The Effect of a Polypeptide Based Vaccine on Fish Welfare and Infestation of Salmon Lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, in Sea Cages with Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
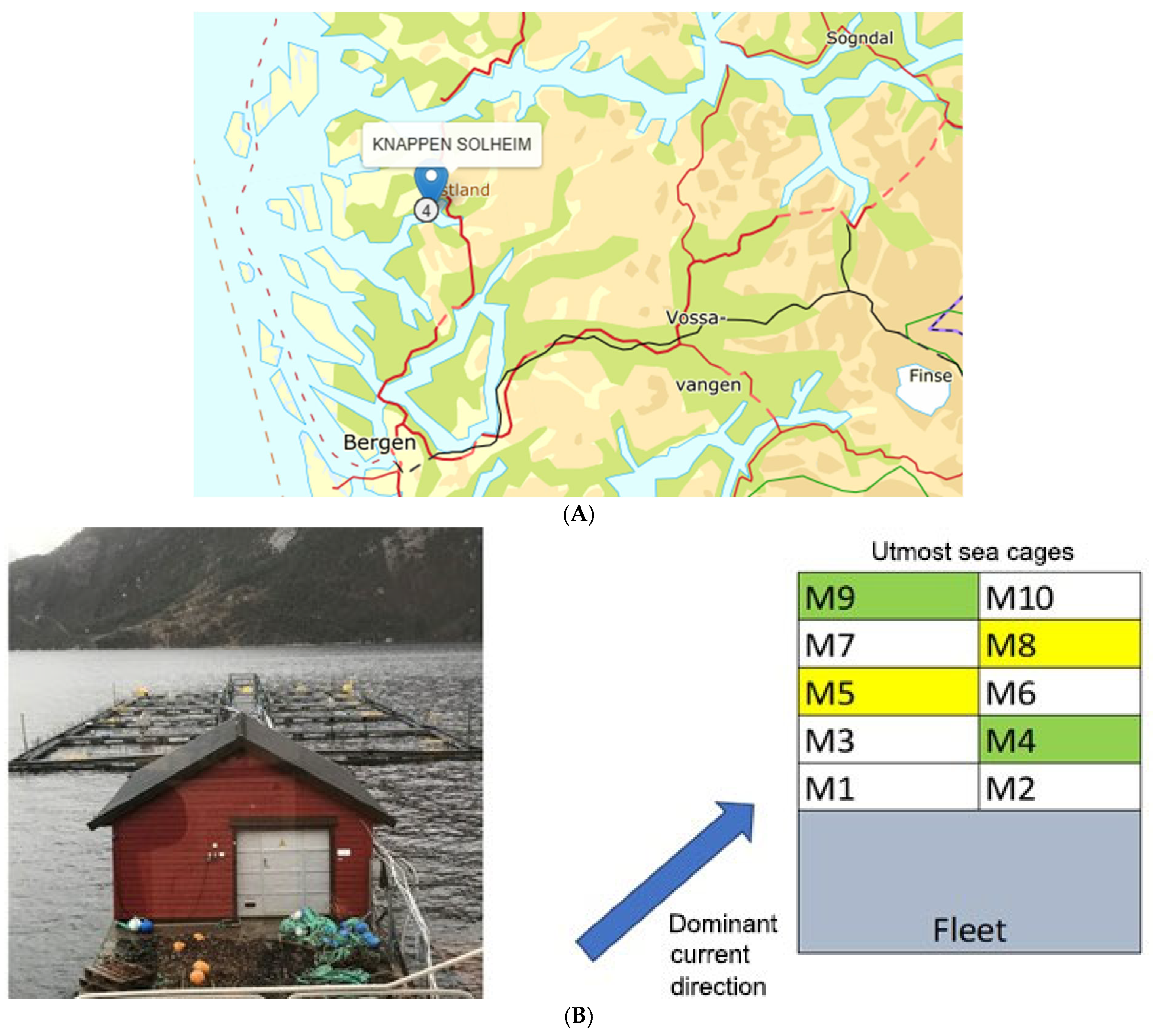
2.1. Experimental Facility and Animal Ethics
2.2. Vaccination
