Factors That Interfere in the Action of Sanitizers against Ochratoxigenic Fungi Deteriorating Dry-Cured Meat Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Standardization of the Initial Inoculum
2.2. Variables Tested
2.3. Application of Variables in the Test
2.4. Statistical Analysis
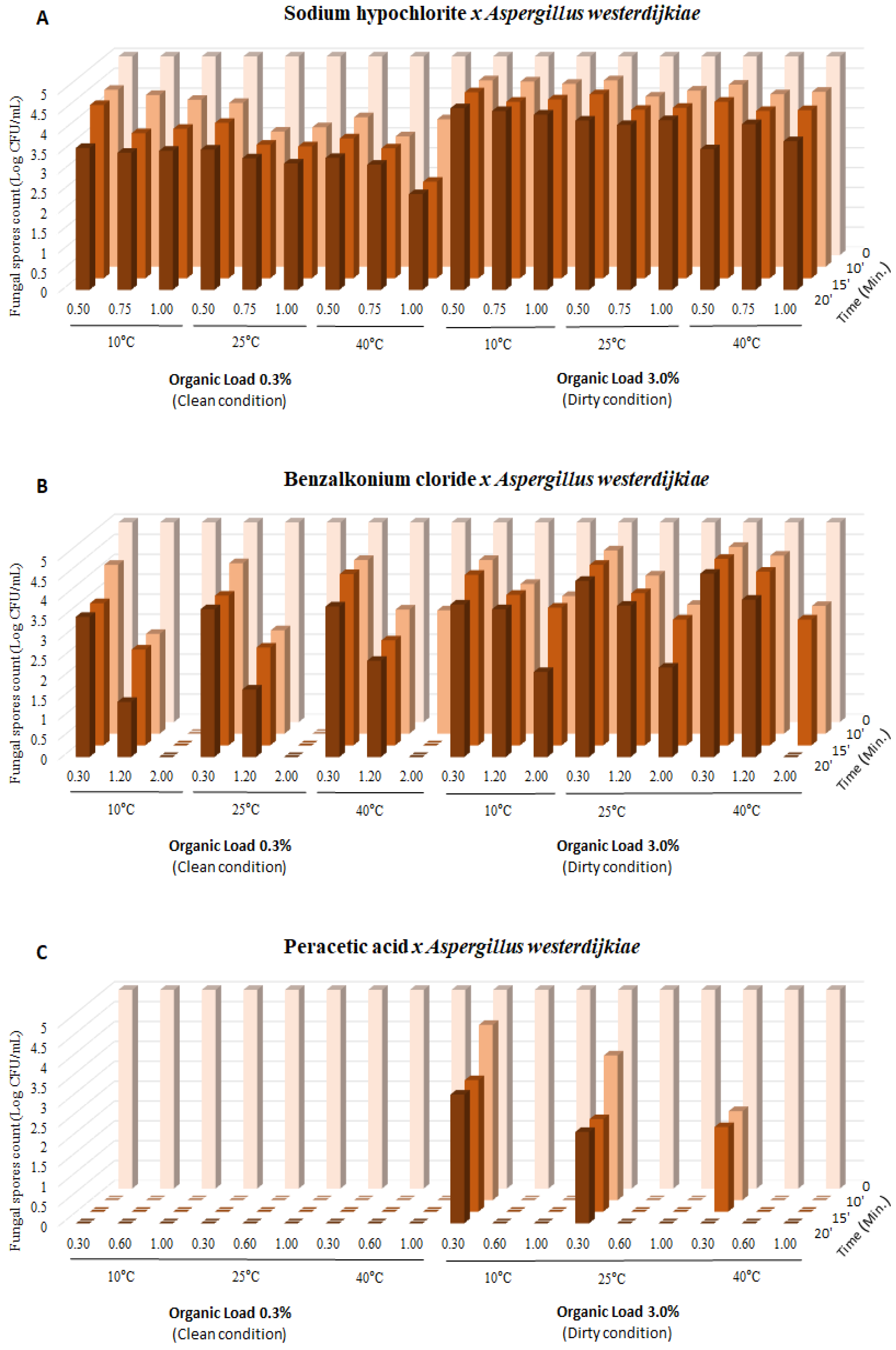
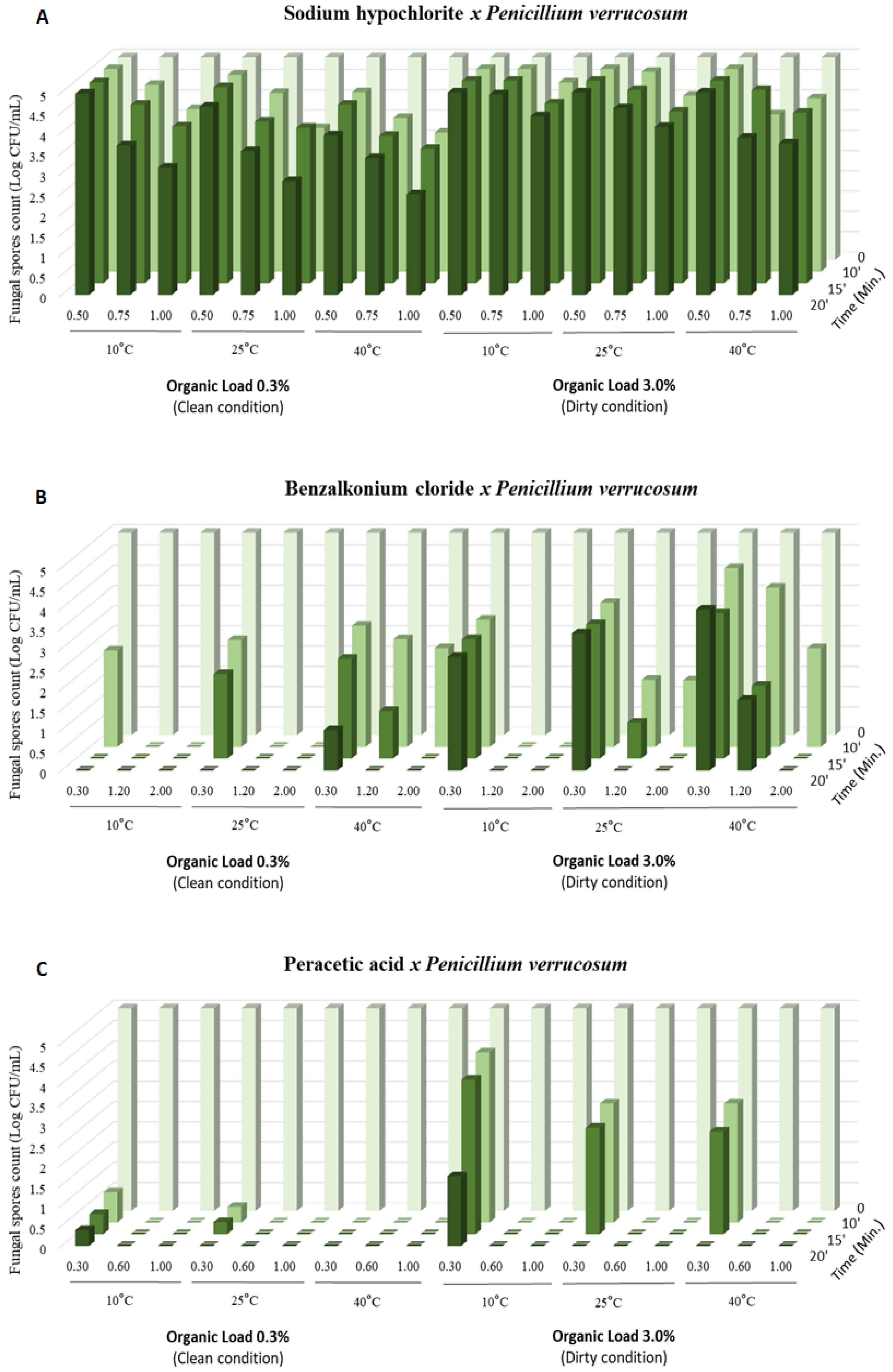
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludemann, V.; Pose, G.; Pollio, M.L.; Segura, J. Determination of growth characteristics and lipolytic and proteolytic activities of Penicillium strains isolated from Argentinean salami. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 96, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, A.; Córdoba, J.J.; Aranda, E.; Córdoba, M.G.; Asensio, M.A. Contribution of a selected fungal population to the volatile compounds on dry-cured ham. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 110, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonjak, S.; Ličen, M.; Frisvald, J.C.; Gunde–Cimerman, N. The mycobiota of three dry-cured meat products from Slovenia. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hocking, A.D. Fungi and Food Spoilage; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; Ochratoxin, A. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants. Sixty-Eight Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Mantle, P.G. Risk assessment and the importance of ochratoxins. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2002, 50, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Martín, A.; Delgado, J.; Córdoba, J.J. Presence of ochratoxin A on the surface of dry-cured Iberian ham after initial fungal growth in the drying stage. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacumin, L.; Chiesa, L.; Boscolo, D.; Manzano, M.; Cantoni, C.; Orlic, S.; Comi, G. Moulds and ochratoxin A on surfaces of artisanal and industrial dry sausages. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, K.; Pleadin, J.; Bevardi, M.; Vahčić, N.; Sokolić-Mihalak, D.; Frece, J. Natural occurrence of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and citrinin in Croatian fermented meat products. Food Control 2013, 34, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, P.; Haidukowski, M.; Epifani, F.; Cimmarusti, M.T.; Moretti, A.; Logrieco, A.; Susca, A. Fungal mycobiota and mycotoxin risk for traditional artisan Italian cave cheese. Food Microbiol. 