Abstract
Nanoparticles are emerging as a fascinating alternative to antibiotics. When stabilized by chemical compounds, magnetite nanoparticles (MagNPs) consistently exhibit bactericidal effects across different types of bacteria. This study describes the synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial properties of magnetite MagNPs prepared by the coprecipitation method under continuous sonication. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) techniques revealed Fe3O4-NPs as spherical, uniform particles with an average size of approximately 16 nm. The antibacterial efficacy of MagNPs was investigated by combining them with methanolic extracts of three medicinal plants known for their antibacterial properties: Aloysia triphylla, Sarcopoterium spinosum, and Urtica pilulifera. The combined effect was assessed against both wild type and resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. The antibacterial synergistic effect of MagNPs and plant extracts was evaluated by the MIC test, which showed significant inhibitory properties against the growth of the four bacterial strains as compared to control samples of plant extracts alone. Furthermore, the synergistic effect of MagNPs combined with extracts from Rosmarinus officinalis, Anchusa azurea, Quercus infectoria, and Urtica pilulifera significantly prevented biofilm development in both sensitive and resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus.
1. Introduction
Nanoparticles (NPs) are minute materials with diameters ranging from 1 to 100 nm, comparable in size to the molecular scale of living cells. They find extensive applications across various scientific sectors. The advent of nanoparticles has sparked a revolution in medicine with a wide variety of applications such as drug delivery, tissue repair, infection control, diagnostics, and bactericidal action [1,2,3,4]. The universal calamity of the ongoing emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains among patients poses a significant challenge, prompting researchers to seek an optimistic solution [5,6], with NPs being among the promising avenues [3,7,8]. To date, several types of metal nanoparticles have been explored for their antimicrobial effects, including silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs), which are effective bactericides against Escherichia coli [9] and inhibitory for Staphylococcus aureus [10], albeit concerns have been raised regarding their environmental toxicity [11]. Gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) exhibit functional bactericidal effects against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, particularly when capped with cefaclor [12]. Combining Au-NPs with grapefruit extract has yielded promising results against S. aureus, Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [13]. Meanwhile, magnetic iron oxide NPs have been used for a long time in a variety of biomedical applications, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents for cell identification, drug delivery systems, and cancer treatments [2,4]. Although magnetic iron oxide NPs were reported to have neurotoxicity in rats [14] other research has reported they are not cytotoxic in in vivo and in vitro assays [15]. These contradictory reports show that further research is required to resolve this controversial point [16]. The unique characteristics of iron oxide NPs make them more compatible for biomedical applications [17]. Magnetic iron oxide NPs are non-toxic to normal mammalian cells when conjugated with an antifungal drug [18] and enhance calcium precipitation in osteoblast cells, hence increasing bone density [19]. Furthermore, they offer advantages over other metal-NPs due to their cost-effectiveness, easy construction methodology, eco-friendliness, and the ability to be manipulated or removed from the treated tissue by an external magnetic field [4,20].
Despite these advantages, the antimicrobial effect of MagNPs has not been thoroughly investigated [21,22,23,24,25]. A study by Auffan et al. (2008) investigated three types of Iron-based NPs and their cytotoxicity toward E. coli. They found that maghemite γFe2O3 had no observable toxicity toward E. coli due to their stable structure [21]. However, coating it with polyrhodanine amplified its effect not only against E. coli but also S. aureus [22]. In contrast, MagNPs and Zero valent Iron NPs (Fe-NPs) demonstrated potent bactericidal effects against E. coli by inducing oxidative stress inside cells [21]. Moreover, Kim (2010) reported that Fe-NPs exerted a stronger effect under anaerobic conditions, compared to aerobic conditions depending on the dose and duration of exposure [23]. This inactivation was attributed to the generation of intracellular oxidants, which compromised membrane integrity and respiratory activity [23]. Similarly, MagNPs stabilized by polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) exerted a toxic effect on S. aureus [24]. The interaction between MagNPs and bacterial interfaces was further explored by Arakha and colleagues (2015). They demonstrated that the negatively charged surface of MagNPs, when coated with positively charged chitosan, enhanced the bactericidal effect against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [25]. Similarly, MagNPs coated with a shell of conjugated silicon-amine groups (SiO2-NH2) effectively targeted multiple drug-resistant (MDR) S. aureus and E. coli [26], destroying their cells and preventing biofilm formation. In short, the hypothesis correlating the effect of stabilizing MagNPs with different materials and their ability to prevent oxidation requires further investigation.
Today, there is an increasing demand to return to ethnomedicine and natural plant products for several types of disease treatments, drug discoveries, and health-care issues. Biologically active compounds found in several plant species have been reported over the years to be effective drugs with minimal side effects in what is conventionally known as traditional medicine [27]. Enhancements in the effect of these biologically active compounds are reported when combined with metal NPs. An in vitro study by Arokiyaraj (2013) on Fe3O4-NPs treated with leaf extract of Argemone mexicana yielded significant antimicrobial results against E. coli and Proteus mirabilis [28]. A different study conducted by Shahriary et al. (2018) found that the combination of leaf extract (Stachys lavandulifolia) with a mixture of MagNPs/Ag-NPs exhibited good bactericidal effects against E. coli and S. aureus [29]. Previous findings have indicated that using MagNPs alone against the tested bacteria is not effective. However, Dinali et al. (2017) discussed the relevant reasons that may decrease their effectiveness, such as low particle stability, agglomeration, low bioavailability caused by undispersed particles, and an overall negative charge. Due to these reasons, using MagNPs requires conjugation or coating with other materials, which is feasible due to their nature [30,31].
On the other hand, the recurring crisis of antibiotic resistance among various pathogenic strains presents a formidable challenge for scientists, urging them to find optimistic solutions without needing to resort to drastic measures as a final option. Using various compounds as alternatives for antibiotics is not enough to solve the challenge of resistance because bacterial strains overcome them with the passage of time. Three innovative solutions have emerged to overcome this problem: leveraging plant secondary metabolites [32], nanoparticles [7], or combinations thereof [33,34]. The strategy of combining different agents has shown promise in most cases, including the pairing of two or more antibiotics, antibiotics with plant extracts, antibiotics with non-antibacterial agents, and antibiotics with NPs [32,35,36,37].
Recent findings confirm that mixing weak bactericidal agents has a synergistic effect against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial strains [33,38,39]. According to our knowledge, this study represents the first instance where chemically synthesized magnetite nanoparticles are combined with methanolic extracts of folkloric plants to evaluate their antibacterial efficacy. This innovative combination, integrating chemically synthesized magnetite NPs and methanolic extracts from diverse plants with known antibacterial properties, is anticipated to significantly enhance the antibacterial efficacy of both components against American Type Culture Collection strains (ATCC).
