Phosphoric Acid and Magnesium Chloride Composite-Modified Biochar Improved Pakchoi Growth by Reducing Pb and Cd Accumulation and Altering Soil Properties and Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection and Biochar Preparation
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Growth Parameters and Pb and Cd Contents in Pakchoi
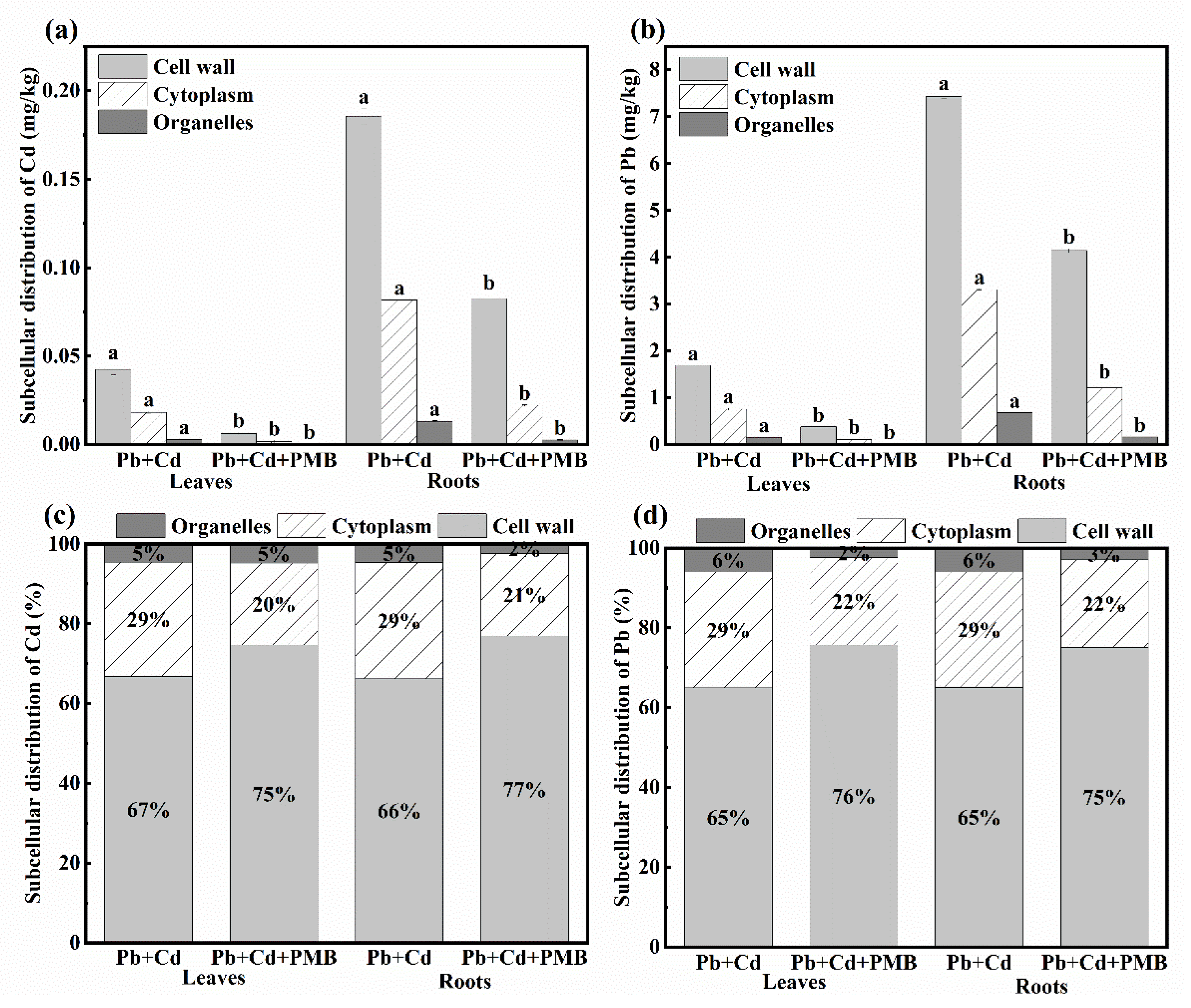
2.4. Pb and Cd Subcellular Distribution in Pakchoi
2.5. Determination of Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Available Content of Heavy Metal
2.6. Microbial Community Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PMB Characterization
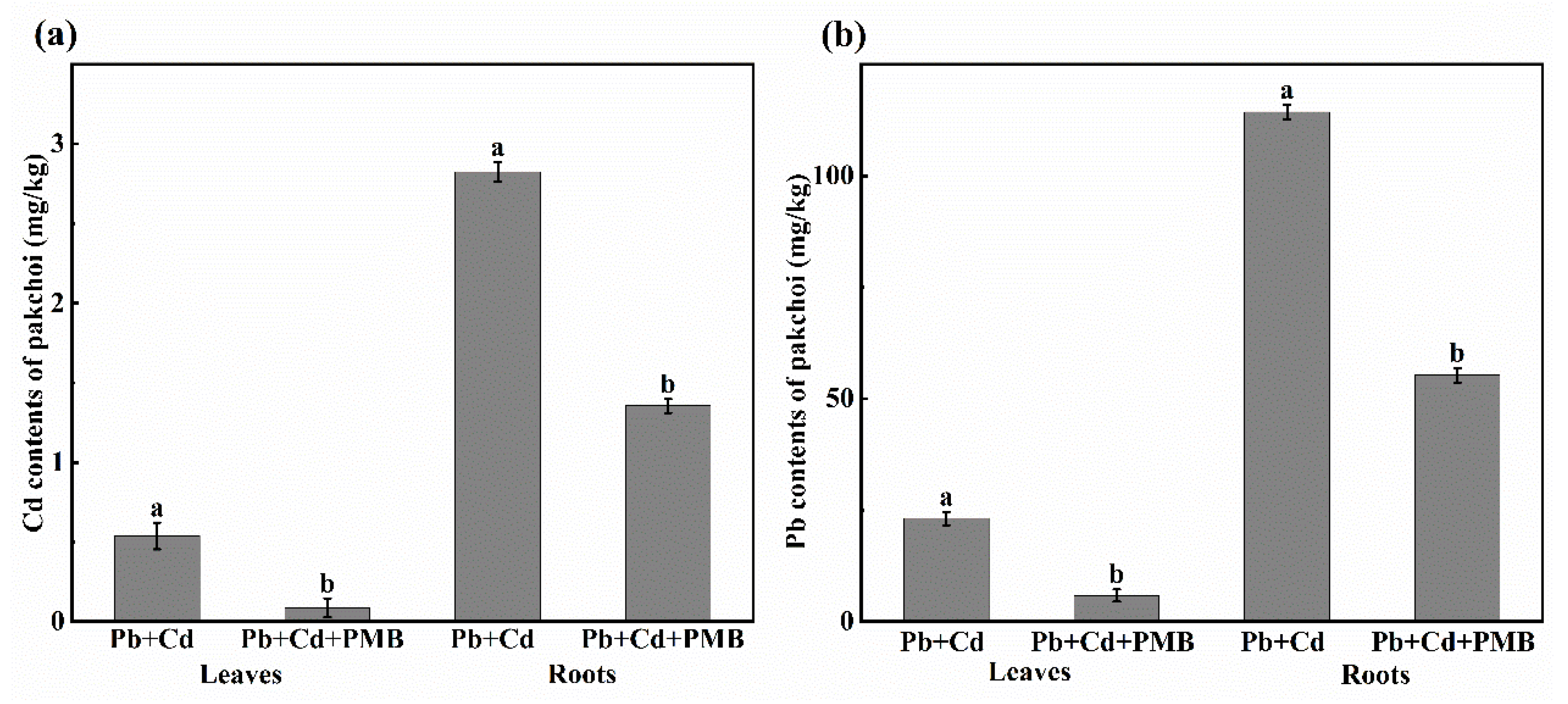
3.2. Effect of PMB on the Growth, Contents, and Subcellular Distribution of Cd and Pb of Pakchoi
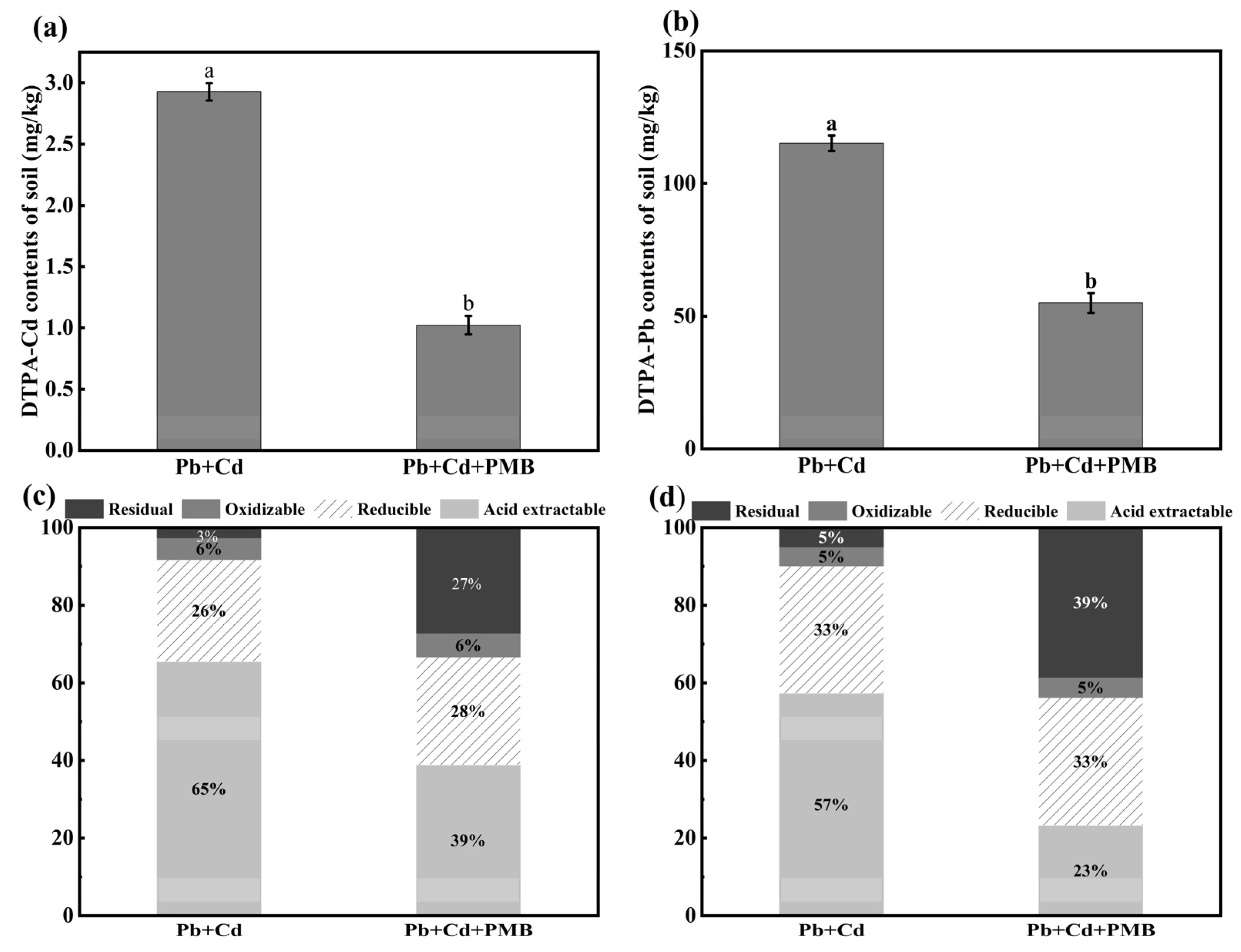
3.3. Effects of PMB on Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, Cd and Pb Contents, and Their Chemical Speciation
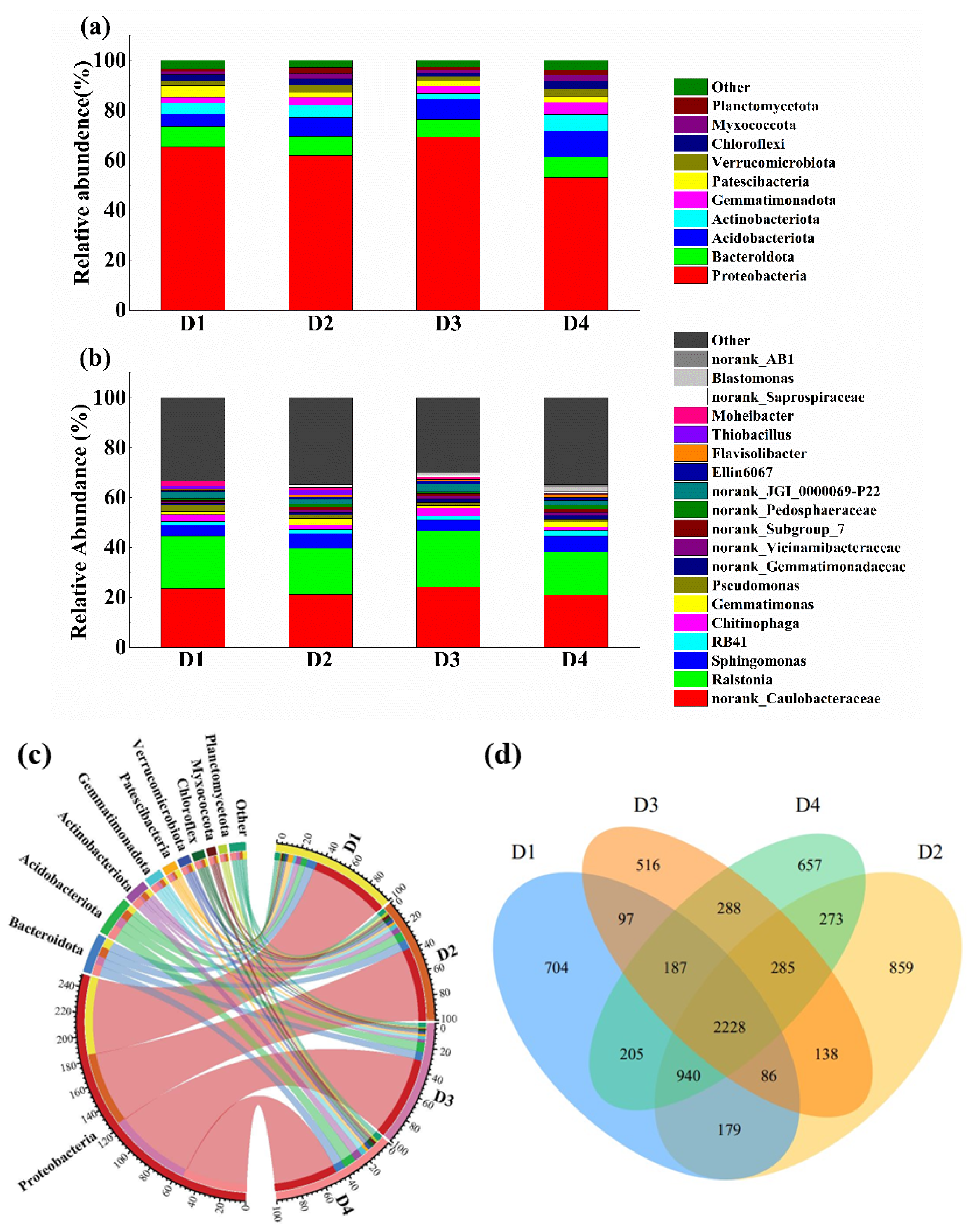
3.4. Effects of PMB on Soil Bacterial Communities
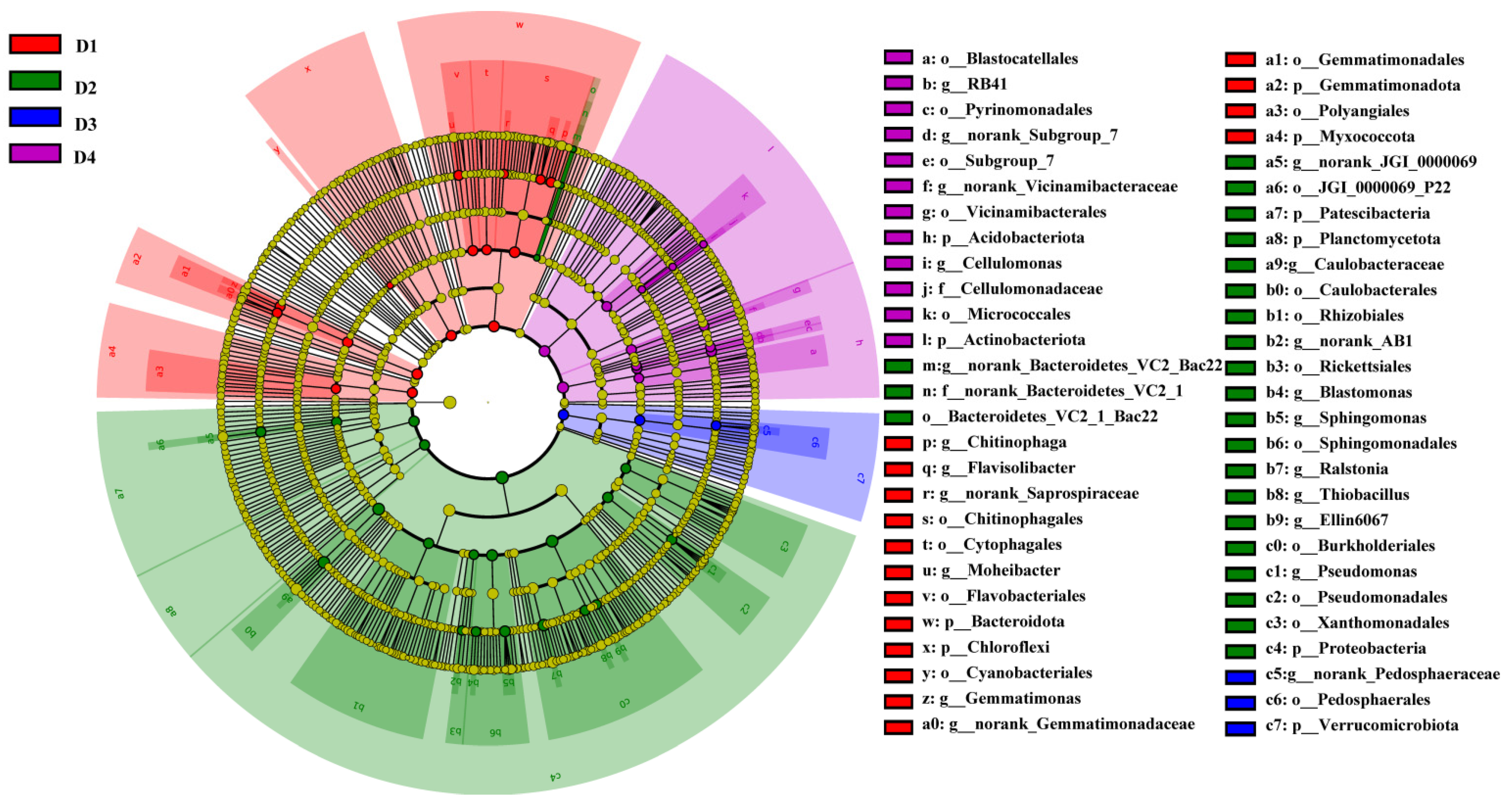
3.4.1. Soil Bacterial Community Composition
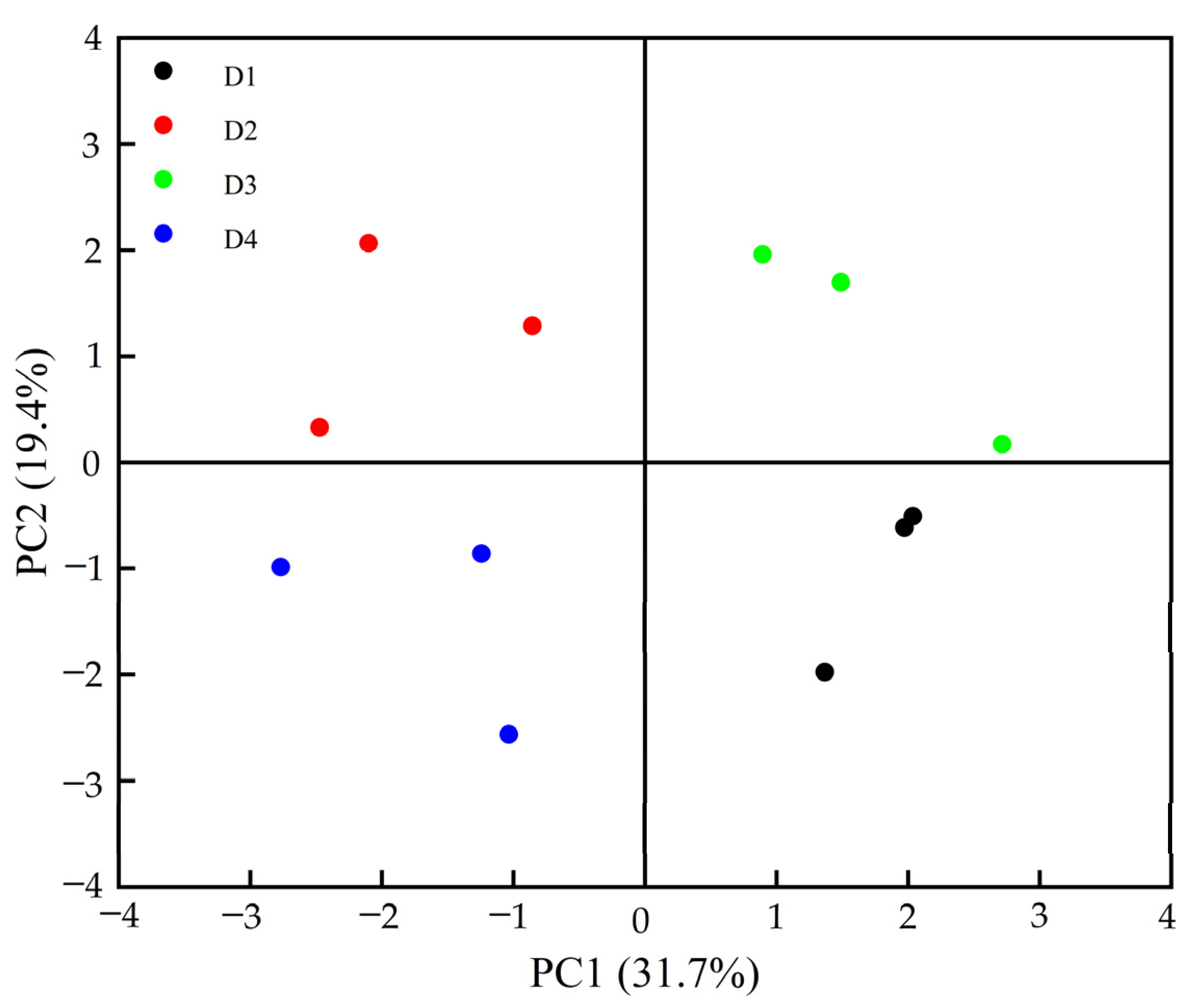
3.4.2. Alpha and Beta Analyses of Soil Bacterial Community
3.4.3. Correlation Analysis and LEFse Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Xue, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wei, Q.; Han, C.; He, J. Preparation of biochar by mango peel and its adsorption characteristics of Cd(II) in solution. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35878–35888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Hu, C.; Jia, X.; Ren, Y.; Su, D.; He, J. Physiological and biochemical bases of spermidine-induced alleviation of cadmium and lead combined stress in rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 189, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Ren, Y.F.; Han, C.; Zhu, W.J.; Gu, J.Y.; He, J.Y. Application of exogenous glycinebetaine alleviates lead toxicity in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) by promoting antioxidant enzymes and suppressing Pb accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25568–25580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Ren, Y.; Lin, D.; Tong, M.; Yang, B.; Xiao, F.; Hou, Y.; Lu, Y.; He, J. Green preparation of bimetallic CuO/ZnO nanoparticles by