Abstract
Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND), caused by the bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus, is a major threat to global shrimp aquaculture. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic effects of phage therapy in Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with AHPND-causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Phage application at various concentrations significantly improved shrimp survival, with the 1 ppm group demonstrating the highest survival rate. Enzymatic assays revealed that phage-treated shrimp exhibited enhanced immune enzyme activities, including acid phosphatase (ACP), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), and lysozyme (LZM). In addition, antioxidant defenses such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) significantly improved, accompanied by reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. Serum biochemical analyses demonstrated marked improvements in lipid metabolism, particularly reductions in triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), alongside higher levels of beneficial high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Transcriptomic analysis identified 2274 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), notably enriched in pathways involving fatty acid metabolism, peroxisome functions, lysosomes, and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling. Specifically, phage treatment upregulated immune and metabolic regulatory genes, including Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MYD88), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), indicating activation of innate immunity and antioxidant defense pathways. These findings suggest that phage therapy induces protective immunometabolic adaptations beyond its direct antibacterial effects, thereby providing an ecologically sustainable alternative to antibiotics for managing bacterial diseases in shrimp aquaculture.
Key Contribution:
This study demonstrates that phage therapy significantly improves the survival, immune response, and antioxidant capacity of Litopenaeus vannamei under Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge by modulating immune and metabolic signaling pathways. This suggests that phage therapy holds potential to support the development of antibiotic-free aquaculture systems.
1. Introduction
Shrimp farming has become a major player of global seafood production, showing impressive growth in recent years. According to a recent report published in February 2025, global farmed shrimp production reached approximately 5.6 million metric tons (MMT) in 2023, representing a slight decline of 0.4% compared to 2022. However, a positive growth of about 4.8% is projected for 2024, with production expected to reach nearly 5.88 MMT [1]. Commercial shrimp farming is focused on species such as Penaeus monodon, Litopenaeus stylirostris, Litopenaeus vannamei, and Marsupenaeus japonicus. However, these species remain highly susceptible to viral and bacterial diseases that threaten the sustainability of farming under intensive aquaculture conditions [2]. With the rapid expansion of aquaculture systems and increasing environmental pressures, the frequency and severity of bacterial outbreaks have been increasing, causing significant economic losses worldwide [3].
Antibiotics have long played a key role in aquaculture, helping to prevent and control diseases in fish and other aquatic animals. However, misuse and overuse of antibiotics have accelerated the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, posing risks to human and environmental health [4]. Antibiotic residues in aquaculture products may enter the human food chain, leading to the spread of antibiotic resistance [5]. Therefore, safe and effective alternatives to antibiotics are urgently needed to control diseases in aquaculture [6]. Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a pathogen primarily associated with seafood, can lead to acute gastroenteritis in humans and is known to infect shrimp, including Penaeus vannamei [7,8,9]. In addition, certain strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND), which has resulted in severe mortality rates (up to 100%) in aquaculture farms of marine shrimp species such as Penaeus vannamei and Penaeus monodon [10].
Bacteriophages, often called phages, are a unique type of virus that target and destroy bacteria. In aquaculture, phages have received increasing attention as a promising alternative to antibiotics [11,12]. Since phages are highly specific, they can destroy target pathogens without destroying the beneficial microbiota, making them a selective and environmentally friendly therapeutic approach [13]. Compared with conventional antibiotics, phages are naturally abundant, economically feasible, and less likely to induce antimicrobial resistance [14]. Recent studies have shown that phage P20211219001–1 exhibits high host specificity and potent lytic activity against Vibrio parahaemolyticus, with optimal performance at a low MOI (0.001). It stays stable over a wide range of temperatures (4–50 °C) and pH levels (3–11). It also helps the hosts survive better in both Artemia salina and Litopenaeus vannamei, especially when used as a preventive measure [15]. In addition, biocontrol experiments showed that pVp-1 was effective in reducing bacterial populations in infected oysters through water baths and surface treatments. Inactivation rates of 90% and 99% were achieved at 48 and 72 h after infection, respectively [16].
In this study, we investigated the efficacy of phage therapy in protecting Litopenaeus vannamei from AHPND infection caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus and the underlying molecular mechanisms. We assessed the effects of different phage concentrations on shrimp survival, histopathological changes, and gene expression responses by transcriptome analysis. This study aims to evaluate phage therapy as a sustainable and effective strategy for bacterial disease control in shrimp aquaculture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria and Phages
The National Pathogen Collection Center for Aquatic Animals at Shanghai Ocean University supplied the strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The stocks were maintained at −50 °C with 50% glycerol. Bacteria were cultivated for 24 h on TCBS agar plates following the commencement of the experiment. The cells were then harvested, washed with PBS to obtain the stock solution (OD600 = 1), and diluted according to the median lethal concentration (LC50) for shrimp. The phage stocks were provided by Noli (Shanghai) Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Experimental Animals and Facilities
The experiment was conducted at a shrimp farm in Dongying, Shandong, China. Healthy Litopenaeus vannamei of similar size, free from visible diseases, were selected and acclimated in 250 L plastic tanks for 24 h before the experiment to allow adaptation to the environment. Each experimental group consisted of three replicates, with 40 shrimp in each replicate, amounting to a total of 600 shrimp. During the experiment, we kept the water parameters steady at (24.0 ± 1.5) °C, pH 8.5 ± 0.5, dissolved oxygen levels at or above 6.0 mg/L, and nitrate levels below 0.03 mg/L.
2.3. Phage Treatment Experiment
Shrimp were randomized to separate treatment groups in order to assess the phages’ therapeutic impact against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. These included a control group that was given the same volume of PBS buffer (P0) and several groups treated with phage at concentrations of 0.5 ppm (P1), 1 ppm (P2), 2 ppm (P3), and 4 ppm (P4). Each group had three replicates, with 40 shrimp in each, bringing our total to 600 shrimp. A pre-experimental trial determined the median lethal concentration (LC50) of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as 7.3 × 106 CFU/mL, and shrimp were injected with this concentration to induce infection. Two hours post-injection, different concentrations of phage were applied by immersion. The shrimp were maintained under the same environmental conditions for seven days, during which mortality was recorded daily, and samples for further examination were gathered at the conclusion of the experiment.
2.4. Sample Collection
At the end of the phage challenge experiment (7 days post-infection and phage treatment), 15 shrimp from each group were randomly selected for sampling. All shrimp were anesthetized with tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222) prior to sampling to minimize suffering. Hemolymph was collected from the ventral sinus using a sterile syringe, and then centrifuged at 3000× g for 10 min at 4 °C to obtain serum, which was stored at −80 °C for further analysis. The hepatopancreas and intestines were carefully excised with sterile scissors and forceps, immediately placed on dry ice for temporary preservation, and subsequently stored at −80 °C. All procedures for culturing and sampling were performed following the ethical guidelines for laboratory animals issued by Shanghai Ocean University.