2. Materials and Methods
The chemicals used in this research were of reagent grade and used as received from the suppliers. This included ferrous and ferric chloride salts (Riedel-de Haën AG, Seelze, Germany); ammonium hydroxide (25%, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH, USA); absolute ethanol (AR grade, VWR chemicals, Radnor, PA, USA); absolute methanol (IsoLab Chemicals, Wertheim, Germany); Müller Hinton Agar (MHA) and broth (Oxoid Limited, Basingstoke, UK|Thermo Fisher Scientific—USA); iodonitrotetrazolium chloride (INT, 98%, Acros Organics|Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH, USA); tryptone soya agar (TSA); Luria Britani agar (LBA), and broth (Biolab Diagnostics Laboratory Inc., Budapest, Hungary); glucose (anhydrous molecular biology grade, GeneON GmbH, Ludwigshafen, Germany); normal saline (NS, 0.9% w/v sodium chloride, pharmaceutical solutions industry, Jaddah, Saudi Arabia); and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 10X, HiMedia Laboratories, Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India). Ultrasonication was performed using ULTRASONIC LC 20H (Elma Ultrasonic Cleaners, Singen am Hohentwiel, Germany). The SEM images were obtained from the Quanta FEG 450 (FEI company, Hillsboro, OR, USA). The XRD data were obtained on Ultima IV X-Ray diffractometer, Rigaku, Japan (40 kV/40 mA, 3 degree/min, 15–90-degree, Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.548 Å). The particle size was calculated using Scherrer formula. The grain pattern was compared to the ideal pattern of pure magnetite. The hydrodynamic size and surface charge of NPs were examined by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). A 1 mg/mL aqueous suspension of the NPs was prepared in distilled water and sonicated for 10 min. One hundred µL of the sonicated solution was then diluted 100 folds in distilled water and sonicated for 10 min. Finally, 2 mL of the sonicated solution was evaluated in the Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS 90 device for size and zeta potential (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Malvern, UK). Equipment used included an orbital shaker SSL1 from Stuart, Cole-Parmer Ltd., St Neots, UK, a vacuum rotary evaporator HAHNVAPOR from Hahnshin Scientific, Gimpo, Republic of Korea, a grinder from IKA Mill M20 Universal mill (IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG Staufen, Germany), a spectrophotometer (BioMate3, Thermo spectronic Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) And a microplate reader from BioTek, Synergy2 SL Luminesence Microplate Reader, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA.
2.1. Synthesis of MagNPs
The MagNPs were synthesized using the coprecipitation method by mixing FeCl2·4H2O (1.99 g) and FeCl3·6H2O (5.41 g) in 2:1 molar ratio in 100 mL distilled water under continuous sonication (50–65 °C, 20–40 min). NH3 (25%, 8 mL) were added dropwise at intervals of 30–40 min where a black precipitation appeared immediately. Sonication continued for about 1 h. and was left to settle overnight at room temperature. The NPs precipitate was separated by filtration using Whatman filter paper no. 1001-150 [40], washed with plenty of deionized water and absolute ethanol three times, and dried in an oven (60–80 °C, 1–2 days). This process produced about 2.31 g of dry black NPs, which were collected and ground into fine powder using a mortar and pestle and kept in a contained container for further analysis, characterization, and use. All equipment, including containers, Whatman filter papers, and solutions, was sterilized using an autoclave and used under sterile conditions. The prepared MagNPs were structurally characterized by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) [17,41,42,43].
2.2. Plant Material Collection
Seven traditional medicinal plant species were utilized to assess the impact of their extracts when combined with Fe3O4-NPs on bacterial growth or inhibition (Table A1). Among these, four species were wild plant species, namely, Urticas pilulifera L., Anchusa azurea Mill., Sarcopoterium spinosum (L.) Spach, Quercus infectoria Olivier, while the other two species, Rosmarinus officinalis L. and Aloysia triphylla (L’Hér.) Britton, are cultivated species. The materials were collected from their natural habitat in northern Jordan during the period of March to May 2021 for wild species and from the JUST campus for cultivated species. The collected plant materials have been authenticated by Dr. Mohammad Al-Gharaibeh (Department of Plant Production, Jordan University of Science and Technology).
2.3. Methanolic Extract Preparation
The plants were collected, dried, and grounded at room temperature in the shade. The selected plant parts for use were processed in a grinder with 100 g of the resulting ground material mixed with 500 mL of methanol and left to sit for 72 h on an orbital shaker at room temperature. The resulting dried extract was then stored in a refrigerator until needed, following the procedure outlined in the literature [44]. The plant list is found in Table A1.
2.4. Bacterial Strains
Four bacterial strains obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) were used in the antibacterial assays, which are Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, S. aureus ATCC 43300, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, and E. coli BAA 2452. Bacterial stocks were preserved as aliquots in Mueller Hinton Broth (MHB) with 10% glycerol at −80 °C.
2.5. Antibacterial Assay of Combined MagNPs—Plant Extracts
Different analytical methods were used to evaluate the bactericidal effect of the combined MagNPs-plant extract, including Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC), Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC), and biofilm formation assay. Antibacterial assays were performed for each plant extract alone and then for the combination of plant extract and MagNPs together after mixing 2MIC of the plant extract and 128 mg/mL of MagNPs for 18–24 h [28,45]. Fresh cultures from cryogenic samples were cultured on MHA incubated overnight at 37 °C, then, one colony was picked into 2 mL MHB incubated for 2 h to prepare 0.5 McFarland standard at 600 nm and optical density (OD) (0.08–0.13) using a spectrophotometer. Biofilm experiment preparation was performed by culturing cryopreserved samples on LBA for about 20 h, then one colony was picked up and suspended in 10 mL TSB, supplemented with 1% glucose, incubated at 37 °C overnight. The OD was measured at 600 nm, then diluted with TSB supplemented with 1% glucose to get 0.1 OD suspension.
2.6. The Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
A minimal inhibitory concentration is defined as the least concentration of an agent that inhibits the growth of the bacteria and is observed by the visible eye. Each plant extract (128 mg/mL) was prepared in MHB according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines [46], and 100 µL was put in the first well of a 96 well plate, 2 fold serial dilutions were performed in 9 wells and the last 50 µL was discarded. Fifty µL of 0.5 McFarland standard inoculum were prepared, then diluted 1:10 in MHB and added to each well. The growth control consisted of inoculum in MHB, and the sterility control consisted of MHB only [44,47]. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 16–20 h. Triplicate and replicate plates were run together for each strain and each agent. A reference plate was prepared from the plant extract using a serial dilution similar to the test plates. However, MHB was added instead of culture to assess for contamination in the plant extracts. After the incubation period, 40 µL of a 0.2 mg/mL solution of Iodonitrotetrazolium chloride (INT) indicator were added to each well after being sterilized with a Mini pore syringe filter (22 µm), and the samples were incubated for 30–40 min at 37 °C. Any color change to red or dark red indicated that there was growth in the well. The lowest concentration of the agent that did not cause a color change was considered the MIC. The addition of INT took place within the reported incubation time of the MIC assay. A positive control of chloramphenicol antibiotic was also included in the MIC assay to ensure that the assay was working properly.
