In lumpfish We Trust? The Efficacy of Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus to Control Lepeophtheirus salmonis Infestations on Farmed Atlantic Salmon: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Lumpfish Efficacy
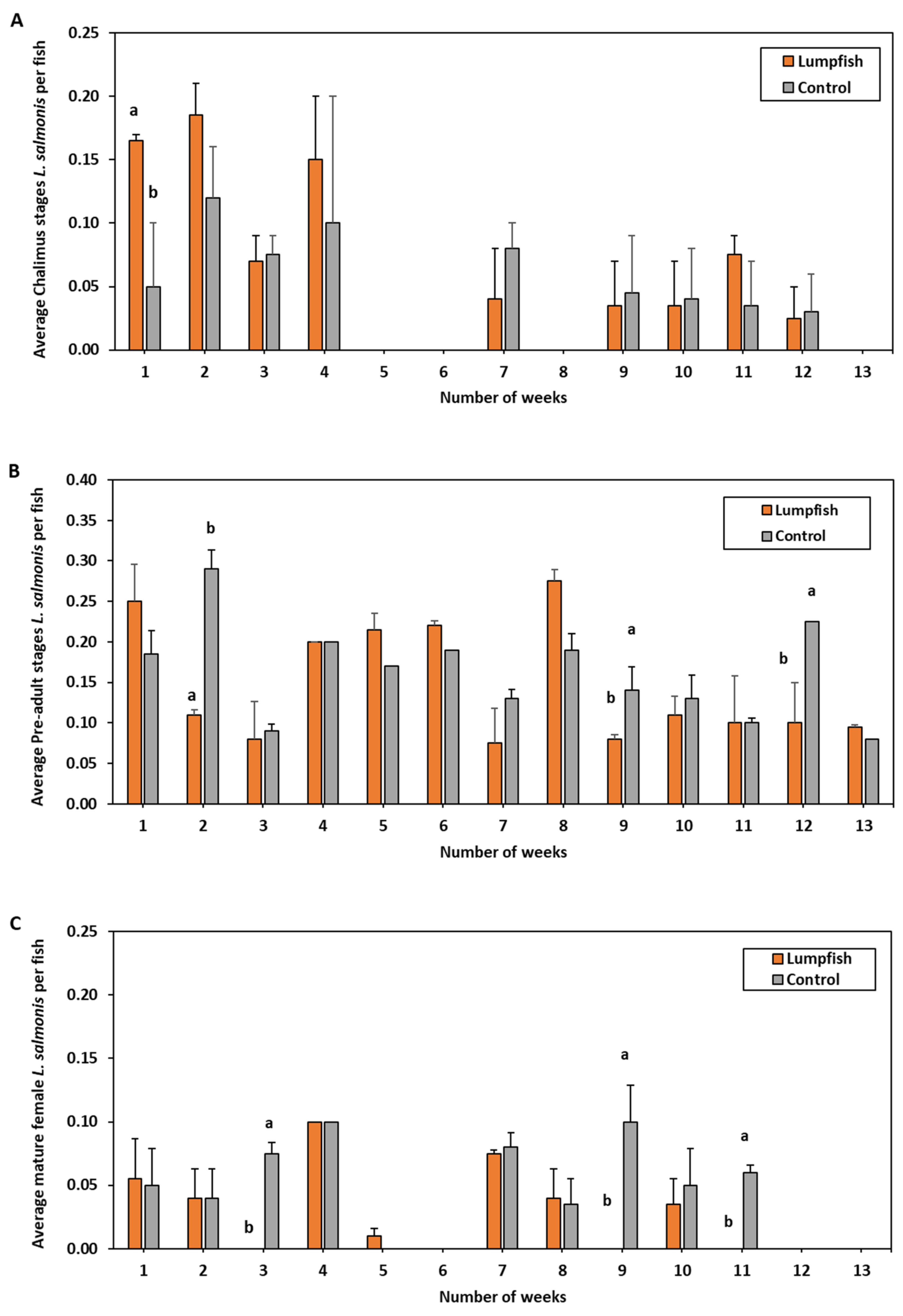
3. Results: Small-Scale Studies
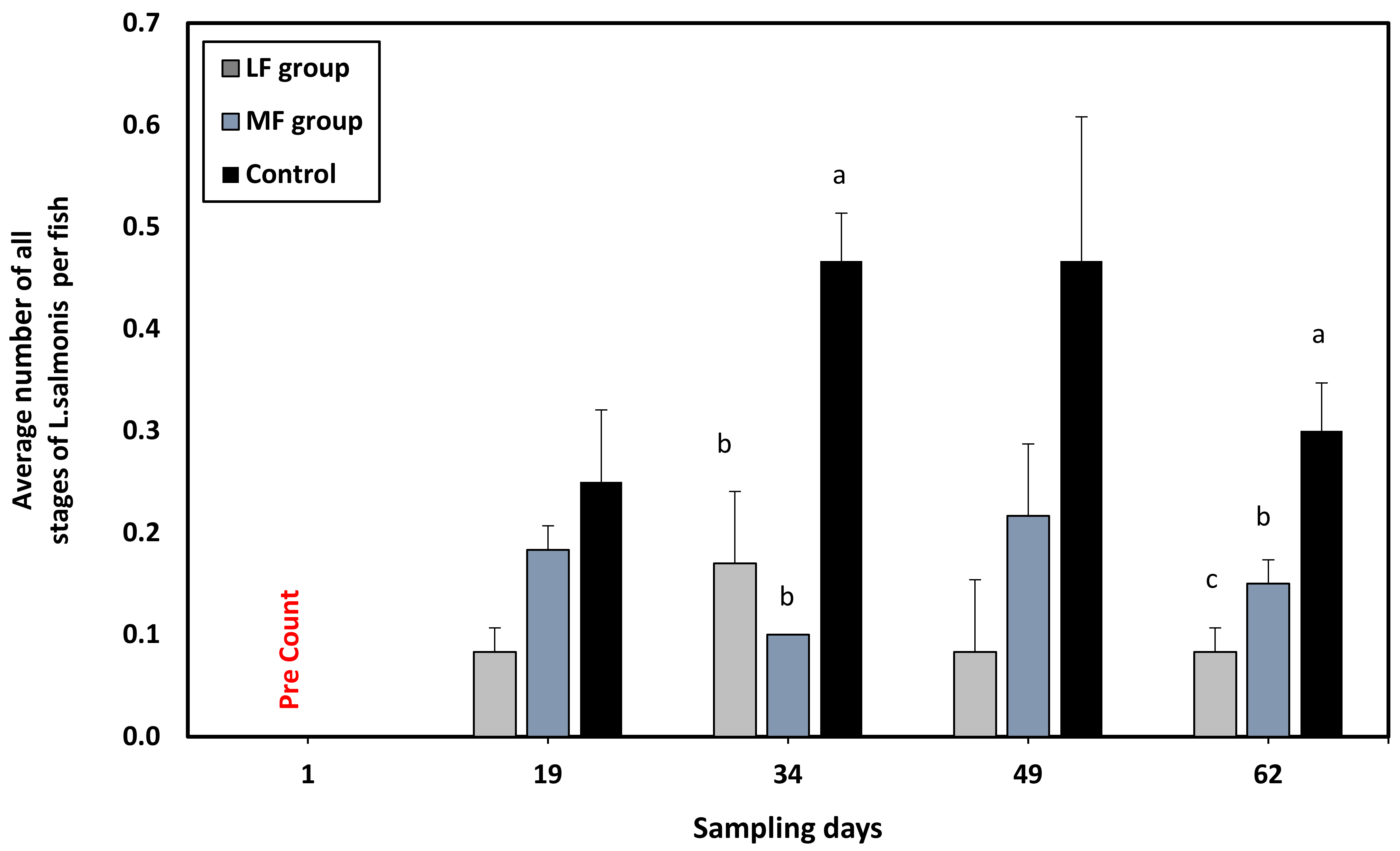
3.1. Different Density of Lumpfish: Effect on Occurrence of L. salmonis on Atlantic Salmon
3.2. Habituation of Lumpfish Prior to Transfer from Net to Pens: Effect on Occurrence of L. salmonis
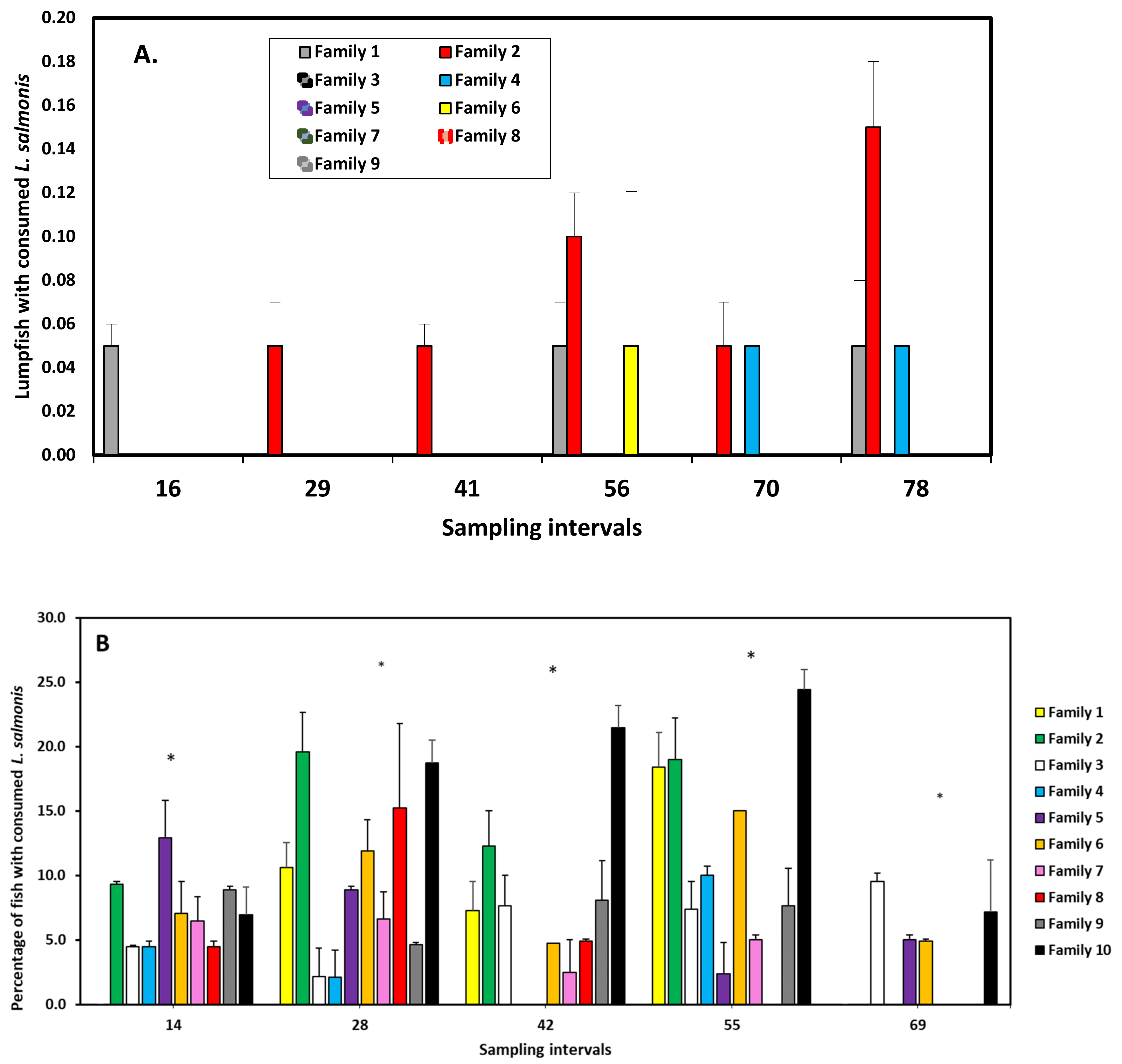
3.3. Lumpfish Grazing on L. salmonis: Possible Parental Control
3.4. Effects of Lumpfish Size on Sea Lice Grazing
4. Results: Large-Scale Observations
4.1. Large-Scale Trial: Autumn and Winter
4.2. Large-Scale Observations: Year Round
4.3. Large-Scale Observation: Summer to Winter
4.4. Large-Scale Observation: Combination of Lumpfish and Tarpaulin Net (Lice Skirt)
4.5. Large-Scale Studies: The Faroe Islands
5. Discussion
5.1. Small-Scale Studies
5.2. Is Lumpfish Consumption of L. salmonis a Heritable Trait?
5.3. Size-Related Sea Lice Grazing of Lumpfish
5.4. Large-Scale Studies
6. Summary of Effects Found Using Lumpfish
7. Conclusion and Best Practice to Increase Lumpfish Efficacy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Igboeli, O.O.; Fast, M.D.; Heumann, J.; Burka, J.F. Role of P-glycoprotein in emamectin benzoate (SLICE (R)) resistance in sea lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Aquaculture 2012, 344, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igboeli, O.O.; Burka, J.F.; Fast, M.D. Lepeophtheirus salmonis: A persisting challenge for salmon aquaculture. Anim. Front. 2014, 4, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolofia, J.; Wilen, J.E.; Asche, F. The cost of lice: Quantifying the impacts of parasitic sea lice on farmed salmon. Mar. Res. Econ. 2017, 32, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrissen, O.; Jones, S.; Asche, F.; Guttormsen, A.; Skilbrei, O.T.; Nilsen, F.; Horsberg, T.E.; Jackson, D. Salmon lice—Impact on wild salmonids and salmon aquaculture. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiftesvik, A.B.; Bjelland, R.M.; Durif, C.M.F.; Johansen, I.S.; Browman, H.I. Delousing of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) by cultured vs. wild ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta). Aquaculture 2013, 402–403, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Foss, A.; Vikingstad, E.; Elvegård, T.A. The use of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) to control sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis Krøyer) infestations in intensively farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2014, 424–425, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.; Treasurer, J.W.; Pooley, C.L.; Keay, A.J.; Lloyd, R.; Imsland, A.K.