In Silico Chromosome Mapping of the Male-Specific/Linked Loci in the Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo) Suggests Chromosome 19 as the Putative Y Sex Chromosome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Silico Mapping of Male-Specific/Linked Loci to the Reference Genome
2.2. Homology Searching
2.3. Functional Annotation and Gene Ontology of Male-Linked Regions
2.4. DNA Marker Validation
2.5. Determination of Repetitive Elements in Male-Linked Regions
2.6. Characterization of Microsatellites in Jade Perch Genome
2.7. Comparative Genomics between Jade Perch and Other Vertebrates
3. Results
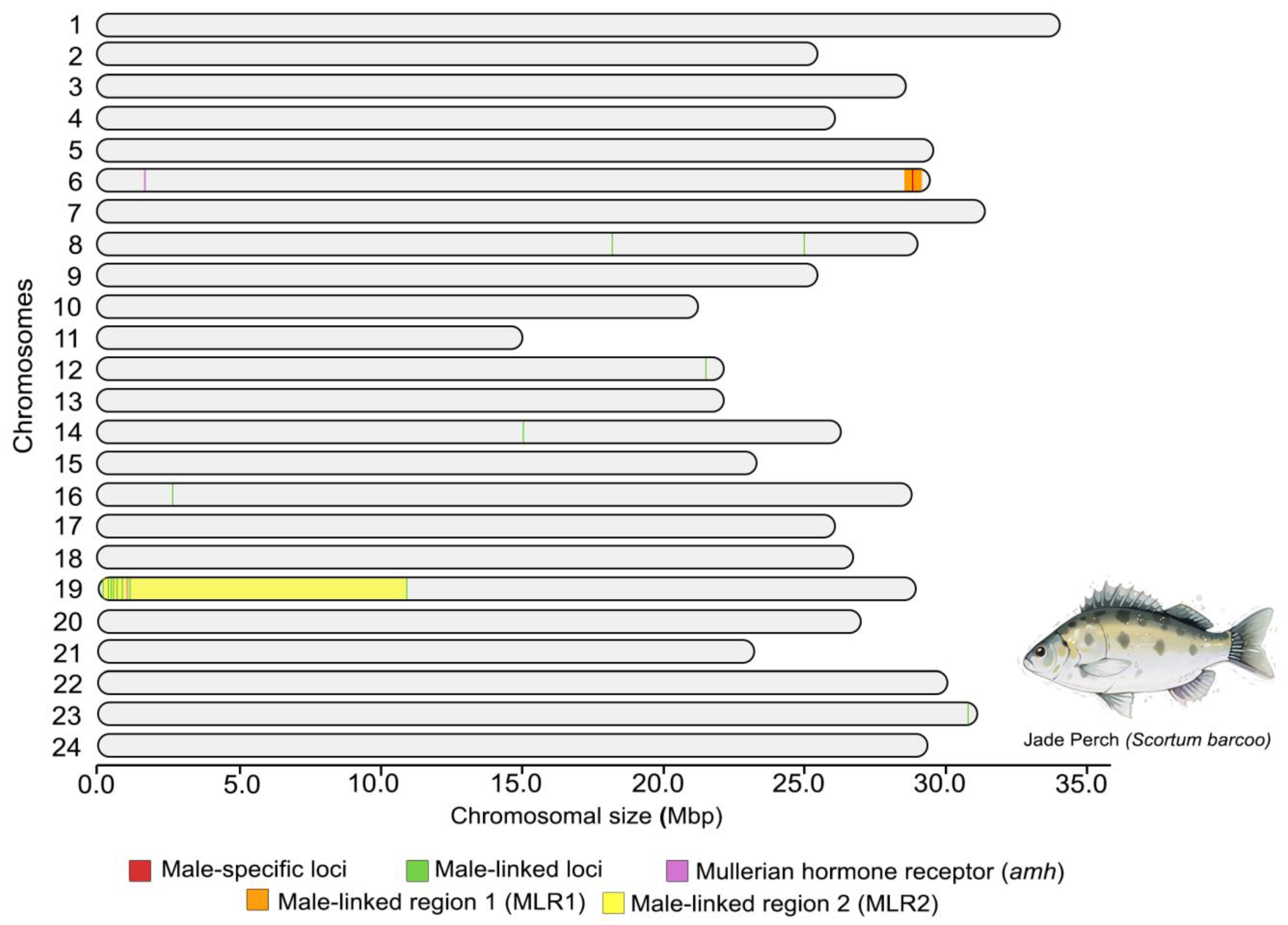
3.1. Chromosomal Localization of Sex-Specific/Linked Loci in Jade Perch
3.2. Homology of Putative Male-Specific/Linked Loci and Gene Mapping to Reference Genome
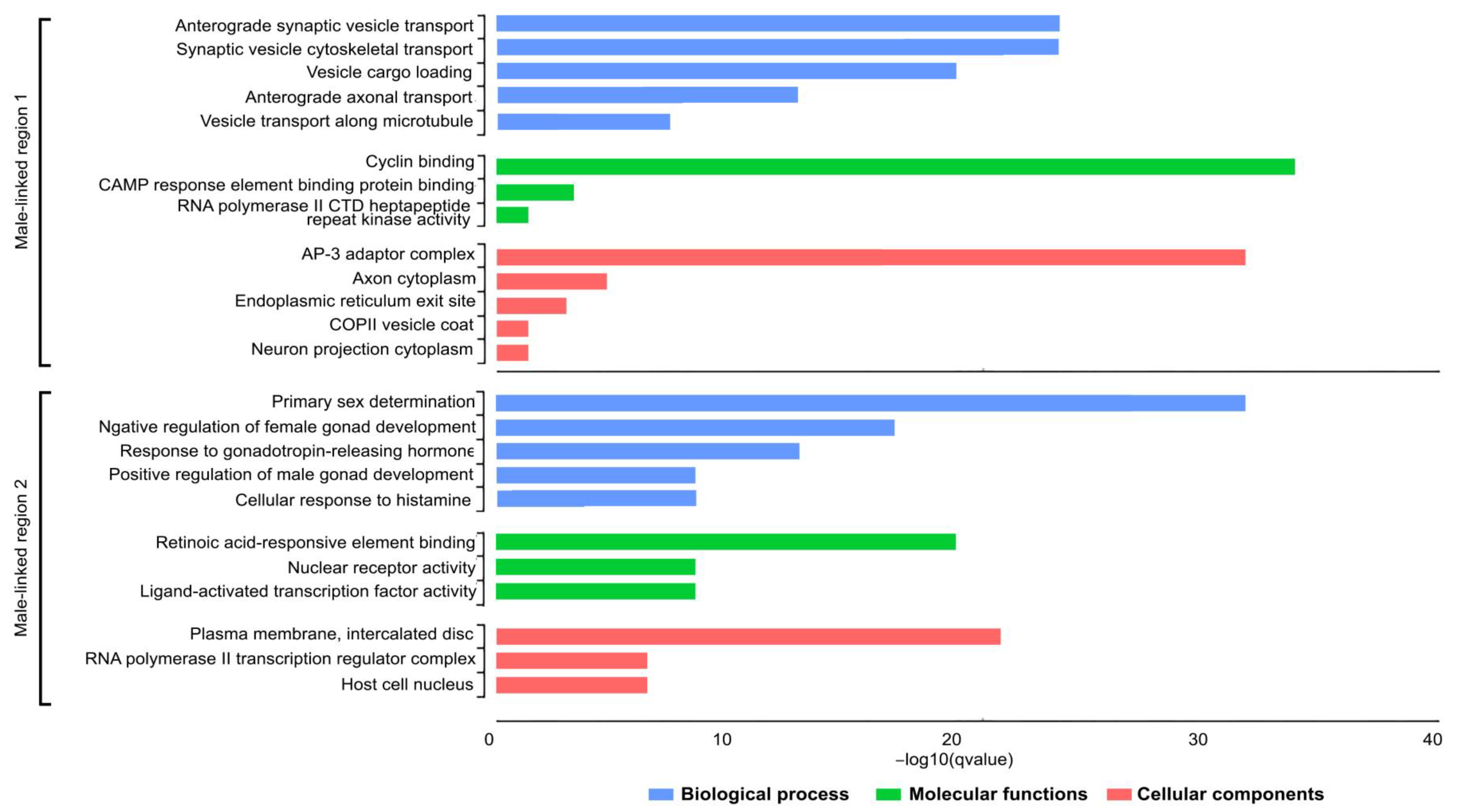
3.3. Functional Classification and Enrichment Analysis of Male-Linked Region
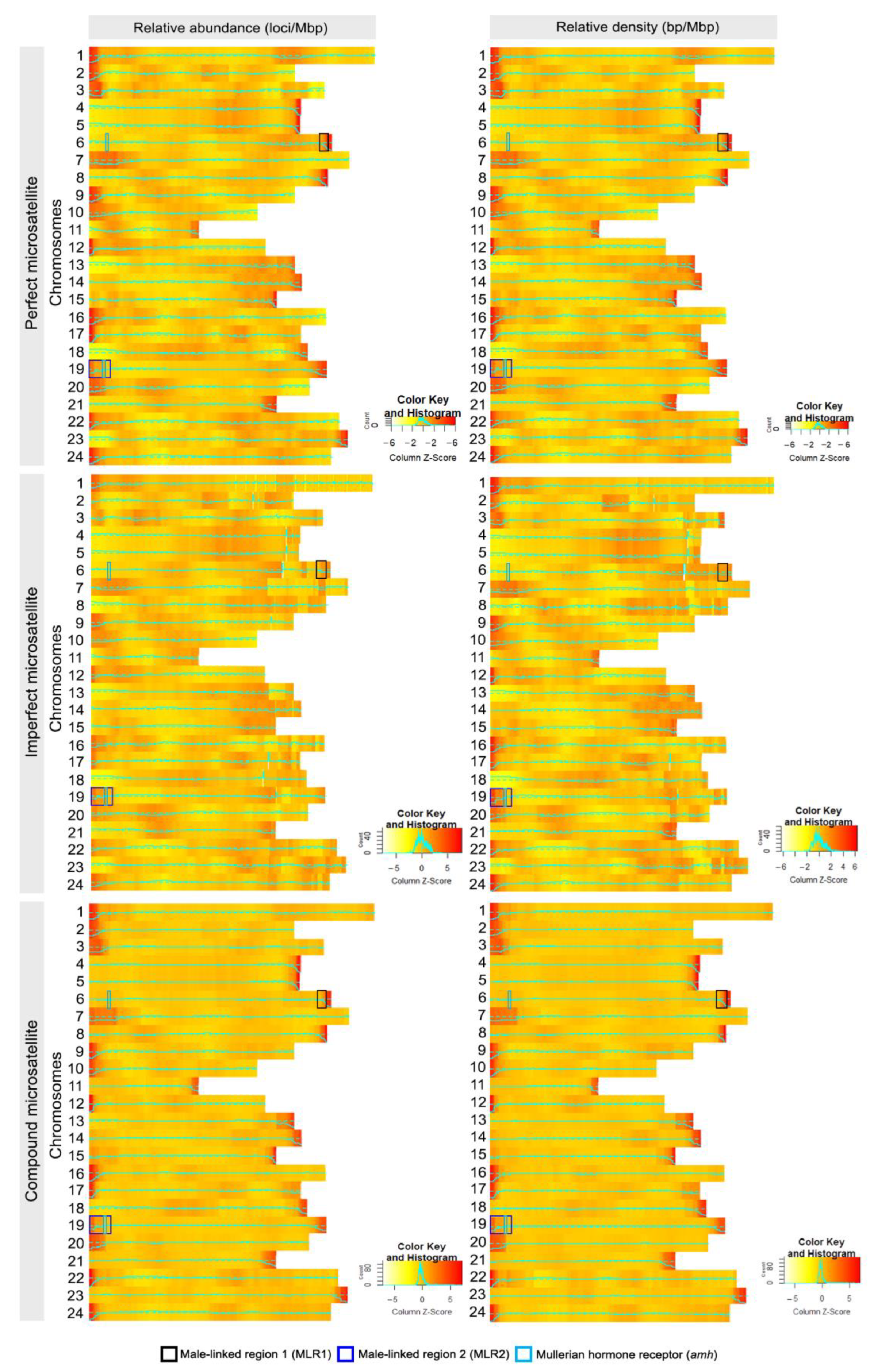
3.4. Annotation of Repetitive Elements in the Specific Region
3.5. Validation of Male-Linked Region with DNA Markers
3.6. Microsatellite Distribution in Jade Perch Genome
3.7. Linkage Homology of Jade Perch and Other Vertebrates
4. Discussion
4.1. Sign of Sex Chromosome in Jade Perch
4.2. The Existence of Amh Gene on SBA19 Might Associate the Sex Determining Region of Jade Perch
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/2374545 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Ihwan, M.; Syahnon, M.; Fakhrul, I.; Marina, H.; Ambak, M. New report on trichodiniasis (Protozoa: Ciliophora: Peritrichida) in Jade perch; Scortum barcoo from Peninsular Malaysia. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 11, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Renaudeau, D.; Collin, A.; Yahav, S.; Basilio, V.D.; Gourdine, J.L.; Collier, R.J. Adaptation to tropical climate and research strategies to alleviate heat stress in livestock production. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2010, 1, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, G.S.; Silva, J.W.A.D.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L. Fish farming techniques: Current situation and trends. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, M.J.S. The Paradox of Alien Invasive Species: Negative and Positive Effects on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; Faculty of Sciences, University of Porto: Porto, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Essl, F.; Lenzner, B.; Bacher, S.; Bailey, S.; Capinha, C.; Daehler, C.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hui, C.; Hulme, P.E.; et al. Drivers of future alien species impacts: An expert-based assessment. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4880–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelson, F.F. Social and Environmental Control of Life History Traits in Poeciliid Fishes. In Ecology and Evolution of Livebearing Fishes (Poeciliidae); Meffe, G.K., Snelson, F.F., Jr., Eds.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1989; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce de Leon, J.L.; Rodríguez, R.; Leon, G. Life-history patterns of Cuban poeciliid fishes (Teleostei: Cyprinodontiformes). Zoo Biol. 2013, 32, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntronpong, A.; Panthum, T.; Laopichienpong, N.; Nguyen, D.H.; Kraichak, E.; Singchat, W.; Ariyaraphong, N.; Ahmad, S.F.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; et al. Implications of genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms in jade perch (Scortum barcoo) reveals the putative XX/XY sex-determination system, facilitating a new chapter of sex control in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2022, 48, 737587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, R.H.; Nagahama, Y. Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 2022, 208, 191–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mank, J.E.; Promislow, D.E.L.; Avise, J.C. Evolution of alternative sex determining mechanisms in teleost fishes. