Abstract
Treatment of common pathogens, such as Salmonella species, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, etc., is a big challenge for a practitioner. Antibiotics’ side effects during their application for the treatment of infectious diseases should not be underestimated as they have many issues, such as the transfer of antibiotics-resistant genes, dysbiosis, and antibiotic-resistant strains, which is the main hurdle in the eradication of diseases. To avoid these antibiotics complications, in modern countries, the interest of using probiotics in feed supplementation to promote health and prevent or treat intestinal infectious diseases has been increasing. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the probiotic potential of three Lactobacilli strains isolated from clinically healthy dogs for their further utilization as a dietary supplement for dogs to avoid pathogenic and antibiotic complication. After 16SrRNA sequencing, in vitro tests were conducted to assess the survival potential of Lactobacilli under simulated gastrointestinal conditions and adhesion ability to the MODE-K cell line, effects on epithelial barrier function, anti-inflammatory activities, effects on host defensin peptides (beta-defensin 3), and inhibitory effects on common pathogens. Lactobacilli showed considerable potential to survive in simulated gastrointestinal environmental conditions, low pH, and high bile salt concentrations along with good adhesion properties with MODE-K cells. Pathogenic bacterial growth and their adhesion to MODE-K cells were significantly inhibited by Lactobacilli. Real-time PCR analyses further demonstrated that the L. acidophilus strain AR1 and AR3 inhibit Salmonella-induced proinflammatory cytokine (IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β) production and reinforce the expression of tight junction protein (occludin). None of the strains induce mRNA expression of beta-defensin 3 in MODE-K cells. Based on the in vitro results, the L. acidophilus strain AR1 has the potential to be supplemented in canine feed. However, further in vivo studies investigating health-promoting effects are awaited.
1. Introduction
Probiotics are live microorganisms that when administered to their host in an adequate amount confer a good health effect. The animal gastrointestinal tract is a very complex ecosystem on the Earth and is continuously affected by host-associated [1,2] and outside environmental factors [3]. Intestinal microbiota has received significant attention in recent years. The use of probiotic microorganisms in animal and human nutrition to improve health [4] as well as to control pathogenic infectious diseases has become an area of great research activity [5]. Antibiotics’ application as a feed additive or during infectious diseases has many side effects [6], i.e., long-lasting changes of the intestinal microbiota toward unhealthy patterns [7], intestinal barrier function damage [8], and many other problems, such as antibiotics residues in foodstuff, bone marrow toxicity, hepatotoxicity, nephropathy, reproductive disorder, carcinogenicity, etc. [9]. Nowadays, probiotics are considered as antibiotic alternatives to prevent and treat pathogenic infections [10]. For any good probiotics candidates, the adhesion abilities to the intestinal epithelium, potential to fortify the barrier function, antimicrobial activities, high survival rate in the gastrointestinal tract, low pH, and activity during bile salt exposure are considered to be crucial for probiotics functionality [11,12,13].
Unfortunately, concerning companion animals, such as dogs, the amount of probiotics research is insufficient. The dog was the first domesticated animal and is the most popular companion animal along with the cat. This is due to their valuable properties, such as better developed sense organs, social behavior, and intelligence [4]. In many countries of the world, dogs are considered part of the family and because of their close contact, which has lots of implications not only on animals but also on the owner, the trend of probiotics therapeutics as well as prophylaxis applications in canines has been increasing in modern cultures [14]. Some studies have investigated the probiotics potential of Lactobacillus species in dogs [14]. L. acidophilus DSM13241 has the potential to survive in the gastrointestinal tracts (GITs) of dogs and change the composition of colon microbiota toward a beneficial pattern by reducing the number of clostridia and increasing the percentage of lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Further, it also increases the concentrations of monocytes, neutrophils, RBCs, hemoglobin, and serum IgG and decreases erythrocyte fragility [15]. The application of the same strain improves the fecal dry matter, fecal consistency, and defecation frequency in dogs [16]). Another strain LAB20 of L. acidophilus isolated from dogs can adhere to canine intestinal epithelial cells, HT-29, and Caco-2 cell lines. This strain improves the intestinal barrier function by increasing the transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and also shows an anti-inflammatory characteristic by attenuating LPS-induced IL-8 in HT-29 cells [11]. L. fermentum CCM 7421 with alginite improves dog health by increasing hemoglobin and serum magnesium levels, and also changes the microbiota composition towards a healthy pattern by decreasing and increasing the number of pathogenic (coliform, clostridia) and beneficial microbes (LAB), respectively [17]. L. murinus strain LbP2 improves dogs’ mental status, appetite, fecal consistency, and clinical score, and with other therapeutic measures, probiotics application appears to be promising to manage canine distemper-associated diarrhea [18].
The composition of dog intestinal microbiota changes with respect to age [19]: as dogs become older, the prevalence and number of Lactobacillus sp. tend to decrease. Therefore, it is necessary to develop feed supplemented with some strains isolated from healthier dogs with good probiotics potential to improve the life quality of both dogs and their owners. This study aimed to assess the probiotic potential of dog-isolated Lactobacilli (L. fermentum, L. acidophilus) to be used in dog food. We conducted some basic necessary tests, which are considered essential for the functionality of any probiotic candidates.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
Several Lactobacilli were successfully isolated from healthy dog feces, purified on selective lactic acid bacterial agar, and then identified by 16S rRNA sequencing. L. acidophilus (strain AR1; GenBank MZ854114), L. acidophilus (strain AR2; GenBank MZ854118), and L. fermentum (strain AR3; GenBank MZ735397) were chosen for further assessment. These 3 strains were anaerobically grown at 37 °C in the De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar medium (MRS). The pathogenic strain, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strain ATCC14028, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strain SL1344, Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli k88 (ETEC) (provided through the courtesy of Prof. Jiufeng Wang from China Agricultural University), and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) (provided by Prof. Aizhen Guo from Huazhong Agricultural University) were grown in Lysogeny broth (LB) medium at 37 °C.
2.2. Lysozyme Resistance Assay
A method described by Zago et al. (2011) [20] was used to assess the lysozyme resistance characteristics of tested strains. Briefly, overnight culture of each strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) was centrifuged and inoculated in 9 mL of sterile electrolyte solutions (2.2 g/L KCl, 0.22 g/L CaCl2, 1.2 g/L NaHCO3, 6.2 g/L NaCl, 0.1 g/L lysozyme) to simulate in vivo dilution by saliva. The bacterial suspensions without lysozyme in sterile electrolyte solution were used as a control. The survival rate of each strain was determined after 90 and 180 min by the agar plate count method and compared to the control. The experiments were repeated three times in triplicate.
2.3. Bile and pH Resistance Assays
Overnight culture of each strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) was inoculated in MRS broth with different pH (2, 3, 4, 5) and bile concentrations (0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2%). The inoculated MRS broth was kept at 37 °C for 3 h. After 3 h, the viable bacterial growth was measured by the agar plate count method and compared with the control. The results were presented as growth percentage compared to the control. The experiments were carried out in triplicate and repeated three times independently.
2.4. In Vitro Resistance to Gastrointestinal Conditions
A method adopted in the study of Falah et al. (2019) [21] was used to prepare simulated gastric and intestinal juices. Briefly, the overnight cultures of the tested strains were centrifuged and resuspended to the original volume and then each strain was inoculated to simulate gastric and intestinal juices. To prepare simulated gastric and intestinal juices, pepsin (final concentration 3 g/L, pH 2) and pancreatin (1 g/L containing 0.2% bile salts with pH 8) were dissolved in 0.5% v/v sterile solution of NaCl and PBS, respectively. Both juices were sterile, using 0.22 µm pore size filters. After different incubation periods (0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min) with these simulated juices, the viable count of Lactobacilli (AR1, AR2, AR3) was calculated by the agar plate count method. The assays were performed in triplicate and repeated three times.
2.5. Exopolysaccharide Production Test
An exopolysaccharides (EPS) production test was performed according to an already described method of Garai-Ibabe et al., (2010). The tested strains were grown at 28 °C in an atmosphere containing 10% CO2 for 48 h, in MRS broth supplemented with 20% (v/v) tomato juice and 5 g/L fructose. By visually observing the culture viscosity, the EPS-producing ability of each strain was assessed. Upon agitation, a ropy liquid culture showed production of EPS [22].