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Cleaner fish for sea-lice control in salmon farming: Challenges and opportunities using lumpfish. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Foss, A.; Vikingstad, E.; Elvegård, T.A. Notes on the behaviour of lumpfish with and without Atlantic salmon present. J. Ethol. 2014, 32, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Nytrø, A.V.; Foss, A.; Vikingstad, E.; Elvegård, T.A. Assessment of growth and sea lice infection levels in Atlantic salmon stocked in small-scale cages with lumpfish. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Nytrø, A.V.; Foss, A.; Vikingstad, E.; Elvegård, T.A. Feeding preferences of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) maintained in open net-pens with Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2015, 436, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Nytrø, A.V.; Foss, A.; Vikingstad, E.; Elvegård, T.A. Assessment of suitable substrates for lumpfish in sea pens. Aquac. Int. 2015, 23, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissonnot, L.; Kharlova, I.; Iversen, N.S.; Staven, F.R.; Austad, M. Characteristics of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) with high cleaning efficacy in commercial Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) production. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsen, W.; Sagerup, K.; Remen, M.; Bloch-Hansen, K.; Imsland, A.K.D. Caligus elongatus and other sea lice of the genus Caligus as parasites of farmed salmonids: A review. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojiri, M.; Ho, J.-S. Systematics of the Caligidae, Copepods Parasitic on Marine Fishes; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 18, pp. 1–448. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, M.J. Ecology of sea lice parasitic on farmed and wild fish. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J. The global economic cost of sea lice to the salmonid farming industry. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.C.; Treasurer, J.W.; Bravo, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Kabata, Z. A review of the impact of parasitic copepods on marine aquaculture. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 229–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata, Z. Parasitic Copepoda of British Fishes; The Ray Society: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, A.W.; Wadsworth, S.L. Sealice on Salmonids: Their Biology and Control. Adv. Parasitol. 1999, 44, 233–337. [Google Scholar]
