Abstract
India is currently facing a mounting challenge related to municipal waste management, due to an increasing urban population, and their high consumption lifestyles. India also has the world’s highest number of young people in the 10–24 years age group. The study applied the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) model to predict school students’ recycling intentions in Delhi, the capital of India and one of the highest producers of municipal solid wastes in the country. Data were collected from a school in New Delhi and the sample size consisted of 272 students from 9th and 10th grades. The TPB model explained 56% of the variance in the students’ intentions to recycling. The predictor ‘subjective norm’ appeared to have the strongest impact on the students’ recycling intentions, followed by ‘attitude’ and ‘perceived behavioural control’. It indicated that social factors are driving the Indian youth’s recycling intentions. It is important that the policymakers promote recycling as a social trend in India and provide adequate facilities to the public so that they can participate in recycling activities without facing difficulties. Schools also have a role in increasing students’ awareness of recycling and motivating them to participate in household waste management practices.
1. Introduction
Recycling of ever-increasing urban waste has become a priority for sustainable environmental management and planning activities in both developed and developing countries. According to an estimate, the total generation of municipal solid waste (MSW) is expected to reach around 2.2 billion tonnes per annum globally by 2025 [1]. Waste generation has a strong linkage to production and consumption patterns in our societies. The current trend shows that the MSW-generation per capita has been growing steadily in the low and middle-income countries, whereas it has been gradually stabilising in the developed economies [2]. Unmanaged urban wastes affect biogeochemical cycles from local to global scales and hazardous wastes are particularly dangerous to the living organisms including humans [3,4,5]. Inadequate management of MSW has become a global concern that affects the quality of life in urban areas in many countries especially in the developing nations [6,7].
India currently produces much lower amount of MSW per day compared with the U.S. and China; however, it is among the top 10 MSW-generating countries due to its large size of urban population and their increasing adoption of high consumption lifestyles [8]. Current MSW-generation in India is about 170,000 tonnes per day (i.e., 62 million tonnes annually) and with an annual growth rate of 5% it is projected to reach about 436 million tonnes per year by 2050 [9]. The growth in urban waste generation is strongly linked with the growth in urban population as it has been projected that almost 50% of India’s population will be residing in urban areas by 2050 from the present 31% urban dwellers in the country [9]. However, existing MSW-management systems in India are inefficient as 75–90% of the waste generated in urban areas is disposed of in open dumping sites, which affects public health, the quality of air, water, and soil, and the economy [10,11,12,13,14]. Therefore, it goes without saying that the development of an efficient and widely implemented urban waste management system in India is significant as it can provide economic benefits, conserve scarce resources, and decrease the quantities of waste ending at landfills [2,13].
A considerable number of studies have investigated waste management practices in various Indian cities [5,6,12,15]. The recycling of MSW is a tradition in many urban areas in India that involves both formal and informal sectors [13,16]. In the dominating informal waste recycling sector in India, waste pickers collect recyclables, segregate and transfer them to scrap dealers, which thereafter arrive at different enterprises for further processing such as recycling [16]. However, the quantity of recyclable materials in wastes is smaller in India than that of in developed countries. Wastes in the community bins in India mainly consist of organic materials, scrap papers and plastic materials [17].
In the recent years, Government of India (GoI) has introduced a wide range of policies to address the issues of urban waste management in the country. The latest policy prescription titled ‘Solid Waste Management Rules’ was introduced in 2016 that replaced the erstwhile ‘Municipal Solid Wastes (Management and Handling) Rules’ that came into being in 2000. Similarly, a new policy instrument called ‘Plastic Waste Management Rules’ emerged in 2016, replacing an earlier set of regulations on plastic waste management that was in place since 2011. Besides these measures, a completely new regulatory instrument called ‘E-waste (Management) Rules’ also appeared in 2015. Although the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (under the GoI) is the nodal agency for implementing and monitoring these regulatory measures, their achievements have remained limited [13]. Additionally, the Prime Minister of India, Mr. Narendra Modi, initiated a ‘Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (SBA)’ or ‘Clean India Mission’ in 2014—the largest nationwide campaign to drive cleanliness in India by involving millions of government employees, the public, school and college students, and civil society organisations. The SBA has both urban and rural missions, and the urban mission known as the ‘Swachh Bharat Urban’ has prescribed guidelines for involving community members in urban waste management practices [18]. That is to say that the success of these programmes requires an active participation of citizens, local governments, and private entrepreneurs [14]. At present, almost no segregation of garbage takes place at source in India and the residents always dispose of garbage improperly [19]. The role of households is particularly important in the Indian context as “it will be nearly impossible for the civic body to provide better surroundings if residents do not make an effort to deposit waste into the bins and stop the practice of throwing garbage onto the road” Joseph [20].
1.1. Social Aspects in Recycling
Urban waste management and recycling practices are not simply technical matters and the technocrats do not entirely regulate them. According to Srivastava et al. [21], “a waste management programme that ignores the social aspects is doomed to failure”. A number of studies appeared during the past two decades where scholars identified and explained the socio-psychological and situational factors influencing households’ recycling behaviours [22]. However, research on social dimensions of MSW is still not expansive and therefore, it is crucial that researchers investigate the management of MSW from a social point of view [23]. In India, urban residents have to take on the majority of the responsibilities for segregating their household wastes and bringing them to community bins from where municipalities and private entrepreneurs will collect them for recycling and other uses [14]. Moving towards a recovery-centric approach of waste management (i.e., the 3R principles: Reuse, recycle, and reduce) from the current disposal-centric approaches requires partnership among the government, private sector, and citizens [14,16,24]. Citizens’ participation in waste management could make it a decentralised and cost-efficient approach [14], and there is a need for civil society organizations and educational institutes to be actively involved in raising awareness of waste management among the masses in India [25].
Positive public opinion and their active participation are central to the long-term success of MSW-management program in the developing countries [26,27,28]. Therefore, waste management policies in many of these countries have tried to promote people-centric approaches in recycling [29]. In the industrialised countries, waste management and recycling are highly sophisticated. In these countries, recycling related studies mainly focus on technical applications such as design and innovation, policy and economic analysis, and explore socio-psychological influences on individuals’ recycling behaviours. Recycling research in developing countries, on the contrary, has not been much oriented towards understanding the influences of indirect factors on individuals’ recycling attitudes and behaviours [30]. However, a recent study by Ma and Hipel [23] has pointed out that social dimension studies in MSW-management have been increasing in the developing countries particularly in the Asian countries because of their high population density and rapid urbanization associated with fast economic growth, which have made MSW-management a daunting task for the local civic bodies in these countries.