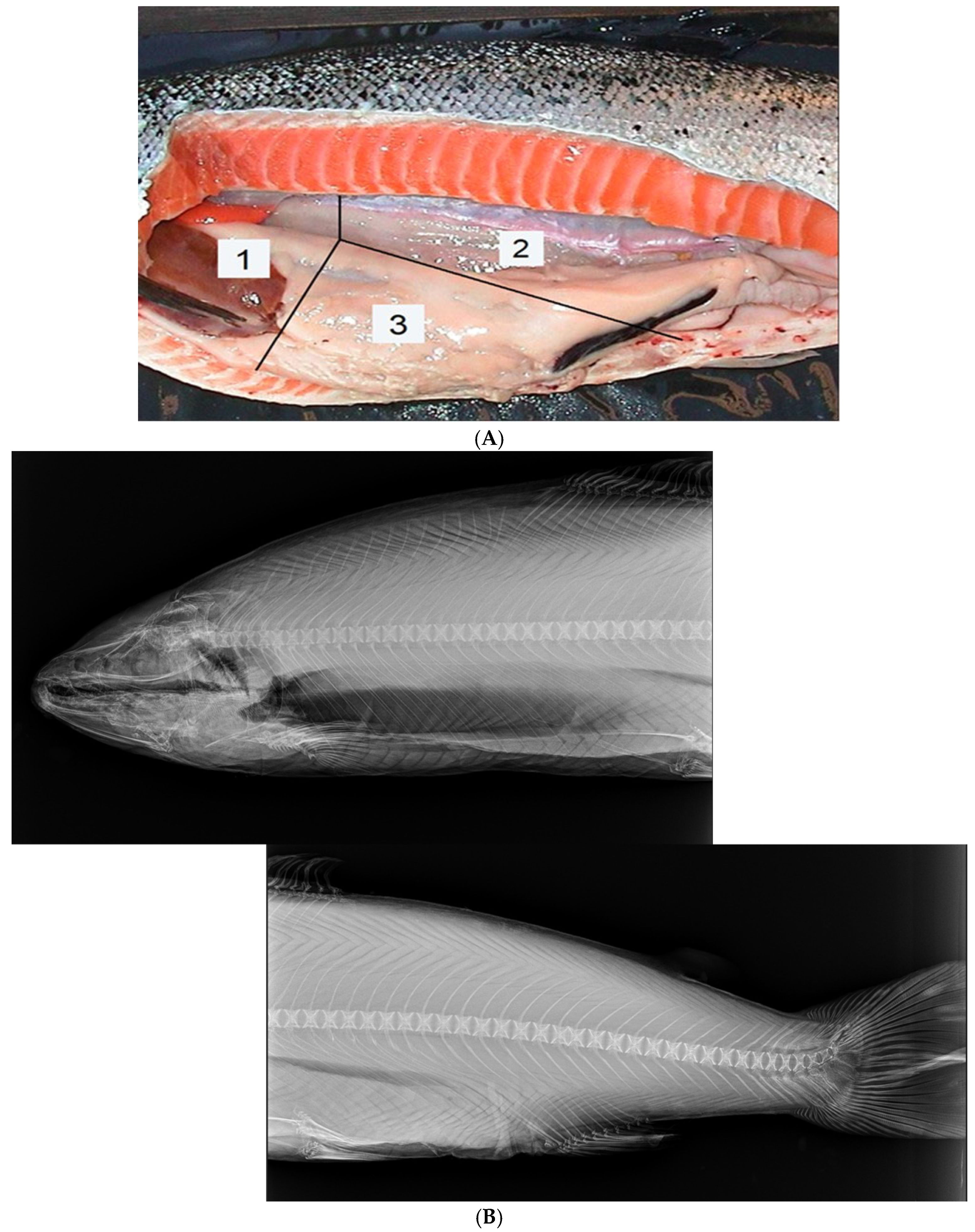
2.3. Sampling and Evaluation
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
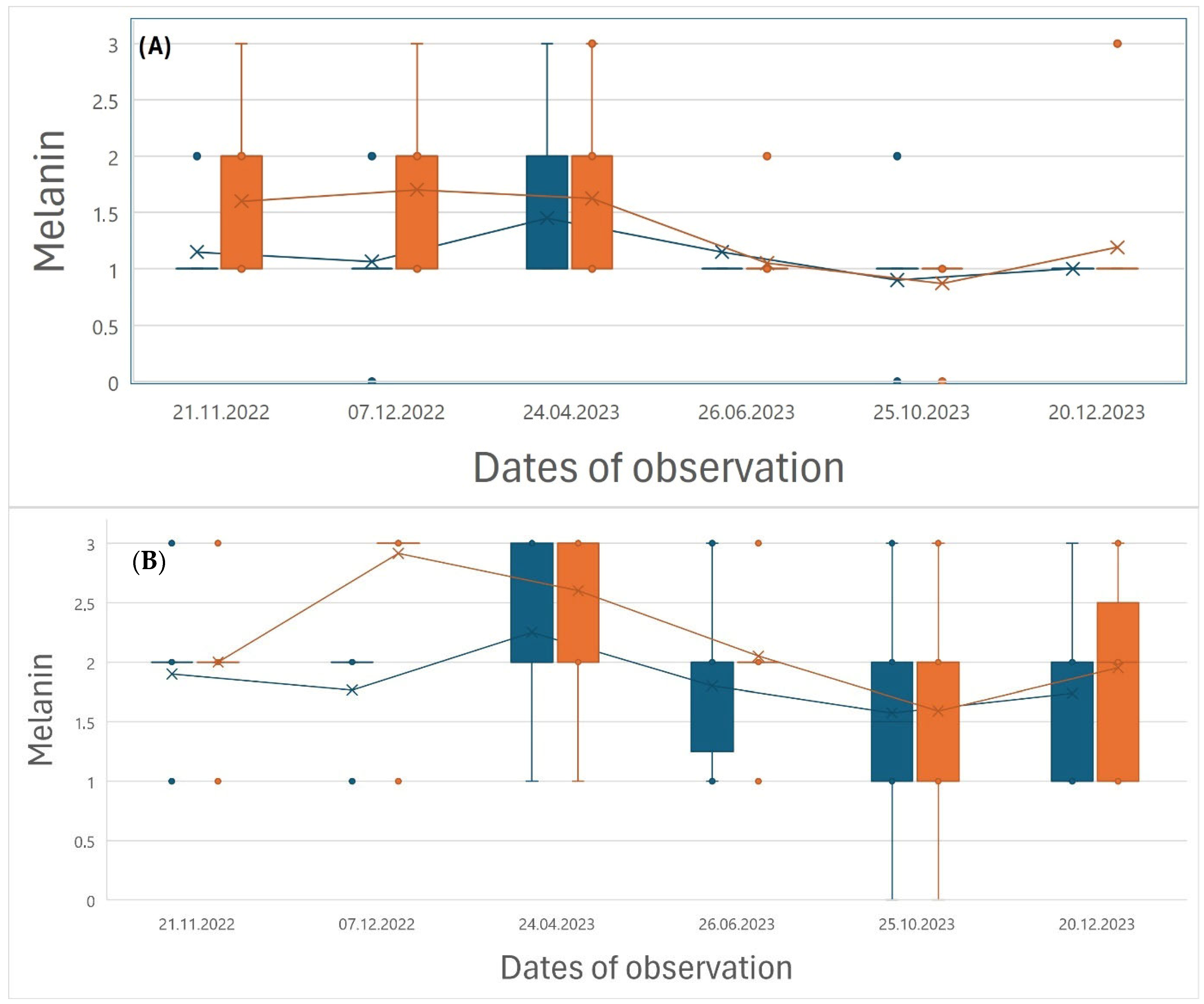
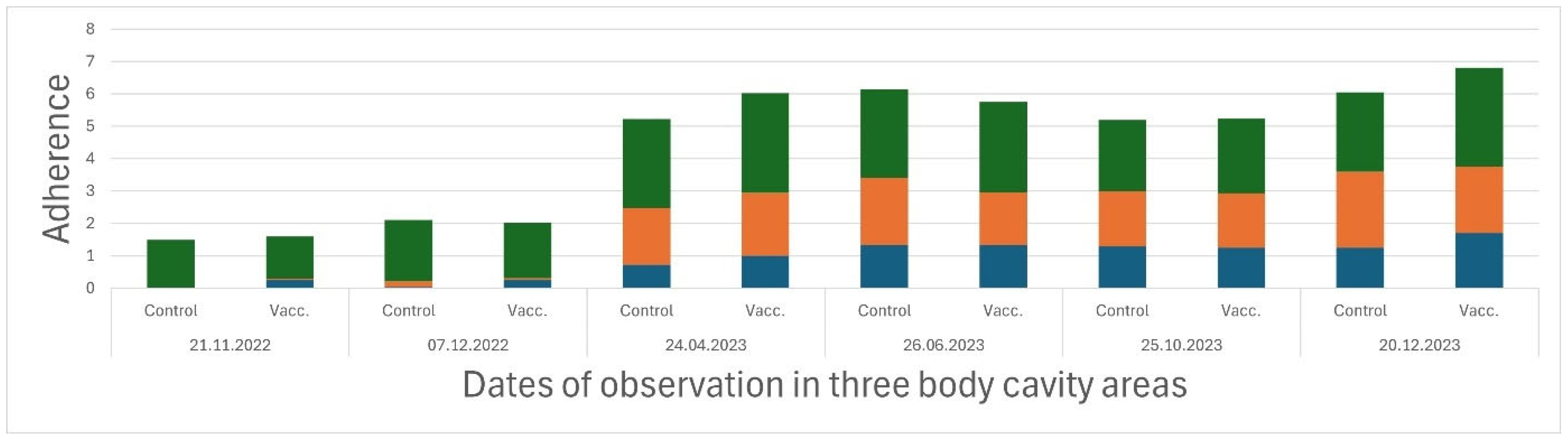
3.1. Welfare, Growth and Sexual Maturation
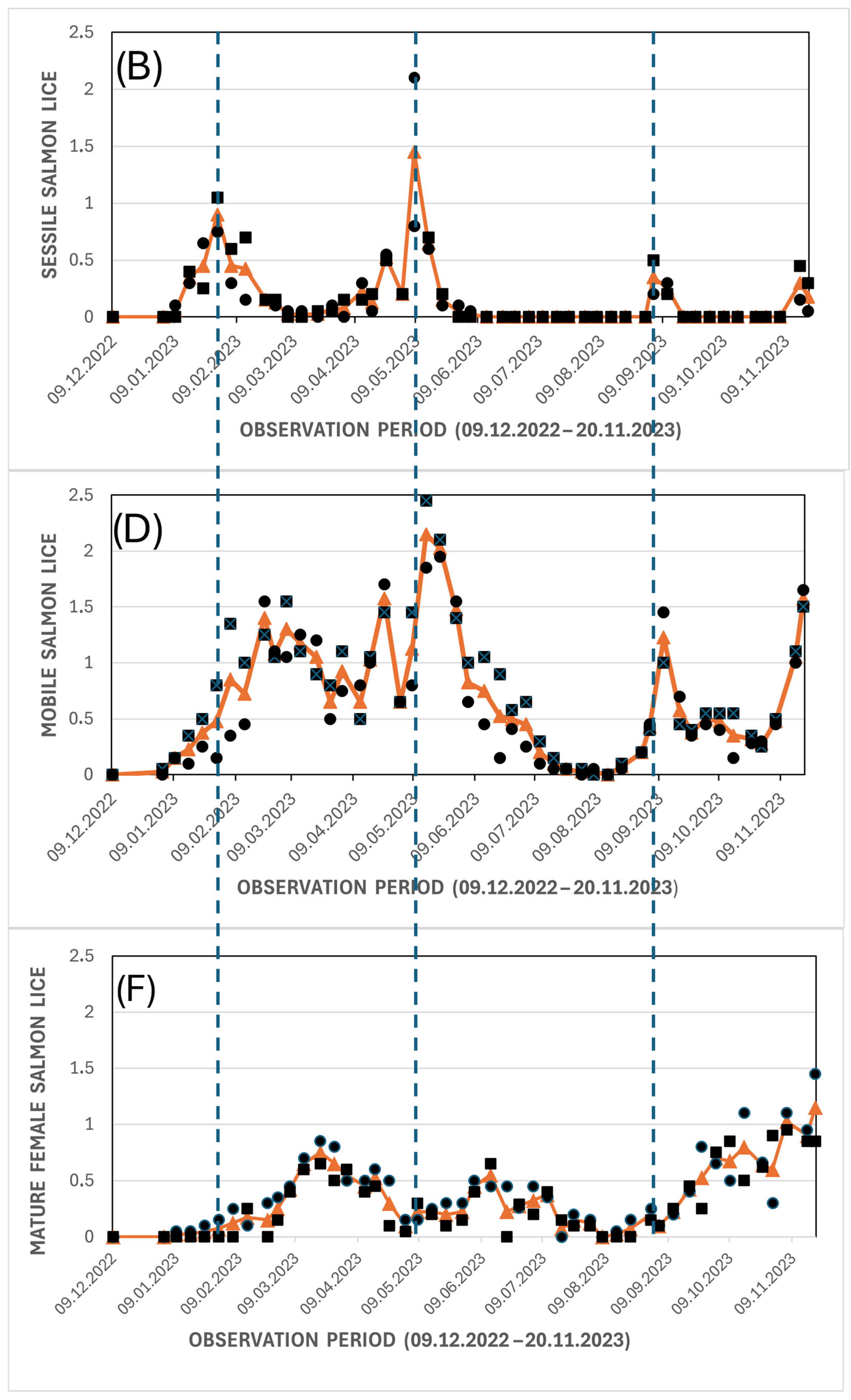
3.2. Lice Infestations
4. Discussion
4.1. Lice Preventive Methods
4.2. The Semi-Commercial Approach
4.3. The Vaccine Candidate
4.4. Effects on Salmon Lice
5. Conclusions
- No adverse effects were observed on a range of salmon welfare-related parameters, mortality, growth, sexual maturation, or slaughter quality from the vaccination towards salmon lice per se.