- Jónsdóttir, Ó.D.B.; Imsland, A.K.; Kennedy, J. Lumpfish biology, genetics, use of microsatellites and SNP for population genetics and parental assignment, seek for QTLs. In Cleaner Fish Biology and Aquaculture Applications; Treasurer, J.W., Ed.; 5M Publishing Ltd.: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 218–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Jónsson, S.Þ.; Ólafsson, H.G.; Kasper, J.M. Observations of vertical movements and depth distribution of migrating female lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) in Iceland from data storage tags and trawl surveys. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J. Synopsis of biological data on the lumpsucker Cyclopterus lumpus (Linnaeus, 1758); FAO Fisheries Synopsis No. 147; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; Volume 147, p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Imsland, A.K.; Hanssen, A.; Reynolds, P.; Nytrø, A.V.; Jonassen, T.M.; Hangstad, T.A.; Elvegård, T.A.; Urskog, T.C.; Mikalsen, B. It works! Lumpfish can significantly lower sea lice infections in large scale salmon farming. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio036301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton-Warberg, M. An overview of cleaner fish use in Ireland. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasurer, J.; Prickett, R.; Zietz, M.; Hempleman, C.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Cleaner fish rearing and deployment in the UK. In Cleaner Fish Biology and Aquaculture Applications; Treasurer, J.W., Ed.; 5M Publishing Ltd.: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 376–391. [Google Scholar]
- Steinarson, A.; Árnason, T. Rearing of cleaner fish in Iceland. In Cleaner Fish Biology and Aquaculture Applications; Treasurer, J.W., Ed.; 5M Publishing Ltd.: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 420–435. [Google Scholar]
- Eliasen, K.; Danielsen, E.; Johannesen, Á.; Joensen, L.L.; Patursson, E.J. The cleaning efficacy of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) in Faroese salmon (Salmo salar L.) farming pens in relation to lumpfish size and season. Aquaculture 2018, 488, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Eliassen, G.; Mortensen, A.; Hansen, Ø.J.; Puvanendran, V.; Hangstad, T.A.; Jónsdóttir, Ó.D.B.; Emaus, P.A.; Elvegård, T.A.; et al. Is cleaning behavior in lumpfish (Cycloptherus lumpus) parentally controlled? Aquaculture 2016, 459, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Nytrø, A.V.; Eliassen, G.; Hangstad, T.A.; Jónsdóttir, Ó.D.B.; Emaus, P.A.; Elvegård, T.A.; Lemmens, S.C.A.; Rydland, R.; et al. Effects of lumpfish size on foraging behaviour and co-existence with sea lice infected Atlantic salmon in sea cages. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.T.; Overton, K.; Stien, L.H.; Oppedal, F.; Dempster, T. Effect of cleaner fish on sea lice in Norwegian salmon aquaculture: A national scale data analysis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, A.J.; Papadopoulou, A.; Gutierrez, C.; Rey, S.; Davie, A.; Migaud, H. Sustainable production and use of cleaner fish for the biological control of sea lice: Recent advances and current challenges. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, K.; Dempster, T.; Oppedal, F.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Gismervik, K. Salmon lice treatments and salmon mortality in Norwegian aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 1398–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, K.; Dempster, T.; Oppedal, F.; Kristiansen, T.S. Sea lice removal by cleaner fish in salmon aquaculture: A review of the evidence base. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2020, 12, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Frogg, N.E.; Stefansson, S.O.; Reynolds, P. Improving sea lice grazing of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) by feeding live feeds prior to transfer to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) net-pens. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Reynolds, P.; Hangstad, T.A.; Madura, S.; Hagen, S.; Jónsdóttir, Ó.D.B.; Spetland, F.; Lindberg, K.S. Quantification of grazing efficacy, growth and health score of different lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) families: Possible size and gender effects. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, B.A.; Consuegra, S.; Carcia de Leaniz, C. Personality profiling may help select better cleaner fish for sea-lice control in salmon farming. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 243, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Reynolds, P.; Remen, M.; Bloch-Hansen, K.; Sagerup, K.; Hemmingsen, W.; Mathisen, R.; Myklebust, E.A. The possible use of lumpfish against Caligus elongatus: A mini review. J. Ocean Uni. China 2020, 19, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.; Reynolds, P.; Jonassen, T.M.; Hangstad, T.A.; Noble, T.; Wilson, W.; Mackie, J.A.; Elvegård, T.A.; Urskog, T.C.; Mikalsen, B. Comparison of diet composition, feeding, growth and health of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) fed either feed blocks or pelleted commercial feed. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 1952–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Reynolds, P.; Lorentzen, M.; Eilertsen, R.A.; Micallef, G.; Tvenning, R. Improving survival and health of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus L.) by the use of feed blocks and operational welfare indicators (OWIs) in commercial Atlantic salmon cages. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, K.; Bui, S.; Oppedal, F.; Bjelland, R.; Nola, V.; Dempster, T. Acclimatisation with lice-infested salmon improves cleaner fish lice consumption. Aquac. Environ. Int. 2021, 13, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staven, F.R.; Nordeide, J.T.; Imsland, A.K.; Andersen, P.; Iversen, N.S.; Kristensen, T. Is habituation measurable in lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus when used as cleaner fish in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar aquaculture? Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, G.F.; Groner, M.L.; Cohen, A.; Imsland, A.K.; Revie, C.W. Modelling the use of lumpfish to control of sea lice on Atlantic salmon farms: Interactions with mate limitation, temperature and treatment rules. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2019, 155, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.B. A review of local adaptation in Salmonidae, with particular reference to pacific and Atlantic salmon. Aquaculture 1991, 98, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomen, R.A.; Hutchings, J.A. Genetic variability in reaction norms in fishes. Environ. Rev. 2005, 23, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.T.; Kelley, J.L.; Graves, J.A.; Magurran, A.E. Kin structure and shoal composition dynamics in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Oikos 2004, 106, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackey, A.C.R.; Boughman, J.W. Divergent sexual selection via male competition: Ecology is key. J. Evol. Biol. 2013, 26, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, N.J.; Smiseth, P.T.; Kolliker, M.; Champagne, F.A.; Curley, J.M. Genetics and epigenetics of parental care. In The Evolution of Parental Care; Royle, N.J., Smiseth, P.T., Kolliker, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 304–324. [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, K.E.; Bell, A.M. Paternal care in a fish: Epigenetics and fitness enhancing effects on offspring anxiety. Proc. R. Soc. B 2014, 281, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia de Leaniz, C.; Gutierrez Rabadan, C.; Barrento, S.I.; Stringwell, R.; Howes, P.N.; Whittaker, B.A.; Minett, J.F.; Smith, R.G.; Pooley, C.L.; Overland, B.J.; et al. Addressing the welfare needs of farmed lumpfish: Knowledge gaps, challenges and solutions. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 14, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, K.; Bui, S.; Oppedal, F.; Dempster, T. Sea lice prevention strategies affect cleaner fish delousing efficacy in commercial Atlantic salmon sea cages. Aquac. Environ. Int. 2020, 12, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøntvedt, R.N.; Kristoffersen, A.B.; Jansen, P.A. Reduced exposure of farmed salmon to salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis L.) infestation by use of plankton nets: Estimating the shielding effect. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, L.H.; Lind, M.B.; Oppedal, F.; Wright, D.W.; Seternes, T. Skirts on salmon production cages reduced salmon lice infestations without affecting fish welfare. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, L.H.; Nilsson, J.; Hevrøy, E.M.; Oppedal, F.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Lien, A.M.; Folkedal, O. Skirt around a salmon sea cage to reduce infestation of salmon lice resulted in low oxygen levels. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 51, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppedal, F.; Dempster, T.; Stien, L. Environmental drivers of Atlantic salmon behaviour in sea-cages:a review. Aquaculture 2011, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerset, I.; Jensen, B.B.; Bornø, B.; Haukaas, A.; Brun, E. Fiskehelserapporten 2020 (Technical Rapport 41a/2021, in Norwegian with Abstract in English). Norwegian Veterinary Institute. 2020. Available online: https://www.vetinst.no/rapporter-og-publikasjoner/rapporter/2021/fiskehelserapporten-2020 (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Hvas, M.; Folkedal, O.; Imsland, A.; Oppedal, F. Metabolic rates, swimming capabilities, thermal niche and stress response of the lumpfish, Cyclopterus lumpus. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio036079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staven, F.R.; Nordeide, J.T.; Gesto, M.; Andersen, P.; Patel, D.M.; Kristensen, T. Behavioural and physiological responses of lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) exposed to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) sensory cues. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsdóttir, K.E.; Hvas, M.; Alfredsen, J.A.; Føre, M.; Alver, M.O.; Bjelland, H.V.; Oppedal, F. Fish welfare based classification method of ocean current speeds at aquaculture sites. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez Rabadan, C.; Spreadbury, C.; Consuegra, S.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Development, validation and testing of an Operational Welfare Score Index for farmed lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus L. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