1.2. Public Attitudes to Recycling in the Developing Countries
Among the studies related to public attitudes and behaviours concerning recycling in the developing countries, Bolaane [29] found from a study in Gaborone (Botswana) that the households’ general awareness of recycling did not translate into actual recycling behaviours due to lack of financial incentives and absence of visible recycling facilities. In another study from Surabaya (Indonesia), Dhokhikah et al. [31] reported that the respondents did not sort and recycle household solid wastes due to lack of time, absence of tradition in separation of waste at source, shortage in collection facilities, inadequate knowledge, and apathy towards recycling as it lacks incentives. Similar attitudes to recycling were also observed among the urban residents of Hat Yai (Thailand), Mekelle (Ethiopia), Dar es Salaam (Tanzania), Putrajaya (Malaysia), and some other Indonesian cities [26,32,33,34,35]. In China, Xiao et al. [28] explored public willingness to participate in waste management practices in the city of Xiamen and they found that the residents’ environmental knowledge and social motivation had the strongest positive effects on their willingness to participate in waste management activities.
A few studies have also explored public attitudes to recycling in different Indian cities. In this regard, Kumar and Nandini [36] found that most of the residents in Bengaluru, the third most populous city in India, were unaware of solid waste management, and they were disposing of their waste into open spaces. However, the authors reported that most of those respondents were willing to segregate their wastes into different bins if the local civic bodies provided such bins to them. A lack of awareness of solid waste management was also evident among the residents of both Kumbakonam, a small town in the state of Tamil Nadu [37] and Jalandhar, a medium-sized city in the state of Punjab [38]. The authors found that the residents of those two cities were disposing of their household wastes into open dumping sites, although many of them were aware of the potential health hazards arising from such a practice. Jayasubramanian et al. [39] reported that a considerable number of the residents in Coimbatore, the second largest city in the state of Tamil Nadu, were recycling their household wastes as they were aware of its benefits. However, the residents informed that the lack of time and inadequate waste disposal facilities in their vicinities were the main obstacles against recycling. There was only one study to our knowledge, which investigated school students’ perceptions and attitudes regarding household waste management in India and reported that the school students in Thrissur city in the state of Kerala were aware of solid waste related issues and they demonstrated their willingness to participate in household waste management practices [40].
1.3. Importance of the Youth Participation in Recycling in India
Although the above studies shed light on the public perceptions and attitudes concerning solid waste management in India, they are by no means exhaustive. India has the world’s highest number of people in the 10–24 years age group (ca. 242 million) [41]. According to the Census data of 2011, the country is expected to have about 34% share of youth (15–24 years) in the total population by 2020 from 19% in 2011 [42]. Therefore, the importance of youth-engagement in civic activities has started receiving greater attention in the Indian society and policies than ever before. There has been a major shift in the way societies now perceive the role of young people in India due to the realization that they are the most important section of the population and the country’s future growth will be determined by the size of its youth and their ability to bring positive changes to the society [41]. However, no study has so far investigated the socio-psychological factors driving young citizens’ such as school students’ recycling intentions in the Indian context. In this regard, recycling intention can be defined as “an individual’s self-commitment to engage in recycling behaviours” [43]. Consumption of electronic gadgets (e.g., mobile phones and computers) and fashionable items (e.g., clothing, bags, and accessories) has been growing rapidly among the youth in Indian cities and this trend is likely to continue in the future as urban households become wealthy. Students should be aware of the problems related to unmanaged urban wastes so that they can participate in waste management practices and become responsible citizens. They can also influence others, particularly the adults, who will follow sustainable waste management behaviours at home and thus can bring much desired behavioural changes to the Indian society related to waste management. The present study from this perspective aims to explain Indian students’ recycling intentions by applying the framework of the Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) developed by Azjen [44], which is a widely applied socio-psychological theory explaining individuals’ behavioural intentions.
1.4. The Theory of Planned Behaviour and Recycling Intention
The TPB is an extension of the Theory of Reasoned Action [45] and the TPB model comprises three independent variables—attitude (Attitude), subjective norm (SN), and perceived behavioural control (PBC), which together act as the predictor of a wide range of intentions (Intention, the dependent variable) [46]. According to the TPB model, an individual’s intention to perform a given behaviour is determined by the positive evaluation of the behaviour (i.e., Attitude: e.g., recycling is useful, recycling is good, etc.), perceived social pressure (i.e., SN) from others who are important to them (e.g., family, friends, and colleagues) to behave (or not) in a certain manner (e.g., waste separation at source, bringing household wastes into community bins, etc.) and their motivations to comply with those views, and perceived ease of performing that behaviour (i.e., PBC; e.g., how difficult it is to perform recycling behaviour, how confident an individual is about performing waste separation behaviour, etc.) [47]. The TPB framework has been applied in several studies for explaining individuals’ recycling intentions and behaviours. Among the most recent studies, Stoeva and Alriksson’s [48] explored university students’ waste separation intentions in Sweden and Bulgaria and reported that Attitude was the strongest predictor of the Swedish students’ waste-separation intentions, whereas both Attitude and PBC were the most significant predictors of the Bulgarian students’ intentions to separate household wastes. In another study, Pikturnienė and Bäumle [49] investigated public intentions for recycling in three Lithuanian cities and found only Attitude having statistically significant positive effect on the recycling intentions. In fact, Attitude appeared to be the most significant predictor of recycling intentions in several studies [50,51,52,53,54]. However, in some studies, PBC emerged as the most significant predictor of recycling intention. For example, PBC was the strongest predictor of recycling intention among the residents of Hong Kong [55], Australia [56], and Turkey [57]. There is also an instance where none of the TPB predictors had any effect on individuals’ recycling intentions and additional factors such as ‘moral obligation’, ‘past behaviour’ and ‘inconvenience’ predicted individuals’ recycling intentions in the Netherlands [58].