2.6. Co-Culture of Lactobacilli Strains (AR1, AR2, AR3) and Pathogens
Overnight cultures of the tested strains and pathogenic strains were adjusted to equal concentrations (107 CFU per mL) by adjusting their OD600 values. In total, 1 mL (107 CFU per mL) of strain AR1 and ATCC14028 was inoculated together in fresh MRS broth to a final volume of 50 mL and named AR1-ST28. Co-cultures of AR1 with SL1344, ETEC, and S. aureus were named AR1-SL44, AR1-ETEC, and AR1-S. aureus, respectively. Co-cultures of AR2 with ATCC14028, SL1344, ETEC, and S. aureus were named AR2-ST28, AR2-SL44, AR2-ETEC, and AR2-S. aureus, respectively. Similarly, co-cultures of strain AR3 with ATCC14028, SL1344, ETEC, and S. aureus were named AR3-ST28, AR3-SL44, AR3-ETEC, and AR3-S. aureus, respectively. The viable bacterial count and pH of co-cultures and pure cultures of each bacteria were measured by the agar plate count method at different intervals (6, 12, 24 h). The experiment was repeated three times [23].
2.7. Assessment of Pathogenic Growth Inhibitory Effects of Lactobacilli Strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) Metabolites
To see whether the growth inhibitory effects on pathogens by Lactobacilli are mainly due to their low pH or their metabolites are also involved, the pathogens were grown in MRS broth with pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of Lactobacilli strains (AR1, AR2, AR3). For this, the AR1 strain was grown for 24 h in MRS broth and the pH of this end culture was measured. Then, ATCC14028 was grown in MRS broth with pH equal to this 24 h culture pH of AR1 and named AR1pH-ST28. The growth of SL1344, ETEC, and S. aureus in MRS broth with pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of AR1 was named AR1pH-SL44, AR1pH-ETEC, and AR1pH-S. aureus, respectively. The growth of ATCC14028, SL1344, ETEC, and S. aureus in MRS broth with pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of AR2 was named AR2pH-ST28, AR2pH-SL44, AR2pH-ETEC, and AR2pH-S. aureus, respectively. Similarly, the growth of ATCC14028, SL1344, ETEC, and S. aureus in MRS broth with pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of AR3 was named AR3pH-ST28, AR3pH-SL44, AR3pH-ETEC, and AR3pH-S. aureus, respectively. The viable count of these pathogens (grown with Lactobacilli and in pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of different Lactobacilli) was counted by plating on LB agar plates after 12 h of incubation at 37 °C and compared with each other.
2.8. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
MODE-K (mouse epithelial cell line) cells were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium supplemented with 1% antibiotic (penicillin-streptomycin) and 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Before infection, the cells were seeded (2.5 × 105/well) in 6-well plates, with each well containing 3 mL of DMEM media supplemented with 10% FBS without antibiotics, and were grown at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% air atmosphere [24].
2.9. Antibacterial Activity of Lactobacilli (AR1, AR2, AR3)-Treated MODE-K Cell Culture Supernatant
The MODE-K cells (provided by Prof. Deshi Shi from Huazhong Agricultural University) were grown in 6-well plates and exposed to each Lactobacilli strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) (100 bacteria/cell) for 6 h and then supernatants were collected to check their antimicrobial activity. The supernatant of MODE-K cells without Lactobacilli strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) exposure was used as a negative control whereas supernatant collected from wells containing only Lactobacilli strain (AR1, AR2, AR3, no MODE-K cells) was used as a positive control. The antimicrobial activity of the supernatants after filtering (0.25-µm pore size filters) was checked against the pathogenic strain (ATCC14028, SL1344, ETEC, S. aureus). A 10 µL suspension of an overnight culture of pathogens in LB broth was inoculated in 500 µL of supernatants. The viability of the pathogen was assessed by the agar plat count method after 2 h of growth incubation at 37 °C and 200 rpm shaking. The experiment was carried out in triplicate and performed three times [25].
2.10. Adhesion and Adhesion Inhibition Assays
The adhesion of probiotics with eukaryotic cells (MODE-K) was assessed by agar plate count methods. The MODE-K cells were grown in 24-well plates. At appropriate confluency, the cells were exposed to Lactobacilli strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) at different concentrations (106 CFU per mL, 107 CFU per mL, 108 CFU per mL) and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% air atmosphere for 2 h. After 2 h, the cells were washed 4–5 times with PBS to remove unbound bacteria and were lysed using 0.2% 100 µL of TritonTM X-100 to assess the viable bacterial count by the agar plate count method. The wells with only bacteria (no MODE-K cells) were kept as a control. The adhesion assay was expressed as a percentage of CFU per mL compared to CFU per mL with control.
Competition, inhibition, and displacement assays were performed to check the inhibitory effects of Lactobacilli strains (AR1, AR2, AR3) on pathogen adhesion with MODE-K cells. Lactobacilli strains (AR1, AR2, AR3) were added before, at the same time, and 1 h after the addition of pathogenic strains to MODE-K cells for the inhibition, competition, and displacement assay, respectively. After 2 h of incubation for each assay, the cells were washed with PBS to remove unbound bacteria and then lysed using 0.2% 100 µL of TritonTM X-100. The viable count of the pathogen was calculated by serial dilution and plating on LB agar plates. The adhesion was expressed as a percentage of the adhering pathogens normalized to the control [21,22,23].
2.11. Real-Time PCR for mRNA Expression of Tight Junction Proteins, Cytokines, and Defensin Peptides
PCR was performed to check the effects of Lactobacilli strains (AR1, AR2, AR3) and pathogenic strain (S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 and S. Typhimurium SL1344) on different gene expression (Occludin, IL-8, IL-6, IL-1β) using MODE-K cells. First, the MODE-K cells were exposed for 2 h before total RNA extraction to all bacteria separately (100 bacteria/cells) to check the mRNA expression of Occludin, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β. To assess the anti-inflammatory activity of Lactobacilli strain (AR1, AR2, AR3) and reinforcement of tight junction protein (occludin) during S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 and S. Typhimurium SL1344, the MODE-K cells were exposed to each Lactobacilli strain for 1 h before addition of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 and S. Typhimurium SL1344 at the same MOI. After 2 h of incubation, the total RNA was extracted from all treated and control groups by Trizol reagent as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. To investigate the effects of Lactobacilli on the gene expression of beta-defensin 3, the confluent MODE-K cells were exposed to each tested strain (100 bacteria/cell) for 6 h before total RNA extraction. Using a FastKing RT Kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), the cDNA was made from this extracted RNA after checking its quality and quantity. For qPCR, the 20 µL reaction mixture containing 1 µL of primers (0.5 µL of forward and 0.5 µL of reverse primer), 7 µL of nuclease-free water, 2 µL of cDNA, and 10 µL of SYBR Green Master mix (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) was used. The experimental program consisted of pre-denaturation for 30 s at 95 °C, followed by denaturation cycles (40) for 10 s at 95 °C, annealing for 30 s at 56 °C, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s. The 2−ΔΔCT method of Livak and Schmittgen [26] was used to calculate the relative expression level of genes using glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a housekeeping gene for normalization of the expression level of genes. The used primer sequences are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Primers sequences used for real-time PCR.
3. Statistical Analysis
Two-way ANOVA followed by turkeys’ multiple comparisons and student t-test was performed to analyze statistically significant (p < 0.05) data. Version 8.0.1 of GraphPad Prism was used to visualize the data.
