Genome-Wide Identification, Cloning and Expression Profile of RanBP2-Type Zinc Finger Protein Genes in Tomato
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth Conditions and Hormone and Stress Treatments
2.2. The qRT-PCR
2.3. Identification and Cloning of SlRBZ Genes
2.4. Gene Structure, Conserved Motifs and Cis-Regulatory Elements of SlRBZ Genes
2.5. Phylogenetic Tree and Duplication Event of SlRBZ Genes
2.6. RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Isolation of the SlRBZ Genes in Tomato
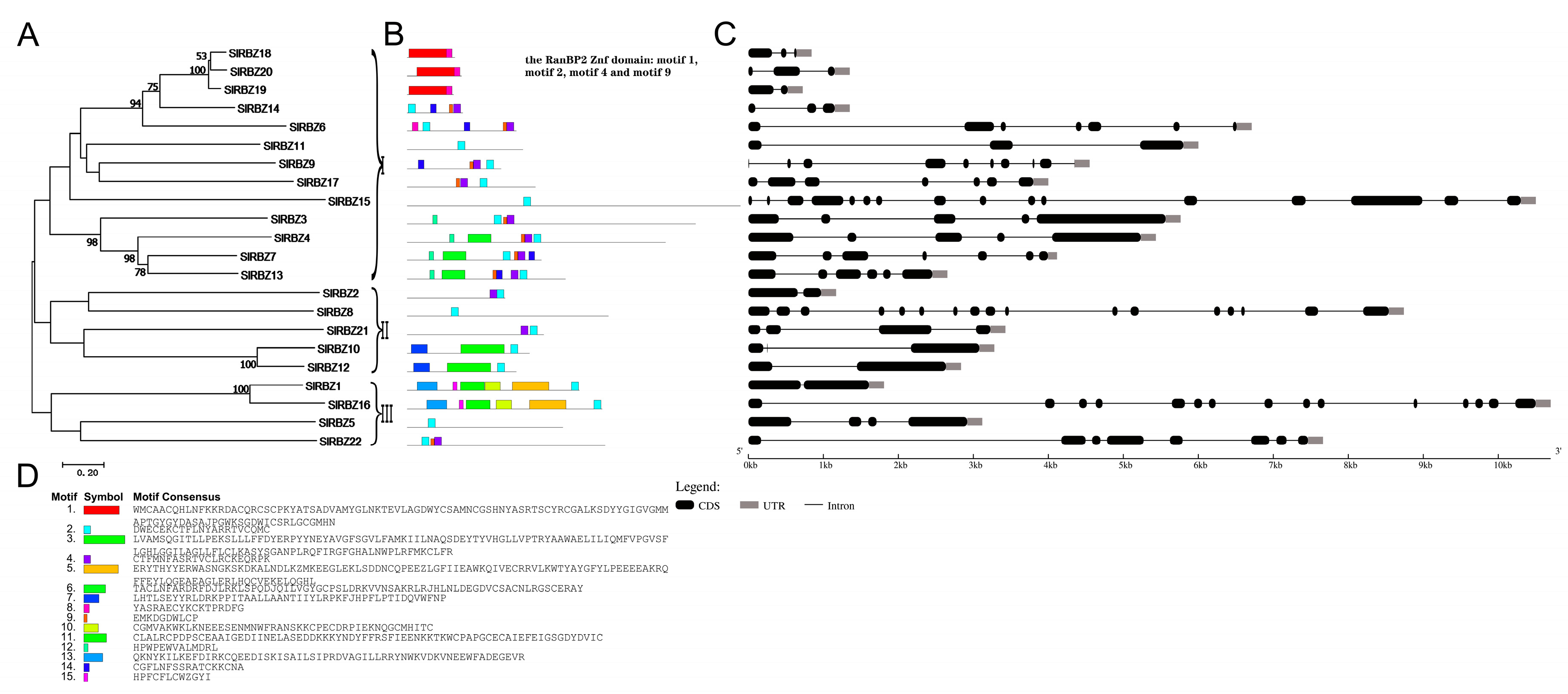
3.2. Multiple Sequence Alignments and Gene Structure of SlRBZ Genes
3.3. Conserved Motif Identification of SlRBZ Proteins
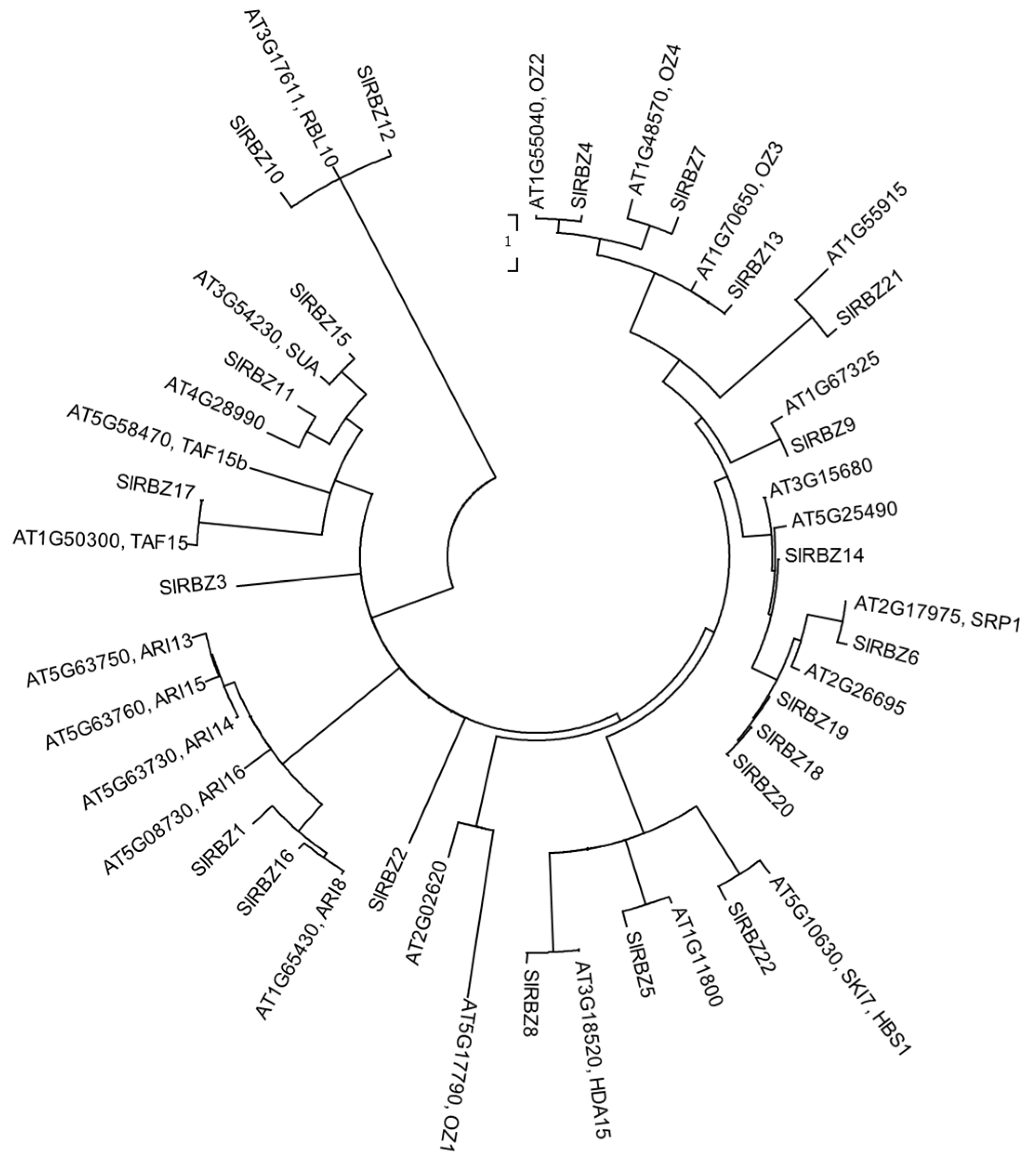
3.4. Evolutionary Relationships and Gene Duplication of the SlRBZ Family Members
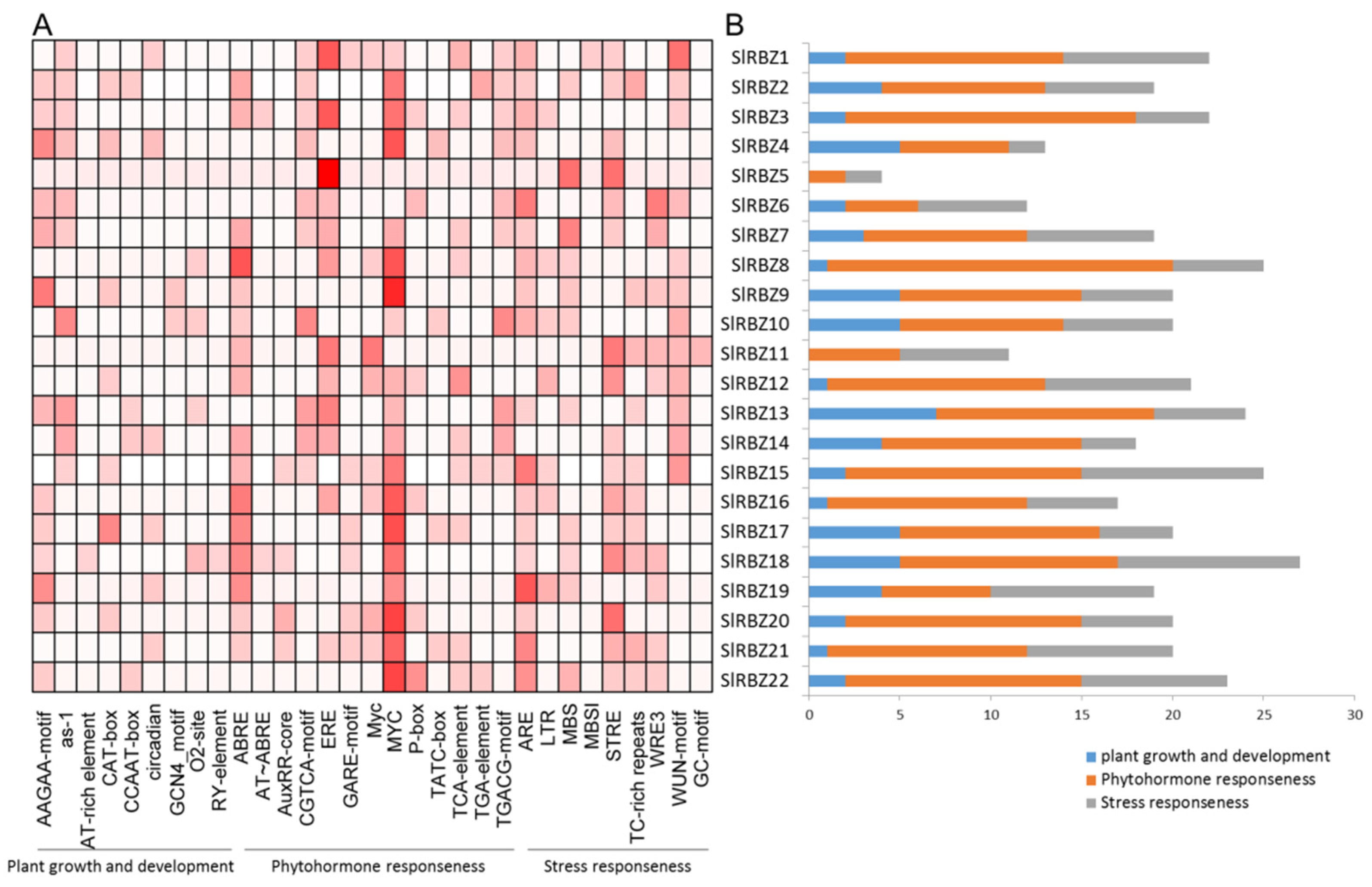
3.5. Cis-Regulatory Elements in the Promoter Regions of SlRBZ Genes
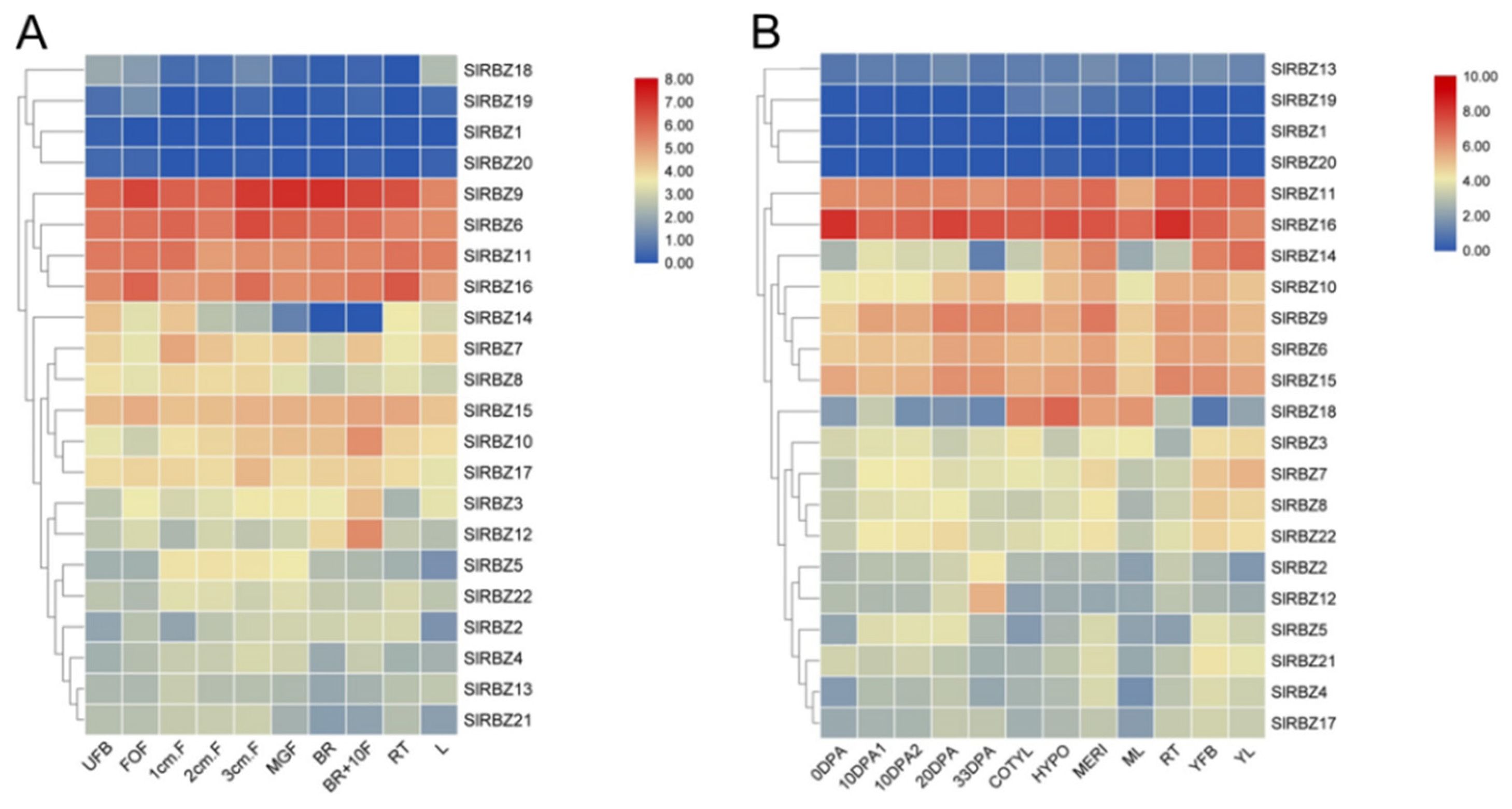
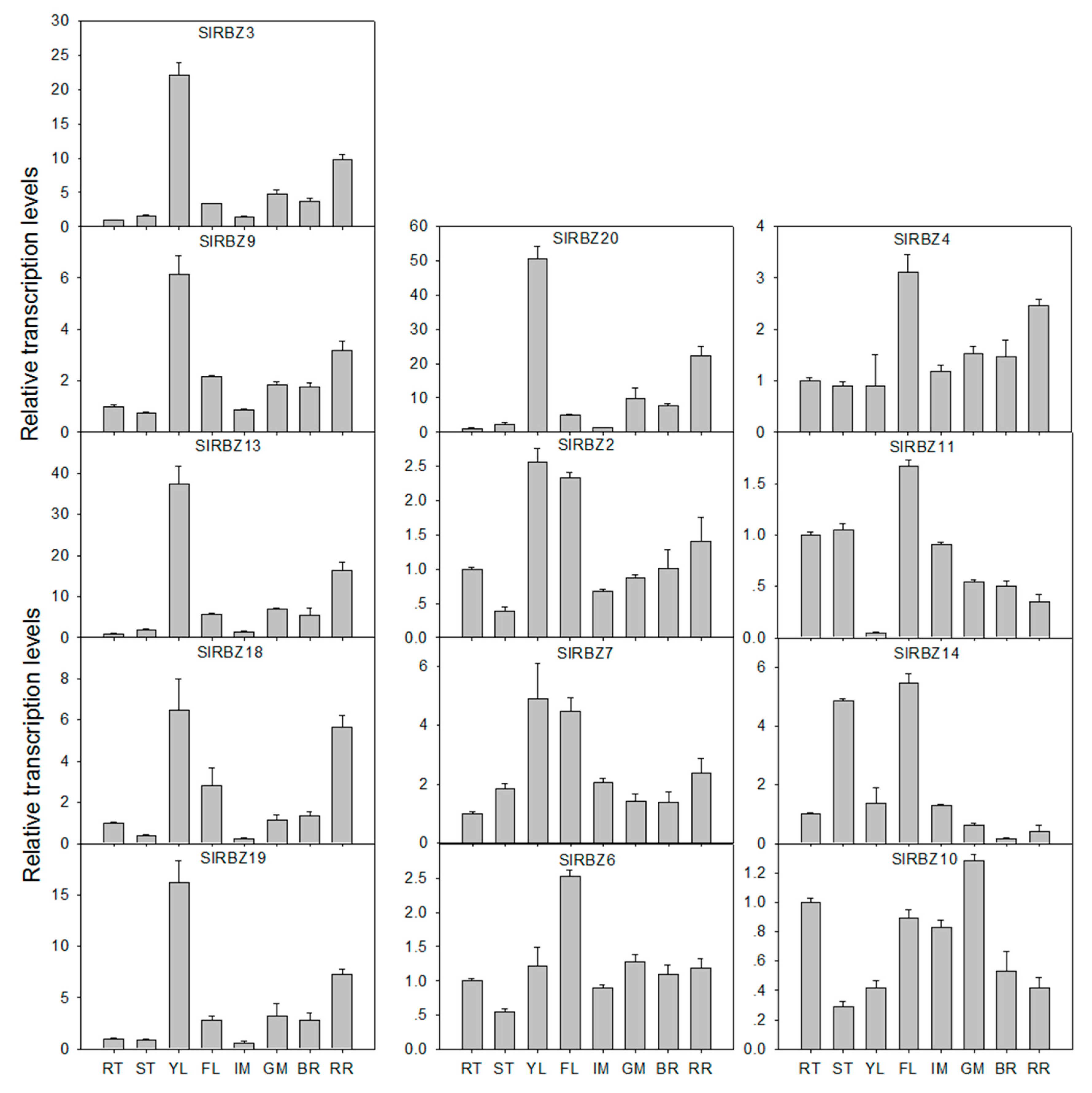
3.6. Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of SlRBZ Genes
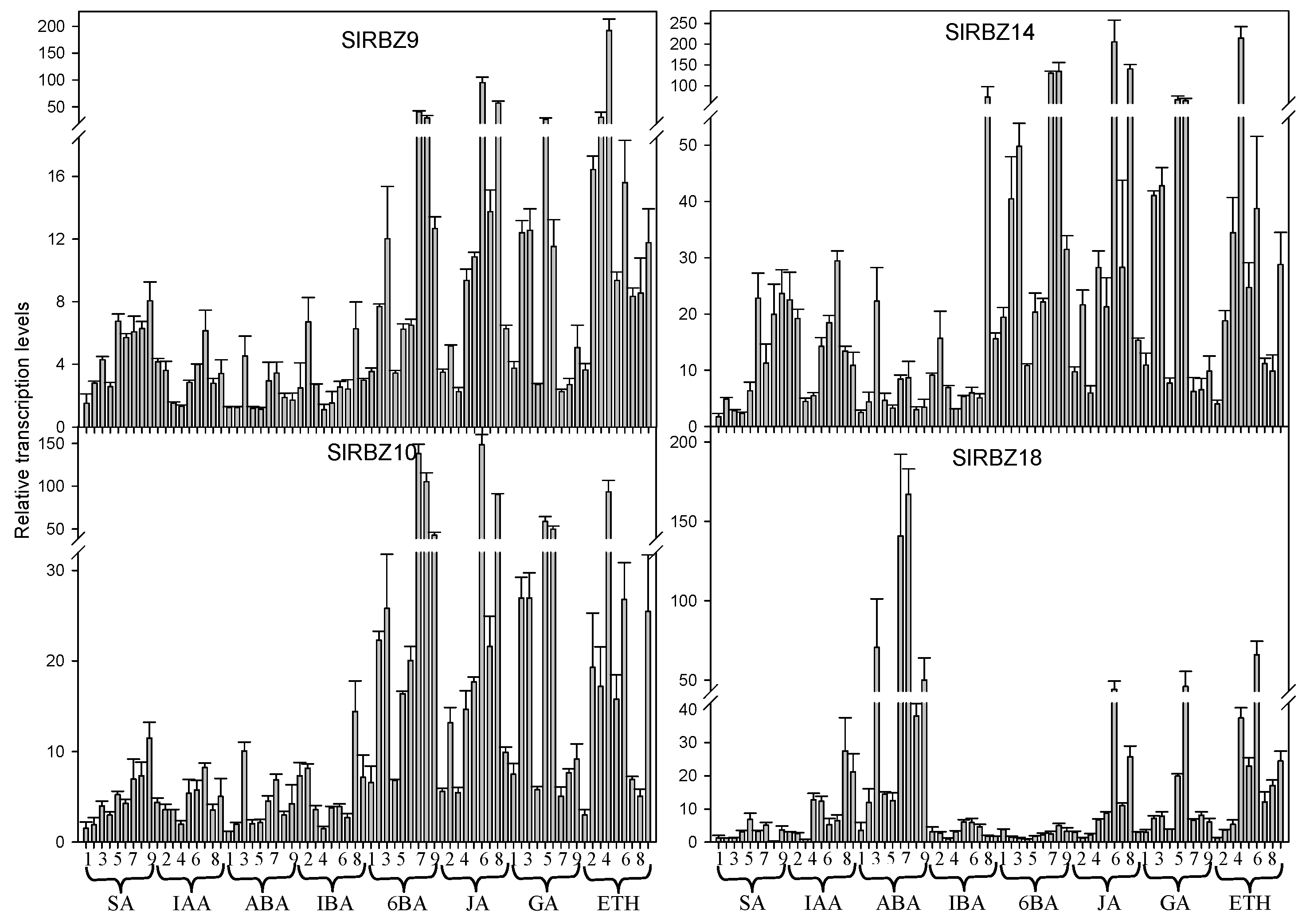
3.7. Expression Pattern of SlRBZ Genes under Different Phytohormones
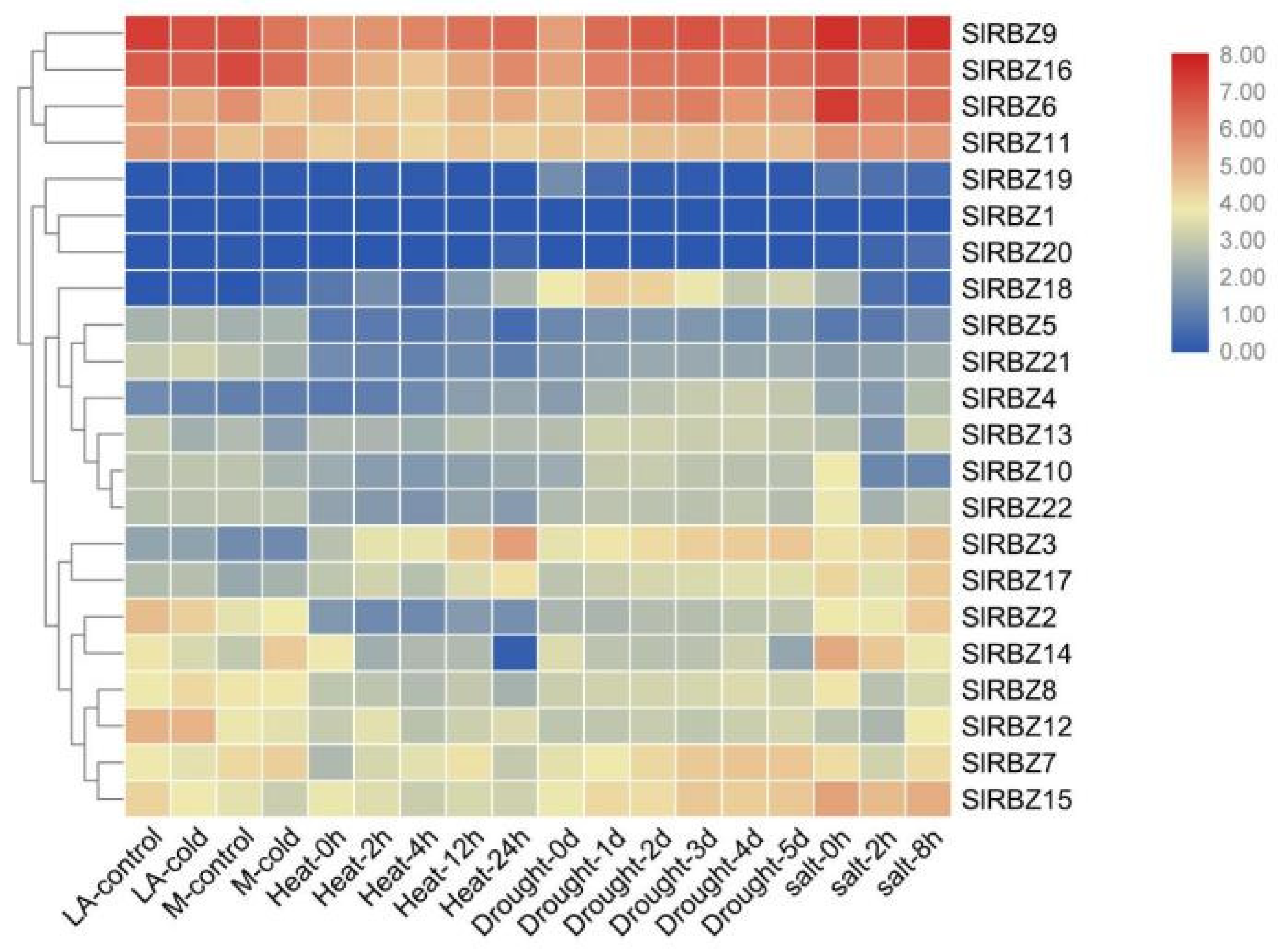
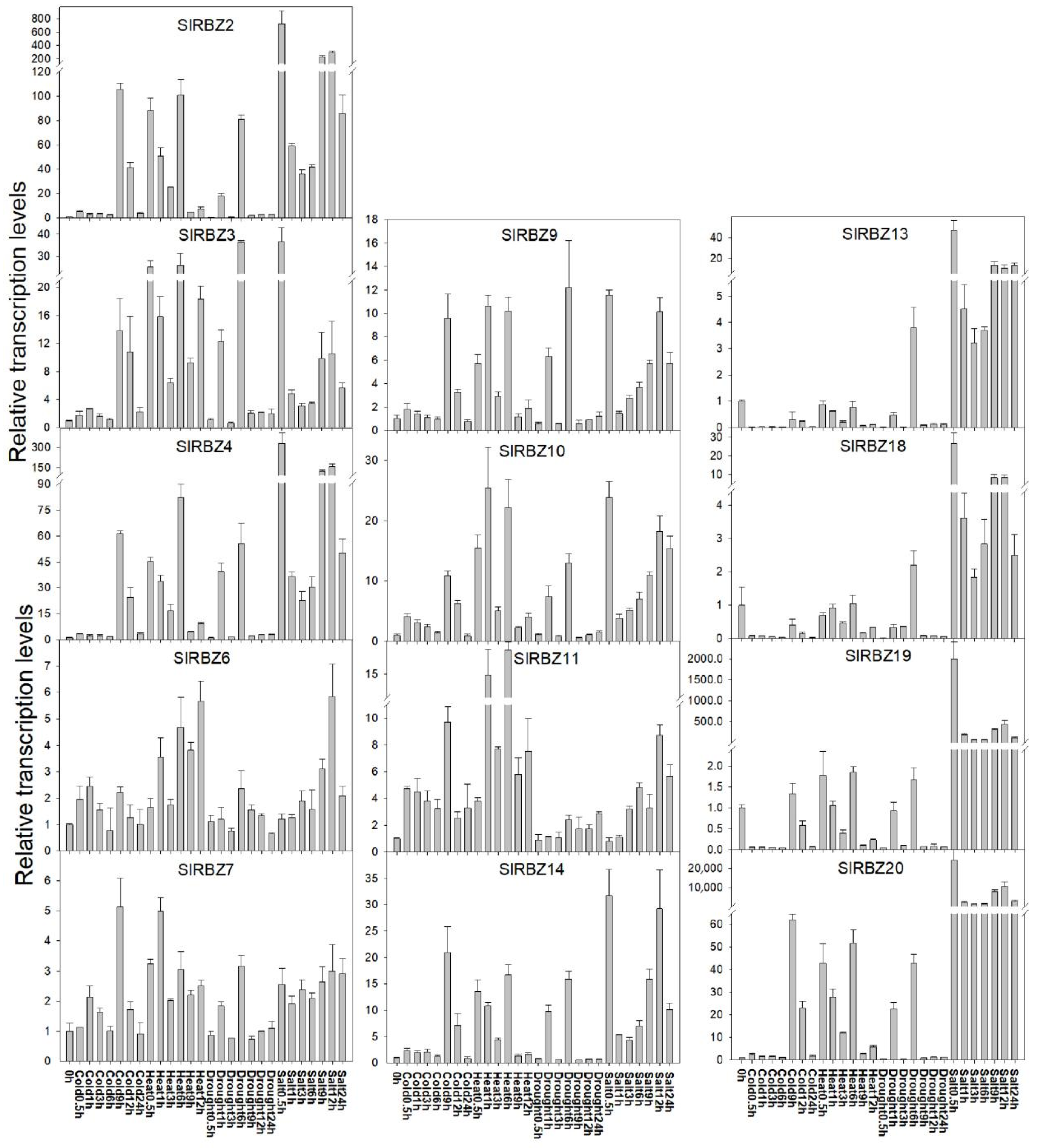
3.8. Expression Characteristics of the SlRBZ Genes under Various Abiotic Stresses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laity, J.H.; Lee, B.M.; Wright, P.E. Zinc finger proteins: New insights into structural and functional diversity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.B.; Patel, H.H.; Roepman, R.; Schick, D.; Ferreira, P.A. The zinc finger cluster domain of RanBP2 is a specific docking site