Evaluation of Silymarin–L-Carnitine as a Dietary Supplement on Growth Performance, Antioxidants and Immunity, Gut/Liver Health, and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Collection, Acclimation, Experimental Design, and Rearing Conditions
2.2. Diet Preparation and Nutritional Composition
2.3. Sampling and Performance Metrics
2.3.1. Growth and Biometric Analysis
2.3.2. Tissue and Blood Collection
2.4. Digestive Enzyme Activity
2.5. Biochemical, Antioxidant, and Innate Immune Parameters
2.6. Histomorphological Analysis
2.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Gene Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Parameters
3.2. Digestive Tract Health
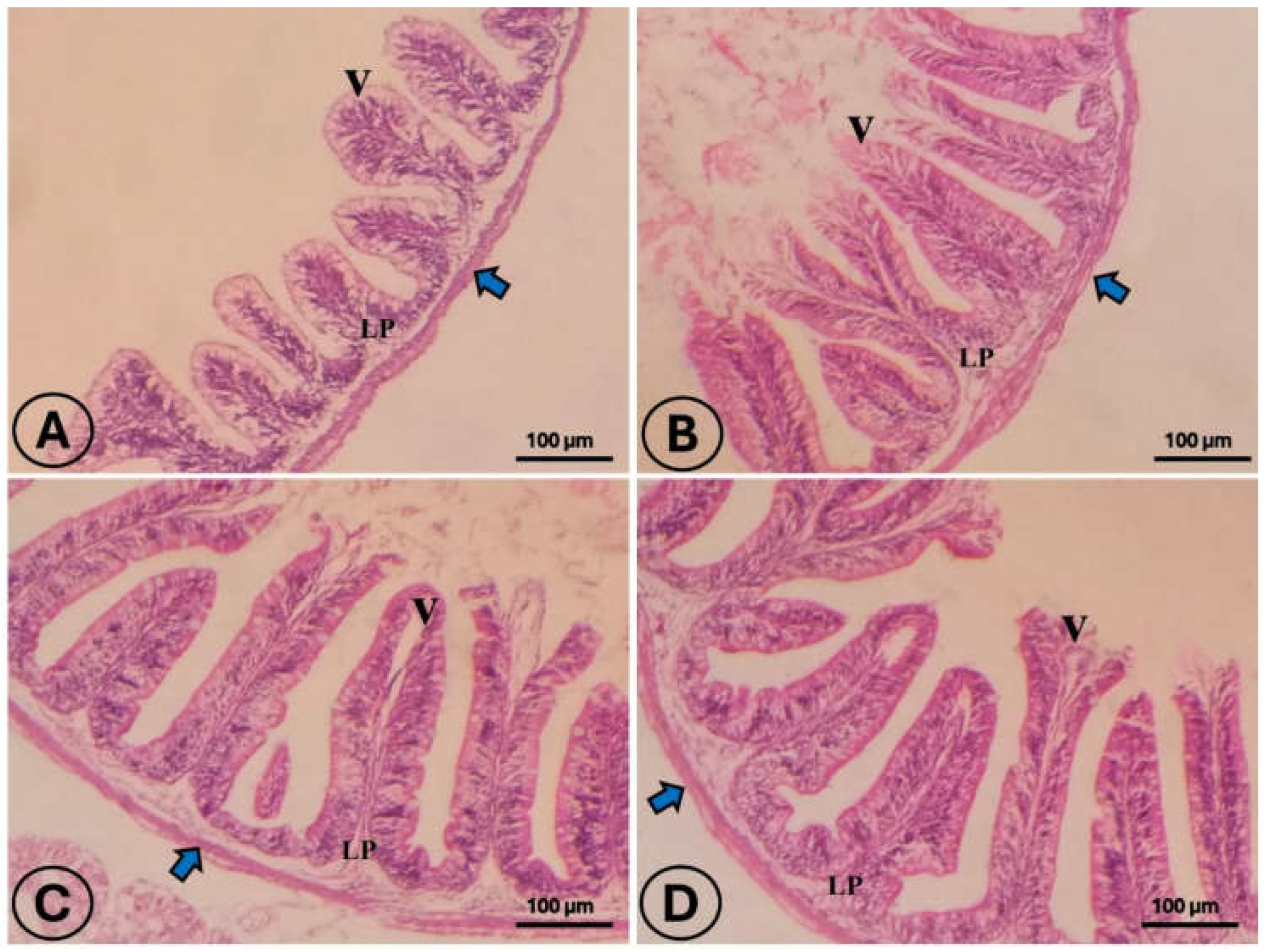
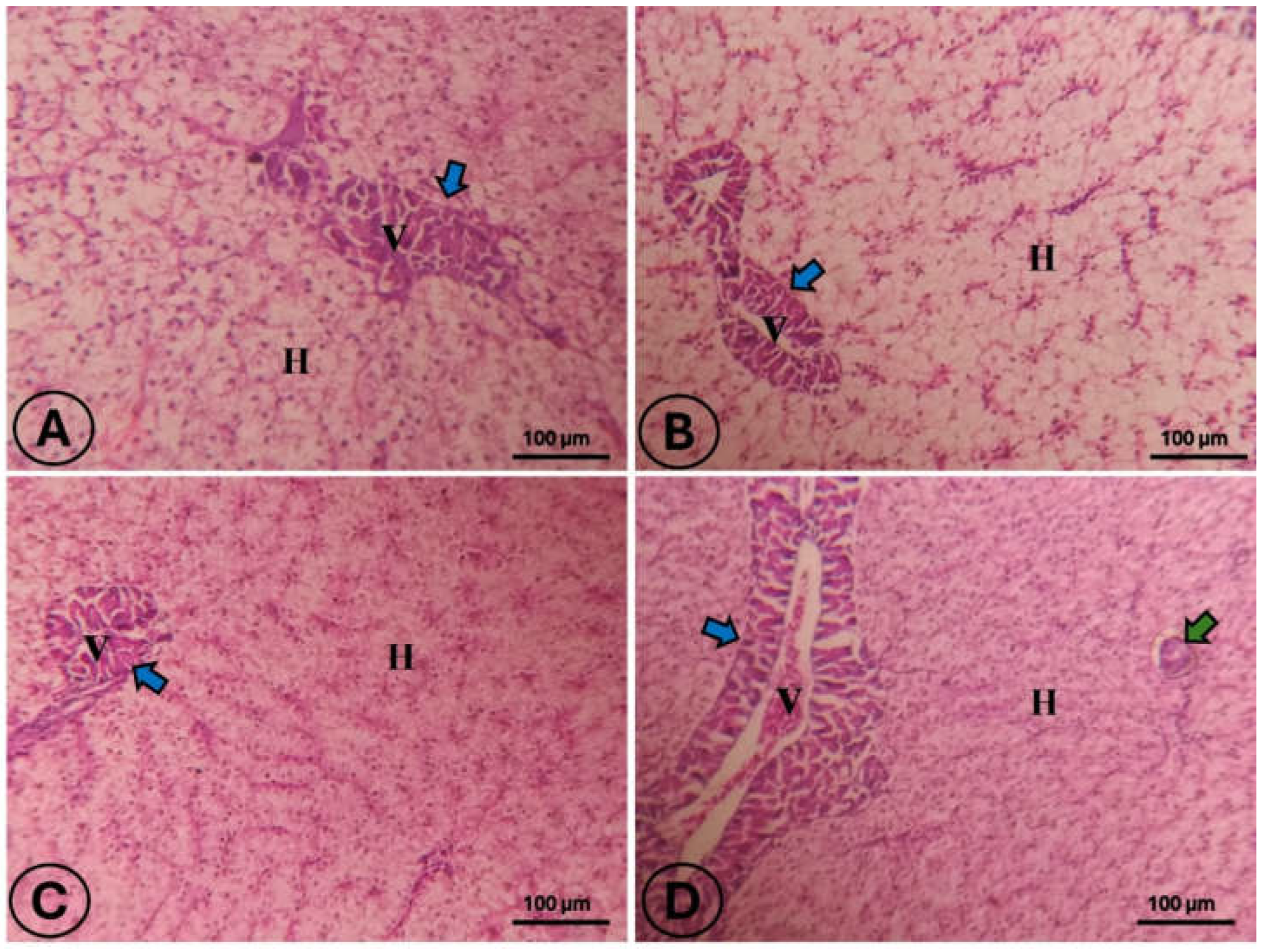
3.3. Intestine and Hepatic Histology
3.4. Blood Composition
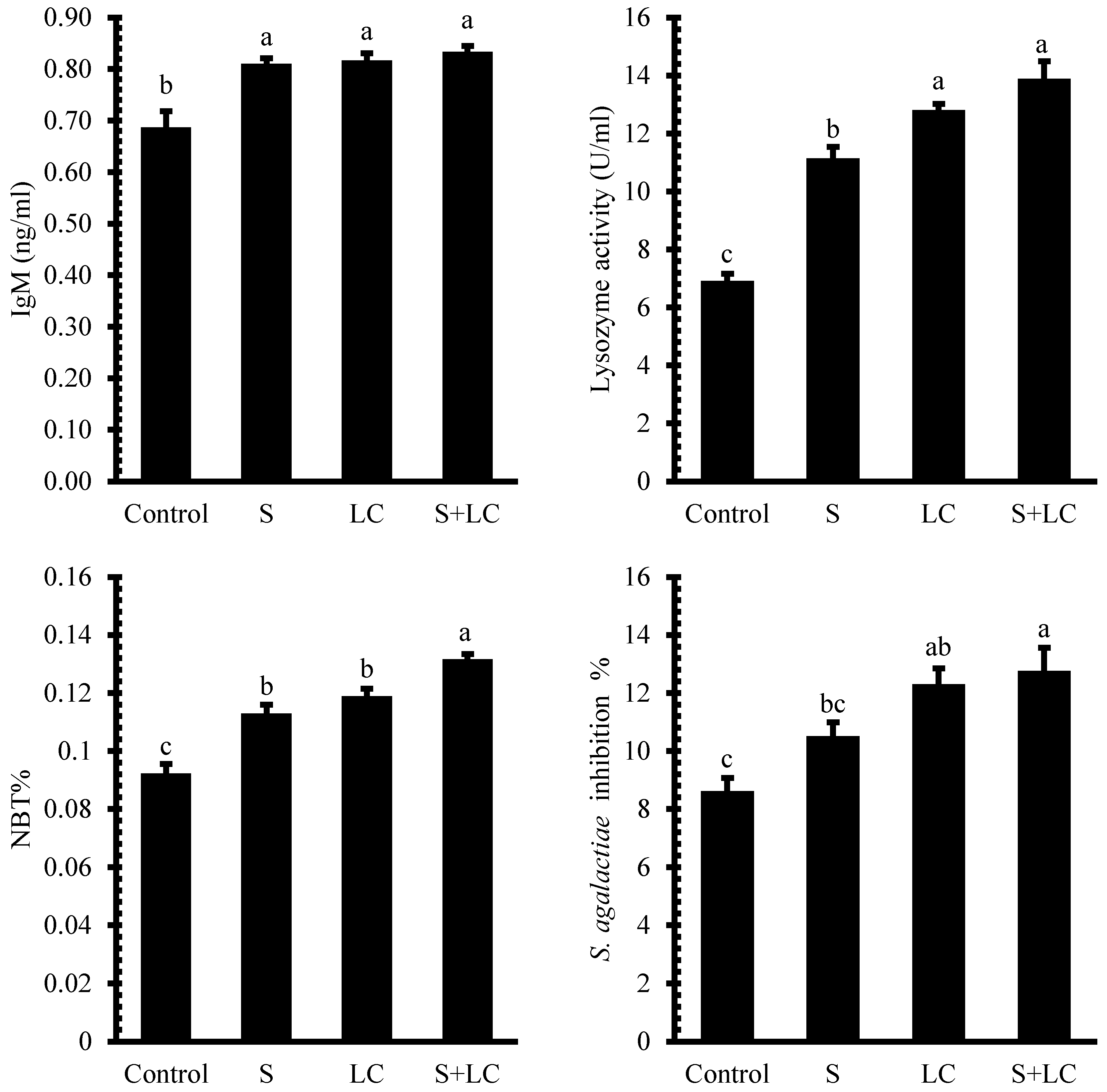
3.5. Immune Responses
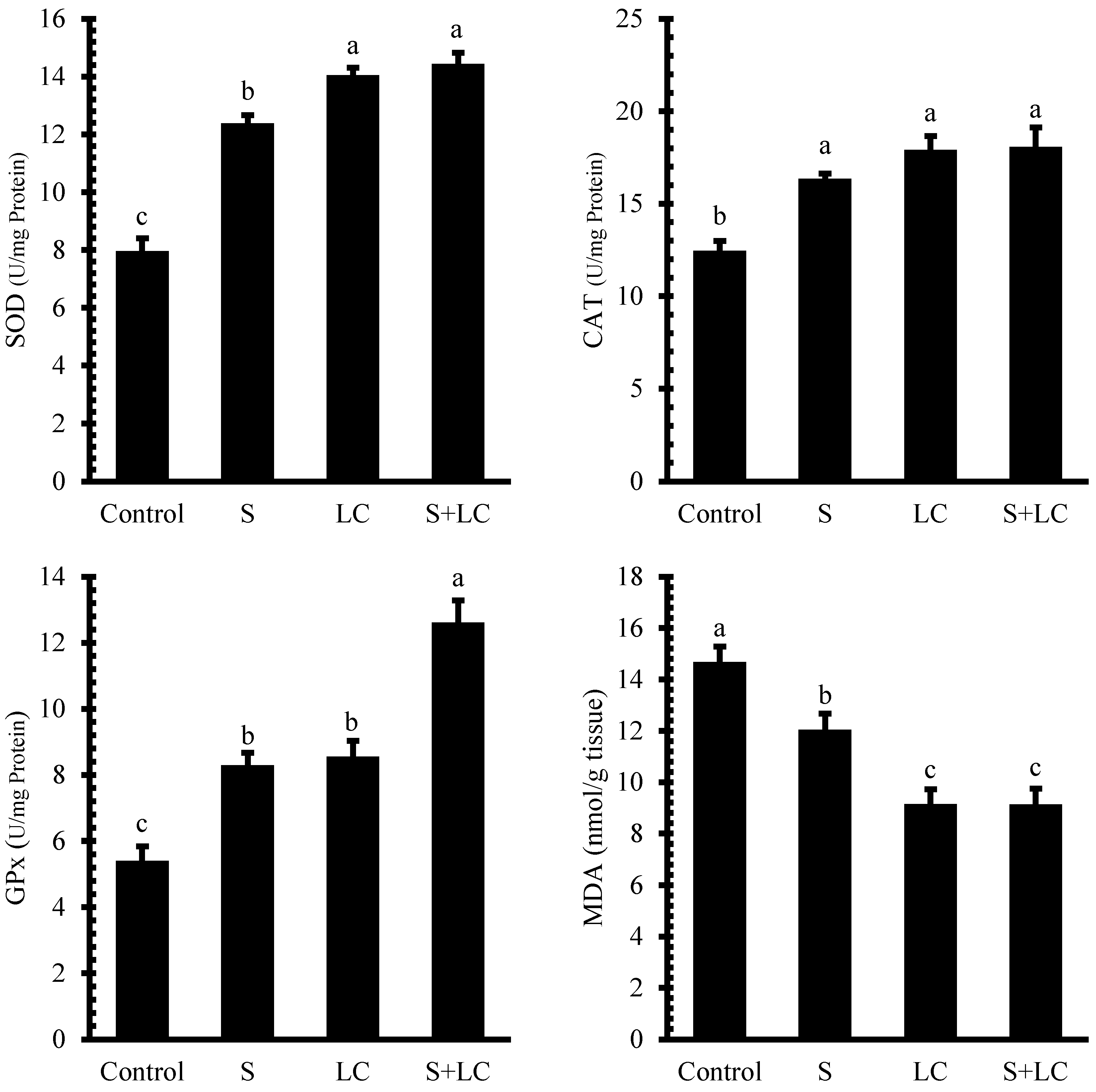
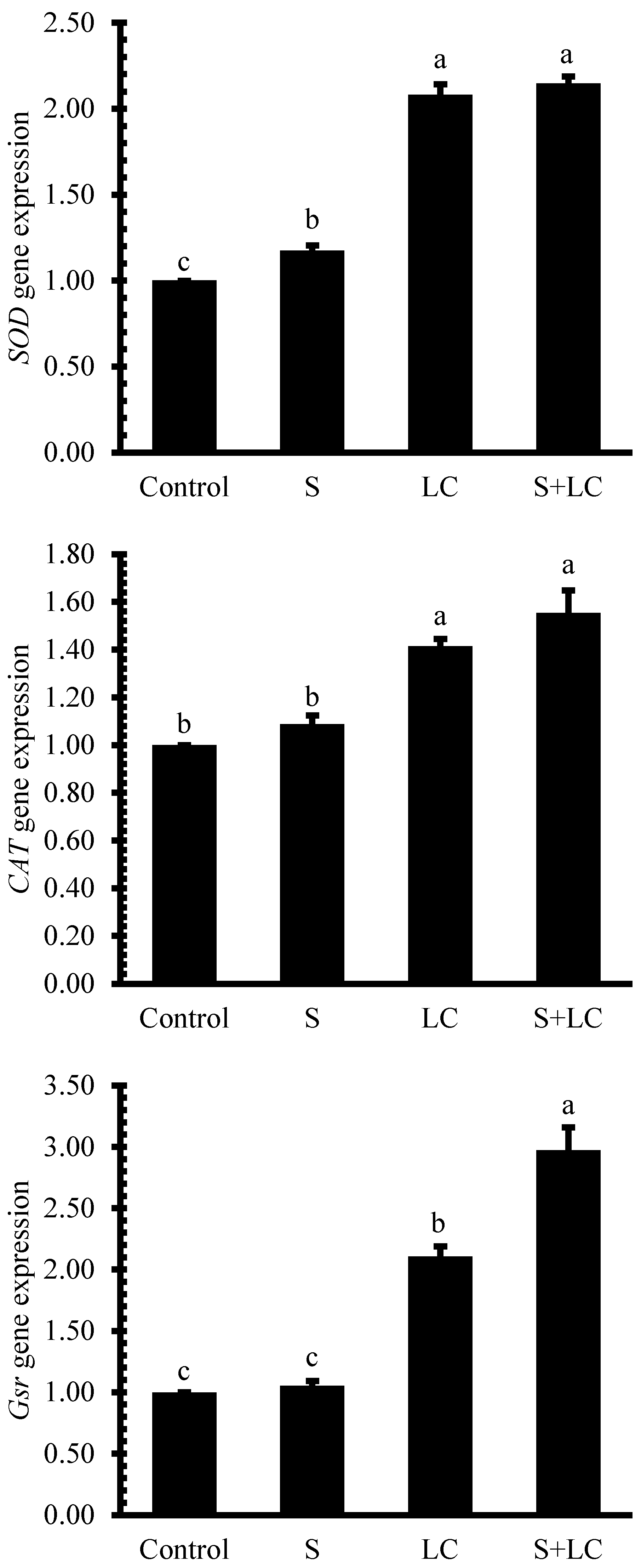
3.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
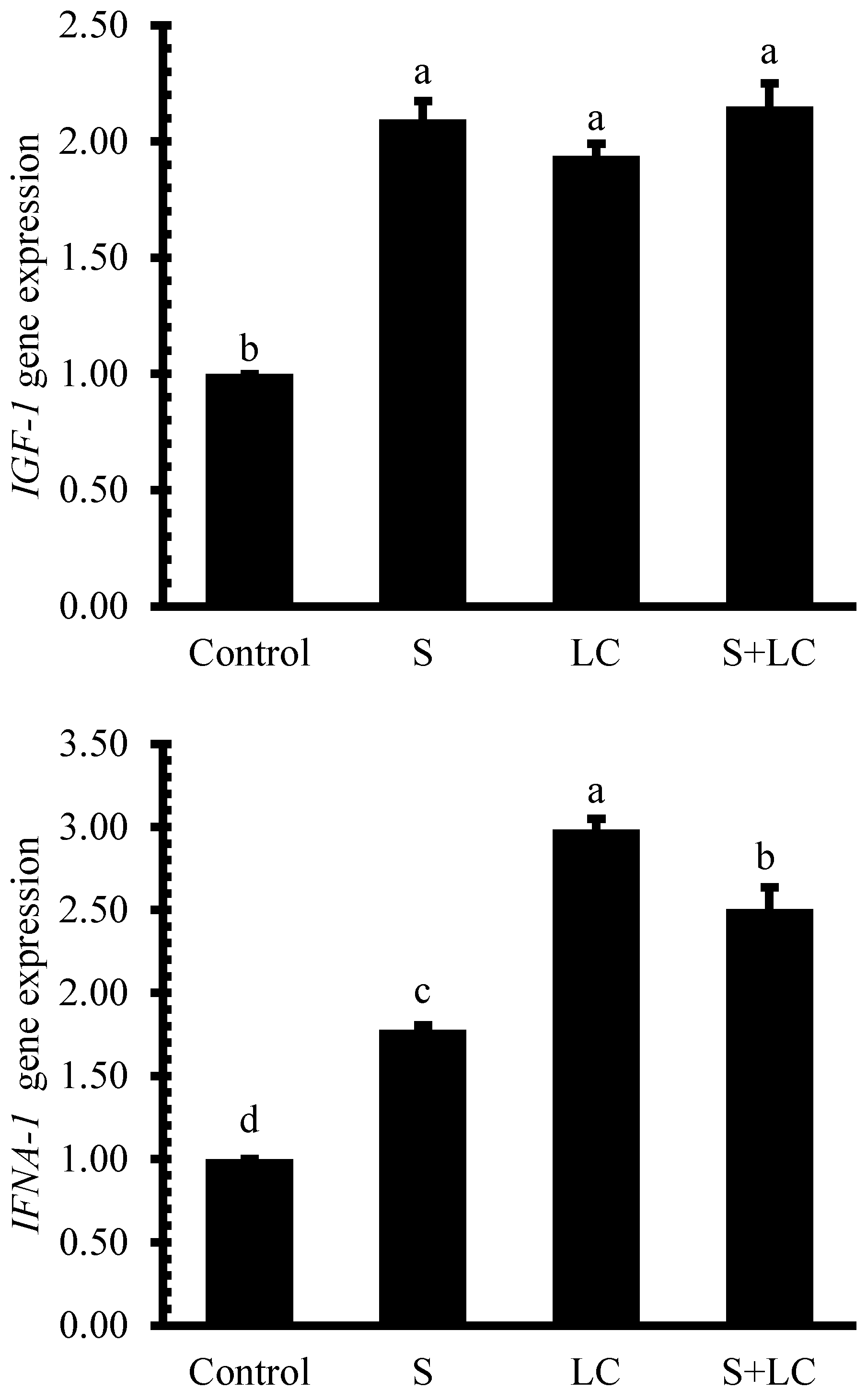
3.7. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, Survival and Somatic Indices
4.2. Digestive Tract Health: Enzymatic Activity and Histomorphology
4.3. Blood Biochemical Profile
4.4. Immune Responses
4.5. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Lipid Peroxidation
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CF | Crude Fiber |
| CL | Crude Lipid |
| CP | Crude Protein |
| DM | Dry Matter |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FCR | Feed Conversion Ratio |
| FBW | Final Body Weight |
| GPx | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| Gsr | Glutathione Reductase |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HPI | Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Interrenal |
| HSI | Hepatosomatic Index |
| IBW | Initial Body Weight |
| IFNA-1 | Interferon-1 |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 |
| ISI | Intestinosomatic Index |
| CF | Condition Factor |
| LC | L-Carnitine |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MS-222 | Tricaine Methanesulfonate |
| NBT | Nitroblue Tetrazolium |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RT-qPCR | Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| S | Silymarin |
| S + LC | Silymarin + L-Carnitine |
| SGR | Specific Growth Rate |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| SR | Survival Rate |
| VSI | Viscerosomatic Index |
| WG | Weight Gain |
References
- Choręziak, A.; Rosiejka, D.; Michałowska, J.; Bogdański, P. Nutritional Quality, Safety and Environmental Benefits of Alternative Protein Sources—An Overview. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obirikorang, K.A.; Quagrainie, K.; Kassah, J.E.; Von Ahnen, M. Editorial: Sustainable aquaculture production for improved food security. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1485956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.I.; Taha, S.A.; Elmaghraby, A.M.; Elhetawy, A.I.G.; Mohamed Srour, T.; El Basuini, M.F.; Shahin, S.A. Effects of dietary bay leaf (Laurus nobilis) aqueous extract on growth performance, feed utilization, antioxidant activity, immunity, and gene expression in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2025, 599, 742155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlock, T.M.; Asche, F.; Anderson, J.L.; Eggert, H.; Anderson, T.M.; Che, B.; Chávez, C.A.; Chu, J.; Chukwuone, N.; Dey, M.M.; et al. Environmental, economic, and social sustainability in aquaculture: The aquaculture performance indicators. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaklader, M.R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Khafaga, A.F.; Shukry, M.; Abo Selema, T.A.M.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Silybum marianum promotes growth, hepatic antioxidative activity, and splenic immunity but does not influence the intestinal barrier function of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2024, 583, 740554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, J.E.; Kalogerinis, P.T.; Milanov, V.; Kalogerinis, C.T.; Poulos, E.J. The Effects of Vitamin E, Silymarin and Carnitine on the Metabolic Abnormalities Associated with Nonalcoholic Liver Disease. J. Diet. Suppl. 2022, 19, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F. Silymarin as a Natural Antioxidant: An Overview of the Current Evidence and Perspectives. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 204–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, A.I.; Shahin, S.A.; Elmaghraby, A.M.; Alhoshy, M.; Soliman, A.A.; Amer, A.A.; Habib, Y.J.; Gewaily, M.S.; El Basuini, M.F. Synergistic benefits of dietary silymarin and selenium on growth, immune functions, antioxidants, and gut/liver health of Thinlip mullet (Liza ramada) juveniles. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.; Surai, A.; Surai, P.F.; Surai, A. Silymarin Puzzle: From Basic Science to Practical Applications in Human and Veterinary Medicine and Nutrition; Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Shukry, M.; Noreldin, A.E.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Bahrawy, A.; Ghetas, H.A.; Khalifa, E. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) extract improves growth, immunity, serum biochemical indices, antioxidant state, hepatic histoarchitecture, and intestinal histomorphometry of striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaee, M.; Impellitteri, F.; Multisanti, C.R.; Sureda, A.; Arfuso, F.; Piccione, G.; Faggio, C. Evaluating Silymarin Extract as a Potent Antioxidant Supplement in Diazinon-Exposed Rainbow Trout: Oxidative Stress and Biochemical Parameter Analysis. Toxics 2023, 11, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-Y.; Limbu, S.M.; Ma, Q.; Chen, L.-Q.; Zhang, M.-L.; Du, Z.-Y. The metabolic regulation of dietary L-carnitine in aquaculture nutrition: Present status and future research strategies. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 1228–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, A.; Lai, W.; Xu, W.; Cao, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Shentu, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Dietary l-carnitine regulates liver lipid metabolism via simultaneously activating fatty acid β-oxidation and suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in large yellow croaker fed with high-fat diets. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, D.H.; Salah, A.S.; Rashwan, A.G.; Al-Hawary, I.I.; Hendam, B.M.; Elsheshtawy, A.; Al Ali, A.; Al Shmrany, H.; Elbialy, Z.I. Dietary l-carnitine supplementation recovers the hepatic damage induced by high-fat diet in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) via activation of Nrf2/Keap pathway and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Sanchez, M.S.; Lins-Rodrigues, M.; Pessini, J.E.; Bittencourt, F.; Boscolo, W.R.; Signor, A. Dietary supplementation with l-carnitine for Nile tilapia juveniles. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi, E.; Mohammadiazarm, H.; Salati, A.P. Effect of dietary l-carnitine and lipid levels on growth performance, blood biochemical parameters and antioxidant status in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2017, 480, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yuan, R.; Guo, Y.; Jia, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cui, H.; Li, B.; Chen, J. L-Carnitine Improves Muscle Nutrient Metabolism and Intestinal Health in High-Fat-Fed Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquac. Nutr. 2025, 2025, 5623889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Yeh, C.-C. Effects of l-carnitine supplementation in diet on growth, lipid metabolism, and carnitine biosynthesis in juvenile giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) fed high plant protein diets. Aquaculture 2025, 609, 742821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikel, S.; Ünalan, B.; Eroldoğan, O.t.; Hunt, A.Ö. Effects of Dietary L-carnitine Supplementation on Growth, Muscle Fatty acid Composition and Economic Profit of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvaran, N.; Sardar, P.; Sahu, N.P.; Shamna, N.; Jana, P.; Paul, M.; Bhusare, S.; Bhavatharaniya, U. Effect of L-carnitine supplemented diets with varying protein and lipid levels on growth, body composition, antioxidant status and physio-metabolic changes of white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei juveniles reared in inland saline water. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 296, 115548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; The Association: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cupp-Enyard, C. Sigma’s Non-specific Protease Activity Assay—Casein as a Substrate. J. Vis. Exp. 2008, 19, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Basuini, M.F.; Ramadan, H.M.; El-Hais, A.M.; Zaki, M.A.A.; Kamel, N.M.; Teiba, I.I.; El-Bilawy, E.H.; Badr, M.R.; Abdel-Aziz, M.F.; Shehata, A.I. Toxicity and therapeutical impacts of Bee venom (Apis mellifera L.) on Nile tilapia juvenile (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Fish. 2025, 10, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumandour, M.; Gewaily, M.S. Morphological studies on the gills of Puffer Fish (Lagocephalus sceleratus, Gmelin, 1789). Int. J. Morphol. 