using Cinnamomum camphora leaf and its potential for antifungal and cadmium removal applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 178, 114577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Dong, Y.Q.; Li, J.H.; Li, S.Y.; Feng, L.; Hou, H.B. Stabilization and passivation of multiple heavy metals in soil facilitating by pinecone-based biochar: Mechanisms and microbial community evolution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algethami, J.S.; Irshad, M.K.; Javed, W.; Alhamami, M.A.M.; Ibrahim, M. Iron-modified biochar improves plant physiology, soil nutritional status and mitigates Pb and Cd-hazard in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1221434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Franks, A.; Xu, J.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Tang, C. Chemical and biological immobilization mechanisms of potentially toxic elements in biochar-amended soils. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 903–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Ain, N.; Khan, I.; Farooq, M.; Habiba Cai, L.; Li, Y. Co-application of biochar and plant growth regulators improves maize growth and decreases Cd accumulation in cadmium-contaminated soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 140515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; Dai, W.J.; Zhao, Z.L.; Zheng, J.T.; Huang, F.; Mei, C.; Huang, S.T.; Liu, C.F.; Wang, P.; Xiao, R.B. Effect of rice straw biochar on three different levels of Cd-contaminated soils: Cd availability, soil properties, and microbial communities. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, F.R.; Manikandan, S.K.; Nair, V. Role of coconut shell biochar and earthworm (Eudrilus euginea) in bioremediation and palak spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) growth in cadmium-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, R.K.; Huang, Q.; Hashimi, R.; Komatsuzaki, M. Enhancing agroecosystem sustainability: Integrative soil health strategies in regenerative organic soybean production on Andosol in Japan. Geoderma Reg. 2025, 40, e00910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, S.; Wu, J.; Yi, X.; Dai, G.; Shu, Y. Three-year field experiments revealed the immobilization effect of natural aging biochar on typical heavy metals (Pb, Cu, Cd). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Pu, S.; He, L.; Ma, H.; Hou, D. Biochar induced modification of graphene oxide & nZVI and its impact on immobilization of toxic copper in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Sun, X.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, C.; Tan, Q. The role of phosphorus speciation of biochar in reducing available Cd and phytoavailability in mining area soil: Effect and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Effect of phosphorus-modified biochars on immobilization of Cu(II), Cd(II), and As(V) in paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Peng, H.B.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, B.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Phosphoric acid pretreatment enhances the specific surface areas of biochars by generation of micropores. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechapanya, W.; Khamwichit, A. Biosorption of aqueous Pb(II) by H3PO4-activated biochar prepared from palm kernel shells (PKS). Heliyon 2023, 9, e17250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherway, P.; Reichman, S.M.; Laidlaw, M.; Scheckel, K.; Pingitore, N.; Gasćo, G.; Méndez, A.; Surapaneni, A.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Phosphorus-rich biochars can transform lead in an urban contaminated soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ke, S.; Xia, M.; Bi, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H. Effects of phosphorous precursors and speciation on reducing bioavailability of heavy metal in paddy soil by engineered biochars. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Synergistic effects of phosphoric acid modified hydrochar and coal gangue-based zeolite on bioavailability and accumulation of cadmium and lead in contaminated soil. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 46, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Yagcioglu, K.D.; Kadioglu, Y.K.; Gunes, A. The importance of acidified biochar as a sustainable phosphorus source and its role in balanced nutrition for spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutri. 2024, 24, 8035–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Munir Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Faraj, A.S.; Ahmad Mahtab Sallam, A.