Reduction of Oxidizable Pollutants in Waste Water from the Wadi El Bey River Basin Using Magnetic Nanoparticles as Removal Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
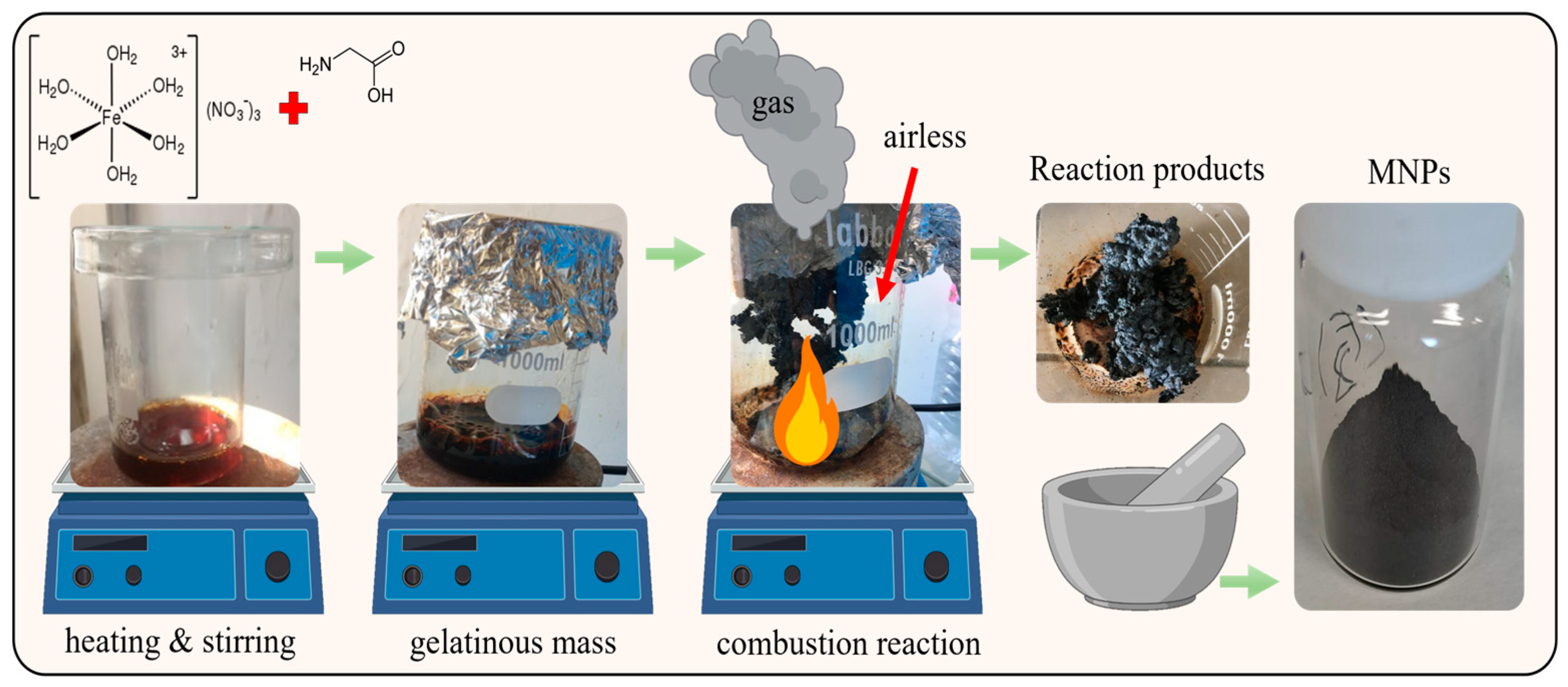
2.1. Synthesis of MNPS
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. COD and BOD5 Measurements
3. Results
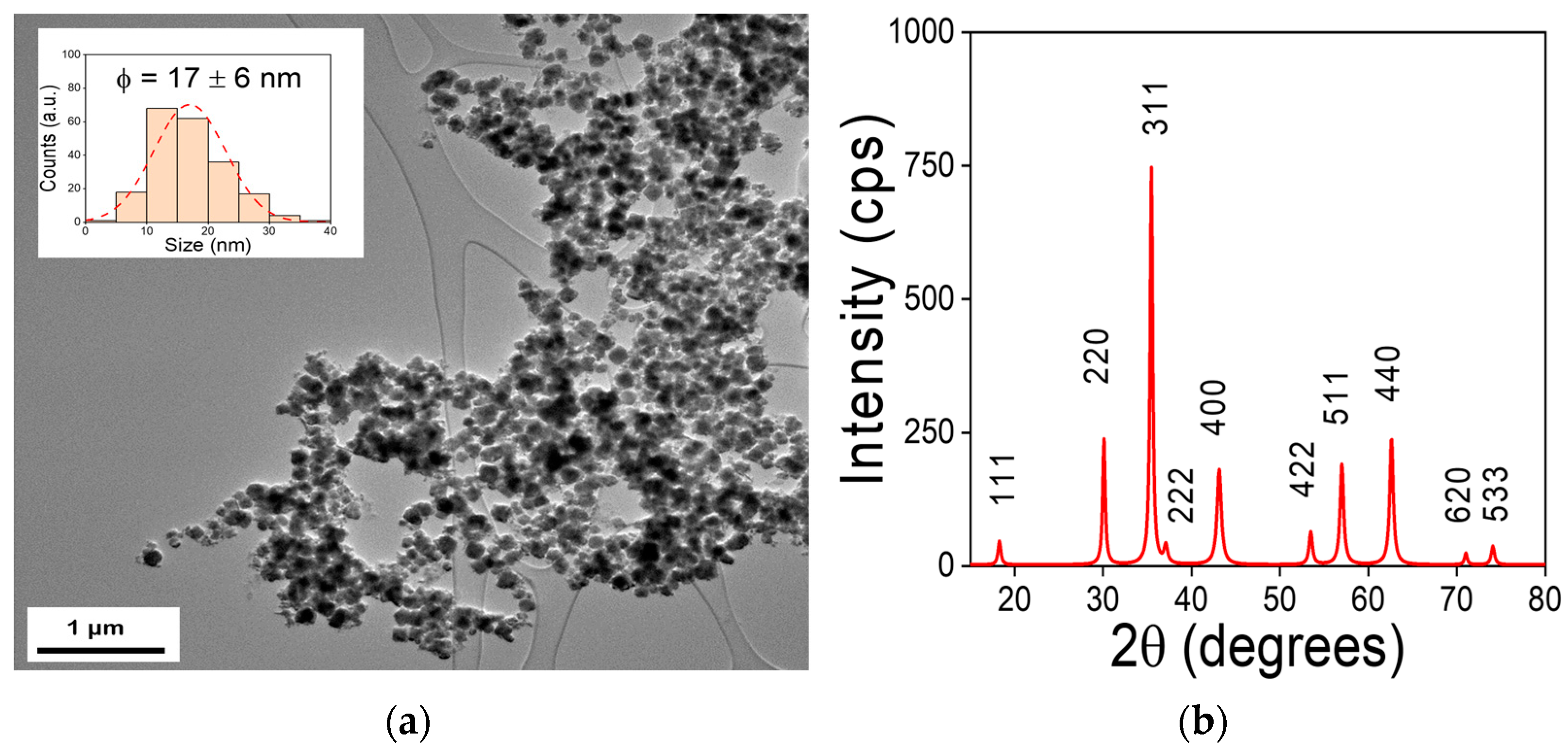
3.1. MNPs Size and Structure
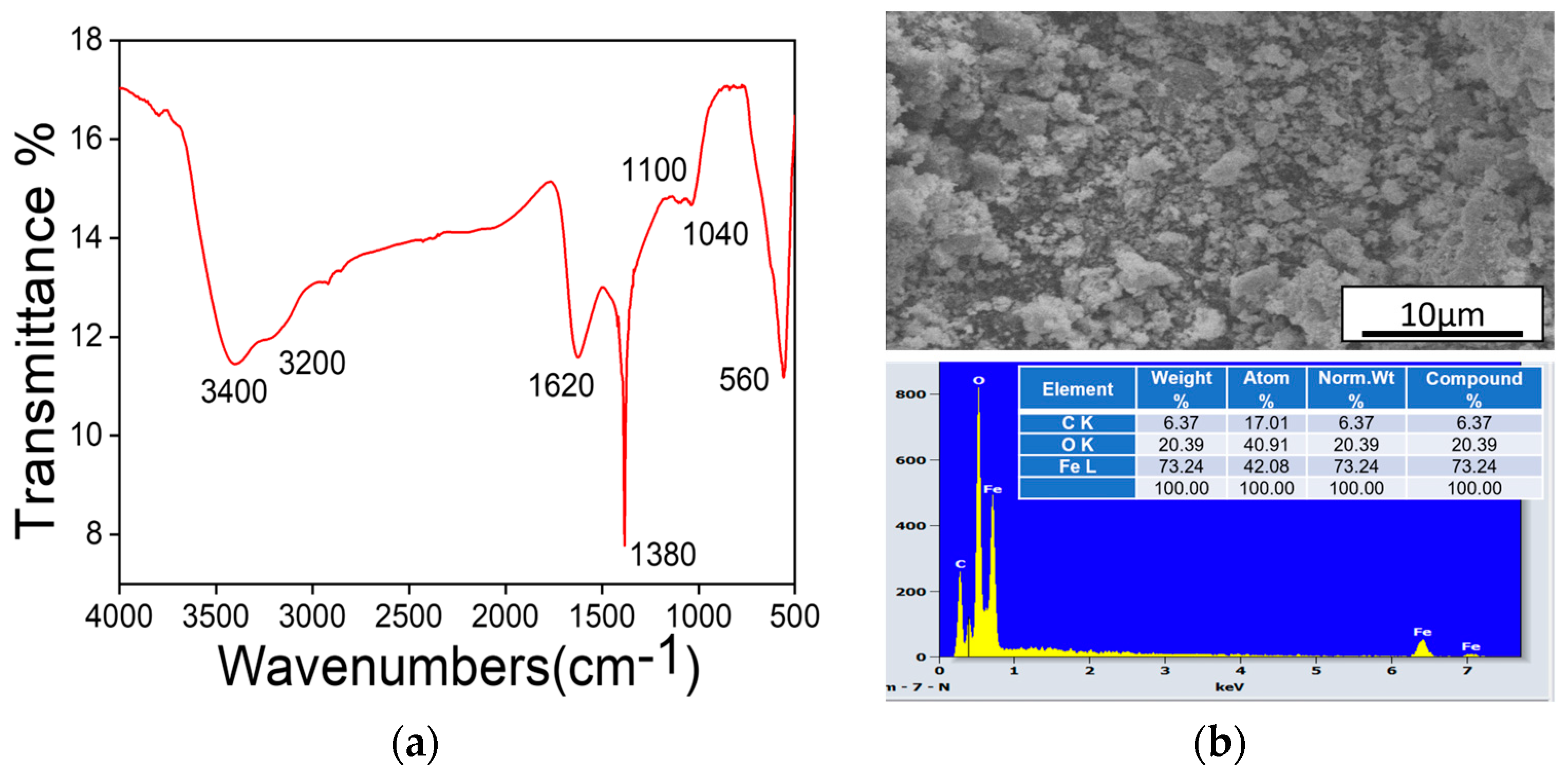
3.2. MNPs Composition
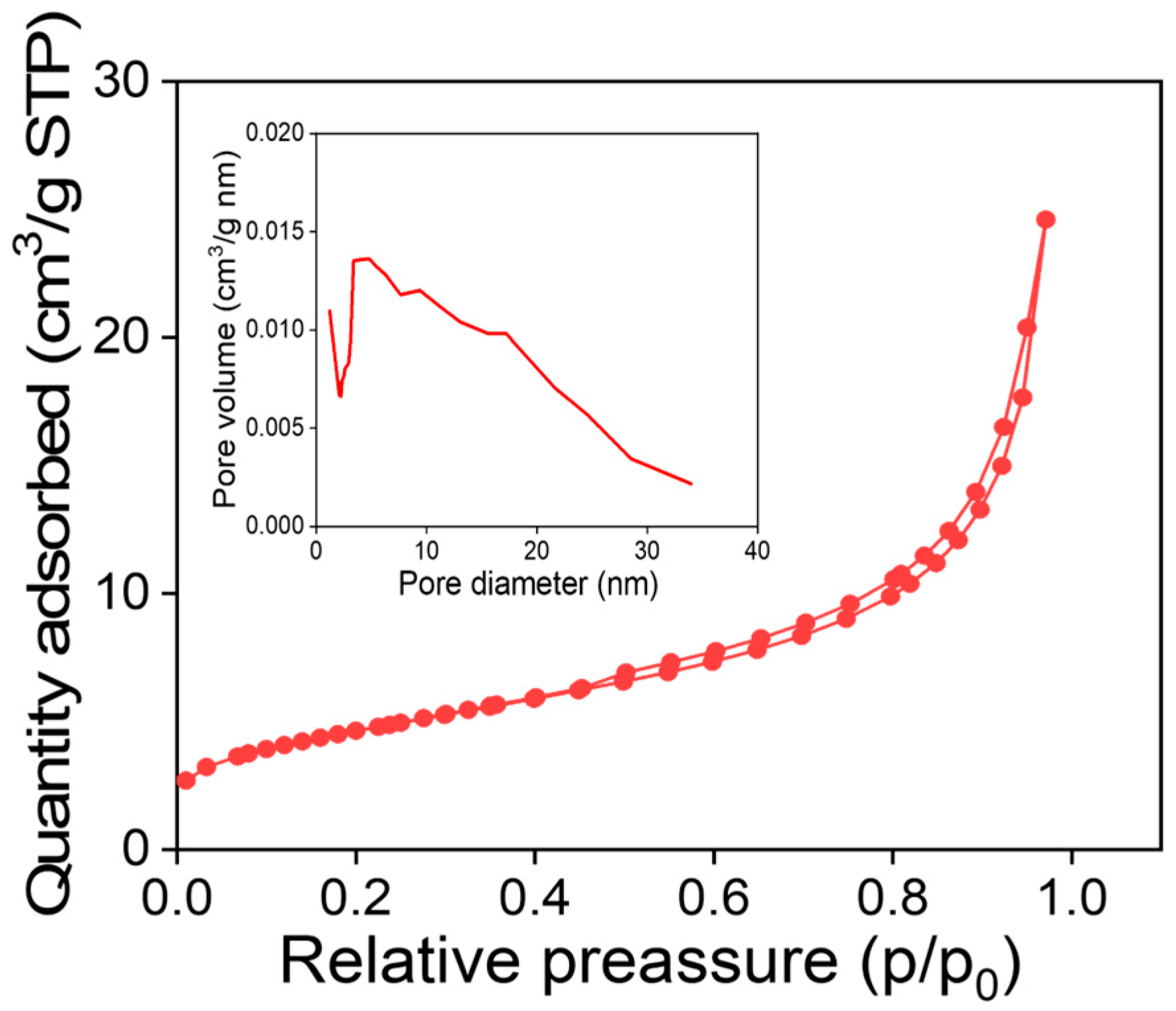
3.3. MNPs Surface Area Analysis
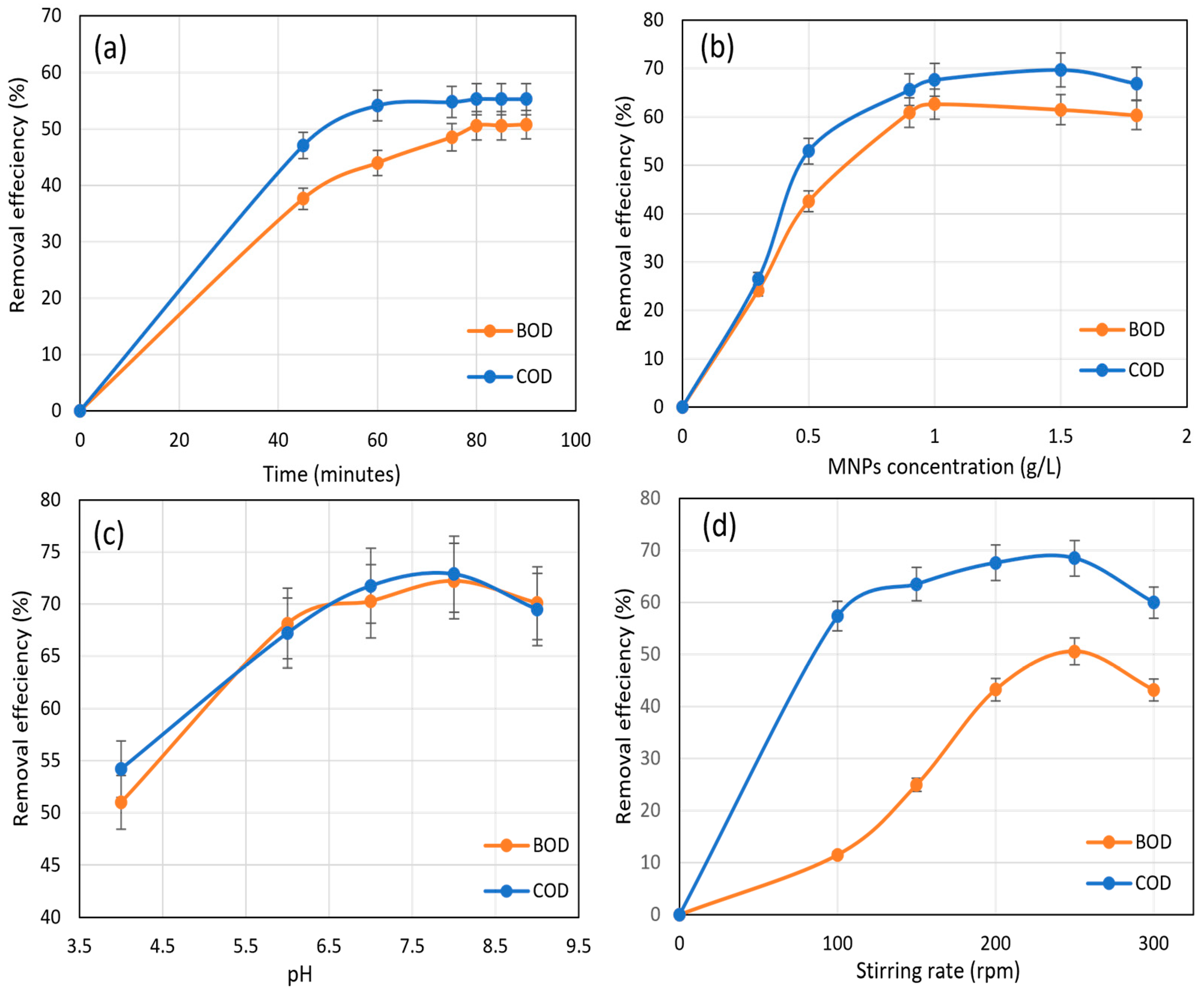
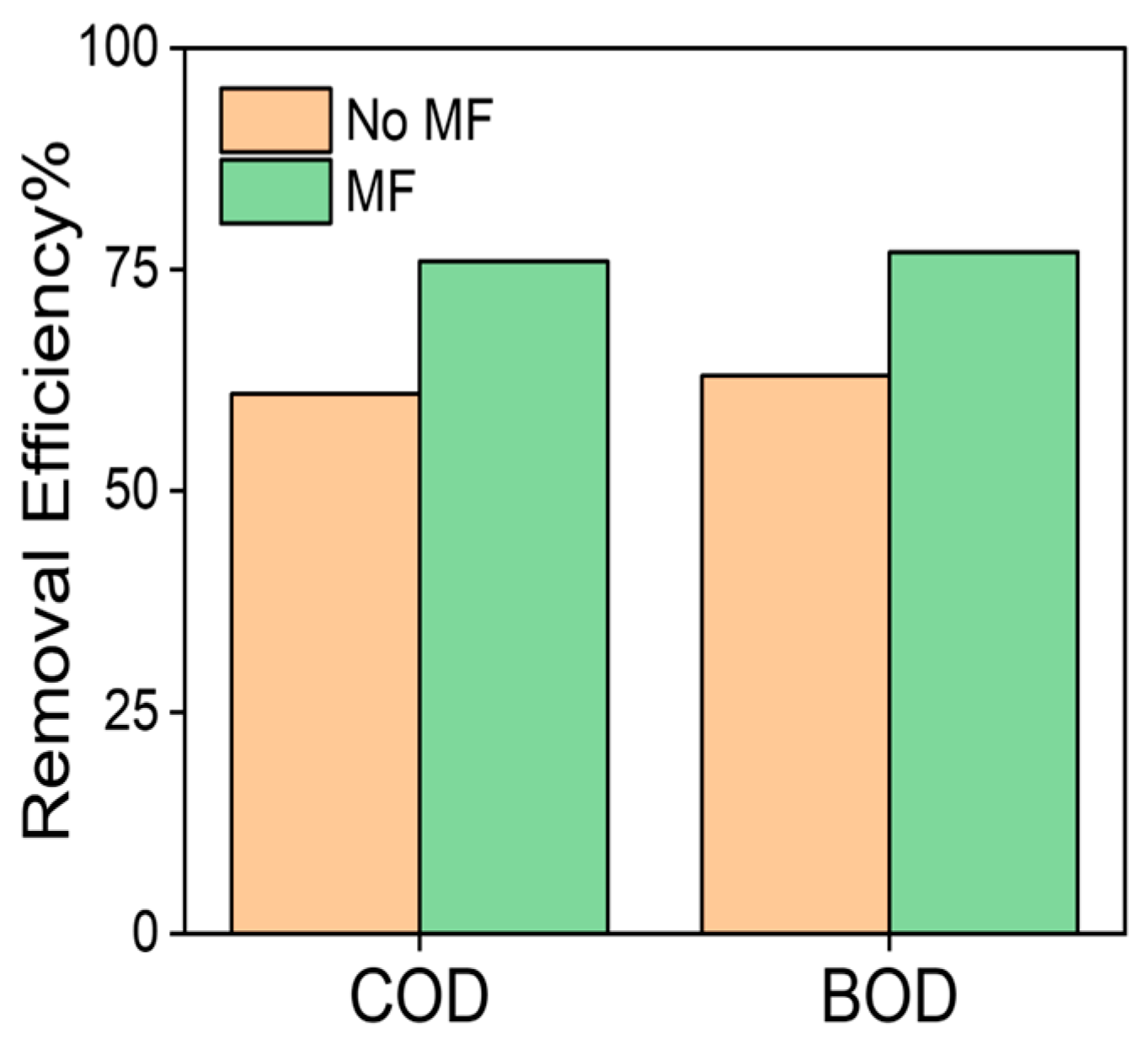
3.4. Removal Efficiency Using MNPs within the BOD5 and COD Experiements
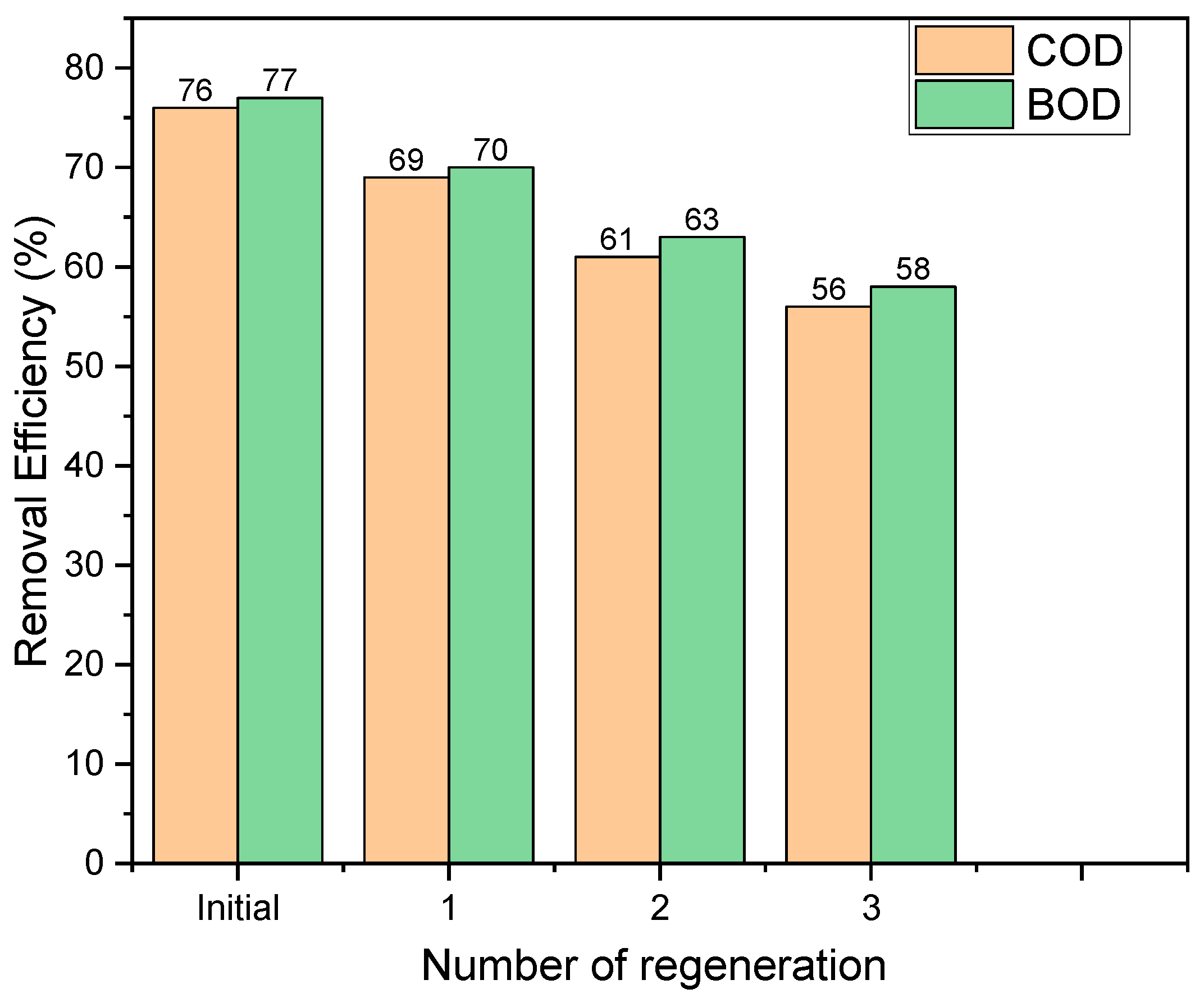
3.5. Regeneration Efficiency
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, X.; Mustavich, L.F.; Li, B.L. Assessment of Surface Water Quality via Multivariate Statistical Techniques: A Case Study of the Songhua River Harbin Region, China. J. Hydro-Environment Res. 2013, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, M.H.; Chamanpour, E.; Fahoul, N. The Ultrasonic Process with Titanium Magnetic Oxide Nanoparticles to Enhance the Amoxicillin Removal Efficiency. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2022, 7, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Vieritz, A.; Goonetilleke, A.; Gardner, T. Health Risk from the Use of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Southeast Queensland, Australia, as Potable or Nonpotable Water, Determined Using Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7382–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.M.; Mazumder, A. Health and Environmental Policy Issues in Canada: The Role of Watershed Management in Sustaining Clean Drinking Water Quality at Surface Sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 68, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louati, M.E.H.; Khanfir, R.; Alouini, A.; El Echi, M.L.; Frigui, L.; Marzouk, A. Guide