Detecting Japanese Eels (Anguilla japonica) and Revealing Their Distribution in Taiwanese Rivers by Environmental DNA Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
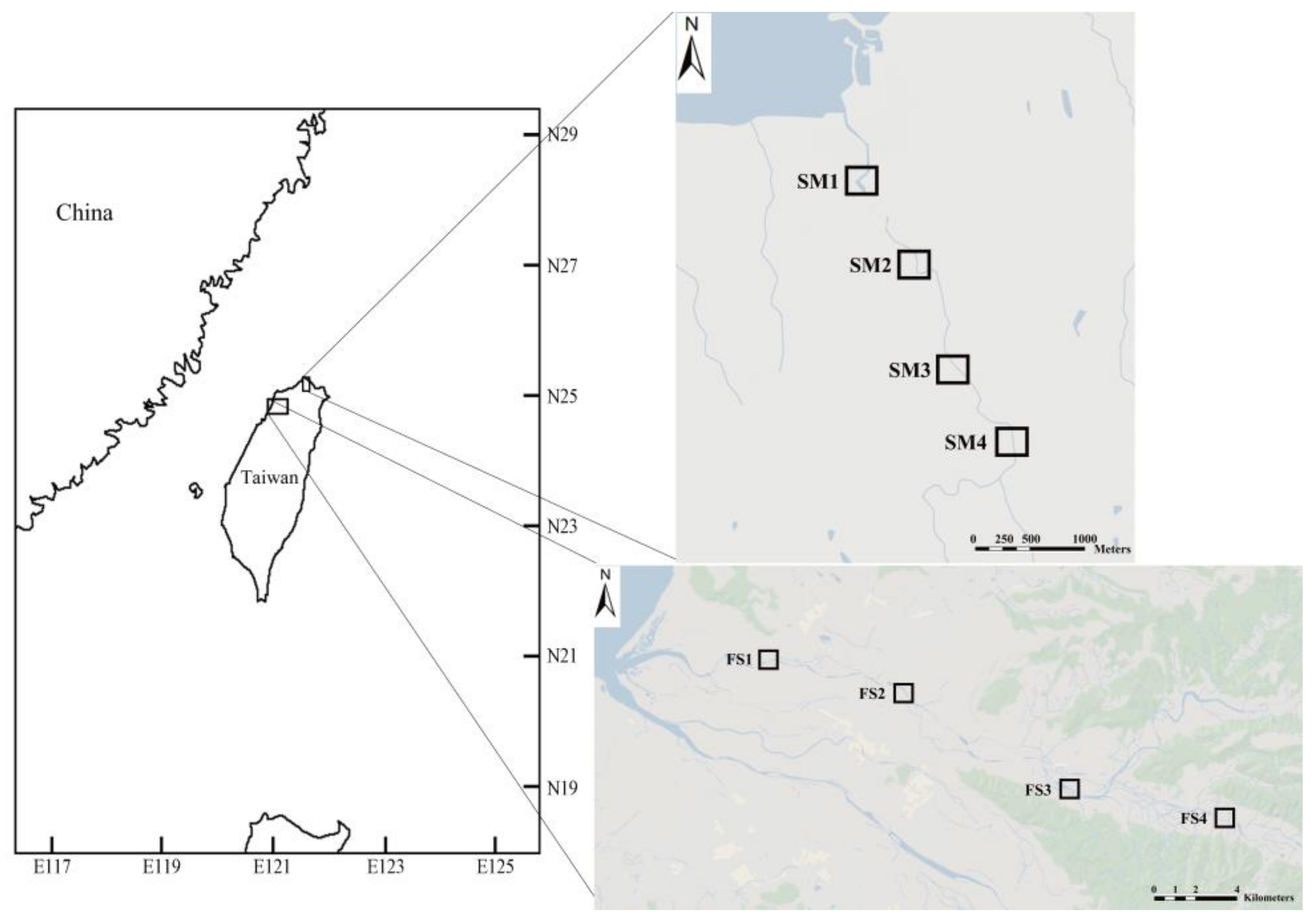
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling and eDNA Extraction
2.3. Electrofishing
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. River Pollution Index (RPI) in Taiwan
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
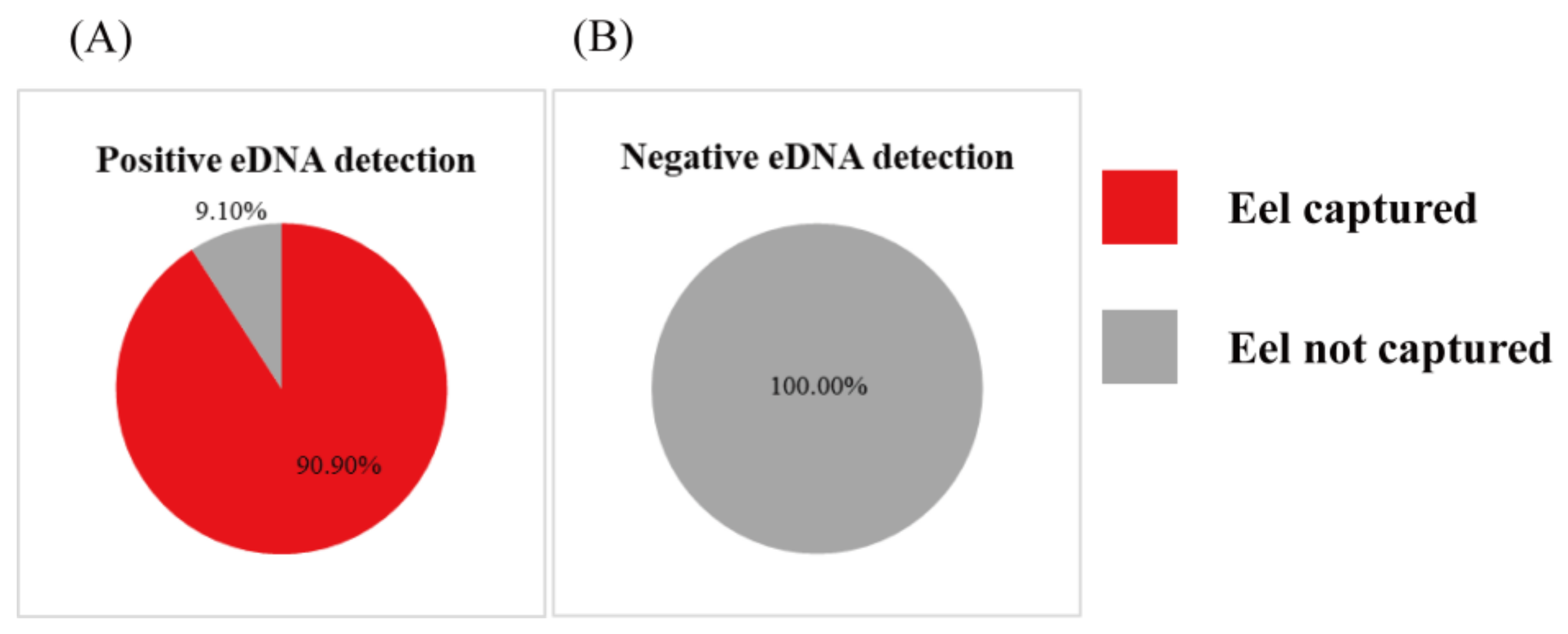
3.1. eDNA Analysis and Electrofishing at Fengshan and Shimen Rivers Study Sites
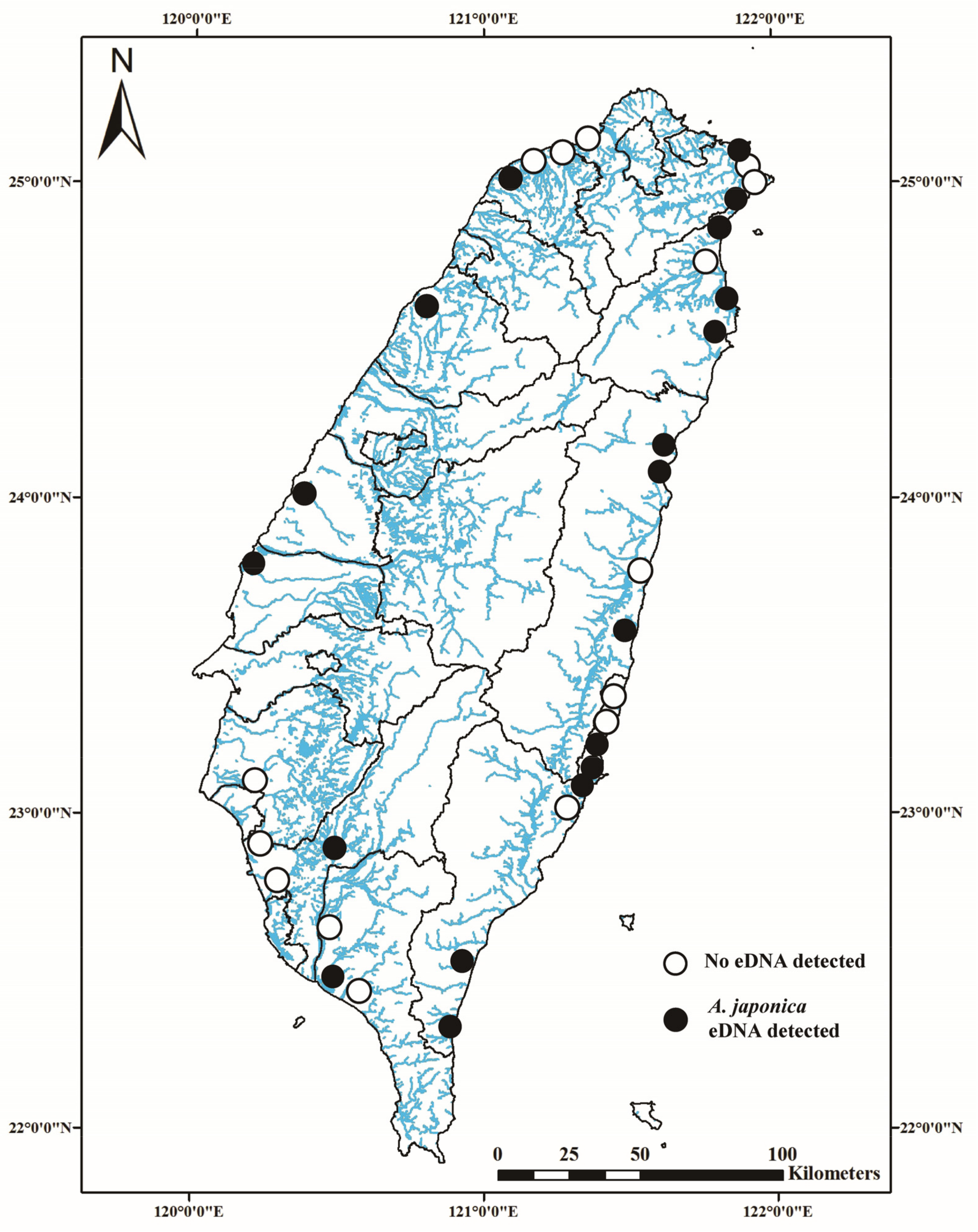
3.2. Survey of Japanese Eel Distribution across Taiwan’s Rivers
3.3. RPI and Cq Values for Taiwan’s Lower Reaches of Thirty-Six Study Rivers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tesch, F.W. The Eel; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama, J.; Wouthuyzen, S.; Miller, M.J.; Sugeha, H.Y.; Kuroki, M.; Watanabe, S.; Syahailatua, A.; Tantu, F.Y.; Hagihara, S.; Triyanto; et al. Reproductive Ecology and Biodiversity of Freshwater Eels around Sulawesi Island Indonesia. Zool. Stud. 2018, 57, e30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Chang, C.R.; Han, Y.S. Seaward Migration Routes of Indigenous Eels, Anguilla japonica, A. marmorata, and A. bicolor pacifica, via Satellite Tags. Zool. Stud. 2018, 57, e21. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, T.; Watanabe, S.; Manabe, R.; Kaku, T.; Okamura, A.; Yamada, Y.; Miller, M.J.; Tsukamoto, K. Tracking Anguilla japonica Silver Eels Along the West Marina Ridge Using Pop-up Archival Transmitting Tags. Zool. Stud. 2018, 57, e24. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.S.; Wu, C.R.; Iizuka, Y. Batch-like Arrival Waves of Glass Eels of Anguilla japonica in Offshore Waters of Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2016, 55, e36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arai, T. Taxonomy and Distribution. In Biology and Ecology of Anguillid Eels; Arai, T., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kaifu, K.; Stein, F.; Dekker, W.; Walker, N.; Dolloff, C.A.; Steele, K.; Aguirre, A.A.; Nijman, V.; Siriwat, P.; Sasal, P. Global exploitation of freshwater eels (genus Anguilla): Fisheries, stock status and illegal trade. In Proceedings of the First International Eel Science Symposium, Zoological Society of London, London, UK, 13–15 June 2017; 5m Books Ltd.: Essex, UK, 2017; pp. 377–422. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Aoyama, J.; Tsukamoto, K. A new species of freshwater eel Anguilla luzonensis (Teleostei: Anguillidae) from Luzon Island of the Philippines. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.S.; Yambot, A.V.; Zhang, H.; Hung, C.L. Sympatric Spawning but Allopatric Distribution of Anguilla japonica and Anguilla marmorata: Temperature- and Oceanic Current-Dependent Sieving. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Han, Y.S. Habitat Partitioning and its Possible Genetic Background Between Two Sympatrically Distributed Eel Species in Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2019, 58, e27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shiao, J.C.; Iizuka, Y.; Chang, C.W.; Tzeng, W.N. Disparities in habitat use and migratory behavior between tropical eel Anguilla marmorata and temperate eel A. japonica in four Taiwanese rivers. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 261, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Huang, S.L.; Han, Y.S. Impact of long-term habitat loss on the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Aoyama, J.; Miller, M.J. Present status of the Japanese eel: Resources and recent research. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2009, 58, 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Gazzard, D.; Scholey, G.; Macdonald, D.W. Concentrations and hazard assessment of PCBs, organochlorine pesticides and mercury in fish species from the Upper Thames: River pollution and its potential effects on top predators. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agradi, E.; Baga, R.; Cillo, F.; Ceradini, S.; Heltai, D. Environmental contaminants and biochemical response in eel exposed to Po river water. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, D.M.P.; Casselman, J.M.; Crook, V.; DeLucia, M.B.; Ahn, H.; Kaifu, K.; Kurwie, T.; Sasal, P.; Silfvergrip, A.M.C.; Smith, K.G.; et al. Synergistic patterns of threat and the challenges facing global anguillid eel conservation. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 4, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.A.; Peres-Neto, P.R.; Olden, J.D. What controls who is where in freshwater fish communities—The roles of biotic, abiotic, and spatial factors. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, B.R.; Willis, D.W. (Eds.) Fisheries Techniques, 2nd ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1996; p. 732. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.E. Invited overview: Conclusions from a review of electrofishing and its harmful effects on fish. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fisher 2003, 13, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janosik, A.M.; Johnston, C.E. Environmental DNA as an effective tool for detection of imperiled fishes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2015, 98, 1889–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.S.; Schumer, G.; Blankenship, S.; Campbell, E. Detection of Adult Green Sturgeon Using Environmental DNA Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Wiuf, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Orlando, L.; Willerslev, E. Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Gotoh, R.O.; Sado, T. MiFish metabarcoding: A high-throughput approach for simultaneous detection of multiple fish species from environmental DNA and other samples. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 939–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.A.; Mahon, A.R. From molecules to management: Adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, H.C.; Maddison, B.C.; Middleditch, D.J.; Patmore, J.R.M.; Gough, K.C. The detection of aquatic animal species using environmental DNA—A review of eDNA as a survey tool in ecology. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, M.M.; Larson, E.R.; Renshaw, M.A.; Gantz, C.A.; Egan, S.P.; Erickson, D.M.; Lodge, D.M. Environmental DNA (eDNA) detects the invasive rusty crayfish Orconectes rusticus at low abundances. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Sato, Y.; Sado, T.; Araki, H.; Kondoh, M.; Minamoto, T.; Miya, M. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, D.M.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Barnes, M.A.; Chadderton, L.; Egan, S.P.; Feder, J.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Pfrender, M.E. Conservation in a cup of water: Estimating biodiversity and population abundance from environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2555–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmann, K.; Evans, A.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Knapp, M.; Yu, D.W.; de Bruyn, M. Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Ishikawa, S.; Nishida, M.; Tsukamoto, K. Are morphological characters distinctive enough to discriminate between two species of freshwater eels, Anguilla celebesensis and A. interioris? Ichthyol. Res. 2000, 47, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, C. The Yellow Eel. In Eel Biology; Aida, K., Tsukamoto, K., Yamauchi, K., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, W.N.; Shiao, J.C.; Iizuka, Y. Use of otolith Sr: Ca ratios to study the riverine migratory behaviors of Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 245, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, A.A.; Yambot, A.V.; Shiao, J.C.; Iizuka, Y.; Tzeng, W.N. Migratory pattern and habitat use of tropical eels Anguilla spp. (Teleostei: Anguilliformes: Anguillidae) in the Philippines, as revealed by otolith microchemistry. Raffles B Zool. 2007, 14, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Itakura, H.; Wakiya, R.; Yamamoto, S.; Kaifu, K.; Sato, T.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA analysis reveals the spatial distribution, abundance, and biomass of Japanese eels at the river-basin scale. Aquat. Conserv. 2019, 29, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, H.; Wakiya, R.; Sakata, M.K.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Yang, C.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Han, Y.S.; Yamamoto, S.; Minamoto, T. Estimations of Riverine Distribution, Abundance, and Biomass of Anguillid Eels in Japan and Taiwan Using Environmental DNA Analysis. Zool. Stud. 2020, 59, e17. [Google Scholar]