2.7. Biofilm Formation Assay
To determine if the strains used in this study are biofilm formers, using a 96 well plate, 200 µL of each strain was inoculated in TSB (supplemented with 1% glucose [48] with OD 0.1 at 600 nm. In addition, S. aureus ATCC 33591, which is a strong biofilm former, was used for comparison [49]. Then, the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The plate contents were discarded directly and washed with PBS 200 µL three times. Plates were allowed to dry at room temperature for 20 min, then placed in an oven at 60 °C for heat fixation. Crystal violet 0.1% solution 170 µL was added to stain the formed biofilm for 20 min at room temperature. Then, the dye was discarded after the incubation time, and the plates were washed with plenty of tap water until a clear solution appeared. The plates were left to dry at room temperature for 2 h at least (or overnight). Next, 200 µL of 80% Ethanol and20% Acetone solution was added, incubated for 30 min at room temperature, and then the results were taken using a plate reader at 570 nm. The experiment was performed in triplicate and replicated on the same day. The strength of the biofilm was determined according to the average OD of the sterility control (SC) and the standard deviation (SD) of the readings, as reported in Singh et al. (2017) [49]. The SC was TSB alone. The biofilm strength was calculated according to the mentioned equation: OD Cutoff value = average ODnegative control + 3 × SD of ODnegative control. If the OD average of the strain ≤ OD cutoff value, the strain is a non-biofilm former (N). If OD cutoff value < OD average of the strain ≤ 2 × OD cutoff value, the strain is a weak biofilm former (W). If 2 × OD cutoff value < OD average of the strain ≤ 4 × OD cutoff value, the strain is a moderate biofilm former (M). And if 4 × OD cutoff value < OD average of the strain, the strain is a strong biofilm former.
2.8. Anti-Biofilm Formation Assay
After determining the strains’ ability to form biofilms, an assay was used to evaluate the effect of plant extract combined with MagNPs to prevent biofilm development in moderate and strong biofilm formers. In microtiter plate 100 µL of inoculum with OD 0.1 at 600 nm was added and incubated for 30 min to allow bacterial cell attachment. Different concentrations of the agents were added, including 2×MIC, MIC, 1/2 MIC, 1/4 MIC, and 1/8 MIC of the plant extract alone, MagNPs alone or combination of both (16–20 h combined). Plates were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. The SC were prepared from TSB alone supplemented with 1% glucose, the GC were prepared from inoculum with TSB supplemented with 1% glucose, reference wells were prepared from the different concentrations of agent with TSB alone, supplemented with 1% glucose, to eliminate color effects from plate reading.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The values of MIC were reported as the means ± SD of 9 results. JMP program version 17.0 from SAS Institute Inc. (Cary, NC, USA, 2022) was used to analyze the data. The data were not normally distributed, as assessed using the Q-Q plot test. Therefore, the nonparametric Kruskal-Walis test and Wilcoxon rank test were used to compare the MIC values of plant extract alone and the MIC of plant extract combined with MagNPs. In addition, the Wilcoxon rank test was used to contrast the MIC values of MagNPs alone and MagNPs combined with plant extract against S. aureus strains. The nonparametric Kruskal-Walis test was used to compare the percentage of biofilm inhibition after treating S. aureus strains with plant extract alone and plant extract combined with MagNPs. A p-value ≤ 0.01 was considered significant.
3. Results
The structure of the obtained powder was examined by three techniques, namely, XRD, SEM, and DLS. The powder-XRD in Figure 1a showed 6 diffraction peaks at 2θ of 30.26°, 35.58°, 43.30°, 53.62°, 57.26°, 62.86° degrees due to the Bragg’s Plane of 220, 311, 400, 422, 511, and 440 with the inverse cubic spinel structure of Fe3O4 corresponding to Fd-3m space group [50] in agreement with the standard XRD pattern of magnetite NPs card # 01-071-6336 in the literature database of 2θ values of 30.24°, 35.58°, 43.26°, 53.83°, 57.26°, 62.80°. The grain size or crystallite size (D) of these NPs was calculated using Scherrer’s formula [50], with a shape factor (κ) of 0.95, X-ray beam wavelength (λ) of 1.548 Å for Cu radiation, FWHM (full width at half maximum) in radians of the most intense peak (β) and Bragg angle (θ). The estimated sizes for different samples ranged between 13 and 21 nm.
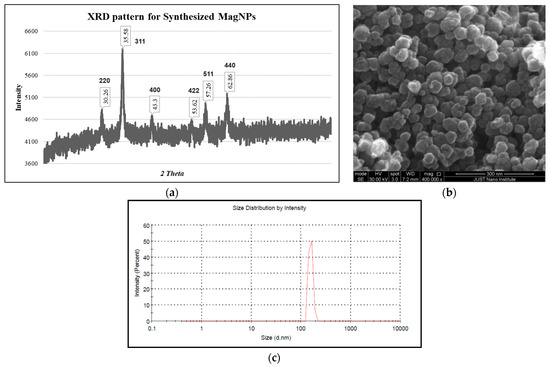
Figure 1.
(a) XRD pattern of the synthesized MagNPs. (b) SEM image illustrates the uniform spherical shape of Fe3O4-NPs with an average size of about 23 nm. (c) DLS analysis for the synthesized NPs.
On the other hand, the SEM images of the synthesized MagNPs showed that the NPs were uniformly spherical in shape with an average size of about 23 nm, consistent with the values obtained from the powder XRD analysis, as depicted in Figure 1b.
Furthermore, DLS analysis showed that the average hydrodynamic diameter size of these NPs in water was 156 ± 14 nm, indicating that water molecules surround the NPs in solution, as shown in Figure 1c. Moreover, the zeta potential was measured and found to be negative at −31.6 ± 13.7 mV. This negative charge on the surface of these NPs shows that the aqueous solution has good potential to keep the particles suspended for a long time.
3.1. Antibacterial Activity of the Combination of MagNPs + Plants Extract
MIC and MBC tests were performed for each plant extract and MagNPs according to CLSI standards. Sub-MICs were then combined for 18–24 h for each plant with MagNPs before performing the test. The results are recorded for comparison and presented in Table 1 and Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3, Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6 and Figure A7 for all agents as MIC values in mg/mL for each examined strain. The MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotics are consistent with those reported in the CLSI 30th edition (Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 2020), showing 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains (Table 1).

Table 1.
MIC and MBC values of chloramphenicol µg/mL, MagNPs alone mg/mL, plant extract alone mg/mL, and plant extract combined with MagNPs mg/mL against S. aureus and E. coli wild type and MDR strains. MIC values represented by mean of 9 reads ± standard deviation.
The results indicate a significant increase in the effectiveness of three plant extracts when combined with MagNPs against the four strains used: A. triphylla (Figure A1), S. spinosum (Figure A5), and U. pilulifera (Figure A6), with p-values of: 0.0002, <0.0001, and 0.01, respectively. The effective concentration is reduced when the plant is combined with MagNPs.
