Structural, Morphological and Ferroelectric Properties of Sr-Cd Co-Doped Nickel Ferrite for Energy Storage Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Material Synthesis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Analysis
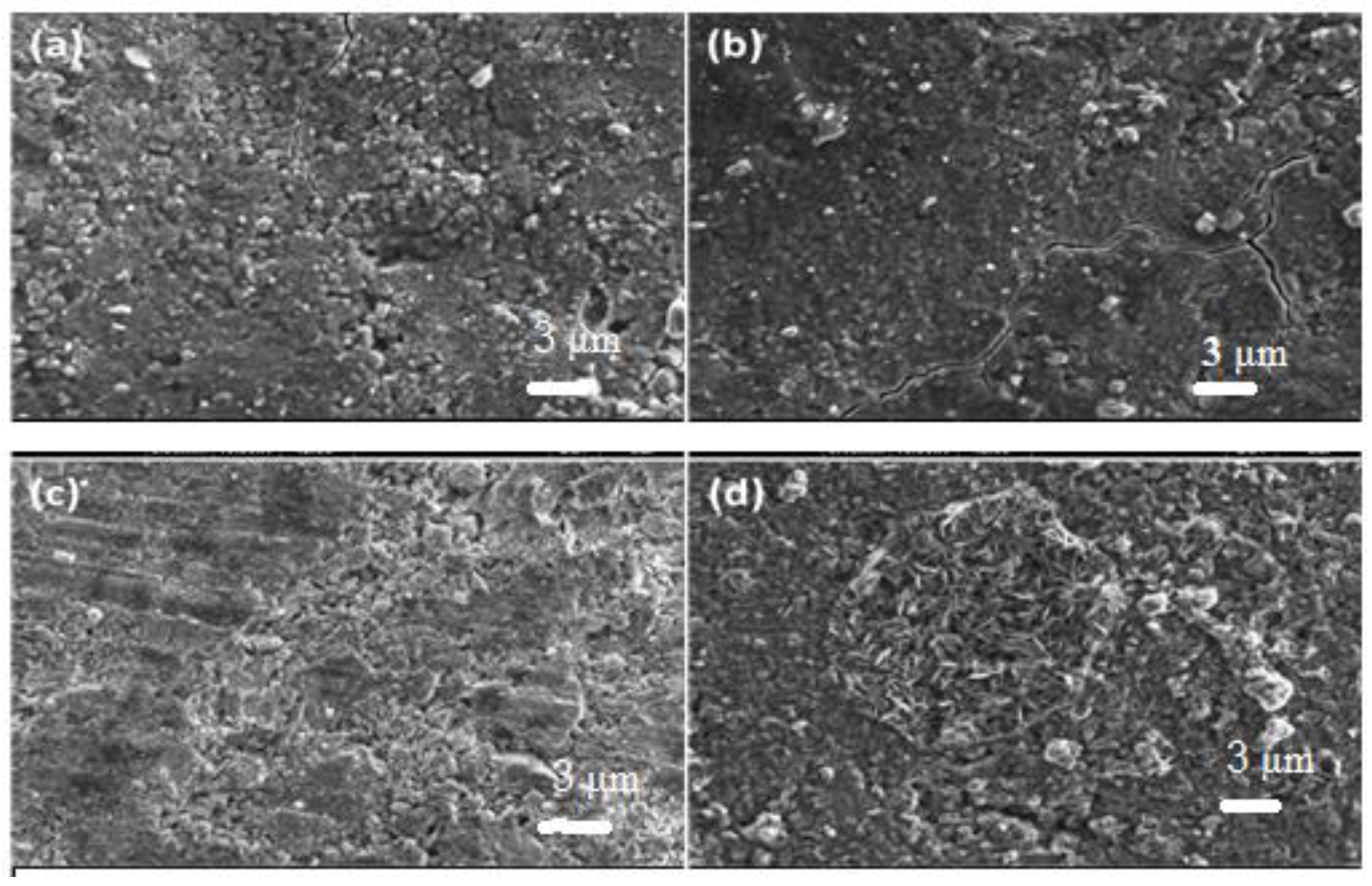
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
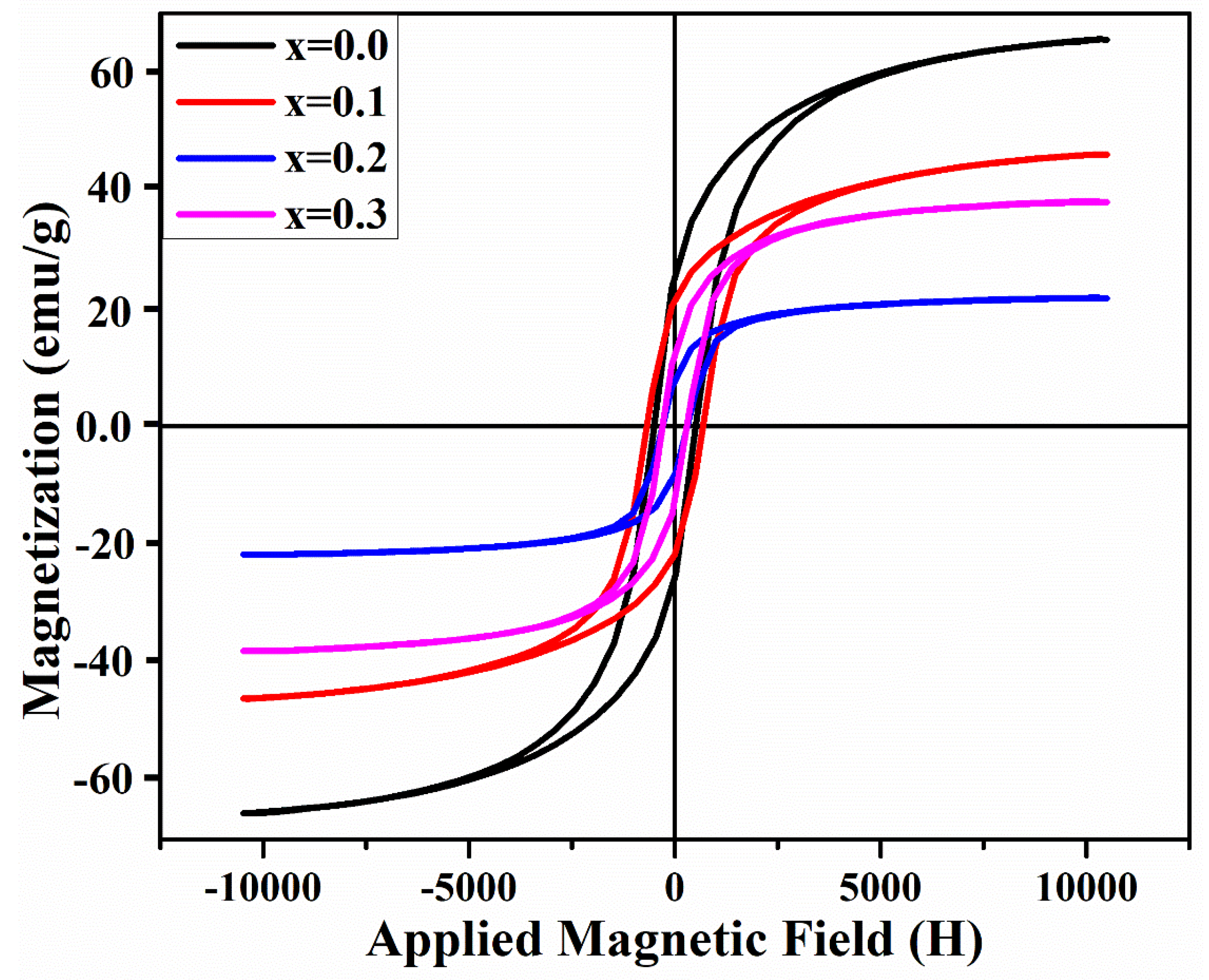
3.3. Magnetic Properties
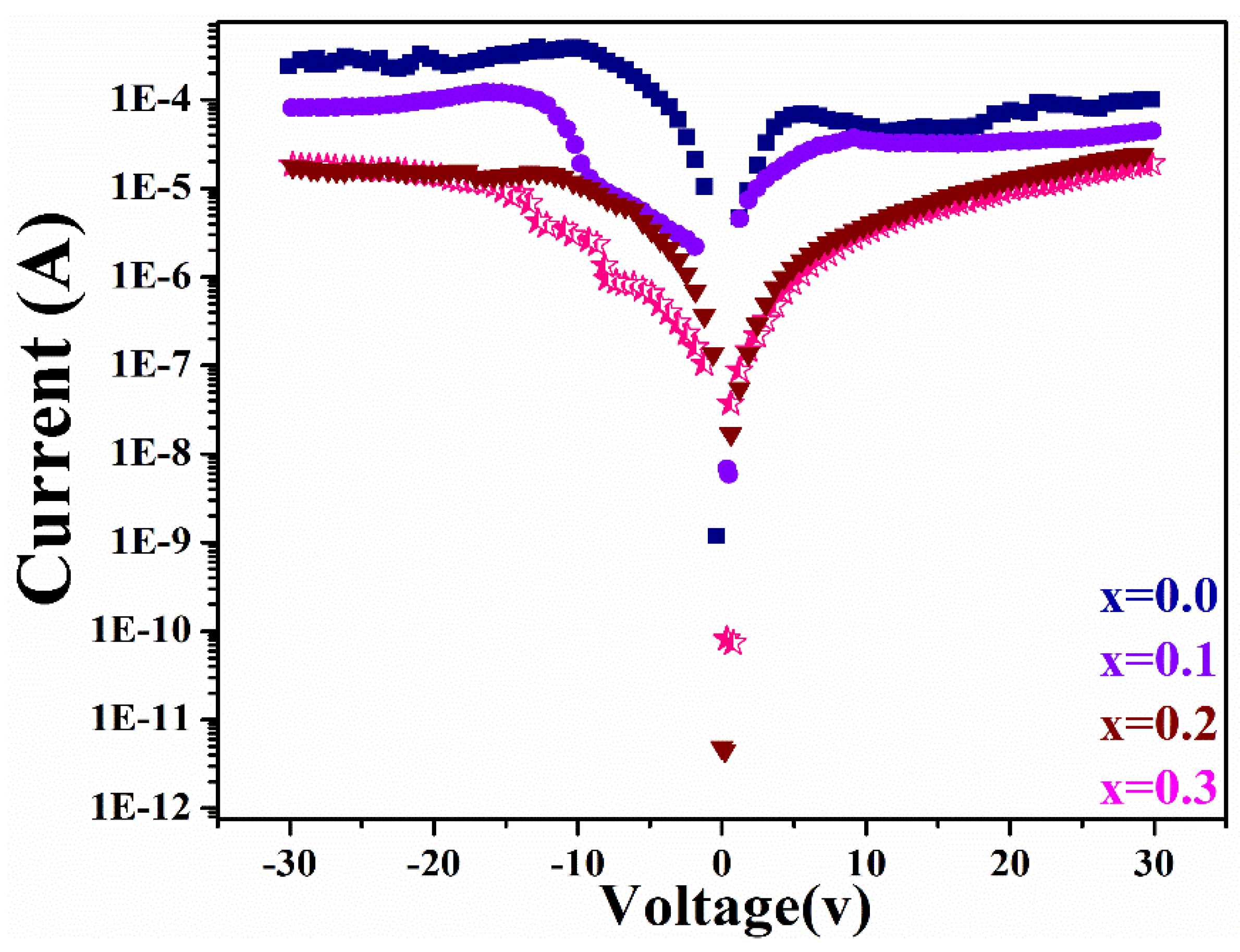
3.4. Ferroelectric Analysis
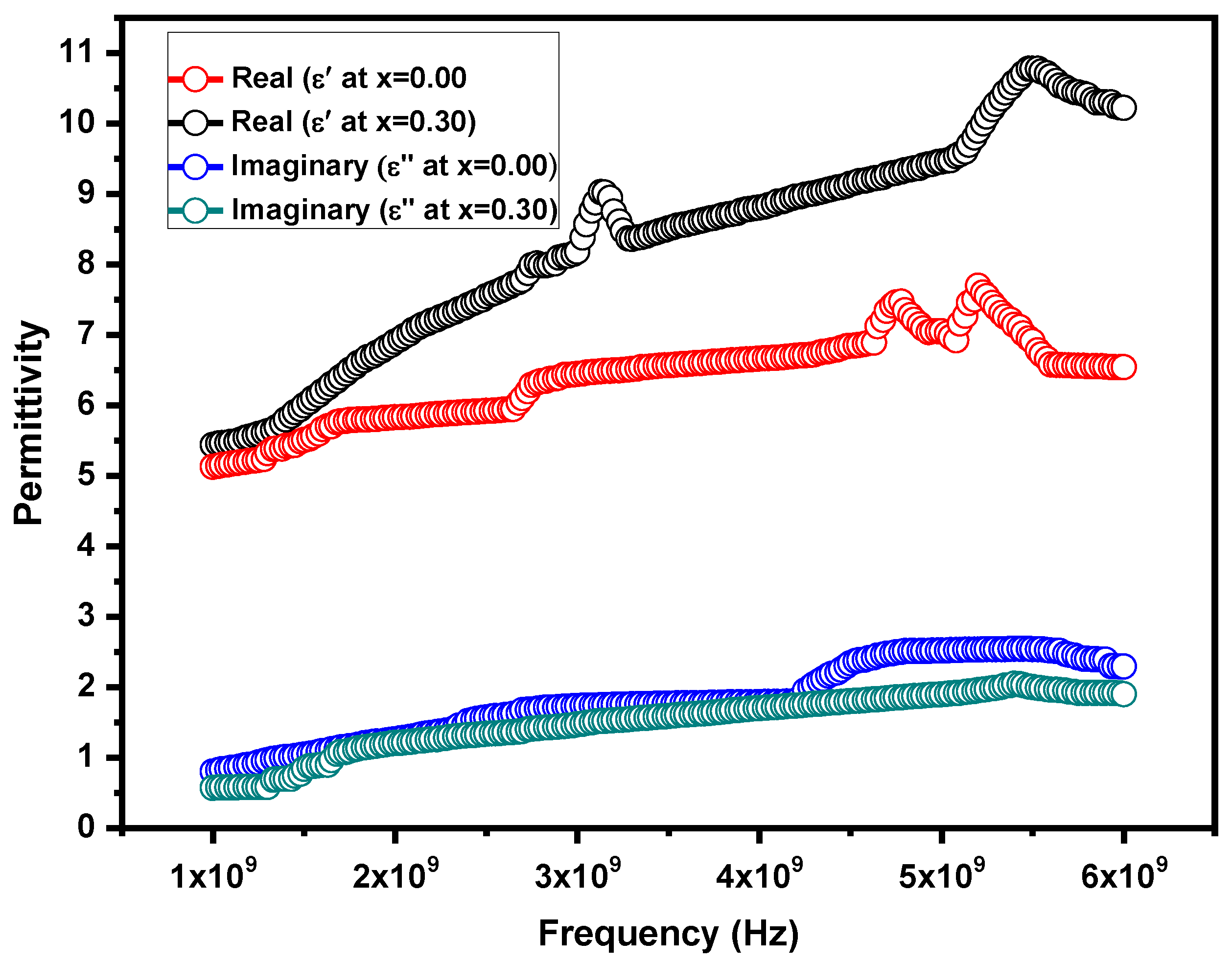
3.5. Dielectric Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramzan, M.; Raza, S.A.; Usman, M.; Sharma, G.D.; Iqbal, H.A. Environmental cost of non-renewable energy and economic progress: Do ICT and financial development mitigate some burden? J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, H.; Messaoudi, Y.; Khelladi, M.R.; Azizi, A. A facile synthesis of metal ferrites (MFe2O4, M = Co, Ni, Zn, Cu) as effective electrocatalysts toward electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 20129–20137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, F.; Yusuf, M.; Kamyab, H.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Chelliapan, S.; Joo, S.-W.; Vasseghian, Y. Latest eco-friendly avenues on hydrogen production towards a circular bioeconomy: Currents challenges, innovative insights, and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.; Vijayakanth, V.; Vattikuti, S.P.; Kim, K.H. Structural, BET and EPR properties of mixed zinc-manganese spinel ferrites nanoparticles for energy storage applications. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 19717–19727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, Y.; Liu, W.; Lim, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, A. A general approach for fabricating 3D MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Ni, Cu, Co)/graphitic carbon nitride covalently functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene nanocomposites as advanced anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, C.; Ren, F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhong, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, H. Preparation of uniform and highly dispersed magnetic copper ferrite sub- micron sized particles regulated by short-chain surfactant with catechol structure: Dual-functional materials for supercapacitor and dye degradation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 870, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.; Vijayakanth, V.; Vattikuti, S.P.; Kim, K.H. Synthesis and characterization of Mg2+ substituted MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for supercapacitor applications. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 30695–30703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.M.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Ramesh, S.; Maile, N.C.; Lee, D.S.; Shinde, S.K. Nanorods to hexagonal nanosheets of CuO-doped manganese oxide nanostructures for higher electrochemical supercapacitor performance. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuja, G.; Ganiger, S.K.; Shashidhar, S.; Preeti, R.; Patil, S.R.; Lagashetty, A. Solid state synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of silver doped nanosized metal oxides. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2023, 12, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.F.; de Oliveira Soares, J.; Miranda, M.O.; Torres, M.A.M.; Braga, T.P. Catalysis Application of Magnetic Ferrites and Hexaferrites. In Handbook of Magnetic Hybrid Nanoalloys and Their Nanocomposites; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Khairy, M.; Bayoumy, W.A.; Selima, S.S.; Mousa, M.A. Studies on characterization, magnetic and electrochemical properties of nano-size pure and mixed ternary transition metal ferrites prepared by the auto-combustion method. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals; Scientific and Technology; Longman Scientific & Technical: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bogle, K.A.; Dhole, S.D.; Bhoraskar, V.N. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis and size control by electron irradiation. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3204–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, P.; Kesavamoorthy, R.; Bera, S.; Magudapathy, P.; Nair, K.G.M.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Narasimhan, S.V. Optical Absorption and Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of the Growth of Silver Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 047403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.A.; Behbahanian, S.; Amighian, J. Synthesis and magnetic properties of NiFe2−xSmxO4 nanopowder. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 410, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aafiya; Abushad, M.; Arshad, M.; Naseem, S.; Ahmed, H.; Ansari, A.; Chakradhary, V.K.; Husain, S.; Khan, W. Synthesis and role of structural disorder on the optical, magnetic and dielectric properties of Zn doped NiFe2O4 nanoferrites. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1253, 132205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Goga, F.; Petean, I.; Avram, A.; Cadar, O. The impact of polyol structure on the formation of Zn0.6Co0.4Fe2O4 spinel-based pigments. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhame, S.D.; Joy, P. Enhanced strain sensitivity in magnetostrictive spinel ferrite Co1−xZnxFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 447, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Bhargava, G.K. Review paper on nickel-zinc nano ferrite. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 3082–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottker, W.E.; Ono, R.; Cobos, M.A.; Hernando, A.; Araujo, J.F.; Bruno, A.C.; Lourenço, S.A.; Longo, E.; La Porta, F.A. Influence of order-disorder effects on the magnetic and optical properties of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 17290–17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoghoghifard, S.; Moradi, M. Influence of annealing temperature on structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of NiFe2O4 nanorods synthesized by simple hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17768–17775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barvinschi, P.; Stefanescu, O.; Dippong, T.; Sorescu, S.; Stefanescu, M. CoFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites by thermal decomposition of some complex combinations embedded in hybrid silica gels. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 112, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Hou, X.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, F.; Xia, Y.; Ru, Q.; Yao, L.; Wu, Y. The influence of manganese ions doping on nanosheet assembly NiFe2O4 for the removal of Congo red. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakradhary, V.K.; Ansari, A.; Akhtar, M.J. Design, synthesis, and testing of high coercivity cobalt doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.F.; Johnson, D.W., Jr. Impurity-induced exaggerated grain growth in Mn-Zn Ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1978, 61, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nahrawy, A.M.; Hemdan, B.A.; Mansour, A.; Elzwawy, A.; Hammad, A.B.A. Integrated use of nickel cobalt aluminoferrite/Ni2+ nano-crystallites supported with SiO2 for optomagnetic and biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 274, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.; Yeasmin, M.; Al-Mamun, A.; Hoque, S.M.; Khan, M. Influence of Gd content on the structural, Raman spectroscopic and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel route. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 33323–33331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, G.S.; Shivhare, A.; Kaur, S.P.; Kumar, T.D.; Srivastava, R. Catalytic interplay of metal ions (Cu2+, Ni2+, and Fe2+) in MFe2O4 inverse spinel catalysts for enhancing the activity and selectivity during selective transfer hydrogenation of furfural into 2-methylfuran. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paswan, S.K.; Pradhan, L.K.; Kumar, P.; Kumari, S.; Kar, M.; Kumar, L. Electrical transport properties of nanocrystalline and bulk nickel ferrite using complex impedance spectroscopy: A comparative study. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 095812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.; Vijayakanth, V.; Vattikuti, S.P.; Kim, K.H. Electrochemical investigation on nickel-doped spinel magnesium ferrite nanoparticles for supercapacitor applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 301, 127601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakash; Nordblad, P.; Mohan, R.; Mukherjee, S. Structural, magnetic and hyperfine characterizations of nanocrystalline Zn-Cd doped nickel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.V.; Byon, C.; Narendra, B.; Dudem, B.; Shim, J.; Moon, S.J.; Vattikuti, S.V.P. Effect of calcination temperature on cobalt substituted cadmium ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 5078–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalawai, S.P.; Gadkari, A.B.; Vasambekar, P.N. Electrical switching in cadmium ferrite with different rare-earth ions (Sm3+, Y3+, and La3+). Rare Met. 2015, 34, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajalilou, A.; Hashim, M.; Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi, R.; Sarami, N. Influence of CaO and SiO2 co-doping on the magnetic, electrical properties and microstructure of a Ni–Zn ferrite. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 145001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygieł, I.; Winiarska, K.; Bieńko, A.; Suracka, K.; Gaworska-Koniarek, D. The effect of the sol–gel autocombustion synthesis conditions on the Mn–Zn ferrite magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 604, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, T.; Hemalatha, J. Chemical control on the size and properties of nano NiFe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel autocombustion method. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.S.; Rao, T.V.; Naheed, S.; Rao, P.V. Structural and optical properties of zinc magnesium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by chemical co-precipitation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, H.; Nong, P.; Kang, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y. Dissolution and Solubility of the Calcite–Otavite Solid Solutions [(Ca1−xCdx)CO3] at 25 °C. Minerals 2022, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashekova, A.; Baltash, Y.; Yegamkulov, M.; Trussov, I.; Bakenov, Z.; Mukanova, A. Polycationic doping of the LATP ceramic electrolyte for Li-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 29595–29601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathy, G.; Senguttuvan, G.; Berchmans, L.J.; Sivakumar, V.; Jegatheesan, P. Influence of cerium substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized by combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17505–17515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Li, J.; Korgel, B.A.; Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Su, F.; Du, J.; Wang, D. General synthesis and gas-sensing properties of multiple-shell metal oxide hollow microspheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 12, 2738–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahwa, C.; Narang, S.B.; Sharma, P. Composition dependent magnetic and microwave properties of exchange-coupled hard/soft nanocomposite ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, A.; Ahmad, M.; Hassan, S.; Hussain, S.Q.; Iqbal, M.W.; Ali, H.E. Ba substituted SrFe2O4 (SrBa0.3Fe1.7O4) for the removal of fluoride ions (F−1) from the drinking water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 295, 127165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Shaukat, S.F.; Haidyrah, A.S.; Akhtar, M.N.; Ahmad, M. Synthesis and investigations of structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Cr-substituted W-type Hexaferrites for high frequency applications. J. Electroceram. 2021, 46, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ali, R.; Rehman, A.U.; Ali, A.; Sultana, I.; Ali, I.; Asif, M. Insight into the Structural, Electrical, and Magnetic Properties of Al-Substituted BiFeO3 Synthesised by the Sol–Gel Method. Z. Naturforschung A 2020, 75, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Grössinger, R.; Ali, I.; Ahmad, I.; Rana, M. Synthesis and characterization of Al-substituted W-type hexagonal ferrites for high frequency applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, K.; Huang, S.; Hui, X. Microwave absorbing properties of W-type hexaferrite Ba(MnZn)xCo2(1−x) Fe16O27. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.X.; Sun, N.X.