Sustainable Production and Characteristics of Dried Fermented Vegetables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Technological Treatment
2.2.1. Fermentation Process
2.2.2. Freeze-Drying
2.3. Analytical Methods
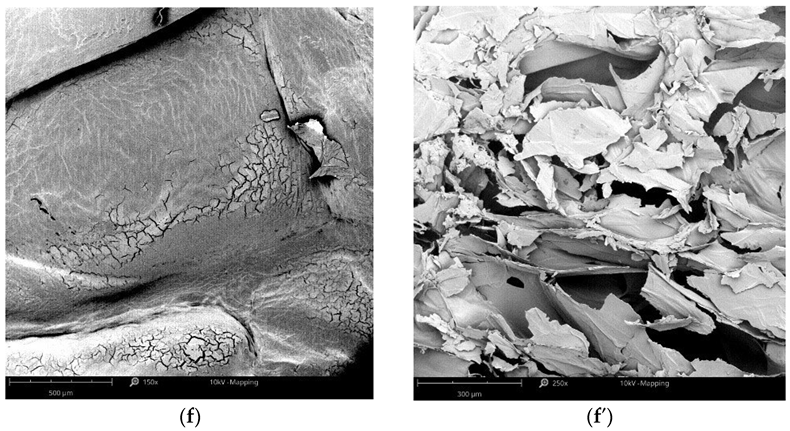
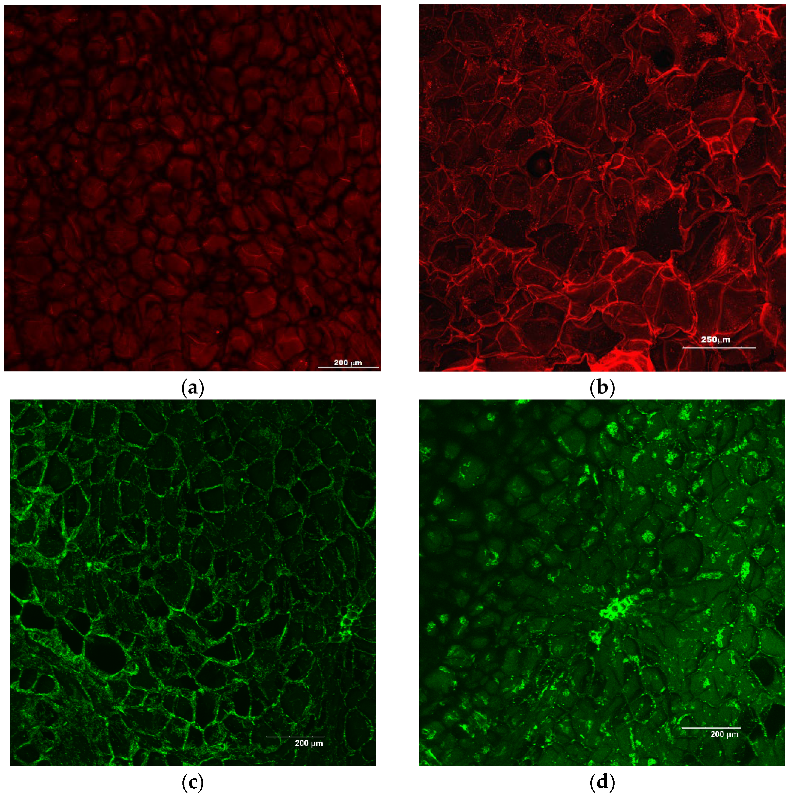
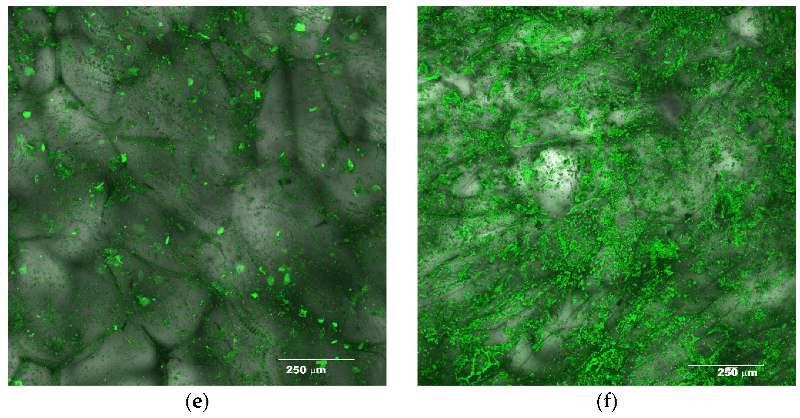
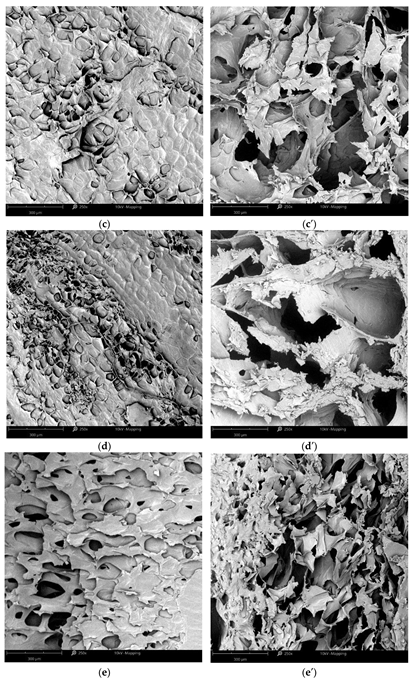
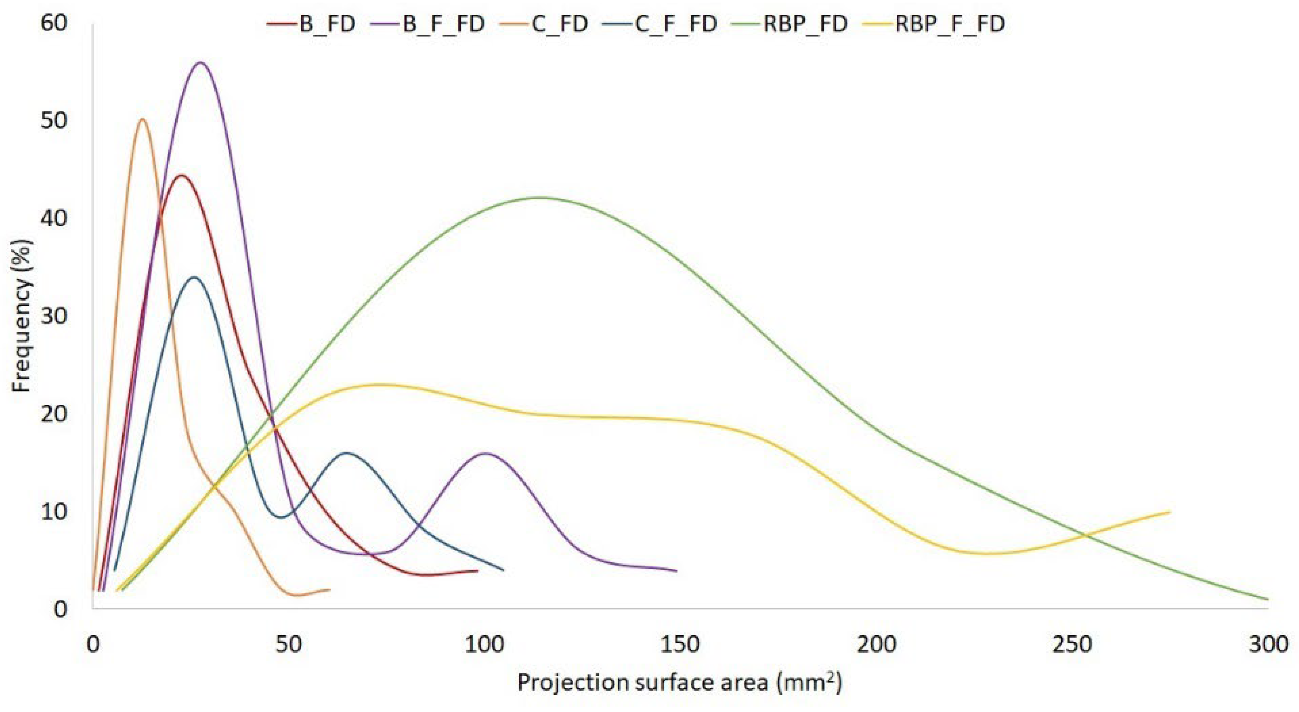
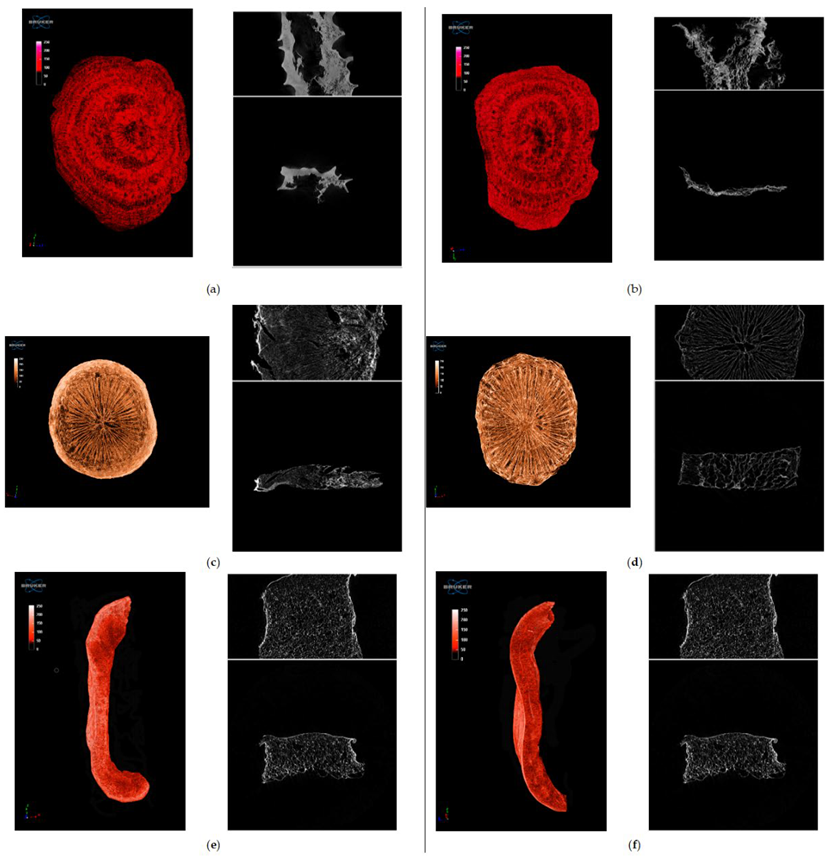
2.3.1. Morphology of Freeze-Dried Vegetables
Scanning Electron Microscope
Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy
Microtomography
Photo-Camera
Image Analysis
2.3.2. Dry Matter
2.3.3. Color
2.3.4. Determination of the Number of Lactic Acid Bacteria
2.4. Statistical Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure
3.2. Physical Properties
3.3. Microbiology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schanes, K.; Dobernig, K.; Gözet, B. Food waste matters-A systematic review of household food waste practices and their policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liegeard, J.; Manning, L. Use of intelligent applications to reduce household food waste. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Rajagukguk, Y.V.; Sidor, A.; Kulczyński, B.; Brzozowska, A.; Suliburska, J.; Wawrzyniak, N.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Innovative Application of Chicken Eggshell Calcium to Improve the Functional Value of Gingerbread. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungowska, J.; Kulczyński, B.; Sidor, A.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Assessment of factors affecting the amount of food waste in households run by polish women aware of well-being. Sustainability 2021, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebnitz, N.; Schuitema, G.; Grunert, K.G. Who buys oddly shaped food and why? Impacts of food shape abnormality and organic labeling on purchase intentions. Psychol. Mark. 2015, 32, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhal, A.; Robertson, K.; Thyne, M.; Mirosa, M. Normalising the “ugly” to reduce food waste: Exploring the socialisations that form appearance preferences for fresh fruits and vegetables. J. Consum. Behav. 2021, 20, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri-Numa, I.A.; Arruda, H.S.; Geraldi, M.V.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R.; Pastore, G.M. Natural prebiotic carbohydrates, carotenoids and flavonoids as ingredients in food systems. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 33, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, R. Recent trends in methods used to obtain natural food colorants by freeze-drying. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, J.; Xie, S.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E. Red Beetroot Betalains: Perspectives on Extraction, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11595–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadipour, E.; Taleghani, A.; Tayarani-Najaran, N.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z. Biological effects of red beetroot and betalains: A review. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1847–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagraj, G.S.; Jaiswal, S.; Harper, N.; Jaiswal, A.K. Carrot. In Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fruits and Vegetables; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 323–337. [Google Scholar]
- USDA1. Beet Raw, FDC ID: 169145. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169145/nutrients (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- USDA3. Carrots Raw FDC ID: 170393. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170393/nutrients (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- USDA2. Peppers, Sweet, Red, Raw FDC ID: 170108. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170108/nutrients (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Petito, N.D.L.; Devens, J.M.; Falcão, D.Q.; Dantas, F.M.L.; Passos, T.S.; Araujo, K.G.d.L. Nanoencapsulation of Red Bell Pepper Carotenoids: Comparison of Encapsulating Agents in an Emulsion Based System. Colorants 2022, 1, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlina, D.; Novita, M.; Karwur, F.F.; Rodonuwu, F.S. Recent Development of Carotenoids Encapsulation Technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Research: Implementation and Education of Mathematics and Sciences, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 18–20 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zeece, M. Chapter Eight—Food colorants. In Introduction to the Chemistry of Food; Zeece, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 313–344. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.S. Chapter 7—Fermentation. In Wine Science, 5th ed.; Jackson, R.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 461–572. [Google Scholar]
- Gänzle, M.G. Food fermentations for improved digestibility of plant foods—An essential ex situ digestion step in agricultural societies? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Cui, C.; Ruan, Z. Fermentation-enabled wellness foods: A fresh perspective. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 203–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska-Turak, E.; Kołakowska, W.; Pobiega, K.