In contrast, R. officinalis, A. azurea, and Q. infectoria extracts show notable effects against both S. aureus wild type and MRSA strains when combined with MagNPs but not against E. coli strains. While Q. infectoria extract alone did not impact MDR E. coli BAA 2452, when combined with MagNPs, 32 mg/mL of Q. infectoria extract inhibited the growth of the MDR strain E. coli BAA 2452 (Figure A4).
Figure 2 illustrates the evaluation of the MIC values of MagNPs alone and in combination with plant extracts to assess their impact. It was observed that MagNPs combined with A. azurea, and S. spinosum extracts had considerable effects against both S. aureus strains, with p-value of 0.001 and <0.001, respectively. Additionally, MagNPs combined with A. azurea extract alone had a substantial effect against S. aureus ATCC 29213. Conversely, S. spinosum extract combined with MagNPs was significantly effective against both wild type S. aureus and MRSA strains.
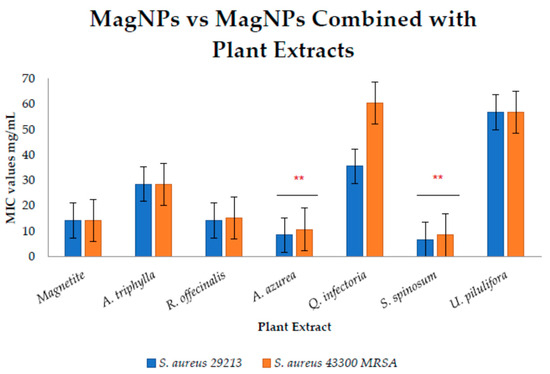
Figure 2.
Comparison between MICs of MagNPs values alone and combined with plant extracts against S. aureus. both strains. (**) indicate p-value < 0.01.
In conclusion, MRSA and MDR E. coli strains used in this study are highly affected by MagNPs, which combined with A. triphylla, S. spinosum, and U. pilulifera extracts significantly reduced the required concentrations compared to using the plant extracts alone. Furthermore, MagNPs showed a notable effect when combined with S. spinosum extract against MRSA strains compared to MagNPs alone.
MBC results were determined based on the number of colonies grown on plates compared to the positive control. The concentration resulting in fewer than five colonies on average was considered the MBC. The MIC and MBC values are presented in Table 1.
3.2. Antibiofilm Assay
A biofilm formation assay was performed to confirm the ability of the tested strains to form biofilms, using the crystal violet quantification assay. The results were as follows: E. coli ATCC 25922 did not form biofilms, E. coli BAA 2452 formed weak biofilms, S. aureus ATCC 29213 formed moderate biofilms, and S. aureus ATCC 43300 formed strong biofilms, in addition to the positive control strain, S. aureus ATCC 33591. The obtained results are shown in Table A2. The calculated value for the OD cutoff value = 0.095 + 3 × 0.006 = 0.113.
2 × OD cutoff value = 0.226 and 4 × OD cutoff value = 0.452.
Both strains of S. aureus were subjected to the antibiofilm formation assay, while the weak biofilm former E. coli BAA 2452 was excluded from this test. Sub-MIC values were used for testing plants alone, MagNPs alone, and the combination assay. The results of plant extracts, MagNPs, and their combination with MagNPs agents against biofilm formation in S. aureus strains are illustrated in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 after subtracting the OD of the reference plate from the OD results.
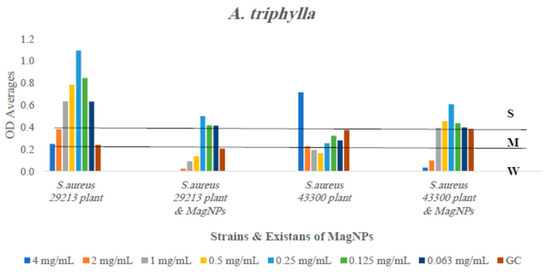
Figure 3.
The antibiofilm formation values for A. triphylla extract alone and A. triphylla extract combined to MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as average OD readings from the crystal violet quantitative assay. The colors indicate the different concentrations used, compared to the GC: strain alone.
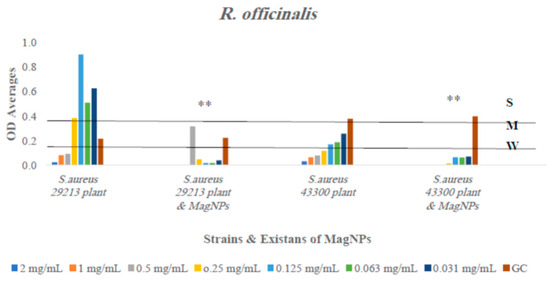
Figure 4.
The antibiofilm formation values for R. officinalis extract alone and R. officinalis extract combined to MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as average OD readings from the crystal violet quantitative assay. The colors indicate the different concentrations used, compared to the GC: strain alone. (**) indicate p-value ≤ 0.01.
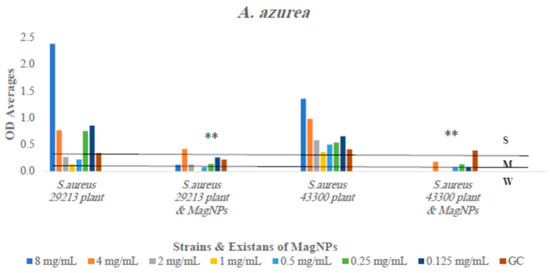
Figure 5.
The antibiofilm formation values for A. azurea extract alone and A. azurea extract combined to MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as average OD readings from the crystal violet quantitative assay. The colors indicate the different concentrations used, compared to the GC: strain alone. (**) indicate p-value ≤ 0.01.
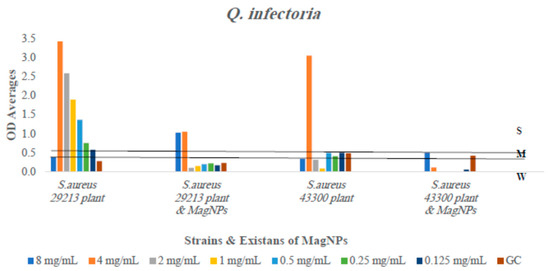
Figure 6.
The antibiofilm formation values for Q. infectoria extract alone and Q. infectoria extract combined to MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as average OD readings from the crystal violet quantitative assay. The colors indicate the different concentrations used, compared to the GC: strain alone.
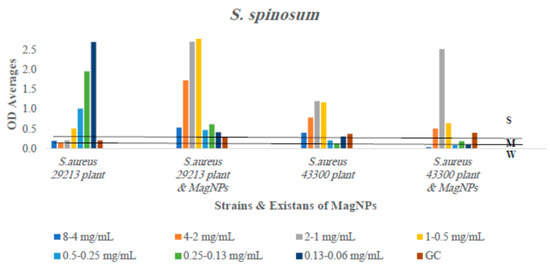
Figure 7.
