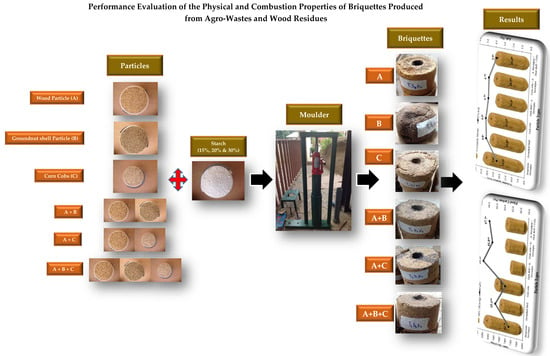
Performance Evaluation of the Physical and Combustion Properties of Briquettes Produced from Agro-Wastes and Wood Residues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Study Site
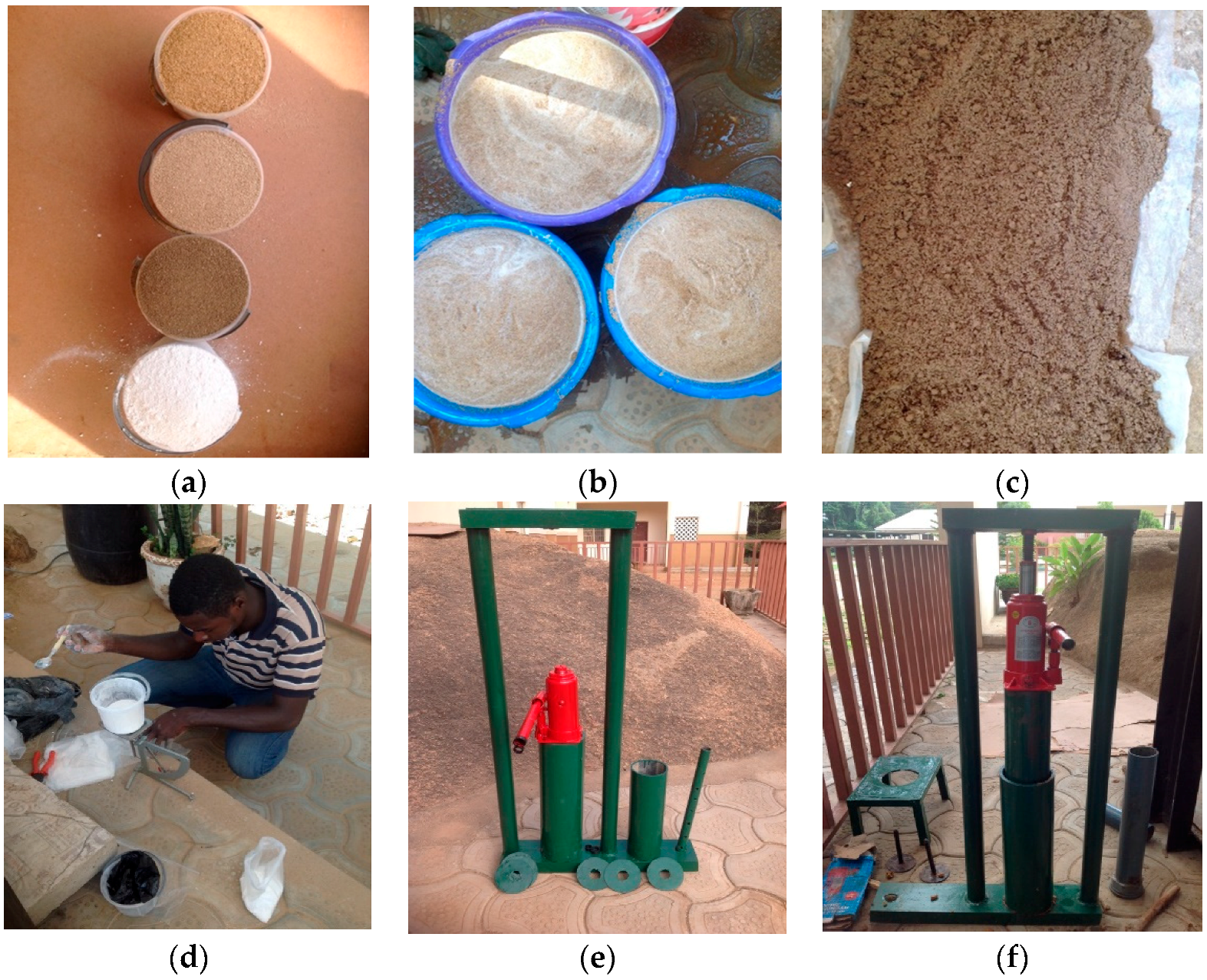
2.2. Materials for the Briquette Production
2.3. Sample Preparation Procedures
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Variables Assessed
- Relaxed density: The relaxed density refers to the density of the briquette measured after certain period of time. This was determined according to the weight and the volume (V = πr2h) of each briquette block based on its shape. The density of each briquette sample was calculated using the formula in Equation (1).