2016, 34, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 40–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Olivier, A.K.; Meyerholz, D.K. Principles for Valid Histopathologic Scoring in Research. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, Q.; Tan, B.-P.; Dong, X.-H.; Chi, S.-Y.; Yang, Q.-H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.-Q. Effects of dietary carbohydrate levels on growth, glucose tolerance, glucose homeostasis and GLUT4 gene expression in Tilapia nilotica. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.; Cordero, H.; Esteban, M.; Soliman, W.S.; Abbas, W.T.; Ibrahim, T.B. Immune and Antioxidant-Related Genes in the Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Collected From Different Locations. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2023, 27, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengmark, A.H.; Slettan, A.; Lee, W.J.; Lie, Ø.; Lingaas, F. Identification and mapping of genes associated with salt tolerance in tilapia. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.B.; Horn, P.; Hancz, C. Application of phytochemicals as growth-promoters and endocrine modulators in fish culture. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Banaee, M.; Vosoghei, A.R.; Mirvaghefei, A.R.; Ataeimehr, B. Evaluation of the immunomodulatory effects of silymarin extract (Silybum marianum) on some immune parameters of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Actinopterygii: Salmoniformes: Salmonidae). Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2012, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpaz, S. l-Carnitine and its attributed functions in fish culture and nutrition—A review. Aquaculture 2005, 249, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z.X. L-carnitine can promote the growth performance of rotifers (Brachionus rotundiformis) by improving their feeding behavior and nutrient composition. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 36, 102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-M.; Guo, G.-L.; Sun, L.; Yang, Q.-S.; Wang, G.-Q.; Zhang, D.-M. Modulatory role of L-carnitine against microcystin-LR-induced immunotoxicity and oxidative stress in common carp. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Elsayed, M.A.M.; Ayyat, A.M.N.; Abdel-Rahman, G.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; Ahmed, N.H. Reversing the detrimental effects of high stocking density in Oreochromis niloticus juveniles using coenzyme Q10 and l-carnitine dietary supplementation. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarasu, T. Herbal biomedicines: A new opportunity for aquaculture industry. Aquac. Int. 2010, 18, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wu, P.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Jiang, W.-D.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Feng, L. Dietary silymarin supplementation enhanced growth performance and improved intestinal apical junctional complex on juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2020, 525, 735311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Ji, H.