for the nuclear export factor, Exportin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37370–37378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2020, 48, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.D.; Mansfield, R.E.; Leung, W.; Vaz, P.M.; Loughlin, F.E.; Grant, R.P.; Mackay, J.P. Characterization of a Family of RanBP2-Type Zinc Fingers that Can Recognize Single-Stranded RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 407, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Lee, I. TAF15b, involved in the autonomous pathway for flowering, represses transcription of FLOWERING LOCUS C. Plant J. 2018, 93, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Gao, S.; Ren, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Ye, Z. Overexpression of SlRBZ results in chlorosis and dwarfism through impairing chlorophyll, carotenoid, and gibberellin biosynthesis in tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, K.C.; Luo, M.; Tai, R.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, M.; Yang, S.; Tian, G.; Cui, Y.; et al. Phytochrome Interacting FACTOR3 Associates with the histone deacetylase HDA15 in repression of chlorophyll biosynthesis and photosynthesis in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1258–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugliani, M.; Brambilla, V.; Clerkx, E.J.M.; Koornneef, M.; Soppe, W.J.J. The conserved splicing factor SUA controls alternative splicing of the developmental regulator ABI3 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.A.; Li, B.; Ni, X.M.; Xie, Y.F.; Cai, Y.F. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a RanBP2 zinc finger protein gene in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 55, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipson, A.B.; Giloteaux, L.; Hanson, M.R.; Bentolila, S. Arabidopsis RanBP2-Type Zinc Finger Proteins Related to Chloroplast RNA Editing Factor OZ1. Plants 2020, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Shi, X.; Friso, G.; Van Wijk, K.; Bentolila, S.; Hanson, M.R. A zinc finger motif-containing protein is essential for chloroplast RNA editing. PLOS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Sodmergen. Arabidopsis mitochondrial protein slow embryo development is essential for embryo development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentolila, S.; Gipson, A.B.; Kehl, A.J.; Hamm, L.N.; Hayes, M.L.; Michael, M.R.; Hanson, M.R. A RanBP2-type zinc finger protein functions in intron splicing in Arabidopsis mitochondria and is involved in the biogenesis of respiratory complex I. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3490–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf, R.R.; Adam, Z. Rhomboid proteases in plants—Still in square one? Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Seo, P.J. MYB96 recruits the HDA15 protein to suppress negative regulators of ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lei, T.; Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, Y.; Guérard, F.; Issakidis-Bourguet, E.; Zhou, D.X. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA15 directly represses plant response to elevated ambient temperature. Plant J. 2019, 100, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Tomato Genome Consortium. The Tomato Genome Sequence Provides Insights into Fleshy Fruit Evolution. Nature 2012, 485, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causse, M.; Desplat, N.; Pascual, L.; Le Paslier, M.