4. Results
4.1. Tolerance to Lysozyme
L. acidophilus AR1 was observed to be more resistant against lysozyme followed by L. acidophilus AR2 and L. fermentum AR3. L. acidophilus AR1 showed a considerable survival percentage of 7.22 ± 1.2% (7.33 ± 6.54 log CFU/mL) after 90 min of incubation in lysozyme. However, the survival percentage decreased to 0.63 ± 0.25% (6.67 ± 6.43 log CFU/mL). The survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR2 after a 90- and 180 in incubation with lysozyme was found to be 3.88 ± 2.20% (7.01 ± 6.48 log CFU/mL) and 0.10 ± 0.07% (6.06 ± 5.48% log CFU/mL), respectively. Whereas the survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR3 after a 90 and 180 min incubation with lysozyme was found to be 1.87 ± 1.25% (6.70 ± 6.29 log CFU/mL) and 0.3 ± 0.51% (4.77 ± 4.48 log CFU/mL), respectively (Figure 1).
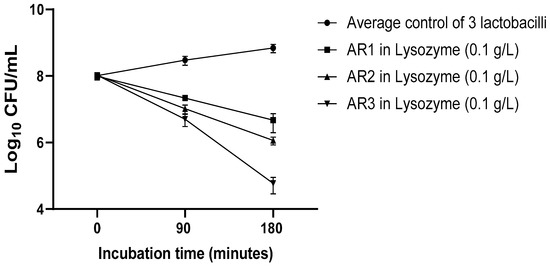
Figure 1.
Lysozyme resistance assay of L. acidophilus AR1, L. acidophilus AR2, and L. fermentum AR3.
4.2. pH and Bile Salt Resistance
L. acidophilus AR1 showed greater resistance against the low pH and high bile salt concentration followed by L. acidophilus AR2 and L. fermentum AR3. The survival rate of each strain increased as pH increased. The survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR1 at pH 5, 4, 3, and 2 was found to be 97 ± 1% (7.99 ± 6.01 log CFU/mL), 76 ± 0.72% (7.88 ± 5.85 log CFU/mL), 40 ± 0.51% (7.60 ± 5.71 log CFU/mL), and 10 ± 0.50% (7.02 ± 5.69 log CFU/mL), respectively. The survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR2 at pH 5, 4, 3, and 2, was calculated to be 95.63 ± 0.86% (7.98 ± 5.93 log CFU/mL), 67 ± 1.85% (7.82 ± 6.26 log CFU/mL), 32.4 ± 1.36% (7.51 ± 6.13 log CFU/mL), and 8.4 ± 0.50% (6.92 ± 5.70 log CFU/mL), respectively. Similarly, the survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR3 at pH 5, 4, 3, and 2 was found to be 95.2 ± 1.36% (7.97 ± 6.13 log CFU/mL), 56.5 ± 1.85% (7.75 ± 6.18 log CFU/mL), 15.7 ± 1.07% (7.19 ± 6.03), and 2.7 ± 0.64% (6.43 ± 5.80 log CFU/mL), respectively. At higher bile salt concentrations, the survival rate of each strain decreased. The survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR1 was observed to be 9 ± 0.50% (6.95 ± 5.69 log CFU/mL), 4.9 ± 0.65% (6.69 ± 5.81 log CFU/mL), and 1.2 ± 0.45% (6.07 ± 5.66 log CFU/mL) at the 0.05%, 0.1%, and 0.2% concentration of bile, respectively. The survival percentage of L. acidophilus AR2 at the 0.05%, 0.1%, and 0.2% concentration of bile was found to be 8 ± 0.88% (6.90 ± 5.94 log CFU/mL), 3.2 ± 0.52% (6.50 ± 5.72 log CFU/mL), and 0.76 ± 0.50% (5.88 ± 5.70 log CFU/mL), respectively. A similar trend of a decreasing percentage at the higher bile salt concentration was also found with L. acidophilus AR3 as indicated by the 4.8 ± 0.56% (6.68 ± 5.75 log CFU/mL), 0.51 ± 0.48% (5.71 ± 5.68 log CFU/mL), and 0.04 ± 0.03% (4.64 ± 4.59 log CFU/mL) survival rate at the 0.05%, 0.1%, and 0.2% concentration of bile, respectively (Figure 2).
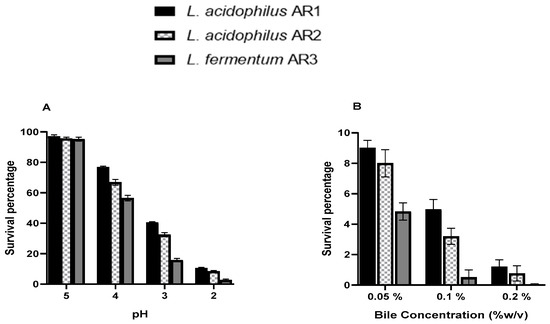
Figure 2.
pH (A) and bile (B) resistance assays of L. acidophilus AR1, L. acidophilus AR2, and L. fermentum AR3.
4.3. Tolerance of the Simulated Condition of GIT
Figure 3 shows that all strains retained their viability during exposure to simulated gastric and intestinal juices. The L. acidophilus strain AR1 was found to be more resistant to simulated gastrointestinal conditions followed by the L. acidophilus strain AR2 and L. fermentum strain AR3. The survival percentage of each strain was greater in simulated intestinal juice as compared to simulated gastric juice. In simulated intestinal juice, the survival percentage of the L. acidophilus strain AR1 was found to be 61.6 ± 1.65% (6.93 ± 5.93 log CFU/mL), 33.7 ± 6.5% (6.78 ± 5.76 log CFU/mL), 15.3 ± 2.22% (6.55 ± 5.54 log CFU/mL), and 6.5 ± 1.39% (6.26 ± 5.51 log CFU/mL) after 30, 60, 90, and 180 min of incubation, respectively. Whereas in simulated gastric juice, the survival percentage of L. acidophilus strain AR1 was found to be 44.9 ± 3.8% (6.83 ± 5.84 log CFU/mL), 19.6 ± 4.1%, (6.55 ± 5.69 log CFU/mL) 7.4 ± 0.87% (6.24 ± 5.39 log CFU/mL), and 2.5 ± 0.23% (5.86 ± 4.87 log CFU/mL) after 30, 60, 90, and 180 min of incubation, respectively.
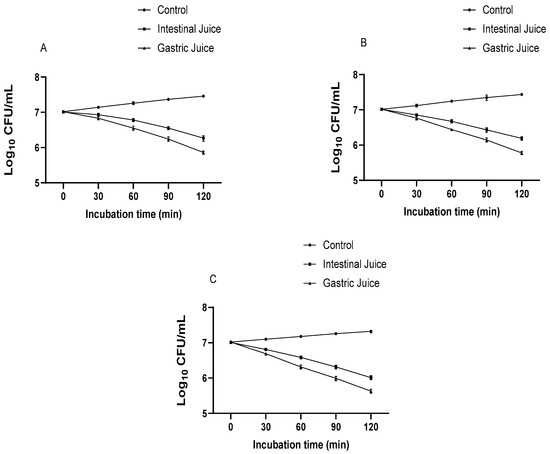
Figure 3.
The survival rate of L. acidophilus AR1 (A), L. acidophilus AR2 (B), and L. fermentum AR3 (C) under simulated GIT conditions.
In simulated intestinal juice, the survival percentage of the L. acidophilus strain AR2 was found to be 54.3 ± 6.4% (6.85 ± 5.64 log CFU/mL), 26.8 ± 2.47% (6.67 ± 5.70 log CFU/mL), 12.1 ± 1.56% (6.43 ± 5.61 log CFU/mL), and 5.6 ± 0.78% (6.19 ± 5.25 log CFU/mL) after 30, 60, 90, and 180 min of incubation, respectively. Whereas in simulated gastric juice, the survival percentage of the L. acidophilus strain AR2 was found to be 44.3 ± 8.07% (6.76 ± 5.82 log CFU/mL), 15.6 ± 1.5% (6.44 ± 5.28 log CFU/mL), 6.1 ± 1.48% (6.24 ± 5.26 log CFU/mL), and 2.1 ± 0.28% (5.37 ± 4.79 log CFU/mL) after 30, 60, 90, and 180 min of incubation, respectively.