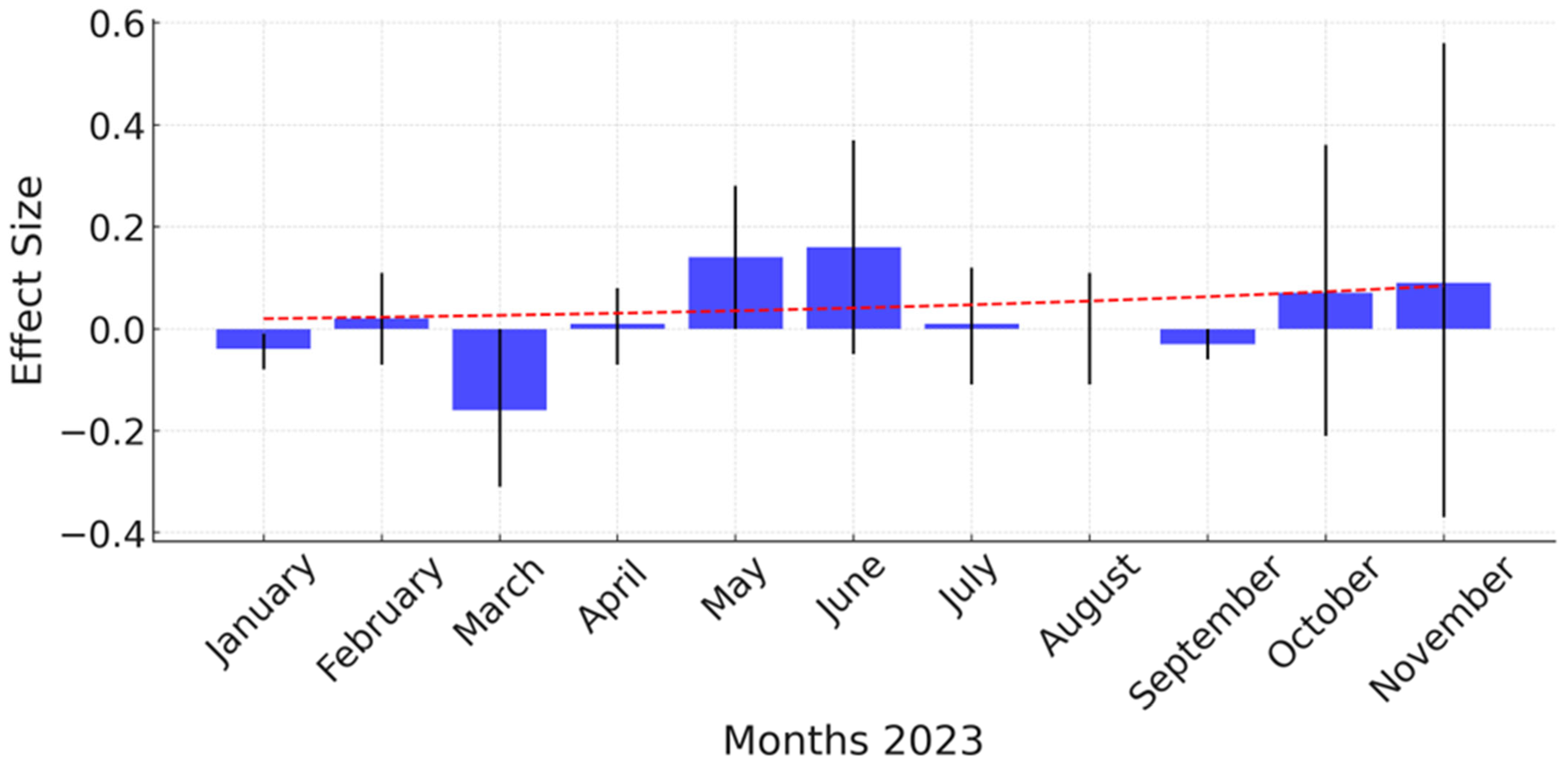
- The effect size showed a moderate positive difference of 0.07 mature female salmon lice per salmon in favor of the vaccinated groups from a fish size above 600 g in May until November, under natural lice infestation pressure in a fjord system.
- Further product development of the vaccine should pay attention to the antigenicity of the peptide, optimization of the purification, finding a better adjuvant, and different doses should be tested at lab-scale.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FOTS | Experimental Animal Administration Supervision and Application System in Norway |
| FCR | Feed Conversion Efficiency |
| HLB | Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| LMM | Linear Mixed Model |
| M1-M10 | Fish Cage Number 1–10 |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| NKEFKEVSLKDYT | Specific 13 Amino Acid Peptide Vaccine Candidate |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares Regression |
| PLS | Partial Least Squares Regression |
| SGR | Specific Daily Growth Rate (%) |
| TFA | Tri-fluoric acid |
References
- Bron, J.E.; Sommerville, C.; Jones, M.; Rae, G.H. The settlement and attachment of early stages of the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, (Copepoda: Caligidae) on the salmon host, Salmo salar. J. Zool. 1991, 224, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxaspen, K. Geographical and temporal variation in abundance of salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) on salmon (Salmo salar L.). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 54, 1144–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxaspen, K. A review of the biology and genetics of sea lice. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Fish Health. Available online: https://www.barentswatch.no/fiskehelse/ (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Szetey, A.; Wright, D.W.; Oppedal, F.; Dempster, T. Salmon lice nauplii and copepodids display different vertical migration patterns in response to light. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2021, 13, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.C.; Albright, L.J. The developmental stages of Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer, 1837) (Copepoda: Caligidae). Can. J. Zool. 1991, 69, 929–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, L.A.; Eichner, C.; Caipang, C.M.A.; Dalvin, S.T.; Bron, J.E.; Nilsen, F.; Boxshall, G.; Skern-Mauritzen, R. The salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae) life cycle has only two chalimus stages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, C.; Hamre, L.A.; Nilsen, F. Instar growth and molt increments in Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae) chalimus larvae. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaen, S.M.; Helgesen, K.O.; Bakke, M.J.; Kaur, K.; Horsberg, T.E. Drug resistance in sea lice: A threat to salmonid aquaculture. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.; Karlsen, M.; Villar, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Leknes, L.M.; Furevik, A.; Yttredal, K.L.; Tartor, H.; Grove, S.; Alberdi, P. Vaccination with Ectoparasite Proteins Involved in Midgut Function and Blood Digestion Reduces Salmon Louse Infestations. Vaccines 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartor, H.; Karlsen, M.; Skern-Mauritzen, R.; Monjane, A.L.; Press, C.M.; Wiik-Nielsen, C.; Olsen, R.H.; Leknes, L.M.; Yttredal, K.; Brudeseth, B.E.; et al. Protective Immunization of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) against Salmon Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) Infestation. Vaccines 2022, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, J.K.; Carpio, Y.; Johansen, L.-H.; Velazquez, J.; Hernandez, L.; Leal, Y.; Kumar, A.; Estrada, M.P. Impact of a candidate vaccine on the dynamics of salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) infestation and immune response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, Y.; Velazquez, J.; Hernandez, L.; Swain, J.K.; Rodríguez, A.R.; Martínez, R.; García, C.; Ramos, Y.; Estrada, M.P.; Carpio, Y. Promiscuous T cell epitopes boosts specific IgM immune response against a P0 peptide antigen from sea lice in different teleost species. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Joshi, M.D.; Singhania, S.; Ramsey, K.H.; Murthy, A.K. Peptide vaccine: Progress and challenges. Vaccines 2014, 2, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slinde, E.; Johny, A.; Egelandsdal, B. Peptides for the Inhibition of Parasite Infection. European Patent NO20211347A. Available online: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/084535741/publication/NO20240348A1?q=Slinde%2C%20E.%3B%20Johny%2C%20A.%3B%20Egelandsdal%2C%20B.%20Peptides%20for%20the%20Inhibition%20of%20Parasite%20Infection (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Johny, A.; Ilardi, P.; Olsen, R.E.; Egelandsdal, B.; Slinde, E. A Proof-of-Concept Study to Develop a Peptide-Based Vaccine against Salmon Lice Infestation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Vaccines 2024, 12, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunsmo, A.; Guttvik, A.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Larssen, R.B.; Evensen, Ø.; Skjerve, E. Association of spinal deformity and vaccine-induced abdominal lesions in harvest-sized Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.; Yurtseva, A.; Hansen, T.; Lajus, D.; Fjelldal, P.G. Vaccinated farmed Atlantic salmon are susceptible to spinal and skull deformities. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Løge-Hagen, A.S.; Dalum, A.S.; Erkinharju, T.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Aunsmo, A. A case of melanization after intramuscular vaccination in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.)