2.5. Immune and Antioxidant Parameter Analysis
A total of 15 shrimp per group (five per tank) were randomly selected for immune and antioxidant capacity analysis. The parameters included alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), total cholesterol (T-CHO), lysozyme (LZM), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), acid phosphatase (ACP), superoxide dismutase (SOD), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) content. The enzyme activity for ALT and AST was defined as the quantity of enzyme required to oxidize NADH to NAD+, which leads to a decrease in absorbance by 0.001 per minute at 340 nm in a 3 mL reaction system that contained 1 mL of serum at 25 °C. For ACP and AKP, one unit was defined as the amount of enzyme that produces 1 mg of phenol per gram of tissue protein when reacting with the substrate at 37 °C and for 30 min and 15 min, respectively. A unit of GSH-PX was identified as the enzyme concentration necessary to reduce the GSH concentration by 1 μmol/L per minute at 37 °C. For CAT, one unit was the quantity of enzyme that decomposes hydrogen peroxide in a system resulting in an absorbance decrease of 0.50–0.55 per second per gram of tissue protein. The MDA content was measured based on the absorbance of the reaction with thiobarbituric acid (TBA) at 532 nm. For T-AOC, one unit was defined as the amount of enzyme that increases absorbance by 0.01 per minute at 37 °C per mL of serum or plasma. For SOD, a unit was defined as the enzyme quantity that achieves a 50% inhibition rate in a 1 mL reaction system per mg of tissue protein. The test kits are provided by Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China).
2.6. Transcriptome Analysis
For transcriptome analysis, hepatopancreas tissues from five shrimp per replicate (a total of 15 shrimp per group) were collected and sent for sequencing. Samples from P0, P1, P2, P3, and P4 were analyzed. Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China) constructed and sequenced the library. Oligo(dT) magnetic beads were utilized to enrich mRNA, which was then broken up and utilized as a template for the production of first- and second-strand cDNA. Following purification, the double-stranded cDNA was subjected to adapter ligation, A-tailing, and end repair. In order to create the cDNA library, we then used AMPure XP beads to choose fragment sizes and PCR to enrich the result. Using CASAVA for base calling, we transformed the raw picture data from Illumina HiSeqTM sequencing into raw sequencing reads. Raw readings were filtered using Trimmomatic to provide clean data. We used DESeq2 to perform differential expression analysis, establishing significant criteria at an FDR < 0.01, |log2(FoldChange)| > 1, and padj ≤ 0.05. Gene expression levels were computed in terms of FPKM. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were performed on DEGs using the clusterProfiler R package (https://www.r-project.org/).
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis
To ensure the reliability of the transcriptome data and to examine major immune and oxidative pathways, five functionally important genes (TLR4, MYD88, IL-1β, Nrf2, and PPAR) were initially selected for qPCR validation based on their pivotal roles in Toll-like receptor signaling, oxidative stress defense, and lipid metabolism, which are all essential pathways identified in the KEGG enrichment analysis. In addition, five representative DEGs (ChyBII, COX5B, GAD, CHST5, and CHST1) with notable differential expression between the P0 and P2 groups were also selected for qPCR validation to further confirm the consistency between transcriptomic and qPCR results.
Total RNA was extracted from hepatopancreas tissues (n = 3 per group) using Trizol Reagent (Tiangen, Beijing, China) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The integrity of the RNA was confirmed via 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, and concentration was measured using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). First-strand cDNA synthesis was carried out using the NovoScript® Plus All-in-one 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (Novoprotein, Shanghai, China).
Gene-specific primers were designed based on sequences from the transcriptome, using Primer 5 software, and were synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). qPCR was performed using NovoStart® SYBR qPCR SuperMix Plus (Novoprotein, Shanghai, China) on a LightCycler system (Roche, Shanghai, China). The thermal cycling involved an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 58 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate. Gene expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method, with β-actin serving as the internal reference gene. The primers for these genes are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sequences of the primers used in real-time qPCR.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Results are presented as mean ± standard error (SE). All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0 software (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). Prior to statistical analysis, the data were tested for normality, homogeneity, and independence of variance. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to evaluate differences among groups, followed by Tukey’s multiple range test for post hoc comparisons. Differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
3. Result
3.1. Protective Effect of Phage Therapy on Shrimp Survival
Check out the survival rates of Litopenaeus vannamei after phage treatment when they were infected with Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Figure 1. After we introduced the bacteria, all the shrimp groups saw a drop in their survival rates over time, but the P0 group (the control) really took a hit, showing the highest levels of mortality pretty quickly. By 72 h post-infection, the survival rate for the P0 group plummeted to 45%, and it did not recover from there, which shows they are pretty vulnerable to Vibrio parahaemolyticus. On the flip side, the groups that received phage treatment really did better. The P2 group had the best survival, hanging on to 78.5% from 72 h to 168 h post-infection. Then we had P3 at 70.5% and P4 at 62.5%. P1 was somewhere in the middle with a survival rate of 57.5%.
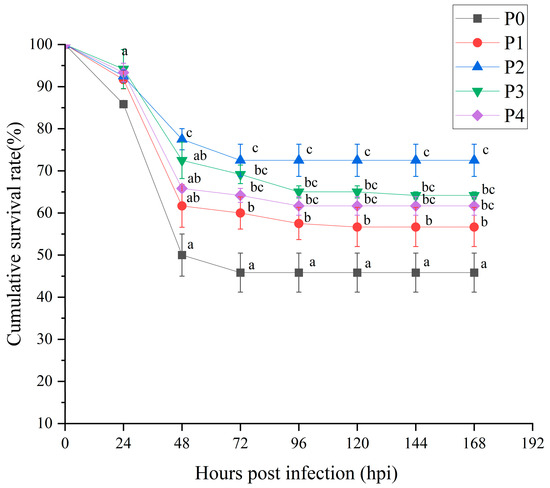
Figure 1.
Survival of shrimp after Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Different groups are as follows: inject an equivalent volume of PBS (P0); inject phages at a concentration of 0.5 ppm (P1); inject phages at a concentration of 1 ppm (P2); inject phages at a concentration of 2 ppm (P3); inject phages at a concentration of 4 ppm (P4). Different letters above the error bars indicate significant differences among groups at each time point (p < 0.05, LSD post hoc test).
3.2. Immune-Related Enzyme Activities
The effects of phage therapy at different concentrations on immune-related enzyme activities in the hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei following Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge are shown in Figure 2. In the hepatopancreas, ACP activity peaked in P2 and was significantly higher than in P0, P1, P3, and P4 (p < 0.05). However, the ACP activity of P1, P3, and P4 was increased compared with that of P0 group, but there was no significant difference (p > 0.05). AKP activity was significantly increased in groups P1, P2, and P3 compared to P0 and P4 (p < 0.05). LZM activity showed a clear increase, with P2 displaying the highest activity, significantly surpassing P0, P3, and P4 (p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between the other treatment groups (p > 0.05).
