Magnetic Janus Particles for Static and Dynamic (Bio)Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
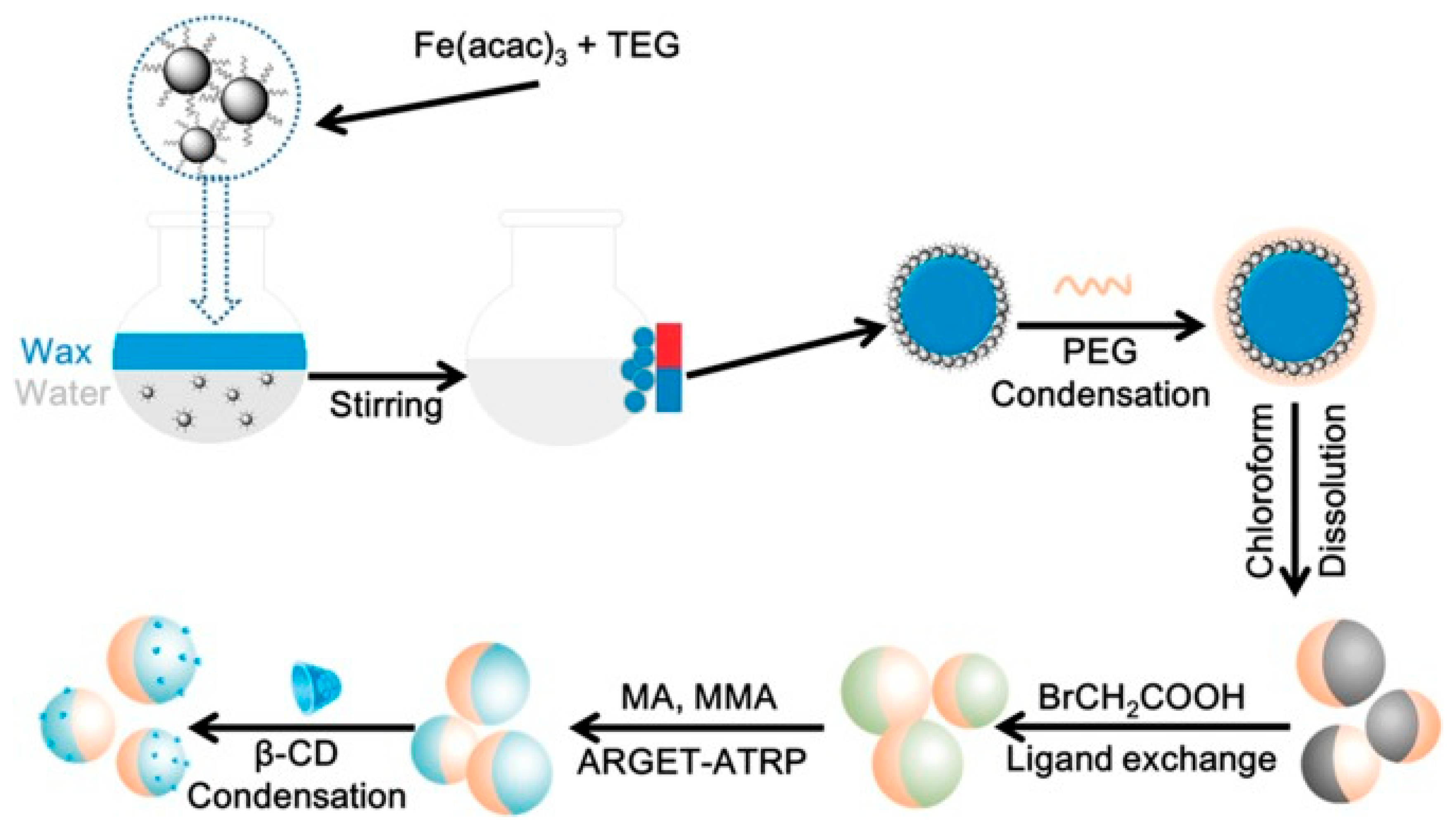
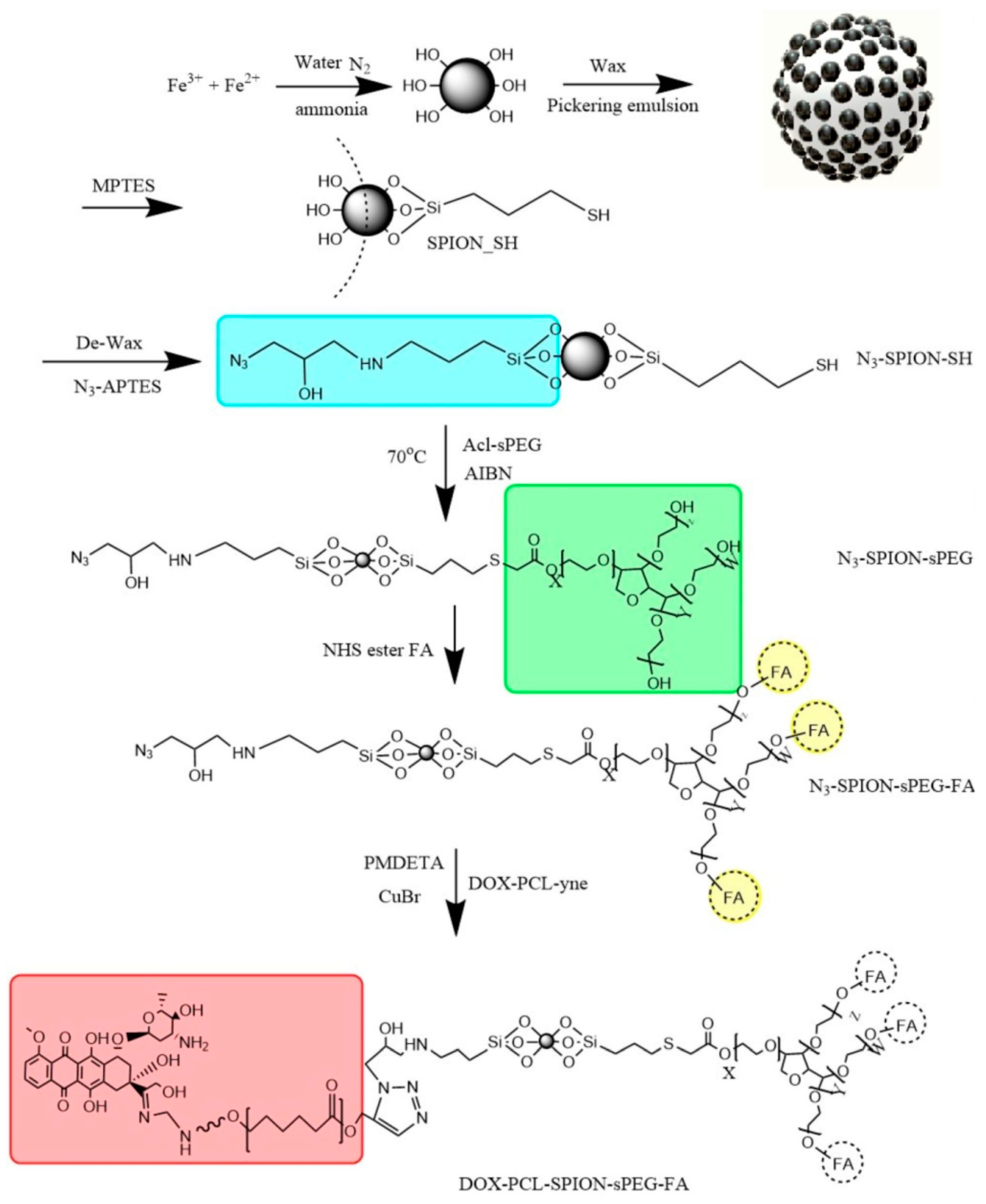
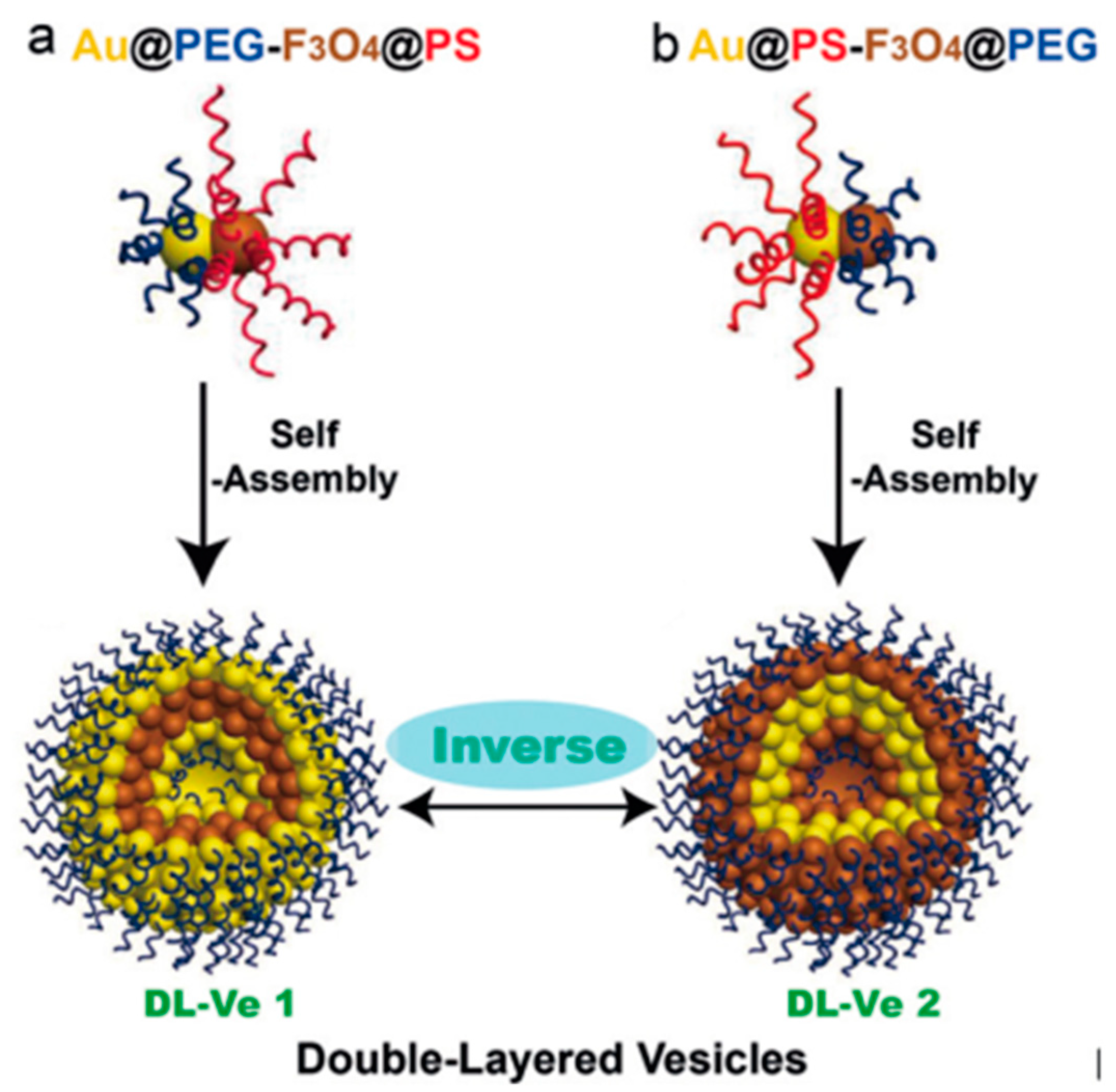
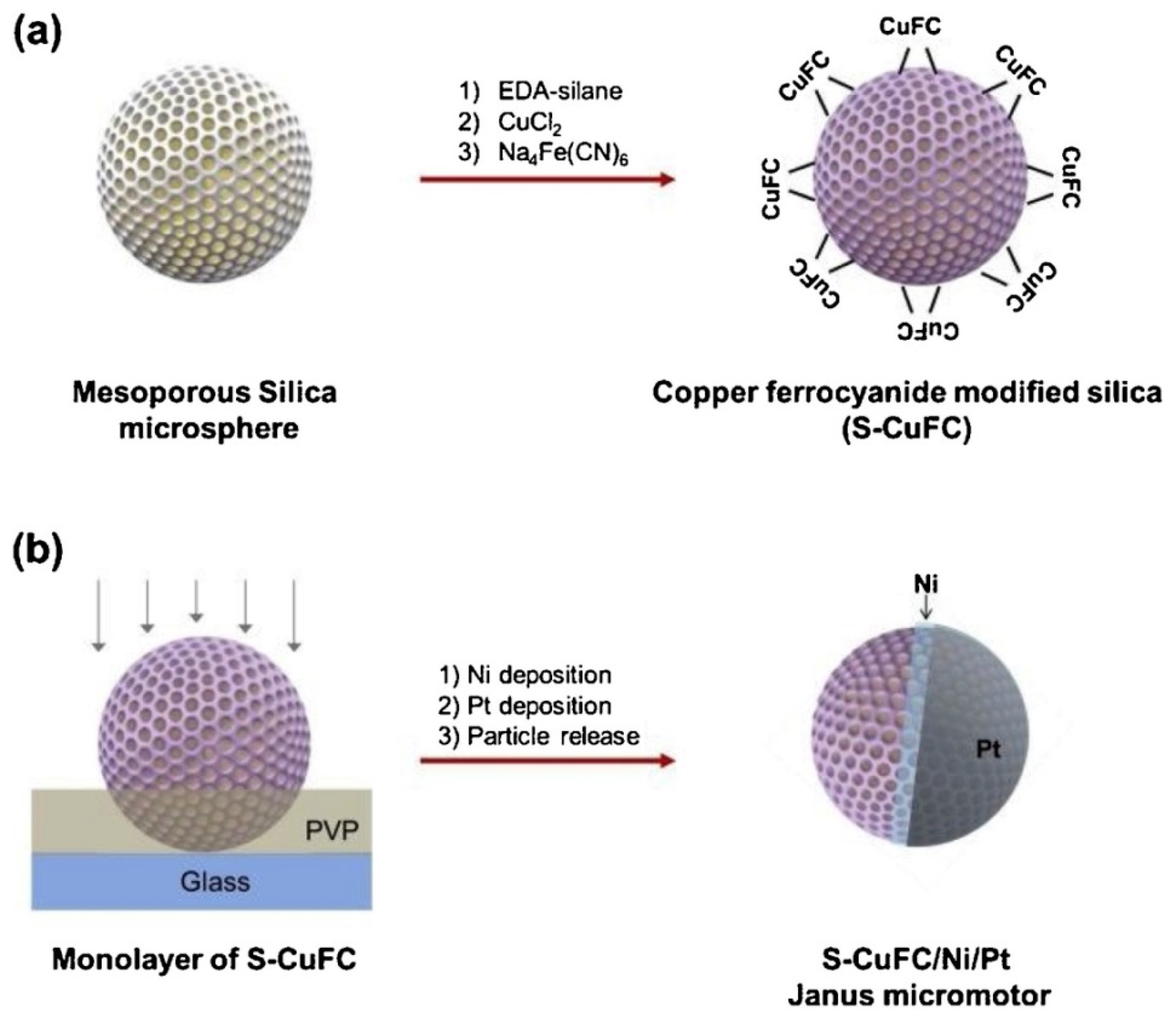
2. Synthesis of Magnetic Janus Particles
3. Magnetic Janus Particles for (Bio)Sensing
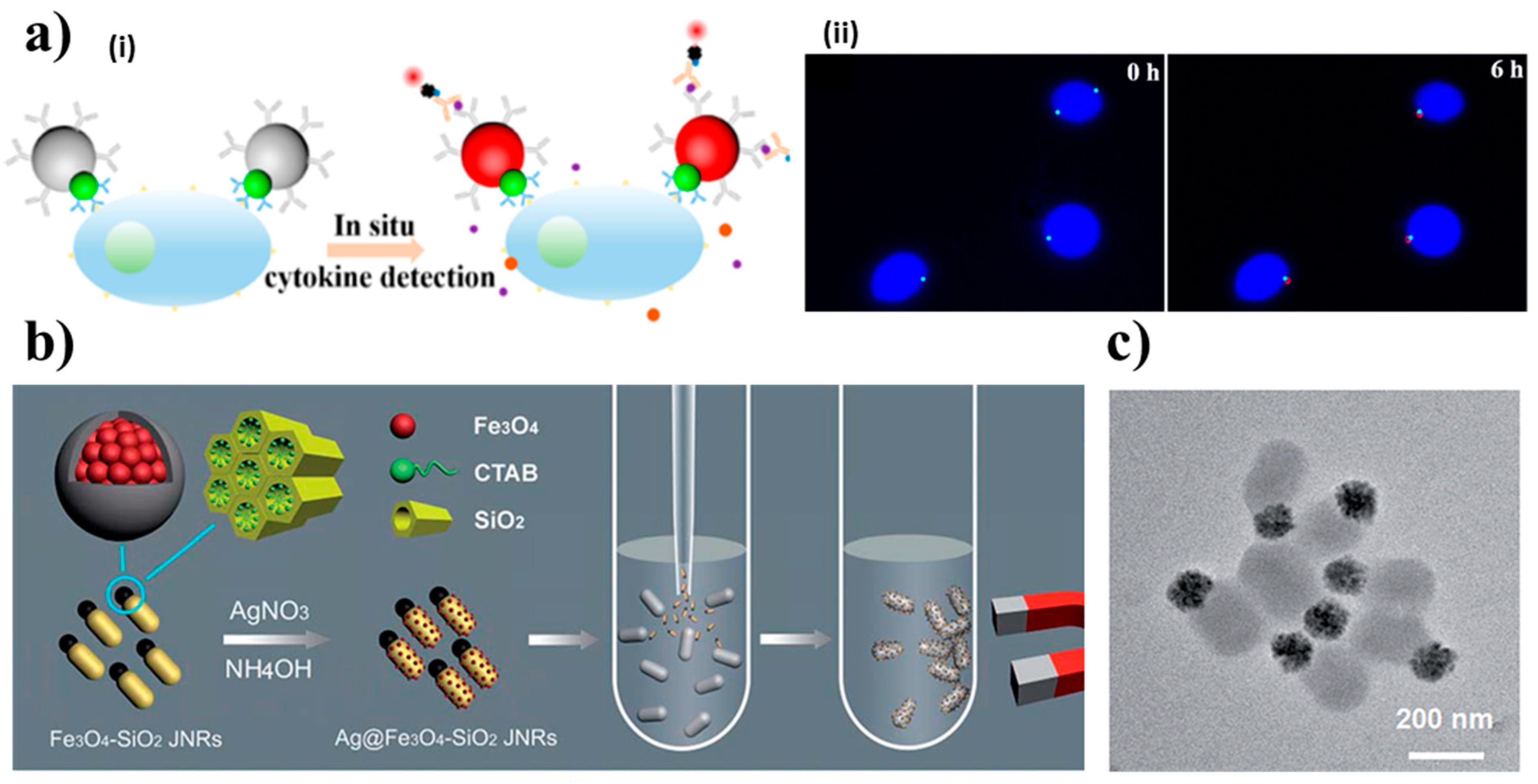
3.1. Static Janus Magnetic Particles for (Bio)Sensing
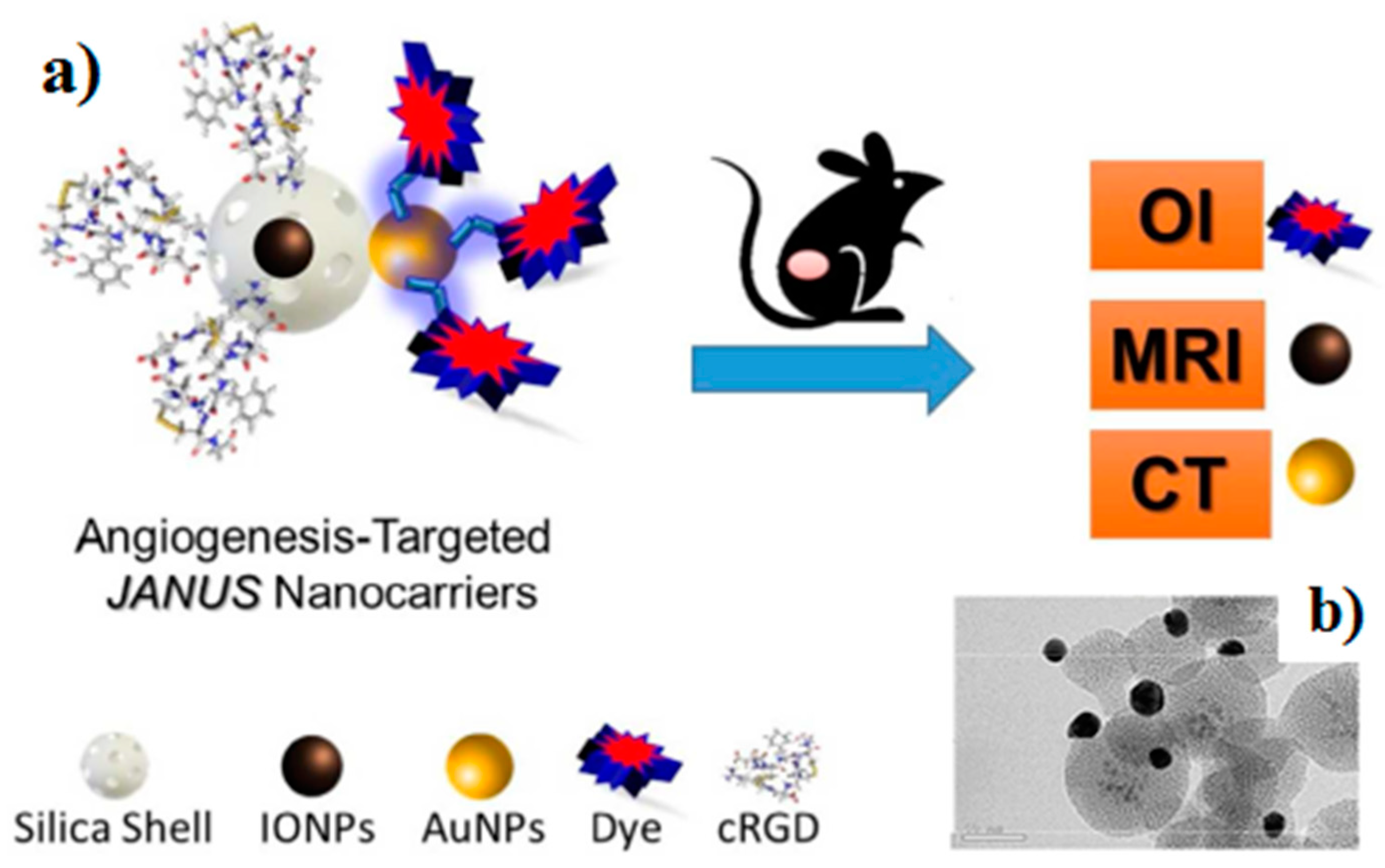
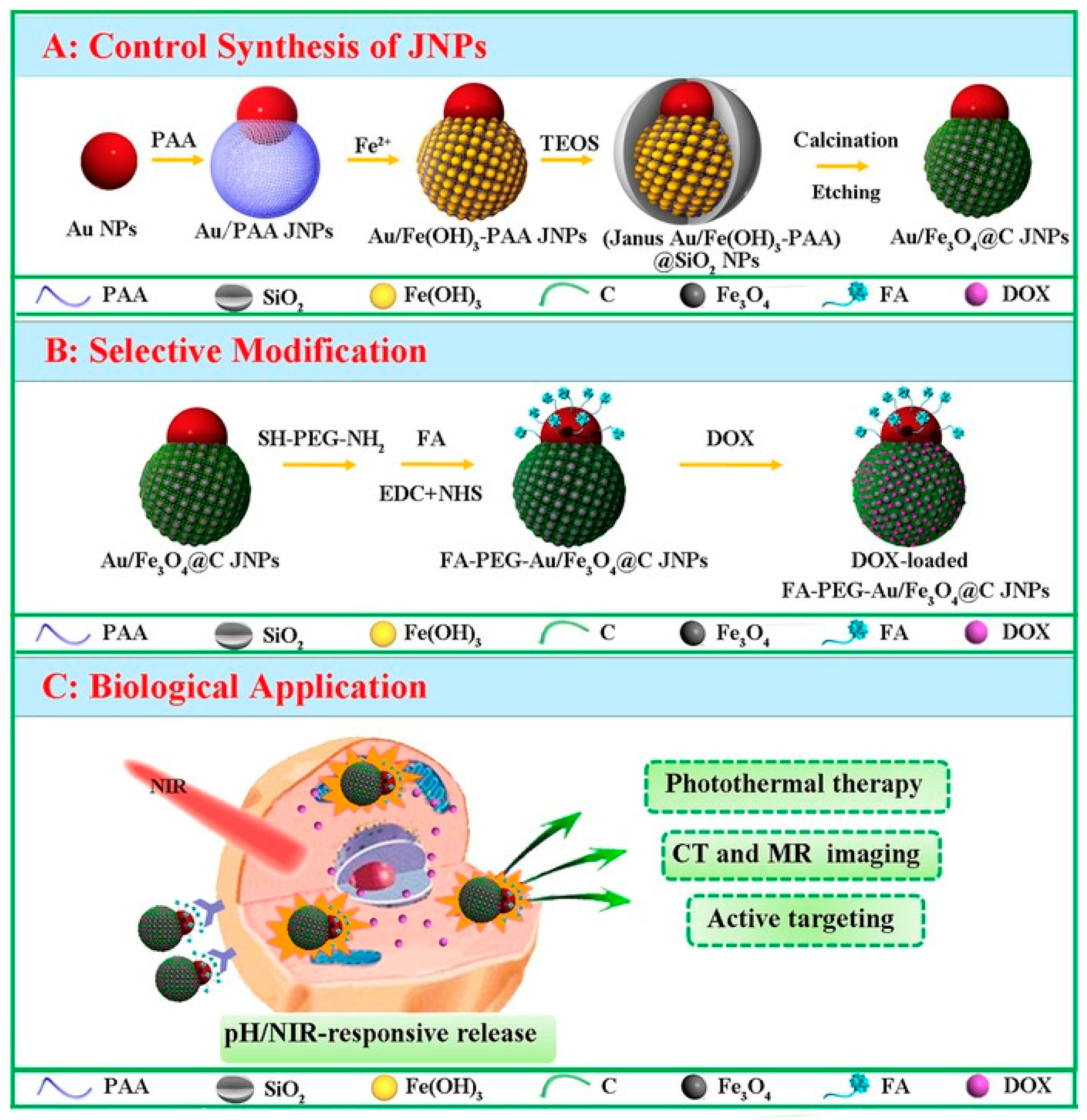
Magnetic Janus Particles for Targeted Biomedical Applications
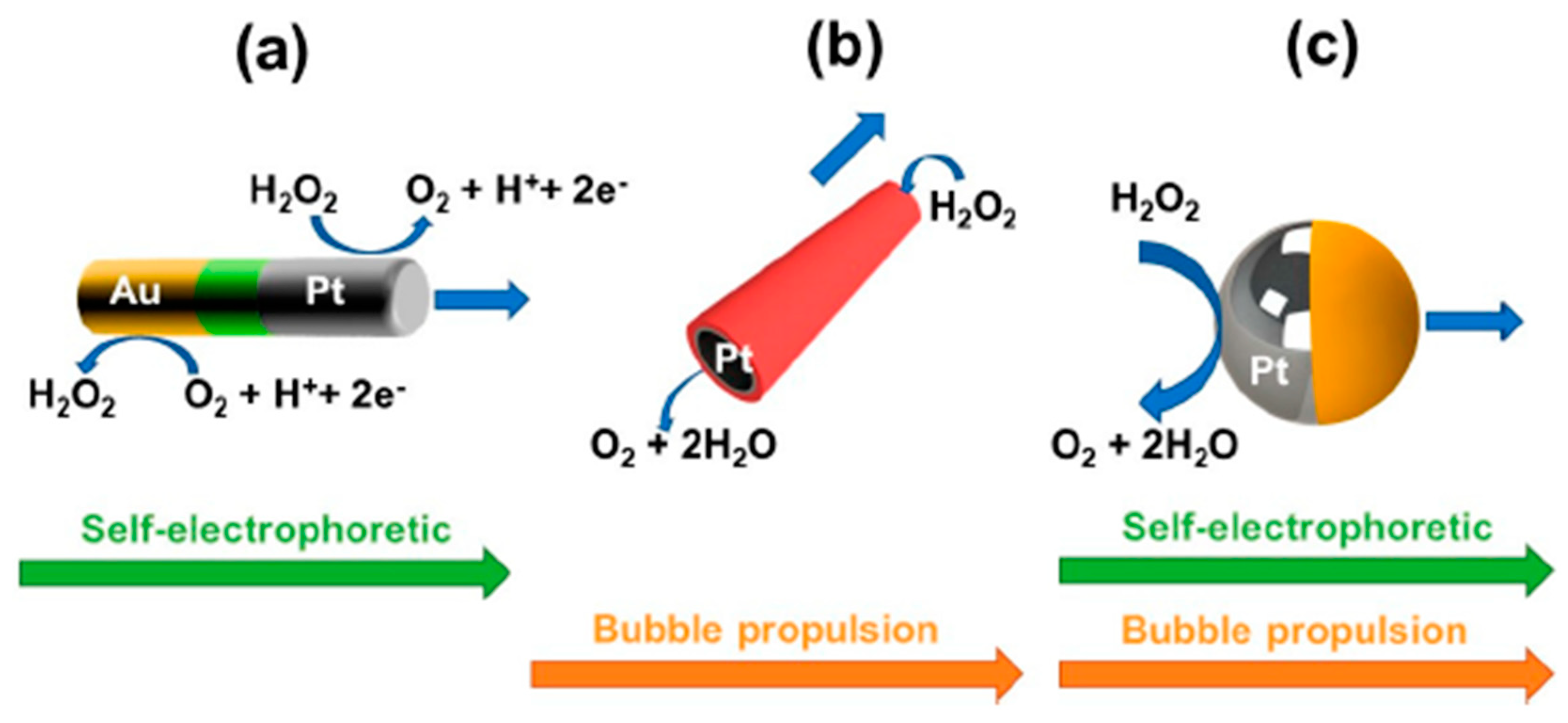
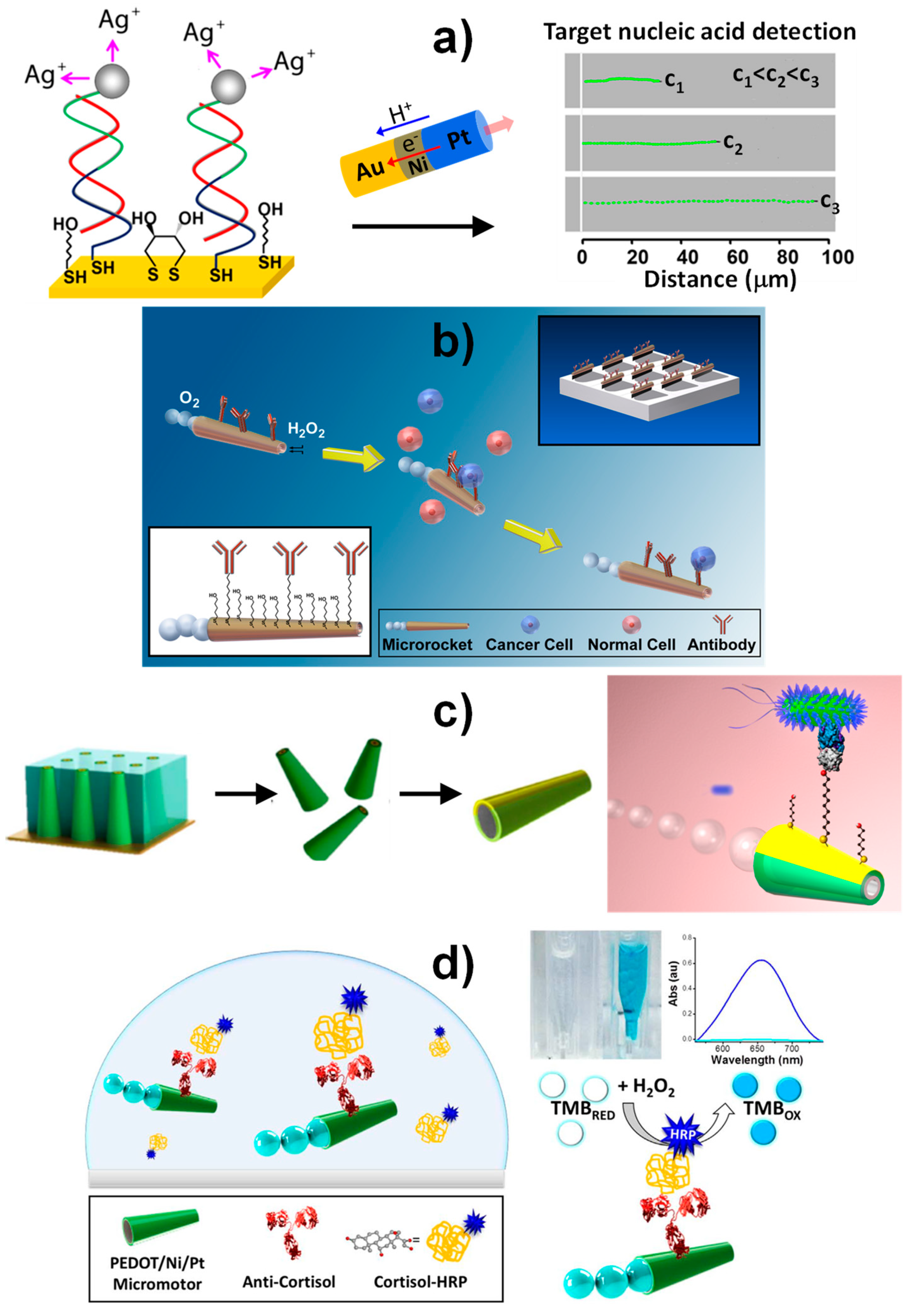
3.2. Self-Propelled Janus Magnetic Particles for (Bio)Sensing
4. Conclusions, Main Challenges to Solve and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casagrande, C.; Fabre, P.; Raphaël, E.; Veyssie, M. “Janus Beads”: Realization and Behaviour at Water/Oil Interfaces. Europhys. Lett. 1989, 9, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.G. Soft matter. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Cao, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Intelligent Janus nanoparticles for intracellular real-time monitoring of dual drug release. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 6754–6760. [Google Scholar]
- Yánez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Janus particles for (bio)sensing. Appl. Mat. Today 2017, 9, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.W.; Jalani, G.; Ko, J.; Choo, J.; Lim, D.W. Synthesis, characterization, and directional binding of anisotropic biohybrid microparticles for multiplexed biosensing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Chen, K.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of Biofunctional Janus Particles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Sanchez, L.; Gao, Y.; Yu, Y. Janus Particles for Biological Imaging and Sensing. Analyst 2016, 141, 3526–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, S.; Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Wang, J. Nano/microvehicles for efficient delivery and (bio)sensing at the cellular level. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6750–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, D.; Sloutski, A.; Elyashiv, A.; Varma, V.B.; Ramanujan, R. In Situ Generated Medical Devices. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 8, e1801066. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.-Z.; Hoop, M.; Mushtaq, F.; Siringil, E.; Hu, C.; Nelson, B.J.; Pané, S. Recent developments in magnetically driven micro- and nanorobots. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Self-propelled affinity biosensors: Moving the receptor around the sample. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrittwieser, S.; Pelaz, B.; Parak, W.J.; Lentijo-Mozo, S.; Soulantica, K.; Dieckhoff, J.; Ludwig, F.; Guenther, A.; Tschöpe, A.; Schotter, J. Homogeneous Biosensing Based on Magnetic Particle Labels. Sensors 2016, 16, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; De Ávila, B.E.-F.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Micro/nanorobots for biomedicine: Delivery, surgery, sensing, and detoxification. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaam6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; de Ávila, B.E.