- Volatile matter (%Vm): The percentage volatile matter was determined by placing the crucible containing the oven dry weight (w2) in the furnace for 10 min at 550 °C to obtain weight (w3) after the escape of its volatile matter. The percentage volatile matter (%Vm) was calculated using the formula as shown in Equation (2);
- Ash content (%Ash): 2 g of oven dried pulverized briquette was placed in a crucible (w2). The crucible was then placed in the furnace for 4 h at 550 °C to obtain the ash weight (w4). Percentage ash content was calculated using Equation (3).
- Fixed carbon (%FC): The percentage fixed carbon was calculated by subtracting the sum of percentage volatile matter and percentage ash content from 100% Equation (4).
- Specific Heat of Combustion (Hc): The specific heat of combustion (Hc) was calculated from the formula as shown in Equation (5);
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
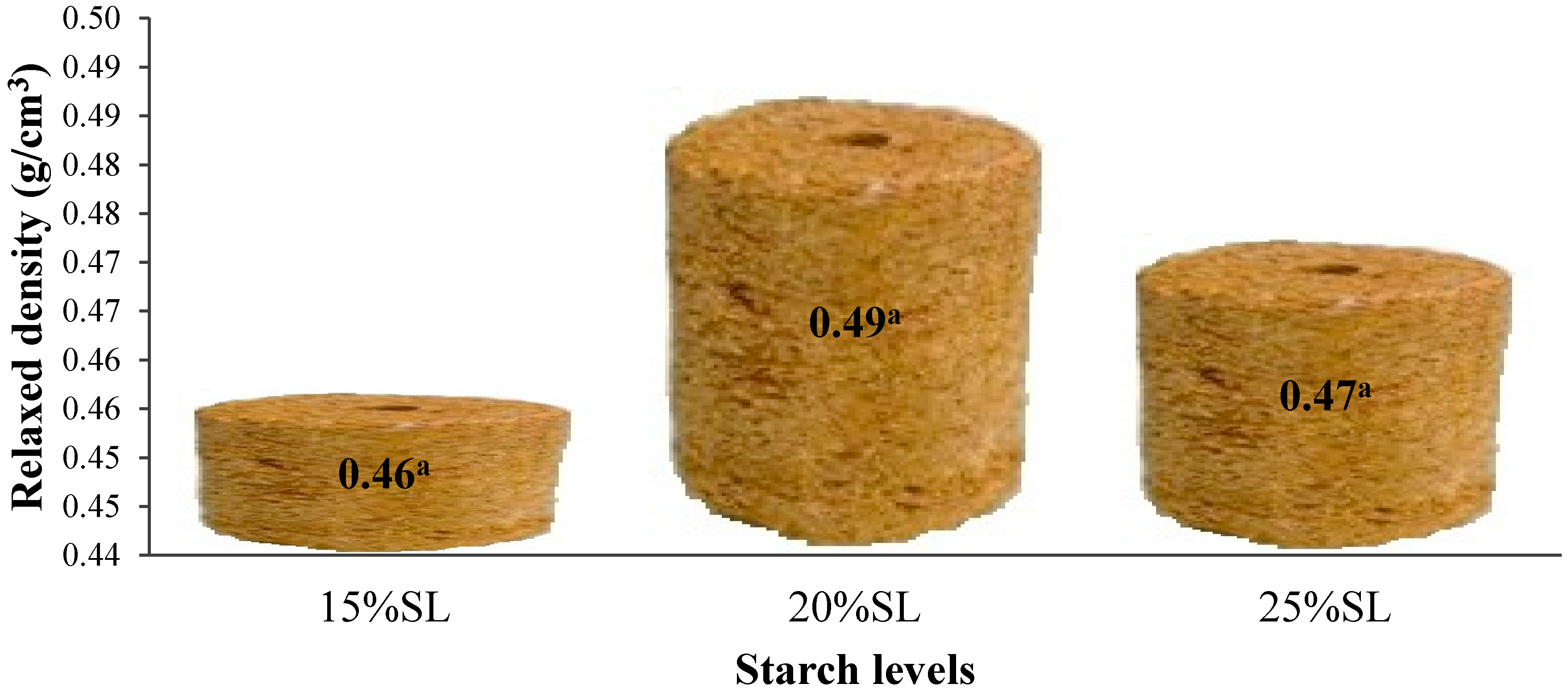
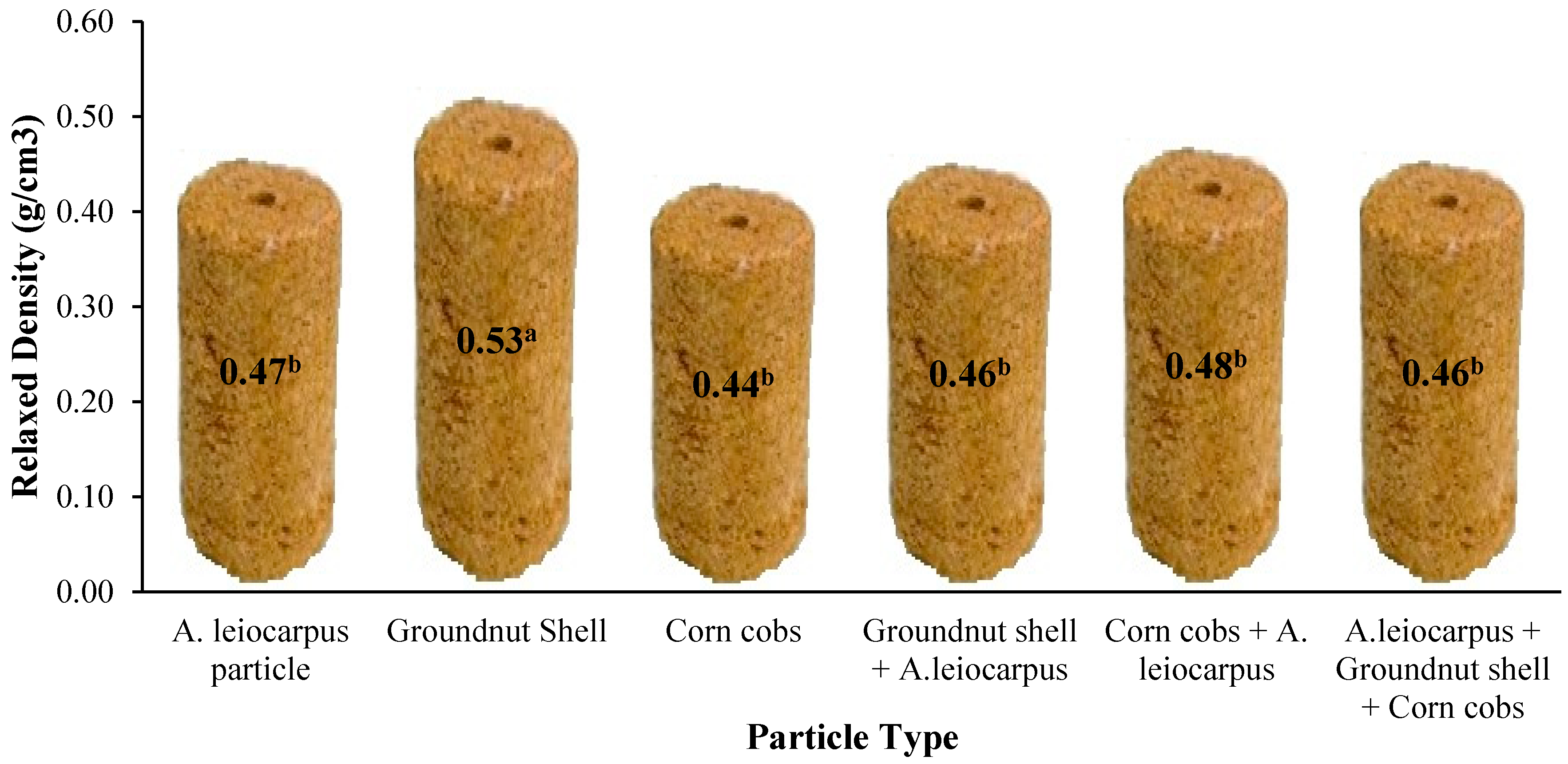