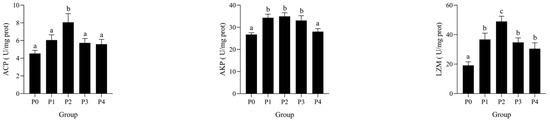
Figure 2.
Effects of bacteriophages on AKP, ACP, and LZM activities in the hepatopancreas of shrimp infected by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) (n = 3). Groups are as follows: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS (control); P1, inject bacteriophages at 0.5 ppm; P2, at 1 ppm; P3, at 2 ppm; P4, at 4 ppm. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. Columns not sharing a common superscript letter (a, b, c) are significantly different at p < 0.05.
The effects of phage therapy at different concentrations on immune-related enzyme activities in the serum of Litopenaeus vannamei following Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge are shown in Figure 3. In serum, ACP activity was significantly increased in groups P1 and P2 compared to the control group P0 (p < 0.05), with the highest value observed in P2. A similar trend was observed for AKP, with significantly elevated activity in P1 and P2, followed by a decline in P3 and P4. LZM activity in serum was significantly higher in P2 than in other groups, while no significant difference was detected between P0, P3, and P4 (p > 0.05). ALT activity showed a significant increase in groups P1 and P2 compared to P0 (p < 0.05), with the highest value detected in P2. However, ALT levels in P3 and P4 returned to baseline, showing no significant difference from P0. Similarly, AST activity was significantly elevated in P1 and P2 groups (p < 0.05), with a peak in P2, followed by a marked decline in P3 and P4.
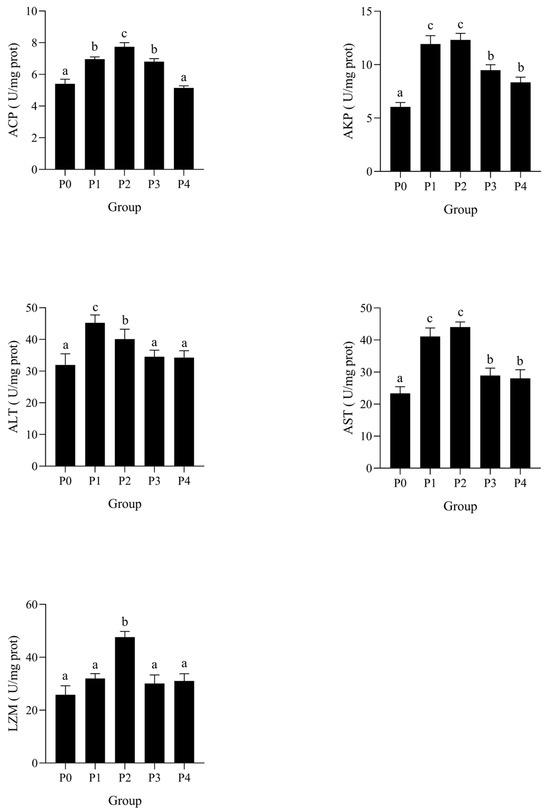
Figure 3.
Effects of phages on AKP, ACP, AST, AST, and LZM activities in the serum of shrimp infected by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) (n = 3). Groups are as follows: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS (control); P1, inject bacteriophages at 0.5 ppm; P2, at 1 ppm; P3, at 2 ppm; P4, at 4 ppm. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. Columns not sharing a common superscript letter (a, b, c) are significantly different at p < 0.05.
3.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
The effects of phage therapy at various concentrations on the activities of antioxidant enzymes in the serum and hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei after a challenge with Vibrio parahaemolyticus are illustrated in Figure 4. SOD activity was significantly higher in the hepatopancreas of groups P2 and P3 compared to P0 (p < 0.05), with the highest activity observed in P2. In serum, SOD activity was significantly lower in P0 than in all other groups (p < 0.05). T-AOC showed a similar pattern: in hepatopancreas, T-AOC was significantly elevated in P2 and P3 (p < 0.05), while in serum, only P2 showed significantly higher T-AOC than P0 and P4. GSH-PX activity in hepatopancreas was significantly increased in P2 and P3, with P2 exhibiting the highest level (p < 0.05). Serum GSH-PX activity followed a similar trend. CAT activity was significantly enhanced in P1–P3 in hepatopancreas compared to P0, with a peak at P2 (p < 0.05), and a significant increase in CAT activity was also observed in serum. MDA, a key lipid peroxidation product, was significantly lower in P1, P2, and P3 groups than in P0 in both tissues (p < 0.05).
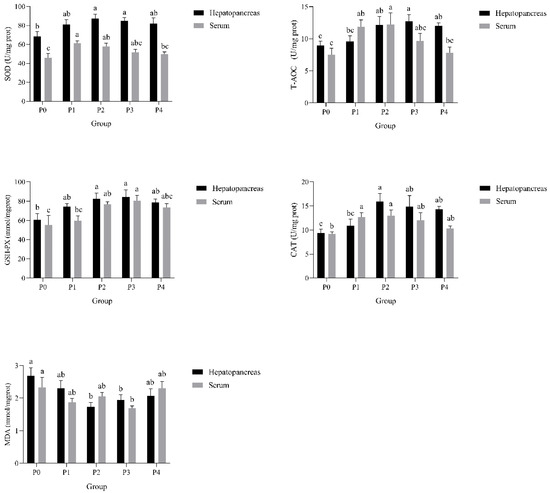
Figure 4.
Effects of phages on SOD, T-AOC, GSH-PX, CAT, and MDA activities in the hepatopancreas and serum of shrimp infected by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) (n = 3). Groups are as follows: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS (control); P1, inject bacteriophages at 0.5 ppm; P2, at 1 ppm; P3, at 2 ppm; P4, at 4 ppm. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. Columns not sharing a common superscript letter (a, b, c) are significantly different at p < 0.05.
3.4. Lipid Metabolism-Related Biochemical Parameters
The effects of phage therapy at different concentrations on lipid metabolism-related biochemical parameters in the serum of Litopenaeus vannamei following Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge are shown in Figure 5. Serum triglyceride (TG) levels significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner from P0 to P4, with the lowest levels observed in P2 and P4 (p < 0.05). Total cholesterol (TC) levels were significantly reduced in P2, P3, and P4 compared to P0 and P1 (p < 0.05). Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels decreased sharply in all phage-treated groups (P1–P4), showing significantly lower levels than the control group P0 (p < 0.05). In contrast, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels increased significantly in P2 and P3 groups compared to P0 (p < 0.05), with P2 showing the highest value.
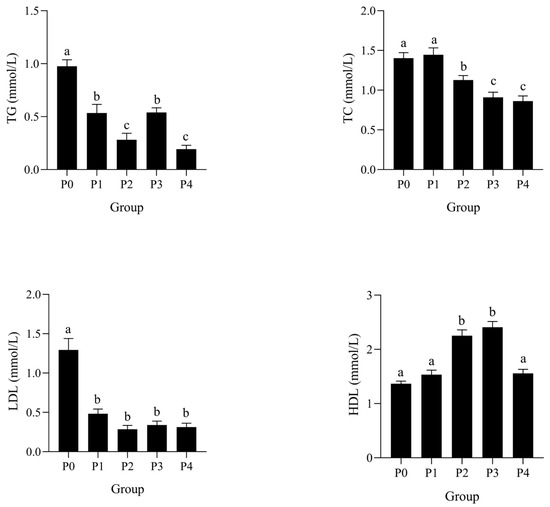
Figure 5.