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Targeting and isolation of cancer cells using micro/nanomotors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 125, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B. Nanoscale Biosensors Based on Self-Propelled Objects. Biosensors 2018, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Müller, A.H.E. Janus Particles: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, Physical Properties, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5194–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugarolas, T.; Tu, F.; Lee, D. Directed assembly of particles using microfluidic droplets and bubbles. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 9046–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Dong, W.-F.; Song, J.-F.; Huo, Q.-S.; Sun, H.-B. Magnetic-mesoporous Janus nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Wang, C.; Ngai, T.; Yang, Y.; Tong, Z. Hollow magnetic Janus microspheres templated from double Pickering emulsions. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5510–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guo, F.; Kiraly, B.; Mao, X.; Lu, M.; Leong, K.W.; Huang, T.J. Microfluidic synthesis of multifunctional Janus particles for biomedical applications. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, T.Y.; Choi, T.M.; Shim, T.S.; Kim, S.-H.; Yang, S.-M. Droplet microfluidics for producing functional microparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.B. Development of Magnetic Structures by Micro-Magnetofluidic Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lattuada, M.; Hatton, T.A. Preparation and Controlled Self-Assembly of Janus Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12878–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Luo, B.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, X.; Lan, F.; Yi, Q.; Wu, Y. pH-responsive superstructures prepared via the assembly of Fe3O4 amphipathic Janus nanoparticles. Regen. Biomater. 2018, 5, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, Y.; Matyjaszewski, K. ARGET ATRP of methyl methacrylate in the presence of nitrogen-based ligands as reducing agents. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghi, B.; Khoee, S.; Bonakdar, S. Preparation of multifunctional Janus nanoparticles on the basis of SPIONs as targeted drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, X.; Duan, W.; Moriga, T. Synthesis and evaluation of the SERS effect of Fe3O4–Ag Janus composite materials for separable, highly sensitive substrates. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lin, L.; Yu, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G.; et al. Double-Layered Plasmonic-Magnetic Vesicles by Self-Assembly of Janus Amphiphilic Gold-Iron(II,III) Oxide Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 8222–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jishkariani, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Van Blaaderen, A.; Murray, C.B. Preparation and Self-Assembly of Dendronized Janus Fe3O4 –Pt and Fe3O4 –Au Heterodimers. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7958–7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, J.; Vilela, D.; Villa, K.; Wang, J.; Sanchez, S. Micro- and Nanomotors as Active Environmental Microcleaners and Sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9317–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Chang, X.; Song, W.; Hu, Y.; Shao, G.; Sandraz, E.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; et al. Magnetically Propelled Fish-Like Nanoswimmers. Small 2016, 12, 6098–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