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 87, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroiller, J.F.; D’Cotta, H.; Bezault, E.; Wessels, S.; Hoerstgen-Schwark, G. Tilapia sex determination: Where temperature and genetics meet. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 153, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Piferrer, F.; Chen, S.L.; Shen, Z.G. Sex Control in Aquaculture; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Pan, Z.; Wang, G.; Ye, B.; Wang, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Zou, J.; Xie, S. Gonadal transcriptome analysis and sequence characterization of sex-related genes in Cranoglanis bouderius. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q. A swimy locus on Y chromosome of the platyfish (Xiphophorus maculatus) is derived from a novel DNA transposon Zisupton. Gene 2012, 503, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, P.; Vinas, A.M.; Sanchez, L.; Díaz, N.; Ribas, L.; Piferrer, F. Genetic architecture of sex determination in fish: Applications to sex ratio control in aquaculture. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson Sayres, M.A. Genetic diversity on the sex chromosomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.H.M.; Panthum, T.; Ponjarat, J.; Laopichienpong, N.; Kraichak, E.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Muangmai, N.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Na-Nakorn, U.; et al. An investigation of ZZ/ZW and XX/XY sex determination systems in North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell, 1822). Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 562856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.H.M.; Ponjarat, J.; Laopichienpong, N.; Panthum, T.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Kraichak, E.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; Peyachoknagul, S.; et al. Genome-wide SNP analysis of hybrid clariid fish reflects the existence of polygenic sex-determination in the lineage. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 789573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthum, T.; Jaisamut, K.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Kongkaew, L.; Wongloet, W.; Dokkaew, S.; Kraichak, E.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; et al. Something fishy about Siamese fighting fish (Betta splendens) sex: Polygenic sex determination or a newly emerged sex-determining region? Cells 2022, 11, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedder, J. Sex determination and male differentiation in Southern swordtail fishes: Evaluation from an evolutionary perspective. Fishes 2023, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.B.; Juntti, S.A.; Coyle, K.P.; Dumont, B.L.; Stanley, M.K.; Ryan, A.Q.; Roberts, R.B. Polygenic sex determination in the cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, C.T. The Asiatic fishes of the family Anabantidae. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1910, B1909, 767–787. [Google Scholar]
- Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/9797255 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Nagabhushana, A.; Mishra, R.K. Finding clues to the riddle of sex determination in zebrafish. J. Biosci. 2016, 41, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, D.; Marlow, F.L. Sexual determination in zebrafish. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, L.; Cheng, J.; Xia, H.; Zhan, Q.; Yu, D.; You, X.; Gu, R.; Xu, J.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the jade perch (Scortum barcoo). Sci. Data. 2022, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Available online: https://www.fishbase.se/summary/dicentrarchus-labrax.html (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer). Available online: https://www.fishbase.se/summary/Lates-calcarifer.html (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Chinese Seabass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/2392026 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Lacépède, B.G.E. Histoire Naturelle des Poissons: IV; Chez Plassan: Paris, France, 1802; Volume 4, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/4285694 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Gasterosteus aculeatus. