Effects of Different Additives on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Communities, and Rumen Degradation of Alfalfa Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care
2.2. Silage Preparation
2.3. Fermentation Variables and Nutritional Content of Alfalfa Silage
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.5. Ruminal Degradation
2.6. Statistics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Fresh Alfalfa
3.2. Fermentation Variables and Nutritional Content of Alfalfa after 60 Days of Ensiling
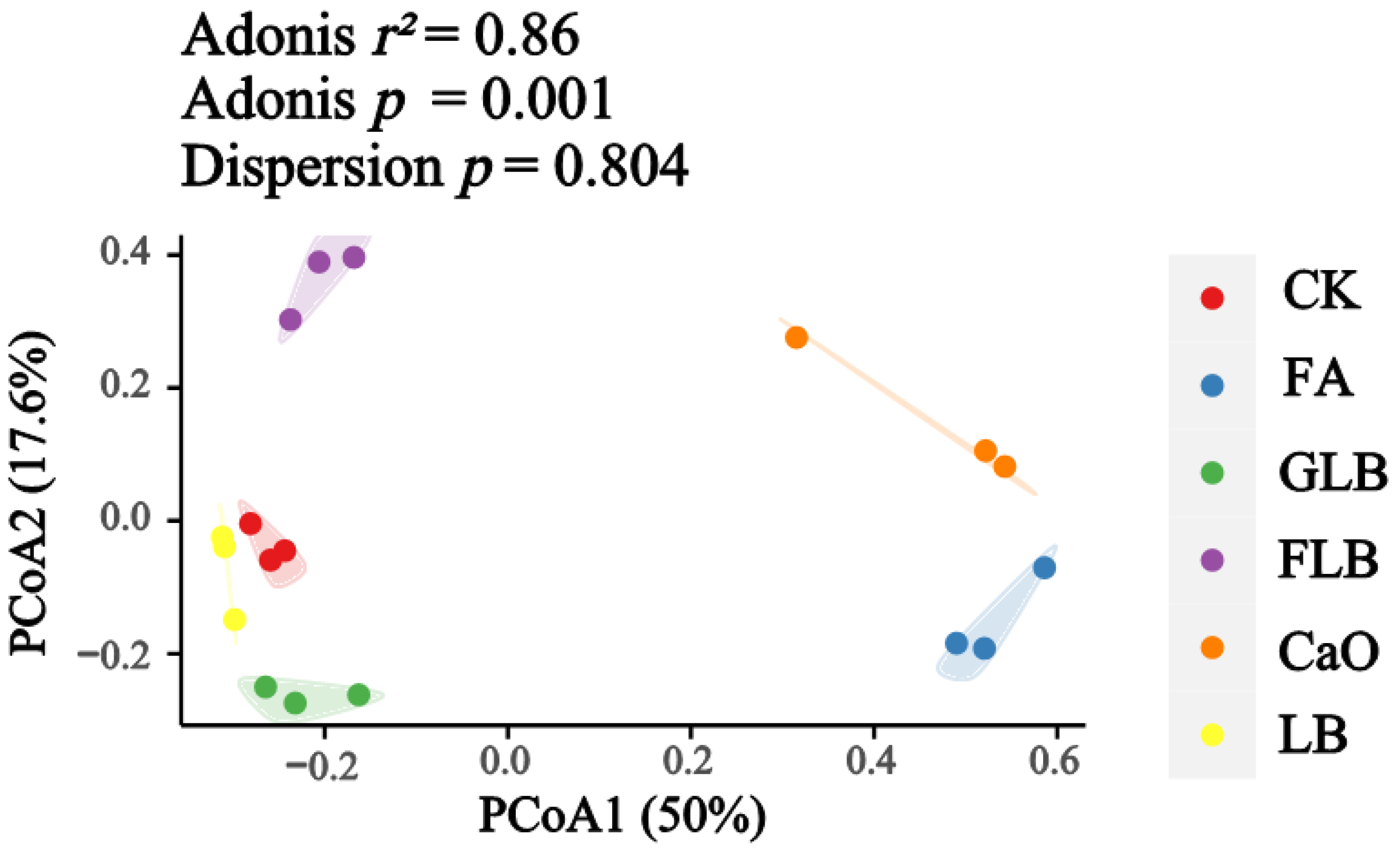
3.3. Effect of Different Additives on the Bacterial Communities of Alfalfa Silage
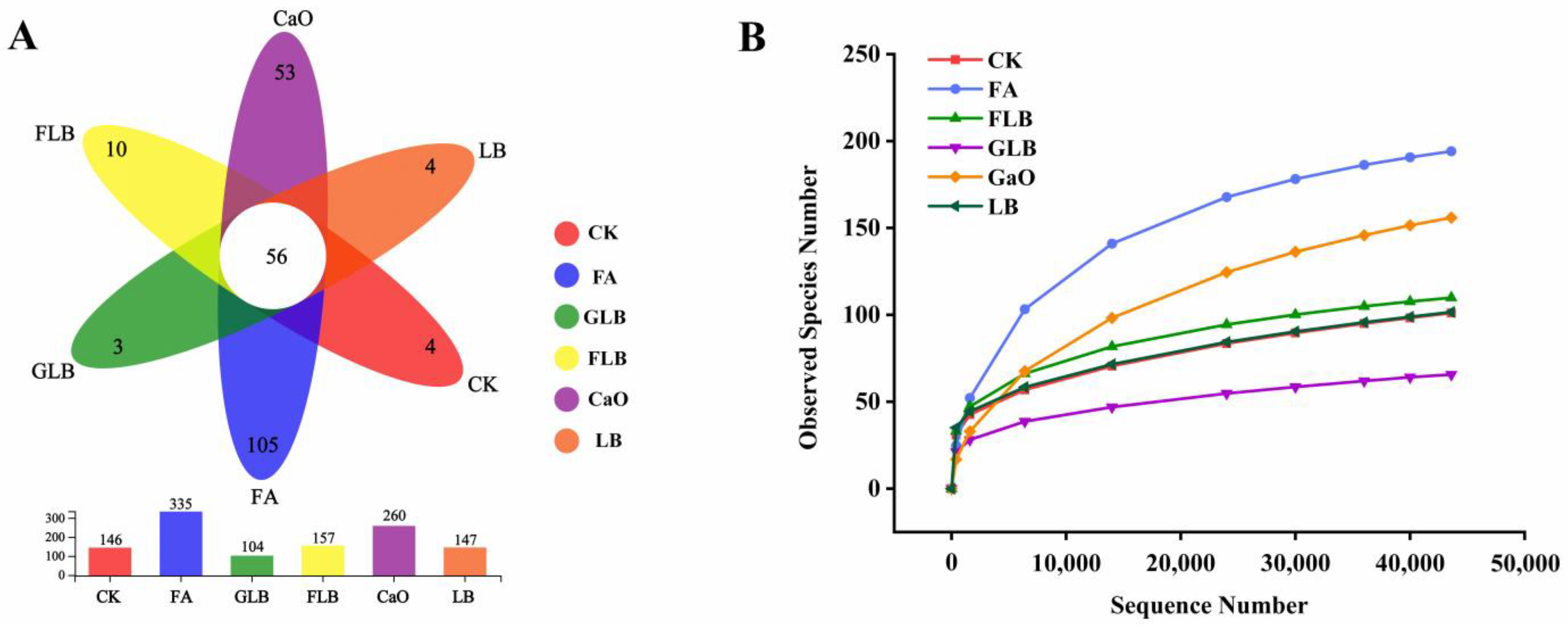
3.3.1. Microbial Diversity of Alfalfa Silage
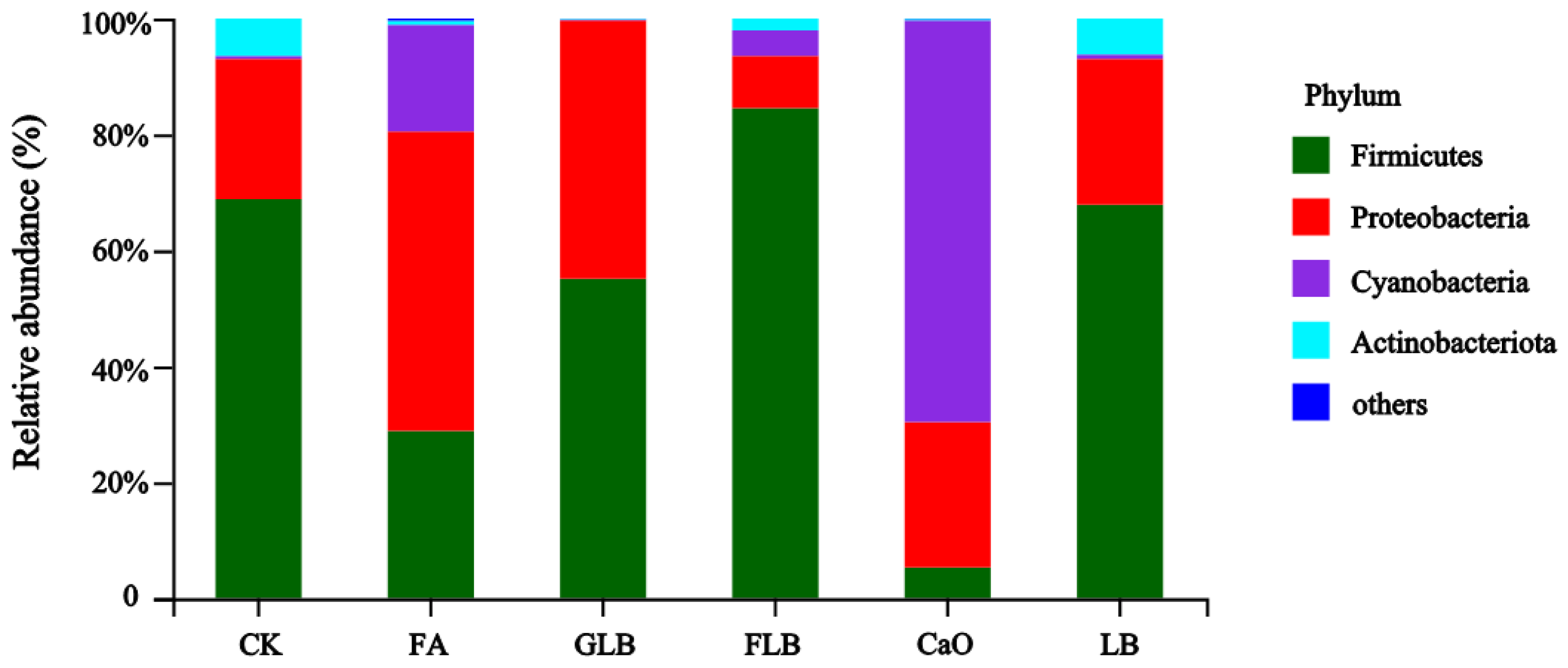
3.3.2. Composition of Bacterial Communities in Alfalfa Silage
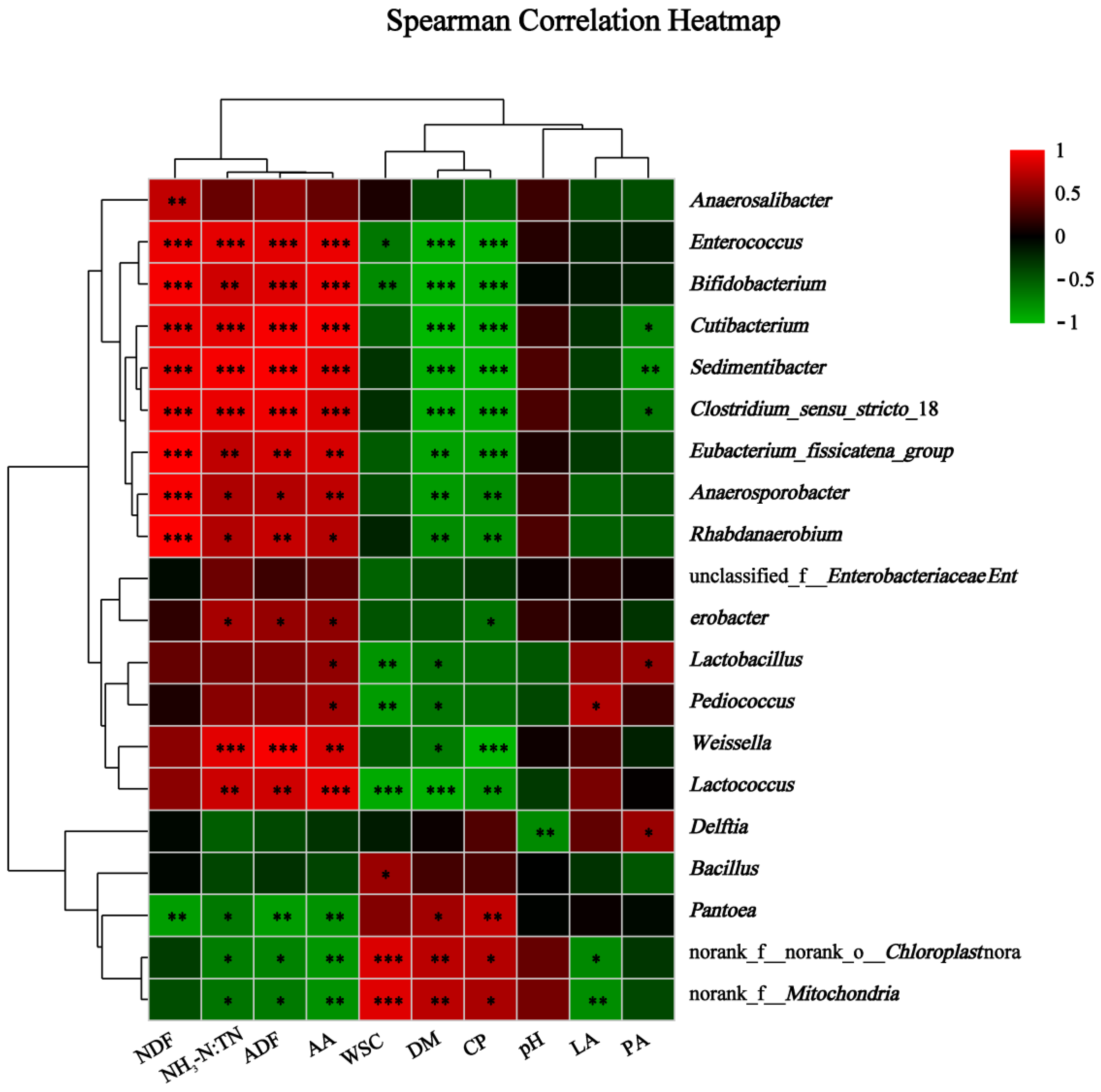
3.3.3. Correlations between Relative Abundance of Bacteria and Nutrient Content or Fermentation Variables of Alfalfa Silage
3.4. Rumen Degradation of Alfalfa Silage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, Y. Dynamics of fermentation parameters and bacterial community in high-moisture alfalfa silage with or without lactic acid bacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcallister, T.A.; Dunière, L.; Drouin, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Munns, K.; Zaheer, R. Silage review: Using molecular approaches to define the microbial ecology of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4060–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, D.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Effects of antibacterial peptide-producing Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial community of alfalfa silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z. Effects of mixing red clover with alfalfa at different ratios on dynamics of proteolysis and protease activities during ensiling. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8954–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Wang, J.; Desta, S.T.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Effects of formic acid and potassium diformate on the fermentation quality, chemical composition and aerobic stability of alfalfa silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, B.F.; O’Kiely, P. Alternatives to formic acid as a grass silage additive under two contrasting ensilability conditions. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2008, 47, 135–149. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/25564586 (accessed on 13 October 2022).