Traditionally, SN has appeared as the weakest predictor of intention in the TPB framework [46] and it was evident in many of the above-mentioned studies on recycling intentions. However, as an exception, SN emerged as the strongest predictor of university students’ recycling intentions in Hong Kong [47]. Nevertheless, there are some examples in other contexts where SN emerged as the strongest predictor of school students’ intentions to use bioenergy in India [59], Taiwanese citizens’ intentions to visit green hotels [60], and Chinese entrepreneurs’ intentions to adopt cleaner production technologies [61]. There is hardly any study, which has applied the TPB framework to investigate recycling intentions among the urban masses in India although there are some studies, which applied the TPB framework to explain Indian consumers’ intentions to purchase green and environmentally sustainable products [62,63,64,65]. In those studies, the effects of both Attitude and PBC on individuals’ purchase intentions of green products appeared to be statistically significant, whereas the effect of SN was inconsistent (i.e., either significant or insignificant). Therefore, it is evident from the above studies that though Attitude, PBC and SN were useful in explaining individuals’ recycling and other pro-environmental intentions, their effects have been varying, which could be the result of different personal, contextual, and situational factors affecting individuals’ pro-environmental intentions.
1.5. Objectives and Hypotheses
The present study was conducted in Delhi, the capital of India, the second most populous city in the country and the second largest megacity in the world [66,67]. MSW-generation in Delhi has been increasing at an alarming rate. It has increased from 8370 tonnes per day during 2014–2015 to 9260 tonnes per day during 2015–2016, i.e., almost 11% increase in one year [68]. It has been estimated to reach up to 18,000 tonnes per day by 2021 [69]. Door to door waste collection system exists in all the urban local bodies under the five municipal authorities in Delhi and the predominant waste management practice carried out in the city is landfills in four designated sites. A recent study by Singh et al. [70] has found that the landfills in Delhi are the major sources of emission of greenhouse gases, particularly the methane and therefore, there is an urgent need for better segregation of household organic wastes and to establish scientifically planned sanitary landfill sites. The first measure clearly requires the residents to be aware of MSW related issues and have positive attitudes to participating in waste management and recycling practices.
The present study is particularly relevant as it investigated the socio-psychological factors determining students’ recycling intentions in Delhi by applying the standard TPB framework. In addition, the study explored students’ awareness of recycling including the analysis of the effects of some of the demographical variables on the TPB constructs and students’ perceptions of learning possibilities of recycling. Based on these findings, the study recommended some measures for developing students’ awareness of and positive intentions to recycling. The main hypotheses of the study were as follows:
H1:
Students’ attitude (Attitude) to recycling significantly influences their intentions (Intention) of recycling.
H2:
Subjective Norm (SN) significantly influences students’ intentions (Intention) of recycling.
H3:
Perceived Behavioural Control (PBC) significantly influences students’ intentions (Intention) of recycling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
The present study was conducted as part of an international survey related to exploring recycling intentions among the youths in China, Greece and India. In Greece, the survey was conducted among university students. However, school students participated in the Chinese and Indian surveys. The findings from the Chinese and Greek surveys will be reported separately elsewhere. The main reason for not producing a comparative study with the data from these three countries was that the researchers aimed to present a detailed analysis of the social dimensions and policy frameworks concerning MSW-management from each country and relate them to the country-specific findings. The Indian data came from a high school based in New Delhi. A local collaborator contacted the Principal of the school for obtaining necessary permission for conducting the survey. The questionnaires were distributed to the students by the local collaborator and a class teacher was responsible for supervising the survey. Prior to distributing the questionnaires, the students were informed about the purpose of the survey and the use of the survey data. They were also assured of anonymity and confidentiality. The respondents spent an average twenty minutes for completing the survey and their participation was voluntary. After the survey, the local collaborator collected the questionnaires and performed an initial data entry in a statistical software package. The local collaborator sent the processed data to the researchers who conducted further analysis and interpreted the results.
2.2. Design of the Survey Instrument
The Indian and Chinese version of the survey instrument differed from the Greek version of the instrument in some respects. The Indian version of the survey instrument consisted of questions concerning students’ demographic profiles and awareness of recycling, a seven-point Likert-type scale with fourteen items related to the TPB constructs, and questions regarding the students’ perceptions of the possibilities to learn about recycling. There were also some questions, which asked the students to present their free comments on both recycling and the survey instrument. The survey instrument was developed in English, as the Indian school followed English as its medium of instructions. Therefore, there was no need for a back translation. The survey instrument can be obtained from the author upon request.
The seven-point Likert-type scale for the TPB constructs ranged from ‘strongly disagree’ to ‘strongly agree’ with a coding value from 1 to 7, respectively where the middle point was ‘neither agree nor disagree’, which was given a coding value of 4. Each of the TPB constructs had multiple statement-like items following the recommendation by Ajzen [44]. The constructs Intention, PBC and SN consisted of a few items from a study by Wan et al. [47]. Specifically, the construct Attitude consisted of five items that aimed to capture the students’ evaluation of recycling, SN included three items that measured the students’ perceptions of the social responses to their decisions about recycling, PBC contained three items that evaluated the students’ perceived ease of practicing recycling, and the dependent variable Intention had three items that explored the students’ planned behaviour towards recycling. In this type of coding, higher scores on the constructs indicated the students’ stronger attitudes to recycling, greater perceptions of social pressure for recycling, higher perceived control over recycling, and stronger intentions to practice recycling. It should be noted that the items under the construct Attitude were formulated to measure students’ attitudes to the relevance of recycling in a broader environmental context. They were somewhat different from the definition of the construct Attitude given by Ajzen [44]. A similar approach can also be found in the study by Wan et al. [47], which used an item ‘Waste separation can create a better community environment’ to formulate the construct Attitude. Two experts from India assessed the content validity of the questionnaire. A pilot test of the questionnaire was also carried out among a small group of students in a Delhi-based school, which helped to improve the clarity of some of the questions related to measuring the students’ awareness of recycling.
2.3. Sample Characteristics, Data Screening and Measurement Model
About 306 students participated in the survey. However, only 272 students (ca. 88%) completed the questionnaires in all aspects with an equal number of male and female participants. The mean age of the students was 14.48 years (SD = 0.66). A reliability check of the TPB constructs was performed to evaluate the internal consistencies of the items corresponding to each latent construct. At first, Cronbach’s alpha (α) values for all the TPB constructs appeared to be less than 0.7, which showed lack of internal consistency [71,72]. To improve the reliability, indicator variables AT5 under Attitude, SN3 under SN, PBC3 under PBC, and IN1 under Intention were removed from the analysis. This procedure raised the ‘α’ values for both Attitude and SN above 0.7 besides improving the ‘α’ values of the other two constructs although they remained below 0.7 (Table 1). The skewness and kurtosis value of the indicator variables was below ±3 and ±10, respectively as recommended by Kline [73].