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/4286327 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2368377 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Japanese Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2407604 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Green-spotted Pufferfish (Tetraodon nigroviridis). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/5213566 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Southern Platyfish (Xiphophorus maculatus). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2350164 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Green Anole (Anolis carolinensis). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2466939 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Indian Cobra (Naja naja). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2470351 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Chicken (Gallus gallus). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/9326020 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D.; et al. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, R.J.; Kähäri, A.; Haider, S.; Zamora, J.; Proctor, G.; Spudich, G.; Almeida-King, J.; Staines, D.; Derwent, P.; Kerhornou, A.; et al. Ensembl BioMarts: A hub for data retrieval across taxonomic space. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2011, 2011, bar030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, T.; Auchincloss, A.H.; Coudert, E.; Keller, G.; Michoud, K.; Rivoire, C.; Bulliard, V.; de Castro, E.; Lachaize, C.; Baratin, D.; et al. HAMAP: A database of completely sequenced microbial proteome sets and manually curated microbial protein families in UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D471–D478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, T.; Kai, W.; Tasumi, S.; Oka, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Mizuno, N.; Fujita, M.; Suetake, H.; Suzuki, S.; Hosoya, S.; et al. A trans-species missense SNP in Amhr2 is associated with sex determination in the tiger pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes (fugu). PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Su, W.; Liao, Y.; Chougule, K.; Agda, J.R.A.; Hellinga, A.J.; Lugo, C.S.B.; Elliott, T.A.; Ware, D.; Peterson, T.; et al. Benchmarking transposable element annotation methods for creation of a streamlined, comprehensive pipeline. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RepeatMasker. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Manee, M.M.; Jackson, J.; Bergman, C.M. Conserved noncoding elements influence the transposable element landscape in drosophila. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanettes, F.; Klopp, C. D-GENIES: Dot plot large genomes in an interactive, efficient and simple way. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yue, B.; Hancock, J. Krait: An ultrafast tool for genome-wide survey of microsatellites and primer design. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanadilokchatkun, P.; Panthum, T.; Jaisamut, K.; Ahmad, S.F.; Dokkaew, S.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; Singchat, W.; Srikulnath, K. Characterization of microsatellite distribution in Siamese fighting fish genome to promote conservation and genetic diversity. Fishes 2022, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, W.Y.; Cho, M.; Sim, M.; Lee, D.; Ko, Y.; Kim, J. Synteny portal: A web based application portal for synteny block analysis. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2016, 44, W35–W40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.T.; Vincens, P.; Crollius, H.R.; Louis, A. Genomicus 2018: Karyotype evolutionary trees and on-the-fly synteny computing. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2018, 46, D816–D822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volff, J.N. Genome evolution and biodiversity in teleost fish. Heredity 2005, 94, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, C.M.; Seetharam, A.S.; Snodgrass, O.; Ortega-García, S.; Hyde, J.R.; Severin, A.J. Insights into teleost sex determination from the Seriola dorsalis genome assembly. