Abstract
This experiment investigated the effects of different additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability of amaranth and wheat bran (AWB) mixed silage. In this experiment, a two-factor (moisture content × additive) completely randomized experimental design was used, with amaranth as the raw silage material, and the moisture content was adjusted to 60%, 65%, and 70% using wheat bran. At each moisture content condition, the silage treatments included groups without any additives (control), with lactic acid bacteria (L), with cellulase (E), and with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase (M). Six replicates of each treatment were analyzed for fermentation quality, chemical composition, and in vitro digestibility of AWB mixed silage after 60 days of ensiling. The results showed that in the same L group, the pH and the lactic acid (LA) in the 60% moisture content (MC) group were lower and higher, respectively, than in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). In the same E and M groups, the ammonia nitrogen to total nitrogen (AN/TN) in the 60% MC group was lower than that in the 70% MC group, and the in vitro crude protein digestibility (IVCPD) was higher than that in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). At the same time, the aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage gradually decreased as the MC of the raw material increased (p < 0.05). Under 60% MC, the IVCPD and in vitro neutral detergent fiber digestibility (IVNDFD) in AWB mixed silage from the E and M groups were higher than those in the control group (p < 0.05). Under 60% MC, the pH and AN/TN in AWB mixed silage from the M group were lower than those in the control group (p < 0.05). Compared with the control under 60% MC, the aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage inoculated with L, E, and M increased by 33 h, 42 h, and 57 h, respectively. It was shown that the addition of M resulted in the best fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage when the amaranth MC was 60%.
1. Introduction
China’s demand for forage hay resources is growing rapidly, and the lack of quality roughage resources has become the primary factor limiting the rapid development of China’s grass-fed livestock industry. According to statistics, in 2022, China imported a total of 1.94 × 106 t of hay (General Administration of Customs of the People’s Republic of China), and the number of imports is still increasing annually. With the shortage of quality roughage resources in China, amaranth can be used as a quality roughage for ruminants with good application prospects.
Amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) is a high-quality annual forage crop with high yield, high quality, strong resistance, and fast growth and is an excellent forage grass for both food and feed. Generally, amaranth is mowed once a year and yields up to 85 t fresh weight/ha and 17 t dry matter/ha at maturity [1]. Amaranth has high nutritional value, containing high crude protein (28% of dry matter), low levels of acid detergent lignin (4% of dry matter), and low concentrations of oxalate and nitrate, and can replace fish meal as a protein feed [2,3]. In tropical and subtropical regions, Amaranthus dubius can be used as an alternative raw material for feeding New Zealand white rabbits [4]. Ngugi et al. [5] confirmed that amaranth (Amaranthus hybridus) leaf protein concentrate can be used as an alternative protein component to fishmeal in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) aquafeeds. The stems and leaves of amaranth are brittle and have a high moisture content, so it is important to process them soon after mowing to avoid a large loss of nutrients and prevent amaranth from spoiling.
Ensiling is an effective method for the safe preservation of amaranth, not only to improve the palatability of the feed but also to extend the storage time of high-moisture feeds. The replacement of corn silage with amaranth silage in fattening lamb diets (30% of dry matter) was feasible and increased the intake and average daily weight gain of fattening lambs [6]. However, fresh amaranth is difficult to use successfully in conventional silage due to its low dry matter and soluble carbohydrate content, low number of attached lactic acid bacteria, high buffer energy value, and high moisture content. Mixed silage is now a common and effective method to improve the feeding value of roughage. Suitable moisture content in the raw material is one of the important conditions to ensure the normal activity of lactic acid bacteria during silage, but high moisture can promote the growth of Clostridium, leading to spoilage of the silage [7]. Amaranth mixed with auxiliary materials with a high dry matter content can quickly reduce the moisture content in raw materials to meet the requirements for lactic acid bacteria fermentation, improve the fermentation quality of silage, and provide ruminants with a continuous and stable quality feed. Rahjerdi et al. [3] studied the silage of two amaranth varieties and maize stover in five different combinations, and the amaranth mixed with maize stover silage was best, with higher crude protein content and dry matter digestibility and lower neutral detergent fiber content compared to maize stover silage. Wheat bran is a common agricultural byproduct with a high crude protein content and contains many vitamins, soluble carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and other nutrients, making it an important source of energy in ruminant farming. Wheat bran is a suitable supplement for high-moisture forage silage mixes, both to regulate the moisture content in the silage material and to improve the nutritional balance of the mixed silage material by increasing the soluble carbohydrate content. Gül et al. [8] added 10% wheat bran to canola silage and showed that the addition of wheat bran increased the crude protein, metabolizable energy, and organic matter digestibility of canola silage.
Biological silage additives can promote the fermentation quality of silage and play a positive role in inhibiting aerobic spoilage, improving forageability, and enhancing nutrient uptake [9]. Lactic acid bacteria, the main microorganisms that play a role in the fermentation of silage, can use water-soluble carbohydrates to produce organic acids that lower pH and can also inhibit the reproduction and growth of undesirable microorganisms by competing for nutrients and forming an acidic anaerobic environment. Cellulase can hydrolyze structural carbohydrates and break down fibrous components into simple sugars, providing sufficient fermentation substrate for the propagation of lactic acid bacteria, which is a proven method for improving silage quality and nutritional value [10]. Inoculation of lactic acid bacteria in Leymus chinensis silage resulted in higher lactic acid content and lower pH and butyric acid content, which improved the fermentation quality of Leymus chinensis silage [11].
Studies on the addition of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase to amaranth and wheat bran (AWB) mixed silage have not been reported. Based on the results of previous studies using mixed silage with soybean residue and corn stover [12], we hypothesized that the combined use of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase could change the situation of insufficient lactic acid bacteria at the beginning of fermentation and produce a large amount of fermentation substrate, thus improving the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage. Therefore, in this study, wheat bran was used to regulate the moisture content (MC) of silage raw materials, and the effects of different additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage were investigated using the addition of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase alone or in combination. The aim was to identify the best preparation scheme for high-quality amaranth silage and to provide a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of commercial amaranth silage.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Design
The test site was in Tongyu County, Baicheng City, Jilin Province (122°02′ E, 44°13′ N, 160 m above sea level). The amaranth variety was K472, which was provided by Daxin Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China). Wheat bran was provided by Tianfeng Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Jinan, China). Lactic acid bacteria (Chikusou-1) were provided by SNOW BRAND SEED Co., Ltd., Sapporo, Japan. The strain number was Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LP1. Cellulase, Acremonium cellulase, was provided by Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, Lot No.: ACCF-6940.