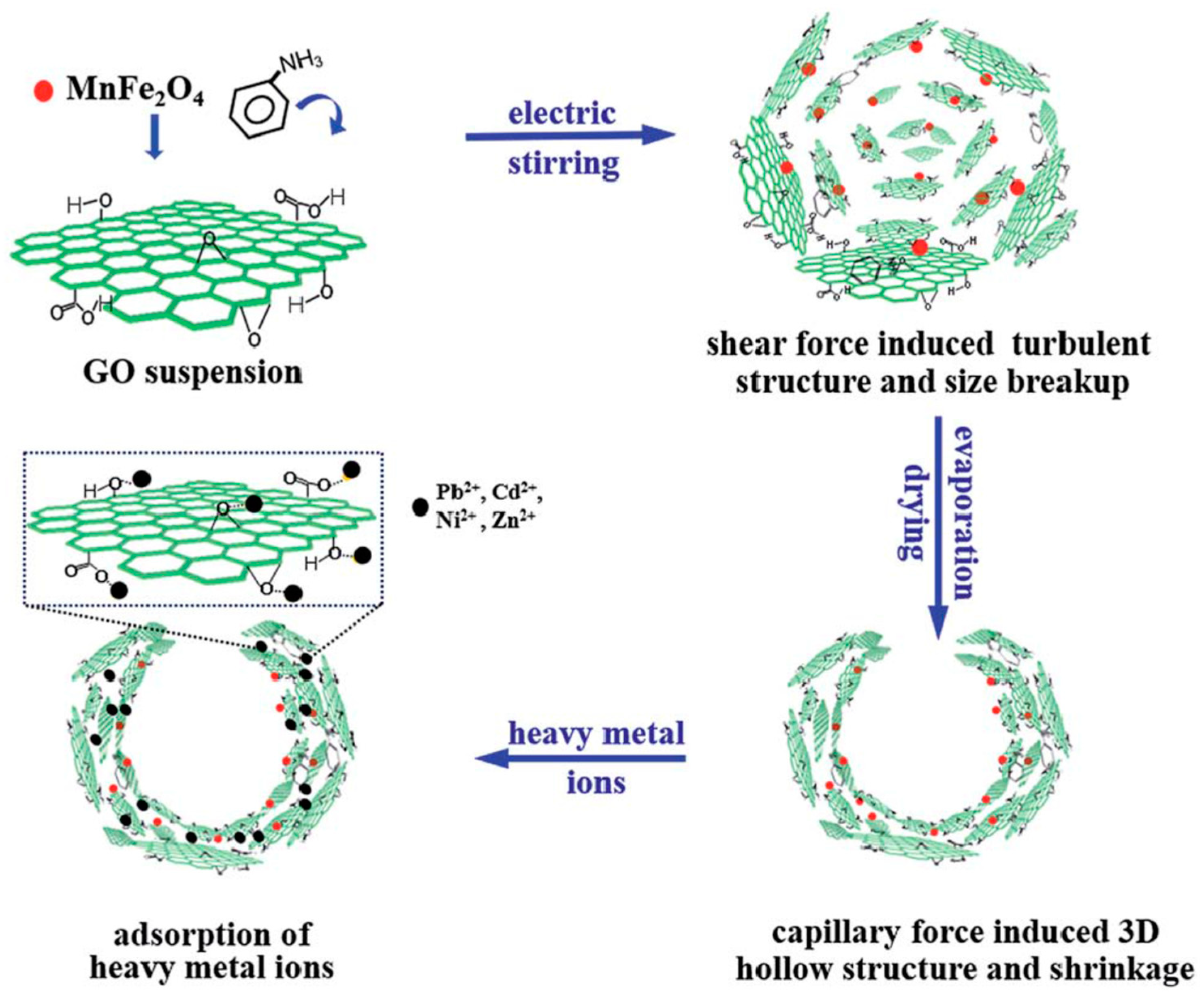
- Peng, X.; Gao, F.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Qu, J.; Fan, H.; Qu, J.Y. Self-assembly of a graphene oxide/MnFe2O4 motor by coupling shear force with capillarity for removal of toxic heavy metals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 20861–20868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Yang, H.-M.; Lee, K.-W.; Jung, Y.-I.; Lee, K.J.; Park, C.W. A remotely steerable Janus micromotor adsorbent for the active remediation of Cs-contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indalkar, Y.R.; Gaikwada, S.S.; Ubale, A.T. Janus particles recent and novel approach in drug delivery: An overview. Curr. Pharma Res. 2013, 3, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Liao, T.; Chen, X.; Jiang, W.; Luo, W.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z. Janus nanoarchitectures: From structural design to catalytic applications. Nano Today 2018, 22, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Lin, J.; Huang, P.; Zhang, Y. Janus nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis, therapy and theranostics. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.-T.-C.; Lesieur, S.; Faivre, V. Janus nanoparticles: Materials, preparation and recent advances in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, B.M.; Young, D.J.; Loh, X.J. Magnetic anisotropic particles: Toward remotely actuated applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2016, 33, 709–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Niu, X.; Fan, Y. Electrospraying magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional Janus PLGA microspheres with dual rare earth ions fluorescent-labeling drugs. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 99034–99043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, P.; Jia, Z.; Qi, B.; Xu, J.; Kang, D.; Liu, M.; Fan, Y. Enhanced fluorescent intensity of magnetic-fluorescent bifunctional PLGA microspheres based on Janus electrospraying for bioapplication. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, F.; Tang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ying, Y. Multifunctional Janus Hematite–Silica Nanoparticles: Mimicking Peroxidase-Like Activity and Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Glucose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15395–15402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.-H.; Yue, S.; Yang, C.-G.; Xu, Z.-R. Multitarget sensing of glucose and cholesterol based on Janus hydrogel microparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuet, K.P.; Hwang, D.K.; Haghgooie, R.; Doyle, P.S. Multifunctional Superparamagnetic Janus Particles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4281–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Bisso, P.W.; Srinivas, R.L.; Kim, J.J.; Swiston, A.J.; Doyle, P.S. Universal process-inert encoding architecture for polymer microparticles. Nat. Mater. 2010, 13, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, V.B.; Wu, R.G.; Wang, Z.P.; Ramanujan, R.V. Magnetic Janus particles synthesized by droplet micro-magnetofluidic techniques for protein detection. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3514–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; George, J.; Li, B.; Amini, N.; Paluh, J.; Wang, J. Clickable Multifunctional Dumbbell Particles for in Situ Multiplex Single-Cell Cytokine Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32482–32488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleyard, D.C.; Chapin, S.C.; Srinivas, R.L.; Doyle, P.S. Bar-coded hydrogel microparticles for protein detection: Synthesis, assay and scanning. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-S.; Sun, Y.-L.; Dong, W.-F.; Liu, J.-Q.; Huo, Q.-S.; Sun, H.-B. High-performance magnetic antimicrobial Janus nanorods decorated with Ag nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23741–23744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lu, M.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, D.; Dong, W. Magnetic Janus nanorods for efficient capture, separation and elimination of bacteria. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3550–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-B.; Park, S.; Mirkin, C.A. Multicomponent Magnetic Nanorods for Biomolecular Separations. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3110–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.-K.; Park, S.; Millstone, J.E.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, K.-B.; Mirkin, C.A. Separation of Tri-Component Protein Mixtures with Triblock Nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11825–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.-M.; Wang, Z.; Shao, D.; Yue, J.; Lü, M.-M.; Li, L.; Ge, M.; Yang, D.; Li, M.-Q.; Yan, H.; et al. Fluorescent-magnetic Janus nanorods for selective capture and rapid identification of foodborne bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Duan, H. Cationic polycarbonate-grafted superparamagnetic nanoparticles with synergistic dual-modality antimicrobial activity. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Chen, X.; Jayawardana, K.W.; Wu, B.; Sundhoro, M.; Yan, M. Shape Control of Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterials Templated with Dual Cationic Surfactants and Their Antibacterial Activities. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-S.; Jun, Y.-W.; Yeon, S.-I.; Kim, H.C.; Shin, J.-S.; Cheon, J. Biocompatible Heterostructured Nanoparticles for Multimodal Biological Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15982–15983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, P.; Orrit, M. Single metal nanoparticles: Optical detection, spectroscopy and applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2001, 74, 106401–106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvan, S.T.; Patra, P.K.; Ang, C.Y.; Ying, J.Y. Synthesis of Silica-Coated Semiconductor and Magnetic Quantum Dots and Their Use in the Imaging of Live Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 2448–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ho, D.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Kohler, N.; Walsh, E.G.; Morgan, J.R.; Chin, Y.E.; Sun, S. Au-Fe3O4 Dumbbell Nanoparticles as Dual-Functional Probes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Hirt, A.M.; Lozach, P.-Y.; Teleki, A.; Krumeich, F.; Pratsinis, S.E. Hybrid, silica-coated, Janus-like plasmonic-magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Paredes, K.O.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Martinez-Ruiz, P.; Pingarron, J.M.; Villalonga, R.; Filice, M. Hybrid Decorated Core@Shell Janus Nanoparticles as Flexible Platform for Targeted Multimodal Molecular Bioimaging of Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31032–31043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, G.; Bai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yao, H.; Wu, M.; Huang, P.