-C.; Sauvage, C.; Bauchet, G.; Bérard, A.; Bounon, R.; Tchoumakov, M.; Brunel, D.; et al. Whole genome resequencing in tomato reveals variation associated with introgression and breeding events. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lun, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into the history of tomato breeding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gonda, I.; Sun, H.; Ma, Q.; Bao, K.; Tieman, D.M.; Burzynski-Chang, E.A.; Fish, T.L.; Stromberg, K.A.; Sacks, G.L.; et al. The tomato pan-genome uncovers new genes and a rare allele regulating fruit flavor. Nat Genet. 2019, 51, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, S.; Xiong, C.; Yu, G.; Chang, J.; Ye, Z.; Yang, C. Comprehensive analysis and expression profile of the homeodomain leucine zipper IV transcription factor family in tomato. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2015, 96, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ouyang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Lu, C.; Han, Q.; Zhao, S.; Ye, Z.; Li, H. Genomic organization, phylogenetic comparison and expression profiles of annexin gene family in tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum). Gene 2012, 499, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-DeltaC(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van De Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.A.; Haubold, B.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Comparative evolutionary analysis of chalcone synthase and alcohol dehydrogenase loci in arabidopsis, arabis, and related genera (Brassicaceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. KaKs_calculator 3.0: Calculating selective pressure on coding and non-coding sequences. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 3, S1672-0229(21)00259-X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamsjaeger, R.; Liew, C.K.; Loughlin, F.E.; Crossley, M.; Mackay, J.P. Sticky fingers: Zinc-fingers as protein-recognition motifs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higa, M.M.; Alam, S.L.; Sundquist, W.I.; Ullman, K.S. Molecular characterization of the Ran-binding zinc finger domain of Nup153. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17090–17100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Deng, C.K.; Wang, M.; Deng, B.; Barber, R.; Huang, G. Identification of novel alternative splicing biomarkers for breast cancer with LC/MS/MS and RNA-Seq. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinsug, M.V.; Chen, F.F.; Luo, M.; Tai, R.; Jiang, L.; Wu, K. Subcellular localization of Class II HDAs in Arabidopsis thaliana: Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HDA15 is driven by light. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.S.; Sintaha, M.; Cheung, M.Y.; Lam, H.M. Plant Hormone Signaling Crosstalks between Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Annotated CDS | Gene Start (bp) | Gene End (bp) | Strand | the Number of RBZ Domains | Exon | ORF * | CDS * | AA * | PIS * | MW * | GRAVY | Domains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlRBZ1 | Solyc01g005650 | 455379 | 456988 | −1 | 1 | 2 | 1610 | 1569 | 523 | 5.36 | 61478.64 | −0.709 | RBZ, IBR domain |
