Isolation and Identification of Lactose-Degrading Yeasts and Characterisation of Their Fermentation-Related Ability to Produce Ethanol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Isolation from Kefir
2.2. Screening for Lactose-Degrading Yeast
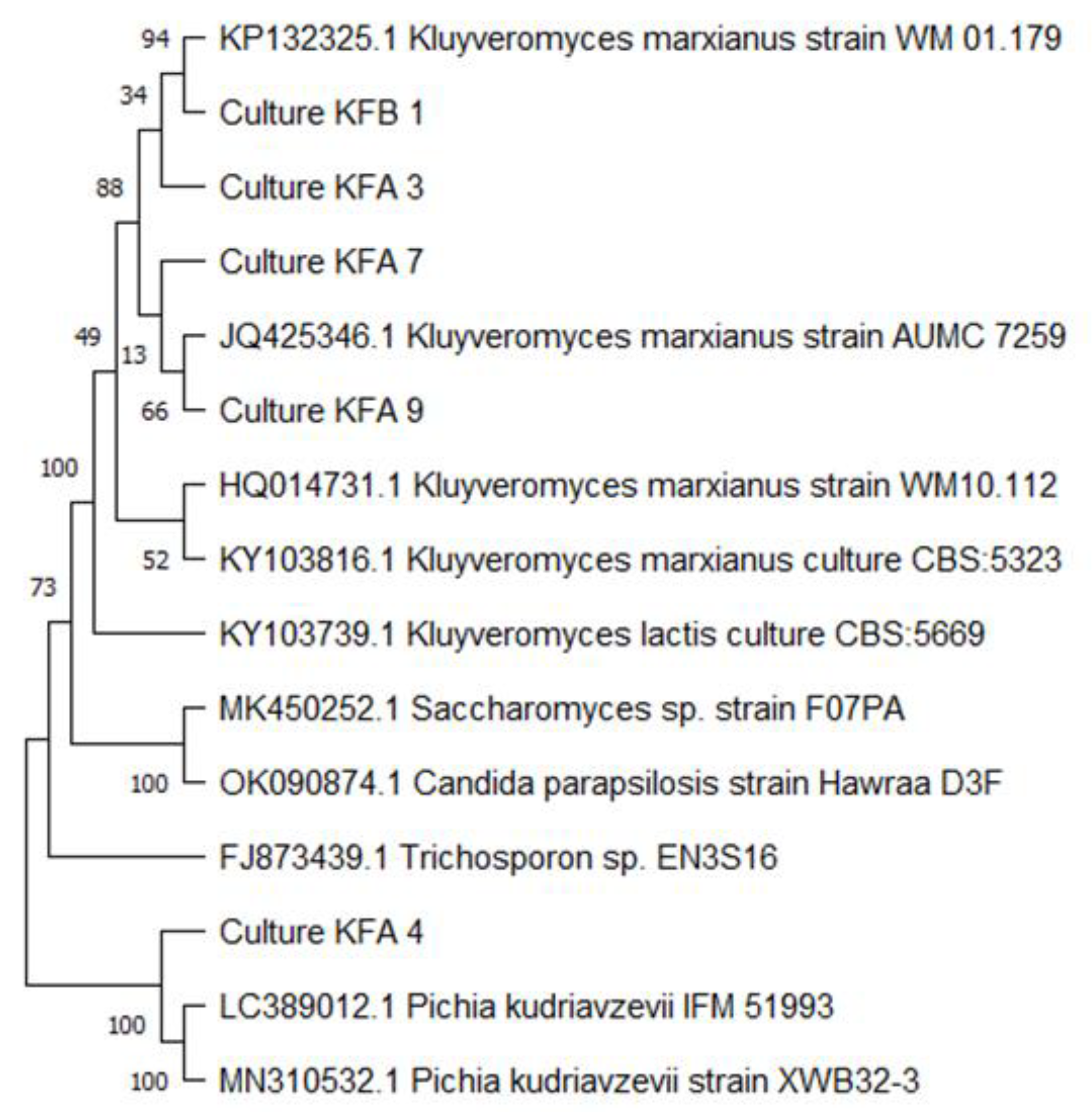
2.3. Molecular Identification of Isolates
2.4. Inoculum Preparation and Ethanolic Fermentation
2.5. Batch Kinetics of Biomass and Ethanolic Production
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Yeast Isolates
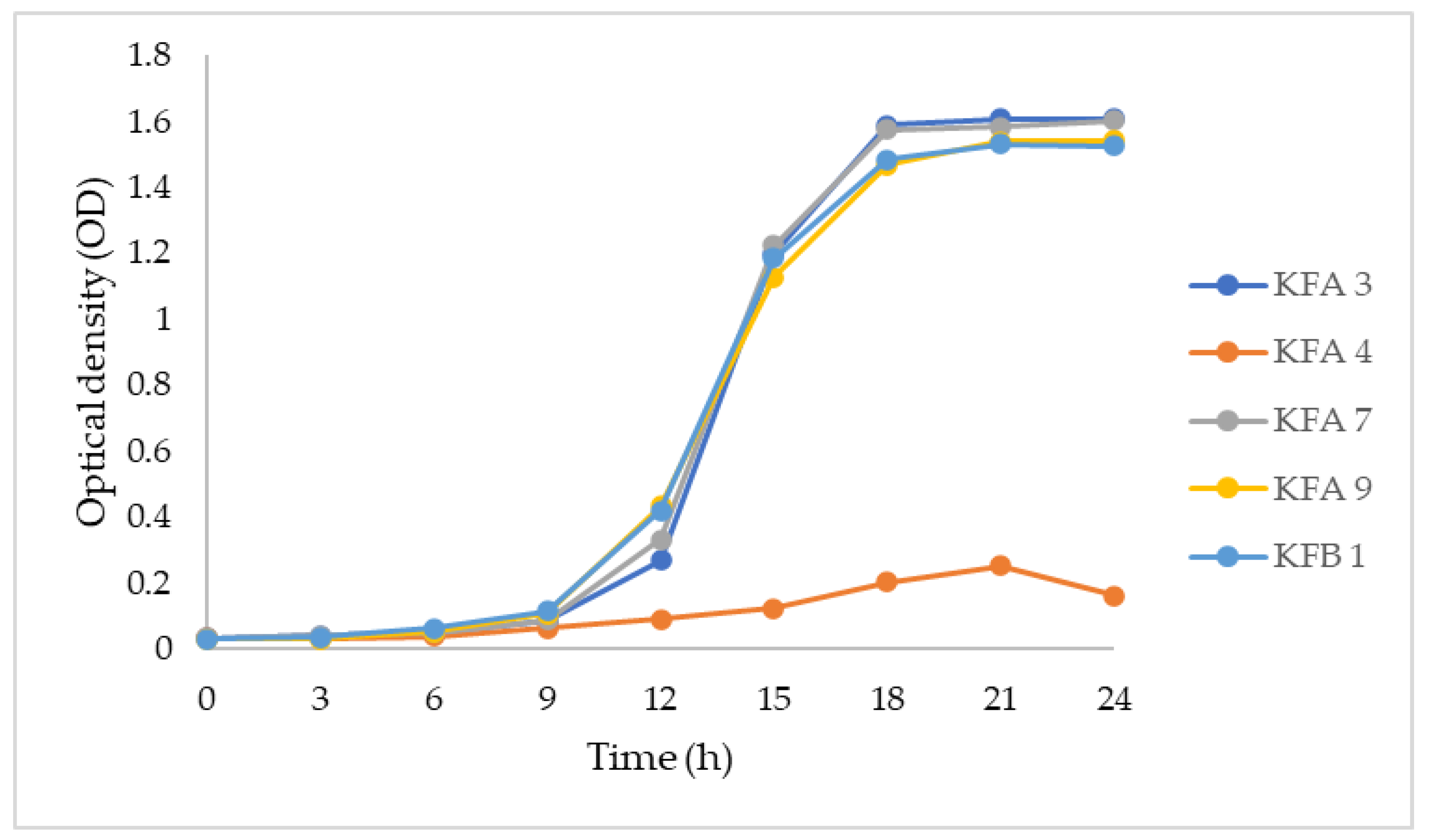
3.2. Growth Pattern on Lactose-Containing Media
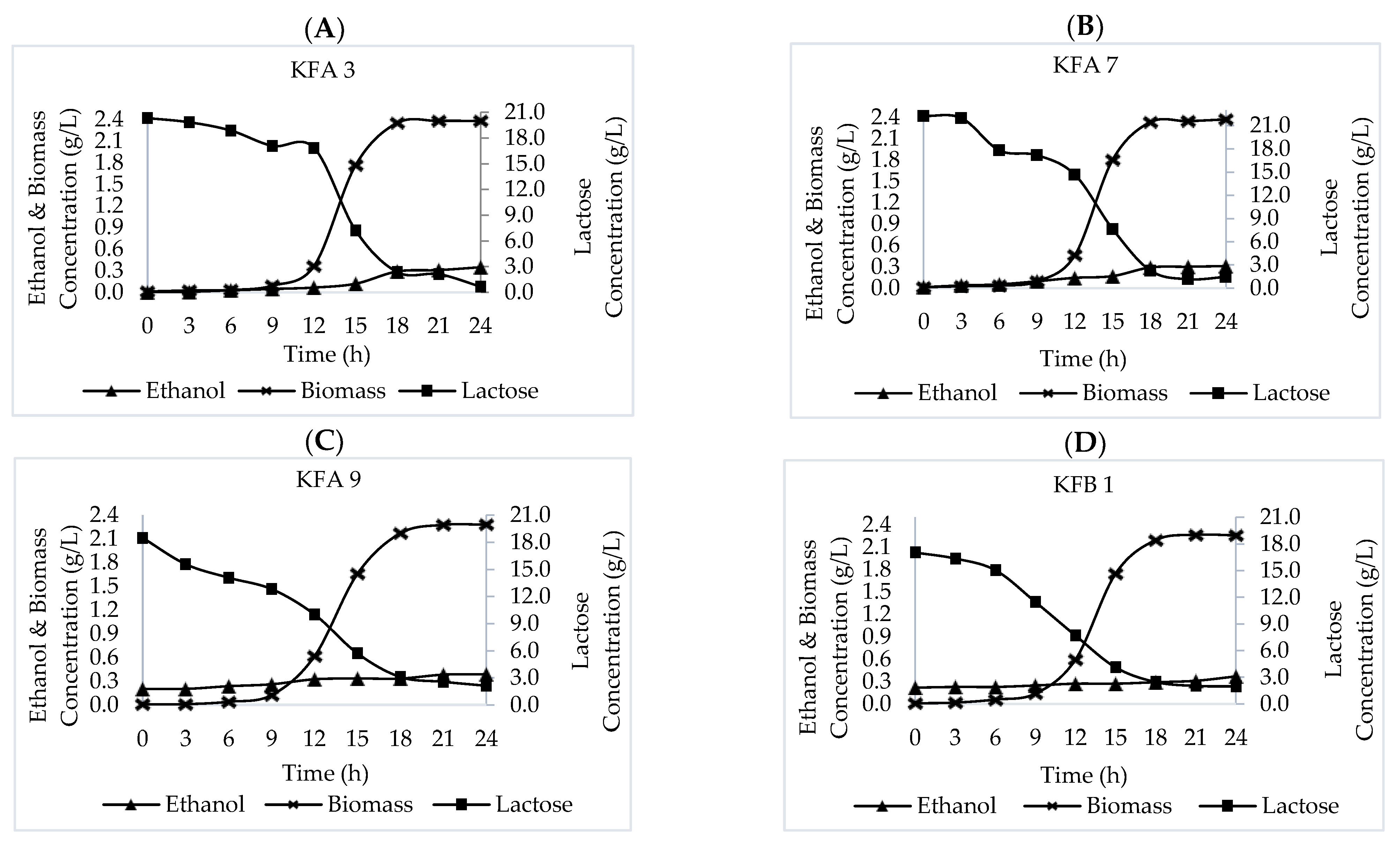
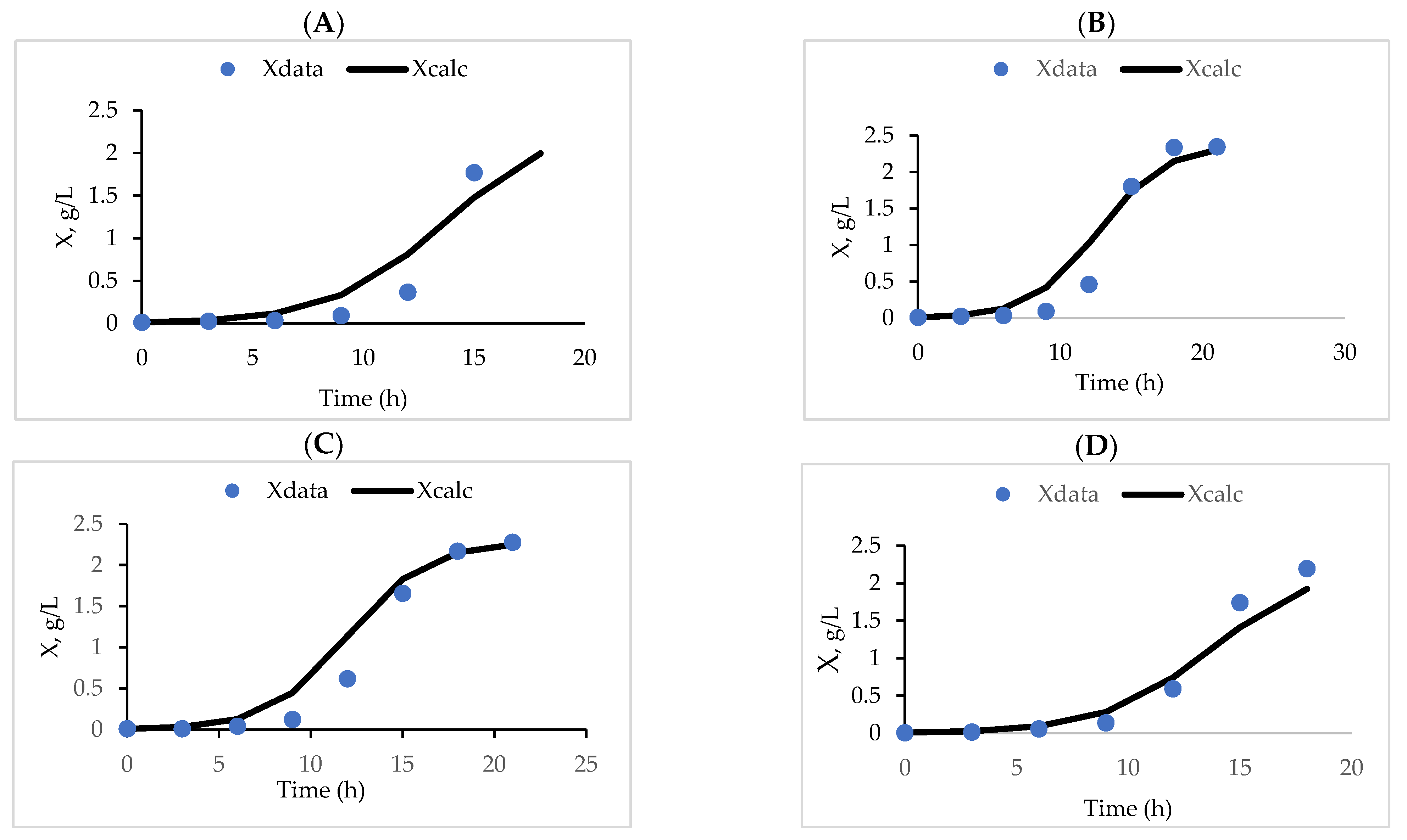
3.3. Fermentation Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bourrie, B.C.T.; Willing, B.P.; Cotter, P.D. The microbiota and health promoting characteristics of fermented baverage Kefir. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarbati, A.; Ciani, M.; Canonico, L.; Galli, E.; Comitini, F. Exploitation of yeast with probiotic traits for kefir production: Effectiveness of the microbial consortium. Fermentation 2022, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraporda, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Rumbo, M.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. The role of lactate on the immunomodulatory properties of the nonbacterial fraction of kefir. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, C.G.; Duarte, J.; Thangavel, D.; Perdigon, G.; Farnworth, E.; Matar, C. Immunomodulating capacity of Kefir. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.T.; Nisa, M.; Ahmad, H.; Afreen, A. Kefir and Health: A contemporary perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2013, 53, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.L.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Schneedorf, J.M. Anti-inflammatory properties of kefir and its polysaccharide extract. Inflammopharmacology 2005, 13, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-R.; Chen, M.