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, C.; Zhang, L. Generic synthesis and versatile applications of molecularly organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with asymmetric Janus topologies and structures. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3790–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Sun, S. Dumbbell-Like Au-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Target-Specific Platin Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4216–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Gao, X. Multifunctional Nanocapsules for Simultaneous Encapsulation of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Compounds and On-Demand Release. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Pauletti, G.M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ewing, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D. Dual Surface-Functionalized Janus Nanocomposites of Polystyrene/Fe3O4 @SiO2 for Simultaneous Tumor Cell Targeting and Stimulus-Induced Drug Release. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3485–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, D.; Lesniak, A.; Rashdan, S.A.; Gandhi, D.; Blasiak, A.; Fannin, P.C.; Von Kriegsheim, A.; Kolch, W.; Lee, G.U. Mechanochemical Stimulation of MCF7 Cells with Rod-Shaped Fe-Au Janus Particles Induces Cell Death Through Paradoxical Hyperactivation of ERK. Adv. Health Mater. 2014, 4, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Wang, C. Designed Synthesis of Au/Fe3O4 @C Janus Nanoparticles for Dual-Modal Imaging and Actively Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Synergistic Therapy of Cancer Cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 17242–17248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Wo, F.; Yuan, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Song, J.; Qu, J.; Yong, K.-T. Novel Magnetic-Luminescent Janus Nanoparticles for Cell Labeling and Tumor Photothermal Therapy. Small 2017, 13, 1701129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Tong, S.; Tian, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Su, X.; Chu, X.; Lin, J.; et al. An attractive multifunctional material for triple-modal imaging-guided tumor photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9239–9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.C.; Kagan, D.; Orozco, J.; Wang, J. Motion-driven sensing and biosensing using electrochemically propelled nanomotors. Analyst 2011, 136, 4621–4630. [Google Scholar]
- Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Escarpa, A. Milli, micro and nanomotors: Novel analytical tools for real-world applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 84, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Escarpa, A. Janus micromotors for electrochemical sensing and biosensing applications: A review. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Pacheco, M.; Maria-Hormigos, R.; Escarpa, A. Perspectives on Janus micromotors: Materials and applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Guan, J.; Pumera, M. Micro- and nanorobots based sensing and biosensing. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, D.; Calvo-Marzal, P.; Balasubramanian, S.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Manesh, K.M.; Flechsig, G.