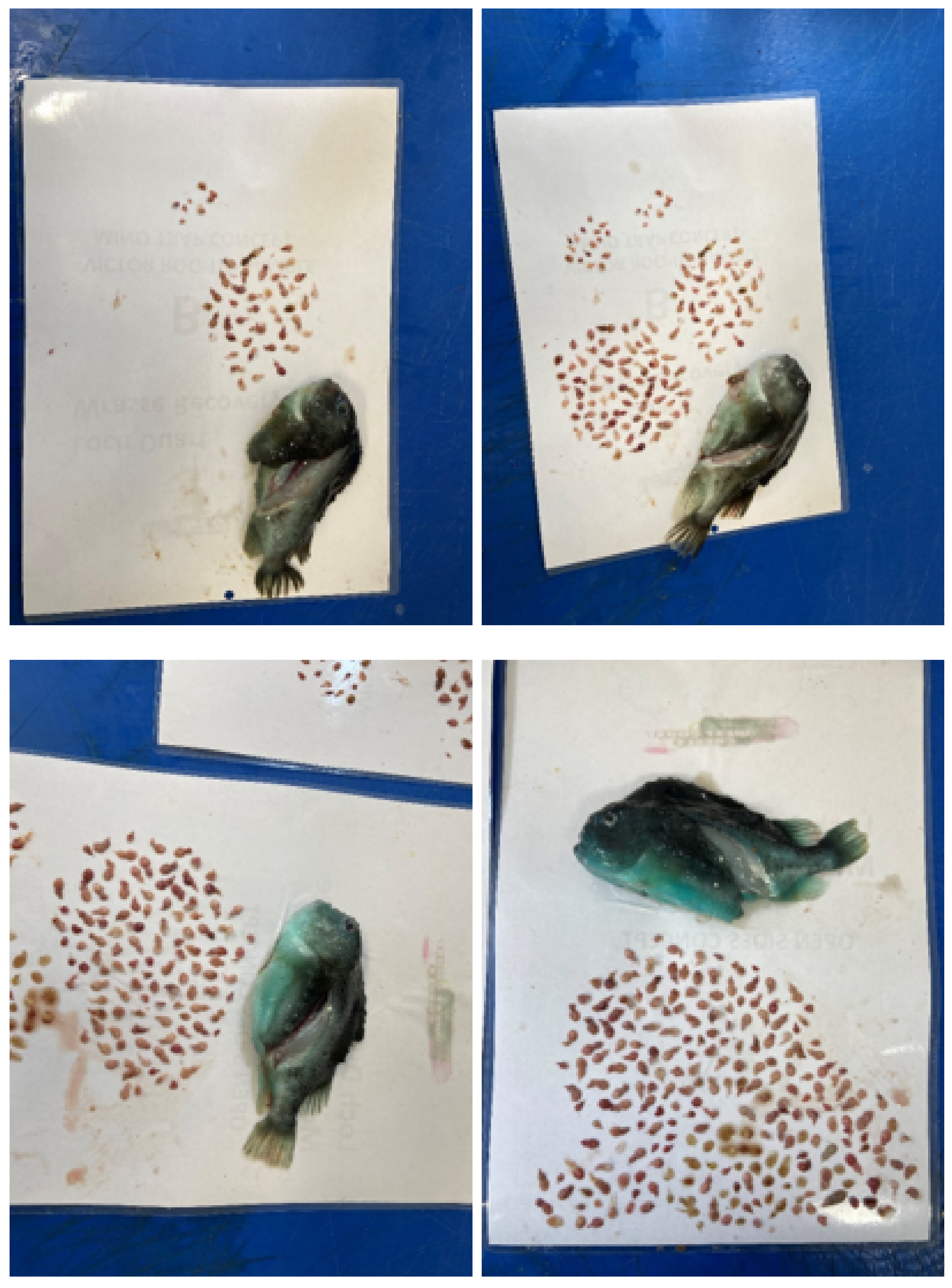



| Citation | Experimental Period and Temperature | Experimental Unit (Number and Size) | Experimental Site/Country | Size and Density of Lumpfish (Numbers in Relation to Salmon) | Effect Investigated | Effect on L. salmonis Found? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small-scale studies | ||||||
| Imsland et al. (2014a) [6] | June–August, 9.0–12.1 °C | 4 small sea cages 5 × 5 × 5 m (125 m3) | Nordland county, Norway | 53–182 g 10% and 15% | Different density of lumpfish | Yes, increased effect at 15% density |
| Imsland et al. (2016a) [28] | May–August, 7.1–13.2 °C | 9 small sea cages, 5 × 5 × 5 m (125 m3) | Nordland county, Norway | 169–549 g 10% | Different families, parental effect | Yes, and varied between families |
| Imsland et al. (2019a) [34] | May–July, 7.2–13.3 °C | 4 small sea cages 5 × 5 × 5 m (125 m3) | Nordland county, Norway | 114–180 g 10% | Habituation of lumpfish | Yes, and habituation of lumpfish increased the effect |
| Imsland et al. (2021) [35] | September–December, 10.5–6.8 °C | 10 small sea cages, 5 × 5 × 5 m (125 m3) | Nordland county, Norway | 30–123 g, 12% | Different families | Yes, and varied between families |
| Large-scale studies | ||||||
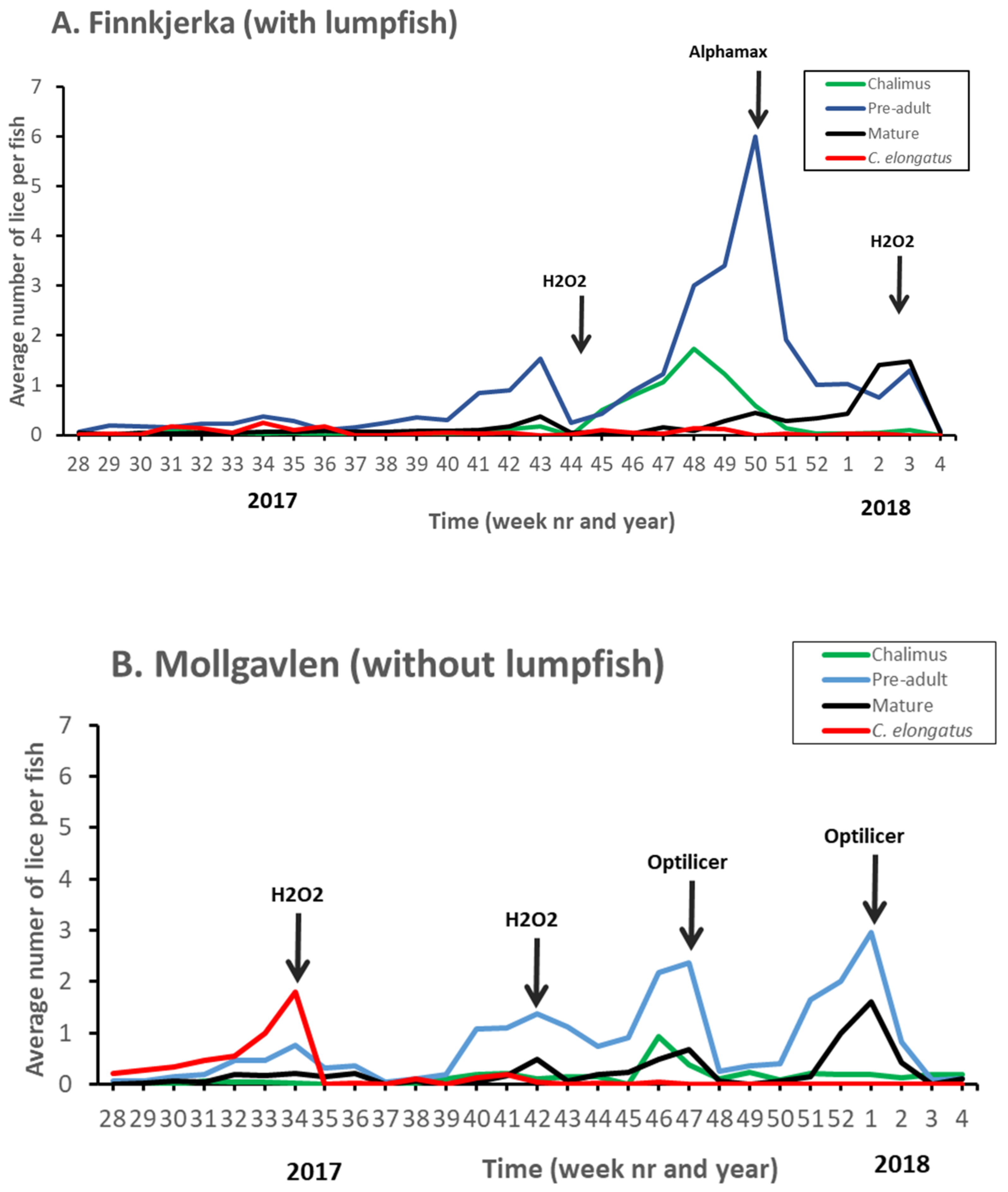
| Imsland et al. (unpublished data) | September–December, 12.1–8.5 °C | 4 large sea cages (90 m circumference) | Røssøy, Nordland county, Norway | 71–125 g, 9.5% | Large-scale evaluation of sea lice grazing in lumpfish | Yes. Increasing effect of lumpfish seen during the trial |
| Imsland et al. (unpublished data) | July–January, 12.2-5.5 °C | 12 large sea cages (160 m circumference, 58,900 m3 volume) | Nordlaks AS, Nordland county, Norway | 32–157 g, 6% | Large-scale evaluation of sea lice grazing in lumpfish | Yes. Less mechanical treatment, 600 g larger salmon at slaughter with lumpfish present |
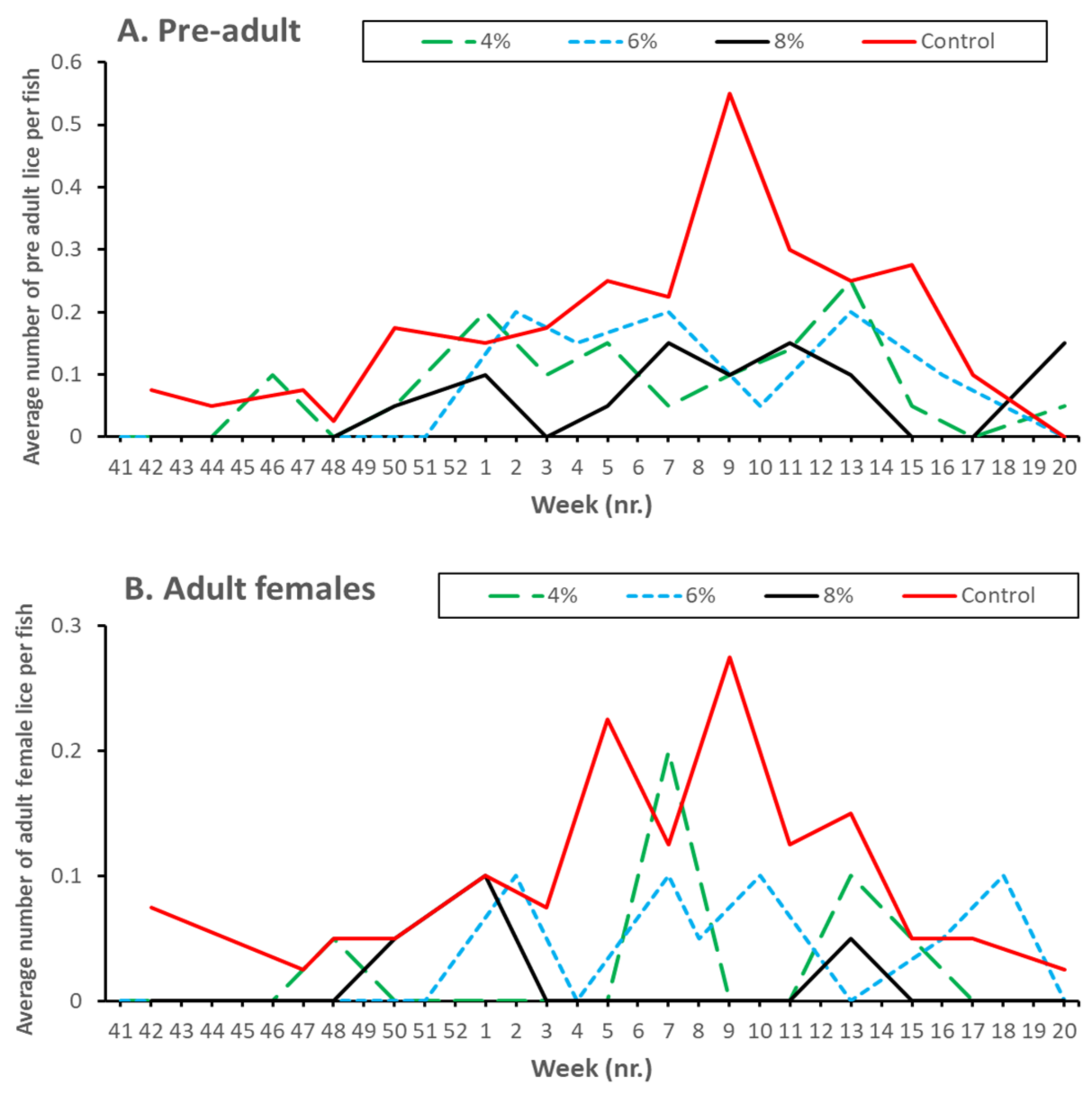
| Imsland et al. (2018a) [23] | October–May, 8.3 °C in October 3.6 °C in March 6.8 °C in May | 8 large sea cages (130 m circumference, 37,688 m3 volume) | Lerøy Aurora AS, Troms county, Norway | 25–115 g, 4, 6, and 8% | Different densities of lumpfish in large-scale sea cages | Yes, similar effect seen at all densities |