-J.; Lin, C.-W. Antimutagenic and antioxidant properties of milk-Kefir and soymilk-Kefir. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gu, F.; Ruan, H.; Chen, Q.; He, J.; He, G. Induction of apoptosis of gastric cancer cells SGC7901 in vitro by a cell-free fraction of Tibetan kefir. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 30, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carasi, P.; Racedo, S.M.; Jacquot, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Serradell, M.A.; Urdaci, M.C. Impact of kefir derived Lactobacillus kefiri on the mucosal immune responseand gut microbiota. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 361604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraporda, C.; Junior, M.A.; Neumann, E.; Nunes, A.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Abraham, A.G.; Garrote, G.L. Biological activity of the non-microbial fraction of kefir: Antagonism against intestinal pathogens. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simova, E.; Beshkova, D.; Angelov, A.; Hristozova, T.; Frengova, G.; Spasov, Z. Lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in kefir grains and kefir made from them. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; De Antoni, G.L. Chemical and microbial characterisation of kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 96, 4149–4159. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, A.M.O.; Leite, D.C.A.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Alvares, T.S.; Peixoto, R.S.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Silva, J.T.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Microbiological and chemical characteristics of Brazilian kefir during fermentation and storage processes. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4149–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogacic, T.; Sinko, S.; Zamberlin, S.; Samarzija, D. Microbiota of kefir grains. Mljekarstvo 2013, 63, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Iraporda, C.