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Du, Z. Dietary silymarin supplementation promotes growth performance and improves lipid metabolism and health status in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fed diets with elevated lipid levels. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, G.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M. Histomorphological Changes in Fish Gut in Response to Prebiotics and Probiotics Treatment to Improve Their Health Status: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owatari, M.S.; Alves Jesus, G.F.; Brum, A.; Pereira, S.A.; Lehmann, N.B.; de Pádua Pereira, U.; Martins, M.L.; Pedreira Mouriño, J.L. Sylimarin as hepatic protector and immunomodulator in Nile tilapia during Streptococcus agalactiae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyan, W.R.; Yohana, M.A.; Yang, Q.; Tan, B.; Chi, S.; Yi, Y. The effects of dietary L-carnitine supplementation in fish diet containing high corn gluten meal on immunity, lipid metabolism, and metabolomics in juvenile hybrid grouper (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatus). Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 833–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhu, C. Liver Structure. In Artificial Liver; Li, L., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Basuini, M.F.; Hussein, A.T.; El-Hais, A.M.; Elhetawy, A.I.G.; Soliman, A.A.; Gabr, S.A.; Abu-Elala, N.M.; Luo, Z.; Zaineldin, A.I.; Teiba, I.I.; et al. Impacts of dietary Ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi L.) on growth, antioxidative capacity, immune responses, and intestinal histology of grey mullet (Liza ramada). Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, C.; Xu, D.-H.; LaFrentz, B.; LaPatra, S. Overview of Fish Immune System and Infectious Diseases. In Dietary Nutrients, Additives, and Fish Health; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-m.; Ghonimy, A.; Wang, Q.-j.; Guo, Z.-x.; Yu, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.-q.; Farouk, M.H.; Zhang, D.-m. L-carnitine inclusion manipulated metabolic stress in terms of cell viability, oxidative capacity, immune response and anti-apoptotic factors during thermal exposure in fathead minnow muscle cell line. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, S.; Sahoo, P.K. Lysozyme: An important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Ciceri, S.; Grisenti, P. Applications of Lysozyme, an Innate Immune Defense Factor, as an Alternative Antibiotic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Mai, K.; He, G. Effects of silymarin on growth performance, antioxidant capacity and immune response in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 50, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastgoo, S.; Fateh, S.T.; Nikbaf-Shandiz, M.; Rasaei, N.; Aali, Y.; Zamani, M.; Shiraseb, F.; Asbaghi, O. The effects of L-carnitine supplementation on inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers in adults: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 2173–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.I.; Rasheed, M.; Rafiq, H.; Khalid, N.; Rafique, A.; Alhoshy, M.; Habib, Y.J.; El Basuini, M.F. Multi-functional application of octacosanol as a feed additive in animal and aquaculture: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 108, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Boiti, A.; Vallone, D.; Foulkes, N.S. Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling and Oxidative Stress: Transcriptional Regulation and Evolution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Soaudy, M.R.; El-Garhy, H.A.S.; Moustafa, M.M.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; El-Haroun, E.R. Effect of Silybum marianum seeds as a feed additive on growth performance, serum biochemical indices, antioxidant status, and gene expression of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2019, 509, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhoshy, M.; Shehata, A.I.; Habib, Y.J.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Nutrigenomics in crustaceans: Current status and future prospects. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.N.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A.; Björnsson, B.T. Regulation of skeletal muscle growth in fish by the growth hormone—Insulin-like growth factor system. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koner, D.; Banerjee, B.; Kumari, A.; Lanong, A.S.; Snaitang, R.; Saha, N. Molecular characterization of superoxide dismutase and catalase genes, and the induction of antioxidant genes under the zinc oxide nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress in air-breathing magur catfish (Clarias magur). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1909–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Formulation (g/kg) 1 | Experimental Diets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | S | LC | S + LC | |
| Fish meal, 65% | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Meat meal, 50% | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| Corn | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 |
| Rice bran | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Wheat bran | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Soybean meal, 48% | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Corn gluten | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Mono calcium | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Premix 2 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Sunflower Oil | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Vitamin C | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Silymarin 3 levels (S, mg/kg) | 0 | 850 | 0 | 425 |
| L-Carnitine 4 (LC, mg/kg) | 0 | 0 | 500 | 250 |
| Nutritional profile (%) | ||||
| Dry matter (%, DM) | 90.12 ± 0.35 | 90.28 ± 0.41 | 90.05 ± 0.39 | 90.24 ± 0.32 |
| Crude protein (CP, % DM basis) | 30.64 ± 0.55 | 30.09 ± 0.69 | 31.01 ± 1.01 | 30.89 ± 0.551 |
| Crude lipid (CL, % DM basis) | 3.75 ± 0.33 | 3.80 ± 0.15 | 3.16 ± 0.54 | 3.77 ± 0.25 |
| Ash (% DM basis) | 4.17 ± 0.62 | 4.44 ± 0.29 | 4.16 ± 0.05 | 4.19 ± 0.22 |