The antibiofilm formation values for S. spinosum extract alone and S. spinosum extract combined to MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as average OD readings from the crystal violet quantitative assay. The colors indicate the different concentrations used, the 1st number for 29213 strain and the 2nd for 43300 strain, compared to the positive control.
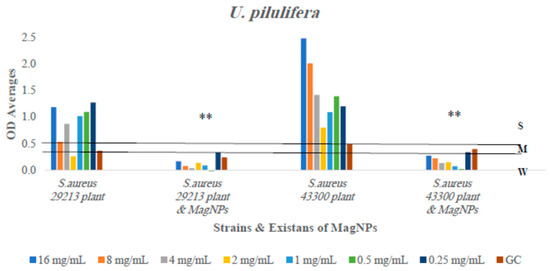
Figure 8.
The antibiofilm formation values for U. pilulifera extract alone and U. pilulifera extract combined to MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as average OD readings from the crystal violet quantitative assay. The colors indicate the different concentrations used, compared to the GC: strain alone. (**) indicate p-value ≤ 0.01.
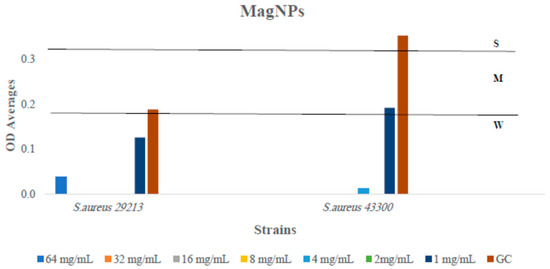
Figure 9.
The antibiofilm formation values for MagNPs against both S. aureus strains presented as OD averages reads from crystal violet quantitative assay after subtracting the optical density (OD) readings obtained from MagNP e alone (reference plate). The colors indicate the different concentrations used, compared to the GC: strain alone.
The outcomes showed inhibition in biofilm formation for four out of six plant extracts used when combined with MagNPs: R. officinalis, A. azurea, Q. infectoria, and U. pilulifera extracts significantly reduced the formation of biofilm by varying percentages against both strains of S. aureus at all concentrations used with p-values of 0.0006, <0.0001, 0.003, and <0.0001, respectively. This indicates that the presence of MagNPs prevents biofilm development. However, the combination between Q. infectoria extract and MagNPs reduced biofilm development at lower concentrations more effectively than at higher concentrations.
In contrast, A. triphylla, as illustrated in Figure 3, inhibited biofilm development in the wild-type strain S. aureus ATCC 29213 at all concentrations. We observed weakened biofilm formation at the higher three concentrations, and the two concentrations used against the wild type and MRSA, respectively, when A. triphylla extract was combined with MagNPs. Regarding S. spinosum extract, as shown in Figure 7, biofilm formation reduction occurred against the wild type strain in the presence of the plant extract alone, not in combination with MagNPs. Biofilm development for the MRSA strain was drastically inhibited at the lowest three concentrations of S. spinosum extract combined with MagNPs.
In conclusion, MagNPs significantly enhance the inhibition of biofilm development at various concentrations used in this study for both assessed strains when tested in combination with R. officinalis, A. azurea, Q. infectoria, and U. pilulifera compared to the use of the plant extract alone.
4. Discussion
Bacterial resistance has become a global challenge that requires innovative solutions to combat this problem. In the present study, we investigated the antibacterial effect of MagNPs combined with plant extracts with known antibacterial properties. MagNPs were chosen for their proven inhibitory effect, whether alone or when stabilized with various materials against different pathogens, as well as their low toxicity and biocompatibility with living cells. Plant methanolic extracts were chosen as a valuable source of secondary metabolites, offering a cost-effective and potentially low-side-effect alternative against resistant bacteria. Therefore, we evaluated this novel combination against S. aureus and E. coli wild type and MDR ATCC strains.
The coprecipitation method, used with continuous sonication, proves to be an efficient approach to producing MagNPs that are uniformly spherical, as demonstrated in SEM images, with an average size of 16 nm as determined by XRD calculations. The smaller size of the MagNPs enhances their efficacy as antibacterial agents. The XRD patterns of the MagNPs in this study are consistent with those in previous studies, validating the reliability of the coprecipitation method with continuous sonication in producing well defined MagNPs. Our findings align with studies by Petcharoen et al. (2012), Alomari et al. (2015), and Saqib et al. (2018) [51,52,53], despite variations in procedural details.
The use of continuous sonication during the synthesis of MagNPs, as employed in the current study, was notably mentioned only in the work of Alomari et al., whereas previous studies on MagNPs primarily focused on stirring without sonication during the coprecipitation procedure [41,42,51,54]. According to Ahn et al. (2012), the mixing step during MagNPs synthesis is critical for producing uniformly spherical MagNPs with a small size and well defined structure [55]. These characteristics render MagNPs a promising option as an antibacterial agent.
The present findings show that MagNPs alone affected S. aureus strains ATCC 29213 and MRSA ATCC 43300 at an MIC of about 15 mg/mL, consistent with the results of Tran et al. Additionally, PVA-coated MagNPs (9 ± 4 nm in size) affected the sensitive strain of S. aureus at 3 mg/mL all tested duration times [24]. However, despite previous studies indicating that MagNPs affect different strains of E. coli, including those by Auffan et al. and Al-Shabib et al., the synthesized MagNPs in this study did not affect the E. coli wild type or MDR strains used [21,56]. Further studies are needed to explore the mechanism of action of the MagNPs against different bacterial strains and to improve their usage as antimicrobial agents.
The current study demonstrates that all the plant methanolic extracts inhibit the growth of the tested strains. The inhibition varied depending on the plant extract, the concentration used, and the bacterial strain. A broad spectrum of antibacterial activity was exhibited by A. triphylla, R. officinalis, A. azurea, S. spinosum, and U. pilulifera, specifically against MRSA and MDR E. coli. Q. infectoria bark extract inhibited wild type E. coli but not the MDR strain.
A. triphylla methanolic extracts inhibit the growth of S. aureus-sensitive MRSA, E. coli wild type, and MDR strains with MIC values of 0.5, 1.0, 32.0, and 32.0 mg/mL, respectively. These results are in agreement with the findings of Hanaa et al. (2011) using the essential oil of A. triphylla and Bataineh et al. (2019) using methanolic extract [57,58]. On the other hand, R. officinalis essential oil exhibited good antibacterial activity against wild type strains of S. aureus ATCC 25923 and E. coli ATCC 25922, with MIC values of 4 and 3.5 mg/mL, respectively. The current study shows that crude methanolic extracts of R. officinalis were effective at 0.5 and 5.0 mg/mL on S. aureus and E. coli strains, respectively, as well as on MRSA and MDR strains at 0.5 and 5.0 mg/mL.