- Xiong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B. Effects of cellulase, Lactobacillus plantarum, and sucrose on fermentation parameters, chemical composition, and bacterial community of hybrid Pennisetum silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Mari, L.J.; Schmidt, R. Lactic acid bacteria as microbial silage additives: Current status and future outlook. In New Advances on Fermentation Processes; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; p. 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; da Silva, É.B.; Apper, E. Changes to the microbiome of alfalfa during the growing season and after ensiling with Lentilactobacillus buchneri and Lentilactobacillus hilgardii inoculant. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Chen, J.; Shao, T. Effects of sugar sources and doses on fermentation dynamics, carbohydrates changes, in vitro digestibility and gas production of rice straw silage. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Tang, J. Effects of sucrose, glucose and molasses on fermentation quality and bacterial community of stylo silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Ji, X. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, C. Natural polysaccharides and their derivates: A promising natural adjuvant for tumor immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 621813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Weelden, G.; Bobiński, M.; Okła, K.; van Weelden, W.J.; Romano, A.; Pijnenborg, J.M.A. Fucoidan structure and activity in relation to anti-cancer mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Li, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Alugongo, G.M.; Doane, P.H. Effects of replacing wild rye, corn silage, or corn grain with CaO-treated corn stover and dried distillers’ grains with solubles in lactating cow diets on performance, digestibility, and profitability. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7183–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.E.; Bender, R.W.; Shinners, K.J.; Combs, D.K. The effects of calcium hydroxide–treated whole-plant and fractionated corn silage on intake, digestion, and lactation performance in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5385–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, H.; Bailey, E.; Meng, K. PSVII-7 Effects of alkali treatment on nutrient content and ergot alkaloid concentration in tall fescue silage. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97 (Suppl. S3), 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, A.; Calsamiglia, S.; Stern, M.D. Nitrogen metabolism in the rumen. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 71–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, C.R.; Fernando, R.L.; Fahey Jr, G.C.; Berger, L.L.; Jaster, E.H. Effects of nutrient additives and sodium hydroxide on ensiling characteristics and in vitro fiber digestion kinetics of dairy cattle waste-energy feedstuff mixtures. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.G.; Grant, R.J.; Kachman, S.D. Effect of wheat straw treated with alkali on ruminal function and lactational performance of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola, K.G.; Oliveira, A.S.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, D.; Silva, H.M.; Kim, S.C.; Amaro, F.X.; Ogunade, I.M.; Sultana, H.; Pech Cervantes, A.A.; et al. Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri, with or without other bacteria, on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and performance of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7653–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, J.L.; Ranjit, N.K. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri and other additives on the fermentation and aerobic stability of barley silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, N.K.; Kung, J.L. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus plantarum, or a chemical preservative on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Sun, W.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M.; Xia, G.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C. Fermentation quality, bacterial community, and aerobic stability of perennial recut Broussonetia papyrifera silage with different additives and wilting time. Fermentation 2022, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Shi, W.; Chen, S.; Degen, A.A.; Qi, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J. Addition of organic acids and Lactobacillus acidophilus to the leguminous forage Chamaecrista rotundifolia improved the quality and decreased harmful bacteria of the silage. Animals 2022, 12, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Hannaway, D. Effect of storage period on the fermentation profile and bacterial community of silage prepared with alfalfa, whole-plant corn and their mixture. Fermentation 2022, 8, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Wang, J.; Desta, S.T.; Dong, Z.H.; Shao, T. Effects of four short-chain fatty acids or salts on fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Ding, W.; Xu, D.; Ding, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, F.; Guo, X. Effects of addition of malic or citric acids on fermentation quality and chemical characteristics of alfalfa silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8958–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; He, N.; Hale, L.; Niu, S.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, J. Soil organic matter availability and climate drive latitudinal patterns in bacterial diversity from tropical to cold temperate forests. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L. ImageGP: An easy-to-use dataEffects of air exposure visualization web server for scientific researchers. iMeta 2022, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza, J.; Benavides, D.; Pulido, R.; Balocchi, O.; Bertrand, A.; Keim, J. Rumen in vitro fermentation and in situ degradation kinetics of winter forage brassicas crops. Animals 2019, 9, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørskov, E.R.; McDonald, I. The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighted according to rate of passage. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 92, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.M.; Murphy, M.R. The nutritional implications of differential passage of particles through the ruminant alimentary tract. Nutr. Res. Rev. 1988, 1, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abdul Rahman, N.; Abd Halim, M.R.; Mahawi, N.; Hasnudin, H.; Al-Obaidi, J.R.; Abdullah, N. Determination of the use of Lactobacillus plantarum and Propionibacterium freudenreichii application on fermentation profile and chemical composition of corn silage. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 1, 2038062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Stough, E.C.; McDonell, E.E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Hofherr, M.W.; Reich, L.J.; Klingerman, C.M. The effect of wide swathing on wilting times and nutritive value of alfalfa haylage. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coblentz, W.K.; Muck, R.E. Effects of natural and simulated rainfall on indicators of ensilability and nutritive value for wilting alfalfa forages sampled before preservation as silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6635–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck, R.E. Factors influencing silage quality and their implications for management. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 2992–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsässer, M. Drying of forage crops—The current practice, future possibilities and research needs. In Forage Conservation towards 2000; Landbauforschung Voelkenrode Sonderheft 123; Bundesforschungsanstalt für Landwirtschaft: Braunscweig, Germany, 1990; pp. 86–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gunathilake, D.M.C.C.; Senanayaka, D.P.; Adiletta, G.; Senadeera, W. Drying of Agricultural Crops. Chapter 14. In Advances in Agricultural Machinery and Technologies; Guangnan, C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 331–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Effect of storage time and the level of formic acid on fermentation characteristics, epiphytic microflora, carbohydrate components and in vitro digestibility of rice straw silage. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Huang, G.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. Effects of sugar cane molasses addition on the fermentation quality, microbial community, and tastes of alfalfa silage. Animals 2021, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichert, A.; Corzett, C.; Schechter, M.; Unfried, F.; Markert, S.; Becher, D.; Fernandez-Guerra, A.; Liebeke, M.; Schweder, T.; Polz, M.; et al. Verrucomicrobia use hundreds of enzymes to digest the algal polysaccharide fucoidan. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Wu, A.; Wu, J.; Shao, T.; Liu, Q. Recycling deteriorated silage to remove hazardous mycotoxins and produce a value-added product. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Takahashi, T.; Horiguchi, K.; Yoshida, N. Effect of adding lactic acid bacteria and molasses on fermentation quality and in vitro ruminal digestion of total mixed ration silage prepared with whole crop rice. Grassl. Sci. 2010, 56, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Yun, Y.; Yu, Z. Propionic acid and sodium benzoate affected biogenic amine formation, microbial community, and quality of oat silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Renaud, J.; Apper, E. Microbiota succession during aerobic stability of maize silage inoculated with Lentilactobacillus buchneri NCIMB 40788 and Lentilactobacillus hilgardii CNCM-I-4785. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, G.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Yu, C.; Shimojo, M.; Shao, T. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria and propionic acid on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of oats-common vetch mixed silage on the Tibetan plateau. Anim. Sci. J. 2015, 86, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vuuren, A.M.; Bergsma, K.; Frol-Kramer, F.; Van Beers, J.A.C. Effects of addition of cell wall degrading enzymes on the chemical composition and the in sacco degradation of grass silage. Grass Forage Sci. 1988, 44, 1365–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Yu, Z. Effects of sucrose, formic acid and lactic acid bacteria inoculant on quality, in vitro rumen digestibility and fermentability of drooping wild ryegrass (Elymus nutans Griseb.) silage. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2017, 26, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.C.; Garcia, R.; de Paula Freita, A.W.; Bernardino, F.S.; Rocha, G.C. Amonização sobre a composição química e digest ibilidade da silagem de capim-elefante. Rev. Ceres 2006, 306, 228–233. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=305226794013 (accessed on 13 October 2022).