A two-factor completely randomized experimental design was used for this trial. Factor one was the moisture content (MC). The theoretical MC of the silage materials after mixing was 60%, 65%, and 70%, and the amaranth to wheat bran mixing ratios were calculated as 70%:30% fresh weight (FW), 76%:24% (FW), and 83%:17% (FW), respectively. Factor two was the additive (A) type, and four additive combinations were designed under each MC condition: (1) no additive (control); (2) lactic acid bacteria (L, with a live count of 5 × 107 colony forming units (CFUs) g−1 FW); (3) cellulase (E, with an enzyme activity of 4.8 × 103 U g−1 FW); and (4) a mixed preparation of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase (M, with a live count of 5 × 107 CFUs g−1 FW and enzyme activity of 4.8 × 103 U g−1 FW). Both lactic acid bacteria and cellulase were added at 50 mg kg−1 FW. Amaranth was planted in June 2020, and then harvested in September 2020, when it reached maturity. Amaranth was mowed according to the 5-point sampling method and dried for 1 day after mowing. Amaranth was chopped to 1–3 cm and mixed thoroughly and evenly, and then the appropriate number of samples was selected for testing. The different additive solutions were sprayed evenly on the mixed silage and mixed thoroughly, and the same dose of distilled water was added to the control group. After mixing well, it was packed into 140 mm × 200 mm polyethylene vacuum packing bags with 300 g per bag, and 6 replicates were designed for each group. Then, vacuum treatment was performed, and the samples were stored at ambient temperatures (21–25 °C) for 60 days to prepare amaranth and wheat bran (AWB) mixed silage.
2.2. Fermentation Quality Analysis
After opening the bag, 20 g of the silage sample was weighed into a 140 mm × 200 mm polyethylene vacuum packing bag, and then 180 mL of distilled water was added, mixed well, and kept in a refrigerator at 4 °C for 24 h. After 24 h, the extracts were filtered through 4 layers of gauze and qualitative filter paper. The pH of the final extracts was determined using a pH meter (PHSJ-4F, Yidian Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Ammonia nitrogen (AN) was determined using the steam distillation method [13]. A portion of the extract was taken and centrifuged using a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (TDL-40B, Anting Scientific Instruments Factory, Shanghai, China) for 5 min and then filtered through a 0.22 µm aqueous membrane. The method of Cao et al. [14] was used for the determination of lactic acid (LA), acetic acid (AA), propionic acid (PA), and butyric acid (BA) using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (column: Shodex Rspak KC-811 s-DVB gel column, Japan; detector: SPD-M10AVP; mobile phase: 3 mmol L−1 perchloric acid; flow rate: 1 mL min−1; column temperature: 50 °C; detection wavelength: 210 nm; injection volume: 5 µL).
2.3. Chemical Composition and Energy Analysis
The remaining silage samples were dried in an electric thermostatic blast dryer (DHG-9145A, Yiheng Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 65 °C for 72 h. The dried samples were crushed through a 1 mm sieve, using a crusher (JG-200, Guangsha Industry & Trade Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), into self-sealing bags for chemical analysis. Dry matter (DM), organic matter (OM), ether extract (EE), crude ash (Ash), crude fiber (CF), and crude protein (CP) contents were determined with reference to the methods of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists [15]. The water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) content was determined with a colorimetric method using sulfuric acid-anthrone [16]. The buffer energy value (BC) was determined with reference to the method of Playne and McDonald [17]. The neutral detergent fiber (NDF), acid detergent fiber (ADF), and acid detergent lignin (ADL) contents were determined using a fiber analyzer (ANKOM A220, ANKOM Technology Corporation, Macedon, NY, USA) with reference to the method of Van Soest et al. [18].
Gross energy (GE) was determined using an oxygen bomb calorimeter [15]. Referring to Gao et al. [19], digestible energy (DE), metabolizable energy (ME), net energy for maintenance (NEm), net energy for weigh. gain (NEf), and net energy for lactation (NEl) were calculated. The calculation formulae are shown below:
Note: (1) ADF, CP, EE, NDF, CF, and Ash are expressed as a percentage of DM (% DM); (2) the units of GE, DE, ME, NEm, NEf, and NEl are MJ kg−1 DM.
2.4. Aerobic Stability Analysis
Aerobic stability was defined as the number of hours required for the core temperature of silage to be 2 °C above the ambient temperature after exposure to air [20]. After opening the self-sealing bag, the silage was mixed well and placed in a clean plastic bucket with a volume of 1 L. A thermometer (America Deltatrak 11050, Layout Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) was inserted in the center of the silage. The ambient temperature was 20.5 ± 1.5 °C, the sample temperature was recorded every 1 h, and the temperature exceeded room temperature by 2 °C as the judgment standard.
2.5. In Vitro Degradability Analysis
The experiment strictly complied with the Chinese Guide to Ethical Review of Experimental Animal Welfare and was approved by the Experimental Animal Welfare Ethics Committee of Jilin University (license number: SY202009600). Before starting the experiment, artificial saliva was prepared according to the method of Longland et al. [21]. Five healthy small-tailed sheep with rumen fistula were used as rumen fluid donors, and rumen fluid was collected through the fistula before morning feeding and filtered through 4 layers of gauze in a 39 °C thermos flask. The rumen fluid was mixed with artificial saliva at a ratio of 1:2 to make a mixed fermentation broth, and CO2 was continuously introduced to maintain an anaerobic environment. A 0.5 g silage sample was weighed into a filter bag (ANKOM F57, aperture 25 µm, ANKOM Technology Corporation, Macedon, NY, USA) and then heat sealed into a 100 mL serum bottle. Then, 60 mL of the mixed fermentation broth was placed into 100 mL serum bottles, continuously ventilated with CO2 to maintain an anaerobic environment, and incubated in a 39 °C water bath for 72 h. At the end of the test, the filter bag was removed from the serum bottle and washed with cold distilled water. After washing, the samples were dried in an electric thermostatic blast dryer (DHG-9145A, Yiheng Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 65 °C for 48 h until constant weight. In vitro dry matter digestibility (IVDMD), in vitro organic matter digestibility (IVOMD), in vitro crude protein digestibility (IVCPD), and in vitro neutral detergent fiber digestibility (IVNDFD) were calculated using an analysis of the residues of DM, OM, CP and NDF [10,22]. IVDMD, IVOMD, IVCPD, and IVNDFD were calculated as follows: (respective weights of DM, OM, CP, and NDF before digestion − respective weights of DM, OM, CP, and NDF remaining)/(respective weights of DM, OM, CP, and NDF before digestion).