Effects of phages on TG, TC, LDL, and HDL activities in the serum of shrimp infected by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) (n = 3). Groups are as follows: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS (control); P1, inject bacteriophages at 0.5 ppm; P2, at 1 ppm; P3, at 2 ppm; P4, at 4 ppm. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. Columns not sharing a common superscript letter (a, b, c) are significantly different at p < 0.05.
3.5. Raw Data, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation and Reference Gene Alignment
A total of 253,655,246 raw reads and 251,806,702 clean reads were obtained from six libraries. The Q20, Q30, and GC content of all samples were above 98.85%, 96.19%, and 45.13%, respectively, indicating high sequencing quality (Table 2). Comparing the above clean reads with the reference genome, the total mapped ratio of all samples ranged from 89.64% to 91.04%, which exceeded the standard of 70% (Table 3). These results showed that the sequencing data quality was reliable and suitable for subsequent analysis.

Table 2.
Summary of transcriptome sequencing data.

Table 3.
RNA-seq alignment results.
3.6. Functional Annotations
We identified 21,401 genes (18,725 known; 2676 novel). Functional annotation via six databases (GO, KEGG, EggNOG, NR, Swiss-Prot, Pfam) revealed 11,633, 10,520, 13,529, 18,125, 12,518, and 13,398 annotated reference genes, respectively. Novel gene annotations were markedly fewer (484, 254, 296, 888, 218, and 257) (Figure 6). The data indicate that although the number of annotated reference genes is higher, the annotation of new genes also shows diversity and potential significance. These results suggest that the functions of many new genes still need to be further revealed and studied.
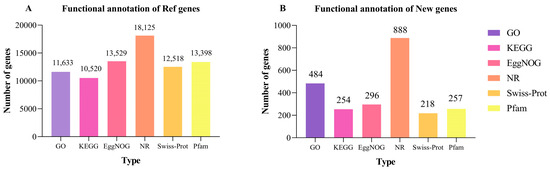
Figure 6.
The number of reference genes (A) and new genes (B) annotated by GO, KEGG, COG, NR, Swiss-Prot, and Pfam.
3.7. DEGs Clustering and GO Functional Annotation Analysis
Comparative analysis between the P2 and P0 groups identified 2274 DEGs (Figure 7), including 821 upregulated and 1453 downregulated genes (|log2FC| ≥ 1, p < 0.05). A volcano plot displays several genes that stand out due to their strong responsiveness (Figure 8). Notably, genes like LOC113808589, LOC113805739, LOC113803502, and LOC113827783 may play important roles in immune regulation, metabolic adaptation, and resilience to oxidative stress considering phage therapy.
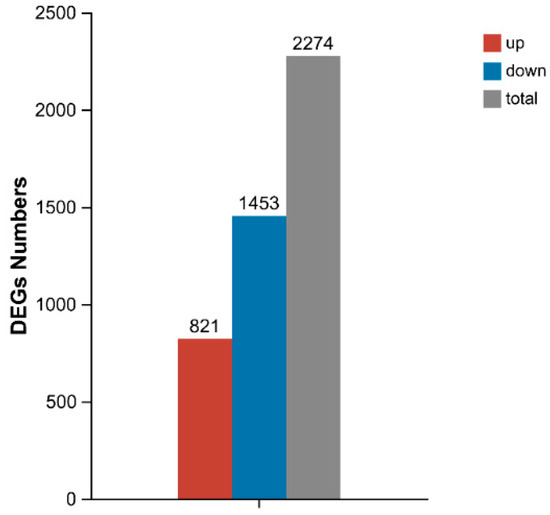
Figure 7.
Number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in hepatopancreas of P2 and P0 groups under phage action. Abbreviations: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS; P2, inject phages at a concentration of 1 ppm.
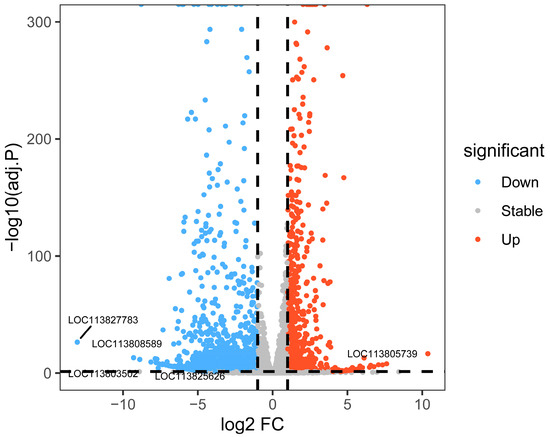
Figure 8.
Results of volcano plot analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the hepatopancreas of shrimp, from phage-treated P2 and P0 groups. Abbreviations: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS; P2, inject phages at a concentration of 1 ppm.
Gene Ontology (GO) annotation of these DEGs revealed classification into three primary categories: biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) (Figure 9). In the BP category, the major associated terms included metabolic process, cellular process, and biological regulation. In the CC category, DEGs were mostly linked to cellular anatomical entity and protein-containing complex. In the MF category, DEGs were mainly involved in catalytic activity and binding, suggesting a prominent role in enzymatic function and molecular interaction during phage-induced regulation.
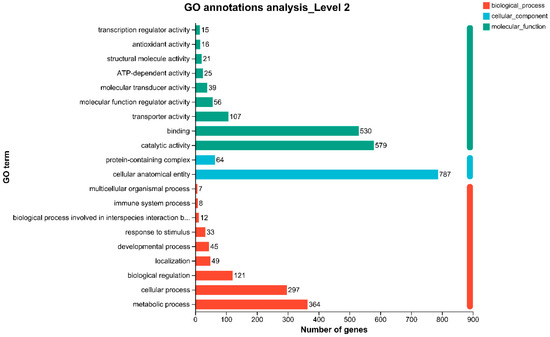
Figure 9.
Gene Ontology (GO) annotations analysis at Level 2 for P2 and P0 groups. BP: Biological Process; CC: Cellular Component; MF: Molecular Function. Abbreviations: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS; P2, inject phages at a concentration of 1 ppm.
3.8. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
The KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the phage treatment had a notable impact on several biological pathways (Figure 10). Among downregulated DEGs, enriched pathways included ECM–receptor interaction, the Wnt signaling pathway, phagosome, neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction, the mTOR signaling pathway, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, glycerolipid metabolism, and autophagy. These pathways are primarily associated with energy production, lipid metabolism, and cellular communication, indicating a potential suppression of energy-intensive processes under bacterial stress.

Figure 10.