Pratique de Gestion de La Sécheresse En Tunisie. Available online: http://www.citet.nat.tn/Portail/doc/SYRACUSE/20391/guide-pratique-de-gestion-de-la-secheresse-en-tunisie (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Khadhar, S.; Mlayah, A.; Chekirben, A.; Charef, A.; Methammam, M.; Nouha, S.; Khemais, Z. Vecteur de La Pollution Metallique Du Bassin Versant de l’Oued El Bey Vers Le Golfe de Tunis (Tunisie). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, T.; Khouni, I.; Ghrabi, A. Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis Methods in Wadi El Bey (Tunisia). Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 22152–22165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębska, K.; Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Gozdowski, D. Changes in Selected Water Quality Parameters in the Utrata River as a Function of Catchment Area Land Use. Water 2021, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Liu, H. A Review on the Sustainability of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: Design and Operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Khan, R.; Daverey, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles, and Their Applications in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, C.C.S.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.; Xavier, A.M.R.B.; Tavares, A.P.M. Optimization of Enzyme Immobilization on Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Laccase Biocatalytic Reactions. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 117, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenibandpei, A.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Hassani, G.; Bahrami, H.; Bahmani, Z.; Alinejad, A.A. Water Solution Polishing of Nitrate Using Potassium Permanganate Modified Zeolite: Parametric Experiments, Kinetics and Equilibrium Analysis. Glob. Nest J. 2016, 18, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Zhao, Z.S.; Jiang, G.B. Coating Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles with Humic Acid for High Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6949–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinowski, P.; Bury, D.; Krupa, M.; Ścieżyńska, D.; Prabhu, P.; Bogacki, J. Magnetite and Hematite in Advanced Oxidation Processes Application for Cosmetic Wastewater Treatment. Processes 2020, 8, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, N.P.; Rathilal, S.; Tetteh, E.K.; Amo-Duodu, G. Evaluation of The Effect Of Recycled Magnetized Coagulants On Wastewater Treatment. J. Pharm. Negat. Results 2022, 13, 3466–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourens, A.; Falch, A.; Malgas-Enus, R. Magnetite Immobilized Metal Nanoparticles in the Treatment and Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 2951–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masudi, A.; Harimisa, G.E.; Ghafar, N.A.; Jusoh, N.W.C. Magnetite-Based Catalysts for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4664–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianoş, R.; Lazău, I.; Păcurariu, C. The Influence of Combustion Synthesis Conditions on the α-Al2O3 Powder Preparation. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukasyan, A.S.; Dinka, P. Novel Approaches to Solution-Combustion Synthesis of Nanomaterials. Int. J. Self-Propagating High-Temp. Synth. 2007, 16, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaoud, A.; Turki, N.; Amor, H.B.; Jalel, R.; Salah, N.B. Influence of the Magnetic Device on Water Quality and Production of Melon. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2016, 6, 2256–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, H.B.; Elaoud, A. Characteristic Study of Some Parameters of Soil Irrigated by Magnetized Waters. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T.A.; Bogale, F.M.; Aragaw, B.A. Iron-Based Nanoparticles in Wastewater Treatment: A Review on Synthesis Methods, Applications, and Removal Mechanisms. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dębowski, M.; Krzemieniewski, M. Effect of Constant Magnetic Field (CMF) with Various Values of Magnetic Induction on Effectiveness of Dairy Wastewater Treatment under Anaerobic Conditions. Pol. J. Environ. 2014, 23, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Taoufik, G.; Khouni, I.; Ghrabi, A. Assessment of Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Surface Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques: A Case Study of the Wadi El-Bey River, Tunisia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhamdi, F.; Khouni, I.; Ghrabi, A. Diagnosis and Characteristics of Water Quality along the Wadi El Bey River (Tunisia). Coagulation/Flocculation Essays of Textile Effluents Discharged into the Wadi. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 22166–22188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrout, H.; Baccouche, H.; Mellah, T.; Jomaa, S. Surface Water Quality Assessment of Wadi El Bey, Tunisia. In Proceedings of the 3rd Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Interration, Sousse, Tunisia, 10–13 June 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khouni, I.; Louhichi, G.; Ghrabi, A. Use of GIS Based Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation to Assess Surface Water Quality: Case of Wadi El Bey, Tunisia. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.; Bridgewater, L. American, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nekuri, B.B. Application of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in the Dye Removal. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2017, 8, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, E.; Jeffryes, C.; Yazdian, F.; Akhavan Sepahi, A.; Hatamian, A.; Rasekh, B.; Ashrafi, S.J. DBT Desulfurization by Decorating Rhodococcus Erythropolis IGTS8 Using Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in a Bioreactor. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; You, C.; Song, Z.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y. Influences of Different Synthesis Conditions on Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Chiang, Y.W.; Santos, R.M. X-ray Diffraction Techniques for Mineral Characterization: A Review for Engineers of the Fundamentals, Applications, and Research Directions. Minerals 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.S.; Amanullah; Manan, A.; Khan, N.; Mahmood, A.; Rahim, A. Transformation Mechanism of Magnetite Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2015, 33, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.J.; Carvalho, E.; Eriksson, J.W.; Crans, D.C.; Aureliano, M. Effects of Decavanadate and Insulin Enhancing Vanadium Compounds on Glucose Uptake in Isolated Rat Adipocytes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood-Garibay, J.A.; Méndez-Rojas, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Wrinkled Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites Containing Fe3O4 or CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Potential Biomedical Applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 126236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Jiang, Y.R.; Huang, K.L.; Ding, P.; Chen, J. Preparation and Properties of Magnetic Fe3O4–Chitosan Nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 466, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Barick, K.C.; Bahadur, D. Development of Citrate-Stabilized Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Conjugation and Release of Doxorubicin for Therapeutic Applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Weier, M.L.; Kloprogge, J.T. Raman Spectroscopy of Some Natural Hydrotalcites with Sulphate and Carbonate in the Interlayer. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P.; Falcaro, P.; Grosso, D.; Babonneau, F. Order−Disorder Transitions and Evolution of Silica Structure in Self-Assembled Mesostructured Silica Films Studied through FTIR Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Shen, H.Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Gu, N. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated by Amino Silane. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, R.D. Infrared Spectra of Ferrites. Phys. Rev. 1995, 99, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparov, L.V.; Tanner, D.B.; Romero, D.B.; Berger, H.; Margaritondo, G.; Forro, L. Infrared and Raman Studies of the Verwey Transition in Magnetite. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, D.; Bhushan, B. Effect of Spherical Au Nanoparticles on Nanofriction and Wear Reduction in Dry and Liquid Environments. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchoudhury, S.; Baalousha, M.; Lead, J.R. Methods for Measuring Concentration (Mass, Surface Area and Number) of Nanomaterials. Front. Nanosci. 2015, 8, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Isotherm Models of Adsorption Processes on Adsorbents and Nanoadsorbents. Interface Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.S.; Farag, R.S.; Elshfai, M.M. Reduction of Organic Matter from Municipal Wastewater at Low Cost Using Green Synthesis Nano Iron Extracted from Black Tea: Artificial Intelligence with Regression Analysis. Egypt. J. Pet. 2019, 29, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saryel-Deen, R.A.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Mahmoud, M.; Mostafa, M.K.; Peters, R.W. Adsorption and Kinetic Studies of Using Entrapped Sewage Sludge Ash in the Removal of Chemical Oxygen Demand from Domestic Wastewater, with Artificial Intelligence Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 Annual AIChE Meeting, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 29 October–3 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, R.S.; Elshfai, M.M.