2.6. Statistical Analyses
All experimental data were analyzed using SPSS statistical software (version 26, International Business Machines Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). A two-factor ANOVA was used to statistically analyze the data from silage fermentation tests to evaluate the effects of moisture content (MC), additives (A), and their interactions (MC × A) on fermentation quality, chemical composition, energy, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability. Significant differences between means were determined using Tukey’s method, where p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
The chemical composition, buffering capacity, and energy of silage raw materials are shown in Table 1. The DM content of wheat bran was 69.86% higher than that of amaranth, the OM content was 1.08 times higher than that of amaranth, and the CP content was 1.76 times higher than that of amaranth. The NDF content of amaranth was 11.04% DM higher than that of wheat bran, the ADF content was 2.65 times higher than that of wheat bran, and the ADL content was 1.56 times higher than that of wheat bran. The WSC contents of amaranth and wheat bran were 12.8% DM and 6.77% DM, respectively. The BC value of amaranth was 331.14 mEq kg−1 DM and that of wheat bran was 113.3 mEq kg−1 DM. Wheat bran had 1.07 times higher GE, 1.84 times higher DE, and 1.87 times higher ME than amaranth.

Table 1.
Chemical composition, buffering capacity, and energy of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage.
3.1. Fermentation Quality of Amaranth and Wheat Bran Mixed Silage
The fermentation quality of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage is shown in Table 2. The MC and A treatments influenced the pH and LA and AA contents (p < 0.001). The A treatment influenced the PA content (p = 0.020). MC, A, and their interaction (MC × A) influenced the proportion of ammonia nitrogen to total nitrogen (AN/TN) and BA content (p = 0.005–0.032; p < 0.001).

Table 2.
Fermentation quality of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage prepared with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase.
The LA content was higher in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group under the same L group (p < 0.05). Under the same L and E groups, the pH of the 60% MC group was lower than that in the 70% MC group, and the BA content was higher than that in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). In the same L, E, and M groups, the AA content was higher in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group, and AN/TN was lower in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). The pH and AN/TN of AWB mixed silage were lower in the M group than in the control group under 60% MC (p < 0.05). The LA and AA contents in AWB mixed silage were higher in the M group than in the control group under 65% MC (p < 0.05).
3.2. Chemical Composition of Amaranth and Wheat Bran Mixed Silage
The chemical composition of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage is shown in Table 3. The MC and A treatments influenced the DM, OM, CP, and NDF contents (p ≤ 0.001). The MC treatment influenced the ADF and ADL contents (p ≤ 0.001).

Table 3.
Chemical composition of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage prepared with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase.
Under the same E and M groups, the NDF and ADL contents were lower in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). Under the same L, E, and M conditions, the DM, OM, and CP contents were higher in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group, and the ADF content was lower in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). Under 60% MC, the AWB mixed silage in the E and M groups had lower DM, OM, and NDF contents and higher CP content than the control group (p < 0.05).
3.3. Energy and In Vitro Digestibility of Amaranth and Wheat Bran Mixed Silage
The energy and in vitro digestibility of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage are shown in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. MC, A, and their interaction (MC × A) influenced GE, DE, ME, NEm, NEl, NEf, and IVNDFD (p = 0.001–0.045; p < 0.001). The MC and A treatments influenced IVCPD (p < 0.001). The MC treatment influenced IVDMD and IVOMD (p < 0.001).

Table 4.
Energy of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage prepared with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase.

Table 5.
In vitro digestibility of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage prepared with lactic acid bacteria and cellulase.
Under the same L and E groups, DE, ME, NEm, and NEl were higher in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). In the same L, E and M groups, GE was lower in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group, and NEf, IVDMD, IVOMD, and IVCPD were higher in the 60% MC group than in the 70% MC group (p < 0.05). Under 60% MC, the NEf of AWB mixed silage was higher in the E group than in the control group, the IVCPD and IVNDFD of AWB mixed silage were higher in the E and M groups than in the control group, and the GE, DE, ME, NEm, and NEl of AWB mixed silage were higher in the L, E, and M groups than in the control group (p < 0.05).
3.4. Aerobic Stability of Amaranth and Wheat Bran Mixed Silage
The temperature changes in the additive in AWB mixed silage at 60%, 65% and 70% MC exposure under aerobic conditions are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. Under the three MC conditions, the temperature increased in all treatment groups within 0–96 h, with the control group showing a more significant increase in temperature. Temperature fluctuations were more pronounced for 70% MC than for 60% and 65% MC. Under 60% MC, the M group took the longest for the temperature to be 2 °C higher than the ambient temperature. Under 65% MC, the E group took the most hours for the temperature to be 2 °C higher than the ambient temperature. Under 70% MC, the E and M groups took the most hours for the temperature to be 2 °C higher than the ambient temperature.
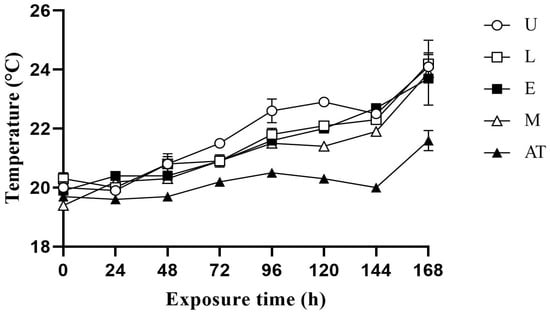
Figure 1.
Effect of additive application on the temperature change in amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage after exposure to aerobic conditions at 60% moisture content. U, control; L, lactic acid bacteria; E, cellulase; M, mixture of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase; AT, ambient temperature.
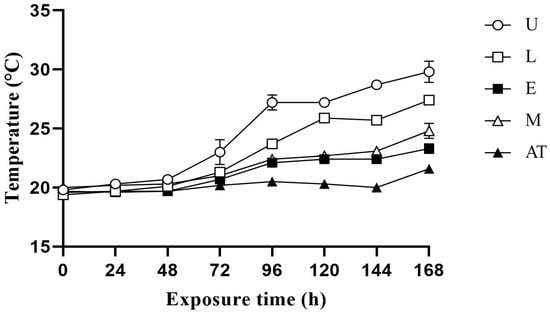
Figure 2.