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Kefir microorganisms: Their role in grain assembly and health properties of fermented milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardjan, T.; Lorbeg, P.M.; Rogelj, I.; Majhenic, A.C. Characterization and stability of lactobacilli and yeast microbiota in kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witthuhn, R.C.; Cilliers, A.; Britz, T.J. Evaluation of different preservation techniques on the storage potential of kefir grains. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.A.; Payne, R.W.; Yarrow, D. Yeasts: Characteristics and Identification, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Belloch, C.; Querol, A.; Barrio, E. Yeasts and Molds-Kluyveromyces spp.; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 1417–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Qvirist, L.A.; Filippo, C.D.; Strati, F.; Stefanini, I.; Sordo, M.; Andlid, T.; Felis, G.E.; Mattarelli, P.; Cavalieri, D. Isolation, identification and characterization of yeast from fermented goat milk of the Yaghnob Valley in Tajikistan. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.L.; Owusu-Kwarteng, J.; Thorsen, L.; Jespersen, L. Biodiversity and probiotic potential of yeasts isolated from Fura, a West African spontaneously fermented cereal. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 159, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianeva, O.D.; Voronina, G.O.; Pidgorskyi, V.S. Isolation and characteristics of the lactose-fermenting yeast Candida kefyr. Cytol. Gen. 2013, 47, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somogyi, M. Notes on sugar determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.J. Microdiffusion Analysis & Volumetric Error; Crosby Lockwood & Son Ltd.: London, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Shuler, M.L.; Kargi, F. Bioprocess Engineering Basic Concepts; Prentice Hall International: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, M.R.P.; Al-Hakami, A.M.; Assiry, M.M.; Jamil, A.S.; Assiry, A.M.; Shaker, M.A.; Hamid, M.E. In vitro anti-yeast activity of chloramphenicol: A preliminary report. Med. Mycol. 