Table 1.
Theory of planned behaviour (TPB) constructs and their corresponding measurement items.
The next step in the data analysis was to perform a structural equation modelling (SEM) using the maximum likelihood method to test the relationships between the predictors Attitude, SN, and PBC with the dependent variable Intention. SEM has two parts—the first one is constructing a measurement model or performing a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), which assesses the validity and reliability of the measurement constructs while the second one is building a structural model, which determines the causal relationships among latent variables [74,75]. The goodness of fit of a CFA model is evaluated based on multiple indicators such as Chi-square normalised by degrees of freedom (χ2/df), goodness off fit index (GFI), adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI), comparative fit index (CFI), Tucker–Lewis index (TLI), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA). Normally, model fit is considered good (Table 2) when indices are ≥0.90, χ2/df is between 2 and 5, and RMSEA is ≤0.08 [76,77,78]. The CFA model in this study showed an acceptable model fit (χ2 = 82.42, χ2/df = 2.75, GFI = 0.94, AGFI = 0.89, CFI = 0.90, TLI = 0.85, RMSEA = 0.08).

Table 2.
The acceptable level of fit indices for the measurement model.
The reliability and convergent validity of the CFA model were checked by the values of average variance extracted (AVE) and composite reliability (CR) scores. According to Fornell and Larcker [79], the AVE and CR values should be more than 0.5 and 0.7, respectively although an AVE value, which is less than 0.05 for a construct is also acceptable if the CR value of that construct is more than 0.6. In this study, the AVE value of only SN was above 0.5 and the CR values of Attitude and SN were 0.7 (Table 3). Therefore, the results of the present study should be treated with some caution. Discriminant validity was ensured by comparing the value of square root of AVE of each construct with the correlation value of each construct. The square root of AVE of each construct was higher than its correlation’s value (Table 4), which ensured discriminant validity [80]. All the quantitative analyses were performed by the IBM SPSS Statistics 23 and IBM SPSS Amos 23 software packages.

Table 3.
Composite reliability (CR) and average variance extracted (AVE) of the TPB predictors in the CFA model.

Table 4.
Effects of the demographic variables on the TPB constructs and their correlations.
3. Results
3.1. Students’ Awareness of Recycling
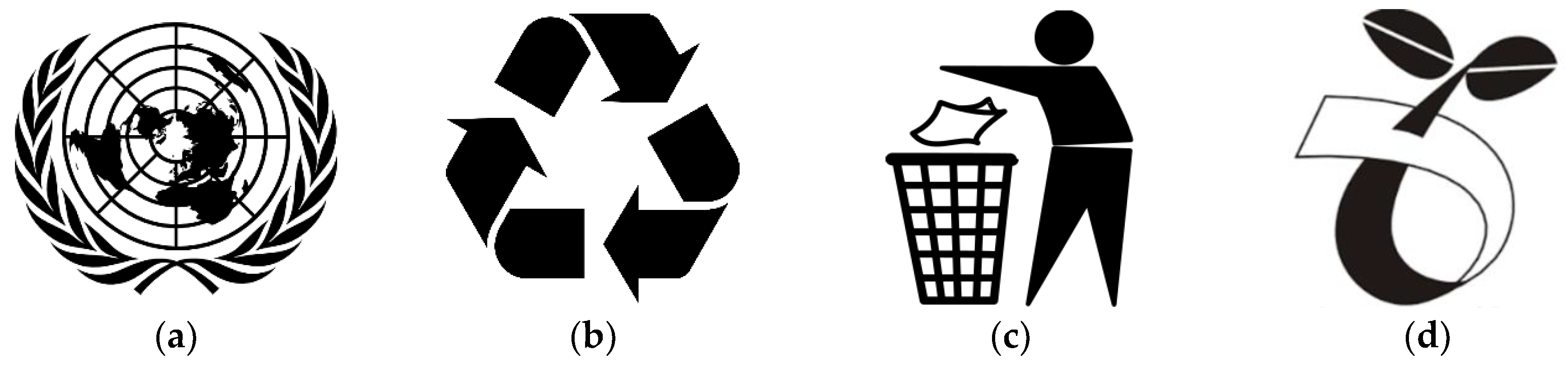
All the respondents informed that they had heard of recycling and their main information sources were textbooks, newspapers and teachers. Students’ understanding of recycling was evaluated with a multiple-option question and almost all the students correctly selected the option that stated, “Recycling is a process of converting waste materials into reusable objects”. The students were also asked to identify the recyclable materials from a list of items. About 75% of them selected paper, 47% selected biodegradable materials, 46% selected plastic and glass, 38% selected metal, 17% selected wood, 16% selected electronics, and 10% selected textile. In addition, the students were asked to identify the universal recycling symbol from a list of four images referring to the symbols of the United Nations, recycling, waste disposal, and compostable (Figure 1). It appeared that almost all the students were able to recognise the recycling symbol.
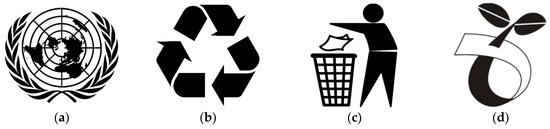
Figure 1.
Symbols: (a) United Nations; (b) recycling; (c) waste disposal; and (d) compostable.
3.2. Test of the TPB Constructs and Their Correlations
One-Way ANOVA tests were conducted to determine whether the demographic variables had any significant effects on the TPB constructs (Table 4). It emerged that ‘gender’ had statistically significant effect on the students’ recycling intentions. The male students appeared to be more positive than their female peers towards related to their recycling intentions although the effect size was small (Cohen’s d = 0.27). In terms of ‘age’, students in the age group of 13–14 years demonstrated greater positive intentions, stronger social pressure, and higher perceived control over behaviour concerning recycling than the students in the age group of 14–15 years. The effect size appeared to be small as Cohen’s d values ranged between 0.33 and 0.46. A Pearson’s correlation test was performed to explore the relationships among the TPB constructs and the results showed some statistically significant and positive correlations among all the constructs except between SN and Attitude though the strengths of such relationships were weak (Table 4).