- Kasai, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Ahn, H.; Yamanaka, H.; Kameyama, S.; Masuda, R.; Azuma, N.; Kimura, S.; Karaki, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; et al. Distribution of Japanese Eel Anguilla japonica Revealed by Environmental DNA. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 621461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.W.; Kathryn, P.H.; Antoinette, J.P. No filters, no fridges: A method for preservation of water samples for eDNA analysis. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Huang, Y.C.; Han, Y.S. Skin coloration and habitat preference of the freshwater Anguilla eels. Int. J. Aquac. Fish. Sci. 2020, 6, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, J.; Yoshinaga, T.; Shinoda, A.; Shirotori, F.; Yambot, A.V.; Han, Y.S. Seasonal Changes in Species Composition of Glass Eels of the Genus Anguilla (Teleostei: Anguillidae) Recruiting to the Cagayan River, Luzon Island, the Philippines. Pac. Sci. 2015, 69, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.S.; Liao, I.C.; Huang, Y.S.; He, J.T.; Chang, C.W.; Tzeng, W.N. Synchronous changes of morphology and gonadal development of silvering Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Aquaculture 2003, 219, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Tzeng, C.S.; Hwang, J.K. Reassessment of morphological characteristics in freshwater eels (genus Anguilla, Anguillidae) shows congruence with molecular phylogeny estimates. Zool. Scr. 2005, 34, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, M.K.; Maki, N.; Sugiyama, H.; Minamoto, T. Identifying a breeding habitat of a critically endangered fish, Acheilognathus typus, in a natural river in Japan. Sci. Nat-Heidelb. 2017, 104, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L. Can we manage fisheries with the inherent uncertainty from eDNA? J. Fish. Biol. 2021, 98, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Sepulveda, A.J.; Shepard, B.B.; Jane, S.F.; Whiteley, A.R.; Lowe, W.H.; Schwartz, M.K. Understanding environmental DNA detection probabilities: A case study using a stream-dwelling char Salvelinus fontinalis. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 194, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvisseau, Q.; Burian, A.; Gibson, C.; Brys, R.; Ramsey, A.; Sweet, M. Influence of accuracy, repeatability and detection probability in the reliability of species-specific eDNA based approaches. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, A.; Matechou, E.; Griffin, J.; Diana, A.; Griffiths, R.A. Optimising sampling and analysis protocols in environmental DNA studies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sint, D.; Kolp, B.; Rennstam Rubbmark, O.; Füreder, L.; Traugott, M. The amount of environmental DNA increases with freshwater crayfish density and over time. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokouchi, K.; Sudo, R.; Kaifu, K.; Aoyama, J.; Tsukamoto, K. Biological characteristics of silver-phase Japanese eels, Anguilla japonica, collected from Hamana Lake, Japan. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2009, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kaifu, K.; Tamura, M.; Aoyama, J.; Tsukamoto, K. Dispersal of yellow phase Japanese eels Anguilla japonica after recruitment in the Kojima Bay-Asahi River system, Japan. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2010, 88, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T.; Matsuhashi, S.; Uchii, K.; Yamanaka, H. Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Outperforms Real-Time PCR in the Detection of Environmental DNA from an Invasive Fish Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5601–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymus, K.E.; Richter, C.A.; Chapman, D.C.; Paukert, C. Quantification of eDNA shedding rates from invasive bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis and silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L.L.; Kielgast, J.; Sand-Jensen, K. Monitoring of animal abundance by environmental DNA—An increasingly obscure perspective: A reply to Klymus et al., 2015. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 192, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.I.; Strand, D.A.; Rusch, J.C.; Vralstad, T. Environmental DNA (eDNA) Monitoring of Noble Crayfish Astacus astacus in Lentic Environments Offers Reliable Presence-Absence Surveillance—But Fails to Predict Population Density. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 612253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, H.; Kaino, T.; Miyake, Y.; Kitagawa, T.; Kimura, S. Feeding, condition, and abundance of Japanese eels from natural and revetment habitats in the Tone River, Japan. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2015, 98, 1871–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, H.; Miyake, Y.; Kitagawa, T.; Kimura, S. Site fidelity, diel and seasonal activities of yellow-phase Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) in a freshwater habitat as inferred from acoustic telemetry. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2018, 27, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakiya, R.; Kaifu, K.; Azechi, K.; Tsukamoto, K.; Mochioka, N. Evaluation of downward movements of Japanese eel Anguilla japonica inhabiting brackish water areas. J. Fish. Biol. 2020, 96, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.A.; Wangensteen, O.S.; O’Gorman, E.J.; Mariani, S.; Sims, D.W.; Genner, M.J. Persistence of environmental DNA in marine systems. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiung, K.M.; Lin, Y.T.; Han, Y.S. Current Dependent Dispersal Characteristics of Japanese Glass Eel around Taiwan. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Leveque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, S.F.; Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Schwartz, M.K.; Lowe, W.H.; Letcher, B.H.; Whiteley, A.R. Distance, flow and PCR inhibition: eDNA dynamics in two headwater streams. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, M.; Durance, I.; Cosby, B.J.; Ransom-Jones, E.; Deiner, K.; Ormerod, S.J.; Colbourne, J.K.; Wilgar, G.; Carvalho, G.R.; de Bruyn, M.; et al. Acidity promotes degradation of multi-species environmental DNA in lotic mesocosms. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Primer Sequences | Amplicon Size (bp) | PCR Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. japonica | AJ-F: 5′–ATGGATGATTCATCCGAAAT–3′ AJ-R: 5′−GTGTAGGTAGAGGCAGATAAAG−3′ | 68 | 98.5% |
| Study Site | Date | Japanese Eel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| eDNA (Cq) | Captures | ||
| FS1 | December 2021 | +, (30.3 ± 0.4) | 2 |
| FS2 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| FS3 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| FS4 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| FS1 | January 2022 | +, (30.5 ± 0.3) | 3 |
| FS2 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| FS3 | +, (28.4 ± 0.4) | 2 | |
| FS4 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| FS1 | February 2022 | +, (32.1 ± 0.3) | 5 |
| FS2 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| FS3 | +, (31.8 ± 0.2) | 3 | |
| FS4 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| SM1 | December 2021 | +, (32.7 ± 0.3) | 3 |
| SM2 | +, (31.5 ± 0.4) | 0 | |
| SM3 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| SM4 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| SM1 | January 2022 | +, (28.7 ± 0.4) | 4 |
| SM2 | +, (30.2 ± 0.2) | 5 | |
| SM3 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| SM4 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| SM1 | February 2022 | +, (32.7 ± 0.5) | 13 |
| SM2 | +, (32.1 ± 0.4) | 12 | |
| SM3 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| SM4 | −, (N/A) | 0 | |
| Name of River | eDNA Detection of Japanese Eel | RPI Value | Level of Pollution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beishikeng River | +, 35.0 ± 0.4 | N | N |