3.1. Effect of Treatments and Starch Levels on Relaxed Density of the Briquette
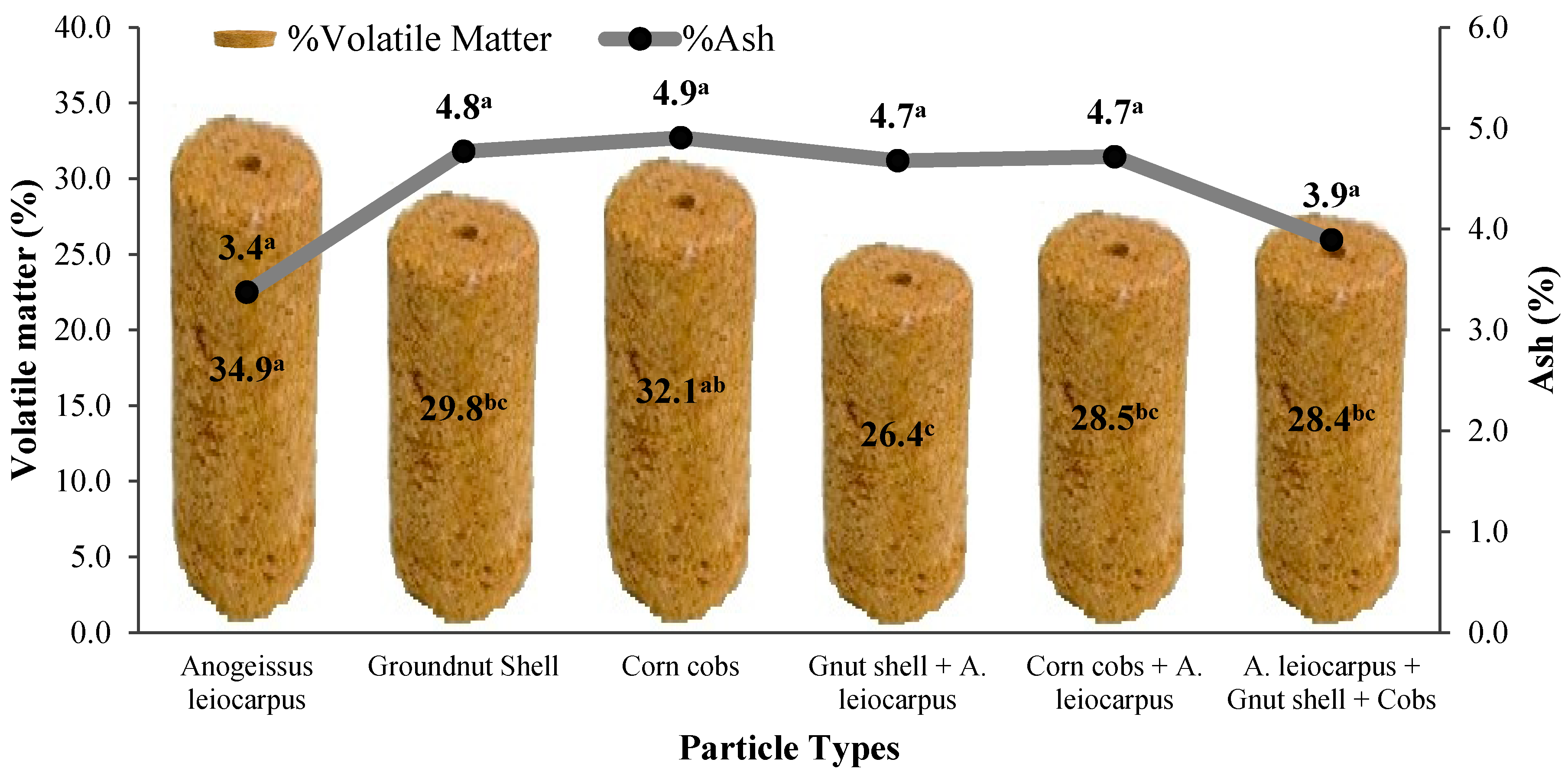
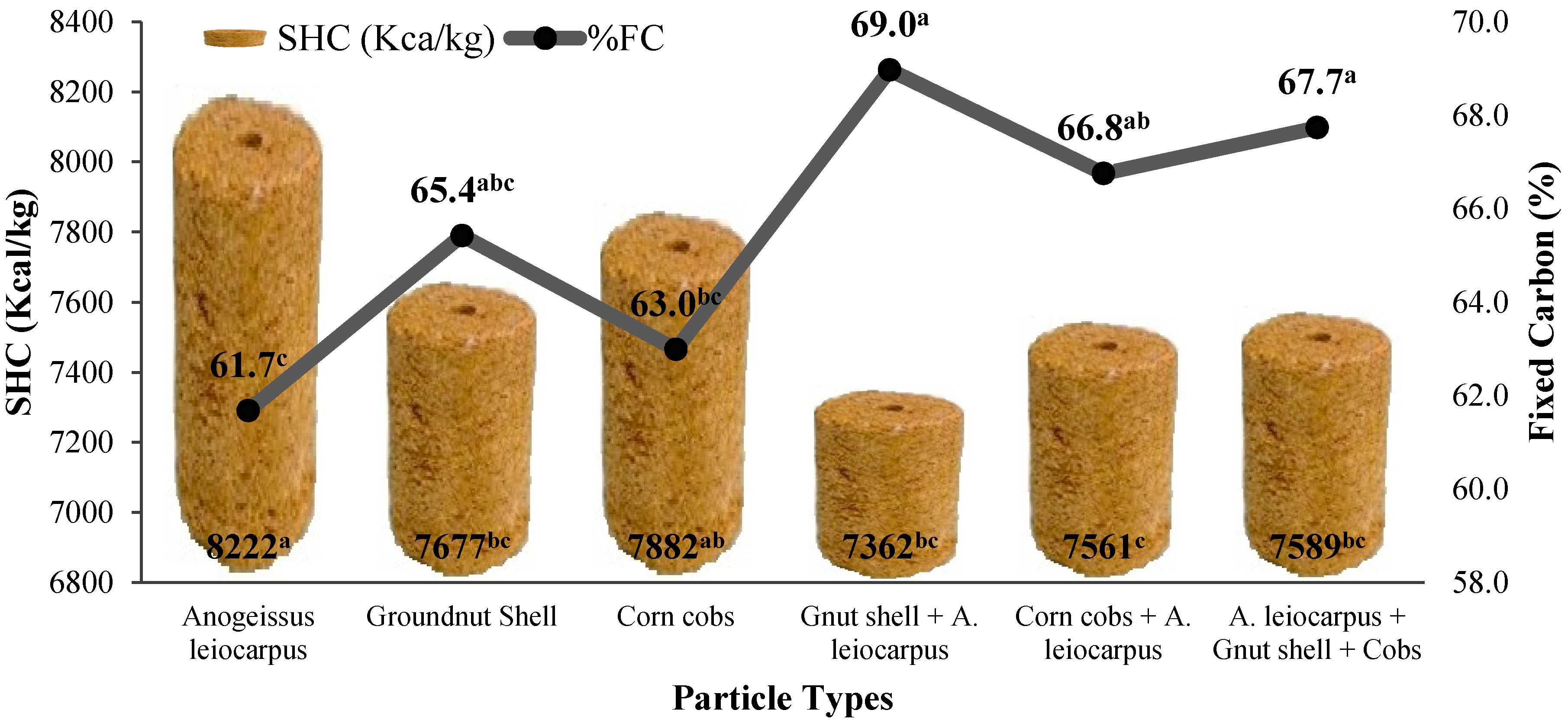
3.2. Effect of Particle Types on Combustion Properties of the Briquettes
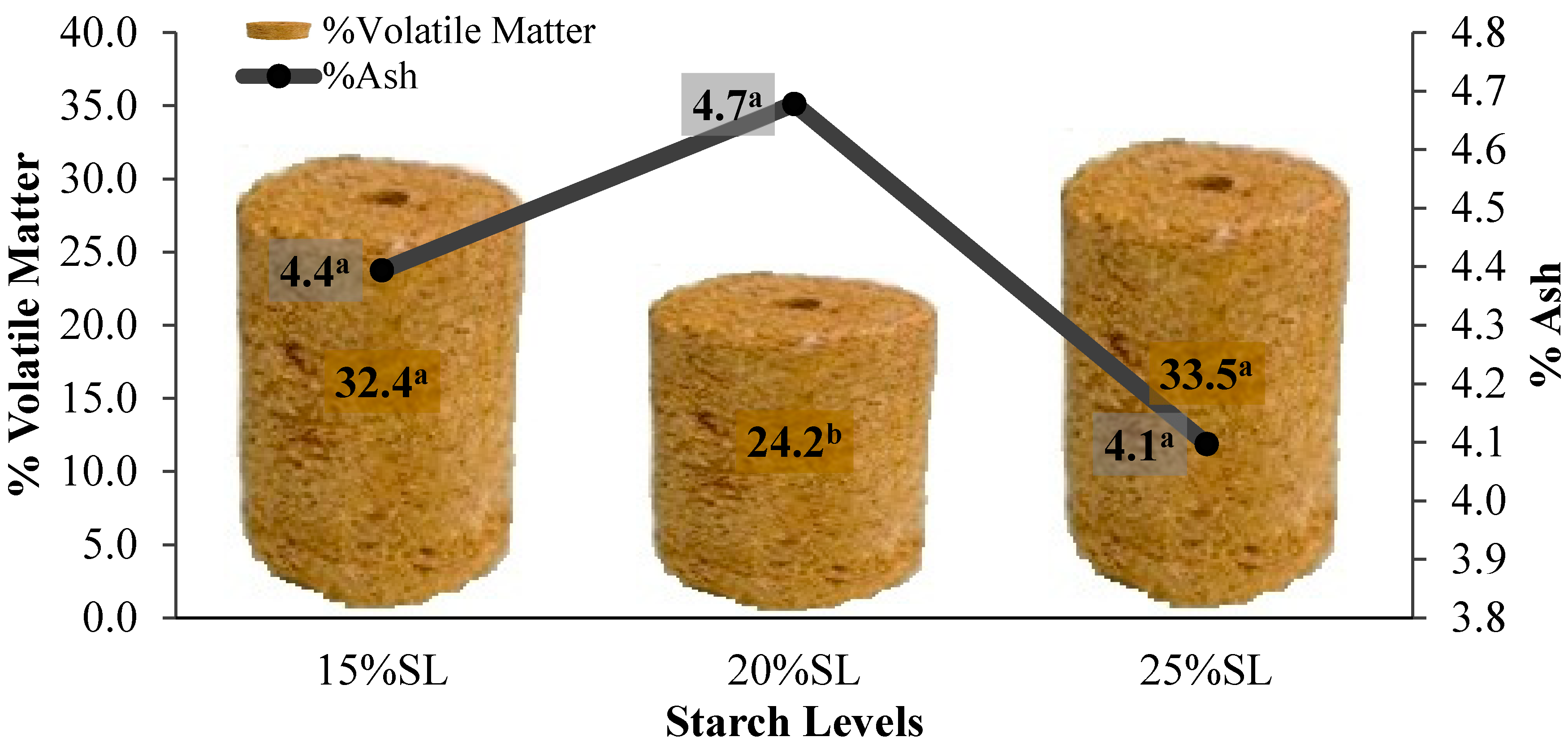
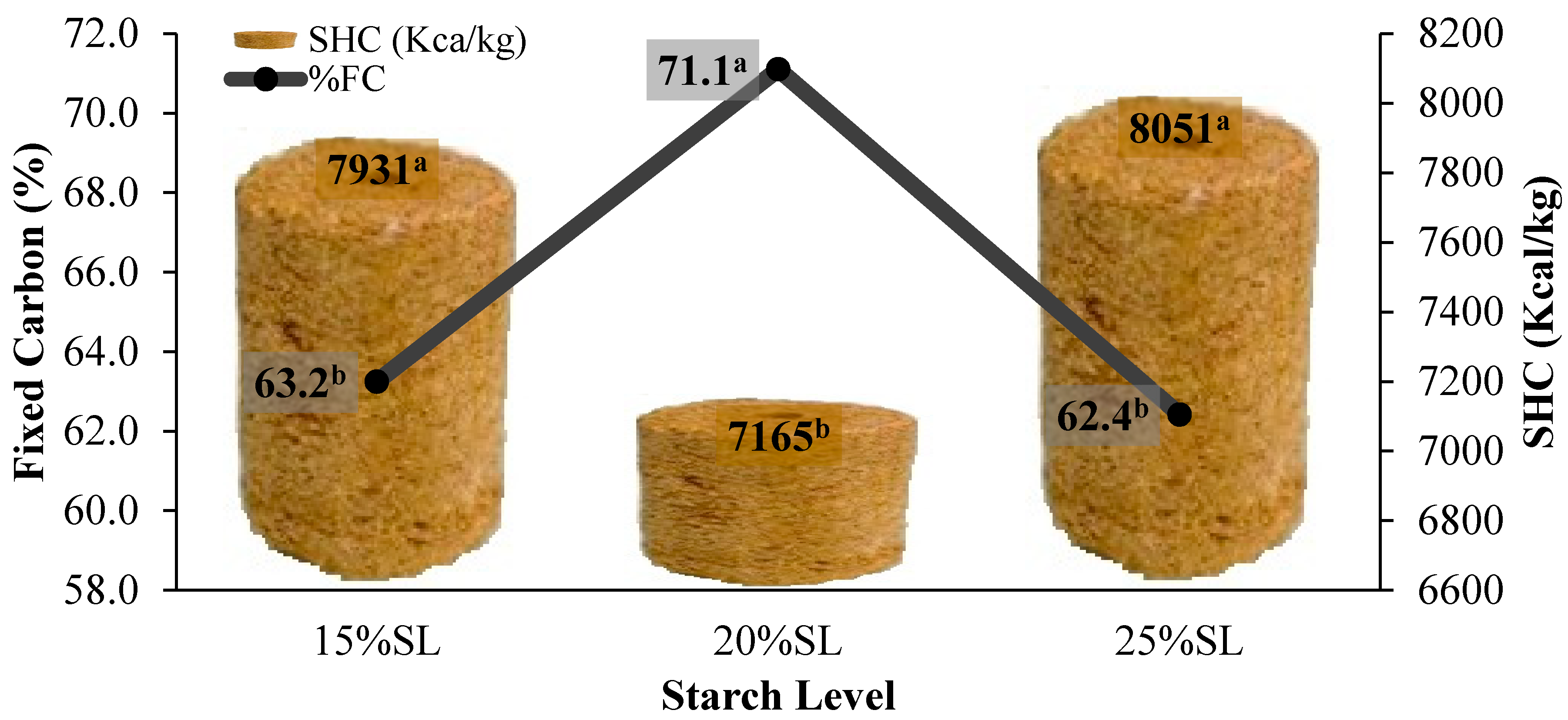
3.3. Effect of Starch Levels on Combustion Properties of the Briquettes
4. Discussion
4.1. Relaxed Density
4.2. Volatile Matter
4.3. Ash Content
4.4. Specific Heat of Combustion
4.5. Fixed Carbon
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Household Air Pollution and Health. Fact Sheet 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/household-air-pollution-and-health (accessed on 4 July 2018).