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Phosphorus-loaded biochar changes soil heavy metals availability and uptake potential of maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrooz, B.A.; Oustan, S.; Hosseini, H.M.; Etesami, H.; Padoan, E.; Magnacca, G.; Marsan, F.A. The importance of presoaking to improve the efficiency of MgCl2-modified and non-modified biochar in the adsorption of cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Ni, F.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ao, T.; Chen, W. Synthesis of magnesium modified biochar for removing copper, lead and cadmium in single and binary systems from aqueous solutions: Adsorption mechanism. Water 2021, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X. Effects of Mg-modified biochar on the bioavailability of cadmium in soil. BioResources 2020, 15, 8008–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Wu, D.; Li, Q.; Ai, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. EDTA functionalized Mg/Al hydroxides modified biochar for Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Ali, A.; Jeyasundar, P.G.S.A.; Li, Y.M.; Abdelrahman, H.; Latif, A.; Li, R.H.; Basta, N.; Li, G.; Shaheen, S.M.; et al. Bone-derived biochar improved soil quality and reduced Cd and Zn phytoavailability in a multi-metal contaminated mining soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Yuan, Y.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, L.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, H.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Y. Stabilization of lead and cadmium in soil by sulfur-iron functionalized biochar: Performance, mechanisms and microbial community evolution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Li, T.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, R. Influences of modified biochar on metal bioavailability, metal uptake by wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) and the soil bacterial community. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, C.; Wnag, S.; Zhao, C.; Yin, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, R.; Wang, X. Remediation of lead and cadmium co-contaminated mining soil by phosphate-functionalized biochar: Performance, mechanism, and microbial response. Chemosphere 2023, 334, 138938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, M.; Ren, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, W.; Song, Y.; He, J.Y. Characterization of pruned tea branch biochar and the mechanisms underlying its adsorption for cadmium in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26832–26843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.J.