| SlRBZ2 | Solyc01g044350 | 43255687 | 43259371 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 969 | 894 | 298 | 9.12 | 31513.46 | −0.432 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ3 | Solyc01g057780 | 63862862 | 63868831 | −1 | 2 | 5 | 5564 | 2625 | 875 | 6.99 | 97971.39 | −0.723 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ4 | Solyc01g099230 | 89530334 | 89535887 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5233 | 2352 | 784 | 6.66 | 89729.05 | −1.11 | RBZ, MSCRAMM_SdrC super family |
| SlRBZ5 | Solyc02g032870 | 29438970 | 29441887 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2707 | 1419 | 473 | 7.97 | 52898.98 | −0.351 | RBZ, TDP2 |
| SlRBZ6 | Solyc03g033560 | 5104384 | 5111275 | −1 | 4 | 7 | 6510 | 996 | 332 | 9.01 | 36450.1 | −0.63 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ7 | Solyc03g118680 | 67538264 | 67542652 | −1 | 3 | 7 | 3994 | 1224 | 408 | 8.94 | 46033.82 | −0.555 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ8 | Solyc03g119730 | 68283528 | 68292067 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 8326 | 1833 | 611 | 5.34 | 66410.65 | −0.274 | RBZ, HDAC_classII |
| SlRBZ9 | Solyc05g015500 | 10760271 | 10764983 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 4350 | 858 | 286 | 9.14 | 30923.51 | −0.859 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ10 | Solyc05g016380 | 16034731 | 16038070 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3078 | 1116 | 372 | 8.46 | 42409.01 | 0.156 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ11 | Solyc05g018340 | 20573843 | 20579911 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5800 | 1056 | 352 | 10.87 | 39607.39 | −1.519 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ12 | Solyc07g042930 | 56485757 | 56488391 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2125 | 996 | 332 | 9.82 | 37398.51 | 0.057 | RBZ, Rhomboid |