Effect of additive application on the temperature change in amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage after exposure to aerobic conditions at 65% moisture content. U, control; L, lactic acid bacteria; E, cellulase; M, mixture of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase; AT, ambient temperature.
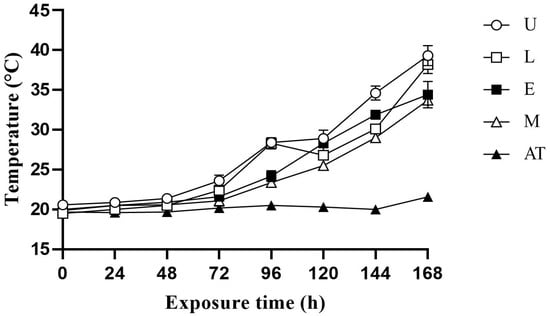
Figure 3.
Effect of additive application on the temperature change in amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage after exposure to aerobic conditions at 70% moisture content. U, control; L, lactic acid bacteria; E, cellulase; M, mixture of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase; AT, ambient temperature.
The time required for the AWB mixed silage temperature to exceed room temperature by 2 °C after exposure to air is shown in Figure 4. The aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage gradually decreased with increasing MC (p < 0.05). At 60% MC, the aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage was increased by 33 h, 42 h, and 57 h in the L, E, and M groups, respectively, compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Under 65% MC, the aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage in U, L, E and M groups was 66 h, 87 h, 117 h and 99 h, respectively;compared to the control group, the aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage was 31.8%, 77.3%, and 50% higher in the L, E, and M groups, respectively (p < 0.05). Under 70% MC, the control group had the worst aerobic stability, with 54 h, which was lower than the other treatment groups (p < 0.05); the best were the E and M groups, with 81 h, which were higher than the L and control groups.
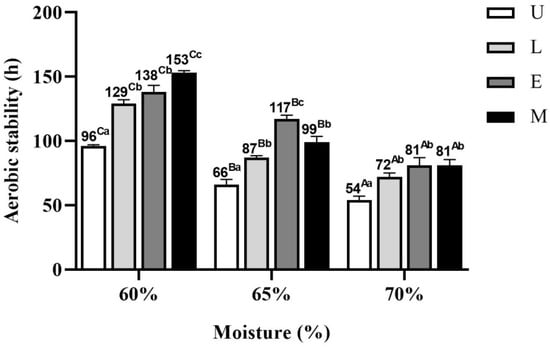
Figure 4.
Time required for the temperature of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage to exceed room temperature by 2 °C after exposure to air. U, control; L, lactic acid bacteria; E, cellulase; M, mixture of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase. A–C Means of moisture contents with different superscripts differ under the same additive treatment (p < 0.05). a–c Means of additives treatments with different superscripts differ under the same moisture content (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Moisture Content and Additives on the Fermentation Quality of AWB Mixed Silage
Raw material MC is one of the key factors affecting the fermentation quality of silage. A raw material MC that is too low results in a dry and rough surface on the raw material, a filling that is difficult to compact, and raw material seams with residual air, causing silage rot and deterioration. Excessive MC in raw materials can produce sap that carries nutrients out, while high moisture can promote the growth of harmful microorganisms such as clostridia and molds, causing a decrease in silage quality [23]. A suitable silage material MC is 60–70%, and the pH of good quality silage should be below 4.2 [24]. In this experiment, under the different MC conditions, the pH of each additive treatment group was lower than 4.2, indicating that all AWB mixed silages with L, E, and M were of high quality. In this experiment, the AWB mixed silage in the 60% MC group had the lowest pH and the highest LA content compared to the remaining MC groups. This was explained by the fact that the reduction in raw material MC concentrated the sugars in the cells and raised the sugar concentration. Moreover, wheat bran as an auxiliary improved the nutritional balance of mixed silage materials by increasing the WSC content and promoting the fermentation of lactic acid bacteria, which improved the fermentation quality of silage. Wan et al. [25] found that a low MC group had lower pH and AN/TN, higher LA content, and better fermentation quality of Sudan grass silage compared to a high MC group, which was consistent with the results of this study. Yang et al. [26] found that the AN/TN of Lolium multiflorum silage gradually decreased with decreasing MC, which is consistent with the results of this study. Under low MC conditions, plant cells were semiarid, resulting in increased osmotic pressure in the plant cytosol of AWB mixed silage, inhibition of the reproductive growth of Clostridium, reduced loss of nutrients, and weakened adverse protein breakdown, especially the process of amino acid deamination, resulting in an improvement in the quality of silage [27]. Tyrolova et al. [28] found that the fermentation quality of low-MC pea silage was better than that of high-MC pea silage, with higher LA content and lower protein hydrolysis in the low-MC group. As shown in Table 2, the fermentation quality of AWB mixed silage increased with the decrease in raw material MC, indicating that silage at 60% MC was an effective way to store amaranth.