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, T.Y.; Jia, X.W.; Lu, D.D.; Ren, Y.F.; He, J.Y. Enhanced removal efficiency of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solution by H3PO4-modified tea branch biochar: Characterization, adsorption performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.F.; Wang, W.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Yang, M. Nitric oxide alleviates salt stress in seed germination and early seedling growth of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) by enhancing physiological and biochemical parameters. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 15618-2018; China: National Standard Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. USDA: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Li, L.; Bao, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Cheng, K.; Pan, G. Cd immobilization in a contaminated rice paddy by inorganic stabilizers of calcium hydroxide and silicon slag and by organic stabilizer of biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10028–10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.M.; Wang, M.F.; Xu, H.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Hu, Q.F.; Ren, Y.F.; He, J.Y. Performance and mechanism of Ficus carica branch waste based biochar in removing Cd2+ from aqueous solution. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2024, 14, 24137–24150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigal, H.J. Jager HJ. Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cadmium in bean. Plant Physiol. 1980, 65, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ren, Y.F.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z. Impact of copper oxide nanoparticles on the germination, seedling growth, and physiological responses in Brassica pekinensis L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31505–31515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidpour, M.; Sadeghi, R.; Abbaszadeh-Dahaji, P.; Alaei, H.; Shafigh, M.; Omidvari, M.; Kariman, K. The effects of EDTA