—Possible causes and implications. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtlyng, P.J.; Reitan, L.J.; Speilberg, L. Experimental studies on the efficacy and side-effects of intraperitoneal vaccination of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) against furunculosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1996, 6, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, E.D.; Schekter, R.C. Growth rates, rations and cohort consumption of marine fish larvae in relation to prey concentrations. Rapp. Proc. Réun. Cons. Int. Exp. Mer. 1981, 178, 441–453. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry, 2nd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1981; 859p, ISBN 0-7167-1254-7. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, C.; Gismervik, K.; Iversen, M.H.; Kolarevic, J.; Nilsson, J.; Stien, L.H.; Turnbull, J.F. Welfare Indicators for Farmed Atlantic salmon: Tools for Assessing Fish Welfare; FHF–Norwegian Seafood Research Fund: Tromsø, Norway, 2018; 351p, ISBN 978-82-8296-556-9. Available online: http://www.nofima.no/fishwell/english (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Barrett, L.T.; Oppedal, F.; Robinson, N.; Dempster, T. Prevention not cure: A review of methods to avoid sea lice infestations in salmon aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2527–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, S.; Skern, R.; Saito, T.; Thompson, C. Optimising delousing strategies: Developing best practice recommendations for maximal efficacy and positive welfare. Rapport fra Havforskningen 2023-29. Available online: https://www.hi.no/en/hi/nettrapporter/rapport-fra-havforskningen-en-2023-29 (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Oppedal, F.; Folkedal, O.; Stien, L.H.; Vågseth, T.; Fosse, J.O.; Dempster, T.; Warren-Myers, F. Atlantic salmon cope in submerged cages when given access to an air dome that enables fish to maintain neutral buoyancy. Aquaculture 2020, 525, 735286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.T.; Larsen, L.-T.U.; Bui, S.; Vågseth, T.; Eide, E.; Dempster, T.; Oppedal, F.; Folkedal, O. Post-smolt Atlantic salmon can regulate buoyancy in submerged sea-cages by gulping air bubbles. Aquac. Eng. 2024, 107, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Myers, F.; Vågseth, T.; Folkedal, O.; Stien, L.H.; Fosse, J.O.; Dempster, T.; Oppedal, F. Full production cycle, commercial scale culture of salmon in submerged sea-cages with air domes reduces lice infestation, but creates production and welfare challenges. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogans, W.E.; Trudeau, D.J. Preliminary studies on the biology of sea lice, Caligus elongatus, Caligus curtus and Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligoida) parasitic on the cage-cultured salmonids in the lower Bay of Fundy. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989. ISSN 0706-6457. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/19900597424 (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Nilsen, F. Recent advances in salmon louse research. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2018, 38, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Arriagada, G.; Vanderstichel, R.; Stryhn, H.; Milligan, B.; Revie, C.W. Evaluation of water salinity effects on the sea lice Lepeophtheirus salmonis found on farmed Atlantic salmon in Muchalat Inlet, British Columbia, Canada. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, T. Salinity and temperature alter the efficacy of salmon louse prevention. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.J.; Robinson, S.M.C.; Fiendel, N.; Sterling, A.; Byrne, A.; Pee Ang, K. Horizontal and vertical distribution of sea lice larvae (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) in and around salmon farms in the Bay of Fundy, Canada. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 41, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Hunter, W.G.; Hunter, J.S. Statistics for Experimenters—An Introduction to Design, Data Analysis, and Model Building; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978; 653p. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Ass. Publishers: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; 567p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, S.; Folkedal, O.; Nerbø, I.S.; Barrett, L.T. A Standard Operating Procedure for validation of automatic louse counts. In Report No. 2024-56 from Institute of Marine Research, Norway; 2024; 26p. Available online: https://www.hi.no/hi/nettrapporter/rapport-fra-havforskningen-2024-56 (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Roitt, I.M.; Brostoff, J.; Male, D.K. Immunology, 2nd ed.; Gower Medical Publishing: London, UK, 1989; pp. 4.1–4.12. [Google Scholar]
- Grimholt, U.; Drabløs, F.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Høyheim, B.; Stet, R.J. The major histocompatibility class I locus in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): Polymorphism, linkage analysis and protein modelling. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, S.; Koop, B.F.; Sandve, S.R.; Miller, J.R.; Kent, M.P.; Nome, T.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Leong, J.S.; Minkley, D.R.; Zimin, A.; et al. The Atlantic salmon genome provides insights into rediploidization. Nature 2016, 533, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtbø, H.M.D.; Eichner, C.; Hamre, L.A.; Dondrup, M.; Flesland, L.; Tysseland, K.H.; Kongshaug, H.; Borchel, A.; Skoge, R.H.; Nilsen, F.; et al. Salmon louse labial gland enzymes: Implications for host settlement and immune modulation. Front. Genet. 2024, 14, 1303898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.K.D.; Balseiro, P.; Handeland, S.; Godø, O.R. Follow-Up Study on Acoustic De-Licing of Atlantic Salmon. (Salmo salar): Lepeophtheirus salmonis and Caligus elongatus Dynamics over Four Consecutive Production Cycles. J. Mar.Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