- Worldometers. Current World Population. Available online: Http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/? (accessed on 4 July 2018).
- Aremu, M.O.; Agarry, S.E. Enhanced biogas production from poultry droppings using corn cob and waste paper as co-substrates. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, O.O.; Akhihiero, T.E. Fuel briquettes from water hyacinth-cow dung mixture as alternative energy for domestic and agro-industrial applications. J. Energy Technol. Policy 2011, 3, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ismaila, A.; Zakari, I.Y.; Nasiru, R.; Tijjani, B.I.; Abdullahi, I.; Garba, N.N. Investigation on biomass briquettes as energy source in relation to their calorific values and measurement of their total carbon and elemental contents for efficient biofuel utilization. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- International Tropical Timber Organization. Tropical Forest Update, 15, 1, 2005; International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO): Yokohama, Japan, 2005; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xing, L.; Han, L. Renewable energy from agro-residues in China: Solid biofuels and biomass briquetting technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladeji, J.T. Utilization of Potential of Melon Shells for Pyrolysis as Biomass Fuels. World Rural Obs. 2012, 4, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Oladeji, J.T.; Ogunsola, A.D. Pyrolysis of Sawdust into Medium-Grade Fuels and Chemical Preservatives. In Proceedings of the 2nd Engineering Conference of the School of Engineering, Federal Polytechnic, Offa, Nigeria, 13–15 July 2010; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Havrland, B.; Ivanova, T.; Łapczyńska-Kordon, B.; Kolarikova, M. Comparative analysis of bio-raw materials and biofuels. In Proceedings of the 12th International Scientific Conference on Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 23–24 May 2013; pp. 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Kambo, H.S.; Dutta, A. A comparative review of biochar and hydrochar in terms of production, physical-chemical properties and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H. High-pressure densification of wood residues to form an upgraded fuel. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 19, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, N.A. Comparative fuel characterization of rice husk and groundnut shell briquettes. NJREDI 2007, 6, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Adegoke, I.A.; Baiyewu, R.A.; Aina, K.S.; Adesope, A.S.; Adejoba, A.L.; Abah, G.B. Combustion properties of briquette produced from mixed sawdust of tropical wood species. Climate Change and Forest Resources Management: The Way Forward. In Proceedings of the 2nd Biennial National Conference of the Forests and Forest Products Society, Akure, Nigeria, 16–18 April 2010; pp. 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbuagu, J.; Onuegbu, T.; Ikelle, I.I.; Chimezie, O.; Anyigor, C. Production and analysis of the heating properties of coal and Rice husk briquettes using CaSO4 as a binder. J. Phys. Sci. Innov. 2013, 1, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Adetogun, A.C.; Ogunjobi, K.M.; Are, D.B. Combustion properties of briquettes produced from maize cob of different particle sizes. J. Res. Forest. Wildl. Environ. 2014, 6, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ige, A.R.; Elinge, C.M.; Hassan, L.G.; Adegoke, I.A.; Ogala, H. Effect of binder on physicochemical properties of fuel briquettes produced from watermelon peels. AASCIT J. Energy 2018, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Somsuk, N.; Srithongkul, K.; Wessapan, T.; Teekasap, S. Design and Fabricate a Low Cost Charcoal Briquette Machine for the Small and Micro Community Enterprises. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of the Council of Deans of Architecture School Thailand (CDAST 2008), Phitsanulok, Thailand, 23–25 May 2008; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Obi, O.F.; Akubuo, C.O.; Okonkwo, W.I. Development of an appropriate briquetting machine for use in rural communities. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2013, 2, 578–582. [Google Scholar]
- Egbewole, Z.T.; Alao, J.S.; Ogunsanwo, O.Y.; Sotunde, O.A.; Aina, K.S.; Akinyemi, O. Potential use of wood production. Altern. Energy Gener. J. 2009, 5, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tembe, E.T.; Adeogun, A.C.; Elaigwu, V.O. Comparative Analysis of Combustion Properties of Briquettes from Groundnut shell and rice husk. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Conference of the Forestry Association of Nigeria, Edo State, Nigeria, 5–10 December 2011; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Fuwape, J.A.; Sobanke, A.O. Combustion characteristics of wood briquettes produced from sawdust. In Proceedings of the National Conference of Nigerian Society of Agricultural Engineering, Kano, Nigeria, 8–11 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Aina, K.S.; Baiyewu, R.A.; Ogunleye, M.B.; Adegoke, I.A.; Adesope, A.S.; Fatade, B.O. Evaluation of Combustion properties of briquette produced from Cedrella odorata, Terminalia superba and Cordia millenii. In Proceedings of the 2nd Biennial National Conference of Forests and Forest Products Society, Akure, Nigeria, 26–29 April 2010; pp. 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Muntean, A.; Ivanova, T.; Havrland, B.; Pobedinsky, P.; Vrancean, V. Particularities of bio-raw material particle agglomeration during solid fuel pressing process. In Proceedings of the 12th International Scientific Conference on Engineering for Rural Development–Proceedings, Latvia University of Agriculture Faculty of Engineering, Jelgava, Latvia, 23–24 May 2013; pp. 505–509. [Google Scholar]