| Boissonnot et al. [12], | Year round 4–15 °C | Large sea cages from 8 farming sites | Norway, northern Trøndelag county | 10 and 1050 g (average of 129.5 ± 131.1 g), density not given | Cleaning efficacy of lumpfish in relation to size, season, diet and sex | Yes, Proportions of lumpfish with sea lice in their stomachs varied from 0 to 47% (average of 8.7% for the whole study). Sea lice grazing most efficient in August –October |
| Eliasen et al. (2018) [27], Kirsten Eliasen, Fiskaaling, Faroe Islands, pers. comm.) | Year round, 6–11 °C | Large sea cages from 9 farming sites | Faroe Islands | 13–545 g, Density not given | Cleaning efficacy of lumpfish in relation to size and season | Yes, but seasonal effect seen. Sea lice grazing most efficient during October–April |
| Eva Dögg Jóhannesdóttir, Arctic Fish Ltd. (pers. comm.) | June–December, 10.1–3.2 °C | 7 sea pens (160 m circumference) | Iceland, Dýrafjörður | 20–255 g, 8–10% | Comparison of sea lice at sites with and without lumpfish | Yes, significantly lower L. salmonis with lumpfish present |
| Hjörtur Methúsalemsson, Arnarlax Ltd. (pers. comm.) | September–September (one year) 1.9 °C (February) 11.1 °C (early September). | 12 sea pens (160 m circumference) | Iceland, Arnarfjörður | 32–340 g 8–10% | Comparison of sea lice at sites with and without lumpfish | Yes, significantly lower L. salmonis with lumpfish present |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imsland, A.K.D.; Reynolds, P. In lumpfish We Trust? The Efficacy of Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus to Control Lepeophtheirus salmonis Infestations on Farmed Atlantic Salmon: A Review. Fishes 2022, 7, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050220
Imsland AKD, Reynolds P. In lumpfish We Trust? The Efficacy of Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus to Control Lepeophtheirus salmonis Infestations on Farmed Atlantic Salmon: A Review. Fishes. 2022; 7(5):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050220
Chicago/Turabian StyleImsland, Albert Kjartan Dagbjartarson, and Patrick Reynolds. 2022. "In lumpfish We Trust? The Efficacy of Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus to Control Lepeophtheirus salmonis Infestations on Farmed Atlantic Salmon: A Review" Fishes 7, no. 5: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050220
APA StyleImsland, A. K. D., & Reynolds, P. (2022). In lumpfish We Trust? The Efficacy of Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus to Control Lepeophtheirus salmonis Infestations on Farmed Atlantic Salmon: A Review. Fishes, 7(5), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050220