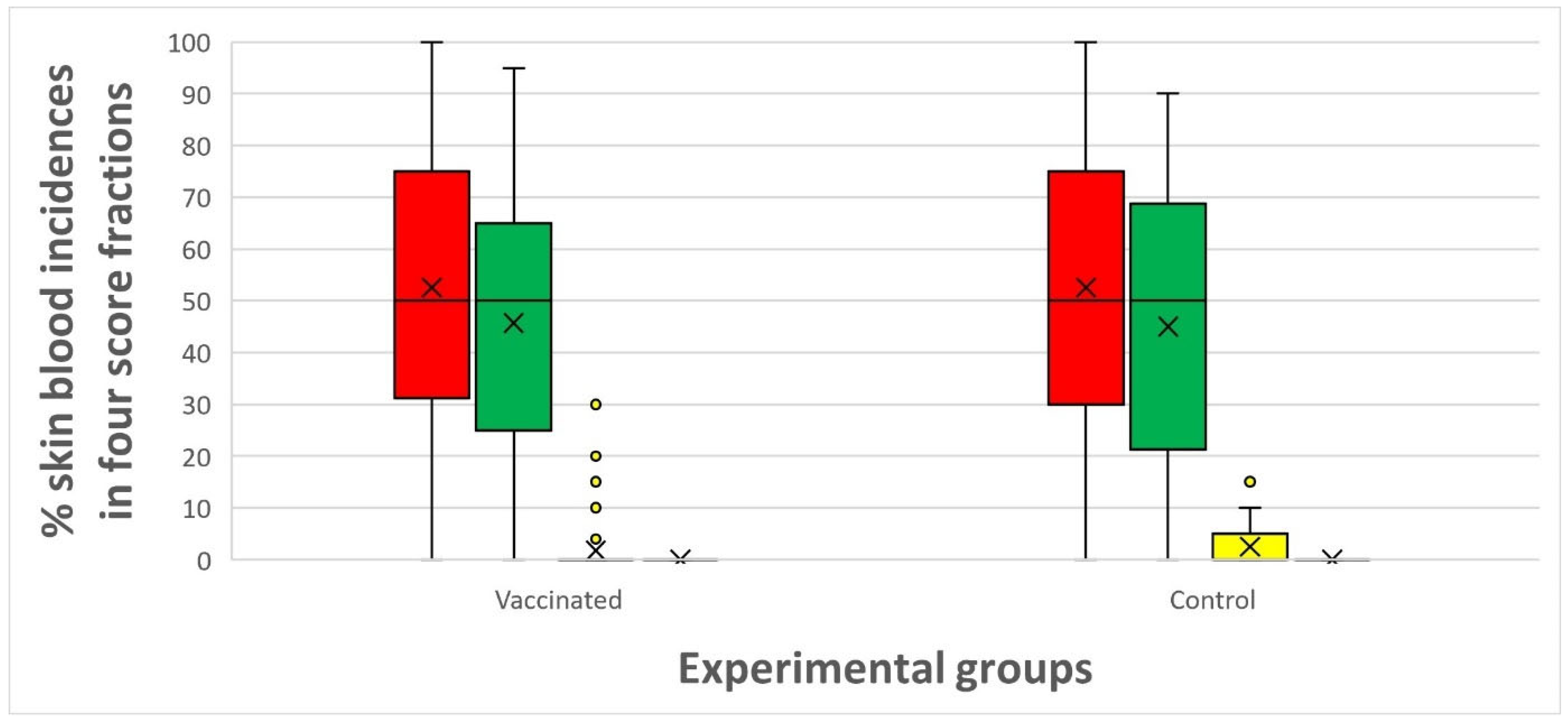
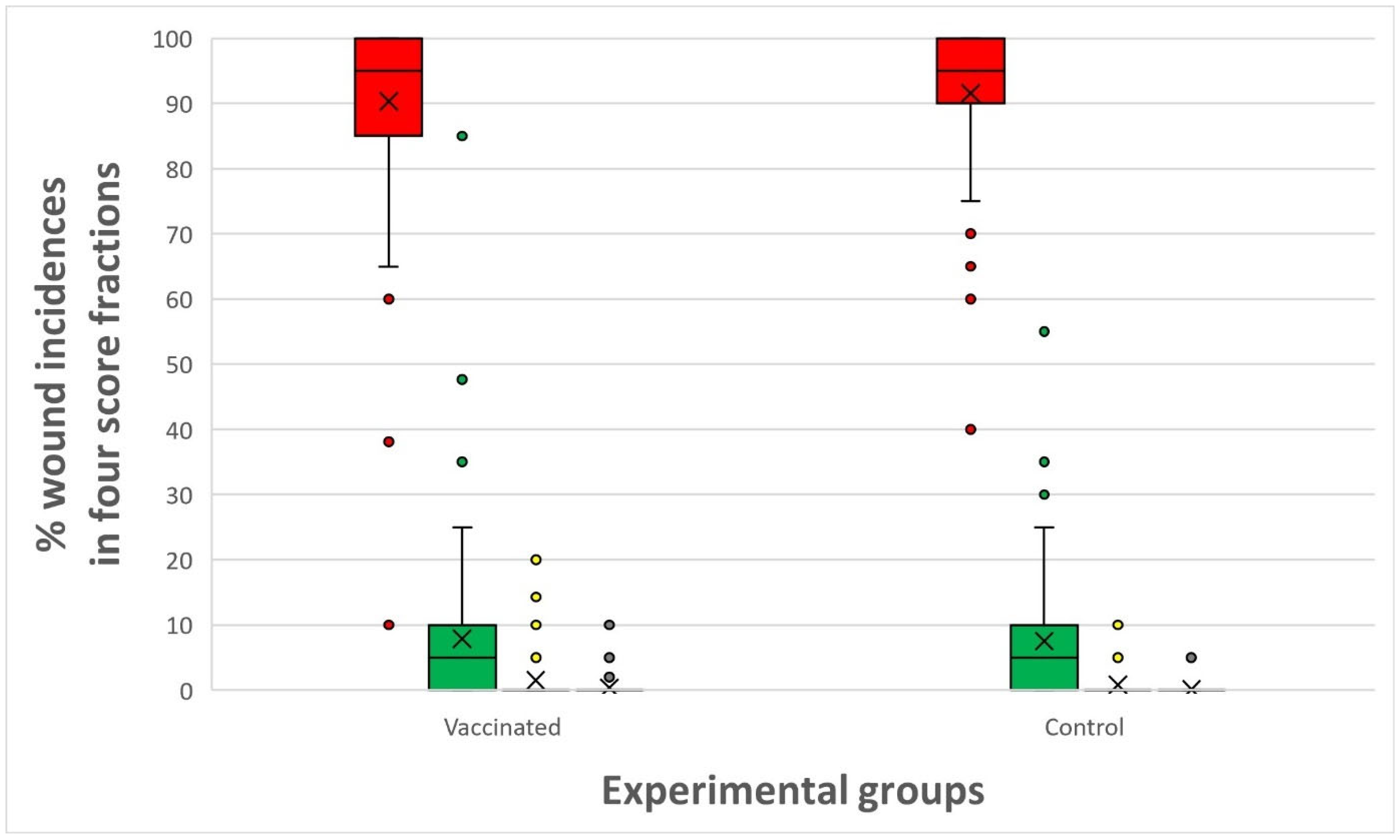
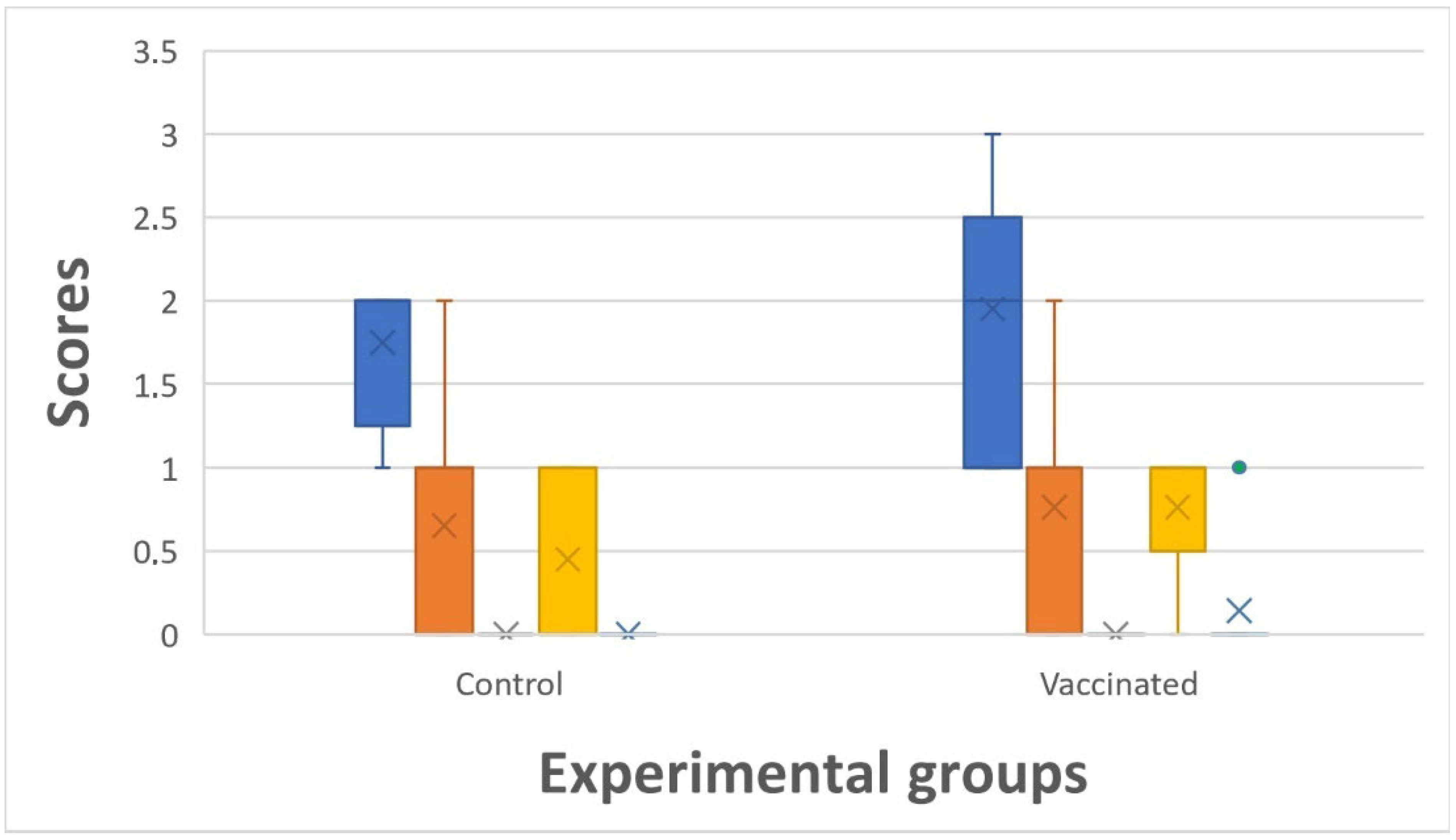

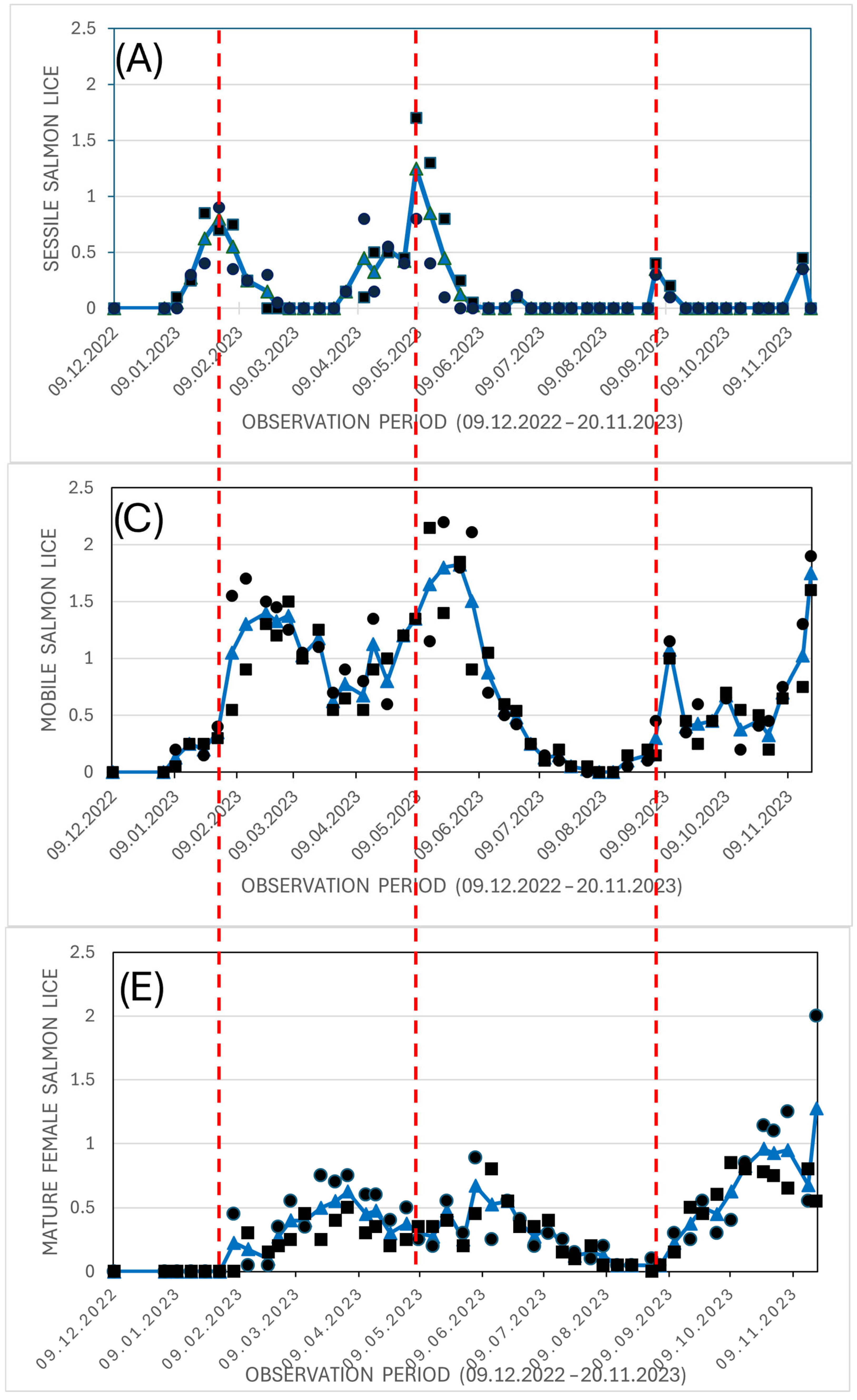
| Date | Group | Score 0 | Score 1 | Score 2 | Score 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 February 2023 | V | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 February 2023 | C | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 April 2023 | V | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 April 2023 | C | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 June 2023 | V | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 June 2023 | C | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 August 2023 | V | 97 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 August 2023 | C | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 October 2023 | V | 75 | 20 | 0 | 5 |
| 25 October 2023 | C | 67 | 30 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 December 2023 | V | 60 | 37 | 0 | 3 |
| 4 December 2023 | C | 65 | 30 | 3 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nortvedt, R.; Dahl-Paulsen, E.; Bizama, L.P.A.; Johny, A.; Slinde, E. The Effect of a Polypeptide Based Vaccine on Fish Welfare and Infestation of Salmon Lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, in Sea Cages with Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fishes 2025, 10, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080405
Nortvedt R, Dahl-Paulsen E, Bizama LPA, Johny A, Slinde E. The Effect of a Polypeptide Based Vaccine on Fish Welfare and Infestation of Salmon Lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, in Sea Cages with Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fishes. 2025; 10(8):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080405
Chicago/Turabian StyleNortvedt, Ragnar, Erik Dahl-Paulsen, Laura Patricia Apablaza Bizama, Amritha Johny, and Erik Slinde. 2025. "The Effect of a Polypeptide Based Vaccine on Fish Welfare and Infestation of Salmon Lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, in Sea Cages with Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.)" Fishes 10, no. 8: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080405
APA StyleNortvedt, R., Dahl-Paulsen, E., Bizama, L. P. A., Johny, A., & Slinde, E. (2025). The Effect of a Polypeptide Based Vaccine on Fish Welfare and Infestation of Salmon Lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, in Sea Cages with Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fishes, 10(8), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10080405