| Crude fiber (CF, % DM basis) | 3.52 ± 0.43 | 3.91 ± 0.42 | 3.96 ± 0.62 | 3.86 ± 0.51 |
| Gene Name | Primer sequences (5′–3′) Forward (F) and Reverse (R) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Tm (°C) | Primer Efficiency (%) | GenBank Accession No | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF-1 | F | GTGGACGAGTGCTGCTTC | 139 | 58 | 98 | XM_019346352.2 | [28] |
| R | TGCTACTAACCTTGGGTGC | ||||||
| IFNA-1 | F | ATGGGAGGAGAACACAGTGG | 94 | 59 | 100 | XM_005466659.4 | [29] |
| R | TGTCGTATTGCTGTGGCTTC | ||||||
| CAT | F | ATGAGGAGGAGCGACAGAGA | 90 | 61 | 97 | JF801726.1 | |
| R | AATTCTCGACCATGCGTTTC | ||||||
| SOD | F | GGAGGTGAACCACAAGGAGA | 99 | 61 | 99 | XM_003449940.5 | |
| R | TACAGCCACCGTAACAGCAG | ||||||
| Gsr | F | TCTGCACGATCATGGTGATT | 104 | 60 | 100 | XM_013271309.3 | |
| R | TGCGATTTAGGTGACTGACG | ||||||
| β-actin | F | GATATCATTTGCCTGAAACCGTTT | 77 | 59 | 100 | XM_003443127.5 | [30] |
| R | CGATTTCATCTTCCATGGCTTT | ||||||
| Variables | Experimental Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | S | LC | S + LC | p_adj Values | |
| IBW (g) | 10.02 ± 0.07 | 10.01 ± 0.02 | 10.01 ± 0.07 | 10.00 ± 0.06 | 0.996 |
| FBW (g) | 44.64 ± 1.23 c | 54.52 ± 1.01 a | 49.98 ± 1.51 b | 56.49 ± 1.47 a | 0.001 |
| WG (g) | 34.62 ± 1.25 c | 44.51 ± 1.02 a | 39.96 ± 1.57 b | 46.49 ± 1.43 a | 0.001 |
| SGR (%/d) | 1.78 ± 0.04 c | 2.02 ± 0.02 ab | 1.92 ± 0.04 b | 2.06 ± 0.03 a | 0.002 |
| FCR | 1.79 ± 0.04 a | 1.49 ± 0.01 b | 1.59 ± 0.06 b | 1.50 ± 0.02 b | 0.003 |
| SR (%) | 95.55 ± 2.22 | 96.67 ± 1.93 | 96.67 ± 1.93 | 97.78 ± 1.11 | 0.864 |
| HSI (%) | 1.81 ± 0.02 | 1.75 ± 0.23 | 2.21 ± 0.25 | 1.80 ± 0.13 | 0.284 |
| ISI (%) | 4.19 ± 0.26 | 5.00 ± 0.3 | 4.62 ± 0.27 | 4.71 ± 0.17 | 0.193 |
| VSI (%) | 9.88 ± 0.7 | 10.09 ± 0.67 | 9.65 ± 0.49 | 9.87 ± 0.64 | 0.969 |
| CF | 2.16 ± 0.11 | 2.32 ± 0.09 | 2.23 ± 0.03 | 2.18 ± 0.08 | 0.502 |
| Enzyme (U/mg) | Experimental Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | S | LC | S + LC | p_adj Values | |
| Amylase | 10.54 ± 0.4 c | 15.69 ± 0.29 a | 12.68 ± 0.42 b | 16.31 ± 0.35 a | 0.001 |
| Lipase | 15.48 ± 0.4 c | 21.99 ± 0.57 b | 22.53 ± 0.39 b | 24.55 ± 0.89 a | 0.001 |
| Protease | 15.37 ± 0.64 b | 18.68 ± 0.44 a | 18.55 ± 0.46 a | 18.43 ± 0.68 a | 0.009 |
| Variables | Experimental Groups | p_adj Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | S | LC | S + LC | ||
| Intestinal Morphometry | |||||
| Villus height (μm) | 162.47 ± 2.58 c | 236.03 ± 3.85 b | 305.07 ± 6.66 a | 306.63 ± 15.10 a | 0.001 |
| Villus width (μm) | 59.34 ± 5.75 c | 69.56 ± 7.08 ab | 75.02 ± 1.76 ab | 85.76 ± 9.81 a | 0.120 |
| Crept depth (μm) | 18.78 ± 2.79 b | 36.33 ± 1.97 a | 33.73 ± 3.13 a | 32.74 ± 2.26 a | 0.005 |
| Muscularis thickness (μm) | 19.64 ± 0.89 c | 24.98 ± 3.09 ab | 28.08 ± 0.45 ab | 22.64 ± 0.70 a | 0.037 |
| Goblet cells | 7.33 ± 1.45 c | 17.33 ± 1.20 b | 18.00 ± 1.73 b | 23.00 ± 1.15 a | 0.001 |
| Hepatic Histopathological Scores | |||||
| Hepatic steatosis score | 2.00 ± 0.01 ab | 2.67 ± 0.33 a | 1.33 ± 0.33 bc | 0.67 ± 0.33 c | 0.006 |