- Onuegbu, T.U. Improving Fuel wood Efficiency in Rural Nigeria: A case for Briquette Technology. Natl. Mag. Chem. Soc. Niger. 2010, 5, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Emerhi, E.A. Physical and combustion properties of briquettes produced from sawdust of three hardwood species and different organic binders. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 236–246. [Google Scholar]
- Sotannde, O.A.; Oluyege, A.O.; Abah, G.B. Physical and combustion properties of charcoal briquettes from neem wood residues. Int. Agrophys. 2010, 24, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Vyas, S. Study of Biomass Bio pellets, Factors Affecting Its Performance and Technologies Based on Bio pellets. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2015, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Maninder, R.; Singh, K.; Grover, S. Using agricultural residues as a Biomass Briquetting: An Alternative source of energy. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2012, 1, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Onukak, I.E.; Mohammed-Dabo, I.A.; Ameh, A.O.; Okoduwa, S.I.R.; Fasanya, O.O. Production and Characterization of Biomass Briquettes from Tannery Solid Waste. Recycling 2017, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akowuah, O.J.; Kermausuor, F.; Mitchual, J.S. Physicochemical characteristics and market potential of sawdust charcoal briquette. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2012, 3, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikelle, I.I.; Anyigor, C. Comparative Thermal Analysis of the Properties of Coal and Corn Cob Briquettes. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 7, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.D. Biomass briquetting: Technical and feasibility analysis under biomass densification research project (Phase II). In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Biomass Briquetting, New Delhi, India, 3–6 April 1995; Grover, P.D., Mishra, S.K., Eds.; FAO Regional Wood Energy Development Programme in Asia: Bangkok, Thailand, 1995; p. 193. [Google Scholar]
- Katimbo, A.; Nicholas, K.; Simon, K.; Hussein, B.K.; Peter, T. Potential of densification of mango waste and effect of binders on produced briquettes. Agric. Eng. Intl. J. 2014, 16, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Asamoah, B.; Nikiema, J.; Gebrezgabher, S.; Odonkor, E.; Njenga, M. A Review on Production, Marketing and Use of Fuel Briquettes; Resource Recovery and Reuse Series 7; International Water Management Institute (IWMI), CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2016; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Thabuot, M.; Pagketanang, T.; Panyacharoen, K.; Mongkuta, P.; Wongwicha, P. Effect of applied pressure and binder proportion on the fuel properties of holey bio-briquettes. Energy Procedia. 2015, 79, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubairu, A.; Gana, S.A. Production and characterization of briquette charcoal by carbonization of agro-waste. Energy Power 2014, 4, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Han, K.; Gao, J.; Li, H.; Lu, C. The pyrolysis of biomass briquettes: Effect of pyrolysis temperature and phosphorus additives on the quality and combustion of bio-char briquettes. Fuel 2017, 199, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falemara, B.C.; Joshua, V.I.; Aina, O.O.; Nuhu, R.D. Performance Evaluation of the Physical and Combustion Properties of Briquettes Produced from Agro-Wastes and Wood Residues. Recycling 2018, 3, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3030037
Falemara BC, Joshua VI, Aina OO, Nuhu RD. Performance Evaluation of the Physical and Combustion Properties of Briquettes Produced from Agro-Wastes and Wood Residues. Recycling. 2018; 3(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalemara, Babajide Charles, Victoria Ibukun Joshua, Oluwaseyi Oluwafunmi Aina, and Rivi David Nuhu. 2018. "Performance Evaluation of the Physical and Combustion Properties of Briquettes Produced from Agro-Wastes and Wood Residues" Recycling 3, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3030037
APA StyleFalemara, B. C., Joshua, V. I., Aina, O. O., & Nuhu, R. D. (2018). Performance Evaluation of the Physical and Combustion Properties of Briquettes Produced from Agro-Wastes and Wood Residues. Recycling, 3(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3030037