- Chaudhry, A.S.; Cowan, R.T.; Granzin, B.C.; Klieve, A.V. The nutritive value of Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana) when treated with CaO, NaOH or a microbial inoculant and offered to dairy heifers as big-bale silage. Anim. Sci. 2001, 73, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Cheng, H.; Liu, D.; Chen, W.; An, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Song, E. Treatment of whole-plant corn silage with lactic acid bacteria and organic acid enhances quality by elevating acid content, reducing pH, and inhibiting undesirable microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 593088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Microbial diversity and fermentation profile of red clover silage inoculated with reconstituted indigenous and exogenous epiphytic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, W.; Cheng, Q.; Bai, S.; Cai, Y. Silage fermentation and bacterial community of bur clover, annual ryegrass and their mixtures prepared with microbial inoculant and chemical additive. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 247, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F. Dynamic succession of microbiota during ensiling of whole plant corn following inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii alone or in combination. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zi, X.; Lv, R.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H. Impacts of citric acid and malic acid on fermentation quality and bacterial community of cassava foliage silage. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 595622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubalde, M.; Brana, V.; Sueiro, F.; Morel, M.; Martinez-Rosales, C.; Marquez, C.; Castro-Sowinski, S. The versatility of Delftia sp isolates as tools for bioremediation and biofertilization technologies. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Bo, H.; Yang, H. The Effect of different lactic acid bacteria inoculants on silage quality, phenolic acid profiles, bacterial community and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristic of whole corn silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.; Heron, S. The Biochemisty of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publications: Marlow, UK, 1991; p. 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kawamoto, H.; Cai, Y. Relationships between the addition rates of cellulase or glucose and silage fermentation at different temperatures. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; He, R.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, Q.; Xia, Z.; Liang, M.; Zhou, J.; Lin, B.; Zou, C. Dynamic changes in fermentation profiles and bacterial community composition during sugarcane top silage fermentation: A preliminary study. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, X.; Elsabagh, M.; Lin, B.; Wang, H. Effects of formic acid and corn flour supplementation of banana pseudostem silages on nutritional quality of silage, growth, digestion, rumen fermentation and cellulolytic bacterial community of Nubian black goats. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2214–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; de Araújo, M.; Edvan, R.; Bezerra, L.; de Sousa, A.; Viana, F.; Dias-Silva, T. Chemical composition, fermentative characteristics, and in situ ruminal degradability of elephant grass silage containing Parkia platycephala pod meal and urea. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3481–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variable | Measurement |
|---|---|
| pH | 6.28 |