| Hepatic vacuolation score | 2.33 ± 0.33 b | 1.67 ± 0.33 a | 1.33 ± 0.33 b | 0.33 ± 0.33 a | 0.017 |
| Variables | Experimental Groups | p_adj Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | S | LC | S + LC | ||
| Total protein (g/dL) | 3.3 ± 0.08 c | 4.01 ± 0.05 ab | 3.97 ± 0.09 b | 4.22 ± 0.05 a | 0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 1.27 ± 0.02 | 1.29 ± 0.06 | 1.31 ± 0.06 | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 0.950 |
| Globulin (g/dL) | 2.03 ± 0.08 b | 2.72 ± 0.11 a | 2.67 ± 0.05 a | 2.93 ± 0.05 a | 0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 90.27 ± 1.32 a | 84.65 ± 0.84 b | 81.05 ± 1.08 c | 76.84 ± 0.78 d | 0.001 |
| Cortisol (ng/mL) | 38.14 ± 0.61 a | 31.41 ± 1.18 b | 31.02 ± 0.87 bc | 28.24 ± 0.82 c | 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 125.6 ± 3.6 a | 117.12 ± 3.21 a | 95.94 ± 2.64 b | 87.9 ± 3.25 b | 0.001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 113.39 ± 3.05 | 117.68 ± 2.78 | 116.65 ± 1.66 | 117.63 ± 1.79 | 0.572 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 6.15 ± 0.32 | 6.19 ± 0.16 | 6.17 ± 0.43 | 6.19 ± 0.15 | 1.000 |
| AST (IU/L) | 41 ± 2.52 | 41.67 ± 1.86 | 42 ± 2.52 | 42.33 ± 1.67 | 0.975 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 5.53 ± 0.28 | 5.3 ± 0.44 | 5.32 ± 0.43 | 5.21 ± 0.04 | 0.921 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 0.962 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehata, A.I.; Tefal, E.; Elmaghraby, A.M.; Amer, A.A.; Teiba, I.I.; Alhoshy, M.; Gewaily, M.S.; Guo, Z.; Li, S.; El Basuini, M.F. Evaluation of Silymarin–L-Carnitine as a Dietary Supplement on Growth Performance, Antioxidants and Immunity, Gut/Liver Health, and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes 2025, 10, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110580
Shehata AI, Tefal E, Elmaghraby AM, Amer AA, Teiba II, Alhoshy M, Gewaily MS, Guo Z, Li S, El Basuini MF. Evaluation of Silymarin–L-Carnitine as a Dietary Supplement on Growth Performance, Antioxidants and Immunity, Gut/Liver Health, and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes. 2025; 10(11):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110580
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehata, Akram Ismael, Eslam Tefal, Ayaat M. Elmaghraby, Asem A. Amer, Islam I. Teiba, Mayada Alhoshy, Mahmoud S. Gewaily, Zhixun Guo, Shengkang Li, and Mohammed F. El Basuini. 2025. "Evaluation of Silymarin–L-Carnitine as a Dietary Supplement on Growth Performance, Antioxidants and Immunity, Gut/Liver Health, and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)" Fishes 10, no. 11: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110580
APA StyleShehata, A. I., Tefal, E., Elmaghraby, A. M., Amer, A. A., Teiba, I. I., Alhoshy, M., Gewaily, M. S., Guo, Z., Li, S., & El Basuini, M. F. (2025). Evaluation of Silymarin–L-Carnitine as a Dietary Supplement on Growth Performance, Antioxidants and Immunity, Gut/Liver Health, and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fishes, 10(11), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10110580