2015, 25, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzman, C.P.; Fell, J.W. Definition, Classification and Nomenclature of the Yeast. In The Yeasts, 4th ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman, J.; Sripuntanagoon, E.M. Pellicle associated adherence film above incubation broth surface-an inexpensive adjunct to recognizing Candida krusei in the laboratory: California. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.P.; Prescott, L.M. Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology, 5th ed.; Mc-Graw Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Naumova, E.S.; Sukhotina, N.N.; Naumov, G.I. Molecular-genetic differentiation of the dairy yeast Kluyveromyces lactis and its closet wild relatives. FEMS Yeast Res. 2004, 5, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesham, A.E.; Wambui, V.; Ogola, J.; Maina, J.M. Phylogenetic analysis of isolated biofuel yeasts based on 5.8S-ITS rDNA and D1/D2 26S rDNA sequences. J. Genetic Eng. Biotechnol. 2014, 12, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, J.-M.; Notredame, C. Bioinformatics for Dummies, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Viera, C.P.; Alvares, T.S.; Gomes, L.S.; Torres, A.G.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Kefir grains change fatty acid profile of milk during fermentation and storage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139910. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, S.; Owais, M. Ethanol production from crude whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 27, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, L.G.S.; Luvizetto, D.J.; Ferreira, L.S.; Rech, R.; Ayub, M.A.Z.; Secchi, A.R. A growth kinetic model of Kluyveromyces marxianus cultures on cheese whey as substrate. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 31, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ariyanti, D.; Hadiyanto, H. Ethanol production from whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus in batch fermentation system: Kinetics parameters estimation. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2013, 7, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Owais, M.; Saleemuddin, M.; Husain, S. Batch kinetics and modelling of ethanolic fermentation of whey. Int. J. Food Sci.Technol. 2005, 40, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigoyen, A.; Arana, I.; Castiella, M.; Torre, P.; Ibanez, F. Microbiological, physicochemical and sensory chatracteristics of kefir during storage. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.; Ntungwe, E.N.; Gregorio, J.; Rodrigues, L.M.; Pereira-Leite, C.; Caleja, C.; Pereira, E.; Barros, L.; Aguilar-Vilas, M.V.; Rosado, C.; et al. Characterization of kefir produced in household conditions: Physicochemical and nutritional profile and storage stability. Foods 2021, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolates | Colour | Gas | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Lactose | Sucrose | Fructose | Glucose | Lactose | Sucrose | Fructose | |
| KFA 3 | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − |
| KFA 4 | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | − |
| KFA 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| KFA 9 | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| KFA 10 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| KFA 11 | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| KFB 1 | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − |
| KFB 2 | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | + |
| KFB 4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| KFB 6 | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − |
| No | Isolates | Sequence Access Number | Species | Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | KFA 3 | KP132325.1 | Kluyveromyces marxianus | 99.86 |