| Dry matter (% FW) | 19.3 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrate (% DM) | 6.04 |
| Crude protein (% DM) | 28.9 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (% DM) | 39.6 |
| Acid detergent fiber (% DM) | 28.8 |
| Lactic acid bacteria (Lg cfu/g FW) | 4.15 |
| Aerobic bacteria (Lg cfu/g FW) | 4.38 |
| Yeast and Molds (Lg cfu/g FW) | 5.81 |
| Variables | Treatment | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | FA | CaO | LB | GLB | FLB | ||
| Fermentation variables | |||||||
| pH | 5.83 ± 0.02 c | 4.47 ± 0.01 e | 8.62 ± 0.14 a | 5.72 ± 0.09 cd | 5.64 ± 0.01 d | 6.14 ± 0.02 b | <0.001 |
| Lactic acid (%DM) | 2.13 ± 0.07 c | 3.55 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.02 e | 2.02 ± 0.01 d | 3.89 ± 0.07 a | 2.01 ± 0.01 d | <0.001 |
| Acetic acid (%DM) | 0.43 ± 0.01 a | 0.12 ± 0.00 e | ND | 0.33 ± 0.01 b | 0.22 ± 0.02 d | 0.28 ± 0.02 c | <0.001 |
| Propionic acid (%DM) | 0.34 ± 0.01 e | 0.90 ± 0.00 b | 0.37 ± 0.02 e | 0.71 ± 0.02 c | 1.08 ± 0.05 a | 0.53 ± 0.04 d | <0.001 |
| Butyric acid (%DM) | 0.05 ± 0.00 ab | 0.04 ± 0.00 abc | 0.01 ± 0.00 d | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.04 ± 0.01 bc | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | <0.001 |
| NH3-N:TN ratio | 13.6 ± 0.08 a | 0.59 ± 0.06 f | 1.84 ± 0.05 e | 10.5 ± 0.23 c | 6.27 ± 0.05 d | 11.2 ± 0.47 b | <0.001 |
| LAB (Lg/cfu/gFW) | 6.52 ± 0.06 c | 6.15 ± 0.02 d | 4.02 ± 0.01 e | 6.96 ± 0.03 b | 7.00 ± 001 b | 7.16 ± 0.02 a | <0.001 |
| Chemical composition | |||||||
| Dry matter (%FW) | 18.9 ± 0.68 d | 22.9 ± 0.93 b | 28.6 ± 0.50 a | 19.2 ± 0.84 d | 22.4 ± 0.82 bc | 21.1 ± 0.65 c | <0.001 |
| Crude protein (%DM) | 17.3 ± 0.51 e | 29.1 ± 0.38 b | 35.2 ± 0.25 a | 20.6 ± 0.46 d | 24.3 ± 0.16 c | 19.7 ± 1.66 d | <0.001 |
| WSC (%DM) | 2.57 ± 0.22 d | 3.39 ± 0.20 c | 4.82 ± 0.36 a | 1.73 ± 0.12 e | 2.68 ± 0.18 d | 4.15 ± 0.11 b | <0.001 |
| NDF (%DM) | 39.4 ± 1.06 a | 36.9 ± 0.77 ab | 26.4 ± 2.91 c | 39.7 ± 2.10 a | 34.5 ± 1.70 b | 40.0 ± 0.44 a | <0.001 |
| ADF (%DM) | 31.7 ± 0.07 a | 24.4 ± 0.21 e | 19.3 ± 0.56 f | 28.8 ± 0.46 c | 25.7 ± 0.15 d | 30.0 ± 0.77 b | <0.001 |
| Treament | Items | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao 1 | Coverage | |
| CK | 2.68 ± 0.13 a | 0.11 ± 0.02 b | 179.6 ± 76.0 ab | 152.1 ± 47.5 b | 1 |
| LB | 2.81 ± 0.04 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 175.4 ± 45.6 ab | 136.9 ± 12.1 b | 1 |
| GLB | 2.36 ± 0.09 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 b | 130.1 ± 16.4 b | 98.3 ± 10.0 b | 1 |
| FLB | 2.63 ± 0.08 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 139.3 ± 27.3 b | 137.6 ± 29.0 b | 1 |
| FA | 1.56 ± 0.46 b | 0.39 ± 0.22 ab | 228.4 ± 4.2 a | 219.7 ± 8.8 a | 1 |
| CaO | 1.17 ± 0.90 b | 0.57 ± 0.35 a | 221.4 ± 28.1 a | 213.2 ± 24.4 a | 1 |
| Items | a, % | b, % | a + b, % | c, h−1 | ED, % | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | CK | 6.4 ± 1.41 d | 63.8 ± 1.43 a | 70.2 ± 0.02 c | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 45.0 ± 0.54 e | 0.98 |
| FA | 21.0 ± 1.70 a | 59.8 ± 1.53 ab | 80.8 ± 0.17 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 62.1 ± 0.65 a | 0.98 | |
| CaO | 16.9 ± 1.80 ab | 47.2 ± 1.67 c | 64.0 ± 0.13 d | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 52.4 ± 0.54 bc | 0.97 | |
| LB | 8.9 ± 0.77 d | 60.9 ± 0.69 ab | 69.8 ± 0.08 c | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 50.6 ± 0.30 d | 0.99 | |
| GLB | 13.6 ± 0.66 bc | 60.7 ± 0.60 ab | 74.3 ± 0.06 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 bc | 53.1 ± 0.27 b | 0.99 | |
| FLB | 9.7 ± 1.53 cd | 56.7 ± 1.41 b | 66.4 ± 0.12 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 51.2 ± 0.50 cd | 0.98 | |