pH is an important parameter to evaluate the degree of silage fermentation and silage quality. The lower the pH, the lower the activity of harmful microorganisms and plant enzymes in the silage, and the better the quality of silage fermentation. A minimum of 105 CFU g−1 lactic acid bacteria in the silage feedstock was required to produce high-quality silage [29]. In contrast, the general number of lactic acid bacteria attached to fresh plants was 103–104 CFU g−1. Therefore, additional lactic acid bacteria need to be added to the silage raw material to promote fermentation during the silage preparation process. The addition of L. plantarum increased the LA content, decreased the pH and PA content, and improved the fermentation quality of Leymus chinensis silage compared to the control, in agreement with the results of the trial with L addition at 60% MC [11]. Marbun et al. [30] showed that the addition of L. plantarum to the silage process reduced the AN/TN and fungal counts in maize silage and effectively improved the fermentation quality of maize silage. Yi et al. [31] inoculated lactic acid bacteria during the silage of spent mushroom substrate, which improved the fermentation quality. This was explained by the fact that the addition of homofermentative lactic acid bacteria preparations can promote the early entry of silage into lactic acid fermentation, change the situation of insufficient lactic acid bacteria in the early stage of fermentation, and produce large amounts of LA to reduce the pH and AN/TN of silage, thus inhibiting the growth and reproduction of yeasts and molds and reducing nutrient losses [32]. Cellulase can degrade cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, which are not easily digested by animals, and hydrolyze cell walls to release contents and increase the fermentation substrate for lactic acid bacteria, improving forage silage quality [33]. The inoculation of alfalfa silage with cellulase resulted in a lower pH and AN/TN and a higher WSC and LA content in a test group compared to a control group, consistent with the results of this study for the tests with E added at 60% and 65% MC conditions [34]. The AN content is mainly related to the degradation of protein and amino acids in silage [35]. A higher AN content indicates more protein and amino acid decomposition and poorer fermentation quality of silage. Under different MC conditions, the AN/TN of each additive treatment group was lower than that in the control group. The explanation was that low pH inhibited harmful microorganisms and plant protease activity, decreased the degree of protein breakdown in AWB mixed silage, and reduced AN production, which was consistent with the findings of Xing et al. [35]. Interestingly, the concentration of AA in the AWB mixed silage was lower in the L group than in the control group at 60% MC. This result contrasted with the results reported by Reis et al. [36], where the AA concentrations of corn silage inoculated with heterotrophic lactobacilli (Lactobacillus hilgardii) were significantly higher than those in the control. The explanation is that the differences in lactic acid bacteria species lead to inconsistent fermentation products (AA) of silage, with homofermentative lactic acid bacteria metabolizing only LA, while heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria can produce high concentrations of AA and multiple metabolites. Lactic acid bacteria can reduce the level of AA to improve the palatability of silage. Zhang et al. [37] found that inoculation of L. plantarum in mulberry silage reduced the AA content, which was consistent with the results of this study for the experiment with L added at 60% MC. The combined addition of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase can significantly reduce the pH of corn stover silage, which was found to be more effective than the addition of lactic acid bacteria alone [19]. At 60% MC, the pH of AWB mixed silage in the M group decreased by 0.03–0.18 units, AN/TN decreased by 0.19–0.3 units, and LA content increased by 10.4–18.9% compared to the control, L, and E groups. According to Tian et al. [38], a combined lactic acid bacteria and cellulase addition group had the highest LA concentration and the lowest pH of silage compared to control and separate addition groups, which effectively improved the fermentation quality of Leymus chinensis silage, which was consistent with the results of this study as stated above. Lactic acid bacteria were more effective on silage with high WSC content [39], indicating that the addition of cellulase to increase the WSC content of AWB mixed silage was more beneficial for the improvement in fermentation quality. Thus, the combination of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase exerted a synergistic effect and had a positive effect on improving the fermentation quality of AWB mixed silage.
4.2. Effect of Moisture Content and Additives on Chemical Composition and In Vitro Digestibility of AWB Mixed Silage
A suitable MC can protect proteins by reducing the protease activity of the silage material itself. In this study, the AWB mixed silage in the 60% MC group had the highest DM and CP content among the three MC groups. Moreover, the NDF, ADF, and ADL contents in AWB mixed silage gradually increased with increasing MC, indicating that a low MC could better preserve the nutrient content in AWB mixed silage. This was explained by the fact that the increase in DM in the silage reduced the leaching of nutrient solutions by appropriately lowering the MC in the raw material, thus reducing the consumption of nutrients in the silage by microorganisms. Under 60% MC conditions, fewer nutrients were lost from the silage material, and the nutrients in the AWB mixed silage were preserved better than those in the other two MC groups, which had high DM content and did not reach the state of physiological drought. A high MC will promote the growth of harmful microorganisms, such as clostridia and molds, and the exudate produced will carry nutrients out and affect the quality of silage. Wan et al. [25] showed that a low MC treatment could increase the DM level of Sudan grass silage and improve the quality of silage. Yang et al. [26] performed silage on Lolium multiflorum with different MCs (85%, 75%, and 65%) and found better results at 65% MC, which concentrated nutrients in the silage, inhibited Clostridium and protease activity, reduced NDF and ADF content, and increased DM and CP content compared to 75% and 85% MC, in agreement with the results of this study. In this study, the highest IVDMD and IVCPD were found for the AWB mixed silage in the 60% MC group. This may be because a proper reduction in MC reduced the loss of DM from silage, better preserved the CP and residual WSC content in silage, and utilized more fermentation substrate during rumen fermentation, thus exhibiting a higher IVDMD and IVCPD.
Changes in the protein content in silage are not only related to the activity of harmful microorganisms such as clostridia and molds but are also influenced by the protein hydrolytic enzymes contained in plants [40]. Marbun et al. [30] showed that when making maize silage, CP and DM were higher and fungal counts were lower in a lactic acid bacteria treatment group than in the control group, indicating that the addition of lactic acid bacteria preserved the nutrient content of the silage and reduced the accumulation of mycotoxins, in agreement with the results of this study for the trials with the addition of L under each MC condition. The WSC content in the two silage feedstocks in this study was high, and the lactic acid bacteria used WSC for growth and reproduction, producing a large amount of LA, and thus creating an acidic environment that increased the inhibition of protease activity and reduced the decomposition of CP. For example, another study found that inoculation of alfalfa silage with lactic acid bacteria preparations increased the CP content and effectively reduced Bacillus Escherichia coli populations [41]. Cellulases, mainly consisting of endo-β-glucanase, exo-β-glucanase, and β-glucosidase, are capable of disrupting the cellulose crystal structure at the nonreducing end of the fiber molecule and releasing simple sugars [42]. The NDF and ADF contents are key indicators to evaluate the quality of silage: when the NDF and ADF contents are approximately low, the silage forage value is approximately high. At 60% MC, the E and M groups had reduced contents of NDF, ADF, and ADL, increased CP content, and an improved nutritional value of AWB mixed silage compared to the control group. AN/TN can reflect the degree of protein degradation in the silage. Under 60% MC conditions, AN/TN was lower in the E and M groups than in the control group. Lower AN/TN also proved that E and M have a good preservation effect on the protein in AWB mixed silage. Li et al. [43] showed that the addition of cellulase increased the ME and CP contents and decreased the NDF and ADF contents in king grass silage, which was consistent with the above experimental results found in this study. Tian et al. [38] found that the combined addition of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase reduced the ADF content in Leymus chinensis silage. In Pennisetum sinese silage, cellulase reduced the crystallinity of lignocellulose and improved its conversion, indicating that it was a very useful silage pretreatment method [44]. Under 60% MC conditions, the NDF, ADF, and ADL contents in the L group were lower than those in the control group, which was consistent with the findings of Yi et al. [31]. These authors also found that inoculation of lactic acid bacteria in Pleurotus eryngii silage reduced the NDF, ADF, and ADL contents in P. eryngii silage. This result was surprising because the lactic acid bacteria silage treatment lacked the relevant cellulose-degrading enzymes and could not substantially affect the structure of the lignin–cellulose–hemicellulose complex [45]. This was explained by the fact that the addition of lactic acid bacteria preparations to silage produced more lactic acid, which acidified the cell wall and led to lower NDF and ADF contents. Under the three MC conditions, the DM content in the L, E, and M groups was lower than that in the control group. Kaewpila et al. [46] showed that the DM content could be depleted by 2% in the presence of lactic acid bacteria or cellulase, which was consistent with the above experimental results found in this study.
