Quantitative Determination of the Main Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity of Aqueous Extracts of Olive Leaves of Greek and Spanish Genotypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Raw Material
2.3. Sample Preparation
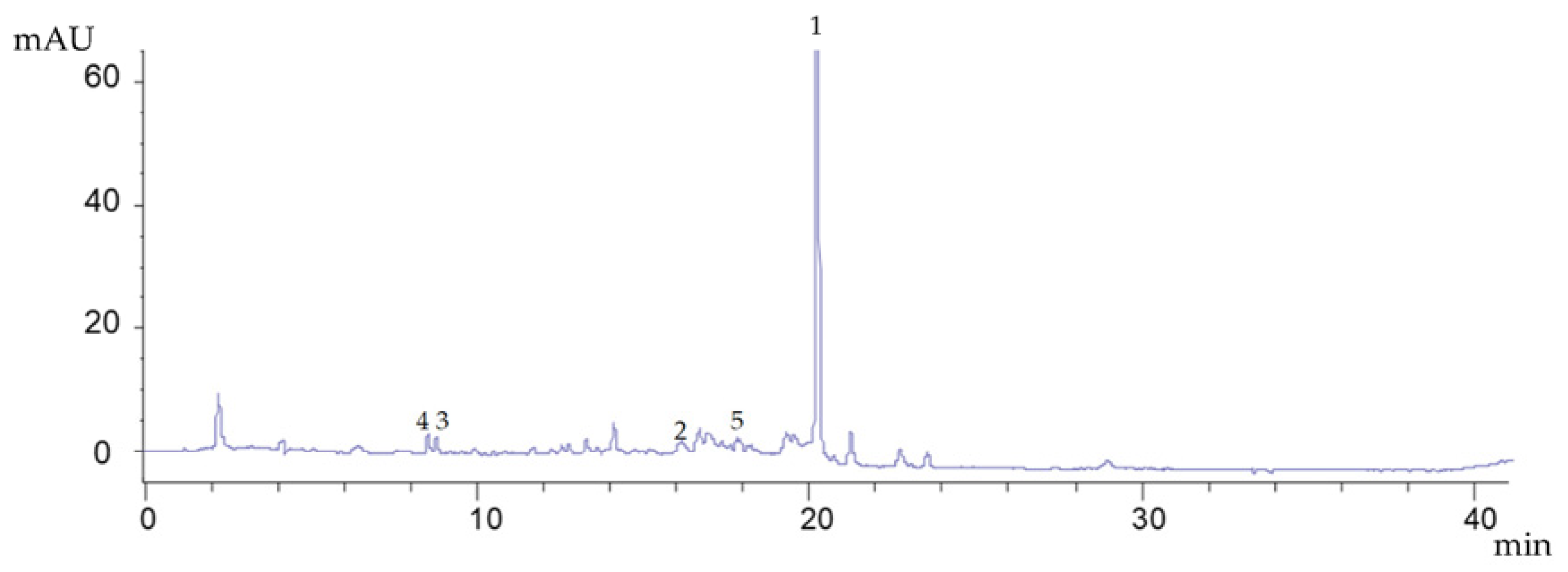
2.4. Determination of Oleuropein and Other Phenolic Compounds
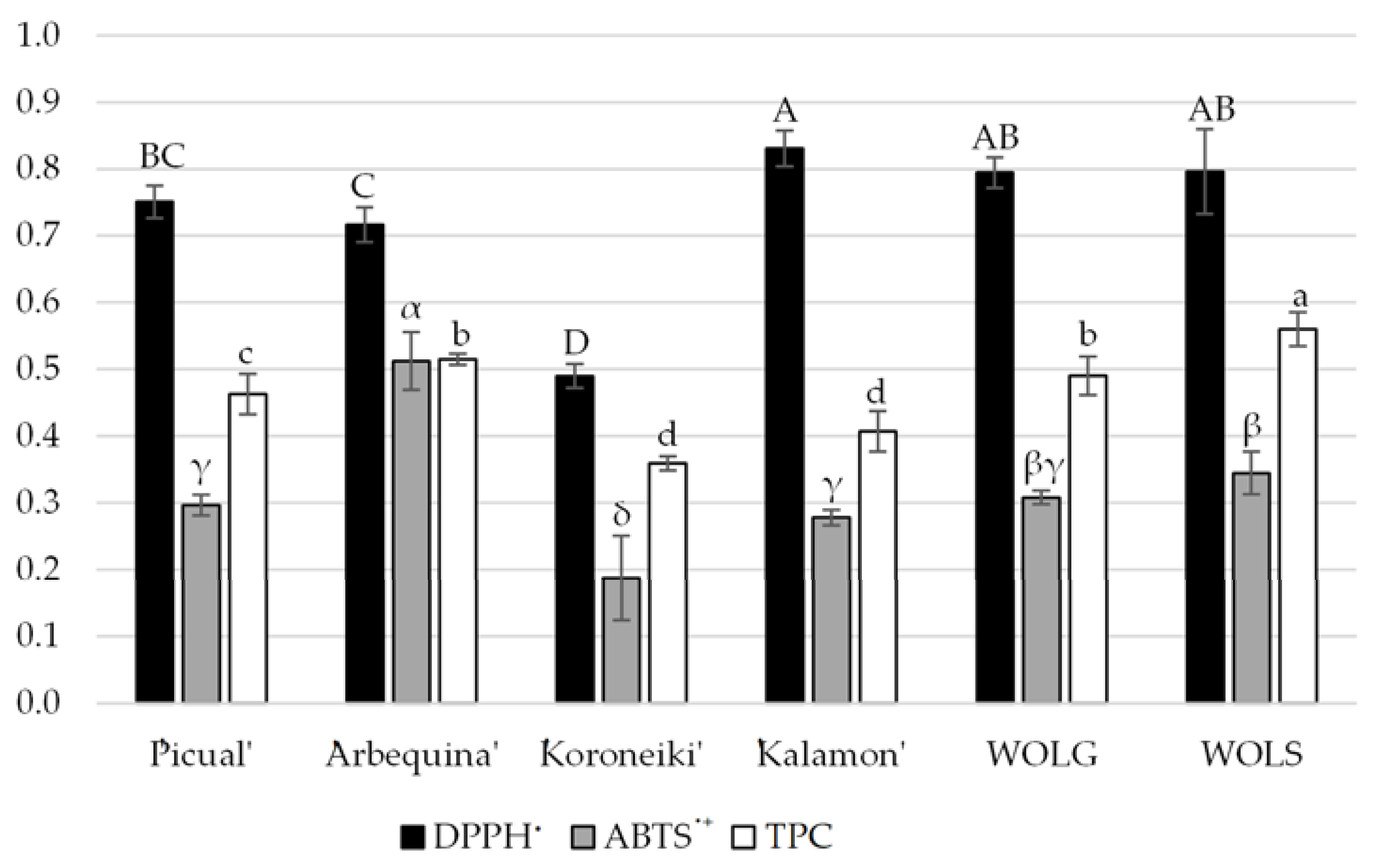
2.5. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.7. Toxicity Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
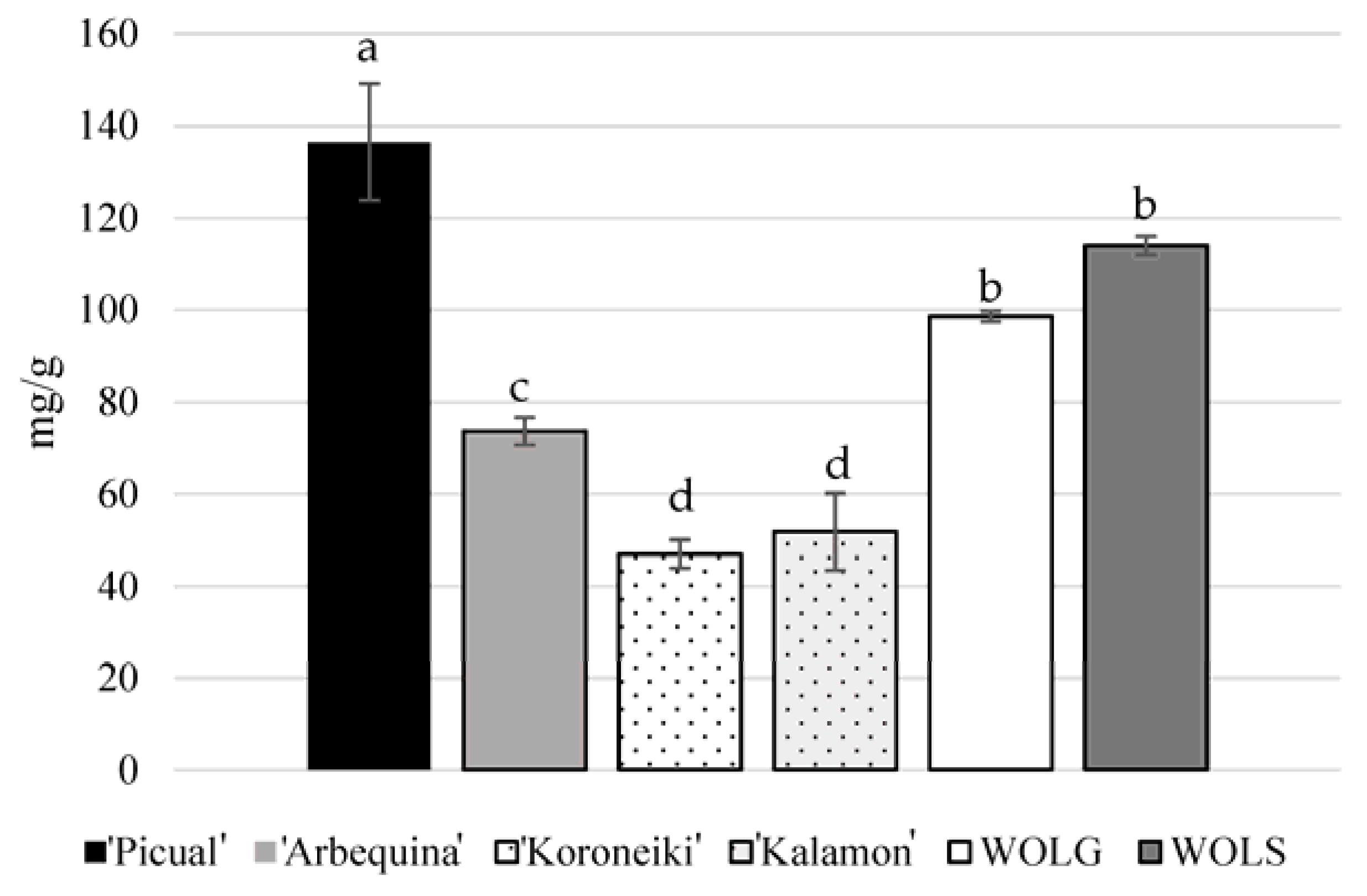
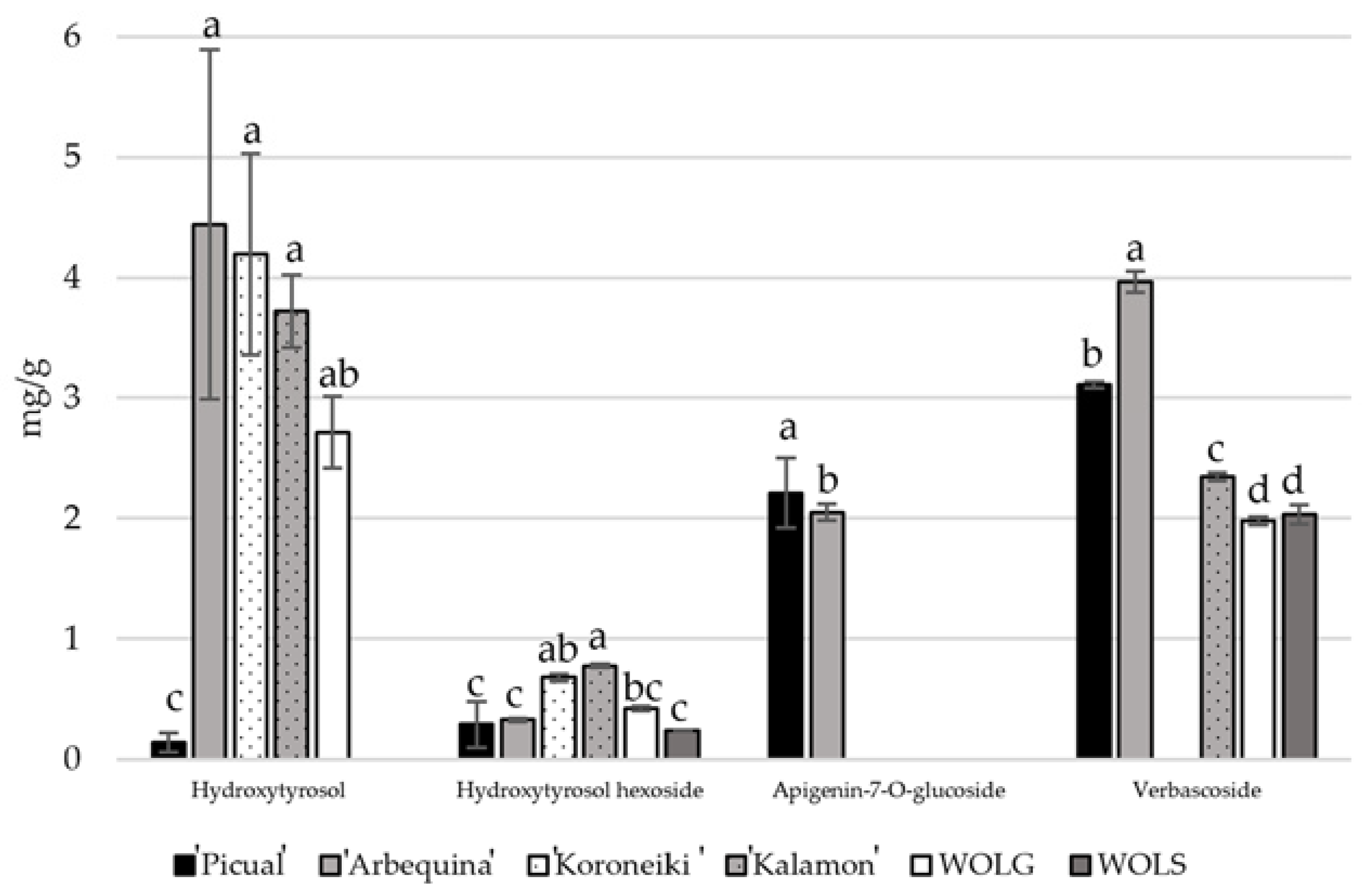
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, P.-J.; Huang, L.-X.; Zhang, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.-L. Phenolic compositions, and antioxidant performance of olive leaf and fruit (Olea europaea L.) extracts and their structure–activity relationships. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 16, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente-García, O.; Castillo, J.; Lorente, J.; Ortuño, A.; Del Rio, J.A. Antioxidant activity of phenolics extracted from Olea europaea L. leaves. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Navarro, M.E.; Cebrián-Tarancón, C.; Oliva, J.; Salinas, M.R.; Alonso, G.L. Oleuropein Degradation Kinetics in Olive Leaf and Its Aqueous Extracts. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.-J.; Wang, C.-Z.; Ye, J.-Z.; Tao, R.; Zhang, Y.-S. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Oleuropein from Olea europea (Olive) Leaf Extract and Antioxidant Activities. Molecules 2015, 20, 2903–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayan, H.; Erener, G. Effect of Olive Leaf (Olea europaea) Powder on Laying Hens Performance, Egg Quality and Egg Yolk Cholesterol Levels. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeso, J.; Isaza, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Sörensen, P.M.; Jurado, P.; Avena-Bustillos, R.d.J.; Olaizola, M.; Arboleya, J.C. Olive Leaf Waste Management. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 660582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COI (International Olive Council). The Wold of Olive Oil. 2022. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/the-world-of-olive-oil (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Topuz, S.; Bayram, M. Oleuropein extraction from leaves of three olive varieties (Olea europaea L.): Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of purified oleuropein and oleuropein extracts. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, N.S.; Megremi, S.F.; Tarantilis, P. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity, Toxicity, and Phenolic Profile of Aqueous Extracts of Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) and Sage (Salvia officinalis L.) Prepared at Different Temperatures. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Adil, M.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Munir, B.; Yameen, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Shar, G.A.; Asif Tahir, M.; Iqbal, M. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Navarro, M.E.; Cebrián-Tarancón, C.; Alonso, G.L.; Salinas, M.R. Determination of the Variability of Bioactive Compounds and Minerals in Olive Leaf along an Agronomic Cycle. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Navarro, E.M.; Cebrián-Tarancón, C.; Moratalla-López, N.; Lorenzo, C.; Alonso, G.L.; Salinas, R.M. Development and validation of an HPLC-DAD method for determination of oleuropein and other bioactive compounds in olive leaf by-products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaparakou, E.H.; Kanakis, C.D.; Gerogianni, M.; Maniati, M.; Vekrellis, K.; Skotti, E.; Tarantilis, P.A. Quantitative determination of aloin, antioxidant activity, and toxicity of Aloe vera leaf gel products from Greece. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. [14] Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 299, pp. 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Azur, M.M. Azur Environmental; Microbics Corporation: Carlsbad, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Navarro, M.E.; Cebrián-Tarancón, C.; Salinas, M.R.; Alonso, G.L. Evolution of Oleuropein and Other Bioactive Compounds in Arbequina Olive Leaves under Different Agronomic Conditions. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, A.; Therios, I.; Samouris, G.; Koundouras, S.; Giannakoula, A. Effect of water deficit on leaf phenolic composition, gas exchange, oxidative damage and antioxidant activity of four Greek olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhaoui, N.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; León, L.; De la Rosa, R.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Determination of phenolic compounds of ‘Sikitita’ olive leaves by HPLC-DAD-TOF-MS. Comparison with its parents ‘Arbequina’ and ‘Picual’ olive leaves. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhaoui, N.; Taamalli, A.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Phenolic compounds in olive leaves: Analytical determination, biotic and abiotic influence, and health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, M.M.; Matthäus, B. A review: Benefit and bioactive properties of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaves. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotti, E.; Anastasaki, E.; Kanellou, G.; Polissiou, M.; Tarantilis, P.A. Total phenolic content, antioxidant activity and toxicity of aqueous extracts from selected Greek medicinal and aromatic plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 53, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Oleae Folium. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/herbal/oleae-folium (accessed on 7 July 2022).