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yabukami, S. Properties of a new soft magnetic material. Nature 2000, 407, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.; Slimani, Y.; Korkmaz, A.; Guner, S.; Sertkol, M.; Shirsath, S.E.; Baykal, A. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Tm3+ substituted cobalt spinel ferrites synthesized via sonochemical approach. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Khan, M.A. Structural, physical and magnetic evaluations of Ce-Zn substituted SrCo2 W-type hexaferrites prepared via sol gel auto combustion route. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12921–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zaag, P.J.; van der Valk, P.J.; Rekveldt, M.T. A domain size effect in the magnetic hysteresis of NiZn-ferrites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 2927–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.; Bertino, M. Temperature dependent coercivity and magnetization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sarkar, K. Effect of Nickel and Cobalt Doping on Nano Bismuth Ferrite Prepared by the Chemical Route. Interceram-Int. Ceram. Rev. 2015, 64, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Archana; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, V.; Das, S.B. Tuning in structural, optoelectronic, magnetic and ferroelectric properties of NiFe2O4 ceramics engineering nanomaterials by substitution of rare earth element, Pr3+ prepared by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 6131–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Bibi, I.; Majid, F.; Jilani, K.; Kamal, S.; Iqbal, M.; Ata, S.; Nazar, N.; Albalawi, H.; Alwadai, N. The electrochemical, dielectric, and ferroelectric properties of Gd and Fe doped LaNiO3 with an efficient solar-light driven catalytic activity to oxidize malachite green dye. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 568–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luqman, M.; Shazaib, R.; Raza, A.; Khan, M.A.; Shar, M.; Ramay, S.M.; Riaz, S.; Atiq, S. Simultaneous existence of magnetic and ferroelectric orders in bi-phase composites for multiferroic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 587, 171361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Concentration (x) | Crystallite Size (Dp) (nm) | d-Spacing (Å) | Lattice Parameter ‘a’ (Å) | Unit Cell Volume (106 pm3) | X-ray Density () (g/cm3) | Dislocation Dendity δ = 1/D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd0.5 Sr0.0 Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 29.67 | 1.5270 | 4.319 | 80.57 | 5.65 | 0.001136 |
| Cd0.4 Sr0.1 Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 35.42 | 1.5736 | 4.450 | 88.12 | 5.12 | 0.000797 |