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sember, A.; Nguyen, P.; Perez, M.F.; Altmanová, M.; Ráb, P.; Cioffi, M.D.B. Multiple sex chromosomes in teleost fishes from a cytogenetic perspective: State of the art and future challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2021, 376, 20200098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.; Antunes, A. Decoding sex: Elucidating sex determination and how high-quality genome assemblies are untangling the evolutionary dynamics of sex chromosomes. Genomics 2022, 114, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejnovsky, E.; Hobza, R.; Cermak, T.; Kubat, Z.; Vyskot, B. The role of repetitive DNA in structure and evolution of sex chromosomes in plants. Heredity 2009, 102, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Uno, Y.; Srikulnath, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Miller, E.; Olsson, M. No interstitial telomeres on autosomes but remarkable amplification of telomeric repeats on the W sex chromosome in the sand lizard (Lacerta agilis). J. Hered. 2015, 106, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carducci, F.; Barucca, M.; Canapa, A.; Biscotti, M.A. Rex retroelements and teleost genomes: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singchat, W.; O’Connor, R.E.; Tawichasri, P.; Suntronpong, A.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Suntrarachun, S.; Muangmai, N.; Baicharoen, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Chanhome, L.; et al. Chromosome map of the Siamese cobra: Did partial synteny of sex chromosomes in the amniote represent “a hypothetical ancestral super-sex chromosome” or random distribution? BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongchum, R.; Singchat, W.; Laopichienpong, N.; Tawichasri, P.; Kraichak, E.; Prakhongcheep, O.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Muangmai, N.; Baicharoen, S.; Suntrarachun, S.; et al. Diversity of PBI-DdeI satellite DNA in snakes correlates with rapid independent evolution and different functional roles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, B.L.S.; Metzger, D.C.H.; Darolti, I.; Wright, A.E.; Sandkam, B.A.; Almeida, P.; Shu, J.J.; Mank, J.E. Sex chromosome evolution: So many exceptions to the rules. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singchat, W.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Muangmai, N.; Baicharoen, S.; Indananda, C.; Duengkae, P.; Peyachoknagul, S.; O’Connor, R.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Srikulnath, K. Do sex chromosomes of snakes, monitor lizards, and iguanian lizards result from multiple fission of an “ancestral amniote super-sex chromosome”? Chromosome Res. 2020, 28, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; Peyachoknagul, S.; O’Connor, R.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Srikulnath, K. Partial amniote sex chromosomal linkage homologies shared on snake W sex chromosomes support the ancestral super-sex chromosome evolution in amniotes. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, J.E.; Ezaz, T. Understanding the evolution of reptile chromosomes through applications of combined cytogenetics and genomics approaches. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2019, 157, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennessen, J.A.; Wei, N.; Straub, S.C.K.; Govindarajulu, R.; Liston, A.; Ashman, T.L. Repeated translocation of a gene cassette drives sex-chromosome turnover in strawberries. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siamese Cobra (Naja kaouthia). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2470368 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Uno, Y.; Asada, Y.; Nishida, C.; Takehana, Y.; Sakaizumi, M.; Matsuda, Y. Divergence of repetitive DNA sequences in the heterochromatin of medaka fishes: Molecular cytogenetic characterization of constitutive heterochromatin in two medaka species: Oryzias hubbsi and O. celebensis (Adrianichthyidae, Beloniformes). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell, 1822). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/5202793 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus, Günther, 1864). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/5202728 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Na, J.K.; Wang, J.; Ming, R. Accumulation of interspersed and sex-specific repeats in the non-recombining region of papaya sex chromosomes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puterova, J.; Kubat, Z.; Kejnovsky, E.; Jesionek, W.; Cizkova, J.; Vyskot, B.; Hobza, R. The slowdown of Y chromosome expansion in dioecious Silene latifolia due to DNA loss and male-specific silencing of retrotransposons. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.H.M.; Panthum, T.; Ponjarat, J.; Laopichienpong, N.; Kraichak, E.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Muangmai, N.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Na-Nakorn, U.; et al. Genome-wide SNP analysis suggests male heterogamety in bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus, Günther, 1864). Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikulnath, K.; Ahmad, S.F.; Singchat, W.; Panthum, T. Do Ty3/Gypsy transposable elements play preferential roles in sex chromosome differentiation? Life 2020, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; O’Meally, D.; Azad, B.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.D.; Graves, J.A.; Matsuda, Y.; Ezaz, T. Amplification of microsatellite repeat motifs is associated with the evolutionary differentiation and heterochromatinization of sex chromosomes in Sauropsida. Chromosoma 2016, 125, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Singchat, W.; Jehangir, M.; Panthum, T.; Srikulnath, K. Consequence of paradigm shift with repeat landscapes in reptiles: Powerful facilitators of chromosomal rearrangements for diversity and evolution. Genes 2020, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Nishida, C.; Matsuda, Y.; Kumazawa, Y. Sex chromosome evolution in snakes inferred from divergence patterns of two gametologous genes and chromosome distribution of sex chromosome-linked repetitive sequences. Zool. Lett. 2016, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopichienpong, N.; Muangmai, N.; Chanhome, L.; Suntrarachun, S.; Twilprawat, P.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Srikulnath, K. Evolutionary dynamics of the gametologous CTNNB1 gene on the Z and W chromosomes of snakes. J. Hered. 2017, 108, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopichienpong, N.; Tawichasri, P.; Chanhome, L.; Phatcharakullawarawat, R.; Singchat, W.; Kantachumpoo, A.; Muangmai, N.; Suntrarachun, S.; Matsubara, K.; Peyachoknagul, S.; et al. A novel method of caenophidian snake sex identification using molecular markers based on two gametologous genes. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4661–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Laopichienpong, N.; Suntronpong, A.; Panthum, T.; Griffin, D.K.; Srikulnath, K. Snake W sex chromosome: The shadow of ancestral amniote super-sex chromosome. Cells 2020, 9, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryamohan, K.; Krishnankutty, S.P.; Guillory, J.; Jevit, M.; Schröder, M.S.; Wu, M.; Kuriakose, B.; Mathew, O.K.; Perumal, R.C.; Koludarov, I. The Indian cobra reference genome and transcriptome enables comprehensive identification of venom toxins. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaz, T.; Srikulnath, K.; Graves, J.A.M. Origin of amniote sex chromosomes: An ancestral super-sex chromosome, or common requirements? J. Hered. 2017, 108, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochvíl, L.; Gamble, T.; Rovatsos, M. Sex chromosome evolution among amniotes: Is the origin of sex chromosomes non-random? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capel, B. Vertebrate sex determination: Evolutionary plasticity of a fundamental switch. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolfi, M.C.; Nakajima, R.T.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Schartl, M. Intersex, hermaphroditism, and gonadal plasticity in vertebrates: Evolution of the Müllerian duct and Amh/Amhr2 signaling. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.L.; Batzel, P.; Titus, T.; Sydes, J.; Desvignes, T.; BreMiller, R.; Draper, B.; Postlethwait, J.H. A hormone that lost its receptor: Anti-Mullerian hormone (amh) in zebrafish gonad development and sex determination. Genetics 2019, 213, 529–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patagonian Pejerrey (Odontesthes hatcheri). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/172797066/verbatim (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Putnam, F.W. Remarks on a supposed nondescript species of Gasterosteus from Massachusetts. Proc. Essex Inst. 1867, 5, 1866–1867. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, M.; Sakai, H.; Goto, A. A new threespine stickleback, Gasterosteus nipponicus sp. nov. (Teleostei: Gasterosteridae), from the Japan sea region. Ichthyol. Res. 2014, 61, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook Stickleback (Culaea inconstans). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2356556 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Hattori, R.S.; Murai, Y.; Oura, M.; Masuda, S.; Majhi, S.K.; Sakamoto, T.; Fernandino, J.I.; Somoza, G.M.; Yokota, M.; Strüssmann, C.A. A Y-linked anti-Müllerian hormone duplication takes over a critical role in sex determination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2955–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, D.L.; Mee, J.A.; Peichel, C.L. Identification of a candidate sex determination gene in Culaea inconstans suggests convergent recruitment of an Amh duplicate in two lineages of stickleback. J. Evol. Biol. 2022, 35, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobaltcap Silverside (Hypoatherina tsurugae). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2411930 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Northern Pike (Esox lucius). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/113226615 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Hilgendorf, F.M. Uebersicht über die japanischen Sebastes-Arten. Ges. Naturforsch. Freunde Berl. 1880, 1880, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shi, H.; Zeng, S.; Ye, K.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, L.; Sun, L.; Tao, W.; et al. A tandem duplicate of anti-Müllerian hormone with a missense SNP on the Y chromosome is essential for male sex determination in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bej, D.K.; Miyoshi, K.; Hattori, R.S.; Strüssmann, C.A.; Yamamoto, Y. A duplicated, truncated amh gene is involved in male sex determination in an old world silverside. G3 Genes. Genomes. Genet. 2017, 7, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Feron, R.; Yano, A.; Guyomard, R.; Jouanno, E.; Vigouroux, E.; Wen, M.; Busnel, J.M.; Bobe, J.; Concordet, J.P.; et al. Identification of the master sex determining gene in Northern pike (Esox lucius) reveals restricted sex chromosome differentiation. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Xie, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Fitzpatrick, C.K.; Vaux, F.; O’Malley, K.G.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, J.; He, Y. A duplicated amh is the master sex-determining gene for Sebastes rockfish in the Northwest Pacific. Open. Biol. 2021, 11, 210063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentinian Silverside (Odontesthes bonariensis Valenciennes, 1835). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/2412370 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Rafati, N.; Chen, J.; Herpin, A.; Pettersson, M.E.; Han, F.; Feng, C.; Wallerman, O.; Rubin, C.J.; Péron, S.; Cocco, A.; et al. Reconstruction of the birth of a male sex chromosome present in Atlantic herring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24359–24368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halm, S.; Rocha, A.; Miura, T.; Prat, F.; Zanuy, S. Anti-Müllerian hormone (Amh/Amh) in the European sea bass: Its gene structure, regulatory elements, and the expression of alternatively-spliced isoforms. Gene 2007, 388, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Xiong, Y.; Xiao, S.; Li, X.Y.; Huang, P.; Liao, Q.; Han, Q.; Lin, Q.; Dan, C.; Zhou, L.; et al. Origin and chromatin remodeling of young X/Y sex chromosomes in catfish with sexual plasticity. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartl, M.; Schories, S.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Nagao, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Bertin, C.; Mourot, B.; Schmidt, C.; Wilhelm, D.; Centanin, L.; et al. Sox5 is involved in germ-cell regulation and sex determination in medaka following co-option of nested transposable elements. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Shinomiya, A.; Sato, T.; Matsuda, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Morrey, C.E.; Shibata, N.; Asakawa, S.; Shimizu, N. DMY is a Y-specific DM-domain gene required for male development in the medaka fish. Nature 2022, 17, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, I.; Kondo, M.; Hornung, U.; Asakawa, S.; Winkler, C.; Shimizu, A.; Shan, Z.; Haaf, T.; Shimizu, N.; Shima, A.; et al. A duplicated copy of DMRT1 in the sex-determining region of the Y chromosome of the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11778–11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, R.; Zahm, M.; Cabau, C.; Klopp, C.; Roques, C.; Bouchez, O.; Eché, C.; Valière, S.; Donnadieu, C.; Haffray, P.; et al. Characterization of a Y-specific duplication/insertion of the anti-Mullerian hormone type II receptor gene based on a chromosome-scale genome assembly of yellow perch, Perca flavescens. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 220, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peichel, C.L.; McCann, S.R.; Ross, J.A.; Naftaly, A.F.S.; Urton, J.R.; Cech, J.N.; Grimwood, J.; Schmutz, J.; Myers, R.M.; Kingsley, D.M.; et al. Assembly of the threespine stickleback Y chromosome reveals convergent signatures of sex chromosome evolution. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/2408877 (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Tsakogiannis, A.; Manousaki, T.; Lagnel, J.; Sterioti, A.; Pavlidis, M.; Papandroulakis, N.; Mylonas, C.C.; Tsigenopoulos, C.S. The transcriptomic signature of different sexes in two protogynous hermaphrodites: Insights into the molecular network underlying sex phenotype in fish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, A.R.; Waite, E.R. Results of the South Australian Museum expedition to strzelecki and cooper creeks. September and October, 1916. (k) Pisces. Trans. R. Soc. S Aust. 1917, 41, 472–475. [Google Scholar]
| Locus ID | SBA6 | SBA8 | SBA12 | SBA14 | SBA16 | SBA19 | SBA23 | % Identity | % Query Cover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100011760 | 397248–397316 | 98.4 | 98.1 | ||||||
| 100017263 | 554368–554436 | 98.1 | 98.4 | ||||||
| 100018397 | 25088227–25088295 | 92.0 | 92.0 | ||||||
| 100021722 | 28916249–28916318 | 64.3 | 64.3 | ||||||
| 100024764 | 2710511–2710579 | 98.6 | 98.6 | ||||||
| 100026092 | 18269334–18269402 | 92.0 | 92.0 | ||||||
| 100026100 | 15105253–15105322 | 64730–64799 | 95.7 (SBA14)/ 98.1 (SBA19) | 97.1 (SBA14)/ 98.4 (SBA19) | |||||
| 100026101 | 15105253–15105322 | 64730–64799 | 95.7 (SBA14)/ 98.1 (SBA19) | 97.1 (SBA14)/ 98.4 (SBA19) | |||||
| 100026527 | 426602–426670 | 426602–426670 | 98.1 | 98.4 | |||||
| 100026834 | 30995241–30995309 | 100.0 | 100 | ||||||
| 100026920 | 10882240–10882308 | 98.1 | 98.4 | ||||||
| 100027734 | 21559150–21559218 | 98.6 | 98.6 | ||||||
| 100033965 | 509282–509350 | 98.1 | 98.4 | ||||||
| 100033966 | 509282–509350 | 98.1 | 98.4 |
| Locus ID | GAC | DLA | LCA | ONI | DRE | OLA | TRU | TNI | XMA | BSP | ACA | LMA | MSA | NNA | GGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100021722 | 20 | 7 | 15 | 11 | 16 | 16 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 16 | scaffold | - | scaffold | micro chromosome | 23 |
| 100026100 | 5 (nrg2b) | 13 | 8 | 2 | 14 | 10 (nrg2b) | 14 | 1 | 23 | 10 | 4 | - | - | 3 | 13 |
| 100026101 | 15 | 3 | 19 | 19 | 17 | 22 | 2 | 10 | 19 | 22 | 1 | 5 | - | 1 | 3 |
| 100011760 | 7 | 21 | scaffold | 10 | 21 | 14 | 15 | - | 11 | 14 | scaffold | 5 | - | micro chromosome | 4 |
| 100017263 | 21 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7 | - | - | - |
| 100018397 | 18 | 8 | 7 | 15 | - | 24 | 16 | 14 | 15 | 24 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 3 |