3.3. Structural Model of the Students’ Intentions to Recycle and Hypothesis Testing
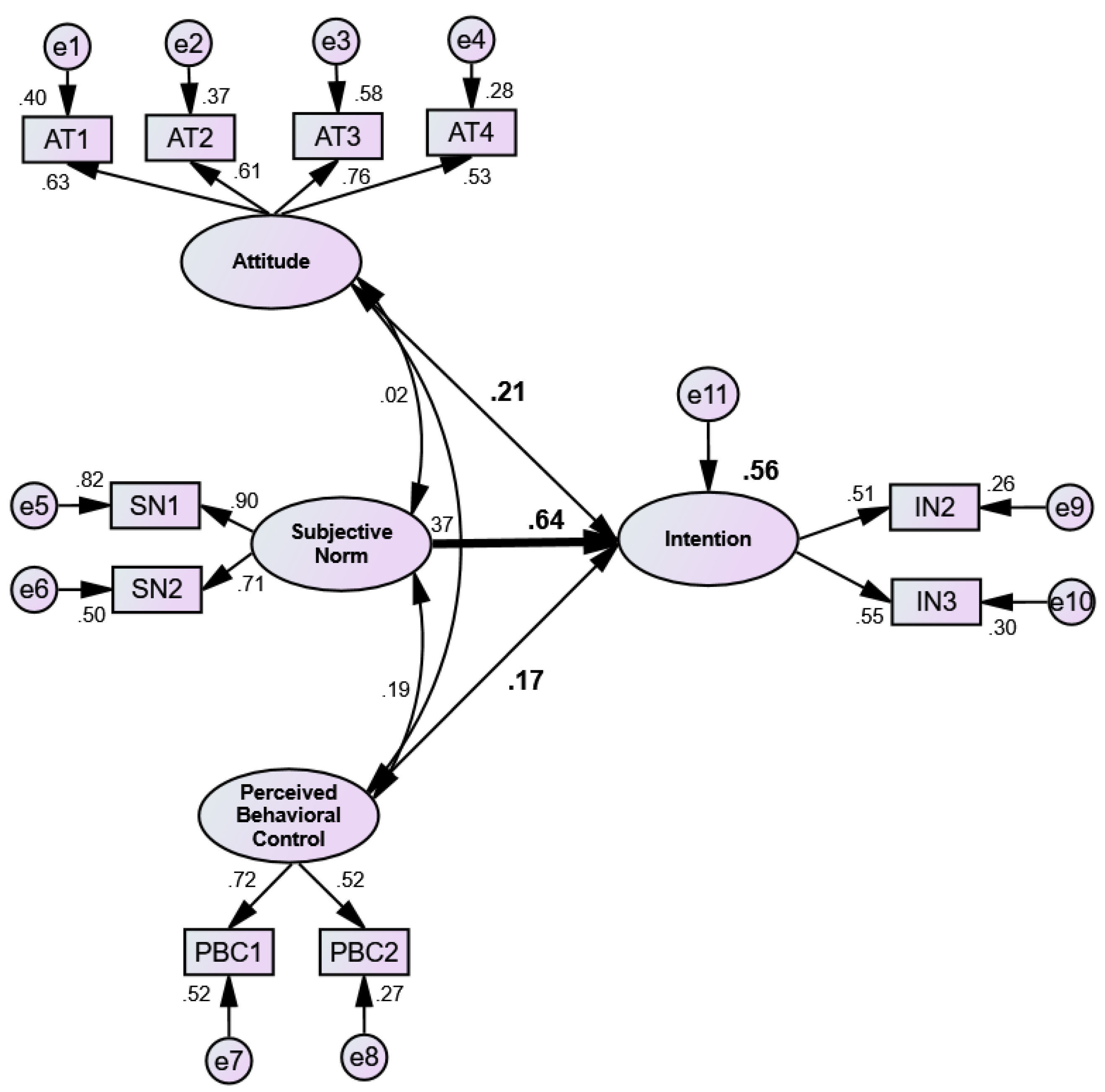
The hypothesised TPB model was statistically significant (p < 0.001) and showed an acceptable fit to the data (χ2 = 82.42, χ2/df = 2.75, GFI = 0.94, AGFI = 0.89, CFI = 0.90, TLI = 0.85, RMSEA = 0.08). It explained about 56% of the variance (R2 = 0.56) in the students’ intentions to recycle (Figure 2). It appeared that the predictor SN had the strongest and statistically significant positive effect (β = 0.64, SE = 0.08, t = 5.49, p < 0.001) on the students’ intentions of recycling. Attitude had the second highest effect on Intention (β = 0.21, SE = 0.11, t = 1.85, p > 0.05) followed by PBC (β = 0.17, SE = 0.11, t = 1.35, p > 0.05), although their effects were insignificant. All the factor loadings on the latent constructs were above 0.50. Among the three hypotheses, only H2 appeared to be acceptable as SN had a statistically significantly effect on Intention, whereas, the other two hypotheses (H1 and H3) were rejected due to their insignificant relationships with Intention.
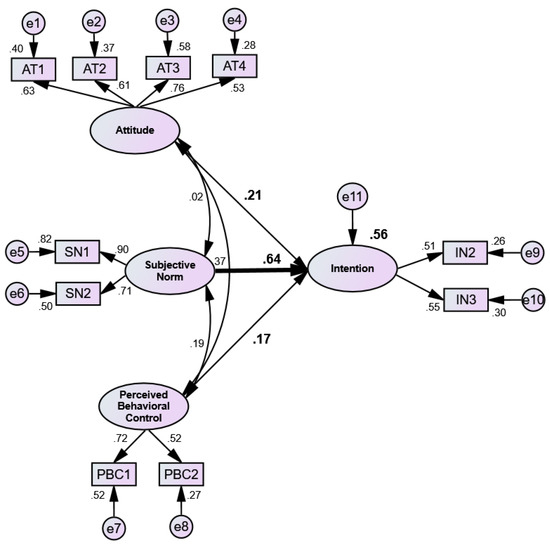
Figure 2.
Structural model of the students’ intentions to recycling (N = 272). The bold straight arrow from Subjective Norm to Intention shows statistically significant relationship.
3.4. Learning Possibility about Recycling and Students’ Feedback
About 92% of the students informed that they could learn more about recycling from their school. When the students were asked about the ways they could learn more about recycling, nearly 75% of them selected ‘visiting a recycling facility’, 62% selected ‘teachers’, 41% selected ‘self-studying’ and 29% selected both ‘watching videos’ and ‘participating in debates’. About 74% of the students provided their free comments related to recycling and the survey procedure. Their comments reflected that they were interested to know more about recycling, as they appeared to be aware of its importance. There were comments from the students such as: “Recycling will make our country clean from waste material; recycling will make the world cleaner and greener; there are not many recycling bins in our county and therefore, some strict action should be taken regarding recycling of waste materials; a little amount of knowledge about recycling is not sufficient and therefore, schools need to take their students to recycling facilities for better understanding of the subject; and I believe that our natural resources are depleting at a faster rate than thought before and thus we must recycle everything as much as possible.”