In simulated intestinal juice, the survival percentage of the L. acidophilus strain AR3 was found to be 51.6 ± 3.12% (6.81 ± 5.51 log CFU/mL), 25.5 ± 3.37% (6.58 ± 5.56 log CFU/mL), 11.4 ± 1.66% (6.31 ± 5.41 log CFU/mL), and 4.9 ± 1.10% (6.01 ± 5.13 log CFU/mL) after 30, 60, 90, and 180 min of incubation, respectively. Whereas in simulated gastric juice, the survival percentage of the L. acidophilus strain AR3 was found to be 38.9 ± 1.47% (6.69 ± 5.63 log CFU/mL), 13.7 ± 1.10%, (6.31 ± 5.41 log CFU/mL) 5.3 ± 0.52% (5.99 ± 5.15 log CFU/mL), and 2 ± 0.28% (5.37 ± 4.73 log CFU/mL) after 30, 60, 90, and 180 min of incubation, respectively.
4.4. Exopolysaccharide Production
The L. acidophilus strain AR1 showed a more ropy character in MRS broth, supplemented with 20% (v/v) tomato juice and 5 g/L fructose, followed by the L. acidophilus strain AR2 and L. fermentum strain AR3.
4.5. Co-Culture of Lactobacilli and Pathogens
The Lactobacilli strain inhibited the growth of pathogenic bacteria when grown together. Figure 4 shows the growth pattern of L. acidophilus AR1 pure culture and coculture with different pathogens. The growth pattern in the pure and co-culture groups was almost similar. However, in the pure culture, the growth was slightly less than the co-culture with pathogens. Similar growth patterns were observed for L. acidophilus AR2 (Figure 5) and L. fermentum AR3 (Figure 6) during co-culture assays and pure culture. However, the growth inhibitory effects of each Lactobacillus on different pathogens were found to be different. The pathogenic bacterial growth was inhibited in co-culture with Lactobacilli. After 24 h, the viable count of each pathogen in pure culture was more than in co-culture with Lactobacilli (Figure 7). The acid production patterns by each probiotic strain, as indicated by a decrease in the pH of the medium (Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10), were almost similar under each of the culture conditions (pure and co-culture assays). The pH decline was slower in the case of pure cultures of pathogenic bacteria than that of co-cultures and pure cultures of Lactobacilli.
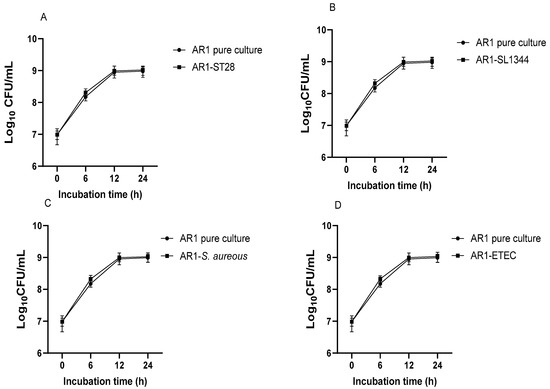
Figure 4.
Growth pattern of L. acidophilus AR1 in pure culture and co-culture with S. Typhimurium 14028. (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D).
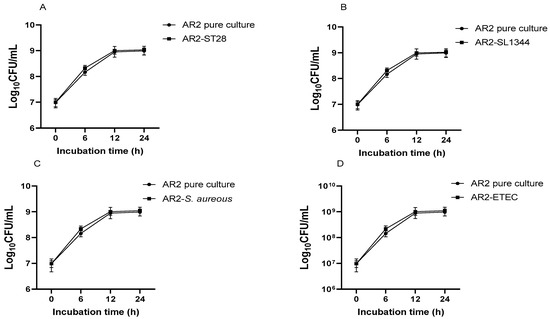
Figure 5.
Growth pattern of L. acidophilus AR2 in pure culture and co-culture with S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D).
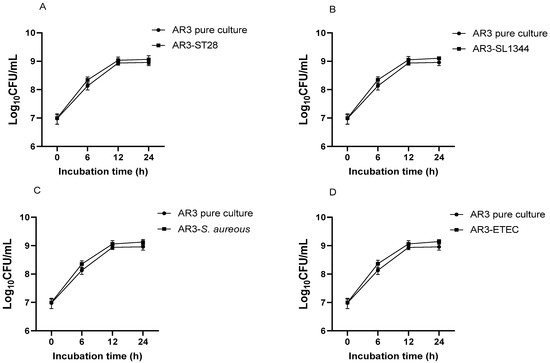
Figure 6.
Growth pattern of L. acidophilus AR3 in pure culture and co-culture with S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D).
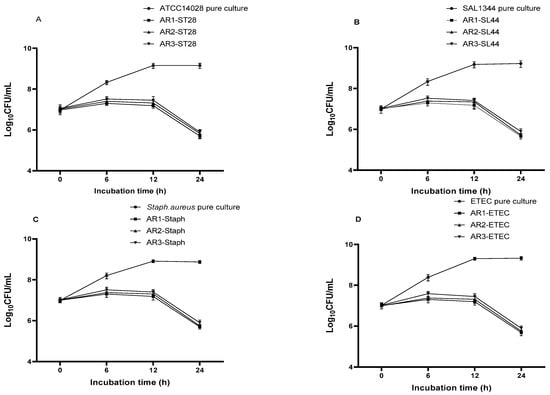
Figure 7.
Growth pattern of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D) in pure and co-culture with different Lactobacilli.
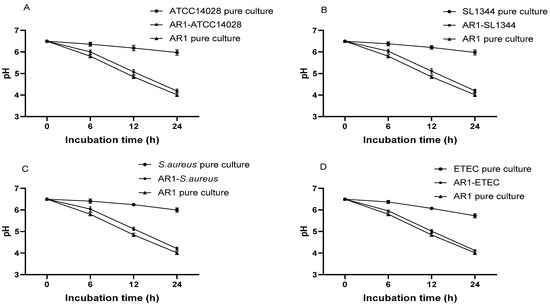
Figure 8.
pH decline patterns of pure cultures of L. acidophilus AR1 and different pathogens, and co- cultures of L. acidophilus AR1 with S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D).
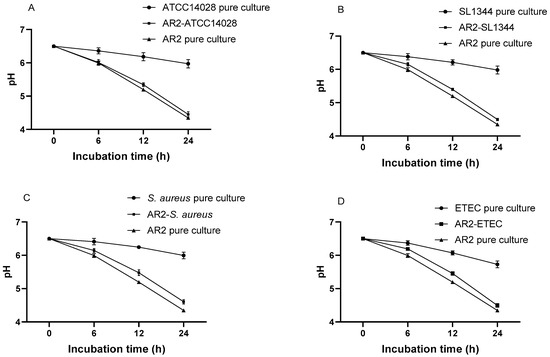
Figure 9.
pH decline patterns of pure cultures of L. acidophilus AR2 and different pathogens, and co-cultures of L. acidophilus AR2 with S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D).
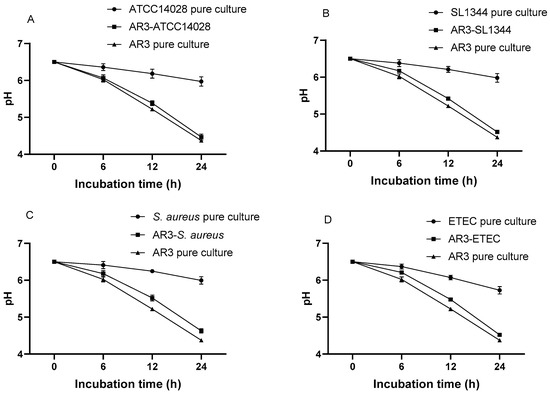
Figure 10.
pH decline patterns of pure cultures of L. acidophilus AR3 and different pathogens, and co-cultures of L. acidophilus AR3 with S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D).