and Trichoderma species on growth and Cu uptake of maize (Zea mays) plants grown in a Cu-contaminated soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Sun, J.; Pan, G.; Qi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J.; Gao, Y. Ball-milling-modified biochar with additives enhances soil Cd passivation, increases plant growth and restrains Cd uptake by chinese cabbage. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Ran, Z.F.; Li, R.; Duan, W.Y.; Song, Z.J.; Fang, L.; Guo, L.P.; Zhou, J. Biochar reduces the cadmium content of Panax quinquefolium L. by improving rhizosphere microecology. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, T.Y.; Lu, Y.Q.; Li, F.; Zeng, W.M.; Shen, L.; Yu, R.L.; Li, J.K. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by regulating cadmium uptake, subcellular distribution and triggering the expression of stress-related genes. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Mustafa, S.K.; Ditta, A.; Hessini, K. Diminishing heavy metal hazards of contaminated soil via biochar supplementation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ming, C.S.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, Y. Amended compost alleviated the stress of heavy metals to pakchoi plants and affected the distribution of heavy metals in soil-plant system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Gou, J.L.; Chen, X.M.; Xiao, S.Q.; Ali, I.; Shang, R.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.W.; Han, M.W.; Luo, X.G. Application of mixed bacteria-loaded biochar to enhance uranium and cadmium immobilization in a co-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Sheng, Y.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, X.Z. Efficacy and microbial responses of biochar- nanoscale zero-valent during in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated sediment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Hussain, Q.; Zhu, J.; Fu, Q.L.; Houben, D.; Hu, H.Q. Efficiency of KOH- modified rice straw-derived biochar for reducing cadmium mobility, bioaccessibility and bioavailability risk index in red soil. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondek, K.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Jarose, R. Effect of willow biochar and fly ash-derived zeolite in immobilizing heavy metals and promoting enzymatic activity in a contaminated sandy soil. Catena 2023, 232, 107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wen, E.; Ge, C.; El-Naggar, A.