In addition, the students showed positive attitudes towards the survey as they thought that such a survey would enhance their awareness of recycling. Their comments were as follows: “This survey is quite inspiring and would promote the practice of recycling among young people; through the survey I am able to express my views on recycling; it has helped all the students to raise their awareness of recycling; some information on recycling should be provided by each school so that students can learn about it; the survey informed us about recycling, which we did not know beforehand; the survey was very useful as from our school we do not get much encouragement towards engaging in recycling; I will learn more about recycling by visiting a recycling facility; and being a nature lover, such environment related surveys are always appreciated by me but recycling facilities are very uncommon in India, which is a matter of concern.”
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Synthesis of the Major Findings
The study investigated the socio-psychological determinants of school students’ recycling intentions in India by applying the standard TPB framework. It also explored students’ awareness of recycling and brought to the fore the educational aspects related to this issue. The findings of this study can be regarded as first-hand information on young citizens’ recycling intentions. Results showed that almost all the students were aware of the concept of recycling. However, many did not perceive that plastic, metal, glass, wood, electronics and textile materials could be recycled. It also appeared that almost half of the students assumed biodegradable materials as recyclables.
The TPB model was able to capture a substantial variance in the students’ recycling intentions, and thus the predictive utility of the model corresponded to a few earlier studies on this topic [47,49,55]. The emergence of SN as the most significant predictor of the students’ recycling intentions contradicted the findings of most of the earlier studies where SN appeared to be the weakest among the TPB predictors although Wan et al. [47,55] found that SN had a significant role in determining individuals’ recycling intentions in Hong Kong. The positive effect of PBC on recycling intentions corresponded to the findings of some earlier studies [55,56,57]. The insignificant effect of Attitude on the students’ intentions of recycling was exceptional considering many studies reported Attitude as the strongest predictor of individuals’ recycling intentions. However, this exception perhaps appeared due to the formulation of some of the items under the construct Attitude, which was somewhat different from the definition of Attitude given by Azjen [44].
These findings indicated that the social pressure would be driving Indian students’ recycling intentions followed by their attitudes to recycling and their perceived ease of carrying out recycling activities. Jain et al. [81] have reported that since a collectivist culture prevails in India, SN tends to have a greater impact on intention than Attitude, and this could hold true in this study. The study found that the demographic variables had statistically significant effects on some of the TPB constructs although such effects were weak. The study by Oztekin et al. [57] found a gender difference in the Turkish university students’ attitudes to recycling where female students were more positive than their male peers. However, the present study found an opposite result among the school students’ attitudes to recycling in India. Overall, the school students demonstrated positive intentions and attitudes towards recycling and they were confident about their ability to participate in recycling activities. To some extent, these results corresponded to the study by Lucy et al. [40].
4.2. Implications and Recommendations
The study revealed that the students had some ambiguities about the materials that are recyclables. Such a lack of conceptual clarity about recyclable materials among the students can affect urban waste management program and make it costly for the municipalities. There is a high probability that due to this lack of knowledge among the youth, the segregation of wastes at source will be carried out improperly by them that will ultimately affect government’s efforts towards urban waste management. Therefore, there is a clear need of raising awareness of recycling and recyclable materials among the youth in India. Wan et al. [55] have suggested that public authorities should position “recycling as a social trend and promote it in the society through encouraging messages from the celebrity personalities and showing the percentage or frequency of the local population performing recycling”. It can be a relevant approach in the context of recycling, as Abrahamese and Steg [82] perceived that “socially desirable behaviours could be achieved in issues related to resource conservation by means of social influences, learning and comparison”. Wan et al. [55] have also suggested that promoting recycling behaviour as a socially desirable trend instead of highlighting its benefits could be an effective strategy. It is evident that without increasing the knowledge of the benefits of recycling and improving individuals’ waste separation abilities, socially desirable behaviours will be difficult to achieve in the context of urban waste management in India. Moreover, when it comes to developing students’ recycling behaviours, schools can play an important role. Schools can initiate various environmental activities in their local communities involving students and residents, as the respondents in this study also suggested, which can enhance their awareness of waste separation and motivate them to take required practical actions both at the household and community levels [54]. There are already a few policies and initiatives existing in India related to urban waste management and therefore, it is the responsibility of the citizens, both young and old, to come forward and help implementing those policies successfully throughout the country.
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Needs
There were some limitations in the study, which are required to be addressed in the future research. The researchers collected data from only one school in Delhi and therefore, the sample cannot be considered a truly representative sample. Future studies should recruit a large sample of students from various Indian cities to improve the representativeness of the study as well as the generalizability of its findings. Moreover, besides school students, university students should be included in the future studies, as this will provide a comprehensive picture of the socio-psychological factors determining Indian youth’s recycling intentions. Future studies could also explore the socio-psychological factors that affect recycling intentions of both the youth and adults to understand their similarities and differences across the two age groups, which could be useful in building relevant hypotheses. Apart from recycling intentions, past recycling behaviours should also be studied to observe possible gaps between intentions and behaviours. A number of studies also added constructs such as ‘personal norm’, ‘awareness of consequences’, ‘environmental knowledge’, ‘past behaviour’, ‘self-identity’, and ‘situation factors’ to the extended TPB frameworks to explain individuals recycling intentions, which appeared to be relevant [54,55,57,83,84,85]. Therefore, future studies could use such extended TPB models to predict young citizens’ recycling intentions and behaviours in India. Future studies could also investigate how economic rewards (i.e., payment for recyclables) could influence young generation’s intentions towards recycling as the lack of financial incentives was identified in many of the previous studies as one of the factors that affected individuals’ recycling intentions.