Major enrichment of KEGG pathways in downregulated genes of P2 and P0 groups. Abbreviations: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS; P2, inject phages at a concentration of 1 ppm.
In contrast, the upregulated DEGs shown in Figure 11 were notably enriched in areas like lysosome activity, fatty acid metabolism and degradation, peroxisomes, the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, and interactions between neuroactive ligands and receptors. These enriched pathways suggest that phage therapy may enhance immune surveillance, oxidative stress resistance, and metabolic flexibility in Litopenaeus vannamei during Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection.
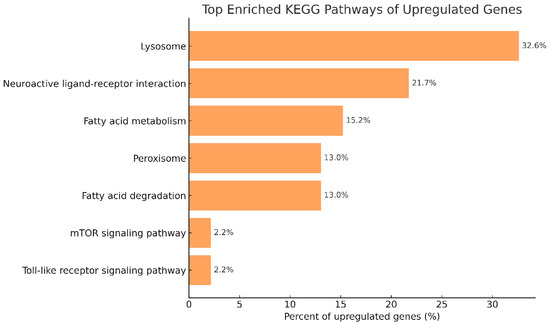
Figure 11.
Major enrichment of KEGG pathways in upregulated genes of P2 and P0 groups. Abbreviations: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS; P2, inject phages at a concentration of 1 ppm.
3.9. qPCR Result
The relative expression levels of TLR4, IL-1β, PPAR, MYD88, and Nrf2 genes in the hepatopancreas were validated by qPCR, as shown in Figure 12. The expression levels of all five genes were significantly upregulated in phage-treated groups compared to the control (P0). Among these, group P2 exhibited the highest expression for most genes, with MYD88 and PPAR showing significantly greater levels than in P0 (p < 0.05). Notably, IL-1β, TLR4, and Nrf2 also showed significantly improved expression in P2 and P3 relative to the control group. In addition, the expression levels of ChyBII, COX5B, GAD, CHST5, and CHST1 were upregulated in the P2 group compared to P0, as shown in Figure 13. These results were consistent with the RNA-Seq data, supporting the reliability of the transcriptomic analysis.
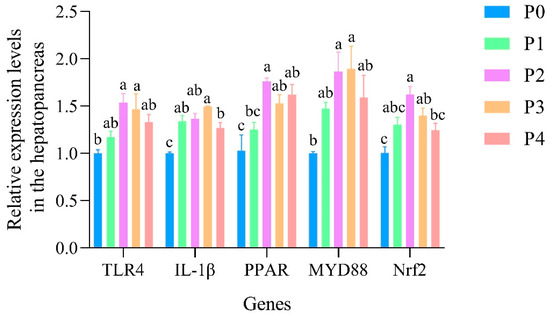
Figure 12.
The relative expression levels of TLR4, IL-1β, PPAR, MYD88, and Nrf2 genes in the hepatopancreas of shrimp. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) (n = 3). Groups are as follows: P0, inject an equivalent volume of PBS (control); P1, inject bacteriophages at 0.5 ppm; P2, at 1 ppm; P3, at 2 ppm; P4, at 4 ppm. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. Columns not sharing a common superscript letter (a, b, c) are significantly different at p < 0.05.
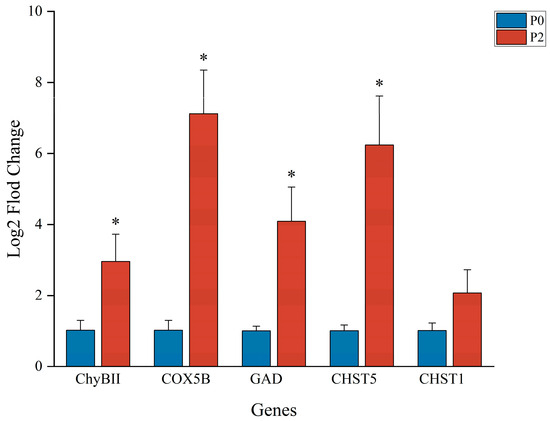
Figure 13.
qPCR results. ∗ There was a significant difference in gene expression in the P2 group compared to the P0 group. Target gene abbreviations are as follows: Chymotrypsin BII-like, ChyBII; Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5B, COX5B; MGlutamate decarboxylase, GAD; Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 5, CHST5; Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 1, CHST1.
4. Discussion
Vibriosis, recognized as a bacterial condition affecting shellfish and fish farming operations, remains a primary contributor to shrimp losses across global aquaculture systems [17]. The pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus poses particular challenges in shrimp cultivation, often leading to significant tissue damage and substantial financial impacts for producers. While antibiotic treatments remain widely employed for controlling such bacterial infections and generally show effectiveness against Vibrio species, their excessive application has unfortunately encouraged the rise of treatment-resistant variants while allowing drug residue buildup in aquatic products [18,19]. This situation raises dual concerns regarding food safety standards and ecological consequences. These challenges have accelerated the exploration of alternative solutions, with phage-based treatments emerging as a targeted and ecologically conscious method for managing bacterial diseases in aquatic environments. Recent investigations demonstrate that phage applications show notable effectiveness against Vibrio infections, particularly within aquaculture settings. For instance, research indicates that phage pVp-1 displays strong activity against certain strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus associated with severe liver-related conditions in shrimp, suggesting its utility as an important tool for mortality reduction and preventive strategies [20]. Similarly, Alagappan et al. found that phage cocktails could effectively reduce the bacterial load of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shrimp gut, enhancing immune responses and survival rates [21]. In another study, Chen et al. isolated a lytic phage, vB-VpaS-SD15, which was capable of lysing 23.9% of Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains found in aquaculture environments, thereby highlighting its potential as an alternative to antibiotics [22]. Research has also indicated that pairing phage therapy with non-pathogenic Vibrio strains can enhance disease resistance in shrimp. This finding reinforces the idea that using phages could be a sustainable strategy for managing diseases linked to Vibrio [23]. These findings emphasize the promise of phage therapy as a viable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional antibiotics in aquaculture. Our study explored the various effects of phage therapy on Litopenaeus vannamei when dealing with Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections, using both enzymatic activity assays and transcriptomic profiling to gain a deeper understanding. Our findings provide mechanistic insight into how phage therapy confers protection via immune enhancement, antioxidant regulation, and metabolic reprogramming.
4.1. Immune Activation and Molecular Mechanisms Revealed by Enzymatic and Transcriptomic Data
Substances including lysozyme, antimicrobial protein compounds, and enzymes with antioxidant properties form fundamental parts of the body’s natural defense mechanisms, operating to identify, attach to, and remove harmful pathogens and viral agents [24,25,26]. In this investigation, we detected marked elevation across various non-specific immune indicators such as acid phosphatase (ACP) and alkaline phosphatase (AKP), along with lysozyme (LZM) measurements. This pattern proved particularly evident within the P2 experimental group, implying that phage applications may substantially stimulate immune responses. These enzymatic changes were supported by transcriptomic data, which showed enrichment in immune-related pathways such as lysosome (ko04142) and Toll-like receptor signaling (ko04620).