4.6. Inhibitory Effects of Lactobacilli Metabolites on Pathogenic Growth
The viable count of pathogens was found to be more when grown in pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of Lactobacilli than that of co-culture with Lactobacilli. Pathogen growth was inhibited more when grown together with Lactobacilli than in low pH equal to the 24 h Lactobacilli culture pH, suggesting the antimicrobial activity of Lactobacilli metabolites. The viable count of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 was significantly less (7.1 ± 6.19 log CFU/mL) during co-culture with L. acidophilus AR1 as compared to the viable count (7.3 ± 6.49 log CFU/mL) when grown in medium with pH equal to the 24 h L. acidophilus AR1 culture pH. Similar observations were noticed when S. Typhimurium ATCC14028, S. Typhimurium SL1344, and S. aureus were grown with the L. acidophilus strain AR1 and AR2, and in medium with pH equal to the 24 h L. acidophilus strain AR2 and AR2 culture pH. No significant difference was observed in the viable count of pathogens in the case of the L. fermentum strain AR3 (Figure 11).
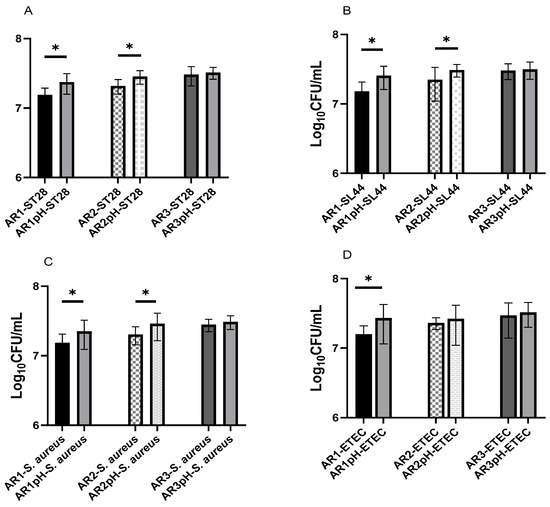
Figure 11.
Viable count of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 (A), S. Typhimurium SL1344 (B), S. aureus (C), and ETEC (D) after 12 h of growth in co-culture with Lactobacilli and low pH equal to the 24 h culture pH of Lactobacilli. Star (*) represents significant difference between the groups.
4.7. Host Defensin Peptide Assessment
No antimicrobial activity of Lactobacilli-treated MODE-K cell culture supernatant was observed. A significant difference was not observed in the viable count of pathogenic bacteria when grown in Lactobacilli culture supernatant and MODE-K cell culture supernatant collected after Lactobacilli stimulation (Figure 12).
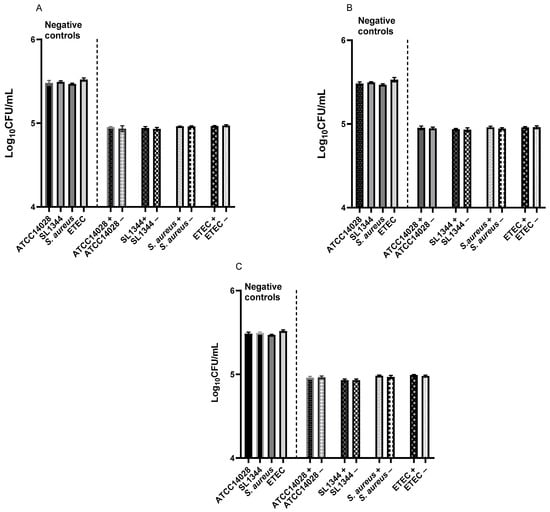
Figure 12.
Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacilli culture supernatant and MODE-K cell culture supernatant collected after stimulation with L. acidophilus AR1 (A), L. acidophilus AR2 (B), and L. fermentum AR3 (C). Positive sign (+) represents Lactobacillus culture supernatant and negative sign (−) represents Lactobacillus-treated MODE-K cell culture supernatant.
4.8. Adhesion and Adhesion Inhibition Assays
Each probiotic strain showed an adhesion ability with MODE-K cells. The adhesion percentage of each probiotic strain increased as the initial concentrations increased (Figure 13). The maximum adhesion (7.5 ± 0.2%) was observed for the L. acidophilus strain AR1 followed by the L. acidophilus strain AR2 (7 ± 0.25%) and L. fermentum strain AR3 (5.8% ± 0.27) at the highest inoculated concentration (108 CFU per mL). The probiotic strain inhibited pathogen adhesion at all concentrations in a concentration-dependent manner. The pathogenic strain’s adhesion percentage decreased considerably when the inoculated concentration of probiotic strains was increased. The maximum inhibitory effects of Lactobacilli on pathogen adhesion were observed during the inhibition assay followed by the competition and displacement assays. The adhesion percentage of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 was decreased to 21.1 ± 0.85%, 50.1 ± 0.86%, and 63.3 ± 0.65% during the displacement, competition, and inhibition assays, respectively, with the L. acidophilus strain AR1. The L. acidophilus strain AR2 also inhibited the adhesion of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028. The adhesion percentage of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 was decreased to 19.8 ± 1.20%, 47.6 ± 1.30%, and 62.3 ± 0.63% during the displacement, competition, and inhibition assays, respectively, with the L. acidophilus strain AR2. Similarly, the adhesion percentage of S. Typhimurium ATCC14028 was decreased to 16.7 ± 1.25%, 45.1 ± 1.60%, and 59.3 ± 1.97% during the displacement, competition, and inhibition assays, respectively, with the L. acidophilus strain AR3. Similar results were noted in the case of the other pathogens during the displacement, competition, and inhibition assays with these Lactobacilli (Figure 13).
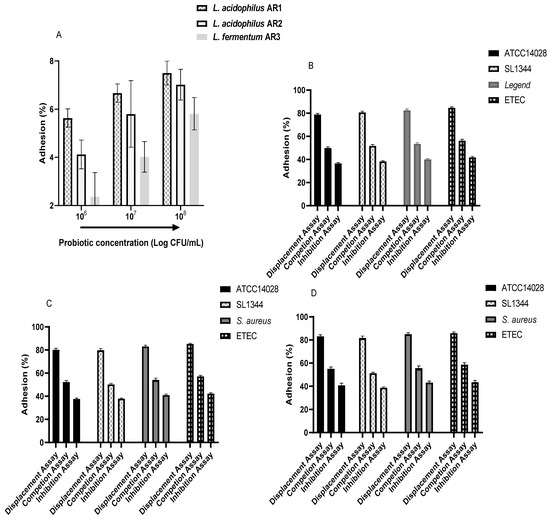
Figure 13.
Adhesion of Lactobacilli with MODE-K cells (A) and inhibitory effects on the adhesion of different pathogenic with MODE-K cells by L. acidophilus AR1 (B), L. acidophilus AR2 (D), and L. fermentum AR3 (C).
4.9. Real-Time PCR for mRNA Expression of Tight Junction Proteins, Cytokines, and Defensin Peptides
The real-time PCR results showed that both strains of Salmonella significantly increased proinflammatory cytokines’ (IL-8, IL-6, IL-1β) mRNA expression. The L. acidophilus strain AR1 and L. fermentum strain AR3 statistically significantly inhibited the Salmonella-induced proinflammatory cytokines. The tight junction protein (occludin) was significantly downregulated by both strains of Salmonella and L. acidophilus strain AR1 and L. fermentum strain AR3 pre-treatment significantly curtailed this effect (Figure 14). As far as host defensin peptide (beta-defensin 3) is concerned, none of the strains induced mRNA expression of beta-defensin 3 in MODE-K cells (Figure 15).
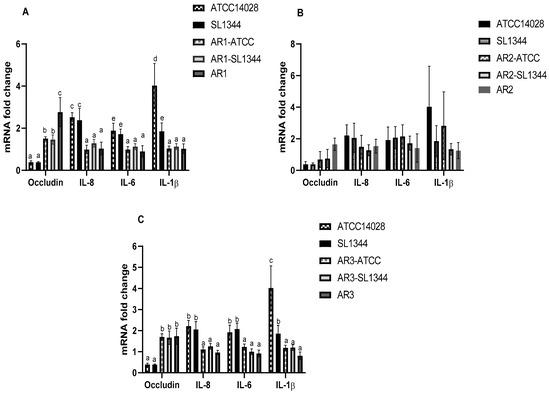
Figure 14.
Modulatory effects of L. acidophilus AR1 (A), L. acidophilus AR2 (B), and L. fermentum AR3 (C) on different gene expression during pathogenic infection. Different letters show significant values.