4.4. Conclusions
In conclusion, it can be said that the TPB model was able to explain school students’ intentions of recycling in the Indian context. All the predictors appeared to have positive effects on the students’ intentions of recycling and the relevance of the TPB model in explaining students’ intentions was apparent. SN appeared to be the strongest predictor of the Indian students’ recycling intentions. Students’ participation in recycling can be significantly enhanced by developing their positive attitudes to recycling, setting a social trend in recycling and making it easier for them to participate in recycling by providing better facilities. It appeared that the students were aware of the concept of recycling, although they lacked clarity about the recyclable materials. Students were also interested in receiving more information on recycling from their school. In addition, they recognised the need for having better waste separation facilities in their households and communities. The selection of the school students appeared to be relevant for this study because of the magnitude of the proportion of youth in India’s population and their importance in addressing the mounting solid waste management problems in the country. The study was one of a kind in the Indian context, and thus could provide future directions in research on the social dimensions particularly on the behavioural aspects in recycling in India. Since India is a highly diverse country in terms of social and cultural settings, there is a need to take into consideration those driving factors while exploring young people’s attitudes and behaviours related to recycling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.H.; Methodology, P.H. and H.S.; Data Curation, H.S.; Formal Analysis, P.H.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, P.H.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly acknowledge the school and the students for participating in the survey. In addition, the valuable comments from the reviewers to improve an earlier version of the manuscript is also acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hoornweg, D.; Bhada-Tata, P. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management; Urban Development Series Knowledge Papers No. 15; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; 98p. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.C.; Rodic, L.; Modak, P.; Soos, R.; Rogero, A.C.; Velis, C.; Iyer, M.; Simonett, O. Global Waste Management Outlook; UNEP DTIE—International Environmental Technology Centre: Osaka, Japan, 2015; 332p. [Google Scholar]
- Cointreau, S. Occupational and Environmental Health Issues of Solid Waste Management Special Emphasis on Middle- and Lower-Income Countries; The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; 48p. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, V.; Pandey, S.D. Hazardous waste, impact on health and environment for development of better waste management strategies in future in India. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Bhattacharyya, B. Estimation of Municipal Solid Waste Generation and Future Trends in Greater Metropolitan Regions of Kolkata, India. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. Innov. 2014, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, S.E.; Tchobanoglous, G. Municipal solid waste and the environment: A global perspective. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 277–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worldwatch Institute. Global Municipal Solid Waste Continues to Grow. 2012. Available online: http://www.worldwatch.org/global-municipal-solid-waste-continues-grow (accessed on 30 October 2017).
- Planning Commission (Government of India). Report of the Task Force on Waste to Energy (Volume I) (In the Context of Integrated Municipal Solid Waste Management). 2014. Available online: http://planningcommission.nic.in/reports/genrep/rep_wte1205.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Biswas, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Babu, S.; Bhattacharyya, J.K.; Chakrabarty, T. Studies on environmental quality in and around municipal solid waste dumpsite. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 55, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, T.; Goel, S. Solid waste management in Kolkata, India: Practices and challenges. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Sharma, C.; Singh, N.; Ramesh, R.; Purvaja, R.; Gupta, P.K. Greenhouse gas emissions from municipal solid waste management in Indian mega-cities: A case study of Chennai landfill sites. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Smith, S.R.; Fowler, G.; Velis, C.; Kumar, S.J.; Arya, S.; Rena; Kumar, R.; Cheeseman, C. Challenges and opportunities associated with waste management in India. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 160764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayana, T. Municipal solid waste management in India: From waste disposal to recovery of resources? Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharholy, M.; Ahmad, K.; Vaishya, V.C.; Gupta, R.D. Municipal solid waste characteristics and management in Allahabad, India. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talyan, V.; Dahiya, D.P.; Sreekrishnan, T.R. State of municipal solid waste management in Delhi, the capital of India. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bhattacharyya, J.K.; Vaidya, A.N.; Chakrabarti, T.; Devotta, S.; Akolkar, A.B. Assessment of the status of municipal solid waste management in metro cities, state capitals, class I cities, and class II towns in India: An insight. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (Government of India). Guidelines for Community Engagement under Swachh Bharat Mission Urban. 2017. Available online: http://www.swachhbharaturban.in/sbm/home/lib/content/Community%20Engagement%20Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2017).
- Joshi, R.; Ahmed, S. Status and challenges of municipal solid waste management in India: A review. Environ. Chem. Pollut. Waste Manag. 2016, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K. Perspectives of solid waste management in India. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Technology and Management of the treatment and Reuse of the Municipal Solid Waste, Shanghai, China; 2002; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Kulshreshtha, K.; Mohanty, C.S.; Pushpangadan, P.; Singh, A. Stakeholder-based SWOT analysis for successful municipal solid waste management in Lucknow, India. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varotto, A.; Spagnolli, A. Psychological strategies to promote household recycling. A systematic review with meta-analysis of validated field interventions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2017, 51, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hipel, K.W. Exploring social dimensions of municipal solid waste management around the globe—A systematic literature review. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Shukla, J.P. Projection and Quantification of Municipal Solid Waste Management in Bhopal city M.P. India. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 2, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, G.P.; Gupta, P. Sustainable municipal solid waste management in low income group of cities: A review. Trop. Ecol. 2011, 52, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Urpelainen, J. Who should take the garbage out? Public opinion on waste management in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhokhikah, Y.; Trihadiningrum, Y. Solid waste management in Asian developing countries: Challenges and opportunities. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2012, 2, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Zhag, G.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, T. Promoting public participation in household waste management: A survey based method and case study in Xiamen city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaane, B. Constraints to promoting people centred approaches in recycling. Habitat Int. 2006, 30, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troschinetz, A.M.; Mihelcic, J.R. Sustainable recycling of municipal solid waste in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhokhikah, Y.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Sunaryo, S. Community participation in household solid waste reduction in Surabaya, Indonesia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 102, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charuvichaipong, C.; Sajor, E. Promoting waste separation for recycling and local governance in Thailand. Habitat Int. 2006, 30, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.K.A.; Abdullah, S.H.; Manaf, L.A. Community participation on solid waste segregation through recycling programmes in Putrajaya. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekito, T.; Prayogo, T.B.; Dote, Y.; Yoshitake, T.; Bagus, I. Influence of a community-based waste management system on people’s behavior and waste reduction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 72, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, T. Environmental concern and its implication to household waste separation and disposal: Evidence from Mekelle, Ethiopia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 53, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Nandini, N. Community attitude, perception and willingness towards solid waste management in Bangalore city, Karnataka, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Indhira, K.; Senthil, J.; Vadivel, S. Awareness and attitudes of people perception towards to household solid waste disposal: Kumbakonam Town, Tamilnadu, India. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Minhas, J. Solid Waste Management—Community Perception, Attitude and Participation. Asian J. Res. Soc. Sci. Hum. 2017, 7, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasubramanian, P.; Saratha, M.M.; Divya, M. Perception of households towards waste management and its recycling in Coimbatore. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Dev. 2015, 2, 510–515. [Google Scholar]
