, E.; Brown, C.; Balshine, S. Understanding fish cognition: A review and appraisal of current practices. Anim. Cogn. 2021, 24, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbia, P.S.; Brown, C. Seasonal variation of sexually dimorphic spatial learning implicates mating systems in the intertidal Cocos frillgoby (Bathygobius cocosensis). Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M. Sexual conflict and dimorphic cognition—Reviewing their relationship in poecilid fishes. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018, 72, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Voyer, A.; Kolm, N. Sex, ecology and the brain: Evolutionary correlates of brain structure volumes in tanganyikan cichlids. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrschal, A.; Buechel, S.D.; Zala, S.M.; Corral-Lopez, A.; Penn, D.J.; Kolm, N. Brain size affects female but not male survival under predation threat. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T. The contribution of executive functions to sex differences in animal cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 138, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollen, A.A.; Dobberfuhl, A.P.; Scace, J.; Igulu, M.M.; Renn, S.C.P.; Shumway, C.A.; Hofmann, H.A. Environmental complexity and social organization sculpt the brain in lake Tanganyikan cichlid fish. Brain Behav. Evol. 2007, 70, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, C.; Broglio, C.; Rodríguez, F. Evolution of forebrain and spatial cognition in vertebrates: Conservation across diversity. Brain Behav. Evol. 2003, 62, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triki, Z.; Emery, Y.; Teles, M.C.; Oliveira, R.F.; Bshary, R. Brain morphology predicts social intelligence in wild cleaner fish. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bijl, W.; Kolm, N. Why direct effects of predation complicate the social brain hypothesis: And how incorporation of explicit proximate behavioral mechanisms might help. BioEssays 2016, 38, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.S.; Andrade, R.; Carneiro, L.A.; Goncalves, E.J.; Kotrschal, K.; Oliveira, R.F. Sex differences in the dorsolateral telencephalon correlate with home range size in blenniid fish. Brain Behav. Evol. 2011, 77, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, L.F. Sexual selection and the brain. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrschal, A.; Räsänen, K.; Kristjánsson, B.K.; Senn, M.; Kolm, N. Extreme sexual dimorphism in sticklebacks: A consequence of the cognitive challenges of sex and parenting? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechel, S.D.; Booksmythe, I.; Kotrschal, A.; Jennions, M.D.; Kolm, N. Artificial selection on male genitalia length alters female brain size. Proc. R. Soc. B 2016, 283, 20161796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglio, C.; Rodríguez Salas, C. Spatial cognition and its neural basis in teleost fish. Fish Fish. 2003, 4, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglio, C.; Gómez, A.; Durán, E.; Ocana, F.M.; Jiménez-Moya, F.; Rodríguez, F.; Salas, C. Hallmarks of a common forebrain vertebrate plan: Specialized pallial areas for spatial, temporal and emotional memory in actinopterygian fish. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 66, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portavella, M.; Vargas, J.P.; Torres, B.; Salas, C. The effects of telencephalic pallial lesions on spatial, temporal, and emotional learning in goldfish. Brain Res. Bull. 2002, 57, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, G.E.; Brown, C. Microhabitat use affects brain size and structure in intertidal gobies. Brain Behav. Evol. 2015, 85, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triki, Z.; Fong, S.; Amcoff, M.; Kolm, N. Artificial mosaic evolution of relative telencephalon size improves inhibitory control abilities in the guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Evolution 2021, 76, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triki, Z.; Granell-Ruiz, M.; Fong, S.; Amcoff, M.; Kolm, N. Brain morphology correlates of learning and cognitive flexibility in a fish species (Poecilia reticulata). Pro. R. Soc. B 2022, 289, 20220844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triki, Z.; Fong, S.; Amcoff, M.; Vásquez-Nilsson, S.; Kolm, N. Experimental expansion of relative telencephalon size improves the main executive function abilities in guppy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 2, pgad2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.G.; Rodd, F.H. Hastiness, brain size and predation regime affect the performance of wild guppies in a spatial memory task. Animal Behav. 2008, 76, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bisazza, A. Discrimination reversal learning reveals greater female behavioural flexibility in guppies. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bisazza, A. Sex differences in spatial abilities and cognitive flexibility in the guppy. Anim. Behav. 2017, 123, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bisazza, A.; Bertolucci, C. Guppies show sex and individual differences in the ability to inhibit behaviour. Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Montalbano, G.; Bertolucci, C. Male and female guppies differ in problem-solving abilities. Curr. Zool. 2020, 66, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, S.; Rogell, B.; Amcoff, M.; Kotrschal, A.; van der Bijl, W.; Buechel, S.D.; Kolm, N. Rapid brain evolution under artificial selection for relative telencephalon size in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houde, A. Sex, Color, and Mate Choice in Guppies, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997; Volume 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kotrschal, A.; Rogell, B.; Bundsen, A.; Svensson, B.; Zajitschek, S.; Brännström, I.; Immler, S.; Maklakov, A.A.; Kolm, N. Artificial selection on brain size in the guppy reveals costs and benefits of evolving a larger brain. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Bijl, W.; Thyselius, M.; Kotrschal, A.; Kolm, N. Brain size affects the behavioural resonse to predators in female guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Pro. R. Soc. B 2015, 282, 20151132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, G.E.; Brown, C. Variation in brain morphology of intertidal gobies: A comparison of methodologies used to quantitatively assess brain volumes in fish. Brain Behav. Evol. 2015, 85, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabadayi, C.; Bobrowicz, K.; Osvath, M. The detour paradigm in animal cognition. Anim. Cogn. 2018, 21, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Laland, K.N. Social learning in fishes: A review. Fish Fish. 2003, 4, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Horik, J.O.; Langley, E.J.G.; Whiteside, M.A.; Laker, P.R.; Beardsworth, C.E.; Madden, J.R. 2018 Do detour tasks provide accurate assays of inhibitory control? Pros. R. Soc. B 2016, 285, 20180150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, J.D.; Dias, R.; Robbins, T.W.; Roberts, A.C. Dissociable contributions of the orbitofrontal and lateral prefrontal cortex of the marmoset to performance on a detour reaching task. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisazza, A.; Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. The origins of cerebral asymmetry: A review of evidence of behavioural and brain lateralization in fishes, reptiles and amphibians. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1998, 22, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models, R Package Version 3.1-148. R Core Team. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme> (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker BWalker, S. lme4: Linear Mixed Effects Models Using Eigen and S4, v.1.1-7. 2014. Available online: http://lme4.r-forge.r-project.org (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Schielzeth, H.; Forstmeier, W. Conclusions beyond support: Overconfident estimates in mixed models. Behav. Ecol. 2009, 20, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.J.; Levy, R.; Scheepers, C.; Tily, H.J. Random effects structure for confirmatory hypothesis testing: Keep it maximal. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 68, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Buechel, S.D.; Boussard, A.; Kotrschal, A.; van der Bijl, W.; Kolm, N. Brain size affects performance in a reversal-learning test. Pro. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20172031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.M.; De Asis-Cruz, J.; Lopez, C.; Quistorff, J.; Kapse, K.; Andersen, N.; Vezina, G.; Limperopoulos, C. Robust sex differences in functional brain connectivity are present in utero. Cereb. Cortex 2023, 33, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacy, N.; McCauley, E.; Kutz, J.N.; Calhoun, V.D. Multilevel mapping of sexual dimorphism in intrinsic functional brain networks. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, M.; Vellema, M.; Gahr, C.; Leitao, A.; de Lima, S.M.A.; Geberzahn, N.; Gahr, M. Mismatch in sexual dimorphism of developing song and song control system in blue-capped cordon-bleus, a songbird species with singing females and males. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 3, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, U.; Roth, G. Neuronal factors determining high intelligence. Phil. Trans. R Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herculano-Houzel, S. Number of neurons as biological correlates of cognitive capability. Curr. Opin. 2017, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowicz, S.; Kocourek, M.; Lucan, R.K.; Portes, M.; Fitch, W.T.; Herculano-Houzel, S.; Nemec, P. Birds have primate-like numbers of neurons in the forebrain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7255–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Detour Learning Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latency (GLS) | χ2 | d.f. | p-Value | Estimate ± SE |
| (Intercept) | 410.40 | 1 | <0.001 | 2.34 (0.12) |
| Telencephalon size | 2.53 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.26 (0.16) |
| Trial | 40.44 | 1 | <0.001 | −2.26 (0.04) |
| Sex | 0.55 | 1 | 0.46 | −0.12 (0.16) |
| Telencephalon size × Trial | 0.16 | 1 | 0.69 | 0.02 (0.06) |
| Telencephalon size × Sex | 0.20 | 1 | 0.65 | −0.10 (0.23) |
| Trial × Sex | 27.32 | 1 | <0.001 | 0.30 (0.06) |
| Telencephalon size × Trial × Sex | 1.66 | 1 | 0.20 | −0.71 (0.08) |
| Number of attacks (GLMM) | ||||
| (Intercept) | 179.08 | 1 | <0.001 | 1.15 (0.09) |
| Telencephalon size | 1.15 | 1 | 0.28 | 0.13 (0.12) |
| Trial | 55.23 | 1 | <0.001 | −0.42 (0.06) |
| Sex | 0.82 | 1 | 0.36 | −0.11 (0.12) |
| Telencephalon size × Trial | 0.38 | 1 | 0.54 | −0.05 (0.08) |
| Telencephalon size × Sex | 0.11 | 1 | 0.74 | −0.06 (0.17) |
| Trial × Sex | 11.95 | 1 | <0.001 | 0.28 (0.08) |
| Telencephalon size × Trial × Sex | 1.96 | 1 | 0.16 | −0.16 (0.11) |
| Binary spatial discrimination test | ||||
| Proportion correct vs. error (GLMM) | ||||
| (Intercept) | 0.21 | 1 | 0.65 | −0.09 (0.20) |
| Telencephalon size | 0.13 | 1 | 0.72 | 0.10 (0.29) |
| Sex | 3.17 | 1 | 0.08 | −0.51 (0.28) |
| Telencephalon size × Sex | 2.03 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.59 (0.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boussard, A.; Edlund, S.; Fong, S.; Wheatcroft, D.; Kolm, N. No Sex-Specific Effects of Artificial Selection for Relative Telencephalon Size during Detour Learning and Spatial Discrimination in Guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Fishes 2023, 8, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110536
Boussard A, Edlund S, Fong S, Wheatcroft D, Kolm N. No Sex-Specific Effects of Artificial Selection for Relative Telencephalon Size during Detour Learning and Spatial Discrimination in Guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Fishes. 2023; 8(11):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110536
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoussard, Annika, Stephanie Edlund, Stephanie Fong, David Wheatcroft, and Niclas Kolm. 2023. "No Sex-Specific Effects of Artificial Selection for Relative Telencephalon Size during Detour Learning and Spatial Discrimination in Guppies (Poecilia reticulata)" Fishes 8, no. 11: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110536
APA StyleBoussard, A., Edlund, S., Fong, S., Wheatcroft, D., & Kolm, N. (2023). No Sex-Specific Effects of Artificial Selection for Relative Telencephalon Size during Detour Learning and Spatial Discrimination in Guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Fishes, 8(11), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110536