The increased activity observed in certain lysosomal genes, including CTSB and CTSL, appeared alongside heightened LZM functionality, suggesting improvements in cellular waste processing capabilities during pathogenic challenges. That is to say, when looking at similar biological responses, Wang et al. [27] previously demonstrated through combined genetic and protein studies that pathways involving cellular digestion structures play essential roles in defensive mechanisms for marine organisms facing Vibrio-type infections. Their work identified notable rises in enzyme categories like CTSL1 and various transport-related proteins such as LAMP1, alongside cellular markers linked to waste ingestion including VAMP3 and CORO1A—findings that collectively emphasize how activation of cellular cleanup processes contributes significantly to organismal immunity, particularly in simpler life forms.
In parallel, we observed upregulation of TLR4 and MYD88, key components of the Toll-like receptor pathway, which are involved in the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and the initiation of innate immune responses. In a similar study involving Crassostrea hongkongensis, researchers found that TLR4 plays an essential role as a pattern recognition receptor. It helps trigger the immune response to Vibrio parahaemolyticus by activating a MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Silencing of ChTLR4 significantly reduced immune enzyme activities (SOD, CAT, ACP, AKP, LZM) and suppressed the expression of downstream signaling molecules, including MyD88, IRAK4, TRAF6, and MKK6, thereby underscoring the functional importance of the TLR4-MyD88 axis in host defense [28].
In addition, phage treatment appeared to influence extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and receptor interactions. Upregulation of COL1A1 and ITGA5 implicates ECM–receptor interaction (ko04512) in the observed immune response, potentially facilitating leukocyte migration and pathogen clearance. Downregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway (CTNNB1, WNT3A)—a key regulator of cellular proliferation—suggests a shift in host resource allocation from growth to immune defense.
4.2. Enhancement of Antioxidant Defenses via Peroxisomal and Glutathione Pathways
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anion (O2−), and hydroxyl radicals (•OH), are natural byproducts of aerobic metabolism and play critical roles in host immune responses by damaging pathogens [29,30]. However, excessive ROS accumulation can result in lipid peroxidation, protein denaturation, and DNA damage, contributing to oxidative stress and cellular dysfunction [31]. To mitigate such damage, crustaceans such as Litopenaeus vannamei rely on a range of antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), to maintain redox homeostasis [32,33].
In this study, phage-treated shrimp—particularly group P2—displayed significant elevation in SOD, GSH-PX, CAT, and T-AOC activities, along with reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, suggesting improved antioxidant capacity. Transcriptomic data supported these findings, revealing enrichment of DEGs in the peroxisome (ko04146) and glutathione metabolism (ko00480) pathways. Notably, the expression of NFE2L2 (Nrf2), a master regulator of oxidative stress responses, and its downstream antioxidant effectors including HO-1, CAT, and GPX were significantly upregulated. This aligns with previous studies reporting that Nrf2 activation plays a central role in maintaining redox balance and protecting against ROS-induced damage in aquatic species [34,35].
In addition, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), particularly PPARα and PPARγ, were activated in phage-treated groups. These nuclear receptors are known to directly or indirectly regulate antioxidant gene expression, including catalase (CAT), GPX, and Bcl-2, by cross-talking with Nrf2 and inhibiting oxidative signaling cascades such as NF-κB [36,37]. Previous findings demonstrated that nutritional or pharmaceutical modulation of the PPAR-Nrf2 axis could enhance antioxidant enzyme activities and attenuate lipid peroxidation in fish models under stress [38]. The present transcriptomic evidence, showing upregulation of PPARA, PPARG, and antioxidant-related genes, supports this mechanism of phage-induced redox protection.
These observations align with previous findings in Penaeus monodon infected by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, where respiratory bursts and ROS production rapidly increased post-infection, triggering antioxidant enzyme expression to counteract oxidative damage [31]. In addition, transcript levels of Mn-SOD and CAT have been reported to increase significantly in the hepatopancreas of shrimp under bacterial challenge, suggesting these enzymes are integral to the early innate immune defense [32].
This connection between the immune system and redox processes really emphasizes the potential of phage therapy. It alleviates oxidative stress in addition to reducing the amount of dangerous microorganisms. For shrimp that are struggling with Vibrio, this might result in improved survival rates and general health.
4.3. Lipid Metabolism Modulation and Its Immunological Implications
Lipid metabolism holds critical importance in maintaining cellular equilibrium, energy supply, and immune system management for crustaceans, particularly when confronting harmful microorganisms or environmental stressors. That is to say, this biological process ensures proper functioning of vital systems under challenging conditions. The metabolic activities related to lipids contribute significantly to shrimp health preservation through energy stability maintenance, cellular membrane protection, and immune response coordination. In crustaceans, the hepatopancreas acts as a central organ responsible for fat breakdown, lipid storage mechanisms, and defense against infections. Pathogenic invasions, such as those by certain Vibrio strains, can disrupt these interconnected processes and exacerbate disease progression [39].
In this study, we observed significant reductions in serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels, along with increased HDL in phage-treated groups, especially P2 and P3. These shifts reflect improvements in lipid handling and hepatic function under bacterial challenge. Similar to our observations, Yin et al. reported that Vibrio alginolyticus infection disrupted glycerophospholipid metabolism and PPAR signaling in the shrimp hepatopancreas, leading to lipid accumulation and tissue necrosis [40]. Such perturbations may facilitate bacterial proliferation by providing accessible lipid substrates or altering immune cell lipid raft dynamics. Transcriptomic analysis further revealed upregulation of genes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation (ACADM, ACADVL), glycerolipid metabolism (PLA2G2A, PLA2G7), and cholesterol transport (ABCG5, CYP7A1), indicating enhanced lipid utilization and clearance.
Importantly, several key genes in the mTOR signaling pathway (ko04150) were differentially expressed in the phage-treated groups. mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) is a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase that functions as a central regulator of cellular metabolism, integrating nutrient availability, energy status, and immune signals. In shrimp, mTOR has been implicated in regulating lipid biosynthesis, autophagy, and immune responses during environmental and microbial stress [41,42]. Studies have shown that activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway can enhance host survival and metabolic adaptation under immune challenge by promoting protein synthesis, inhibiting excessive autophagy, and supporting intestinal epithelial barrier integrity [43].
Our findings suggest that phage therapy may induce beneficial metabolic reprogramming via mTOR-linked nutrient sensing mechanisms. By promoting lipid degradation and reducing pro-inflammatory lipid intermediates, phage treatment not only relieves metabolic burden but may also indirectly contribute to immune regulation and tissue protection.