| SlRBZ13 | Solyc08g014510 | 4645215 | 4647952 | −1 | 3 | 6 | 2452 | 1443 | 481 | 8.46 | 55095.32 | −0.756 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ14 | Solyc08g067180 | 56155346 | 56156822 | −1 | 3 | 3 | 878 | 513 | 171 | 8.71 | 18130.78 | −0.782 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ15 | Solyc08g077310 | 61209403 | 61219976 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 10300 | 3033 | 1011 | 7.96 | 111526.92 | −0.983 | RBZ, RRM, OCRE domain, G_patch |
| SlRBZ16 | Solyc11g008580 | 2764823 | 2775320 | −1 | 1 | 15 | 10498 | 1776 | 592 | 5.21 | 66955.47 | −0.659 | RBZ, Ring finger |
| SlRBZ17 | Solyc11g040050 | 40024447 | 40028245 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3799 | 1170 | 390 | 8.62 | 43070.15 | −1.155 | RBZ, RRM_SARFH |
| SlRBZ18 | Solyc12g006590 | 1079645 | 1080287 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 643 | 438 | 146 | 8.20 | 16061.15 | −0.537 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ19 | Solyc12g006600 | 1083786 | 1084309 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 524 | 426 | 142 | 8.4 | 15446.45 | −0.472 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ20 | Solyc12g011060 | 3931559 | 3932709 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1151 | 498 | 166 | 8.61 | 18535.23 | −0.41 | RBZ |
| SlRBZ21 | Solyc12g015660 | 5655855 | 5659081 | −1 | 2 | 4 | 3227 | 1245 | 415 | 8.7 | 45811.89 | −0.626 | RBZ, WLM domain |