The current study also investigated the antibacterial activity of Q. infectoria bark methanolic extract. It is worth mentioning that Q. infectoria nut gall extract has been extensively studied for its antibacterial effect [59]. However, Q. infectoria bark extract has received less research attention for its antibacterial activity, especially against MDR bacteria. The present findings showed that a methanolic extract of Q. infectoria bark inhibited S. aureus against both strains by 8 mg/mL; however, the wild type E. coli MIC was inhibited by 32 mg/mL with no effect on the MDR E. coli strain. S. spinosum root methanolic extract exhibits substantial activity against all the tested strains compared to aqueous and ethanolic S. spinosum extracts, which have been shown to have activity against wild type strains of S. aureus and E. coli [45].
The combination of plant extract and MagNPs boosted the effectiveness of both plant extract and MagNPs against the examined strains, including MDR strains. Exceptional inhibition was observed against the MRSA strain when using the combination of MagNPs with all plants. In addition to the S. aureus strains examined, E. coli wild type and MDR strains were significantly inhibited when treated with A. triphylla, S. spinosum, and U. pilulifera extracts. In contrast, MagNPs synthesized using R. officinalis aqueous extract produced 1–12 nm particles and exhibited antibacterial activity against E. coli PTCC 1330 at a concentration of 250 µg/mL [60]. A recent study successfully synthesized iron oxide NPs from Zingiber officinale (Ginger) with a size of 5.1 nm. The synthesized Iron oxide NPs exhibited antibacterial activity against E. coli [61]. Arokiaraj et al. (2013) achieved comparable results using MagNPs combined with Argemone mexicana leaf ethanolic extract for 12 h against E. coli, P. mirabilis, and B. subtilis [28]. The synergistic effect of plant extract and MagNPs was achieved by combining sub-MICs for 24 h. However, no significant effect was observed at the MIC values of the plant extract. Therefore, we doubled the MIC and used 2 × MIC or 4 × MICs. E. coli typically employs multiple metabolic pathways to resist external agents, necessitating the use of higher concentrations of the plant extract when combined with MagNPs. The combination of MagNPs and plant extracts was efficient in preventing the development of biofilm in the resistant strain MRSA and the sensitive strain S. aureus. Among the plant extracts used, R. officinalis, A. azurea, Q. infectoria, and U. pilulifera methanolic extracts successfully reduced biofilm development. These findings are important in the challenge of bacterial resistance emergence, even though the combination had no effect against planktonic cells. Preventing the development of biofilm in resistant strains could provide scientists with an opportunity to overcome these infections.
The outcomes of this novel approach, combining MagNPs with plant extracts, align with the synergistic use of plant extracts with various antibiotics, NPs, or other therapeutic combinations. Therefore, these results suggest that alternatives to antibiotics can be explored to combat the emergence of antibiotic resistance. The combination of different materials is a promising new strategy for resistant bacterial infections. Thus, MagNPs have the advantage of magnetism, enabling their reproducibility, targeted delivery, and easy separation from fluids using an external magnet.
5. Conclusions
The urgent need to address antibiotic resistance drives research into plant extracts as a source of secondary metabolites and a safe alternative to fighting resistant bacteria. This work describes the effectiveness of combining different plant extracts with chemically synthesized MFeO-NPs against different strains of bacteria. Such investigations hold promise for their potential use in treating bacterial infections as an alternative to antibiotics. The plant extracts used in this study have several degrees of effectiveness against Gram-positive, Gram-negative strains, and wild type and resistant strains. When combined with MFeO-NPs, plant extracts of A. triphylla, S. spinosum, and U. pilulifera boosted the antibacterial growth against all examined strains: S. aureus and E. coli. Combining MagNPs with R. officinalis, A. azurea, Q. infectoria, and U. pilulifera extracts exhibits antibiofilm activity against both S. aureus strains. The combination of MagNPs with plant extracts inhibited biofilm development at least at two of the seven evaluated concentrations.
6. Recommendation and Future Work
The present study paves the way for additional experiments to determine the precise mechanisms of action for the effective combinations. One of the recommended future research directions is to fractionate the plant extract using phytochemical investigation combined with MagNPs. In addition, further testing using animal models and performing toxicity and safety analyses are also required. This could lead to novel drug synthesis and contribute to the development of effective treatments for antibiotic-resistant infections. Furthermore, in vitro analysis can be used to determine the specific mode of action of MagNPs against viable cells or biofilm-forming strains. Tracking specific molecules is recommended for understanding the mechanisms of action.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.B.B. and I.M.A.; Methodology, S.M.B.B., I.M.A. and S.M.A.-Z.; Software, H.M.H.; Validation, S.M.B.B. and I.M.A.; Formal analysis, S.M.A.-Z.; Investigation, S.M.B.B., I.M.A. and S.M.A.-Z.; Resources, S.M.B.B., M.M.A.-G. and Y.H.T.; data curation, S.M.A.-Z. and H.M.H., Writing—original draft, S.M.A.-Z.; Writing—review & editing, S.M.B.B., S.M.A.-Z., I.M.A., M.M.A.-G., H.M.H. and H.D.; Visualization, S.M.A.-Z., S.M.B.B. and I.M.A.; Supervision, S.M.B.B. and I.M.A.; Project administration, S.M.B.B.; Funding acquisition, S.M.B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Deanship of Research in Jordan University of Science and Technology, grant number (556/2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of research in Jordan University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 556/2020) for the financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Plant’s used parts with their local names.
Table A1.
Plant’s used parts with their local names.
| Plant Name | Plant Type | Part Used | Arabic Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rosmarinus officinalis | Bush | Aerial parts | Eklel El-Jabal |
| Aloysia triphylla | Bush | Aerial parts | Mallisa |
| Anchusa azurea | Herb | Aerial parts | Hamham /Lesan El-Thour |
| Quercus infectoria | Tree | Bark | Dbbagh |
| Sarcopoterium spinosum | Bush | Roots | Billan |
| Urtica pilulifera | Herb | Aerial parts | Qarass |
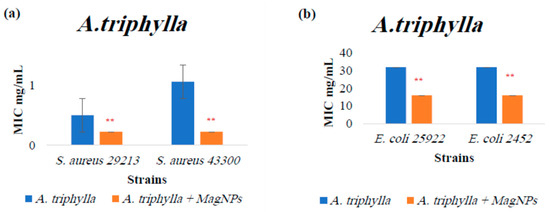
Figure A1.
MIC values for A. triphylla extract alone and A. triphylla extract combined with MagNPs against (a): S. aureus, (b): E. coli. (**) indicates p-value ≤ 0.01. MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.
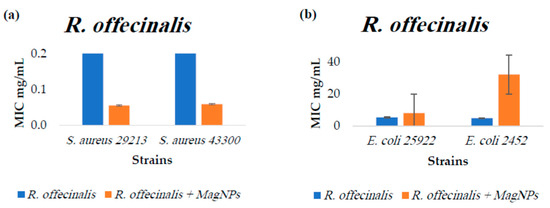
Figure A2.