| 2. | KFA 4 | MN310532.1 | Pichia kudriavzevii | 99.80 |
| 3. | KFA 7 | HQ014731.1 | Kluyveromyces marxianus | 99.86 |
| 4. | KFA 9 | KY103816.1 | Kluyveromyces marxianus | 99.86 |
| 5. | KFB 1 | JQ425346.1 | Kluyveromyces marxianus | 99.86 |
| K. marxianus Strains | X (g/L) | S (g/L) | P (g/L) | K (h−1) | Yx/s | Yp/s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 | X∞ | S0 | St | P0 | Pt | ||||
| KFA 3 | 0.092 | 2.380 | 17.080 | 7.201 | 0.047 | 0.120 | 0.385 | 0.170 | 0.007 |
| KFA 7 | 0.094 | 2.370 | 17.177 | 7.637 | 0.095 | 0.168 | 0.425 | 0.179 | 0.008 |
| KFA 9 | 0.124 | 2.281 | 12.818 | 5.700 | 0.261 | 0.334 | 0.470 | 0.216 | 0.010 |
| KFB 1 | 0.137 | 2.258 | 11.462 | 4.102 | 0.246 | 0.270 | 0.410 | 0.218 | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurniawati, M.; Nurliyani, N.; Budhijanto, W.; Widodo, W. Isolation and Identification of Lactose-Degrading Yeasts and Characterisation of Their Fermentation-Related Ability to Produce Ethanol. Fermentation 2022, 8, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040183
Kurniawati M, Nurliyani N, Budhijanto W, Widodo W. Isolation and Identification of Lactose-Degrading Yeasts and Characterisation of Their Fermentation-Related Ability to Produce Ethanol. Fermentation. 2022; 8(4):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040183
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurniawati, Murni, Nurliyani Nurliyani, Wiratni Budhijanto, and Widodo Widodo. 2022. "Isolation and Identification of Lactose-Degrading Yeasts and Characterisation of Their Fermentation-Related Ability to Produce Ethanol" Fermentation 8, no. 4: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040183
APA StyleKurniawati, M., Nurliyani, N., Budhijanto, W., & Widodo, W. (2022). Isolation and Identification of Lactose-Degrading Yeasts and Characterisation of Their Fermentation-Related Ability to Produce Ethanol. Fermentation, 8(4), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040183