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.S.; Kwon, E.E.; Song, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Wang, H.L.; et al. Iron-modified phosphorus- and silicon-based biochars exhibited various influences on arsenic, cadmium, and lead accumulation in rice and enzyme activities in a paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, M.; Ciriello, M.; Rouphael, Y.; Campana, E.; Vaccari, F.P.; De Pascale, S. Harnessing biochar for sustainable horticulture: Strategies to cope with abiotic stress. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.K.; Singh, N.S.; Kumar, U.; Mishra, S.; Perumal, R.C.; Benny, J.; Thatoi, H. Illumina MiSeq based assessment of bacterial community structure and diversity along the heavy metal concentration gradient in Sukinda chromite mine area soils. India Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 15, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendrula-Kotha, R.; Nkongolo, K. Bacterial and fungal community structure and diversity in a mining region under long-term metal exposure revealed by metagenomics sequencing. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 2, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Tong, C.X.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B.Q.; Xing, S.H.; Mao, Y.L. Biochar-fertilizer interaction modifies N-sorption, enzyme activities and microbial functional abundance regulating nitrogen retention in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.H.; Li, C.J.; Wang, S.S.; Zhou, B.Q.; Mao, Y.L.; Rensing, C.; Xing, S.H. Influence of biochar and biochar-based fertilizer on yield, quality of tea and microbial community in an acid tea orchard soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Zhu, L.; Zhong, L.M.; Dong, Y.X.; Wang, G.J.; Shi, K.X. Cd immobilization mechanisms in a Pseudomonas strain and its application in soil cd remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, J.; Mao, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X. Effect of H3PO4-modified biochar on the fate of atrazine and remediation of bacterial community in atrazine-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Type | pH | Cation Exchange Capacity (cmol/L) | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Total Nitrogen (g/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow-brown soil | 6.2 | 1.25 | 20.32 | 1.71 | 27.84 | 157.14 |
