Life-Long Experience with Male Mating Tactics Shapes Spatial Cognition and Coercion Evasion in Female Swordtails
Abstract
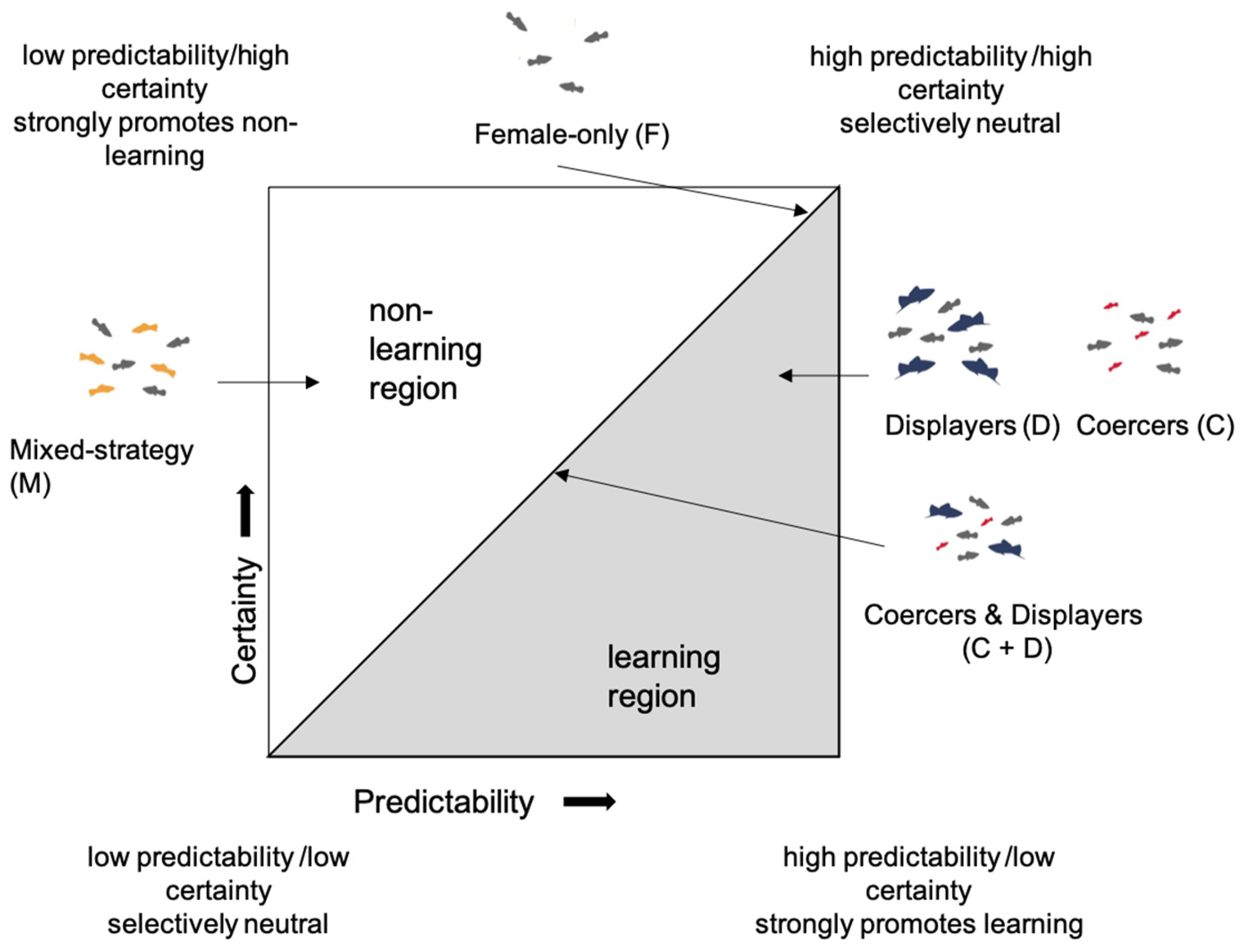
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
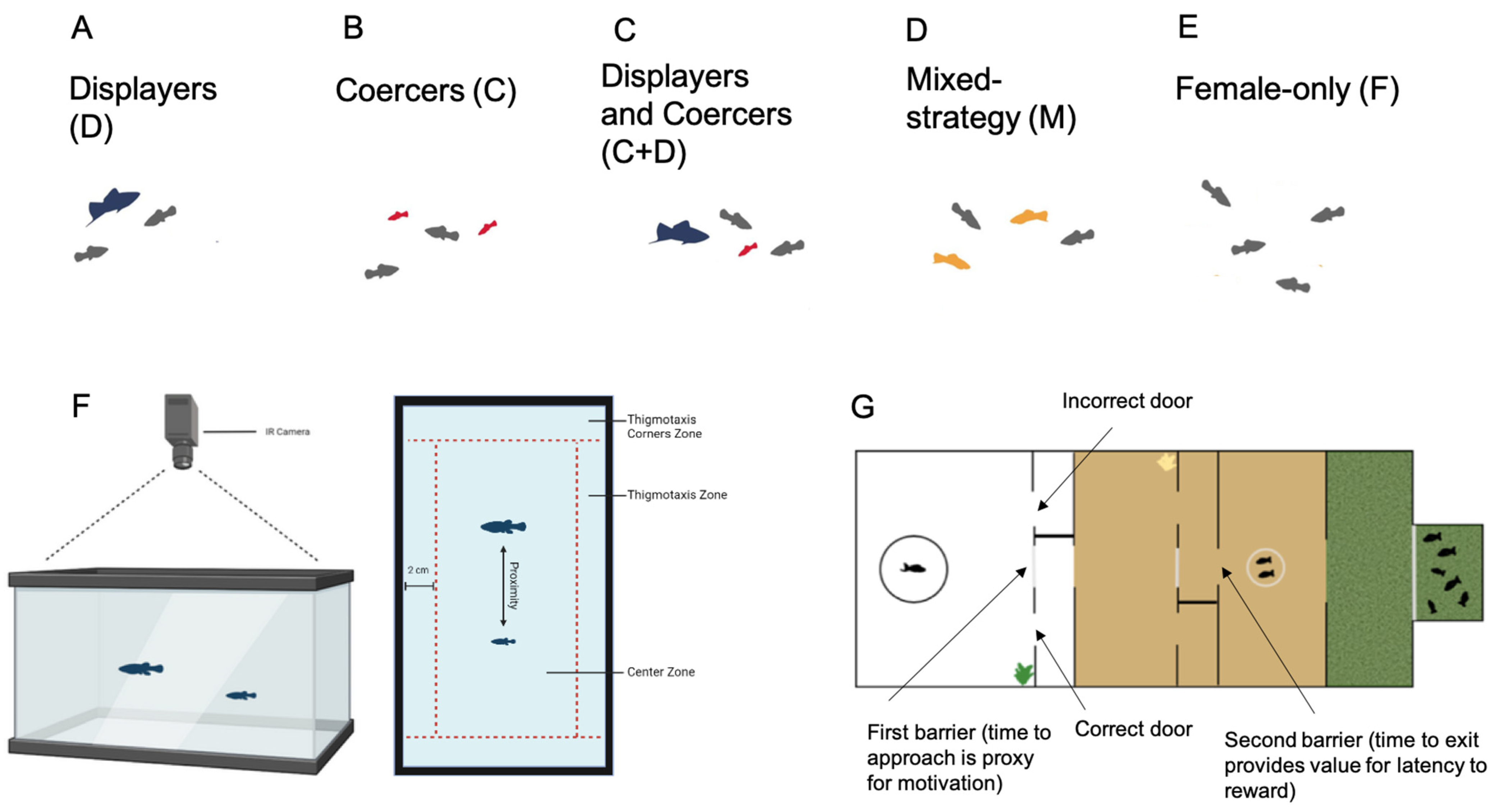
2.1. Social Rearing Environments
2.2. Schedule
2.3. Coercion Evasion
2.4. Route Learning
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
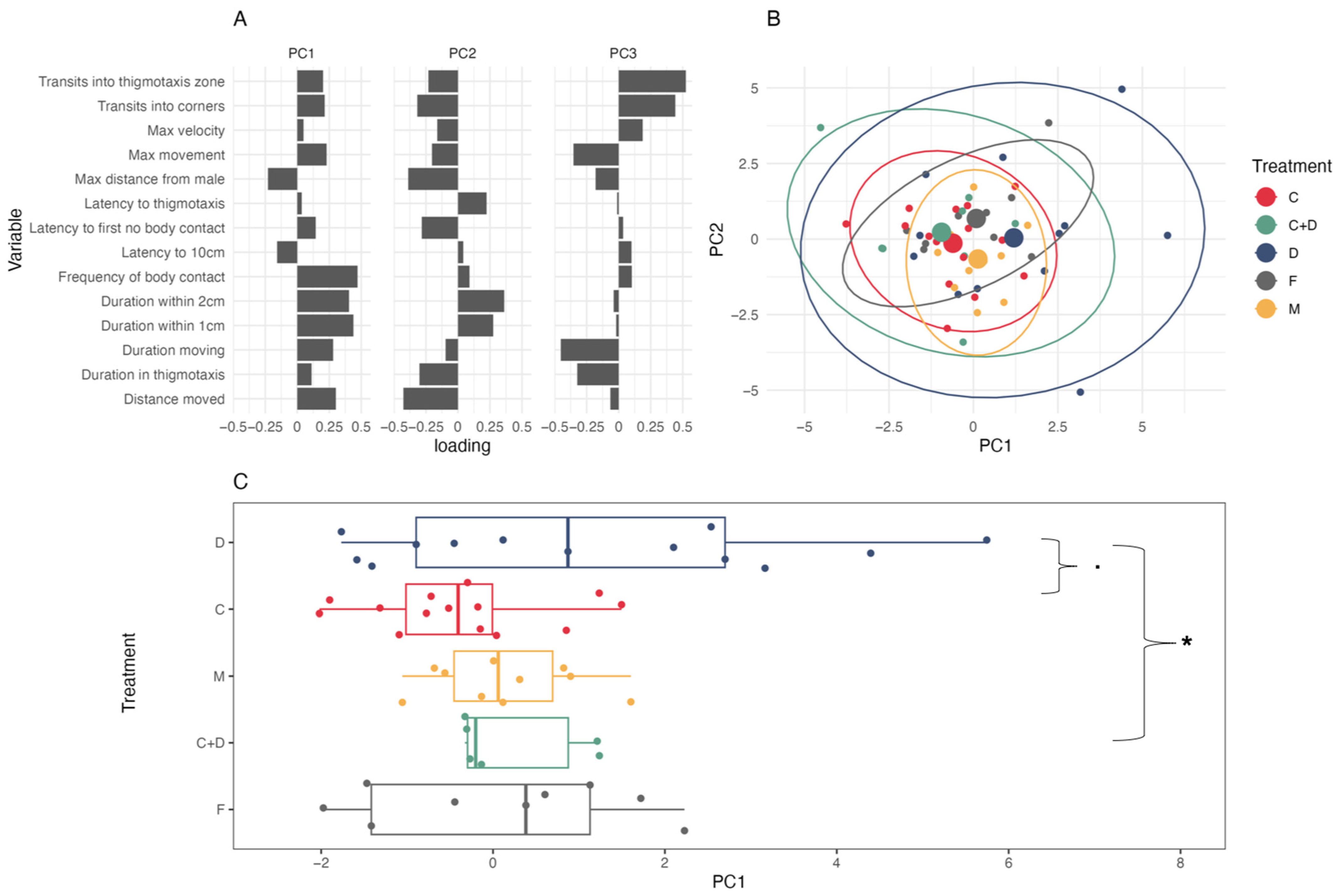
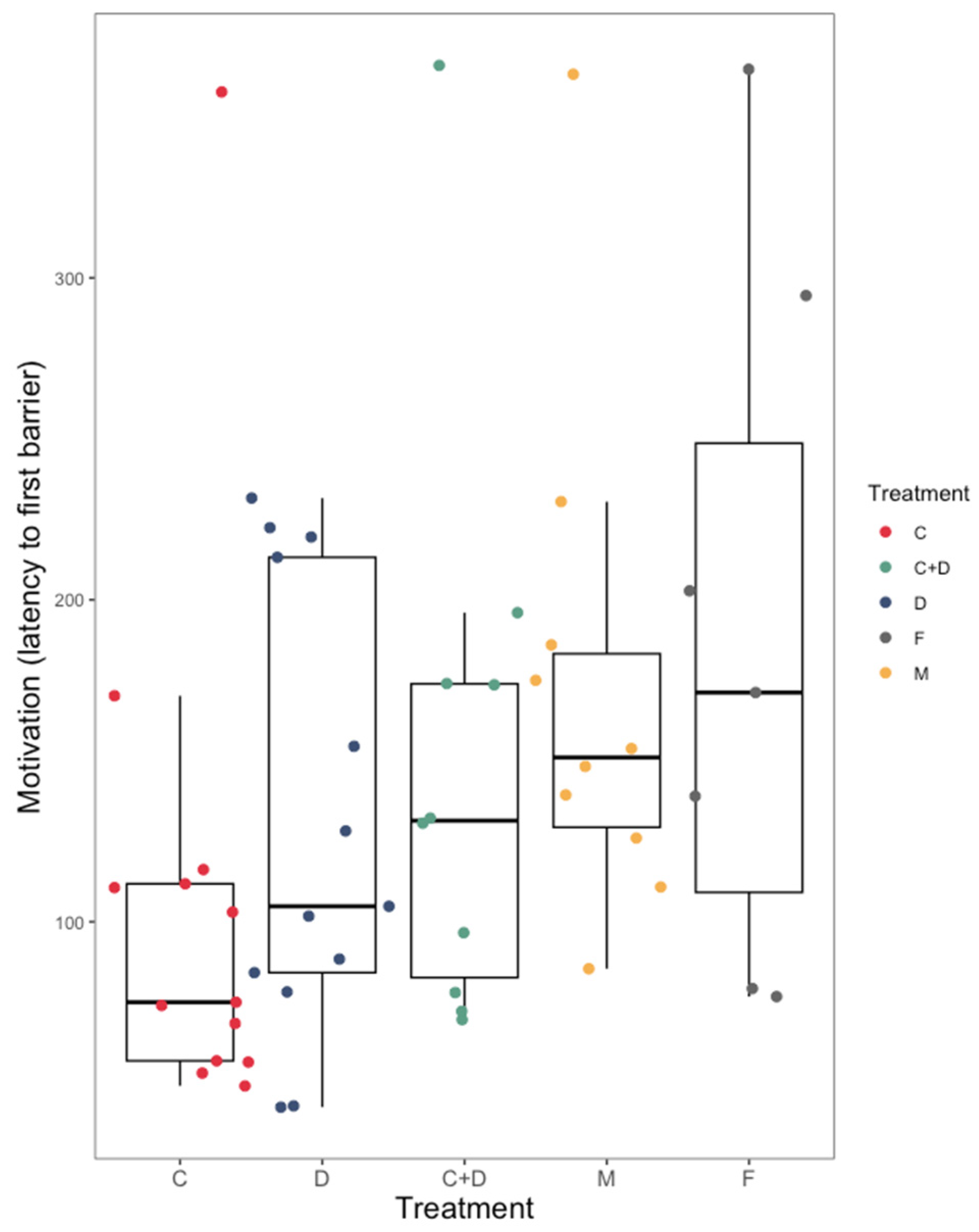
3.1. Coercion Evasion
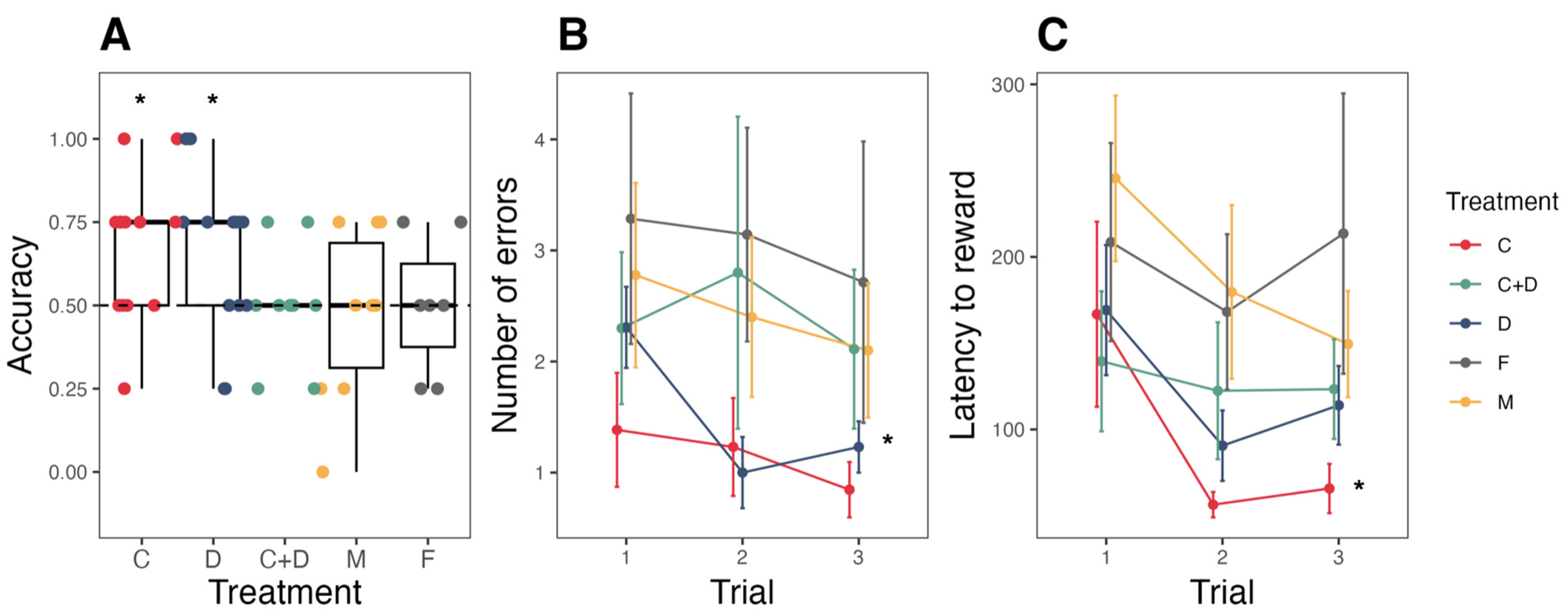
3.2. Route Learning
4. Discussion
4.1. Coercion Evasion
4.2. Spatial Cognition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dukas, R. Evolutionary Biology of Animal Cognition. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 347–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.W.; Bates, L.A. Sociality, Evolution and Cognition. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R714–R723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettleworth, S.J.; Hampton, R.R. 3-Adaptive Specializations of Spatial Cognition in Food-Storing Birds? Approaches to Testing a Comparative Hypothesis. In Animal Cognition in Nature; Balda, R.P., Pepperberg, I.M., Kamil, A.C., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1998; pp. 65–98. ISBN 978-0-12-077030-4. [Google Scholar]
- Healy, S.D.; de Kort, S.R.; Clayton, N.S. The Hippocampus, Spatial Memory and Food Hoarding: A Puzzle Revisited. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, D.F. Neuroecology. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2006, 57, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravosudov, V.V.; Roth, T.C., II. Cognitive Ecology of Food Hoarding: The Evolution of Spatial Memory and the Hippocampus. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2013, 44, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigueno, M.F.; Snow, D.A.; MacDougall-Shackleton, S.A.; Sherry, D.F. Female Cowbirds Have More Accurate Spatial Memory than Males. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, D.F.; Forbes, M.R.; Khurgel, M.; Ivy, G.O. Females Have a Larger Hippocampus than Males in the Brood-Parasitic Brown-Headed Cowbird. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7839–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Braithwaite, V.A. Effects of Predation Pressure on the Cognitive Ability of the Poeciliid Brachyraphis Episcopi. Behav. Ecol. 2005, 16, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila Pouca, C.; Mitchell, D.J.; Lefèvre, J.; Vega-Trejo, R.; Kotrschal, A. Early Predation Risk Shapes Adult Learning and Cognitive Flexibility. Oikos 2021, 130, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.G.; Rodd, F.H. Hastiness, Brain Size and Predation Regime Affect the Performance of Wild Guppies in a Spatial Memory Task. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiten, A.; Byrne, R.W. The Machiavellian Intelligence Hypotheses: Editorial. In Machiavellian Intelligence: Social Expertise and the Evolution of Intellect in Monkeys, Apes, and Humans; Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-0-19-852179-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bshary, R.; Wickler, W.; Fricke, H. Fish Cognition: A Primate’s Eye View. Anim. Cogn. 2002, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrberg, A.A.; Riggio, R.J. Acoustically Mediated Individual Recognition by a Coral Reef Fish (Pomacentrus partitus). Anim. Behav. 1985, 33, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinski, M. TIT FOR TAT in Sticklebacks and the Evolution of Cooperation. Nature 1987, 325, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugatkin, L.A. Do Guppies Play TIT FOR TAT during Predator Inspection Visits? Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1988, 23, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.; Sandmann, S.; Bakker, T.C.M.; Thünken, T. Impact of Social Rearing-Environment on Performance in a Complex Maze in Females of a Cichlid Fish. Behav. Processes 2019, 167, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Montalbano, G.; Reddon, A.R.; Bertolucci, C. Social Environment Affects Inhibitory Control via Developmental Plasticity in a Fish. Anim. Behav. 2022, 183, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello-Ramos, M.C.; Branch, C.L.; Kozlovsky, D.Y.; Pitera, A.M.; Pravosudov, V.V. Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility Trade-Offs: To Be or Not to Be Flexible, That Is the Question. Anim. Behav. 2019, 147, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, A.S.; Stephens, D.W. Components of Change in the Evolution of Learning and Unlearned Preference. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, A.S.; Stephens, D.W. Reliability, Uncertainty, and Costs in the Evolution of Animal Learning. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 12, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechtel, P.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Effects of Early Life Stress on Cognitive and Affective Function: An Integrated Review of Human Literature. Psychopharmacology 2011, 214, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugers, H.J.; Joëls, M. Long-Lasting Consequences of Early Life Stress on Brain Structure, Emotion and Cognition. In Behavioral Neurobiology of Stress-Related Disorders; Pariante, C.M., Lapiz-Bluhm, M.D., Eds.; Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; pp. 81–92. ISBN 978-3-662-45126-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pravosudov, V.V. Long-Term Moderate Elevation of Corticosterone Facilitates Avian Food-Caching Behaviour and Enhances Spatial Memory. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenes, J.C.; Lackinger, M.; Höglinger, G.U.; Schratt, G.; Schwarting, R.K.W.; Wöhr, M. Differential Effects of Social and Physical Environmental Enrichment on Brain Plasticity, Cognition, and Ultrasonic Communication in Rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1586–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, S.; Buechel, S.D.; Boussard, A.; Kotrschal, A.; Kolm, N. Plastic Changes in Brain Morphology in Relation to Learning and Environmental Enrichment in the Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb200402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocklington, R.; Dill, L.M. Predation on Females or Males: Who Pays for Bright Male Traits? Anim. Behav. 1995, 49, 1122–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilastro, A.; Benetton, S.; Bisazza, A. Female Aggregation and Male Competition Reduce Costs of Sexual Harassment in the Mosquitofish Gambusia Holbrooki. Anim. Behav. 2003, 65, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadda, M.; Pilastro, A.; Bisazza, A. Male Sexual Harassment and Female Schooling Behaviour in the Eastern Mosquitofish. Anim. Behav. 2005, 70, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, A.; Hildenbrand, P.; Schleucher, E.; Riesch, R.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Streit, B.; Plath, M. Effects of Male Sexual Harassment on Female Time Budgets, Feeding Behavior, and Metabolic Rates in a Tropical Livebearing Fish (Poecilia mexicana). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2011, 65, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, C.; Devigili, A.; Pilastro, A. Cross-Generational Effects of Sexual Harassment on Female Fitness in the Guppy. Evolution 2012, 66, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, S.K.; Croft, D.P. Male Harassment Drives Females to Alter Habitat Use and Leads to Segregation of the Sexes. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.J.; Causey, B.A. “Alternative” Mating Behavior in the Swordtails Xiphophorus nigrensis and Xiphophorus Pygmaeus (Pisces: Poeciliidae). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1989, 24, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, K.P.; Schmidt, C.; Fischer, P.; Volff, J.-N.; Hoffmann, C.; Muck, J.; Lohse, M.J.; Ryan, M.J.; Schartl, M. Determination of Onset of Sexual Maturation and Mating Behavior by Melanocortin Receptor 4 Polymorphisms. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.C.; Harris, R.M.; Lampert, K.P.; Schartl, M.; Hofmann, H.A.; Ryan, M.J. Copy Number Variation in the Melanocortin 4 Receptor Gene and Alternative Reproductive Tactics the Swordtail Xiphophorus Multilineatus. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.R.; Batra, P.; Ryan, M.J. Male-Male Competition and Access to Females in the Swordtail Xiphophorus nigrensis. Copeia 1992, 1992, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, G.G.; Flores Martinez, T.Y.; García de León, F.J.; Ryan, M.J. Shared Preferences by Predators and Females for Male Ornaments in Swordtails. Am. Nat. 2001, 158, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, M.; Mollaghan, D. Repeatability and Consistency of Female Preference Behaviours in a Northern Swordtail, Xiphophorus nigrensis. Anim. Behav. 2006, 72, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.E.; Ramsey, M.E. Mate Choice as Social Cognition: Predicting Female Behavioral and Neural Plasticity as a Function of Alternative Male Reproductive Tactics. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 6, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.E. Sexual Conflict and Sexually Dimorphic Cognition—Reviewing Their Relationship in Poeciliid Fishes. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018, 72, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queller, P.S.; Shirali, Y.; Wallace, K.J.; DeAngelis, R.S.; Yurt, V.; Reding, L.P.; Cummings, M.E. Complex Sexual-Social Environments Produce High Boldness and Low Aggression Behavioral Syndromes. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1050569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Bisazza, A. Sex Differences in Spatial Abilities and Cognitive Flexibility in the Guppy. Anim. Behav. 2017, 123, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, F.B.; Altschul, D. Data Reduction Analyses of Animal Behaviour: Avoiding Kaiser’s Criterion and Adopting More Robust Automated Methods. Anim. Behav. 2019, 149, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.Y.; So, P.; Cummings, M.E. How Female Size and Male Displays Influence Mate Preference in a Swordtail. Anim. Behav. 2011, 82, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Fiore, P. Early Social Experience Significantly Affects Sexual Behaviour in Male Guppies. Anim. Behav. 2012, 84, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborsky, B.; Arnold, C.; Junker, J.; Tschopp, A. The Early Social Environment Affects Social Competence in a Cooperative Breeder. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, C.; Fischer, S.; Aubin-Horth, N.; Taborsky, B. Effect of the Early Social Environment on Behavioural and Genomic Responses to a Social Challenge in a Cooperatively Breeding Vertebrate. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3186–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Bessert-Nettelbeck, M.; Kotrschal, A.; Taborsky, B. Rearing-Group Size Determines Social Competence and Brain Structure in a Cooperatively Breeding Cichlid. Am. Nat. 2015, 186, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesse, S.; Anaya-Rojas, J.M.; Frommen, J.G.; Thünken, T. Social Deprivation Affects Cooperative Predator Inspection in a Cichlid Fish. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 140451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliveira, R.F. Social Behavior in Context: Hormonal Modulation of Behavioral Plasticity and Social Competence. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2009, 49, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborsky, B.; Oliveira, R.F. Social Competence: An Evolutionary Approach. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, B.J.; Ridley, A.R.; Edwards, E.K.; Thornton, A. Cognitive Performance Is Linked to Group Size and Affects Fitness in Australian Magpies. Nature 2018, 554, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Ulrich, L.; Holekamp, K.E. Group Size and Social Rank Predict Inhibitory Control in Spotted Hyaenas. Anim. Behav. 2020, 160, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.B.; Ward, A.J.W.; Krause, J. Schooling and Learning: Early Social Environment Predicts Social Learning Ability in the Guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, M.L.; Braithwaite, V.A.; Gonçalves-de-Freitas, E. Isolation Impairs Cognition in a Social Fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2015, 171, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Montalbano, G.; Bertolucci, C. Adaptive Phenotypic Plasticity Induces Individual Variability along a Cognitive Trade-Off. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 290, 20230350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Del Giudice, M. Linking Behavioural Syndromes and Cognition: A Behavioural Ecology Perspective. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugatkin, L.A.; Alfieri, M.S. Boldness, Behavioral Inhibition and Learning. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2003, 15, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, I.M.; Jennions, M.D.; van Veen, E.; Fichtel, C.; Kappeler, P.M.; Fox, R.J. The Effect of Sex, Age and Boldness on Inhibitory Control. Anim. Behav. 