| Hemei River | − | N | N |
| Jingshawan River | − | N | N |
| Daxi River | +, 27.2 ± 0.3 | 1 | non/mildly polluted |
| Gengfang River | +, 29.8 ± 0.3 | N | N |
| Dezikou River | − | 3.75 | moderately polluted |
| Xinchen River | +, 28.9 ± 0.2 | 1 | non/mildly polluted |
| Dongao North River | +, 27.8 ± 0.3 | 1 | non/mildly polluted |
| Liwu River | +, 34.6 ± 0.4 | 1 | non/mildly polluted |
| Sanzhan River | +, 31.5 ± 0.4 | 1 | non/mildly polluted |
| Shuliao River | − | N | N |
| Xiuguluan River | +, 38.1 ± 0.2 | 3.25 | moderately polluted |
| Ningpu River | − | N | N |
| Dabin River | − | N | N |
| Duwei River | +, 32.3 ± 0.2 | N | N |
| Fujia River | +, 31.3 ± 0.3 | 1.25 | non/mildly polluted |
| Hsinkang River | +, 33.3 ± 0.2 | N | N |
| Mawu River | − | 1.25 | non/mildly polluted |
| Taimali River | +, 30.2 ± 0.3 | N | N |
| Anshuo River | +, 35.9 ± 0.4 | N | N |
| Nanwan River | − | N | N |
| Nankan River | − | 4 | moderately polluted |
| Shuangxikou River | − | N | N |
| Xinwu River | +, 36.0 ± 0.3 | 2.25 | lightly polluted |
| Zhonggang River | +, 32.5 ± 0.3 | 2 | non/mildly polluted |
| Oldzhuoshui River | +, 34.5 ± 0.3 | 2.25 | lightly polluted |
| Newhuwei River | +, 31.4 ± 0.2 | 4.25 | moderately polluted |
| Yanshui River | − | 6.25 | severely polluted |
| Erren River | − | 4.75 | moderately polluted |
| Tianliao River | +, 31.1 ± 0.2 | N | N |
| Dianbao River | − | 7.25 | severely polluted |
| Gaoping River | − | 3.25 | moderately polluted |
| Donggang River | +, 37.9 ± 0.3 | 5.5 | moderately polluted |
| Linbian River | − | 1.5 | non/mildly polluted |
| Fengshan River | +, 30.5 ± 0.3 | 2.25 | lightly polluted |
| Shimen River | +, 28.7 ± 0.3 | N | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, H.-Y.; Wu, K.-J.; Han, Y.-S. Detecting Japanese Eels (Anguilla japonica) and Revealing Their Distribution in Taiwanese Rivers by Environmental DNA Analysis. Fishes 2023, 8, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100483
Hsu H-Y, Wu K-J, Han Y-S. Detecting Japanese Eels (Anguilla japonica) and Revealing Their Distribution in Taiwanese Rivers by Environmental DNA Analysis. Fishes. 2023; 8(10):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100483
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Hsiang-Yi, Kai-Jen Wu, and Yu-San Han. 2023. "Detecting Japanese Eels (Anguilla japonica) and Revealing Their Distribution in Taiwanese Rivers by Environmental DNA Analysis" Fishes 8, no. 10: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100483
APA StyleHsu, H.-Y., Wu, K.-J., & Han, Y.-S. (2023). Detecting Japanese Eels (Anguilla japonica) and Revealing Their Distribution in Taiwanese Rivers by Environmental DNA Analysis. Fishes, 8(10), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100483