Nutrient digestibility is one of the important factors affecting feed intake [47]. Under 60%, 65%, and 70% MC, the IVDMD, IVCPD, IVOMD, and IVNDFD contents in AWB mixed silage were higher in the E and M groups than in the control group. The nutrient digestibility of AWB mixed silage was enhanced due to the superimposed effect of the enzymatic interaction between the rumen microbiota and exogenously added cellulase [48]. Kaewpila et al. [10] supported these findings regarding increased IVDMD after exogenous addition of cellulase. ADF and NDF are the most effective indicators that reflect the quality of fiber at this stage. The ADF content is negatively correlated with animal digestibility; the lower its value is, the higher the digestibility of the feed and the greater the feeding value. Nawaz et al. [49] added an enzyme preparation containing cellulase to buffalo calf diets and found that calves fed the enzyme preparation had significantly higher IVDMD, IVCPD, and IVNDFD than the control group, which was consistent with the results in this study for trials in which E and M were added at 60%, 65%, and 70% MC. The total calf weight gain and average daily weight gain were also significantly higher than those in the control group, indicating that the addition of the enzyme preparation improved the productive performance and nutrient digestibility of the animals. This may be because cellulose and its derivatives in silage can be catalytically degraded by cellulase preparations, breaking the cell wall barrier composed of cellulose, pectin, hemicellulose, and lignin together, and the nutrients in the cell wall can be released, which then interact with digestive enzymes to improve feed digestibility and animal growth performance. According to Weinberg et al. [50], lactic acid bacteria can survive in rumen fluid, suggesting that lactic acid bacteria may directly influence rumen fermentation in a way that enhances rumen microbial biomass. Alfalfa silage inoculated with lactic acid bacteria produced more microbial biomass and altered rumen fermentation compared to a control group, which may positively affect the productive performance of ruminants. This change in rumen fermentation may be associated with better preservation of feed proteins during silage fermentation [51]. At 60% MC, the L treatment increased the IVDMD and IVCPD of the AWB mixed silage compared to the control. This was because the addition of lactic acid bacteria reduced the loss of DM in silage, generated an acidic environment that inhibited protease activity, and reduced the breakdown of CP, thus increasing IVDMD and IVCPD. The addition of lactic acid bacteria to wilted Sudan grass silage increased IVDMD and IVCPD, which was consistent with the above experimental results found in this study [25]. Feeding silage inoculated with homofermentative lactic acid bacteria preparations improved feed digestibility in dairy cows [52]. According to Table 2, the fermentation quality of AWB mixed silage improved gradually with decreasing MC, and the best fermentation quality was achieved at 60% MC. This was reflected in the high LA content (7.74–9.20), low pH (3.70–3.88), and low AN/TN (1.38–1.68). If high MC AWB mixed silage inoculated with additives is fed to ruminants, then the growth performance of ruminants will be affected due to poor silage fermentation quality. Zhao et al. [12] inoculated lactic acid bacteria and cellulase in soybean residue and corn stover mixed silage and showed that the highest rumen dry matter and crude protein degradation rates were observed in the combined addition group. The combined application of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase resulted in an improved rumen degradation rate and microbial diversity of the silage. The combination of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase in silage can compensate for the deficiencies of single inoculants and improve the digestibility of silage in the rumen of ruminants. The introduction of AWB mixed silage inoculated with M into ruminant diets at 60% MC will promote the nutritional balance of ruminant diets and improve the productive performance of ruminants.
4.3. Effect of Moisture Content and Additives on the Aerobic Stability of AWB Mixed Silage
The multiplication and growth of yeasts and molds will cause silage to spoil during aerobic exposure. When silage was exposed to air, the anaerobic environment became aerobic. Due to the lack of oxygen, yeasts and molds start to proliferate and decompose LA and CP, which leads to silage spoilage, as evidenced by increased temperature and pH [53]. In this study, the aerobic stability of AWB mixed silage gradually decreased with increasing MC. Compared with 60% MC, the aerobic stability was reduced by 57 h, 57 h, and 72 h in the L, E, and M groups, respectively, under 70% MC conditions. This was explained by the fact that a high MC in raw materials can promote the growth of harmful microorganisms such as clostridia and molds, which are more likely to cause aerobic spoilage. Tao et al. [54] found that an appropriate reduction in MC could improve the aerobic stability of alfalfa silage, which was consistent with the results of this study.