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Influence of Drying Type of Selected Fermented Vegetables Pomace on the Natural Colorants and Concentration of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.M.; Chua, L.S. 13—Green Technological Fermentation for Probioticated Beverages for Health Enhancement. In Biotechnological Progress and Beverage Consumption; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 407–434. [Google Scholar]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Sachadyn-Król, M.; Varzakas, T. Lactic acid bacteria as antibacterial agents to extend the shelf life of fresh and minimally processed fruits and vegetables: Quality and safety aspects. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, M.R.; Anandharaj, M.; Ray, R.C.; Parveen Rani, R. Fermented fruits and vegetables of Asia: A potential source of probiotics. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 250424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubber, S.; Marti-Quijal, F.J.; Tomasevic, I.; Remize, F.; Barba, F.J. Lactic acid fermentation as a useful strategy to recover antimicrobial and antioxidant compounds from food and by-products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontsidis, C.; Mallouchos, A.; Terpou, A.; Nikolaou, A.; Batra, G.; Mantzourani, I.; Alexopoulos, A.; Plessas, S. Microbiological and Chemical Properties of Chokeberry Juice Fermented by Novel Lactic Acid Bacteria with Potential Probiotic Properties during Fermentation at 4 degrees C for 4 Weeks. Foods 2021, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska-Turak, E.; Walczak, M.; Rybak, K.; Pobiega, K.; Gniewosz, M.; Woźniak, Ł.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. Influence of Fermentation Beetroot Juice Process on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Spray Dried Powder. Molecules 2022, 27, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; El Sheikha, A.F.; Hammami, R.; Kumar, A. Traditionally fermented pickles: How the microbial diversity associated with their nutritional and health benefits? J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, K.; Wiktor, A.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; Parniakov, O.; Nowacka, M. The quality of red bell pepper subjected to freeze-drying preceded by traditional and novel pretreatment. Foods 2021, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropelewska, E.; Wrzodak, A.; Sabanci, K.; Aslan, M.F. Effect of lacto-fermentation and freeze-drying on the quality of beetroot evaluated using machine vision and sensory analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 248, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagukguk, Y.V.; Arnold, M.; Sidor, A.; Kulczyński, B.; Brzozowska, A.; Schmidt, M.