| SlRBZ22 | Solyc12g036410 | 52193551 | 52201012 | −1 | 2 | 8 | 7462 | 1803 | 601 | 8.59 | 65495.48 | −0.168 | RBZ, translation elongation factor EF-1a (GTPase) |
| Gene1 | Gene2 | Ks | Ka | Ka/Ks | Date (Mya) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlRBZ1 | SlRBZ16 | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3 | 31.6 |
| SlRBZ10 | SlRBZ12 | 2.09 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 69.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Li, N.; Ruan, J.; Li, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, C. Genome-Wide Identification, Cloning and Expression Profile of RanBP2-Type Zinc Finger Protein Genes in Tomato. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8110985
Gao Y, Li N, Ruan J, Li Y, Liao X, Yang C. Genome-Wide Identification, Cloning and Expression Profile of RanBP2-Type Zinc Finger Protein Genes in Tomato. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(11):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8110985
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yanna, Ning Li, Jiaojiao Ruan, Ying Li, Xiaoli Liao, and Changxian Yang. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification, Cloning and Expression Profile of RanBP2-Type Zinc Finger Protein Genes in Tomato" Horticulturae 8, no. 11: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8110985
APA StyleGao, Y., Li, N., Ruan, J., Li, Y., Liao, X., & Yang, C. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification, Cloning and Expression Profile of RanBP2-Type Zinc Finger Protein Genes in Tomato. Horticulturae, 8(11), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8110985