4.4. Transcriptomic Insights into Immune-Metabolic Cross-Talk and Long-Term Effects
Looking beyond just immediate immune protection, the analysis of gene activity showed a lasting boost in the expression of innate immune signaling genes like TLR4, MYD88, and IL-1Β. This suggests that exposure to phages could actually lead to long-term changes in how the immune system operates. In vertebrates, such sustained immune activation is associated with the formation of immune memory. Although classical adaptive immunity is absent in invertebrates, mounting evidence indicates that invertebrates can exhibit memory-like responses known as “trained immunity,” characterized by heightened and faster innate responses upon repeated pathogen exposure [44,45,46].
This form of non-specific immune “priming” has been observed in mollusks, crustaceans, and insects, where epigenetic reprogramming of immune effector genes leads to enhanced protection against subsequent infections [45]. In oysters, for example, TLR4 has been shown to be a key sensor mediating the MyD88–NF-κB axis and coordinating both antimicrobial and inflammatory gene expression in response to Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge. When TLR4 was silenced in Crassostrea hongkongensis, it not only decreased levels of MYD88, TRAF6, and downstream cytokines like COX2, but it also led to a noticeable drop in antibacterial activity in the hemolymph, along with reduced enzyme activities such as SOD, CAT, and LZM. This emphasizes how important TLR4 is for both quick and overall immune responses [46].
Concurrently, upregulation of peroxisome and fatty acid degradation genes suggests that metabolic reprogramming accompanies immune activation, contributing to inflammation resolution and enhanced host resilience. In crustaceans, the hepatopancreas (or midintestinal gland) is not only a primary site for nutrient metabolism but also plays a critical immunological role, integrating both functions through its epithelial cells which produce lectins, hemocyanin, ferritin, and antimicrobial peptides—hallmarks of innate immunity [47]. This organ plays a key role in spotting germs, presenting antigens, and releasing immune molecules, making it an essential part of how our immune and metabolic systems work together. Additionally, dietary interventions such as Clostridium autoethanogenum protein (CAP) have been shown to enhance this cross-talk. Under high-density rearing conditions, CAP supplementation in Pacific white shrimp significantly upregulated immune- and metabolism-related genes (TLR, Imd, and PI3K-Akt) while also reshaping the intestinal microbiota by promoting beneficial genera such as Motilimonas and Ruegeria [48]. Such modulation not only boosted disease resistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus but also supported hepatic lipid handling and intestinal stability. These findings reinforce the notion that phage or microbial-based treatments may activate parallel immunometabolic axes, with the hepatopancreas serving as a central hub for adaptive host defense through integrated immune and metabolic responses.
Previous studies have shown that phages have gained renewed attention as targeted and environmentally friendly alternatives to antibiotics in aquaculture. In addition to lysing pathogens, they may influence host immunity and metabolism through complex host–microbe–phage interactions [49]. Phage therapy has a lot of advantages for fish farming. It helps to lower harmful bacteria like Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shrimp and Vibrio anguillarum in flatfish. This not only cuts down on these bad bacteria but also helps the fish and shrimp stay alive longer and improves their chances of survival [50,51]. Beyond bacteriolysis, phage exposure induced sustained upregulation of immune-related genes including TLR4, MYD88, and IL-1β, suggesting the activation of innate immune reprogramming mechanisms reminiscent of trained immunity. Concurrently, it triggered metabolic reprogramming by upregulating genes associated with peroxisome function and fatty acid degradation, thereby facilitating inflammation resolution and enhancing host resilience [52]. In addition, phage therapy preserved microbial diversity while suppressing pathogenic bacteria, highlighting its ecological specificity and safety [52].
Our findings in phage-treated Litopenaeus vannamei, particularly the continued upregulation of TLR4 and pro-inflammatory mediators like IL-1Β, are consistent with this model of immune reprogramming. Such transcriptomic patterns may reflect a heightened state of immune vigilance that can be rapidly mobilized upon secondary pathogen exposure, mimicking memory-like behavior. These observations expand the current understanding of phage therapy beyond its bactericidal role, revealing its potential as an immunomodulatory strategy that enhances innate immunity durability in shrimp.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that phage therapy provides effective protection against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in Litopenaeus vannamei, significantly improving shrimp survival and alleviating tissue damage. Through a combination of enzymatic assays and transcriptomic profiling, we show that phage administration enhances non-specific immune responses, boosts antioxidant defenses, and restores lipid metabolic balance. Notably, phage treatment upregulated key genes involved in innate immunity (TLR4, MYD88, and IL-1β), antioxidant signaling (Nrf2 and PPAR), and metabolic regulation (PPAR, mTOR, peroxisome), indicating the induction of a coordinated immunometabolic adaptation beyond direct bacteriolysis. These findings show that phage therapy could be a great, environmentally friendly alternative to antibiotics. It not only helps fight infections but also supports the health of the hosts, which is really important for managing diseases in aquaculture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z. and G.-F.Z.; Methodology, L.Q. and C.-L.G.; Investigation, Y.-Y.H., H.-Z.Z. and C.W.; Data curation, Y.-L.C. and L.Q.; Writing—original draft preparation, Y.-L.C. and L.Q.; Writing—review and editing, G.-F.Z.; Resources, Y.-R.Z. and Y.-C.D.; Supervision and funding acquisition, C.Z. and G.-F.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Experimental funding was provided by the Vannamei shrimp healthy aquaculture technology services (D-8006-24-0633).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The general culturing and sampling of experimental shrimps were in accordance with Shanghai Ocean University’s ethical guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals (approval code: SHOU-DW-2024-162, approval date 20 October 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Chao Zeng was employed by the company Dong Ying Xiang Xin Aquaculture Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Mandal, A.; Singh, P. Global Scenario of Shrimp Industry: Present Status and Future Prospects. In Shrimp Culture Technology: Farming, Health Management and Quality Assurance; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.C.; Chengchu, L. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.R. Vogl, Key performance characteristics of organic shrimp aquaculture in southwest Bangladesh. Sustainability 2012, 4, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Rheman, S.; Debnath, N.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Ghosh, S.; Parveen, S.; Islam, K.; Islam, A.; Rashid, M.; et al. Antibiotics usage practices in aquaculture in Bangladesh and their associated factors. One Health 2022, 15, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Andreevna, S.L.; Sarra, S.; Khelifi, I.; Sergueïevna, D.M. The public health issue of antibiotic residues in food and feed: Causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Vet. World 2022, 15, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culot, A.; Grosset, N.; Gautier, M. Overcoming the challenges of phage therapy for industrial aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadisman, T.A., Jr.; Nelson, R.; Molenda, J.R.; Garber, H.J. Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis in Maryland. I. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1972, 96, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.W.; Colwell, R.R.; Kaper, J.B. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related halophilic Vibrios. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1982, 10, 77–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches-Fernandes, G.M.M.; Sá-Correia, I.; Costa, R. Vibriosis Outbreaks in Aquaculture: Addressing Environmental and Public Health Concerns and Preventive Therapies Using Gilthead Seabream Farming as a Model System. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 904815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, T.W. Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in Asia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vivas, J.; Superio, J.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Acosta, F. Phage therapy as a focused management strategy in aquaculture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Kaur, B.; Singh, P.; Singh, A.; Benjakul, S.; Reddy, S.V.K.; Nagar, V.; Tyagi, A. Perspectives on phage therapy for health management in aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 1349–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwka, P.; Ochocka, M.; Skaradzinska, A. Applications of phages against intracellular bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroz-Guzman, E.; Pena-Rodriguez, A.; Vazquez-Juarez, R.; Barajas-Sandoval, D.R.; Balcazar, J.L.; Martínez-Díaz, S.F. Bacteriophage cocktails as an environmentallyfriendly approach to prevent Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi infections in brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana) production. Aquaculture 2018, 492, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Ahn, J. Characterization of novel bacteriophage as a promising alternative for controlling Vibrio infections in shrimp. Aquaculture 2025, 606, 742579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, H.