-U.; Wang, J. Chemical sensing based on catalytic nanomotors: Motion-based detection of trace silver. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12082–12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kagan, D.; Manesh, K.M.; Campuzano, S.; Wang, J. Motion-based DNA detection using catalytic nanomotors. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Cinti, S.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; Palleschi, G.; Wang, J. Microengine-assisted electrochemical measurements at printable sensor strips. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8668–8671. [Google Scholar]
- Moo, J.G.S.; Pumera, M. Self-Propelled Micromotors Monitored by Particle-Electrode Impact Voltammetry. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Kagan, D.; Hu, C.-M.J.; Campuzano, S.; Lobo-Castañon, M.J.; Lim, N.; Kang, D.Y.; Zimmerman, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Micromachine-Enabled Capture and Isolation of Cancer Cells in Complex Media. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 4247–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Orozco, J.; Kagan, D.; Guix, M.; Gao, W.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Claussen, J.C.; Merkoçi, A.; Wang, J. Bacterial isolation by lectin-modified microengines. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, D.; Campuzano, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kuralay, F.; Flechsig, G.-U.; Wang, J.; Ruiz, S.C. Functionalized Micromachines for Selective and Rapid Isolation of Nucleic Acid Targets from Complex Samples. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.; Campuzano, S.; Kagan, D.; Zhou, M.; Gao, W.; Wang, J.; Ruiz, S.C. Dynamic Isolation and Unloading of Target Proteins by Aptamer-Modified Microtransporters. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7962–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Pacheco, M.; Rojo, J.; Escarpa, A.; Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Jurado-Sánchez, B. Magnetocatalytic Graphene Quantum Dots Janus Micromotors for Bacterial Endotoxin Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6957–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.; Escarpa, A.; Sánchez, B.J. Sensitive Monitoring of Enterobacterial Contamination of Food Using Self-Propelled Janus Microsensors. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2912–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Zhao, M.; Campuzano, S.; Ricci, F.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Mascini, M.; Wang, J. Rapid micromotor-based naked-eye immunoassay. Talanta 2017, 167, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Feng, X.; Pei, A.; Gu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Seawater-driven magnesium based Janus micromotors for environmental remediation. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4696–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Composition | Morphology | Preparation Method | Application | Target Analyte | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Janus mesoporous silica nanoparticles | Rod | Sol-gel method | Capture, separation and elimination | Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus on LB-agar plates | [49] |
| Magnetic Janus mesoporous silica nanoparticles | Rod | Sol-gel method | Capture and identification | Foodborne bacteria in milk samples | [52] |
| Au-Ni-Au | Rod | Porous template synthesis | Therapeutics and separations | Separation His-tagged proteins and Ab to poly-His | [50] |
