Oral Administration of Animal and Plant Protein Mixture with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IDCC 3501 Improves Protein Digestibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture
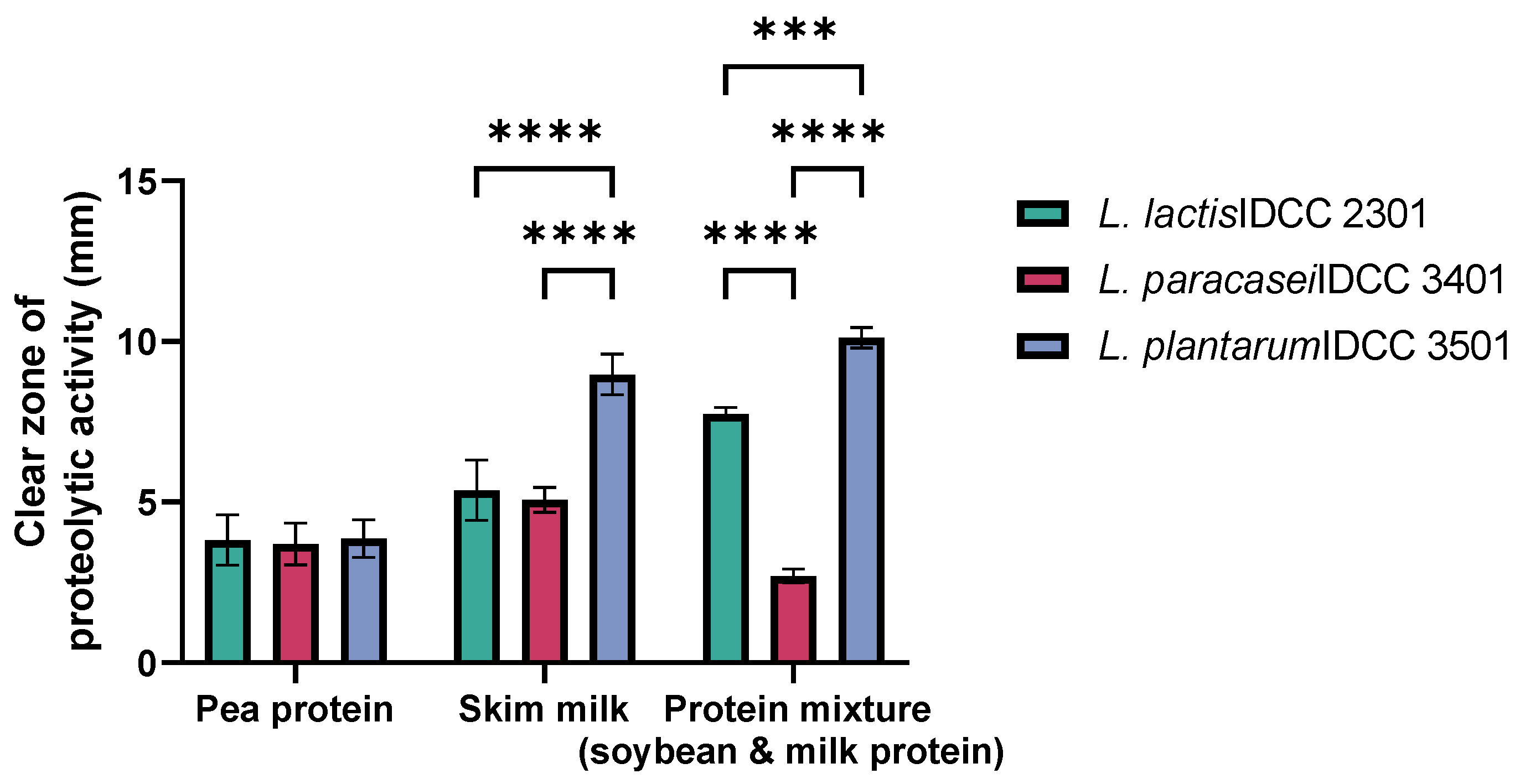
2.2. Proteolytic Activity
2.3. Genome-Wide Identification of Genes Encoding the Proteolytic System
2.4. Mouse Experiment for Quantification of the Concentration of Amino Acids in Blood Serum and Measurement of Body and Muscle Weights of Mice
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Proteolytic Activities of Probiotic Strains on Animal and Plant Protein Mixture
3.2. Simultaneous Oral Administration of Animal and Plant Protein Mixture with Different Concentrations of L. plantarum to Mice
3.2.1. Food and Water Consumption and Body Weight
3.2.2. Concentration of Amino Acids in Blood Serum
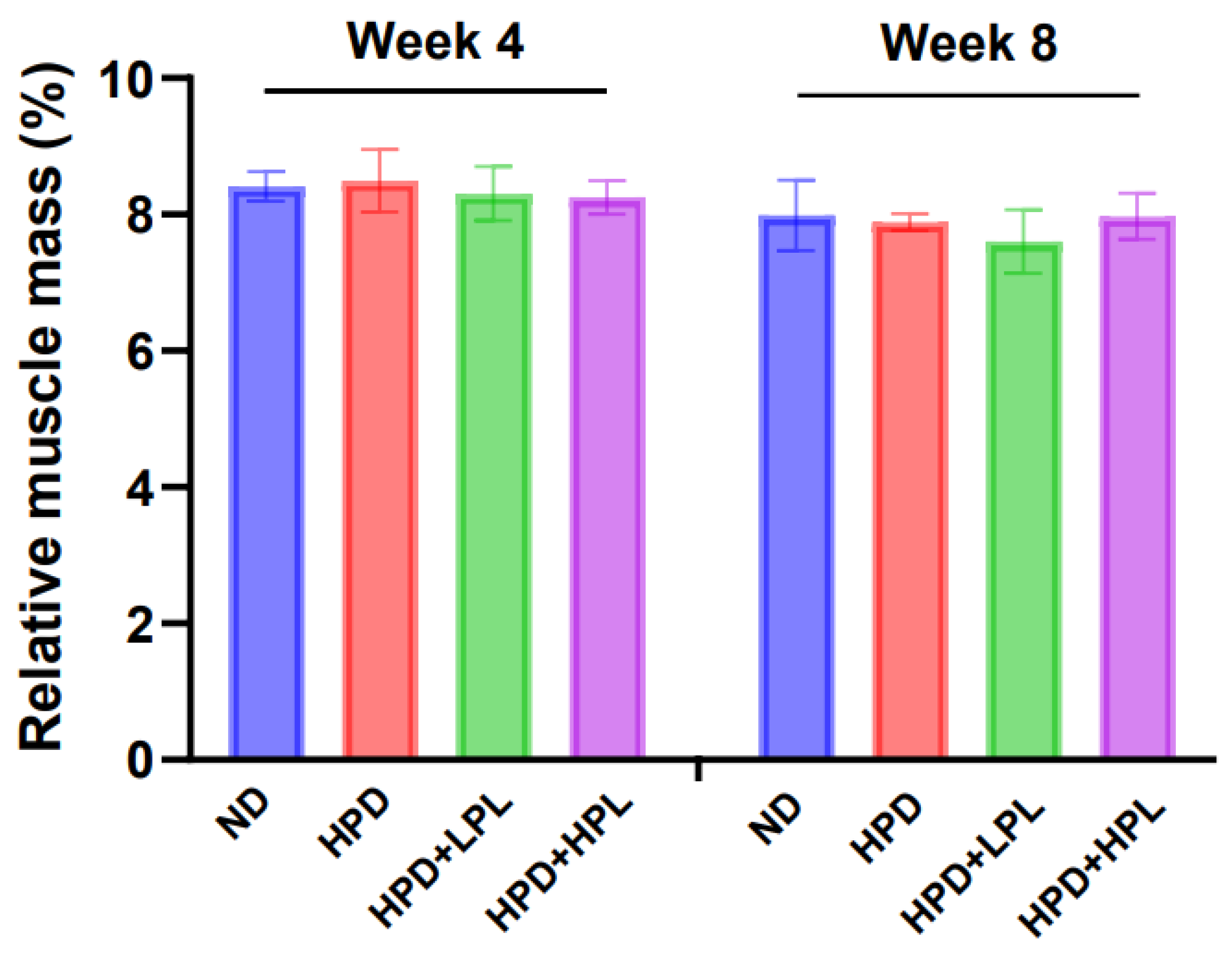
3.2.3. Muscle Mass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, M.E.; Swanson, J.E.; Thomas, B.L.; Hostetter, T.H. Glomerular and Hormonal Responses to Dietary Protein Intake in Human Renal Disease. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 1987, 253, F1083–F1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sans, M.D.; Crozier, S.J.; Vogel, N.L.; D’Alecy, L.G.; Williams, J.A. Dietary Protein and Amino Acid Deficiency Inhibit Pancreatic Digestive Enzyme MRNA Translation by Multiple Mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosterlitz, H.W. The Effects of Changes in Dietary Protein on the Composition and Structure of the Liver Cell. J. Physiol. 1947, 106, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamerow, M.M.; Mettler, J.A.; English, K.L.; Casperson, S.L.; Arentson-Lantz, E.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Layman, D.K.; Paddon-Jones, D. Dietary Protein Distribution Positively Influences 24-h Muscle Protein Synthesis in Healthy Adults. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounous, G.; Létourneau, L.; Kongshavn, P.A.L. Influence of Dietary Protein Type on the Immune System of Mice. J. Nutr. 1983, 113, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Falvo, M.J. Protein–Which Is Best? J. Sports Sci. Med. 2004, 3, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary Essentiality of “Nutritionally Non-Essential Amino Acids” for Animals and Humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauw, W.M.; Rydhmer, L.; Kyriazakis, I.; Øverland, M.; Gilbert, H.; Dekkers, J.C.; Hermesch, S.; Bouquet, A.; Gómez Izquierdo, E.; Louveau, I.; et al. Prospects for Sustainability of Pig Production in Relation to Climate Change and Novel Feed Resources. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, M.J.; Rae, A.N.; Vereijken, J.M.; Meuwissen, M.P.M.; Fischer, A.R.H.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Rutherfurd, S.M.; Gruppen, H.; Moughan, P.J.; Hendriks, W.H. The Future Supply of Animal-Derived Protein for Human Consumption. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarocostas, J. The UN Reports Global Asymmetries in Population Growth-The Lancet. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)01323-X/fulltext (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Bohrer, B.M. An Investigation of the Formulation and Nutritional Composition of Modern Meat Analogue Products. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackis, J.J.; Sessa, D.J.; Honig, D.H. Flavor Problems of Vegetable Food Proteins. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittermeier-Kleßinger, V.K.; Hofmann, T.; Dawid, C. Mitigating Off-Flavors of Plant-Based Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9202–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.C.; Tavares, G.M. Mixing Animal and Plant Proteins: Is This a Way to Improve Protein Techno-Functionalities? Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, S.; Formica, F.A.; Denkel, C. Mixing Plant-Based Proteins: Gel Properties of Hemp, Pea, Lentil Proteins and Their Binary Mixtures. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Pouvreau, L.; Martin, A.H. Mixing Whey and Soy Proteins: Consequences for the Gel Mechanical Response and Water Holding. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Du, M. Effect of Partial Replacement of Water-Soluble Cod Proteins by Soy Proteins on the Heat-Induced Aggregation and Gelation Properties of Mixed Protein Systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomarc’h, F.; Arvisenet, G.; Bouhallab, S.; Canon, F.; Deutsch, S.-M.; Drigon, V.; Dupont, D.; Famelart, M.-H.; Garric, G.; Guédon, E.; et al. Mixing Milk, Egg and Plant Resources to Obtain Safe and Tasty Foods with Environmental and Health Benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Eve, A.; Irlinger, F.; Pénicaud, C.; Souchon, I.; Marette, S. Consumer Preferences for New Fermented Food Products That Mix Animal and Plant Protein Sources. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 90, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kies, C. Bioavailability: A Factor in Protein Quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, Y.D.; Ganapathy, V. Chapter 47-Protein Digestion and Absorption. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, 6th ed.; Said, H.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1063–1086. ISBN 978-0-12-809954-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, B.N.P.; McAinch, A.J.; Vasiljevic, T. Modulation of Bovine Whey Protein Digestion in Gastrointestinal Tract: A Comprehensive Review. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 62, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.U.; Brodin, B.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Frokjaer, S.; Steffansen, B. Human Peptide Transporters: Therapeutic Applications. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2002, 12, 1329–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan-Mihan, A.; Luhovyy, B.L.; El Khoury, D.; Anderson, G.H. Dietary Proteins as Determinants of Metabolic and Physiologic Functions of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Nutrients 2011, 3, 574–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wielen, N.; Moughan, P.J.; Mensink, M. Amino Acid Absorption in the Large Intestine of Humans and Porcine Models. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.A.; Macfarlane, G.T. Enumeration of Amino Acid Fermenting Bacteria in the Human Large Intestine: Effects of PH and Starch on Peptide Metabolism and Dissimilation of Amino Acids. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1998, 25, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Liu, W.; Piao, M.; Zhu, H. A Review of the Relationship between the Gut Microbiota and Amino Acid Metabolism. Amino. Acids 2017, 49, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, H. Influence of Probiotics on Dietary Protein Digestion and Utilization in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, R.; Zaragoza, J.; Purpura, M.; Iametti, S.; Marengo, M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Anzalone, A.J.; Oliver, J.M.; Fiore, W.; Biffi, A.; et al. Probiotic Administration Increases Amino Acid Absorption from Plant Protein: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Crossover Study. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2020, 12, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Jeon, H.J.; Moon, J.S.; Jung, Y.H.; Yang, J. Increased Amino Acid Absorption Mediated by Lacticaseibacillus Rhamnosus IDCC 3201 in High-Protein Diet-Fed Mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini, C.V.; Peralta, G.H.; Milesi, M.M.; Hynes, E.R. Growth, Survival, and Peptidolytic Activity of Lactobacillus Plantarum I91 in a Hard-Cheese Model. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5465–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Akino, A.; Takano, T. Antihypertensive Effect of the Peptides Derived from Casein by an Extracellular Proteinase from Lactobacillus Helveticus CP790. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, S.; Oliver, G.; Vignolo, G. Protein Degradation by Lactobacillus Plantarum and Lactobacillus Casei in a Sausage Model System. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.M.; Marth, E.H. Proteolytic Activity by Strains of Lactobacillus Plantarum and Lactobacillus Casei. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 3068–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, W.Y.; Kim, H.; Chae, S.A.; Yang, S.-Y.; Ban, O.-H.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kwon, H.-S.; Jung, Y.H.; Yang, J. A Quadruple Coating of Probiotics for Enhancing Intestinal Adhesion and Competitive Exclusion of Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanas, N. Proteolytic Activity of Microorganisms Isolated from Freshwater Fish. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.-H.; Xue, Q.-Y.; Wei, B.-Q.; Wang, Y.-M.; Li, S.-M.; Chen, L.-F.; Guo, J.-H. Screening of Antagonistic Bacterial Strains against Meloidogyne Incognita Using Protease Activity. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Bayjanov, J.R.; Renckens, B.; Nauta, A.; Siezen, R.J. The Proteolytic System of Lactic Acid Bacteria Revisited: A Genomic Comparison. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, C.J. Plant-Based Animal Product Alternatives Are Healthier and More Environmentally Sustainable than Animal Products. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.S. Proteolysis of Proteins. In Co- and Post-Translational Modifications of Therapeutic Antibodies and Proteins; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 183–202. ISBN 978-1-119-05335-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Food Processing for the Improvement of Plant Proteins Digestibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3367–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Poel, A.F.B. Effect of Processing on Antinutritional Factors and Protein Nutritional Value of Dry Beans (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.). A Review. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 1990, 29, 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, M.; Ghosh, J. Study of Proteinase Activity of Lactobacillus Plantarum NCIM 2083. Int. J. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Strahinic, I.; Kojic, M.; Tolinacki, M.; Fira, D.; Topisirovic, L. The Presence of PrtP Proteinase Gene in Natural Isolate Lactobacillus Plantarum BGSJ3–18. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, A.J. The Multicatalytic Proteinase: Multiple Proteolytic Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12215–12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeven, M.K.; Kok, J.; Poolman, B. Specificity and Selectivity Determinants of Peptide Transport in Lactococcus Lactis and Other Microorganisms. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.E.; Dudley, E.G.; Pederson, J.A.; Steele, J.L. Peptidases and Amino Acid Catabolism in Lactic Acid Bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999, 76, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enferadi, M.H.N.; Mohammadizadeh, F.; Soltani, M.; Bahri, H.; Sheikhzadeh, N. Effects of Lactobacillus Plantarum on Growth Performance, Proteolytic Enzymes Activity and Intestine Morphology in Rainbow Trout. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Daniel, R.C.; Okeugo, B.; Armbrister, S.A.; Luo, M.; Taylor, C.M.; Wu, G.; Rhoads, J.M. Impact of Probiotic Limosilactobacillus Reuteri DSM 17938 on Amino Acid Metabolism in the Healthy Newborn Mouse. Amino. Acids 2022, 54, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Harper, G.M.; Dimitroglou, A.; Ringø, E.; Davies, S.J. Possible Influence of Probiotic Adhesion to Intestinal Mucosa on the Activity and Morphology of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Enterocytes. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirarat, N.; Pinpimai, K.; Endo, M.; Katagiri, T.; Ponpornpisit, A.; Chansue, N.; Maita, M. Modulation of Intestinal Morphology and Immunity in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus) by Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 91, e92–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Shoaie, S.; Bergentall, M.; Ghaffari, P.; Zhang, C.; Larsson, E.; Bäckhed, F.; Nielsen, J. The Gut Microbiota Modulates Host Amino Acid and Glutathione Metabolism in Mice. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-L. Amino Acid Metabolism in Intestinal Bacteria: Links between Gut Ecology and Host Health. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei-Nejad, S.; Rezaei, M.H.; Takami, G.A.; Lovett, D.L.; Mirvaghefi, A.-R.; Shakouri, M. The Effect of Bacillus Spp. Bacteria Used as Probiotics on Digestive Enzyme Activity, Survival and Growth in the Indian White Shrimp Fenneropenaeus Indicus. Aquaculture 2006, 252, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Qi, M.; Li, J.; Tan, B. Glutamine, Glutamate, and Aspartate Differently Modulate Energy Homeostasis of Small Intestine under Normal or Low Energy Status in Piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.-H.; Coloff, J.L. The Diverse Functions of Non-Essential Amino Acids in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y. Dietary Requirements of “Nutritionally Non-Essential Amino Acids” by Animals and Humans. Amino. Acids 2013, 44, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, G. Nutritionally Essential Amino Acids. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.J.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, A.E.; Miller, R.H.; Block, K.P. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1984, 4, 409–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, B.; Gao, J.; Htoo, J.K.; Chen, D. Regulation of Intestinal Health by Branched-Chain Amino Acids. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, S.; Zou, D.; Dong, D.; He, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, W.; Huang, L. Metabolic Shifts and Structural Changes in the Gut Microbiota upon Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation in Middle-Aged Mice. Amino. Acids 2016, 48, 2731–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Yamaoka, I.; Fukunaga, T.; Nakayama, M. Isoleucine, a Potent Plasma Glucose-Lowering Amino Acid, Stimulates Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Myotubes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, I. Impairment of Innate Immune Responses in Cirrhotic Patients and Treatment by Branched-Chain Amino Acids. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7298–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, F.-Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. Lysine Stimulates Protein Synthesis by Promoting the Expression of ATB0,+ and Activating the MTOR Pathway in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torricelli, P.; Fini, M.; Giavaresi, G.; Giardino, R.; Gnudi, S.; Nicolini, A.; Carpi, A. L-Arginine and L-Lysine Stimulation on Cultured Human Osteoblasts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Türkmen, M. Changes in the Digestive Enzymes and Hormones of Gilthead Seabream Larvae (Sparus Aurata, L. 1758) Fed on Artemia Nauplii Enriched with Free Lysine. Aquacult. Int. 2008, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, D.J. The Nutritional Value of Plant-Based Diets in Relation to Human Amino Acid and Protein Requirements. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1999, 58, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangolli, S.D.; Simson, P.; Lis, M.T.; Cheng, B.; Crampton, R.F.; Matthews, D.M. Amino Acid and Peptide Uptake in Protein Absorption. Clin. Sci. 1970, 39, 18P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.N. High-Protein Diets: Potential Effects on the Kidney in Renal Health and Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 44, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, J.P.; Luong, L.; Parsons, W.F.; Oh, S.; Sanford, D.; Gabalski, A.; Lighton, J.R.; Pisegna, J.R.; Germano, P.M. Long-Term Intake of a High-Protein Diet Affects Body Phenotype, Metabolism, and Plasma Hormones in Mice. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shertzer, H.G.; Woods, S.E.; Krishan, M.; Genter, M.B.; Pearson, K.J. Dietary Whey Protein Lowers the Risk for Metabolic Disease in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.R. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Muscle Protein Synthesis in Humans: Myth or Reality? J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2017, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overduin, J.; Guérin-Deremaux, L.; Wils, D.; Lambers, T.T. NUTRALYS ® Pea Protein: Characterization of in Vitro Gastric Digestion and in Vivo Gastrointestinal Peptide Responses Relevant to Satiety. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 59, 25622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-Parabiotics: The New Horizons in Microbial Biotherapy and Functional Foods. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type | Gene Name | Annotation | IDCC 3501 | 299v | WFCS1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oligopeptides ABC transport (Opp) system | OppA | Oligopeptide binding protein OppA | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| OppB | Oligopeptide transport system permease protein OppB | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| OppC | Oligopeptide transport system permease protein OppC | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| OppD | Oligopeptide transport ATP binding protein OppD | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Number of oligopeptide-related genes | 6 | 6 | 6 | ||
| Endopeptidases | PepO | Endopeptidase PepO | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| PepE | Dipeptidase E | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| PepB | Group B oligopeptidase PepB | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Aminopeptidases | PepN | Membrane alanyl aminopeptidase | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PepC | Cysteine aminopeptidase | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Tripeptidases | PepT | Tripeptide aminopeptidase | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Dipeptidases | PepD | Dipeptidase | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Proline-specific | PepQ | Xaa-Pro dipeptidase | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| PepX | Xaa-Pro dipeptidyl-peptidase | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| PepP | Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Number of peptide-related genes | 16 | 16 | 16 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, M.; Moon, J.; Kim, J.; Yang, J.; Jung, Y.H. Oral Administration of Animal and Plant Protein Mixture with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IDCC 3501 Improves Protein Digestibility. Fermentation 2023, 9, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060560
Jeon HJ, Kim H, Lee M, Moon J, Kim J, Yang J, Jung YH. Oral Administration of Animal and Plant Protein Mixture with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IDCC 3501 Improves Protein Digestibility. Fermentation. 2023; 9(6):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060560
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Hyeon Ji, Hayoung Kim, Minjee Lee, Jinseok Moon, Jungyeon Kim, Jungwoo Yang, and Young Hoon Jung. 2023. "Oral Administration of Animal and Plant Protein Mixture with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IDCC 3501 Improves Protein Digestibility" Fermentation 9, no. 6: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060560
APA StyleJeon, H. J., Kim, H., Lee, M., Moon, J., Kim, J., Yang, J., & Jung, Y. H. (2023). Oral Administration of Animal and Plant Protein Mixture with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IDCC 3501 Improves Protein Digestibility. Fermentation, 9(6), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060560