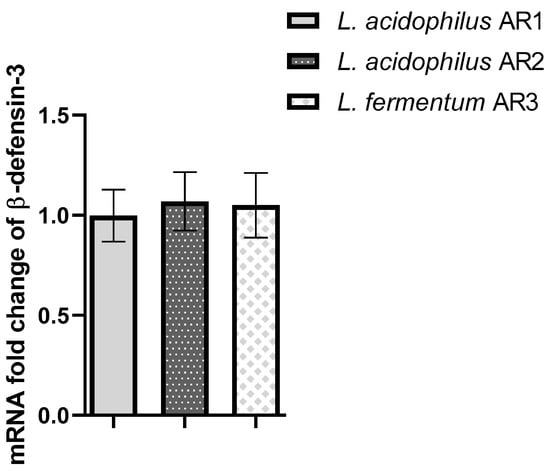
Figure 15.
Represents the effect of L. acidophilus AR1, L. acidophilus AR2, and L. fermentum AR3 on beta-defensin 3 mRNA expression. No significant difference was observed with respect to the control (1).
5. Discussion
The present study was conducted to evaluate the probiotic potential of Lactobacilli (L. acidophilus AR1, L. acidophilus AR2, L. fermentum AR3) isolated from dog feces. Resistance to the harsh environment of the GI tract is an important step towards the selection of potential probiotic candidates. The first barrier that should be overcome is the mouth, which contains a high lysozyme concentration, then the low pH and digestive enzymes of the stomach and the antimicrobial action of bile of the intestine [27]. Our results showed that the isolates have the potential to survive in the harsh GI tract environment. The isolated Lactobacilli showed a considerable number even after 180 min of incubation with lysozyme. A 180 min incubation with lysozyme is considered a severe treatment during probiotics lysozyme resistance assays [28]. The survival rate of Lactobacilli in the presence of lysozyme has also been reported by many other studies [20,28,29]. To reach the end of the GIT, stomach acid is one of the major issues for microorganisms. Therefore, pH is considered to be crucial for the selection of probiotics [30]. When food is swallowed, the stomach pH ranges from 3–6 depending on the food composition, so a pH range of 2–5 is usually examined to evaluate the pH resistance potential of probiotics [21]. In various other studies, it has been reported that Lactobacilli can survive well in low pH [31,32,33]. The results of our study are also in concordance with these facts, showing that the new isolated Lactobacilli can survive under low pH. Several mechanisms are associated with the survival of Lactobacilli in low pH, such as protein and DNA damage repair, several metabolic pathways, proton pumps, neutralization processes, and changes of the cell membrane composition and cell density [31,34,35,36,37]. Moreover, the survivability in low pH is also associated with the production of polysaccharides, which protect the microorganisms against lethal pH effects [38], which was found to be positive in this study. Our results are in agreement with Aziz and Falah, who reported that L. fermentum can survive in low pH [21,39].
The probiotic functions in the duodenum are compromised because of the secretion of bile salts, which act as antimicrobial molecules [21]. Therefore, to evaluate LAB’s potential as a probiotic, their resistance to bile salts is essential. Resistance to bile salts has been considered a condition for bacterial metabolic activity and colonization in the intestine of the host [30]. Bile salt concentrations of 0.15% to 0.5% are usually investigated [40], and to select a strain considered to have good bile resistant ability, a limit of a 0.3% bile concentration was established by Mathara et al. (2008) [41]. In this study, the tested strains showed resistance against different concentrations of bile salts. These findings were consistent with Hashemi et al. (2014) [38], Sagdic et al. (2014) [42], and Vasiee et al. (2018) [30], who found that LAB can resist bile acids very well. When bacteria are exposed to bile salts, their cellular homeostasis is disturbed, leading to cell death. It has been proposed that the bile salt-resistant activity of probiotics is related to bile salt hydrolases enzymes [38]. A study was carried out on wild-type and bile salt hydrolase (bsh) mutant pairs of L. plantarum and L. amylovorus, which provided a correlation between bile salt hydrolysis and bile tolerance. The findings demonstrate that mutated cells were much more vulnerable to bile and bile salts and exhibited less growth rates when bile salts were present [43]. The protective effects of the food matrix are another proposed factor that contributes to the survival of microorganisms in the presence of higher bile salt concentrations [44]. Further, we evaluated the survival potential of isolated Lactobacilli under simulated GIT conditions. Our results showed that the isolated Lactobacilli have a considerable survival rate under simulated gastric juice; however, the survival rate of all strains under simulated gastric juice of pH 2 was found to be less than the pH resistance assay at pH 2. It could be due to the antimicrobial action of pepsin. Similarly, the isolated Lactobacilli can also maintain their viable count under simulated intestinal juice containing pancreatin and bile salts. A similar finding in the case of L. fermentum strain 4–17 was also reported by Falah et al.’s (2019) [21]. Many other studies have also reported that Lactobacilli can maintain their viable count under simulated conditions of GIT [28,45].
Pathogenic bacterial growth inhibition is one of the striking properties of probiotics. Many studies of LAB have shown their broad spectrum of antimicrobial activities [46,47]. The present study indicated that these Lactobacilli can inhibit the growth of selected common pathogens based on co-culture assays. In our co-culture assays, the pH decline pattern of MRS broth of pure culture of Lactobacilli and their respective co-cultures with pathogens was almost similar (from 0–24 h), but Lactobacilli’s inhibitory effect on the pathogen viable count was not as prominent during the first 12 h of the co-culture period; however, the pathogen viable count was less during this period than respective pure cultures of pathogens. Moreover, when pathogenic bacteria were grown in pH equal to 24 h Lactobacilli culture pH, their viable count was more than their co-culture assays with Lactobacilli. These findings indicate that Lactobacilli’s growth inhibitory effects on pathogens are not only by their low pH but their metabolites also have antimicrobial activity. Fayol-Messaoudi et al.’s (2005) study also reported that non-lactic acid molecules of LAB inhibited pathogen growth [48]. Similar findings were also reported by Wang et al. (2018) [23]. LAB can produce a variety of antimicrobial molecules, such as bacteriocin, hydrogen peroxide, bacteriocin-like compound, and extracellular organic acids [49,50,51,52,53,54].
Probiotics’ colonization potential is one of the most important properties recommended by WHO/FAO. Most probiotics’ important functions, such as immune modulation or antagonisms to harmful microbes, are linked to their intestinal colonization, which is usually investigated in vitro using simulated intestinal cells [21]. Intestinal adhesion and colonization are mediated by the interaction between bacterial cell surface molecules and gut epithelial cell receptors and are highly variable for different bacterial strains. García-Ruiz et al. (2014) reported 0.37 to 12.2% adhesion of wine-isolated LAB with Caco-2 cells whereas LAB isolated from Sardinian dairy products showed 3 to 20% adhesion with Caco-2 cells [45]. Our results are in line with these findings showing that the adhesion property of probiotics is strain-specific with maximum adhesion of L. acidophilus AR1 (7.5 ± 0.20%) followed by L. acidophilus AR2 (7 ± 0.25%) and L. fermentum AR3 (5.8 ± 0.27%) with MODE-K cells. The adhesion percentage of these LAB depended on the initial concentrations and significantly increased when the initial inoculated concentration was increased. This concentration-dependent relationship verifies the findings of Wang et al. (2018), who reported that Lactobacillus (L. plantarum ZLP001) adhesion with IPEC-J2 significantly increased as the inoculated bacterial concentration increased [23]. The pathogenic infections are usually associated with their adhesion to the host epithelium, which sometimes results in destruction of the epithelium, facilitating entry of the pathogens and their toxins into the host organ [23]. LAB has the potential to inhibit pathogens’ adhesion to host cells by producing different kinds of adhesive surface molecules (e.g., enolases, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, pyruvate dehydrogenase) [55]. These adhesive molecules assist LAB adhesion to host cells as well as in contesting and preventing pathogenic bacterial attachment and colonization [56,57,58]. Our results are consistent with these reports showing inhibitory effects of dog-isolated LAB on the adhesion of different pathogens with MODE-K cells. The adhesion percentage of all tested pathogens was less during the inhibition assay followed by the competition and displacement assays. This is because during pre-addition of probiotic Lactobacilli, they occupy most of the host cellular receptors. The anti-infection properties of LAB against pathogens may also be due to their ability to secrete different kinds of antimicrobial compounds (such as organic acids, primarily lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide, volatile compounds, such as diacetyl and ethanol, carbon dioxide, and bacteriocins), and bio-surfactant production [59]. These anti-infective properties of LAB have been reported in various studies. Lactobacillus can inhibit the adhesion of different pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Clostridium difficile, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium) with Caco-2 cells [60]. Similar results of LAB’s potential to inhibit the adhesion of pathogens with epithelial cells have also been reported by many other researchers [21,23,28,45,61]. However, our finding of LAB’s anti-infective potential did not match with Nowak and Motyl (2017), Wang et al. (2018), and Falah et al., (2019). Anti-infection relies on both pathogenic and probiotic strains and should be assessed on a case-by-case [28,62]. The intestinal epithelial barrier prevents systemic entry of toxins and bacteria and many other unwanted molecules by acting as a physical and biochemical barrier. Therefore, its integrity and function are very important. Many studies have reported that LAB has the potential to improve the intestinal barrier damage induced by enteric pathogens [63,64,65,66,67,68].