| CP | CK | 21.6 ± 3.04 cd | 50.6 ± 2.89 bc | 72.2 ± 0.15 e | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 63.7 ± 0.63 c | 0.95 |
| FA | 33.9 ± 2.31 b | 44.0 ± 2.22 c | 79.2 ± 1.28 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 70.9 ± 0.45 a | 0.96 | |
| CaO | 49.2 ± 1.64 a | 31.7 ± 1.49 d | 80.9 ± 0.15 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 d | 71.8 ± 0.58 a | 0.98 | |
| LB | 21.5 ± 3.07 cd | 53.2 ± 2.92 ab | 74.7 ± 0.16 d | 0.11 ± 0.01 b | 64.4 ± 0.72 bc | 0.94 | |
| GLB | 28.0 ± 2.31 bc | 49.1 ± 2.18 bc | 77.1 ± 0.13 c | 0.09 ± 0.01 c | 66.6 ± 0.59 b | 0.96 | |
| FLB | 13.2 ± 3.41 d | 60.9 ± 3.28 a | 74.2 ± 0.13 d | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 65.5 ± 0.59 bc | 0.96 | |
| ADF | CK | 4.9 ± 1.10 c | 49.4 ± 1.00 ab | 54.3 ± 0.09 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 40.6 ± 0.37 c | 0.99 |
| FA | 17.1 ± 0.75 a | 42.6 ± 0.71 c | 59.7 ± 0.04 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 43.7 ± 0.30 b | 0.99 | |
| CaO | 12.2 ± 1.30 ab | 50.9 ± 1.19 a | 63.1 ± 0.11 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 45.2 ± 0.53 a | 0.98 | |
| LB | 10.7 ± 1.81 b | 45.2 ± 1.64 bc | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 42.7 ± 0.65 b | 0.96 | |
| GLB | 7.5 ± 1.20 bc | 45.4 ± 1.09 bc | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 40.1 ± 0.42 c | 0.98 | |
| FLB | 16.6 ± 0.93 a | 43.1 ± 0.89 c | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 43.4 ± 0.38 b | 0.98 | |
| NDF | CK | 8.3 ± 1.03 bc | 53.3 ± 0.97 a | 61.6 ± 0.06 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 41.9 ± 0.42 c | 0.99 |
| FA | 18.8 ± 0.83 a | 45.3 ± 0.77 c | 64.6 ± 0.50 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 47.6 ± 0.34 a | 0.99 | |
| CaO | 15.0 ± 0.87 a | 48.8 ± 0.78 bc | 63.8 ± 0.09 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 48.8 ± 0.33 a | 0.99 | |
| LB | 6.8 ± 1.28 bc | 53.8 ± 1.16 a | 60.6 ± 0.12 c | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 44.9 ± 0.46 b | 0.98 | |
| GLB | 5.6 ± 1.32 c | 52.3 ± 1.21 ab | 57.9 ± 0.11 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 43.7 ± 0.44 b | 0.98 | |
| FLB | 10.7 ± 0.80 b | 46.8 ± 0.73 c | 57.4 ± 0.07 d | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 44.1 ± 0.28 b | 0.99 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, W.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Degen, A.A.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. Effects of Different Additives on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Communities, and Rumen Degradation of Alfalfa Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110660
Ling W, Zhang L, Feng Q, Degen AA, Li J, Qi Y, Li Y, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Yang F, et al. Effects of Different Additives on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Communities, and Rumen Degradation of Alfalfa Silage. Fermentation. 2022; 8(11):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Wenqing, Lei Zhang, Qixian Feng, Abraham Allan Degen, Jue Li, Yue Qi, Yan Li, Yi Zhou, Yijia Liu, Fulin Yang, and et al. 2022. "Effects of Different Additives on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Communities, and Rumen Degradation of Alfalfa Silage" Fermentation 8, no. 11: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110660
APA StyleLing, W., Zhang, L., Feng, Q., Degen, A. A., Li, J., Qi, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, F., & Zhou, J. (2022). Effects of Different Additives on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Communities, and Rumen Degradation of Alfalfa Silage. Fermentation, 8(11), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110660