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Antioxidant Activity, Probiotic Survivability, and Sensory Properties of a Phenolic-Rich Pulse Snack Bar Enriched with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Foods 2022, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, J.-C.; Moon, H.; Yang, J.-Y.; Kim, M. Determination of sodium contents in traditional fermented foods in Korea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 56, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Remize, F. Lactic acid fermentation of fruit and vegetable juices and smoothies: Innovation and health aspects. In Lactic Acid Bacteria in Food Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Niakousari, M.; Razmjooei, M.; Nejadmansouri, M.; Barba, F.J.; Marszałek, K.; Koubaa, M. Current Developments in Industrial Fermentation Processes. In Fermentation Processes: Emerging and Conventional Technologies; Koubaa, M., Barba, F.J., Roohinejad, S., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 23–96. [Google Scholar]
- Marszałek, K.; Woźniak, Ł.; Wiktor, A.; Szczepańska, J.; Skąpska, S.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; Saraiva, J.A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J. Emerging Technologies and Their Mechanism of Action on Fermentation. In Fermentation Processes: Emerging and Conventional Technologies; Koubaa, M., Barba, F.J., Roohinejad, S., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 117–144. [Google Scholar]
- Janowicz, M.; Lenart, A. Selected physical properties of convection dried apples after HHP treatment. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, K.; Parniakov, O.; Samborska, K.; Wiktor, A.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; Nowacka, M. Energy and quality aspects of freeze-drying preceded by traditional and novel pre-treatment methods as exemplified by red bell pepper. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska, E. Microencapsulated beetroot juice as a potential source of betalain. Powder Technol. 2014, 264, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.D.; Saunders, D.; Vincent, J.; Jeronimidis, G. An engineering method to evaluate the crisp texture of fruit and vegetables. J. Texture Stud. 2000, 31, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialik, M.; Wiktor, A.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; Samborska, K.; Gondek, E.; Findura, P. Osmotic dehydration and freezing pretreatment for vacuum dried of kiwiberry: Drying kinetics and microstructural changes. Int. Agrophys. 