| 100026920 | 12 (kazna) | 15 | 6 | 20 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 9 (kazna) | 1 | 7 | - | 1 | - | micro chromosome | 21 |
| 100027734 | 5 (mybpc2b) | 12 | 23 | 8 | 24 (mybpc2b) | 19 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 19 | 6 | 8 | - | Z | 31 |
| 100026092 | 8 | 18 | 17 | 4 | 22 | 4 | 20 | - | 9 | 4 | - | 6 | scaffold | 1 | 28 |
| 100024764 | 5 (sdk2b) | 12 | 23 | - | 12 | 19 | - | 2 | 10 | 19 | - | - | scaffold | 2 | 18 |
| 100033965 | 21 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 100033966 | 21 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 100026527 | 2 | 19 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 13 | 5 | 4 | 3 | scaffold | 9 | - | 3 | 10 |
| 100026834 | 9 | 20 | 5 | - | 22 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 3 | scaffold | 1 | 3 |
| Repeat Class | Chromosome 6 | Male-Linked Region 1 | Chromosome 19 | Male-Linked Region 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragments | Percentage (%) | Fragments | Percentage (%) | Fragments | Percentage (%) | Fragments | Percentage (%) | |
| LTR retrotransposon | 9.00 | 4.07 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 21.00 | 7.98 | 11.00 | 4.18 |
| Ty3/Gypsy | 9.00 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 20.00 | 7.60 | 10.00 | 3.80 |
| Ty1/Copia | - | - | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 0.38 | |
| Long terminal repeat (LTR) | 18.00 | 8.14 | 4.00 | 1.81 | 42.00 | 15.97 | 22.00 | 8.37 |
| DNA transposon | 167.00 | 75.57 | 9.00 | 4.07 | 137.00 | 52.09 | 56.00 | 21.29 |
| Helitron | 5.00 | 2.26 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8.00 | 3.04 | 3.00 | 1.14 |
| hAT | 12.00 | 5.43 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 4.00 | 1.52 | 2.00 | 0.76 |
| Terminal inverted repeat (TIR) | ||||||||
| -CACTA | 99.00 | 44.80 | 3.00 | 1.36 | 78.00 | 29.66 | 31.00 | 11.79 |
| -Tc1/mariner | 8.00 | 3.62 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 5.00 | 1.90 | 1.00 | 0.38 |
| -PIF/Harbinger | 4.00 | 1.81 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.00 | 3.42 | 4.00 | 1.52 |
| -Mutator | 39.00 | 17.65 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 33.00 | 12.55 | 15.00 | 5.70 |
| Target site duplication | 18.00 | 8.14 | 4.00 | 1.81 | 42.00 | 15.97 | 22.00 | 8.37 |
| Repeat region (unclassified) | 9.00 | 4.07 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 21.00 | 7.98 | 11.00 | 4.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panthum, T.; Wattanadilokchatkun, P.; Jaisamut, K.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; Antunes, A.; Srikulnath, K. In Silico Chromosome Mapping of the Male-Specific/Linked Loci in the Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo) Suggests Chromosome 19 as the Putative Y Sex Chromosome. Fishes 2023, 8, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100482
Panthum T, Wattanadilokchatkun P, Jaisamut K, Singchat W, Ahmad SF, Muangmai N, Duengkae P, Antunes A, Srikulnath K. In Silico Chromosome Mapping of the Male-Specific/Linked Loci in the Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo) Suggests Chromosome 19 as the Putative Y Sex Chromosome. Fishes. 2023; 8(10):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100482
Chicago/Turabian StylePanthum, Thitipong, Pish Wattanadilokchatkun, Kitipong Jaisamut, Worapong Singchat, Syed Farhan Ahmad, Narongrit Muangmai, Prateep Duengkae, Agostinho Antunes, and Kornsorn Srikulnath. 2023. "In Silico Chromosome Mapping of the Male-Specific/Linked Loci in the Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo) Suggests Chromosome 19 as the Putative Y Sex Chromosome" Fishes 8, no. 10: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100482
APA StylePanthum, T., Wattanadilokchatkun, P., Jaisamut, K., Singchat, W., Ahmad, S. F., Muangmai, N., Duengkae, P., Antunes, A., & Srikulnath, K. (2023). In Silico Chromosome Mapping of the Male-Specific/Linked Loci in the Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo) Suggests Chromosome 19 as the Putative Y Sex Chromosome. Fishes, 8(10), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8100482