2022, 193, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenjager, M.J.; Hoppitt, W.; Dugatkin, L.A. Personality Composition Determines Social Learning Pathways within Shoaling Fish. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.L.; Wagner, T.; Gowan, C.; Braithwaite, V.A. Can Personality Predict Individual Differences in Brook Trout Spatial Learning Ability? Behav. Processes 2017, 141, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Korte, S.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Van Der Vegt, B.J.; Van Reenen, C.G.; Hopster, H.; De Jong, I.C.; Ruis, M.A.W.; Blokhuis, H.J. Coping Styles in Animals: Current Status in Behavior and Stress-Physiology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1999, 23, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettke-Hofmann, C. Cognitive Ecology: Ecological Factors, Life-Styles, and Cognition. WIREs Cogn. Sci. 2014, 5, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Queller, P.S.; Adams, E.R.M.; Cummings, M.E. Life-Long Experience with Male Mating Tactics Shapes Spatial Cognition and Coercion Evasion in Female Swordtails. Fishes 2023, 8, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110562
Queller PS, Adams ERM, Cummings ME. Life-Long Experience with Male Mating Tactics Shapes Spatial Cognition and Coercion Evasion in Female Swordtails. Fishes. 2023; 8(11):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110562
Chicago/Turabian StyleQueller, Philip S., Elena R. M. Adams, and Molly E. Cummings. 2023. "Life-Long Experience with Male Mating Tactics Shapes Spatial Cognition and Coercion Evasion in Female Swordtails" Fishes 8, no. 11: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110562
APA StyleQueller, P. S., Adams, E. R. M., & Cummings, M. E. (2023). Life-Long Experience with Male Mating Tactics Shapes Spatial Cognition and Coercion Evasion in Female Swordtails. Fishes, 8(11), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8110562