2020, 34, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; Surico, R.F.; Minervini, G.; De Angelis, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. Use of autochthonous starters to ferment red and yellow peppers (Capsicum annum L.) to be stored at room temperature. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; Surico, R.F.; Siragusa, S.; De Angelis, M.; Paradiso, A.; Minervini, F.; De Gara, L.; Gobbetti, M. Selection and use of autochthonous mixed starter for lactic acid fermentation of carrots, French beans or marrows. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 127, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubaa, M. Introduction to Conventional Fermentation Processes. In Fermentation Processes: Emerging and Conventional Technologies; Koubaa, M., Barba, F.J., Roohinejad, S., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Czapski, J. The effect of heating conditions on losses and regeneration of betacyanins. Z. Für Lebensm. Unters. Und Forsch. 1985, 180, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardelli, C.; Benucci, I.; Mazzocchi, C.; Esti, M. Betalain Extracts from Beetroot as Food Colorants: Effect of Temperature and UV-Light on Storability. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2021, 76, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbu, V.; Cotârleț, M.; Bolea, C.A.; Cantaragiu, A.; Andronoiu, D.G.; Bahrim, G.E.; Enachi, E. Three Types of Beetroot Products Enriched with Lactic Acid Bacteria. Foods 2020, 9, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishabh, D.; Athira, A.; Preetha, R.; Nagamaniammai, G. Freeze dried probiotic carrot juice powder for better storage stability of probiotic. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ten, M.M.Z.; Zwe, Y.H.; Li, D. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v as starter culture suppresses Enterobacteriaceae more efficiently than spontaneous fermentation of carrots. Food Microbiol. 2022, 103, 103952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Carrot | Red Bell Pepper | Beetroot | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image resolution | 12 μm | 12 μm | 12.4 μm |
| Lamp voltage and amperage | 49 kV/200 mA | 49 kV/200 mA | 59 kV/167 mA |
| Exposure time | 615 ms | 615 ms | 615 ms |
| Filters | no additional filter | ||
| Unit rotation angle | 0.4° | 0.4° | 0.4° |
| Vegetable Type | Dry Matter (%) | Color Coefficients | Projection Surface Area 50% (mm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L * | a * | b * | |||
| Beetroot (B) | 18.5 ± 0.2 b | 18.52 ± 0.13 ab | 2.09 ± 0.12 a | 0.47 ± 0.05 b | - |
| Fermented Beetroot (F_B) | 15.2 ± 0.3 a | 16.28 ± 2.26 a | 15.02 ± 1.30 b | 2.03 ± 0.44 b | - |