| Cd0.3 Sr0.2 Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 38.05 | 1.6256 | 4.597 | 97.14 | 4.96 | 0.000691 |
| Cd0.2 Sr0.3 Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 39.93 | 1.7464 | 4.9395 | 120.5 | 4.66 | 0.000627 |
| X | Ms emu/g ±0.01 | Mr emu/g ±0.01 | Mr/Ms | nB (μB) | Hc Oe ±0.01 | K ergg−1 | Hk (108) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 65.58 | 25.16 | 0.38 | 3.076448 | 504 | 34,429.5 | 8.75 |
| 0.1 | 46.10 | 21.28 | 0.46 | 2.137851 | 681 | 32702.19 | 11.82 |
| 0.2 | 21.80 | 7.73 | 0.35 | 1.003151 | 297 | 6744.375 | 5.15 |
| 0.3 | 38.16 | 12.12 | 0.31 | 1.735477 | 295 | 11,726.25 | 5.12 |
| Contents X | Ec (KV/cm) ±0.02 | WR (J/cm3) | WL (J/cm3) | WT (J/cm3) | Efficiency (η) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd0.5Sr0.0Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 0.02999 | 0.12 | 1.965 | 2.0844 | 5.75 |
| Cd0.4Sr0.1Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 0.02802 | 0.426 | 1.045 | 1.471 | 28.95 |
| Cd0.3Sr0.2Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 0.02889 | 0.0578 | 0.0876 | 0.1454 | 39.73 |
| Cd0.2Sr0.3Ni0.5Fe2O4 | 0.02822 | 0.0734 | 0.0549 | 0.1282 | 57.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alburaih, H.A.; ul Haq, M.A.; Jabbar, A.; ur Rehman, A.; Laref, A.; Saad Hasb Elkhalig, M.M.; Noor, N.A. Structural, Morphological and Ferroelectric Properties of Sr-Cd Co-Doped Nickel Ferrite for Energy Storage Devices. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10070048
Alburaih HA, ul Haq MA, Jabbar A, ur Rehman A, Laref A, Saad Hasb Elkhalig MM, Noor NA. Structural, Morphological and Ferroelectric Properties of Sr-Cd Co-Doped Nickel Ferrite for Energy Storage Devices. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(7):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10070048
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlburaih, Huda A., Muhammad Ahsan ul Haq, Abdul Jabbar, Atiq ur Rehman, Amel Laref, Mohamed Musa Saad Hasb Elkhalig, and Naveed Ahmad Noor. 2024. "Structural, Morphological and Ferroelectric Properties of Sr-Cd Co-Doped Nickel Ferrite for Energy Storage Devices" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 7: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10070048
APA StyleAlburaih, H. A., ul Haq, M. A., Jabbar, A., ur Rehman, A., Laref, A., Saad Hasb Elkhalig, M. M., & Noor, N. A. (2024). Structural, Morphological and Ferroelectric Properties of Sr-Cd Co-Doped Nickel Ferrite for Energy Storage Devices. Magnetochemistry, 10(7), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10070048