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Mostafa, M.K.; Karam, A.; Peters, R.W. (670d) Study the Degradation and Adsorption Processes of Organic Matters from Domestic Wastewater Using Chemically Prepared and Green Synthesized Nano Zero-Valent Iron. In Proceedings of the AIChE Annual Meeting 2019, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–15 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, N.N.; Arar, L.A.; Marei, N.N.; Ghanim, M.M.A.; Dwekat, M.S.; Sawalha, S.H. Treatment of Olive Mill Based Wastewater by Means of Magnetic Nanoparticles: Decolourization, Dephenolization and COD Removal. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2014, 1, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.K.; Moustafa, A.F. Industrial Solid Waste for Heavy Metals Adsorption Features and Challenges; a Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10235–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, S.A.; Etim, U.J.; Israel, A.U. Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Industrial Effluent Using Poly (Vinyl Alcohol). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, O.P.; Chaudhari, P.K. Review on Chemical Treatment of Industrial Waste Water. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2013, 17, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y. Decolorization and COD Removal of Secondary Yeast Wastewater Effluents by Coagulation Using Aluminum Sulfate. Desalination 2008, 225, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; Yue, T.; Li, R.; William, W.Y. Food Related Applications of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Enzyme Immobilization, Protein Purification, and Food Analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 27, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phouthavong, V.; Yan, R.; Nijpanich, S.; Hagio, T.; Ichino, R.; Kong, L.; Li, L. Magnetic Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment: Advancements in Their Synthesis Methods. Materials 2022, 15, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Tran, H.V.; Xu, S.; Lee, T.R. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Structures, Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, Surface Functionalization, and Emerging Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnwell, F.H.; Brown, F.A. Responses of Planarians and Snails. In Biological Effects of Magnetic Fields; Barnothy, M.F., Ed.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1964; pp. 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomska, A.; Wolny, L. Enhancement of Biological Wastewater Treatment by Magnetic Field Exposure. Desalination 2008, 222, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tlili, H.; Elaoud, A.; Asses, N.; Horchani-Naifer, K.; Ferhi, M.; Goya, G.F.; Fuentes-García, J.A. Reduction of Oxidizable Pollutants in Waste Water from the Wadi El Bey River Basin Using Magnetic Nanoparticles as Removal Agents. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060157
Tlili H, Elaoud A, Asses N, Horchani-Naifer K, Ferhi M, Goya GF, Fuentes-García JA. Reduction of Oxidizable Pollutants in Waste Water from the Wadi El Bey River Basin Using Magnetic Nanoparticles as Removal Agents. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(6):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060157
Chicago/Turabian StyleTlili, Hajer, Anis Elaoud, Nedra Asses, Karima Horchani-Naifer, Mounir Ferhi, Gerardo F. Goya, and Jesús Antonio Fuentes-García. 2023. "Reduction of Oxidizable Pollutants in Waste Water from the Wadi El Bey River Basin Using Magnetic Nanoparticles as Removal Agents" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 6: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060157
APA StyleTlili, H., Elaoud, A., Asses, N., Horchani-Naifer, K., Ferhi, M., Goya, G. F., & Fuentes-García, J. A. (2023). Reduction of Oxidizable Pollutants in Waste Water from the Wadi El Bey River Basin Using Magnetic Nanoparticles as Removal Agents. Magnetochemistry, 9(6), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060157