The aerobic stability of silage is very important, and if silage can sustain a high aerobic stability, it can greatly preserve the nutrient content in silage and reduce the accumulation of mycotoxins [53]. At 60% MC, the aerobic stability of the control, L, E, and M groups was 96 h, 129 h, 138 h, and 153 h, respectively. The control group had the highest DM content, which limited the degree of fermentation of the silage, resulting in higher concentrations of residual WSC in the silage and promoting the growth of undesirable microorganisms such as yeasts and molds that were exposed to air to multiply [55]. This may explain the worst aerobic stability of the AWB mixed silage in the control group. AA and PA are highly active antifungals and can effectively inhibit the activity of aerobic microorganisms [56]. According to Table 2, the higher content of AA and PA in L-, E-, and M-inoculated silages at 60% MC may be one of the reasons for their improved aerobic stability. Silage of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves with lactic acid bacteria can improve aerobic stability up to 128 h [55], which was consistent with the results of this study. In this study, the aerobic stability of the L-inoculated silage was improved. However, it was reduced by 7% and 19% compared to the E and M groups, respectively. Lactic acid bacteria fermentation increased the LA content in the silage, which showed poor antifungal activity compared to AA and PA [57]. Lactobacillus plantarum belongs to homofermentative lactic acid bacteria, whose fermentation mainly produces lactic acid, while the amount of short-chain fatty acids produced that can inhibit the growth and reproduction of yeasts and molds is very small. The exposure of silage to air and the gradual oxidation of LA by lactic acid-assimilating yeasts leads to an increase in silage pH, which provides the necessary conditions for the growth and reproduction of undesirable microorganisms [58]. Homofermentative lactic acid bacteria promote the growth of yeast and reduce aerobic stability. Heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria such as Lactobacillus brucei fermentation produce AA that better inhibits the activity of undesirable microorganisms, such as yeasts and molds, and prolongs the aerobic stability of silage [59]. Thus, the L-inoculated silage showed lower aerobic stability than the E and M groups. Cellulase can degrade the lignocellulosic components in the cell wall of silage to WSC, provide sugar for many fungi, and make silage corrupt. This was inconsistent with the results of AWB mixed silage inoculated with E in this experiment. Ohyama et al. [60] showed that there was no clear link between WSC content and silage stability in an aerobic environment and that the aerobic stability of silage was prolonged at higher WSC content, in agreement with the results of E-inoculated AWB mixed silage in this study. The best aerobic stability (153 h) of AWB mixed silage was obtained with the addition of the lactic acid bacteria and cellulase mixture at 60% MC, indicating that the addition of the lactic acid bacteria and cellulase mixture was more favorable to prolong the aerobic stability of silage.
5. Conclusions
Both the low-moisture-content treatment and the addition of lactic acid bacteria and cellulase improved the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability of amaranth and wheat bran mixed silage. Among them, the best results were obtained with the addition of M to AWB mixed silage when the MC of silage raw material was 60%. However, in vivo trials are needed to validate our findings and evaluate the silage quality and the effect of E-inoculated AWB silage on ruminant growth performance before recommending it to farmers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Y. and P.W.; methodology, Q.Y., M.Y., X.L. and H.T.; software, Q.Y., T.Z., M.Y. and X.L.; validation, P.W., X.L., M.Y. and T.Z.; formal analysis, Q.Y., P.W. and X.L.; investigation, M.Y.; resources, H.T.; data curation, Q.Y., P.W. and M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Y. and P.W.; writing—review and editing, Q.Y., P.W. and T.Z.; visualization, P.W.; supervision, P.W.; project administration, P.W.; funding acquisition, P.W. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20210101375JC) and the Major Science and Technology Special Fund for the Development of Beef Cattle Industry in Jilin Province (YDZJ202203CGZH042).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study strictly followed the Chinese Laboratory Animal Welfare Ethical Review Guidelines and was approved by the Laboratory Animal Welfare Ethics Committee of Jilin University (permit number: SY202009600).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The author is solely responsible for the completeness and accuracy of all data in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abbasi, D.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Rezaei, J. Effect of harvest date and nitrogen fertilization rate on the nutritive value of amaranth forage (Amaranthus hypochondriacus). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 171, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Fazaeli, H. Nutritive value of fresh and ensiled amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) treated with different levels of molasses. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 151, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahjerdi, N.K.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Fazaeli, H.; Rezaei, J. Chemical composition, fermentation characteristics, digestibility, and degradability of silages from two amaranth varieties (kharkovskiy and sem), corn, and an amaranth-corn combination. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 5781–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, E.; González-Redondo, P.; Moreno-Rojas, R.; Montero-Quintero, K.; Sánchez-Urdaneta, A. Effect of the inclusion of Amaranthus dubius in diets on carcass characteristics and meat quality of fattening rabbits. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngugi, C.C.; Oyoo-Okoth, E.; Manyala, J.O.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Kimotho, A. Characterization of the nutritional quality of amaranth leaf protein concentrates and suitability of fish meal replacement in nile tilapia feeds. Aquac. Rep. 2017, 5, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Fazaeli, H.; Zahedifar, M. Effects of substituting amaranth silage for corn silage on intake, growth performance, diet digestibility, microbial protein, nitrogen retention and ruminal fermentation in fattening lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 192, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Undersander, D.J.; Combs, D.K. Effect of Lactobacillus inoculants and forage dry matter on the fermentation and aerobic stability of ensiled mixed-crop tall fescue and meadow fescue. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, S.; Coskuntuna, L.; Koç, F.; Özdüven, L. The effect of wheat bran added to canola silage on feed value and in vitro organic matter digestibility. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 10823–10829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xu, N.; Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Dong, C.; Ding, C. Interaction effect of silo density and additives on the fermentation quality, microbial counts, chemical composition and in vitro degradability of rice straw silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewpila, C.; Khota, W.; Gunun, P.; Kesorn, P.; Cherdthong, A. Strategic addition of different additives to improve silage fermentation, aerobic stability and in vitro digestibility of napier grasses at late maturity stage. Agriculture 2020, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Yang, H.; Na, R.S. The effects of stage of growth and additives with or without cellulase on fermentation and in vitro degradation characteristics of Leymus chinensis silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y. Cellulase interacts with lactic acid bacteria to affect fermentation quality, microbial community, and ruminal degradability in mixed silage of soybean residue and corn stover. Animals 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D. Compensatory Changes in the Partitioning of Dry Matter in Relation to Nitrogen Uptake and Optimal Variations in Growth. Ann. Bot. 1986, 58, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hirakubo, T.; Fukui, H.; Matsuyama, H. Fermentation characteristics and microorganism composition of total mixed ration silage with local food by-products in different seasons. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC Int.: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Deriaz, R.E. Routine analysis of carbohydrates and lignin in herbage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1961, 12, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playne, M.J.; McDonald, P. The buffering constituents of herbage and of silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1966, 17, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; and Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Y.M. Chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of corn stover during field exposure and their fermentation characteristics of silage prepared with microbial additives. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.J.; Sheperd, A.C.; Smagala, A.M.; Endres, K.M.; Bessett, C.A.; Ranjit, N.K.; Glancey, J. The effect of preservatives based on propionic acid on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage and a total mixed ration. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longland, A.C.; Theodorou, M.K.; Sanderson, R.; Lister, S.J.; Powell, C.J.; Morris, P. Non-starch polysaccharide composition and in vitro fermentability of tropical forage legumes varying in phenolic content. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1995, 55, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria and cellulase on the fermentation quality, nutritive value, tannins profile and in vitro digestibility of Neolamarckia cadamba leaves silage. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolford, M.K. The detrimental effects of air on silage. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 68, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zhang, Z.X.; Shimojo, M.; Wang, T.; Masuda, Y. Comparison of fermentation characteristics of italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) and guineagrass (Panicum maximum Jacq.) during the early stage of ensiling. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.C.; Xie, K.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, B. Effects of wilting and additives on the ensiling quality and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics of sudangrass silage. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Ma, X.; Huang, L.; Peng, Y. Influence of moisture content on the silage quality of Lolium multiflorum. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2014, 13, 702–705. [Google Scholar]
- Greenhill, W.L. Plant juices in relation to silage fermentation. III. effect of water activity of juice. Grass Forage Sci. 1964, 19, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrolova, Y.; Vyborna, A. The effects of wilting and biological and chemical additives on the fermentation process in field pea silage. Czech. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 56, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publications: Marlow, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Marbun, T.D.; Lee, K.; Song, J.; Kwon, C.H.; Yoon, D.; Lee, S.M.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, S.B.; Kim, E.J. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on the nutritive value and in vitro ruminal digestibility of maize and rice straw silage. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.X.; Wang, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Yu, M.; Zhao, T.Y.; Sheng, Z.Y.; Luo, H.L. Fermentation Quality, in vitro digestibility, and aerobic stability of ensiling spent mushroom substrate with microbial additives. Animals 2023, 13, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted italian ryegrass silage inoculated with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Ni, K.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, W.; Yan, L.; Jie, C.; Zhong, J. Effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing Lactobacillus fermentum and cellulase additives on the fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa silage. PeerJ 2019, 10, e7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Chen, L.J.; Han, L.J. The effect of an inoculant and enzymes on fermentation and nutritive value of sorghum straw silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.B.; de Oliveira dos Santos, S.; Andréia Carvalho, B.F.; Schwan, R.F.; Carla Luiza da Silva, Á. Wild Lactobacillus hilgardii (CCMA 0170) strain modifies the fermentation profile and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, X.K.; Li, D.X.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, F.Y.; Ni, K.K. Impact of wilting and additives on fermentation quality and carbohydrate composition of mulberry silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shao, T.; Na, R.; Zhao, M. Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants and cellulase on fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of Leymus chinensis silage. Grassl. Sci. 2014, 60, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Liu, S.M.; Tayo, G.O.; Tang, S.X.; Tan, Z.L.; Lin, B.; He, Z.X.; Hang, X.F.; Zhou, Z.S.; Wang, M. Effects of cellulase or lactic acid bacteria on silage fermentation and in vitro gas production of several morphological fractions of maize stover. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 152, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooke, J.A.; Armstrong, D.G. The importance of the form of nitrogen on microbial protein synthesis in the rumen of cattle receiving grass silage and continuous intrarumen infusions of sucrose. Br. J. Nutr. 1989, 61, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Bao, W.; Li, W.; Zhao, F.; Kwok, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. Changes in physico-chemical characteristics and viable bacterial communities during fermentation of alfalfa silages inoculated with Lactobacillus plantarum. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Gangawane, A.K. Isolation of Potential Extracellular Cellulase Producer and Determination of Cellulase Production Efficiency with Various Raw Substrates. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2021, 11, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zi, X.; Zhou, H.; Hou, G.; Cai, Y. Effects of sucrose, glucose, molasses and cellulase on fermentation quality and in vitro gas production of king grass silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ke, W.; Ding, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Pretreatment of Pennisetum sinese silages with ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase at two dry matter contents: Fermentation characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholsen, S.; Khota, W.; Pang, H.; Higgs, D.; Cai, Y. Characterization and application of lactic acid bacteria for tropical silage preparation. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewpila, C.; Thip-Uten, S.; Cherdthong, A.; Khota, W. Impact of cellulase and lactic acid bacteria inoculant to modify ensiling characteristics and in vitro digestibility of sweet corn stover and cassava pulp silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtanen, P.; Rinne, M.; Nousiainen, J. Evaluation of the factors affecting silage intake of dairy cows: A revision of the relative silage dry-matter intake index. Animal 2007, 1, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgavi, D.P.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Nsereko, V.L.; Rode, L.M.; Iwaasa, A.D.; Yang, W.Z.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Synergy between ruminal fibrolytic enzymes and enzymes from Trichoderma longibrachiatum. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Shahzad, N.; Saif-ur-Rehman, M.; Ali, M. Effect of feeding xylanase and cellulase treated oat silage on nutrient digestibility, growth performance and blood metabolites of nili ravi buffalo calves. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 53, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Muck, R.E.; Weimer, P.J. Survival of silage inoculant lactic acid bacteria in rumen fluid. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Muck, R.E.; Mertens, D.R.; Weimer, P.J. Microbial inoculant effects on silage and in vitro ruminal fermentation, and microbial biomass estimation for alfalfa, bmr corn, and corn silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 163, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Muck, R.E. New trends and opportunities in the development and use of inoculants for silage. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 19, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Guo, G.; Wen, A.; Desta, S.T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, T. The effect of different additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and aerobic stability of a total mixed ration silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 207, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, N.; Si, B.; Tu, Y.; Ma, T.; Diao, Q. Effects of different source additives and wilt conditions on the pH value, aerobic stability, and carbohydrate and protein fractions of alfalfa silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Effects of additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and aerobic stability of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves silage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filya, I. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus plantarum on the fermentation, aerobic stability, and ruminal degradability of low dry matter corn and sorghum silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.; Tapio, I.; Rinne, M. Preservation characteristics and bacterial communities of crimped ensiled barley grains modulated by moisture content and additive application. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1092062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.; Driehuis, F.; Oude Elferink, S.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of Ensiling. Silage Sci. Technol. 2003, 42, 31–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.; Prencipe, S.; Spadaro, D.; Gullino, M.L.; Cavallarin, L.; Piano, S.; Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G. Increase in aflatoxins due to Aspergillus section Flavi multiplication during the aerobic deterioration of corn silage treated with different bacteria inocula. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, Y.; McDonald, P. The effect of some additives on aerobic deterioration of silages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1975, 26, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).