| Encoded particles | - | Stop-flow lithography | Determination and identification | miRNAs | [44] |
| γ-Fe2O3- SiO2/Glucose oxidase | Sphere | One-step flame-assisted spray-pyrolysis | Enzymatic biosensing | Glucose | [41] |
| NitroStrep-Au-Ni-Au-NitroStrep | Rod | Porous template synthesis | Magnetic protein separation | Separation of a mixture of Histag-Uniquitin, Biotin-BSA and protein A | [51] |
| Con A/dextran-γ-Fe2O3/esterase | Sphere | Centrifugal microfluidic chip | Enzymatic biosensing | Glucose and cholesterol in serum samples | [42] |
| EMG 507 ferrofluid/polymeric phase (PEGDA) | Sphere | Droplet micromagnetofluidic technique | Protein detection | BSA | [45] |
| Janus Hydrogel particles (Fe3O4/PEG/Darocur) | Acorn | Microfluidic synthesis | Bioimaging and imaging-guided therapies | DNA detection | [43] |
| AgNPs@Fe3O4-SiO2 | Rod | Sol-gel method | Antimicrobial | Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis | [48] |
| TCO-bMS and Tz-sMS | Dumbbell | Click Chemistry | Bioimaging, single-cell analysis and biomedical diagnostics | In situ TNFα detection released by cancer cells. | [46] |
| Composition | Morphology | Preparation Method | Use | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au-Fe2C/affibody | Snowman | Carburization process | Imaging-guided photothermal therapy | In vivo targeted tumor ablation and imaging | [68] |
| FITC-Fe3O4-PS16-PAA10/DNA | Sphere | Phase separation | Target therapy | DNA release in cells | [63] |
| Fe-Au/PEG/Heregulin | Rod | Templated electrodeposition | Targeted diagnosis and therapy | Imaging and magnetic hyperthermia breast cancer cells | [65] |
| Au-IONP/Dye@MS | Snowman | Pickering emulsion interfacial synthesis | Fluorescence imaging, Magnetic resonance imaging, Computed tomography | In vitro and in vivo tumor-targeted imaging of Fibrosarcoma. | [60] |
| SiO2 coated-Ag-Fe2O3/antibody | Snowman | Flame aerosol technology | Targeted bioimaging | Hela Cells | [59] |
| Folic acid/polystyrene/Fe3O4@SiO2/DOX | Sphere | Combined process of miniemulsion and sol-gel reaction | Targeted drug release | Drug delivery in cancer cells | [64] |
| MnFe2O4-NaYF4/folic acid | Dumbbell | Thermolysis | Targeted multimodal imaging and therapy. | Targeted photothermal therapy and imaging of human esophagus carcinoma cells | [67] |
| Au-Fe3O4/EGFR antibody | Dumbbell | Decomposing iron on the surfaces of Au nanoparticles | Bioimaging | Targeted bioimaging of human epithelial carcinoma cells | [57] |
| Pt complex/Au-Fe2O3/Herceptin | Dumbbell | Decomposition and oxidation | Target chemotherapy | Targeted Pt release to Her2-positive breast cancer cells | [62] |
| FA-PEG-Au/Fe3O4@C/DOX loaded | Snowman | - | Imaging, drug delivery and therapy | Targeted delivery of DOX, photothermal therapy, MRI and CT in Hela cells | [66] |
| Type of Self-Propelled Janus Magnetic Particles | Propulsion Mechanism (Fuel) | Fundamentals | Type of Detection | Target Analyte | Analytical Characteristics | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au-Ni-Pt nanowires | Self-electrophoretic propulsion mechanism (H2O2) | Selective acceleration in the presence of silver ions (Ag+) in connection with sandwich DNA hybridization approach onto a photolithography-prepared gold electrode | Optical (speed/distance travelled) | 30-mer synthetic DNA or E. coli 16S mRNA | 40 amol (synthetic DNA), 2000 cfus mL−1 of E. coli | untreated bacterial lysates | [75] |