- Lucy, C.D.; Vivek, R.; Saritha, K.; Anies, T.K.; Josphina, C.T. Awareness, Attitude and Practice of School Students towards Household Waste Management. J. Environ. 2013, 2, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision—Key Findings and Advance Tables. 2015. Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/publications/files/key_findings_wpp_2015.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Central Statistics Office (Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation, Government of India). Youth in India: 2017. Available online: http://mospi.nic.in/sites/default/files/publication_reports/Youth_in_India-2017.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Park, J.; Ha, S. Understanding consumer recycling behavior: Combining the theory of planned behavior and the norm activation model. Fam. Consum. Sci. Res. J. 2014, 42, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I.; Fishbein, M. Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Social Behavior; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Armitage, C.J.; Conner, M. Efficacy of the Theory of Planned Behaviour: A meta-analytic review. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2001, 40, 471–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Cheung, R.; Shen, G.Q. Recycling attitude and behaviour in university campus: A case study in Hong Kong. Facilities 2012, 30, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, K.; Alriksson, S. Influence of recycling programmes on waste separation behaviour. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikturnienė, I.; Bäumle, G. Predictors of recycling behaviour intentions among urban Lithuanian inhabitants. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2016, 17, 780–795. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K. Mass communication and pro-environmental behvior: Waste recycling in Hong Kong. J. Environ. Manag. 1998, 52, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, G.W.A.; Rusli, I.F.; Biak, D.R.A.; Idris, A. An application of the theory of planned behaviour to study the influencing factors of participation in source separation of food waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigbur, D.; Lyons, E.; Uzzell, D. Attitudes, norms, identity and environmental behavior: Using an expanded theory of planned behaviour to predict participation in a kerbside recycling programme. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2010, 49, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonglet, M.; Phillips, P.S.; Read, A.D. Using the theory of planned behavior to investigate the determinants of recycling behaviour: A case study from Brixworth, UK. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 41, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, G.; Yin, X.; Gong, Q. Residents’ Waste Separation Behaviors at the Source: Using SEM with the Theory of Planned Behavior in Guangzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2015, 12, 9475–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Shen, G.Q.; Choi, S. Experiential and instrumental attitudes: Interaction effect of attitude and subjective norm on recycling intention. J. Environ. Psychol. 2017, 50, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Bishop, B. A moral basis for recycling: Extending the theory of planned behaviour. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 36, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztekin, C.; Teksöz, G.; Pamuk, S.; Sahin, E.; Kilic, D.S. Gender perspective on the factors predicting recycling behavior: Implications from the theory of planned behavior. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippsen, Y. Factors Influencing Students’ Intention to Recycle. Master’s Thesis, School of Management and Governance, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2015; 96p. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, P.; Pietarinen, J.; Havu-Nuutinen, S.; Pöllänen, S.; Pelkonen, P. The Theory of Planned Behavior Model and Students’ Intentions to Use Bioenergy: A Cross-Cultural Perspective. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Tung, P.J. Developing an extended Theory of Planned Behavior model to predict consumers’ intention to visit green hotels. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 36, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Young, S.; Bi, J. Enterprises’ willingness to adopt/develop cleaner production technologies: An empirical study in Changshu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 40, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B. Theory of Planned Behaviour Approach to Understand the Purchasing Behaviour for Environmentally Sustainable Products; Working Paper No. 2012-12-08; Indian Institute of Management: Ahmedabad, India, 2012; 43p. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, J.; Modi, A.; Patel, J. Predicting green product consumption using theory of planned behavior and reasoned action. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2016, 29, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Pathak, G.S. Young consumers’ intention towards buying green products in a developing nation: Extending the theory of planned behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Pathak, G.S. Determinants of Consumers’ Green Purchase Behavior in a Developing Nation: Applying and Extending the Theory of Planned Behavior. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 134, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Census of India. City Census 2011. Available online: http://www.census2011.co.in/city.php (accessed on 12 November 2017).
- UN (United Nations). The World’s Cities in 2016. Available online: http://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/urbanization/the_worlds_cities_in_2016_data_booklet.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2017).
- CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board, Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change, Government of India). Consolidated Annual Review Report Prepared in Compliance to the Provision 24(4) of the SWM Rules, 2016. Available online: http://cpcb.nic.in/MSW_AnnualReport_2015-16.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Chakraborty, M.; Sharma, C.; Pandey, J.; Singh, N.; Gupta, P.K. Methane Emission Estimation from Landfills in Delhi: A comparative Assessment of Different Methodologies. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7135–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Anunay, G.; Rohit, G.; Shivangi, G.; Vipul, V. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Landfills: A Case of NCT of Delhi, India. J. Climatol. Weather Forecast. 2016, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 2nd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, J.C.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychometric Theory; McGraw Hill: New York, NU, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed.; The Guildford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.C.; Gerbing, D.W. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 103, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, J.L. Amos7.0 User’s Guide; SPSS: Chicago, IL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, M.W.; Cudek, R. Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In Testing Structural Equation Models; Bollen, K.A., Long, J.S., Eds.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 136–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L.; Black, W.C. Multivariate Data Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Market. Sci. 1988, 16, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W.; Gopal, A.; Salisbury, W.D. Advancing the theory of adaptive structuration: The development of a scale to measure faithfulness of appropriation. Inf. Syst. Res. 1997, 8, 342–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Mohammed Khan, M.N.; Mishra, S. Understanding consumer behavior regarding luxury fashion goods in India based on the theory of planned behavior. J. Asia Bus. Stud. 2017, 11, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, W.; Steg, L. Social influence approaches to encourage resource conservation: A meta-analysis. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakpour, A.H.; Zeidi, I.M.; Emamjomeh, M.M.; Asefzadeh, S.; Pearson, H. Household waste behaviours among a community sample in Iran: An application of the theory of planned behaviour. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham-Rowe, E.; Jessop, D.C.; Sparks, P. Predicting household food waste reduction using an extended theory of planned behaviour. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 101, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.S.; Abdullah, S.H.; Manaf, L.A.; Sharaai, A.H.; Nabegu, A.B. Examining the Moderating Role of Perceived Lack of Facilitating Conditions on Household Recycling Intention in Kano, Nigeria. Recycling 2017, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).