| Oleuropein | HT | HT Hexoside | Apigenin-7-O-glucoside | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT | −0.851 ** | |||
| HT hexoside | −0.683 ** | −0.605 ** | ||
| Apinegin-7-O-glucoside | 0.428 | −0.274 | −0.447 | |
| Verbascoside | 0.685 ** | −0.741 ** | −0.429 | 0.662 ** |
| Genotype | Linear Regression Equation for DPPH· Radical Scavenging | C.V. (m) | C.V (n) | R2 | EC50DPPH (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Picual’ | y = 0.192x + 1.027 | 0.004 | 0.521 | 0.995 | 10.21 ± 0.03 |
| ‘Arbequina’ | y = 7.250x + 0.299 | 1.719 | 9.199 | 0.999 | 6.86 ± 0.08 |
| ‘Koroneiki’ | y = 4.268x + 3.060 | 1.101 | 5.889 | 0.997 | 11.00 ± 0.09 |
| ‘Kalamon’ | y = 6.715x + 8.489 | 1.851 | 9.906 | 0.996 | 5.10 ± 0.13 |
| WOLG | y = 7.901x + 2.346 | 1.803 | 9.645 | 0.999 | 6.62 ± 0.00 |
| WOLS | y = 7.484x + 5.815 | 1.949 | 10.327 | 0.994 | 5.90 ± 0.02 |
| Oleuropein | HT | HT Hexoside | Apigenin-7-O-glucoside | Verbascoside | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH· | 0.418 | −0345 | −0.244 | 0.25 | 0.653 ** |
| ABTS·+ | 0.669 ** | −0.600 * | −0.399 | −0.089 | 0.702 ** |
| TPC | 0.649 ** | −0.453 | −0.805 ** | 0.294 | 0.101 |
| Genotypes | EC5015 (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| ‘Picual’ | 20.9 ± 4.5 c |
| ‘Arbequina’ | 13.9 ± 3.4 c |
| ‘Koroneiki’ | 11.8 ± 1.1 c |
| ‘Kalamon’ | 69.1 ± 7.9 a |
| WOLG | 45.2 ± 12.5 b |
| WOLS | 82.5 ± 1.0 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Navarro, M.E.; Kaparakou, E.H.; Kanakis, C.D.; Cebrián-Tarancón, C.; Alonso, G.L.; Salinas, M.R.; Tarantilis, P.A. Quantitative Determination of the Main Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity of Aqueous Extracts of Olive Leaves of Greek and Spanish Genotypes. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010055
Martínez-Navarro ME, Kaparakou EH, Kanakis CD, Cebrián-Tarancón C, Alonso GL, Salinas MR, Tarantilis PA. Quantitative Determination of the Main Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity of Aqueous Extracts of Olive Leaves of Greek and Spanish Genotypes. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Navarro, María Esther, Eleftheria H. Kaparakou, Charalabos D. Kanakis, Cristina Cebrián-Tarancón, Gonzalo L. Alonso, María Rosario Salinas, and Petros A. Tarantilis. 2023. "Quantitative Determination of the Main Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity of Aqueous Extracts of Olive Leaves of Greek and Spanish Genotypes" Horticulturae 9, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010055
APA StyleMartínez-Navarro, M. E., Kaparakou, E. H., Kanakis, C. D., Cebrián-Tarancón, C., Alonso, G. L., Salinas, M. R., & Tarantilis, P. A. (2023). Quantitative Determination of the Main Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity of Aqueous Extracts of Olive Leaves of Greek and Spanish Genotypes. Horticulturae, 9(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010055