Our qPCR results indicated that LAB significantly inhibits the Salmonella-decreased gene expression of occludin. Further, we checked the anti-inflammatory effects of these LAB during Salmonella infection as pathogenic-induced proinflammatory cytokines have been reported to be associated with barrier damage by pathogens [69]. Our results indicated that Salmonella significantly induced proinflammatory cytokines and our LAB alleviated this effect. Several other reports of LAB study during Salmonella infection have also shown that LAB ameliorates the intestinal barrier damage and proinflammatory cytokine production induced by Salmonella [64,70]. Our results did not match with findings of other researchers [71], where they reported that L. fermentum AGR1487 has negative effects on epithelial barrier integrity. This could possibly be due to strain differences and we used the MODE-K cell line and Anderson used the Caco-2 cell line.
We also evaluated dog-isolated Lactobacilli’s potential to induce antimicrobial peptide (such as host defensin peptides) production by MODE-K cells, based on previous study of probiotics (LAB) induction of antimicrobial peptides in their hosts [72,73,74,75]. Our results indicated that dog-isolated Lactobacilli-treated MODE-K cell culture supernatant has no antimicrobial activity. These findings were verified by our qPCR results that none of the strains induced mRNA expression of defensin peptides (beta-defensin 3) in the MODE-K cell line. These results were in disagreement with the reports of Wang et al. (2018) and Zhang et al. (2011) [23,75]. This could be due to the difference of the probiotic species and cell lines used in these studies. Our Lactobacilli were L. acidophilus and L. fermentum and we used the MODE-K cell line. Wang used L. plantarum and the Caco-2 cell line whereas Zhang used L. salivariu and took samples by biopsy from neonatal pigs.
Author Contributions
G.Z., A.R. and X.G. conducted the experiments and wrote the manuscript, J.Z., M.Y., M.L., L.S. helped the G.Z. and A.R. Y.Y. and S.L. reviewed the manuscript and performed some experiment. X.C., X.Y., M.W., H.W. reviewed the manuscript and performed statistical analysis, T.Q. supervised, design the experiment, and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (Grant number: ASTIP-IAS15) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Grant number: 2021-YWF-ZYSQ-10).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Great thanks are given to Shangjin Cui for his valuable discussion and kind guidance.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no competing interest exist.
References
- Adriana, N.; Ilona, M.; Katarzyna, Ś.; Zdzisława, L.; Elżbieta, K. Adherence of probiotic bacteria to human colon epithelial cells and inhibitory effect against enteric pathogens—In vitro study. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2016, 69, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Cookson, A.L.; McNabb, W.C.; Park, Z.; McCann, M.J.; Kelly, W.J.; Roy, N.C. Lactobacillus plantarum MB452 enhances the function of the intestinal barrier by increasing the expression levels of genes involved in tight junction formation. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, R.C.; Young, W.; Clerens, S.; Cookson, A.L.; McCann, M.J.; Armstrong, K.M.; Roy, N.C. Human Oral Isolate Lactobacillus fermentum AGR1487 Reduces Intestinal Barrier Integrity by Increasing the Turnover of Microtubules in Caco-2 Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, K.; Zaidi, A.H.; Fatima, H.N.; Tariq, M. Lactobacillus fermentum strains of dairy-product origin adhere to mucin and survive digestive juices. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, F.; Najafi, M.B.H.; Dovom, M.R.E. The biodiversity of Lactobacillus spp. from Iranian raw milk Motal cheese and antibacterial evaluation based on bacteriocin-encoding genes. AMB Express 2017, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacanlı, M.; Başaran, N. Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillon, M.-L.A.; Marshall-Jones, Z.V.; Butterwick, R.F. Effects of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus strain DSM13241 in healthy adult dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baindara, P.; Korpole, S.; Grover, V. Bacteriocins: Perspective for the development of novel anticancer drugs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 10393–10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, S.; Taur, Y.; Pamer, E.G. Antibiotic-induced changes in the intestinal microbiota and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 458–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begley, M.; Gahan, C.G.; Hill, C. The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 625–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begley, M.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrero, J.; Kelly, E.; O’Connor, P.M.; Kelleher, P.; Scully, C.; Cotter, P.D.; van Sinderen, D. Plantaricyclin A, a novel circular bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum NI326: Purification, characterization, and heterologous production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01801-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.Y.; Tsen, H.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Yu, B.; Chen, C.S. Oral administration of a combination of select lactic acid bacteria strains to reduce the Salmonella invasion and inflammation of broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; O’Sullivan, O. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coman, M.; Verdenelli, M.; Cecchini, C.; Belà, B.; Gramenzi, A.; Orpianesi, C.; Silvi, S. Probiotic characterization of Lactobacillus isolates from canine faeces. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, G.; Gilliland, S. Bile salt hydrolase activity of three strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C. Surviving the acid test: Responses of gram-positive bacteria to low pH. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delucchi, L.; Fraga, M.; Zunino, P. Effect of the probiotic Lactobacillus murinus LbP2 on clinical parameters of dogs with distemper-associated diarrhea. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 81, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Dinev, T.; Beev, G.; Tzanova, M.; Denev, S.; Dermendzhieva, D.; Stoyanova, A. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum against pathogenic and food spoilage microorganisms: A review. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 21, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Halfawy, N.M.; El-Naggar, M.Y.; Andrews, S.C. Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum 10CH, a potential probiotic lactic acid bacterium with potent antimicrobial activity. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01398-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falah, F.; Vasiee, A.; Behbahani, B.A.; Yazdi, F.T.; Moradi, S.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Roshanak, S. Evaluation of adherence and anti-infective properties of probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum strain 4–17 against Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infection in humans. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayol-Messaoudi, D.; Berger, C.N.; Coconnier-Polter, M.H.; Lievin Le Moal, V.; Servin, A.L. pH-, Lactic acid-, and non-lactic acid-dependent activities of probiotic Lactobacilli against Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6008–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, H.; Wang, F. Antibiotics induced intestinal tight junction barrier dysfunction is associated with microbiota dysbiosis, activated NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K. Is it feasible to control pathogen infection by competitive binding of probiotics to the host? Virulence 2017, 8, 1502–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garai-Ibabe, G.; Areizaga, J.; Aznar, R.; Elizaquivel, P.; Prieto, A.; Irastorza, A.; Dueñas, M.A.T. Screening and selection of 2-branched (1, 3)-β-D-glucan producing lactic acid bacteria and exopolysaccharide characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6149–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, A.; de Llano, D.G.; Esteban-Fernández, A.; Requena, T.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Assessment of probiotic properties in lactic acid bacteria isolated from wine. Food Microbiol. 2014, 44, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, H.G.; Qazi, R.K.; Somiah, T.; Psthak, S.K.; Sjölinder, H.; Sverremark-Ekström, E.; Jonsson, A.B. Lactobacillus gasseri suppresses the production of the proinflammatory cytokines in Helicobacter pylori-infected macrophages by inhibiting the expression of ADAM17. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenting, J.; Beck, H.C.; Vrang, A.; Riemann, H.; Ravn, P.; Hansen AMMadsen, S. Anchorless surface associated glycolytic enzymes from Lactobacillus plantarum 299v bind to epithelial cells and extracellular matrix proteins. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Ordaz, A.; González-Ortiz, G.; La Ragione, R.; Woodward, M.; Collins, J.; Pérez, J.; Martín-Orúe, S. Lactulose and Lactobacillus plantarum, a potential complementary synbiotic to control postweaning colibacillosis in piglets. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Shahidi, F.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Milani, E.; Eshaghi, Z. Potentially probiotic Lactobacillus strains from traditional Kurdish cheese. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2014, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeney, D.D.; Zhai, Z.; Bendiks, Z.; Barouei, J.; Martinic, A.; Slupsky, C.; Marco, M.L. Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriocin is associated with intestinal and systemic improvements in diet-induced obese mice and maintains epithelial barrier integrity in vitro. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jankowska, A.; Laubitz, D.; Antushevich, H.; Zabielski, R.; Grzesiuk, E. Competition of Lactobacillus paracasei with Salmonella enterica for adhesion to Caco-2 cells. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2008, 2008, 357964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayashree, S.; Karthikeyan, R.; Nithyalakshmi, S.; Ranjani, J.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rajendhran, J. Anti-adhesion property of the potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus fermentum 8711 against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kainulainen, V.; Tang, Y.; Spillmann, T.; Kilpinen, S.; Reunanen, J.; Saris, P.E.; Satokari, R. The canine isolate Lactobacillus acidophilus LAB20 adheres to intestinal epithelium and attenuates LPS-induced IL-8 secretion of enterocytes in vitro. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karczewski, J.; Troost, F.J.; Konings, I.; Dekker, J.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.-J.M.; Wells, J.M. Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by Lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G851–G859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koponen, J.; Laakso, K.; Koskenniemi, K.; Kankainen, M.; Savijoki, K.; Nyman, T.A.; Varmanen, P. Effect of acid stress on protein expression and phosphorylation in Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1357–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehri, B.; Seddon, A.; Karlyshev, A. Lactobacillus fermentum 3872 as a potential tool for combatting Campylobacter jejuni infections. Virulence 2017, 8, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Lin, Z.; Xu, P. Mechanisms of acid tolerance in bacteria and prospects in biotechnology and bioremediation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuoka, H.; Shimada, K.; Kiyosue Yasuda, T.; Kiyosue, M.; Oishi, Y.; Kimura SHirayama, K. Transition of the intestinal microbiota of dogs with age. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2017, 36, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathara, J.M.; Schillinger, U.; Kutima, P.M.; Mbugua, S.K.; Guigas, C.; Franz, C.; Holzapfel, W.H. Functional properties of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Maasai traditional fermented milk products in Kenya. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 56, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Motyl, I. In vitro anti-adherence effect of probiotic Lactobacillus strains on human enteropathogens. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 8, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Otte, J.-M.; Podolsky, D.K. Functional Modulation of Enterocytes by Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Microorganisms. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G613–G626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paolillo, R.; Carratelli, C.R.; Sorrentino, S.; Mazzola, N.; Rizzo, A. Immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on human colon cancer cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascher, M.; Hellweg, P.; Khol Parisini, A.; Zentek, J. Effects of a probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus strain on feed tolerance in dogs with non-specific dietary sensitivity. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 62, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.G.V.; Franz, C.M.; Schillinger, U.; Holzapfel, W.H. Lactobacillus spp. with in vitro probiotic properties from human faeces and traditional fermented products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.B.; Viale, S.; Conti, S.; Fadda, M.E.; Deplano, M.; Melis, M.P.; Cosentino, S. Preliminary evaluation of probiotic properties of Lactobacillus strains isolated from Sardinian dairy products. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 286390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hang, X.; Jiang, Y.L. plantarum prevents enteroinvasive Escherichia coli-induced tight junction proteins changes in intestinal epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory Effects of Probiotics During Pathogenic Infections With Emphasis on Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagdic, O.; Ozturk, I.; Yapar, N.; Yetim, H. Diversity and probiotic potentials of lactic acid bacteria isolated from gilaburu, a traditional Turkish fermented European cranberrybush (Viburnum opulus L.) fruit drink. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagheddu, V.; Guidesi, E.; Galletti, S.; Elli, M. Original Paper Selection and Characterization Criteria of Probiotics Intended for Human Use from the Past to the Future. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 3, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Schlee, M.; Harder, J.; Köten, B.; Stange, E.; Wehkamp, J.; Fellermann, K. Probiotic Lactobacilli and VSL† 3 induce enterocyte β-defensin 2. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Ley, R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strompfová, V.; Kubašová, I.; Farbáková, J.; Maďari, A.; Gancarčíková, S.; Mudroňová, D.; Lauková, A. Evaluation of Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum CCM 7421 Administration with Alginite in Dogs. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 10, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strompfová, V.; Kubašová, I.; Lauková, A. Health benefits observed after probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum CCM 7421 application in dogs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6309–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Rokana, N.; Panwar, H. Probiotics, Selection criteria, safety and role in health and. J. Innov. Biol. Jan. 2016, 3, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Turchi, B.; Mancini, S.; Fratini, F.; Pedonese, F.; Nuvoloni, R.; Bertelloni, F.; Cerri, D. Preliminary evaluation of probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Italian food products. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Van de Wiele, T.; Verstraete, W.; Possemiers, S. The host selects mucosal and luminal associations of coevolved gut microorganisms: A novel concept. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 681–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasiee, A.; Behbahani, B.A.; Yazdi, F.T.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Noorbakhsh, H. Diversity and probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from horreh, a traditional Iranian fermented food. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastano, V.; Salzillo, M.; Siciliano, R.A.; Muscariello, L.; Sacco, M.; Marasco, R. The E1 beta-subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase is surface-expressed in Lactobacillus plantarum and binds fibronectin. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Chen, Z.; Shah, N.; El-Nezami, H. Modulation of intestinal epithelial defense responses by probiotic bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2628–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.L.; Ling, K.; Wang, M.; El Nezami, H. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves epithelial barrier function by inducing the production of antimicrobial peptide pBD-1 and pBD-2 in monolayers of porcine intestinal epithelial IPEC-J2 cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.L.Y.; Forsythe, S.J.; El-Nezami, H. Probiotics interaction with foodborne pathogens: A potential alternative to antibiotics and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3320–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Mechanisms and improvement of acid resistance in lactic acid bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Ji, H. Swine-derived probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits growth and adhesion of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and mediates host defense. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, E.; Yan, L.; Li, T.; Zhuang, H. Antimicrobial compounds produced by vaginal Lactobacillus crispatus are able to strongly inhibit Candida albicans growth, hyphal formation and regulate virulence-related gene expressions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Tong, T.; Ma, Y. Lactobacillus casei DBN023 protects against jejunal mucosal injury in chicks infected with Salmonella pullorum CMCC-533. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 127, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R. Progress in engineering acid stress resistance of lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Aspartate protects Lactobacillus casei against acid stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4083–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Lactobacillus casei combats acid stress by maintaining cell membrane functionality. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, F.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Zhang, P.; Bi, D. Enterococcus faecium HDR sEf1 elevates the intestinal barrier defense against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and regulates occludin expression via activation of TLR2 and PI3K signalling pathways. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, M.; Fornasari, M.E.; Carminati, D.; Burns, P.; Suàrez, V.; Vinderola, G.; Giraffa, G. Characterization and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from cheeses. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Raheem, A.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.J.A. Modulatory Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the Performance, Morphology, Cecal Microbiota and Gut Barrier Function of Laying Hens. Animals 2021, 11, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q. The effect of Lactobacillus on the expression of porcine β-defensin-2 in the digestive tract of piglets. Livest. Sci. 2011, 138, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-G.; Wu, S.; Xia, Y.; Sun, J. Salmonella infection upregulates the leaky protein claudin-2 in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).