| Photolithography prepared Pt/Au/Ni/Ti microtubes | Bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Sandwich DNA hybridization assay onto thiolated DNA capture probe modified microtubes | Indirect fluorescent (streptavidin fluorescent nanoparticles) | 30-mer synthetic DNA or E. coli 16S mRNA | ~25 nM synthetic target DNA | Spiked 100% human serum, 10% human urine and saliva and raw bacterial lysates | [80] |
| Photolithography prepared Pt/Au/Ni/Ti microtubes | Bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Sandwich aptameric assay onto thiolated aptameric capture probe modified microtubes | Indirect fluorescent (streptavidin fluorescent nanoparticles) | Human thrombin | ~100 nM | Spiked untreated serum and plasma pretreated to precipitate fibrinogen | [81] |
| Photolithography prepared Pt/Au/Ni/Ti microtubes | Bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Selective recognition onto anti CEA-modified microtubes | Direct optical | CEA+ cancer cells | ? | 1:4 diluted human serum | [78] |
| Template electrodeposited Au/Ni/PANI/Pt microtubes | Bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Selective recognition onto ConA-modified microtubes | Direct optical | E. coli | ? | Spiked drinking water, apple juice and seawater | [79] |
| Template electrodeposited Au/PEDOT/Ni/Pt microtubes | Bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Direct competitive immunoassay using cortisol-HRP onto anticortisol-modified microtubes | Indirect optical/naked-eye using H2O2/TMB | Cortisol | 0.1 μg mL−1 | ? | [84] |
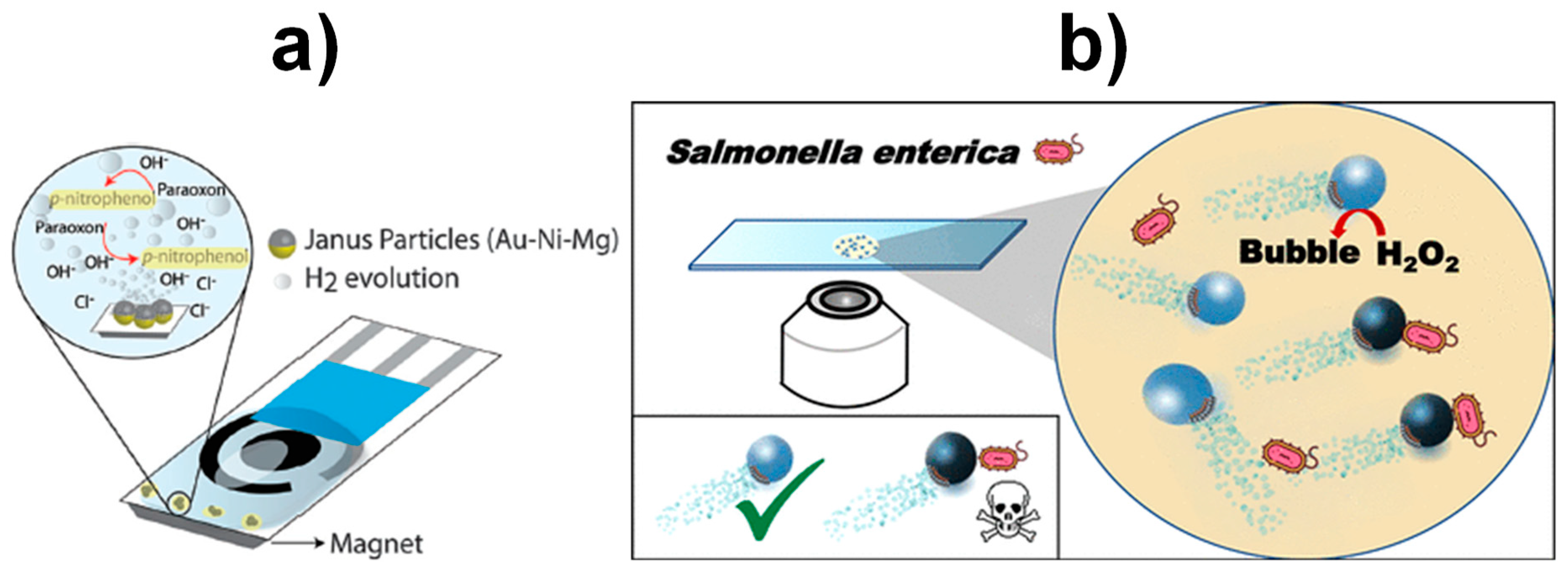
| Au-Ni-Mg Janus particles | Bubble propulsion (water) | Produce OH− ions to increase the medium pH and promote the paraoxon degradation | Amperometric (+0.9 V vs. Ag/AgCl) | Paraoxon | ~4 mM | ? | [76] |
| Magnetocatalytic hybrid Janus spherical particles (GQDs, PtNPs and Fe3O4NPs) modified with PABA | Magnetic and bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Interaction between PABA-modified GQDs and targeted bacterial LPS | Fluorescence quenching | E. coli | ? | Unprocessed urine and serum samples | [82] |
| Magnetocatalytic hybrid Janus spherical particles (GQDs, PtNPs and Fe3O4NPs) modified with PABA | Magnetic and bubble propulsion (H2O2 + NaCh) | Interaction between PABA-modified GQDs and targeted bacterial LPS | Fluorescence quenching | Salmonella enterica | 0.07 ng mL−1 of endotoxin | Spiked milk, mayo, egg yolk, and egg white | [83] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campuzano, S.; Gamella, M.; Serafín, V.; Pedrero, M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Magnetic Janus Particles for Static and Dynamic (Bio)Sensing. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5030047
Campuzano S, Gamella M, Serafín V, Pedrero M, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM. Magnetic Janus Particles for Static and Dynamic (Bio)Sensing. Magnetochemistry. 2019; 5(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampuzano, Susana, Maria Gamella, Verónica Serafín, María Pedrero, Paloma Yáñez-Sedeño, and José Manuel Pingarrón. 2019. "Magnetic Janus Particles for Static and Dynamic (Bio)Sensing" Magnetochemistry 5, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5030047
APA StyleCampuzano, S., Gamella, M., Serafín, V., Pedrero, M., Yáñez-Sedeño, P., & Pingarrón, J. M. (2019). Magnetic Janus Particles for Static and Dynamic (Bio)Sensing. Magnetochemistry, 5(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5030047