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Zhou, X. Application of a phage in decontaminating Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 275, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavilla-Pitogo, C.R.; Leano, E.M.; Paner, M.G. Mortalities of pond-cultured juvenile shrimp, Penaeus monodon, associated with dominance of luminescent vibrios in the rearing environment. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kijak, P.J.; Turnipseed, S.B.; Cui, W. Analysis of veterinary drug residues in shrimp: A multi-class method by liquid chromatography–quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 836, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Panda, S.K.; Luyten, W. Anti-vibrio and immune-enhancing activity of medicinal plants in shrimp: A comprehensive review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.W.; Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.; Lightner, D.V.; Kim, J.; Seo, S.W.; Park, S.C. Bacteriophage pVp-1: Agent combating Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains associated with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 457, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagappan, K.; Karuppiah, V.; Deivasigamani, B. Protective effect of phages on experimental Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection and immune response in shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Du, H.; Zhang, K.; Cao, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Biological properties of Vibrio parahaemolyticus lytic phages and transcriptome analysis of their interactions with the host. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Tanni, L.N.; Rahman, A.; Farjana, N.; Moon, R.S.; Tonni, N.Z.; Mekat, M.R.; Mojumdar, S.; Rahman, N.; Sen, B.K.; et al. Bacteriophage and non-pathogenic Vibrio to control diseases in shrimp aquaculture. Comp. Immunol. Rep. 2024, 6, 200126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.H.; Guu, Y.K.; Liu, C.H.; Pan, T.M.; Cheng, W. Immune responses and gene expression in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, induced by Lactobacillus plantarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, T.; Kjuul, A.K.; Stensvåga, K.; Sandsdalenb, E.; Styrvold, O.B. Antibacterial activity in four marine crustacean decapods. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 12, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderhäll, K.; Cerenius, L. Role of the prophenoloxidase-activating system in invertebrate immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, B. The lysosome-phagosome pathway mediates immune regulatory mechanisms in Mesocentrotus nudus against Vibrio coralliilyticus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Zhong, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lei, X. TLR4 involved in immune response against Vibrio Parahaemolyticus by MyD88-dependent pathway in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 134, 108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenvoorden, D.P.; van Henegouwen, G.M.B. The use of endogenous antioxidants to improve photoprotection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1997, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, P.; Gao, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. The cytosolic manganese superoxide dismutase cDNA in swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus: Molecular cloning, characterization and expression. Aquaculture 2010, 309, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. Oxidative stress response of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon to Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.F.; Yao, C.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Reactive oxygen system plays an important role in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei defense against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and WSSV infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 96, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Xiang, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, G.; Cheng, J.; Cao, X.; Fan, X.; Shen, H. An in-depth study of the growth inhibition of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Surfactin and its effects on cell membranes, ROS levels and gene transcription. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2025, 211, 108298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.; Liu, J. Role of Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in the antioxidant defense response induced by low salinity in the kuruma shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus). Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 2793–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Yang, S.; Jian, J. Silencing of Nrf2 in Litopenaeus vannamei, decreased the antioxidant capacity, and increased apoptosis and autophagy. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 122, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Jing, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F.; Cui, X. Astaxanthin suppresses oxidative stress and calcification in vertebral cartilage endplate via activating Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 119, 110159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhu, X.; Duan, Y.; Huang, J.; Nan, Y.; Zhang, J. Toxic effects of nitrite and microplastics stress on histology, oxidative stress, and metabolic function in the gills of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, B.; Xu, P.; Ge, X.; Zhang, H. Emodin ameliorates metabolic and antioxidant capacity inhibited by dietary oxidized fish oil through PPARs and Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Tung, T.C.; Ng, T.H.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, H.C. Metabolic alterations in shrimp stomach during acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease and effects of taurocholate on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 631468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhuang, X.; Liao, M.; Huang, L.; Cui, Q.; Liu, C.; Dong, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Transcriptome analysis of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) hepatopancreas challenged by Vibrio alginolyticus reveals lipid metabolic disturbance. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, M.; Li, F. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of gill reveals genes belonging to mTORC1 signaling pathway associated with the resistance trait of shrimp to VPAHPND. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1150628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, X.-Y.; Guo, Z.-X.; Wang, S.; Wan, J.-W.; Liu, H.-J.; Chen, Y.-K.; Wang, G.-Q.; Wang, Q.-J.; Zhang, D.-M. The immuneoreaction and antioxidant status of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) involve protein metabolism and the response of mTOR signaling pathway to dietary methionine levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Tian, X.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, W.; Dong, S. Effect of Clostridium butyricum in different forms on growth performance, disease resistance, expression of genes involved in immune responses and mTOR signaling pathway of Litopenaeus vannamai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.-W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Qian, P.-Y. Viruses in marine invertebrate holobionts: Complex interactions between phages and bacterial symbionts. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2024, 16, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, R.B.; Acharya, A.; Robina, A.J.; Banu, H.; Tripathi, G. The immune system of marine invertebrates: Earliest adaptation of animals. Comp. Immunol. Rep. 2024, 7, 200163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, R.; Yuan, K.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yi, Q.; Wang, J. Molecular characterization of a cation-dependent mannose-6-phosphate receptor gene in Crassostrea hongkongensis and its responsiveness in Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rőszer, T. The invertebrate midintestinal gland (“hepatopancreas”) is an evolutionary forerunner in the integration of immunity and metabolism. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xie, M.; Chen, J.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S. The role of dietary Clostridium autoethanogenum protein in the growth, disease resistance, intestinal health and transcriptome response of Pacific white shrimp under different stocking densities. Aquaculture 2024, 589, 740962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalatzis, P.G.; Castillo, D.; Katharios, P.; Middelboe, M. Bacteriophage interactions with marine pathogenic vibrios: Implications for phage therapy. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doss, J.; Culbertson, K.; Hahn, D.; Camacho, J.; Barekzi, N. A review of phage therapy against bacterial pathogens of aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Viruses 2017, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, J.P.; Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Serrano-Hernández, J.M.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; López-Cuevas, O.; Chaidez, C. Effect of phage therapy on survival, histopathology, and water microbiota of Penaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, Y.; Cong, C.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Evaluation of the preventive effect of phage cocktails on turbot ascites and its influence on main physiological indicators. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).