MIC values for R. officinalis extract alone and R. officinalis extract combined with MagNPs against (a): S. aureus, (b): E. coli. MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.
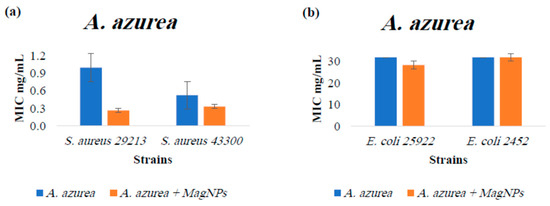
Figure A3.
MIC values for A. azurea extract alone and A. azurea extract combined with MagNPs against (a): S. aureus, (b): E. coli. MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.
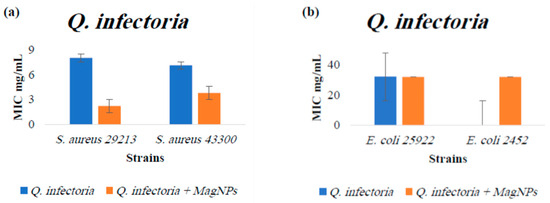
Figure A4.
MIC values for Q. infectoria extract alone and Q. infectoria extract combined with MagNPs against (a): S. aureus, (b): E. coli. MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.
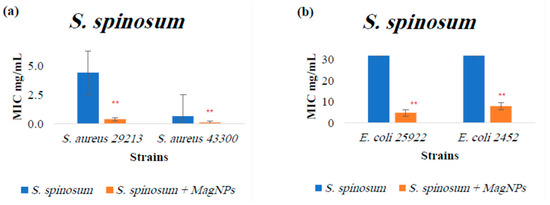
Figure A5.
MIC values for S. spinosum extract alone and S. spinosum extract combined with MagNPs against (a): S. aureus, (b): E. coli. (**) indicates p-value ≤ 0.01. MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.
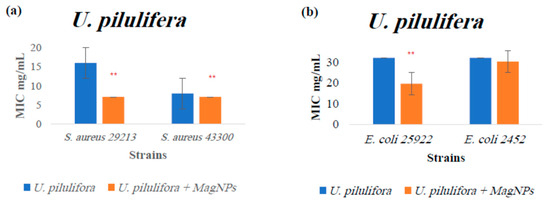
Figure A6.
MIC values for U. pilulifera extract alone and U. pilulifera extract combined with MagNPs against (a): S. aureus, (b): E. coli. (**) indicates p-value ≤ 0.01. MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.
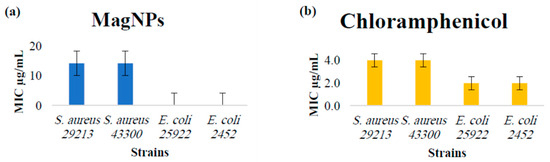
Figure A7.
(a) MIC values for MagNPs against S. aureus, E. coli. (b) MIC values for chloramphenicol antibiotic as a positive control were: 4.0 µg/mL for both S. aureus strains, and 2.0 µg/mL for both E. coli strains.

Table A2.
The biofilm formation strength for the studied strains was assessed relative to the strength of biofilm formation determined by the negative control OD cutoff value, and contrasted with the positive control (a strong biofilm former strain). The classification used was as follows: N: non biofilm former, W: weak biofilm former, M: moderate biofilm former, and S: strong biofilm former. Negative control represented by mean ± SD used to calculate OD cutoff value of the negative control.
Table A2.
The biofilm formation strength for the studied strains was assessed relative to the strength of biofilm formation determined by the negative control OD cutoff value, and contrasted with the positive control (a strong biofilm former strain). The classification used was as follows: N: non biofilm former, W: weak biofilm former, M: moderate biofilm former, and S: strong biofilm former. Negative control represented by mean ± SD used to calculate OD cutoff value of the negative control.
| Bacterial Strain | S. aureus ATCC 29213 | S. aureus ATCC 43300 MRSA | E. coli ATCC 25922 | E. coli BAA 2452 MDR | S. aureus ATCC 33591 Positive Control | Negative Control (TSB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD average | 0.365 | 0.527 | 0.108 | 0.193 | 0.482 | 0.095 ± 0.006 |
| Strength of biofilm | M | S | N | W | S | N |
References
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Bridot, J.L.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Future Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 427–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.; Saini, S.; Sharma, S. Nanotechnology: The future medicine. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2010, 3, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Webster, T.J. Magnetic nanoparticles: Biomedical applications and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8760–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, H.C. The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 1992, 257, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Courvalin, P.; Dantas, G.; Davies, J.; Eisenstein, B.; Huovinen, P.; Jacoby, G.A.; Kishony, R.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Kutter, E.; et al. Tackling antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Lotfipour, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.; Gunasekara, T.; Holton, J. Antimicrobial Nanoparticles: Applications and mechanisms of action. Sri Lankan J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 8, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Newell, S.E.; Yin, G.; Yu, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Gao, D.; Gao, J.; et al. Effects of silver nanoparticles on nitrification and associated nitrous oxide production in aquatic environments. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.; Prabhune, A.; Perry, C.C. Antibiotic mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles with potent antimicrobial activity and their application in antimicrobial coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6789–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokina, S.; Narayanan, V. Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activity of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized from Grapes Fruit Extract. Chem. Sci. Trans. 2013, 2, S105–S110. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Aly, E.M.; Mohamed, F.F.; Noor, N.A.; Elsayed, A.A. Neurotoxicity of green- synthesized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in different brain areas of wistar rats. Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodan, A.M.; Iconaru, S.L.; Ciobanu, C.S.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Stoicea, M.; Predoi, D. Iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: Characterization and toxicity evaluation by in vitro and in vivo assays. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 587021. [Google Scholar]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Kilic, G.; Costa, C.; Fernandez-Bertolez, N.; Pasaro, E.; Teixeira, J.P.; Laffon, B. Effects of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity, Developmental Toxicity, and Neurotoxicity Vanessa. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2014, 56, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Zafar, H.; Zia, M.; ul Haq, I.; Phull, A.R.; Ali, J.S.; Hussain, A. Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, C.A.; Garcia, M.P.; Iocca, D.C.; Rebelo, L.G.; Souza, A.C.O.; Bocca, A.L.; Almeida Santos, M.d.F.M.; Morais, P.C.; Azevedo, R.B. Antifungal Activity of Amphotericin B Conjugated to Nanosized Magnetite in the Treatment of Paracoccidioidomycosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareta, R.A.; Taylor, E.; Webster, T.J. Increased osteoblast density in the presence of novel calcium phosphate coated magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 265101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Naregalkar, R.R.; Vaidya, V.D.; Gupta, M. Recent advances on surface engineering of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffan, M.; Achouak, W.; Rose, J.; Roncato, M.-A.; Chanéac, C.; Waite, D.T.; Masion, A.; Woicik, J.C.; Wiesner, M.R.; Bottero, J.-Y. Relation between the Redox State of Iron-Based Nanoparticles and Their Cytotoxicity toward Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6730–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Song, J.; Jang, J. One-step fabrication of magnetic γ-Fe2O3/polyrhodanine nanoparticles using in situ chemical oxidation polymerization and their antibacterial properties. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6735–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, C.; Nelson, K.L.; Sedlak, D.L.; Yoon, J. Inactivation of escherichia coli by nanoparticulate zerovalent iron and ferrous ion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7668–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Mir, A.; Mallik, D.; Sinha, A.; Nayar, S.; Webster, T.J. Bactericidal effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Samantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, A.K.; Thorat, N.D.; Tandon, A.; Kim, J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.K. Coupling of radiofrequency with magnetic nanoparticles treatment as an alternative physical antibacterial strategy against multiple drug resistant bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricant, D.S.; Farnsworth, N.R. The value of plants used in traditional medicine for drug discovery. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Arokiyaraj, S.; Saravanan, M.; Prakash, N.U.; Arasu, M.V.; Vijayakumar, B.; Vincent, S. Enhanced antibacterial activity of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles treated with Argemone mexicana L. leaf extract: An in vitro study. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 3323–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriary, M.; Veisi, H.; Hekmati, M.; Hemmati, S.; Nemmati, S. In situ green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles on herbal tea extract (Stachys lavandulifolia)-modified magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as antibacterial agent and their 4-nitrophenol catalytic reduction activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, F.; Seddigh, M. Magnetite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method: The effects of various iron anions on specifications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 184, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinali, R.; Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Manley-Harris, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Berenjian, A. Iron oxide nanoparticles in modern microbiology and biotechnology. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubair, N.; Rajagopal, M.; Chinnappan, S.; Abdullah, N.B.; Fatima, A. Review on the Antibacterial Mechanism of Plant-Derived Compounds against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria (MDR). Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3663315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Luo, J.; Deng, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H. Antibiotic Combination Therapy: A Strategy to Overcome Bacterial Resistance to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 839808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamoud, R.; Zimmermann, S.; Reichling, J.; Wink, M. Synergistic interactions in two-drug and three-drug combinations (thymol, EDTA and vancomycin) against multi drug resistant bacteria including E. coli. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, Y.; Irwin, P.L.; Jin, T.; Shi, X. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suffredini, I.B.; Paciencia, M.L.B.; Varella, A.D.; Younes, R.N. Antibacterial activity of Brazilian Amazon plant extracts. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 10, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.M.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, I.P.; Woo, S.O.; Kim, S.G.; Jang, H.R.; Pak, S.C. Antibacterial activity and antibiotic-enhancing effects of honeybee venom against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2016, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, V.I.; Hufnagel, D.A.; Jaggavarapu, S.; Sherman, E.X.; Wozniak, J.E.; Satola, S.W.; Farley, M.M.; Jacob, J.T.; Burd, E.M.; Weiss, D.S. Antibiotic combinations that exploit heteroresistance to multiple drugs effectively control infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyers, M.; Wright, G.D. Drug combinations: A strategy to extend the life of antibiotics in the 21st century. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandpal, N.D.; Sah, N.; Loshali, R.; Joshi, R.; Prasad, J. Co-precipitation method of synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2014, 73, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Isobe, T.; Senna, M. Preparation of ultrafine Fe3O4 particles by precipitation in the presence of PVA at high pH. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 177, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaagac, O.; Kockar, H.; Tanrisever, T. Properties of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized at different temperatures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2011, 24, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, G.; Logeshwaran, V.; Sarathbabu, S.; Jha, P.K.; Jeyaraj, M.; Rajkuberan, C.; Senthilkumar, N.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Couroupita guianensis Aubl. fruit extract for their antibacterial and cytotoxicity activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, W.H.; Mahasneh, A.M. Antimicrobial, cytotoxicity and phytochemical screening of Jordanian plants used in traditional medicine. Molecules 2010, 15, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali-Shtayeh, M.S.; Yaghmour, R.M.R.; Faidi, Y.R.; Salem, K.; Al-Nuri, M.A. Antimicrobial activity of 20 plants used in folkloric medicine in the Palestinian area. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 60, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lade, H.; Park, J.H.; Chung, S.H.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, J.M.; Joo, H.S.; Kim, J.S. Biofilm formation by staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates is differentially affected by glucose and sodium chloride supplemented culture media. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Prakash, P.; Achra, A.; Singh, G.; Das, A.; Singh, R. Standardization and classification of in vitro biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Datt, G.; Raja, M.M.; Abhyankar, A.C. Steering of Magnetic Interactions in Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2−x(Mn)xO4 Nanoferrites via Substitution-Induced Cationic Redistribution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 10693–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, A.; Ghanem, H.M.E.; Lehlooh, A.; Arafa, I.M.; Bsoul, I.; Batra, A. Mössbauer, VSM and X-ray Diffraction Study of Fe3O4 (NP’s)/PVOH for Biosensors Applications. Sens. Transducers 2015, 192, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Saqib, S.; Munis, M.F.H.; Zaman, W.; Ullah, F.; Shah, S.N.; Ayaz, A.; Farooq, M.; Bahadur, S. Synthesis, characterization and use of iron oxide nano particles for antibacterial activity. Wiley Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 82, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Chang, T.; Chen, W.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Zuo, Y.; Kang, L.; Yang, F.; Hostetter, M.; Volinsky, A.A. Temperature effects on magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by the sol-gel explosion-assisted method. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, T.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, J. Formation Pathways of Magnetite Nanoparticles by Coprecipitation Method. J. Phys. Chemisrty C 2012, 116, 6069–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ansari, F.A.; Alam, M.Z.; Ahmed, M.A.; Khan, M.S.; Baig, M.H.; et al. Low temperature synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and their ROS mediated inhibition of biofilm formed by food-associated bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.F.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Nasr, N.F. Evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Aloysia triphylla. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 10, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar]
- Bataineh, S.M.B.; Tarazi, Y.H.; Ahmad, W.A. Antibacterial Efficacy of Some Medicinal Plants on Multidrug Resistance Bacteria and Their Toxicity on Eukaryotic Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D. Oak trees (Quercus spp.) as a source of extracts with biological activities: A narrative review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Aflatoonian, M.R.; Azizi, H.; Mosazade, F.; Hooshmand, A.; Lima Nobre, M.A.; Minab Poodineh, F.; Khatami, M.; Khraazi, S.; Mirzaeei, H. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Int. J. Basic Sci. Med. 2017, 2, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirdat, P.N.; Dandge, P.B.; Hagwane, R.M.; Nikam, A.S.; Mahadik, S.P.; Jirange, S.T. Synthesis and characterization of ginger (Z. officinale) extract mediated iron oxide nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).