| Freeze-dried Beetroot (B_FD) | 97.9 ± 0.4 c | 22.09 ± 0.05 bc | 22.92 ± 1.09 c | 1.48 ± 0.09 b | 20.5 ± 1.2 a |
| Freeze-dried Fermented Beetroot (F_B_FD) | 97.7 ± 0.1 c | 26.27 ± 2.83 c | 20.93 ± 1.68 c | −10.29 ± 1.45 a | 24.3 ± 1.8 a |
| Carrot (C) | 17.4 ± 0.2 b | 55.73 ± 0.79 b | 19.15 ± 1.80 a | 28.57 ± 0.80 a | - |
| Fermented Carrot (F_C) | 13.2 ± 0.4 a | 47.82 ± 0.08 a | 22.84 ± 0.23 b | 35.83 ± 0.19 b | - |
| Freeze-dried Carrot (C_FD) | 96.6 ± 0.4 c | 65.43 ± 1.17 c | 20.15 ± 1.89 ab | 35.60 ± 1.91 b | 39.3 ± 2.5 a |
| Freeze-dried Fermented Carrot (F_C_FD) | 96.3 ± 0.3 c | 68.31 ± 2.68 c | 17.77 ± 0.38 a | 33.44 ± 0.24 b | 105.8 ± 4.1 b |
| Red Bell Pepper (RBP) | 13.6 ± 0.3 b | 24.65 ± 1.53 a | 27.46 ± 2.72 a | 20.15 ± 3.45 a | - |
| Fermented Red Bell Pepper (F_RBP) | 10.4 ± 0.1 a | 27.93 ± 0.12 a | 25.64 ± 0.10 a | 16.97 ± 0.18 a | - |
| Freeze-dried Red Bell Pepper (RBP_FD) | 98.4 ± 0.4 c | 54.08 ± 1.72 b | 29.43 ± 1.59 a | 35.35 ± 0.55 b | 10.1 ± 2.4 a |
| Freeze-dried Fermented Red Bell Pepper (F_RBP_FD) | 98.6 ± 0.4 c | 50.80 ± 2.24 b | 33.90 ± 9.44 a | 32.17 ± 1.80 b | 76.6 ± 6.6 b |
| Vegetable Type | Beetroot | Carrot | Red Bell Pepper |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFU/g d.m. | |||
| Unfermented | 2.09 ± 0.12 a | 2.98 ± 0.05 b | 2.24 ± 0.18 a |
| Fermented | 7.62 ± 0.03 b | 7.13 ± 0.06 c | 8.25 ± 0.03 c |
| Unfermented freeze-dried | 2.42 ± 0.17 a | 2.14 ± 0.11 a | 2.03 ± 0.11 a |
| Fermented freeze-dried | 7.57 ± 0.06 b | 7.66 ± 0.08 d | 7.48 ± 0.29 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janiszewska-Turak, E.; Rybak, K.; Pobiega, K.; Nikodem, A.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Sustainable Production and Characteristics of Dried Fermented Vegetables. Fermentation 2022, 8, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110659
Janiszewska-Turak E, Rybak K, Pobiega K, Nikodem A, Gramza-Michałowska A. Sustainable Production and Characteristics of Dried Fermented Vegetables. Fermentation. 2022; 8(11):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110659
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaniszewska-Turak, Emilia, Katarzyna Rybak, Katarzyna Pobiega, Anna Nikodem, and Anna Gramza-Michałowska. 2022. "Sustainable Production and Characteristics of Dried Fermented Vegetables" Fermentation 8, no. 11: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110659
APA StyleJaniszewska-Turak, E., Rybak, K., Pobiega, K., Nikodem, A., & Gramza-Michałowska, A. (2022). Sustainable Production and Characteristics of Dried Fermented Vegetables. Fermentation, 8(11), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110659