2019, 78, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancardi, A.; Piro, R.; Galaverna, G.; Dall’Asta, C. A simple and reliable liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of ochratoxin A in hard cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattono, D.; Grosso, A.; Stocco, P.P.; Pazzi, M.; Zeppa, G. Survey of the presence of patulin and ochratoxin A in traditional semi-hard cheeses. Food Control 2013, 33, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Pereira, J.; Mareze, J.; Patrinou, E.; Santos, J.A.; Lopez-Díaz, T.M. Polyphasic identification of Penicillium spp. isolated from Spanish semi-hard ripened cheeses. Food Microbiol. 2019, 84, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakin, F.T.; Ozan, I.; Yipel, M.; Kürekci, C. Occurrence and health risk assessment of aflatoxins and ochratoxin a in Sürk, a Turkish dairy food, as studied by HPLC. Food Control 2018, 90, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Kovačević, D.; Perši, N. Ochratoxin A contamination of the autochthonous dry-cured meat product “Slavonski Kulen” during a six-month production process. Food Control 2015, 57, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Asta, C.; Galaverna, G.; Bertuzzi, T.; Moseriti, A.; Pietri, A.; Dossena, A.; Marchelli, R. Occurrence of ochratoxin A in raw ham muscle, salami and dry-cured ham from pigs fed with contaminated diet. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.M.; Jacobsen, T.; Nielsen, P.V.; Frisvad, J.C.; Kock, A.G. Mycobiota in the processing areas of two different meat products. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, E.; Montagna, I.; Restivo, F.M.; Degola, F. Ochratoxin A control in meat derivatives: Intraspecific biocompetition between Penicillium nordicum strains. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 8370106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parussolo, G.; Oliveira, M.S.; Garcia, M.V.; Bernardi, A.O.; Lemos, J.G.; Stefanello, A.; Mallmann, C.A.; Copetti, M.V. Ochratoxin A production by Aspergillus westerdijkiae in Italian-type salami. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Samson, R.A. Polyphasic taxonomy of Penicillium subgenus Penicillium. A guide to identification of food and air-borne terverticillate Penicillia and their mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2004, 49, 1–173. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, A.B.; Churey, J.J.; Worobo, R.W. Association of fungal genera from spoiled processed foods with physicochemical food properties and processing conditions. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilani, P.; Formenti, S.; Toscani, T.; Virgili, R. Influence of abiotic parameters on ochratoxin A production by a Penicillium nordicum strain in dry-cured meat model systems. Food Control 2010, 21, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Bernáldez, V.; Rodrígues, M.; Andrade, M.J.; Núñez, F.; Córdoba, J.J. Effect of selected protective cultures on ochratoxin A accumulation in drycured Iberian ham during its ripening process. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.; Magistà, D.; Lippolis, V.; Cervellieri, S.; Susca, A.; Perrone, G. Effect of Penicillium nordicum contamination rates on ochratoxin A accumulation in dry-cured salami. Food Control 2016, 67, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montero, L.; Córdoba, J.J.; Peromingo, B.; Álvarez, M.; Núñez, F. Effects of environmental conditions and substrate on growth and ochratoxin A production by Penicillium verrucosum and Penicillium nordicum: Relative risk assessment of OTA in dry-cured meat products. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.J.; Peromingo, B.; Rodríguez, M. Effect of cured meat product ingredients on the Penicillium verrucosum growth and ochratoxin A production. Food Control 2019, 96, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peromingo, B.; Sulyok, M.; Lemmens, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M. Diffusion of mycotoxins and secondary metabolites in dry-cured meat products. Food Control 2019, 101, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, G.S.; Pose, G.N.; Segura, J.A.; Ludemann, V. Diversidad de hongos filamentosos en el emplume de embutidos secos producidos en la región pampeana. SNS 2016, 10, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Castellari, C.; Quadrelli, A.M.; Laich, F. Surface mycobiota on Argentinean dry fermented sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canel, R.S.; Wagner, J.R.; Stenglein, S.A.; Ludemann, V. Indigenous filamentous fungi on the surface of Argentinean dry fermented sausages produced in Colonia Caroya (Córdoba). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacumin, L.; Milesi, S.; Pirani, S.; Comi, G.; Chiesa, L.M. Ochratoxigenic mold and ochratoxin A in fermented sausages from different areas in Northern Italy: Occurrence, reduction or prevention with ozonated air. J. Food Saf. 2011, 31, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parussolo, G.; Garcia, M.V.; Stefanello, A.; Silva, T.S.; Bernardi, A.O. Fungal microbiota in environmental air, raw materials and surface of dry fermented sausage produced in Southern Brazil. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 108, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, A.O.; Stefanello, A.; Garcia, M.; Parussolo, G.; Stefanello, R.F.; Moro, C.B.; Copetti, M.V. Efficacy of commercial sanitizers against fungi of concern in the food industry. LWT 2018, 97, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, A.O.; Garcia, M.V.; Copetti, M.V. Food industry spoilage fungi control through facility sanitization. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 29, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, A.O.; Stefanello, A.; Lemos, J.G.; Garcia, M.V.; Copetti, M.V. Antifungal activity of commercial sanitizers against strains of Penicillium roqueforti, Penicillium paneum, Hyphopichia burtonii, and Aspergillus pseudoglaucus: Bakery spoilage fungi. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, A.O.; Stefanello, A.; Lemos, J.G.; Garcia, M.V.; Copetti, M.V. The control of cheese and meat product spoilage fungi by sanitizers: In vitro testing and food industry usage. LWT 2021, 144, 111204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H. Process hygiene: Overall approach to hygienic processing. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities. 2008. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/disinfectionmethods/chemical.html/ (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- European Standard, n. 13697. Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics–Quantitative non-porous surface test for the evaluation of bactericidal and/or fungicidal activity of chemical disinfectants used in food, industrial, domestic and institutional areas-Test method and requirements without mechanical action (phase 2, step 2). 2001. Available online: https://www.situbiosciences.com/product/en-13697-chemical-disinfectants-and-antiseptics-quantitative-non-porous-surface-test-for-the-evaluation-of-bactericidal-and-or-fungicidal-activity-of-chemical-disinfectants-used-in-food-in/ (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Jaenisch, F.R.F.; Kuchiishi, S.S.; Coldebella, A. Atividade antibacteriana de desinfetantes para uso na produção orgânica de aves. Ciência Rural. 2010, 40, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanello, A.; Fracari, J.C.; Silva, M.; Lemos, J.G.; Garcia, M.V.; Alves dos Santos, B.; Copetti, M.V. Influence of type, concentration, exposure time, temperature, and presence of organic load on the antifungal efficacy of industrial sanitizers against Aspergillus brasiliensis (ATCC 16404). Food Microbiol. 2021, 97, 103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.L.; Kawamoto, S. Process hygiene: Types of sterilant. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology (Second Edition); Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Vandekinderen, I.; Devlieghere, F.; De Meulenaer, B.; Ragaert, P.; Van Camp, J. Optimization and evaluation of a decontamination step with peroxyacetic acid for fresh-cut produce. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, J.G.; Stefanello, A.; Olivier, A.B.; Valle, M.G.; Nicoloso, L.M.; Cichoski, A.J.; Wagner, R.; Copetti, M.V. Antifungal efficacy of sanitizers and electrolyzed waters against toxigenic Aspergillus. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, V.P.P.; Furtado, M.M.; Iwase, C.H.T.; Brondi-Mendes, J.S.; Nascimento, M.S. Microbial resistance to sanitizers in the food industry: Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanello, A.; Magrini, L.N.; Lemos, J.G.; Garcia, M.V.; Bernardi, A.O.; Cichoski, A.J.; Copetti, M.V. Comparison of electrolized water and multiple chemical sanitizer action against heat-resistant molds (HRM). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 335, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegaro, A.; Flores, A.F.; Simer, P.; Silva, F.I.; Sbardelotto, P.R.R.; Pinto, E.P. Sanitizantes: Concentrações e aplicabilidade, na indústria de alimentos. Sci Agrary Parana. 2016, 15, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, N.G.; Schilling, M.W.; Gravani, R.B. Sanitizers. In Principles of Food Sanitation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigmann, É.F.; Saccomori, F.; Bernardi, A.O.; Frisvad, J.C.; Copetti, M.V. Toxigenic Penicillia spoiling frozen chicken nuggets. Food Res. Int. 2015, 67, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sanitizers | Concentration (%) | Temperature (°C) | Exposure Time (min) | Organic Matter (%) | Neutralizers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzalkonium chloride | 0.3, 1.2, 2 | 10, 25, 40 | 10, 15, 20 | 0.3, 3 | Nutrient broth with 0.5% Tween 80 and 1% tryptone |
| Peracetic acid | 0.3, 0.6, 1 | 10, 25, 40 | 10, 15, 20 | 0.3, 3 | Nutrient broth with 0.6% sodium sulfate |
| Sodium hypochlorite | 0.5, 0.75, 1 | 10, 25, 40 | 10, 15, 20 | 0.3, 3 | Nutrient broth with 0.6% sodium sulfate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, S.; Stefanello, A.; Santos, B.; Fracari, J.; Leães, G.; Copetti, M. Factors That Interfere in the Action of Sanitizers against Ochratoxigenic Fungi Deteriorating Dry-Cured Meat Products. Fermentation 2023, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020083
Silva S, Stefanello A, Santos B, Fracari J, Leães G, Copetti M. Factors That Interfere in the Action of Sanitizers against Ochratoxigenic Fungi Deteriorating Dry-Cured Meat Products. Fermentation. 2023; 9(2):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Sarah, Andrieli Stefanello, Bibiana Santos, Juliana Fracari, Graziela Leães, and Marina Copetti. 2023. "Factors That Interfere in the Action of Sanitizers against Ochratoxigenic Fungi Deteriorating Dry-Cured Meat Products" Fermentation 9, no. 2: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020083
APA StyleSilva, S., Stefanello, A., Santos, B., Fracari, J., Leães, G., & Copetti, M. (2023). Factors That Interfere in the Action of Sanitizers against Ochratoxigenic Fungi Deteriorating Dry-Cured Meat Products. Fermentation, 9(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020083