| Treatments | Plant Height (cm) | Root Length (cm) | Leaf Dry Weight (g/plant) | Root Dry Weight (g/plant) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.60 ± 0.49 c | 5.88 ± 0.23 ab | 2.16 ± 0.14 c | 0.175 ± 0.014 b |
| PMB | 22.27 ± 0.76 a | 6.56 ± 0.51 a | 2.45 ± 0.16 a | 0.206 ± 0.021 a |
| Cd + Pb | 15.18 ± 0.42 d | 4.08 ± 0.45 c | 0.83 ± 0.054 d | 0.088 ± 0.007 c |
| Cd + Pb + PMB | 19.57 ± 0.35 b | 5.45 ± 0.42 b | 1.51 ± 0.12 b | 0.151 ± 0.013 b |
| Treatments | Chao1 | Shannon |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 2040.32 ± 73.48 b | 4.13 ± 0.04 b |
| PMB | 2263.10 ± 65.31 a | 4.59 ± 0.04 a |
| Pb + Cd | 1744.18 ± 81.64 c | 3.81 ± 0.08 c |
| Pb + Cd + PMB | 2012.62 ± 85.73 b | 4.08 ± 0.11 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, X.; Xu, H.; Ren, Y.; Lin, D.; Li, K.; He, J. Phosphoric Acid and Magnesium Chloride Composite-Modified Biochar Improved Pakchoi Growth by Reducing Pb and Cd Accumulation and Altering Soil Properties and Microbial Communities. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060632
Dong X, Xu H, Ren Y, Lin D, Li K, He J. Phosphoric Acid and Magnesium Chloride Composite-Modified Biochar Improved Pakchoi Growth by Reducing Pb and Cd Accumulation and Altering Soil Properties and Microbial Communities. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(6):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060632
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Xuejie, Haojie Xu, Yanfang Ren, Dongming Lin, Ke Li, and Junyu He. 2025. "Phosphoric Acid and Magnesium Chloride Composite-Modified Biochar Improved Pakchoi Growth by Reducing Pb and Cd Accumulation and Altering Soil Properties and Microbial Communities" Horticulturae 11, no. 6: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060632
APA StyleDong, X., Xu, H., Ren, Y., Lin, D., Li, K., & He, J. (2025). Phosphoric Acid and Magnesium Chloride Composite-Modified Biochar Improved Pakchoi Growth by Reducing Pb and Cd Accumulation and Altering Soil Properties and Microbial Communities. Horticulturae, 11(6), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060632






